BIOL 314 Urinary System & Urinalysis Lab
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UW- Eau Claire Anatomy and Physiology II
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
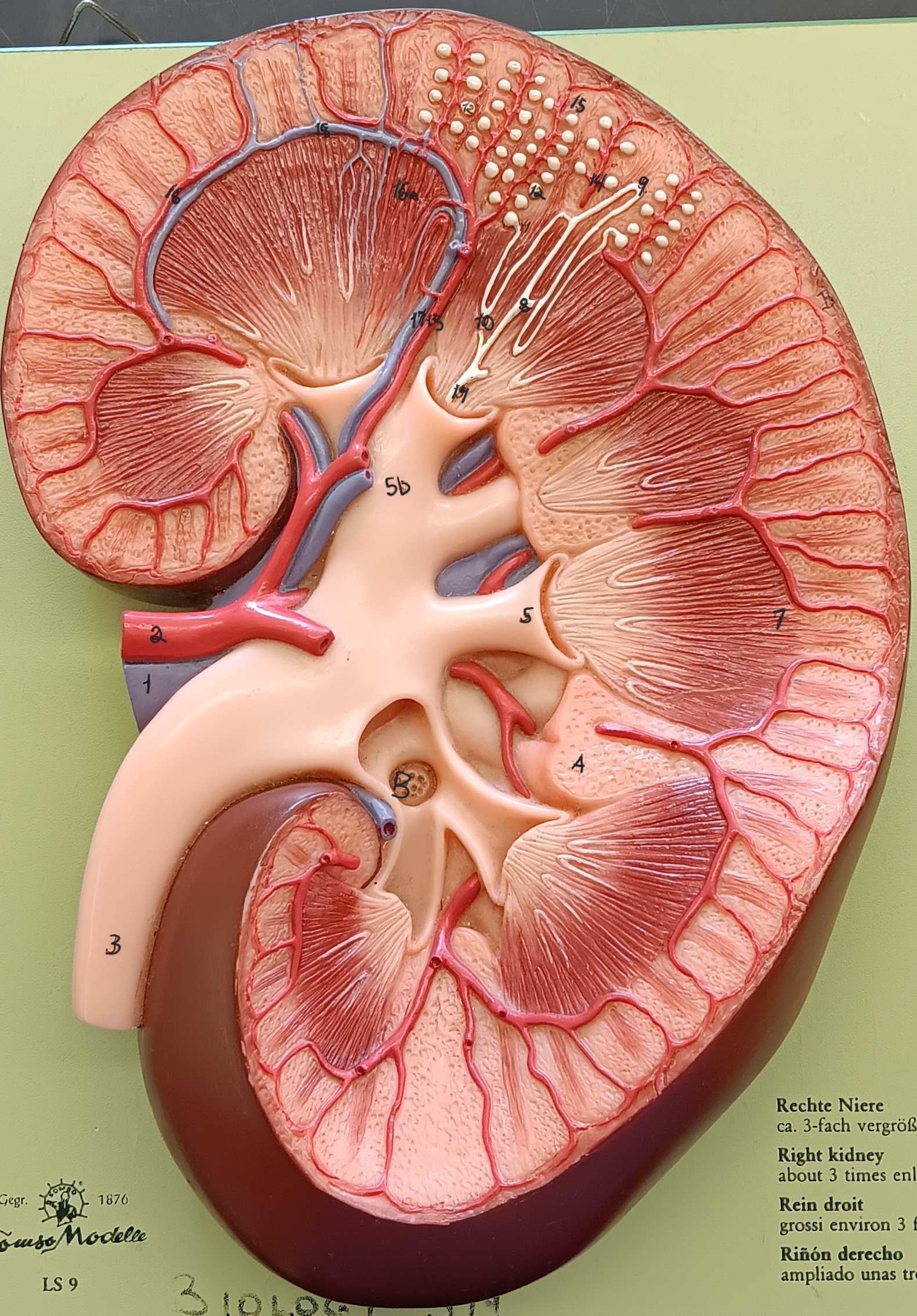
Kidney
organ over all
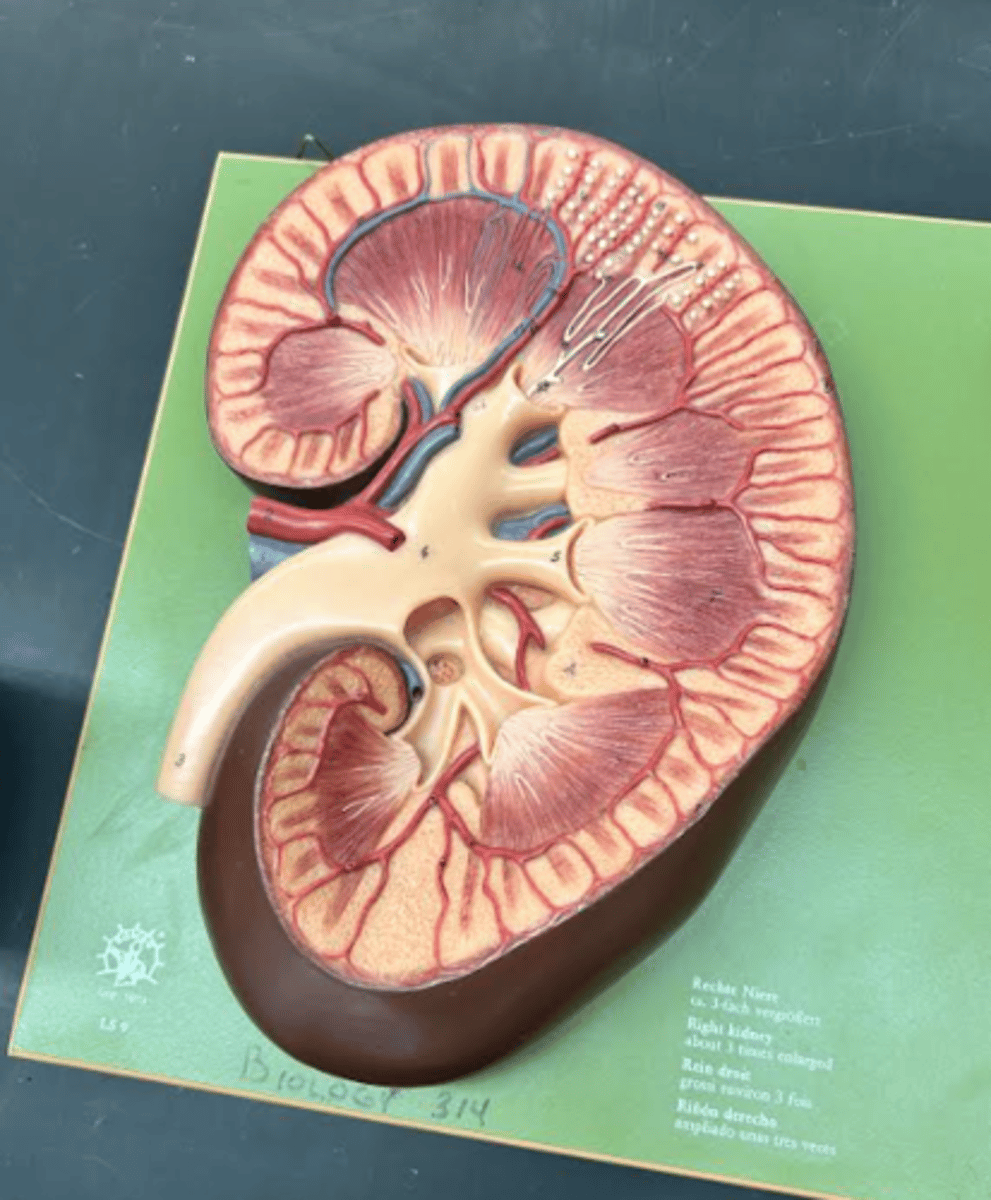
Kidney
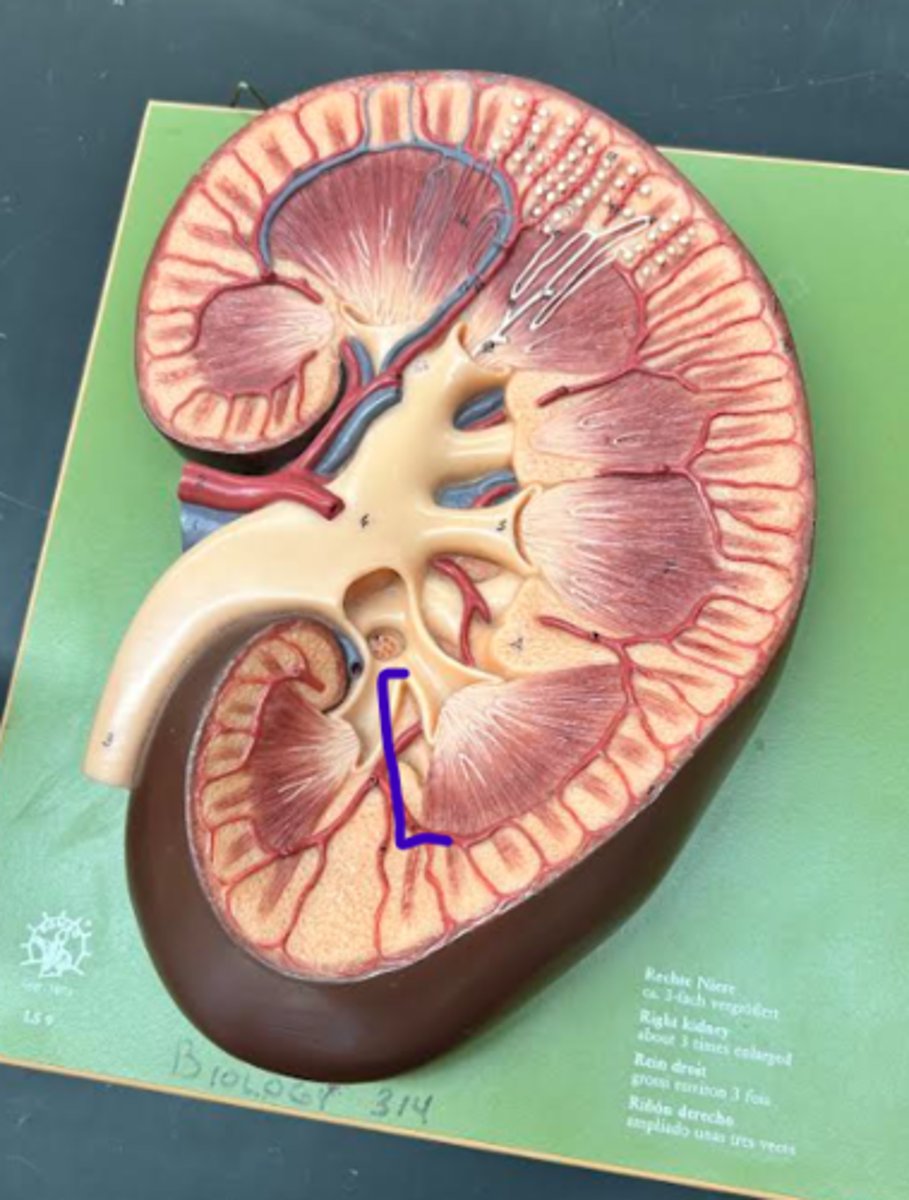
