5. ABC transporters
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:23 PM on 1/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
1
New cards
primary active transport
Movement of molecules/ions across cell membrane against concentration gradient (from region of low conc to region of high conc) using ATP.
2
New cards
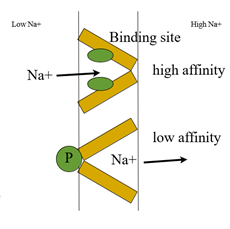
A simple allosteric model for membrane pumps- Jardetzky (1966)
principle of active transport
·Interior cavity transports molecule.
· Alternating access – protein has 2 conformations. Access to one side or another.
· Binding site has different affinities in the 2 conformations.
· Energy input required to drive conformational and binding affinity change.
· Energy input can be light (bacteriorhodopsin) or conc grad or proton grads in secondary transporters.
·Interior cavity transports molecule.
· Alternating access – protein has 2 conformations. Access to one side or another.
· Binding site has different affinities in the 2 conformations.
· Energy input required to drive conformational and binding affinity change.
· Energy input can be light (bacteriorhodopsin) or conc grad or proton grads in secondary transporters.
3
New cards
ABC transporters
primary active transporters.
· Superfamily
· Can be importers or exporters.
· 2 NBD – similar across all ABC transporters.
NBD forms ATP sandwich in closed conformation.
ATPase Subdomain contains walker A & B motifs – hydrolyse ATP.
· 2 TMD – subunits normally separate in prokaryotes and fused in higher organisms.
TMD forms cavity where molecule sits.
· bacterial Importers will have soluble substrate binding proteins.
· Coupling helices - helix held by salt bridge interactions in cavity (like ball in socket joint.) communicate structural changes in NBD due to binding of nucleotide to TBD. Helix swivels within cavity – rotates TBD to give large movement. Coincides with opening and closing of NBD interface. Couples ATP hydrolysis to transport.
· Superfamily
· Can be importers or exporters.
· 2 NBD – similar across all ABC transporters.
NBD forms ATP sandwich in closed conformation.
ATPase Subdomain contains walker A & B motifs – hydrolyse ATP.
· 2 TMD – subunits normally separate in prokaryotes and fused in higher organisms.
TMD forms cavity where molecule sits.
· bacterial Importers will have soluble substrate binding proteins.
· Coupling helices - helix held by salt bridge interactions in cavity (like ball in socket joint.) communicate structural changes in NBD due to binding of nucleotide to TBD. Helix swivels within cavity – rotates TBD to give large movement. Coincides with opening and closing of NBD interface. Couples ATP hydrolysis to transport.