Renal hilum
Fibrous capsule
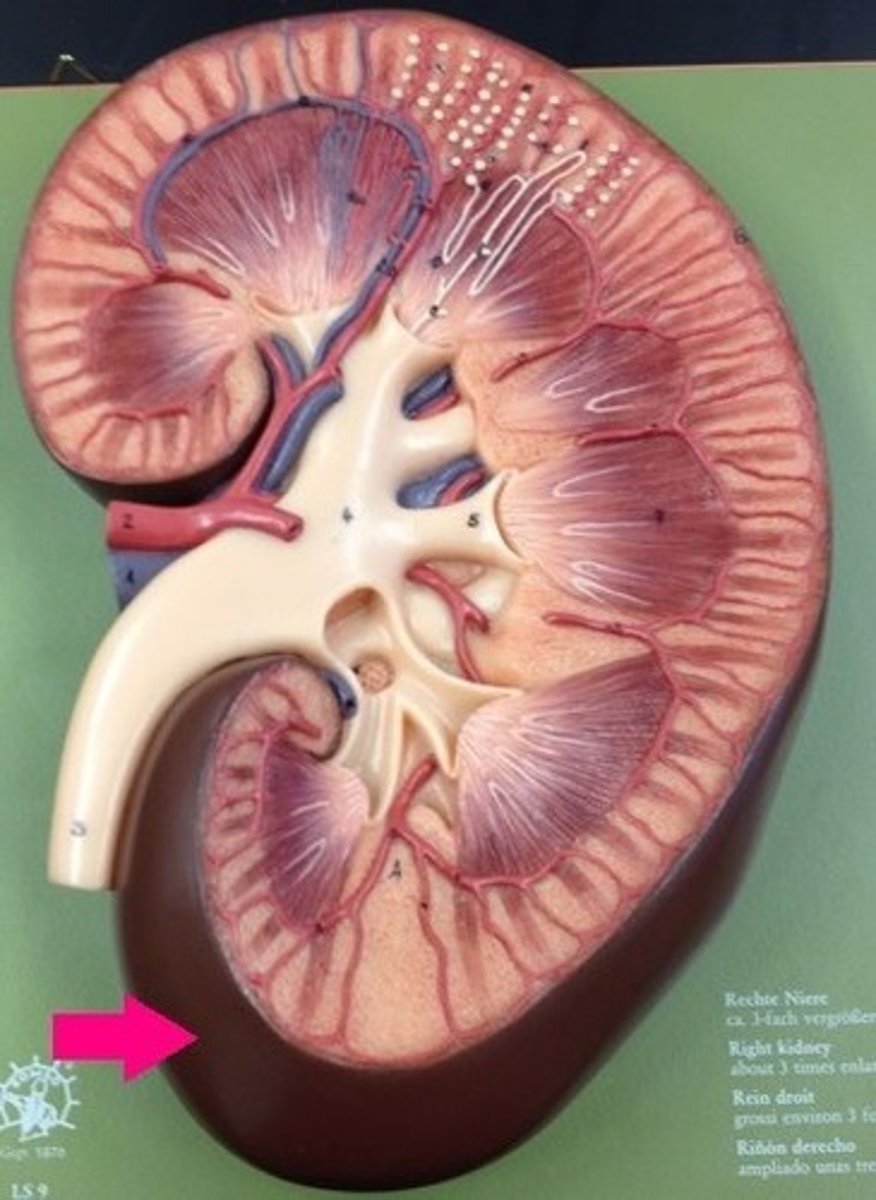
Renal column
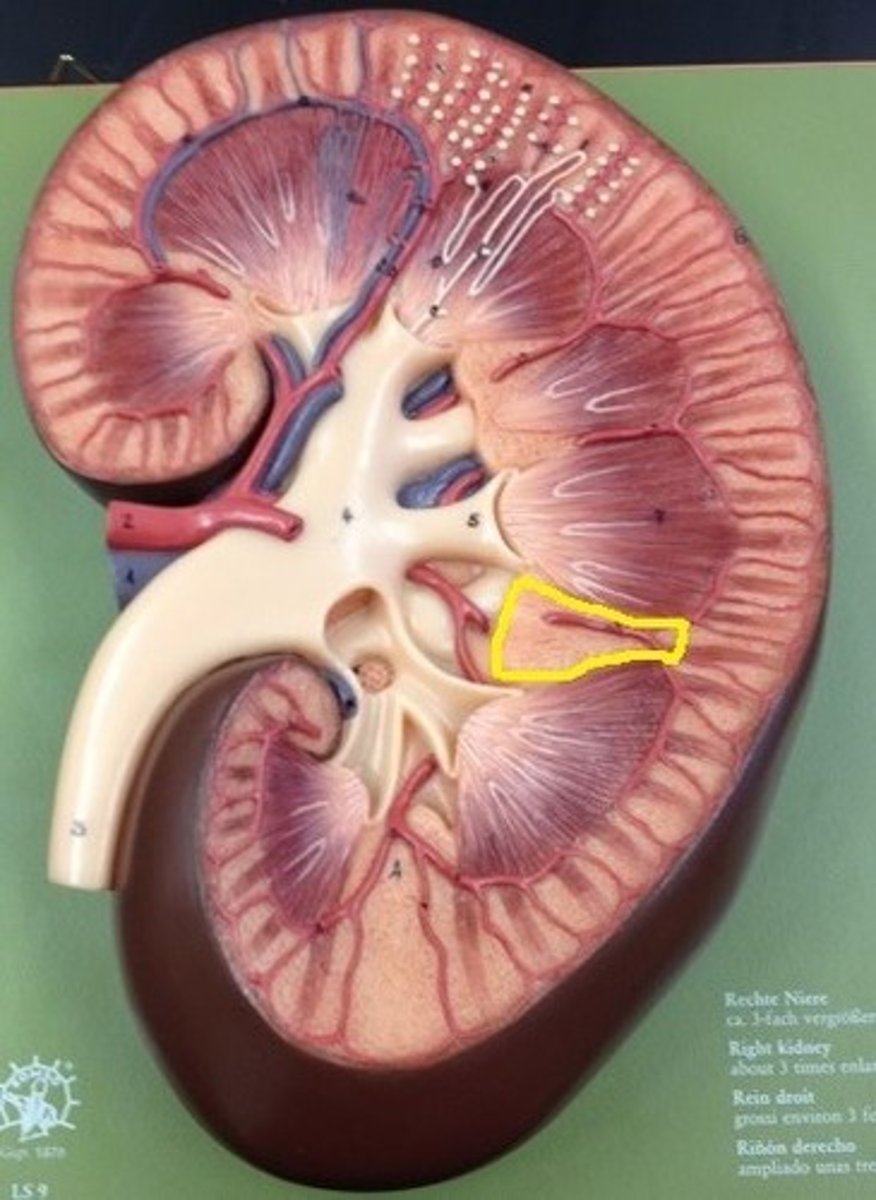
Renal column