4
New cards
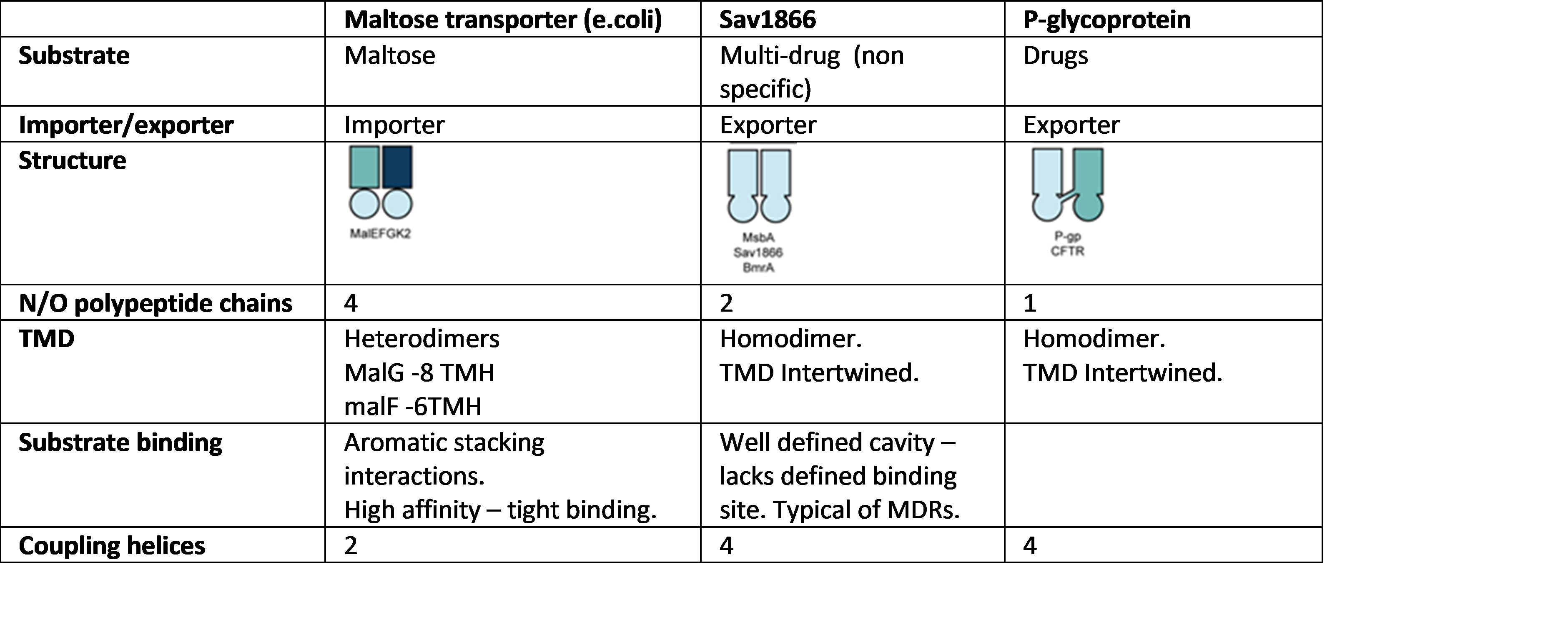
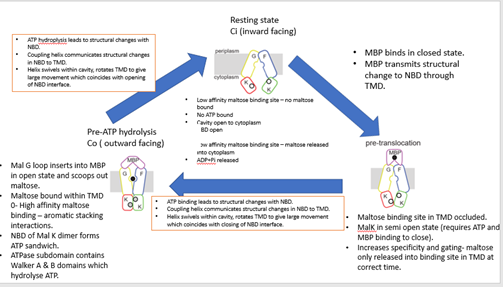
E.coli Maltose transporter
__X-ray structures show 3 conformational states__
Co (outward facing)
· Structure trapping
· E159Q mutation prevents ATP hydrolysis and traps structure in 1 conformation (Co).
· WT structures with ADP+Pi analogues look similar
· Makes crystallisation easier.
Ci (inward facing)
· TM1 of malF removed
· Doesn’t affect transport or ATPase activity.
· Makes crystallisation possible.
Co (outward facing)
· Structure trapping
· E159Q mutation prevents ATP hydrolysis and traps structure in 1 conformation (Co).
· WT structures with ADP+Pi analogues look similar
· Makes crystallisation easier.
Ci (inward facing)
· TM1 of malF removed
· Doesn’t affect transport or ATPase activity.
· Makes crystallisation possible.
5
New cards
Sav1866
· Multi-drug transporter (exporter).
· 2 polypeptide chains form homodimer.
· TMD intertwined. Constraint on movement – don’t act independently.
· Large internal cavity lacks defined drug binding site (typical of MDRs)
· Cavity lined by hydrophilic residues. Low affinity for hydrophobic drugs.
· Biochemical evidence suggests Ci conformation protien has high affinity for drugs.
· Each TMD has pseudo symmetry.
· Coupling helcies interact with NBDs – one contacts both and one contacts opposite NBD.
· Whole structure intertwined –suggests coupling between NBDs and TMDs differ from importers.
· Homolog of human P-glycoprotien
· 2 polypeptide chains form homodimer.
· TMD intertwined. Constraint on movement – don’t act independently.
· Large internal cavity lacks defined drug binding site (typical of MDRs)
· Cavity lined by hydrophilic residues. Low affinity for hydrophobic drugs.
· Biochemical evidence suggests Ci conformation protien has high affinity for drugs.
· Each TMD has pseudo symmetry.
· Coupling helcies interact with NBDs – one contacts both and one contacts opposite NBD.
· Whole structure intertwined –suggests coupling between NBDs and TMDs differ from importers.
· Homolog of human P-glycoprotien
6
New cards
P-gylcoprotien
· Human exporter.
· Involved in drug resistance in cancer cells.
· One polypeptide with 2 homologous wings – each with 2 coupling helices.
· 4 coupling helices in total
· Binds drugs from cytoplasm or hydrophobic drugs from membrane.
· Involved in drug resistance in cancer cells.
· One polypeptide with 2 homologous wings – each with 2 coupling helices.
· 4 coupling helices in total
· Binds drugs from cytoplasm or hydrophobic drugs from membrane.