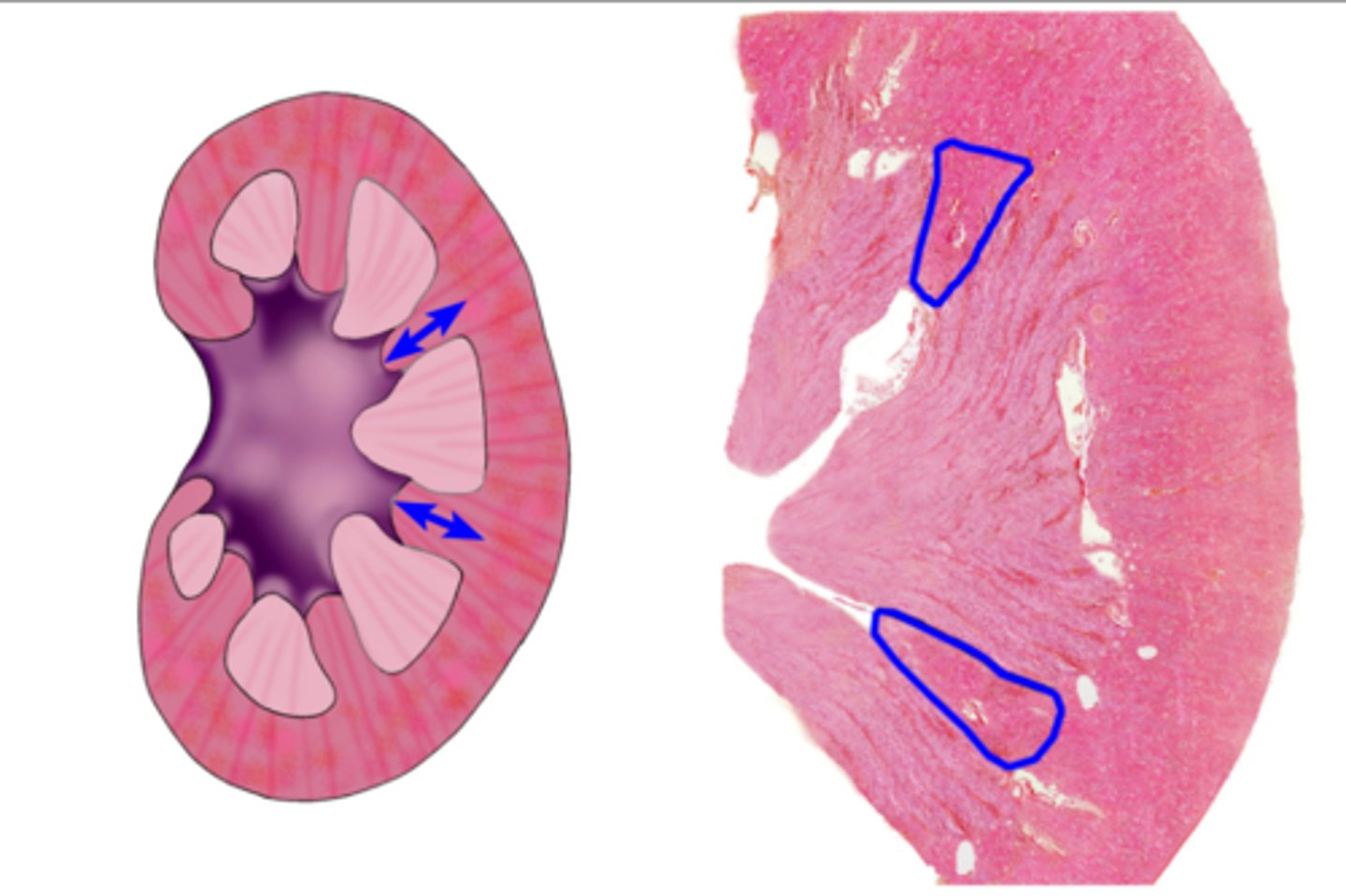
Renal cortex
outside area of kidney
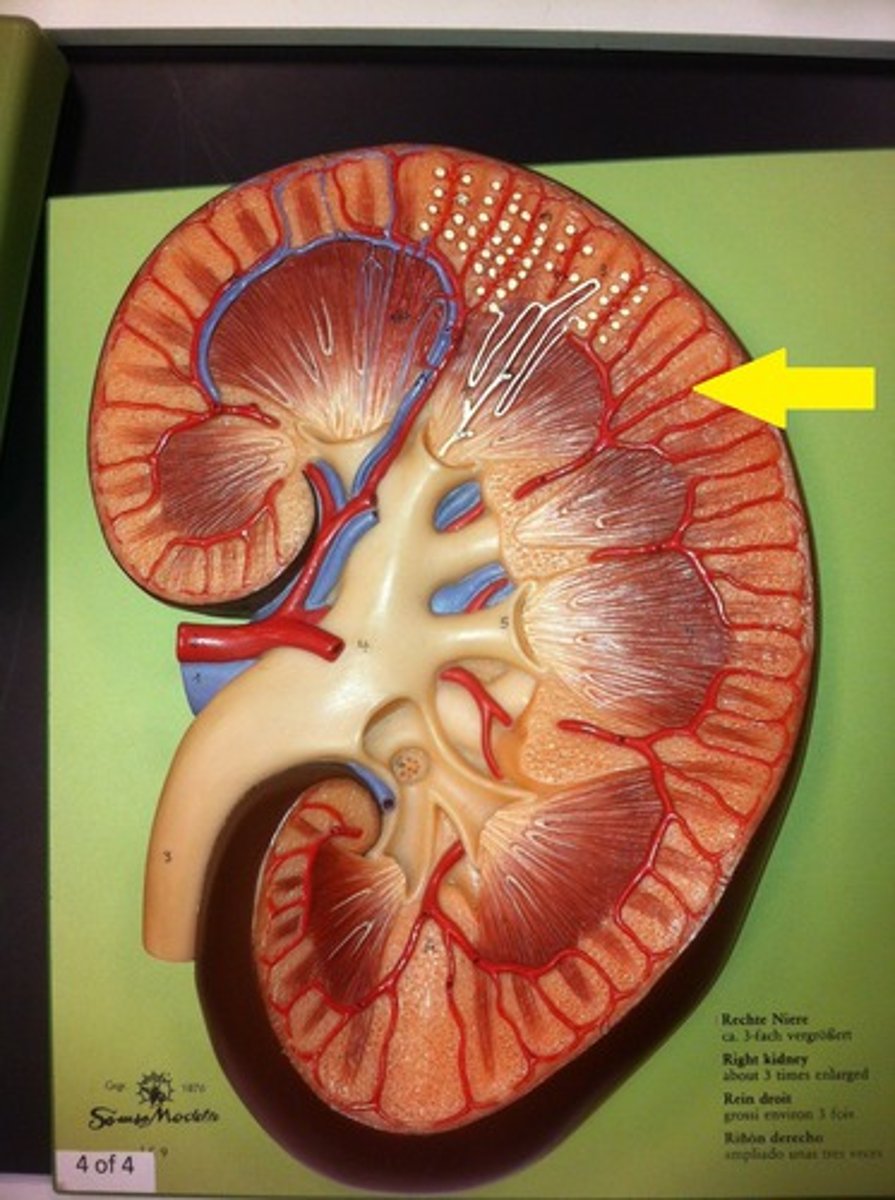
Renal cortex
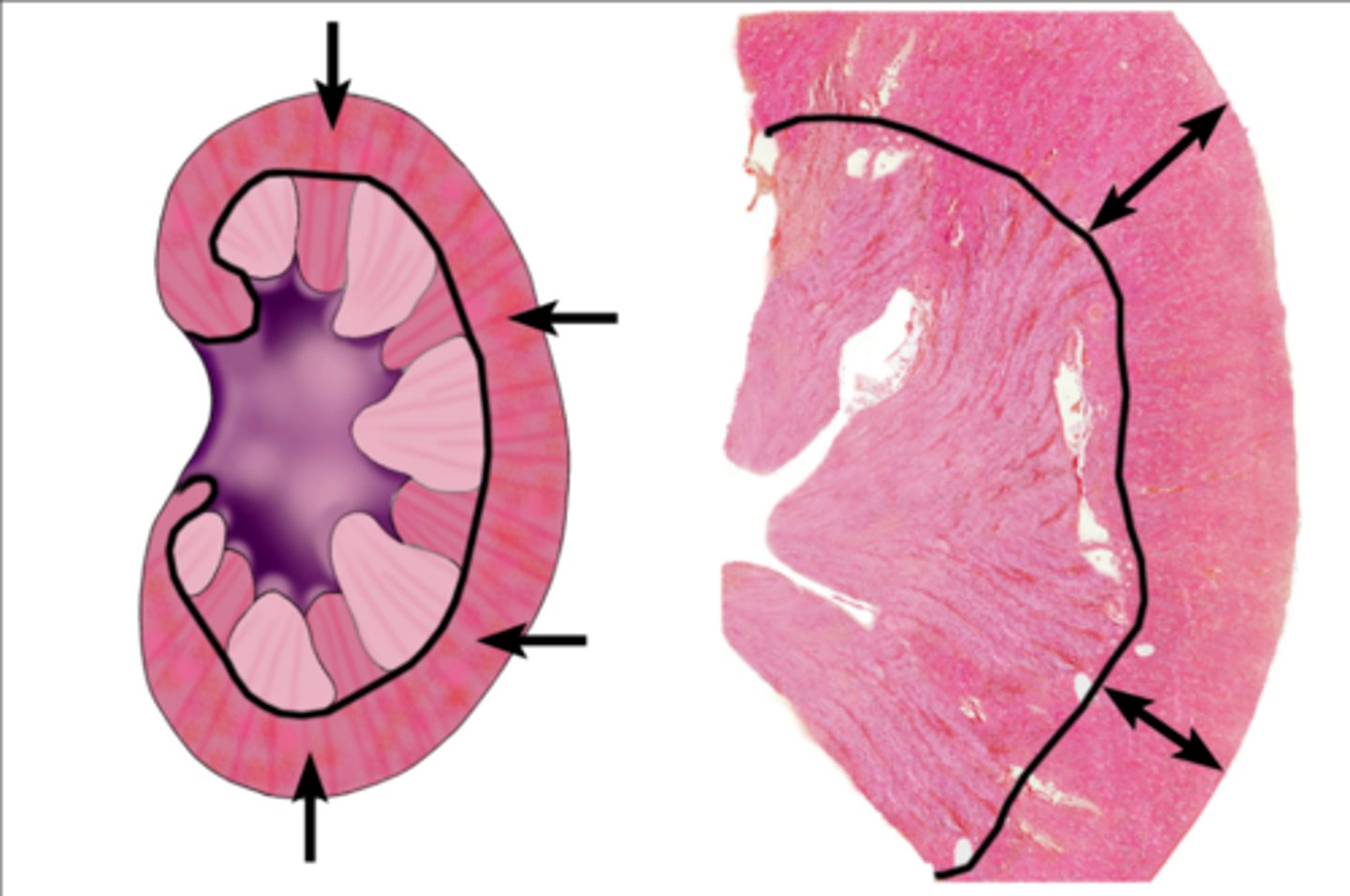
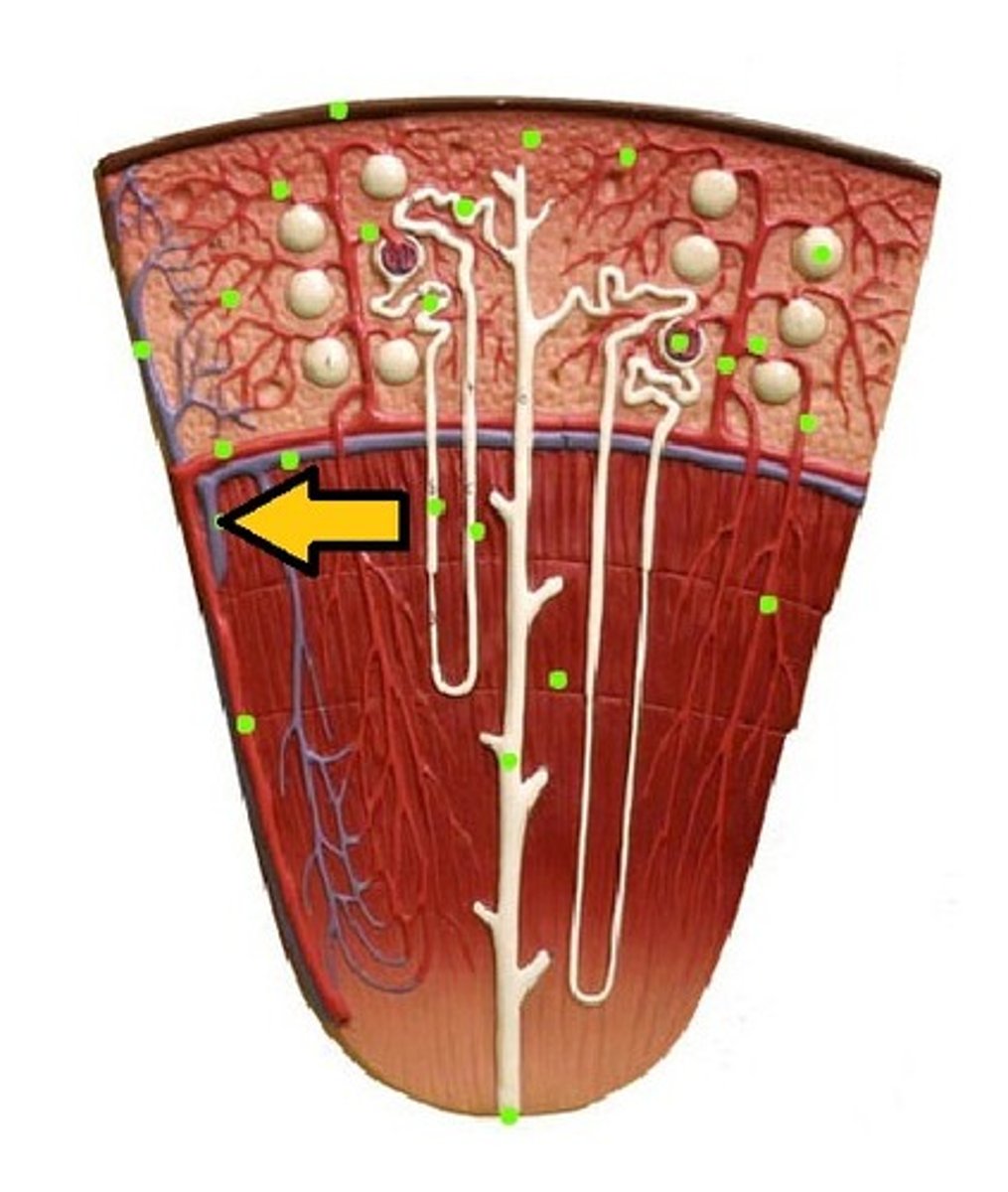
Renal medulla
Renal medulla
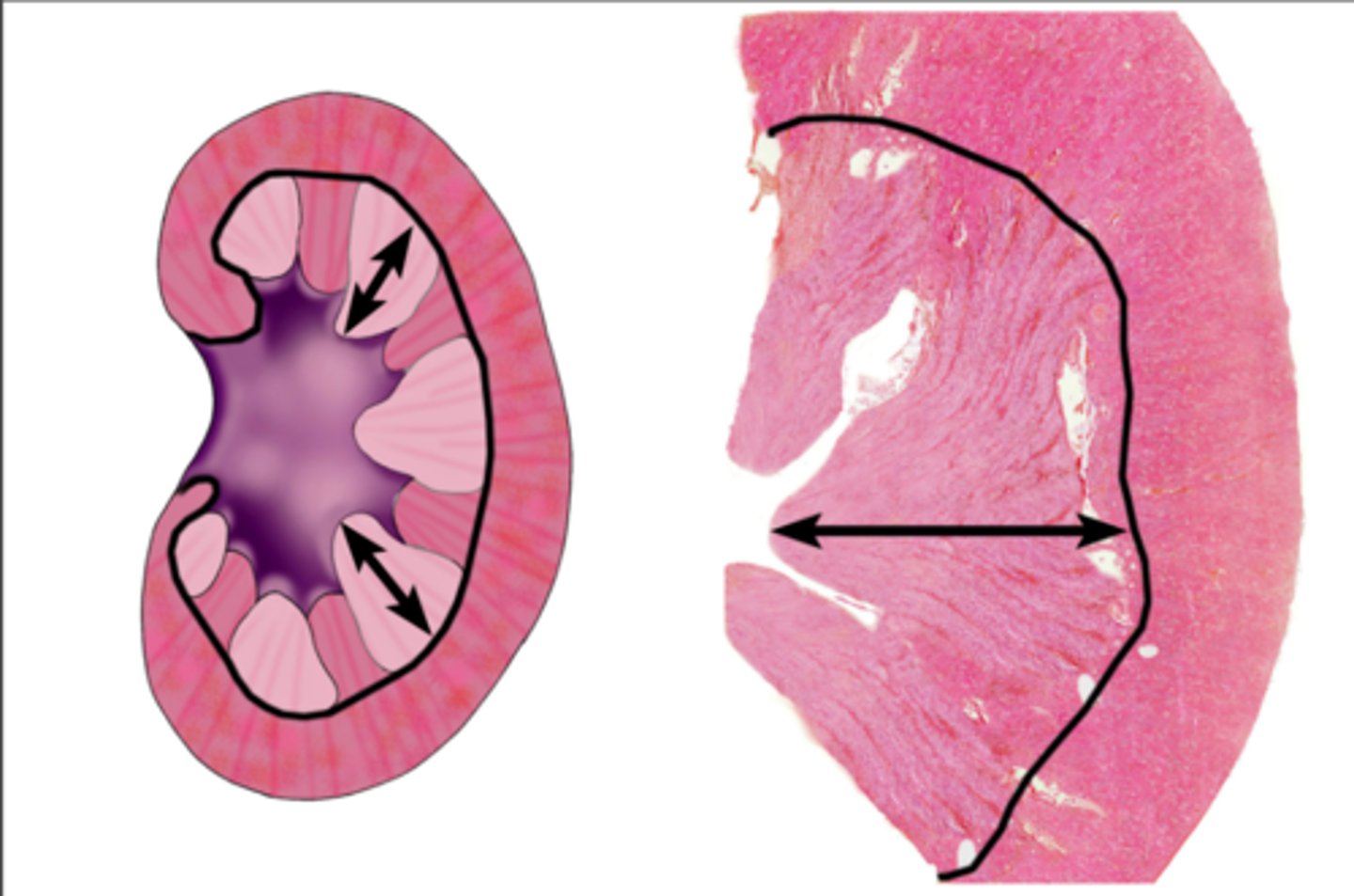
Renal pyramid
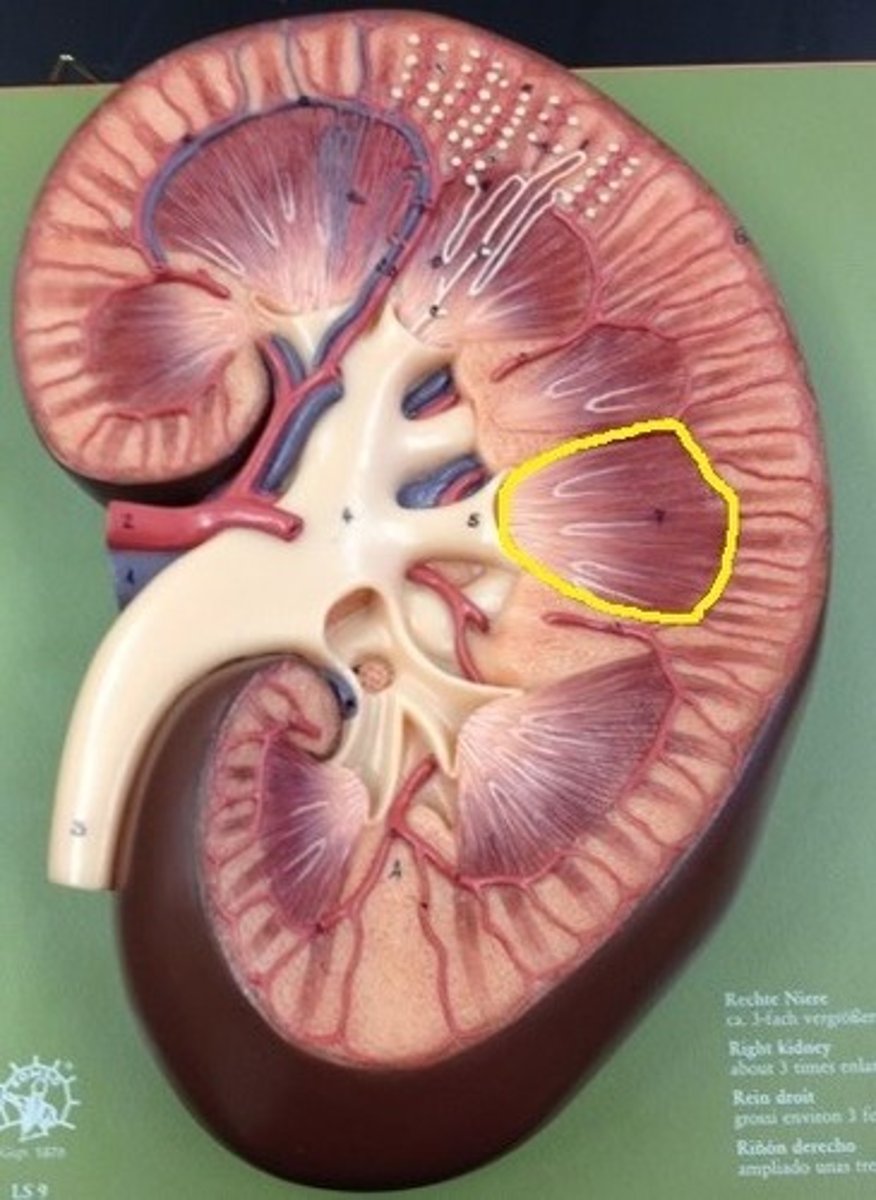
Renal pyramid
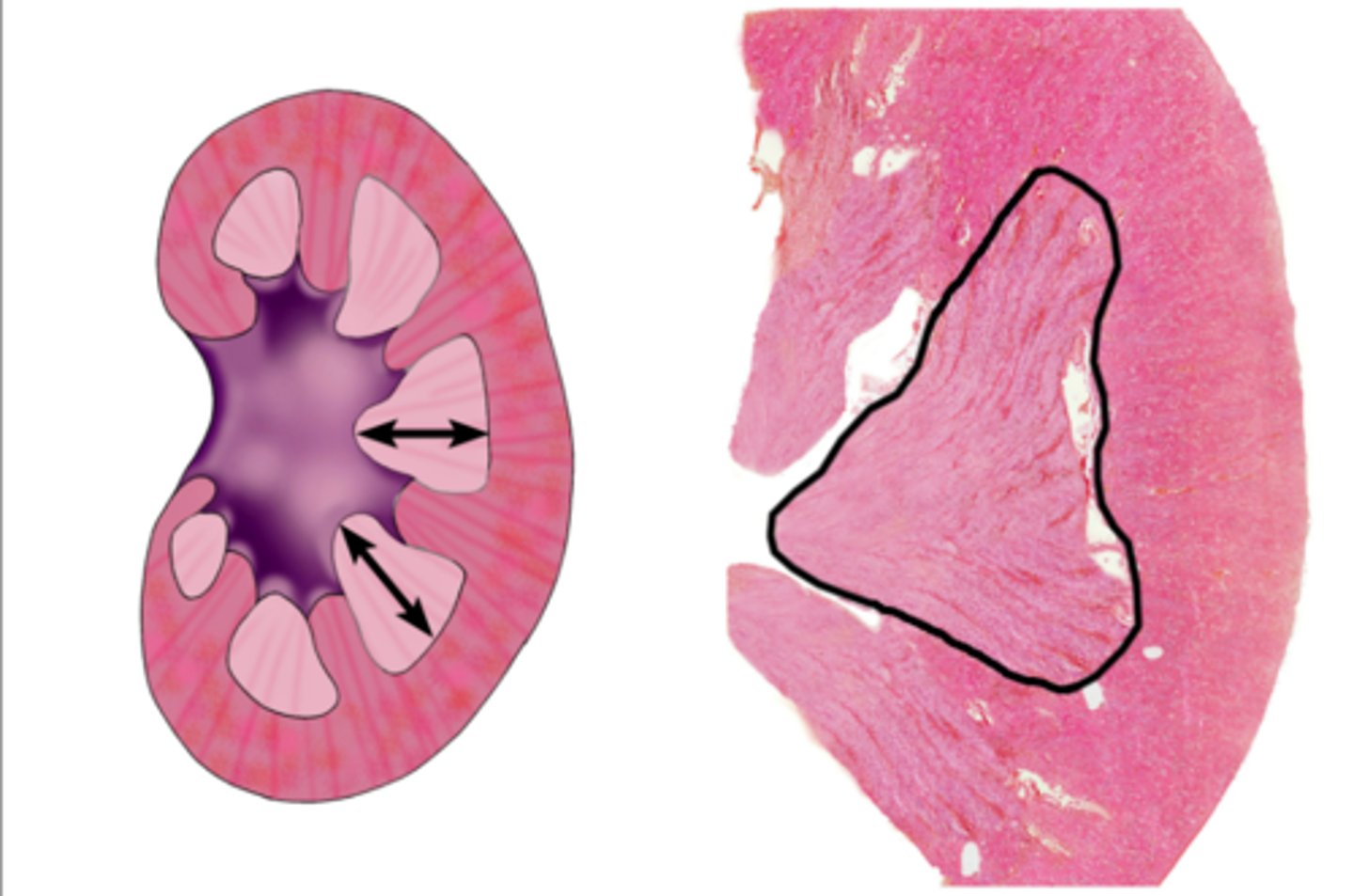
Renal papilla
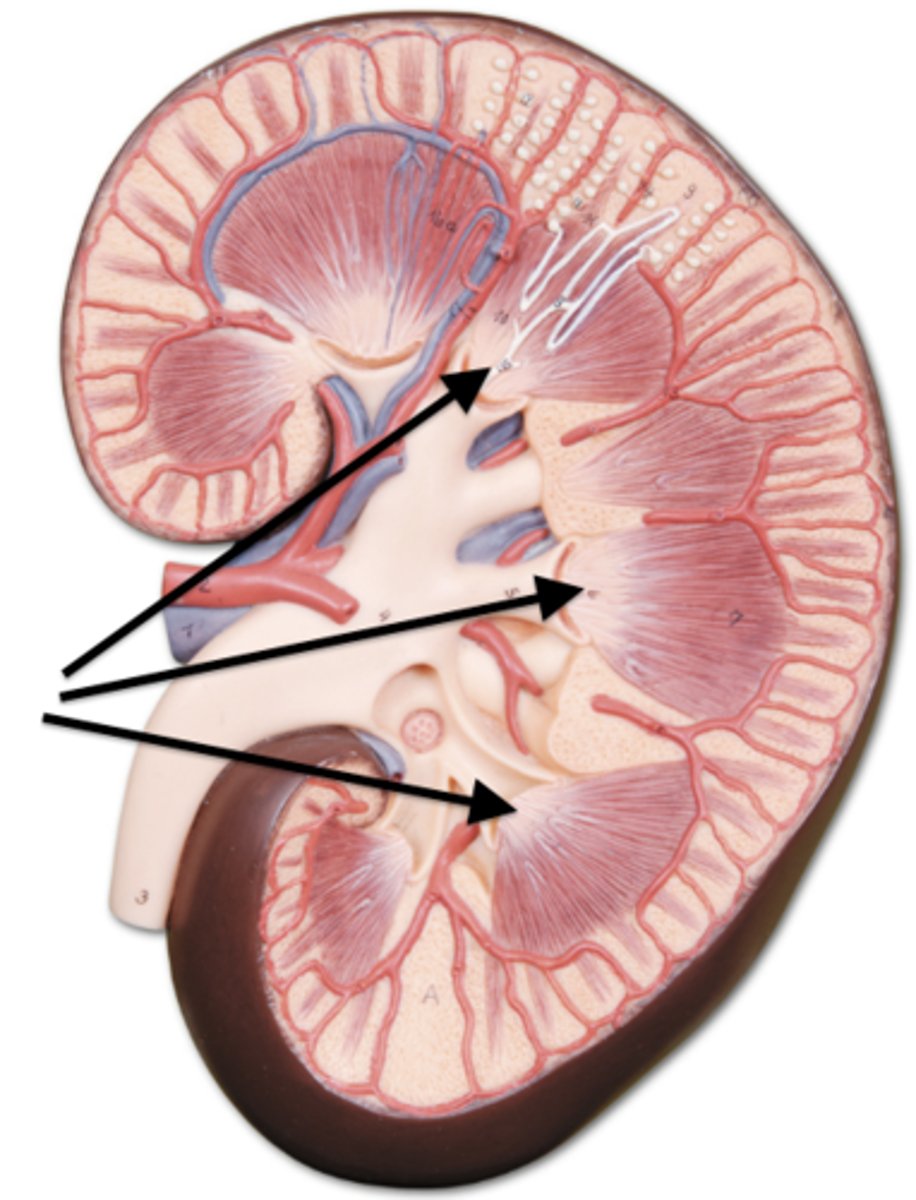
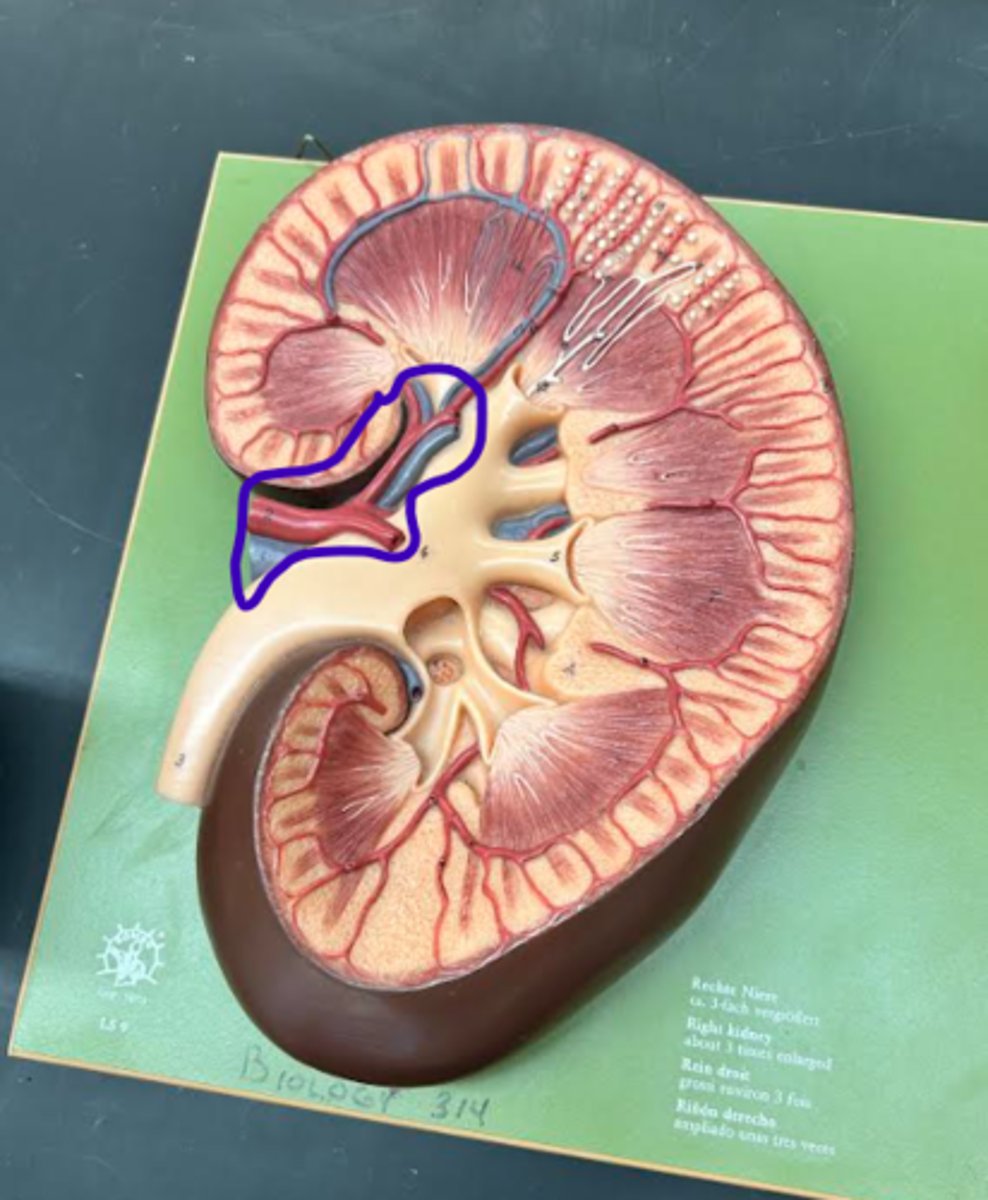
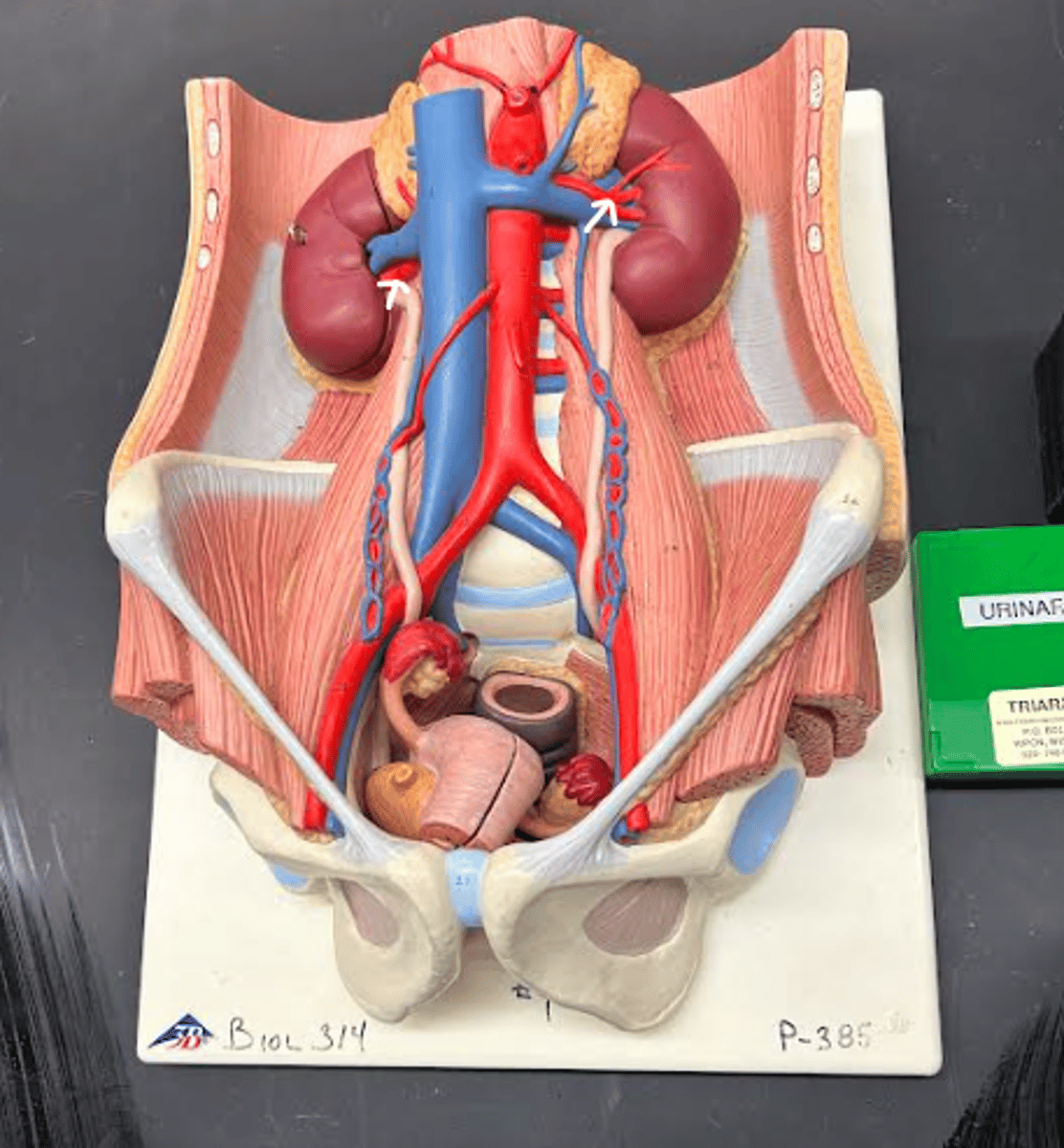
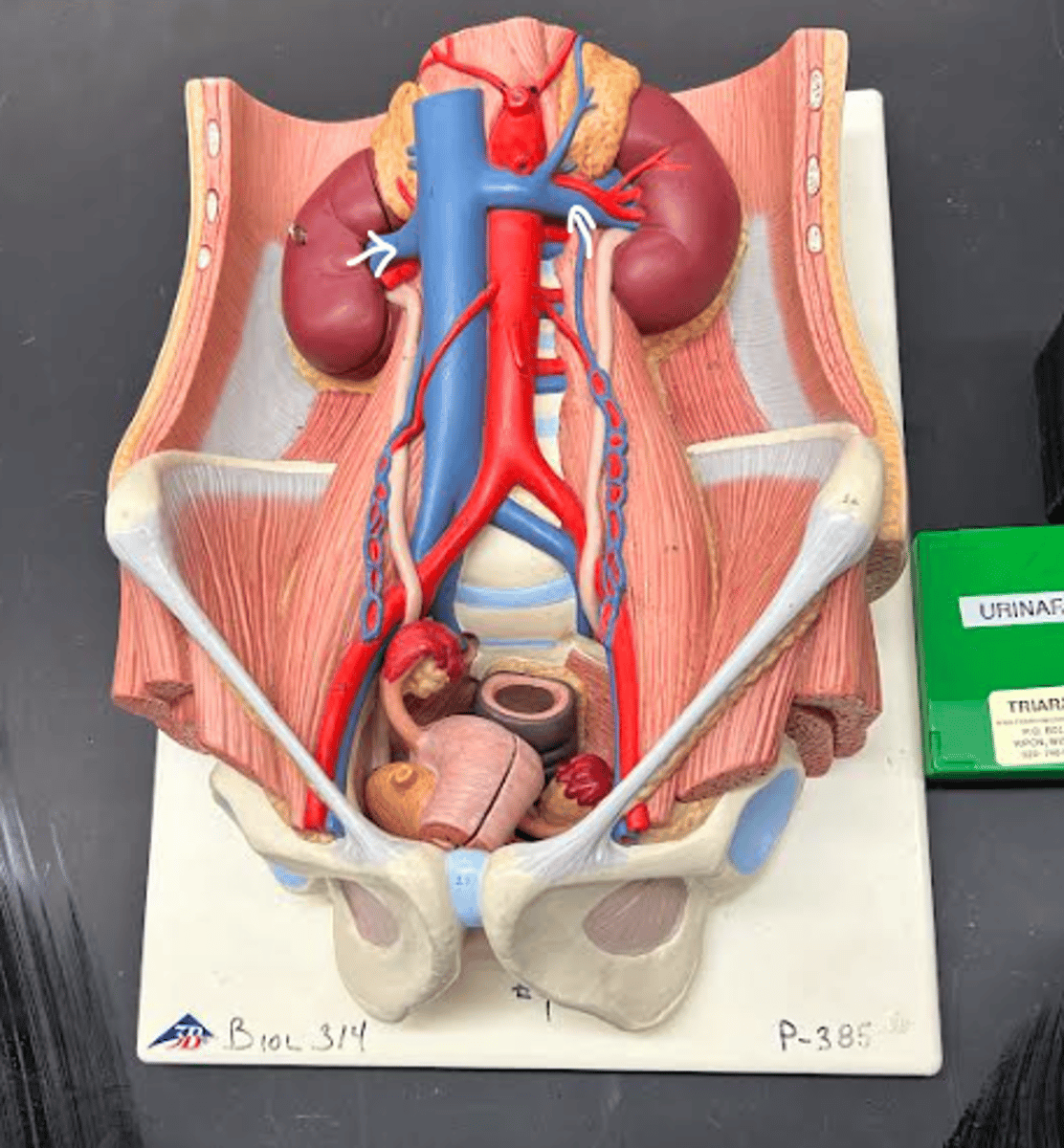
Renal artery
Interlobar artery
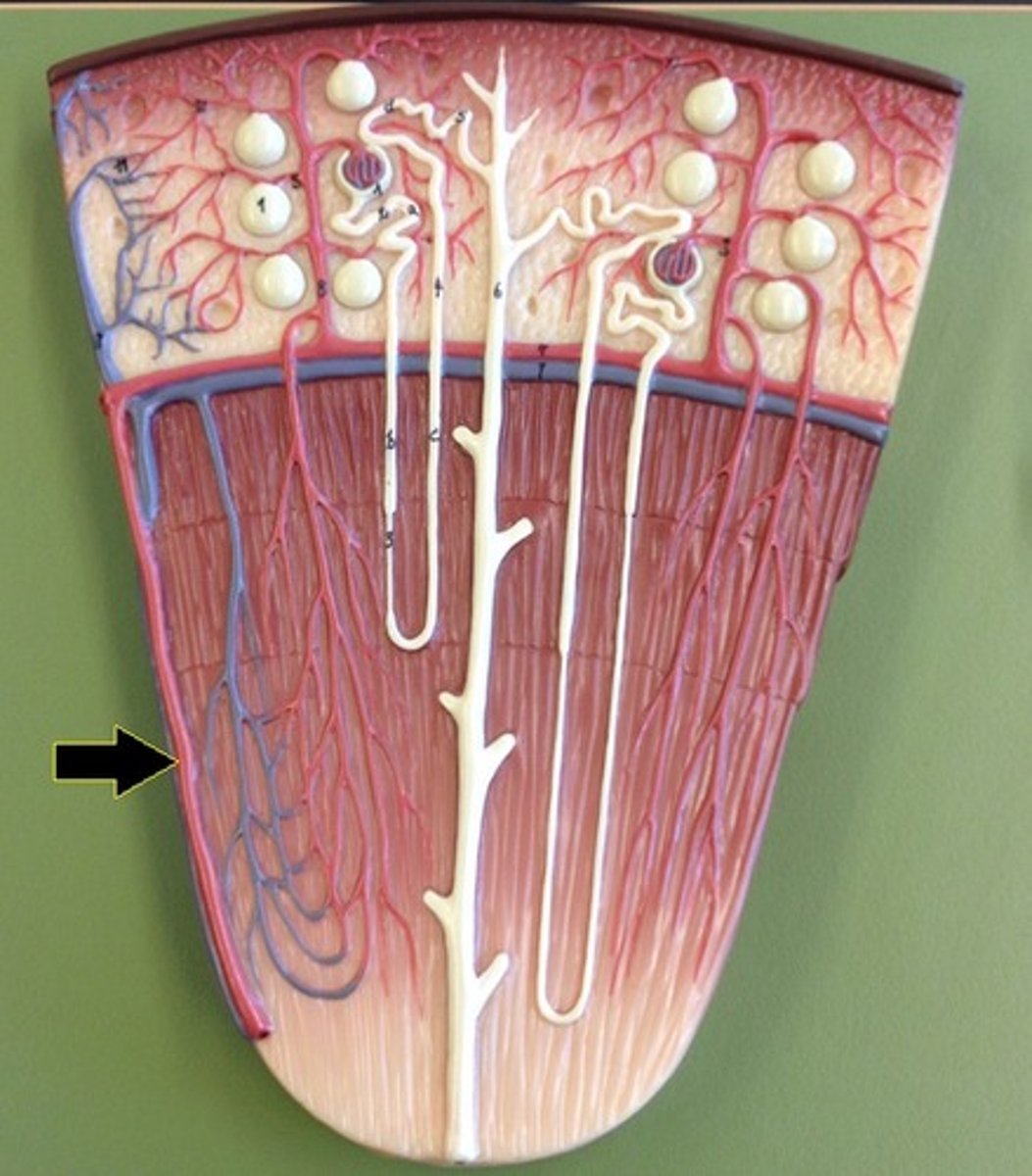
Cortical radiate vein
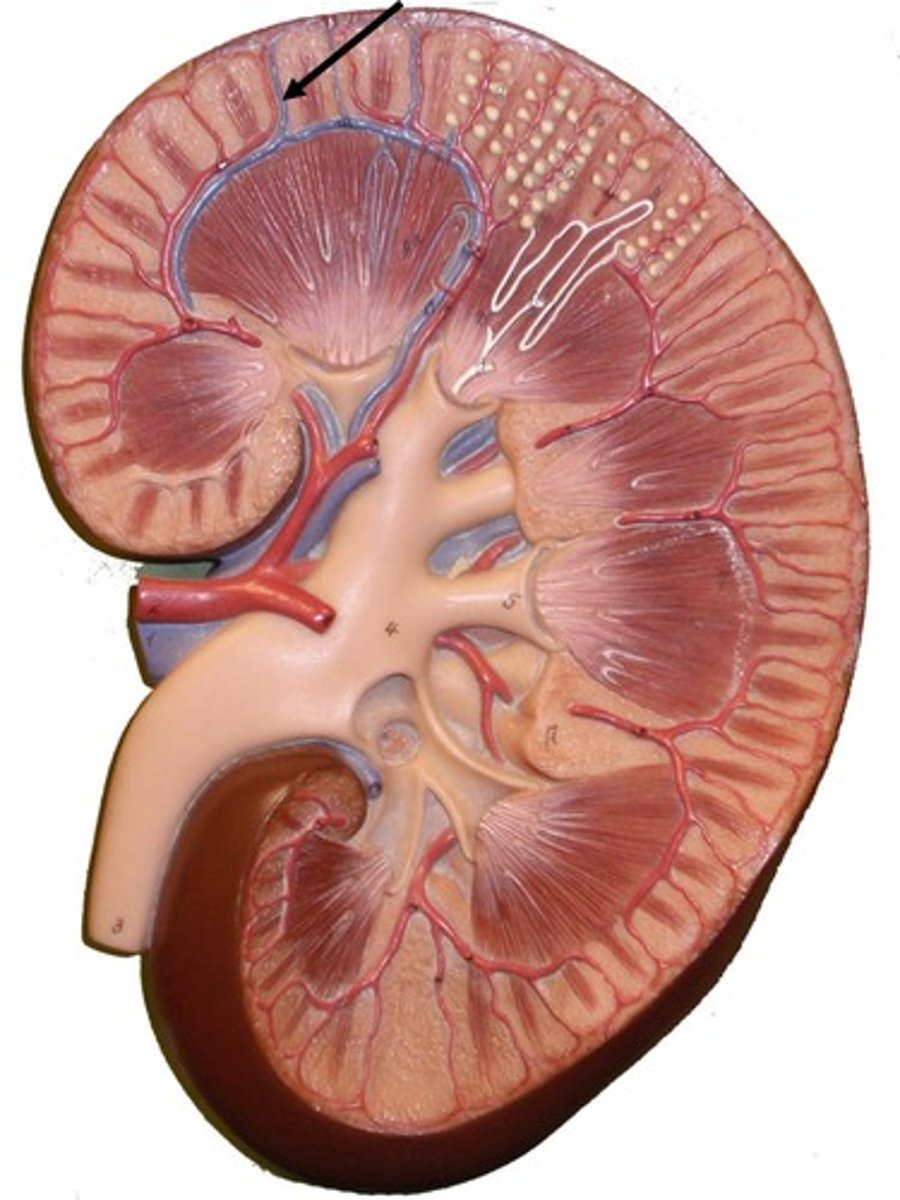
Cortical radiate artery
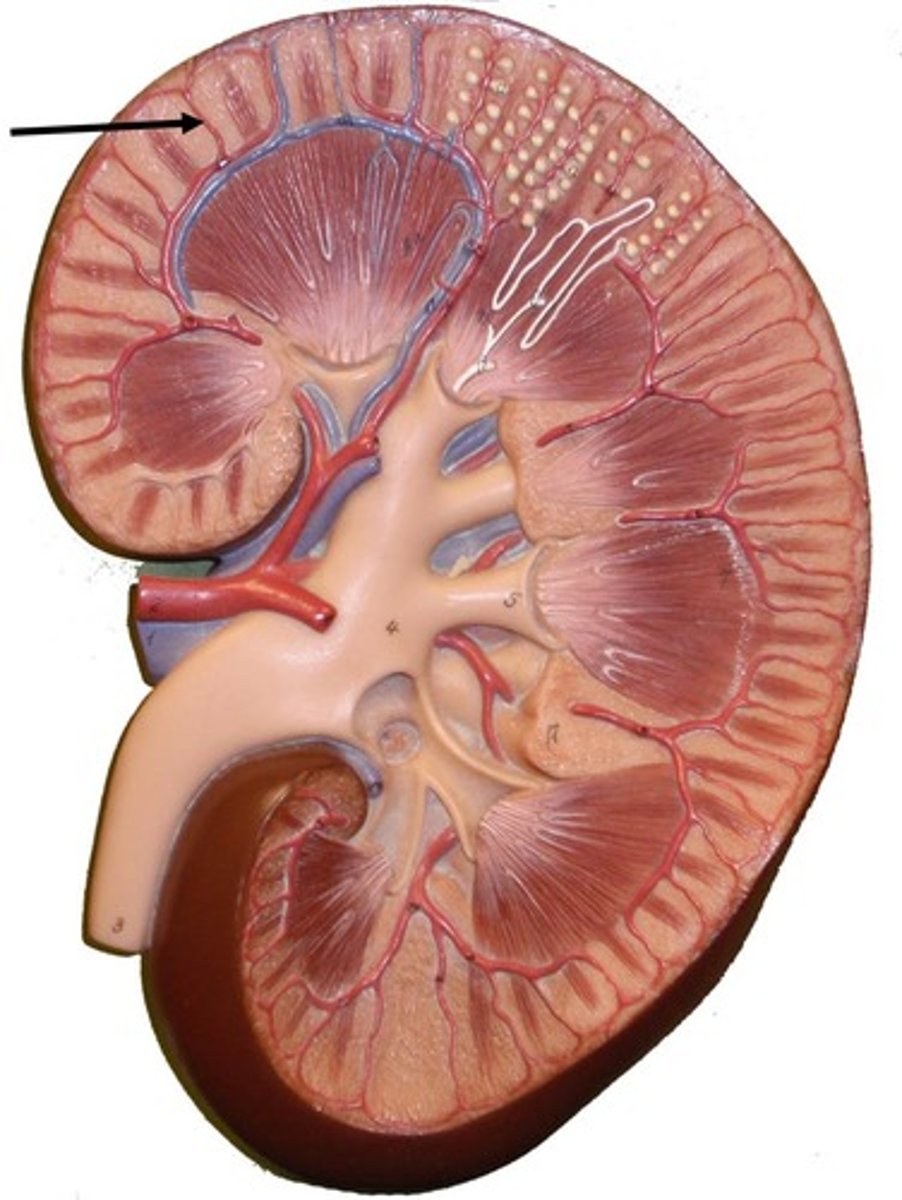
Glomerulus
Vasa recta
Renal vein
Interlobar vein
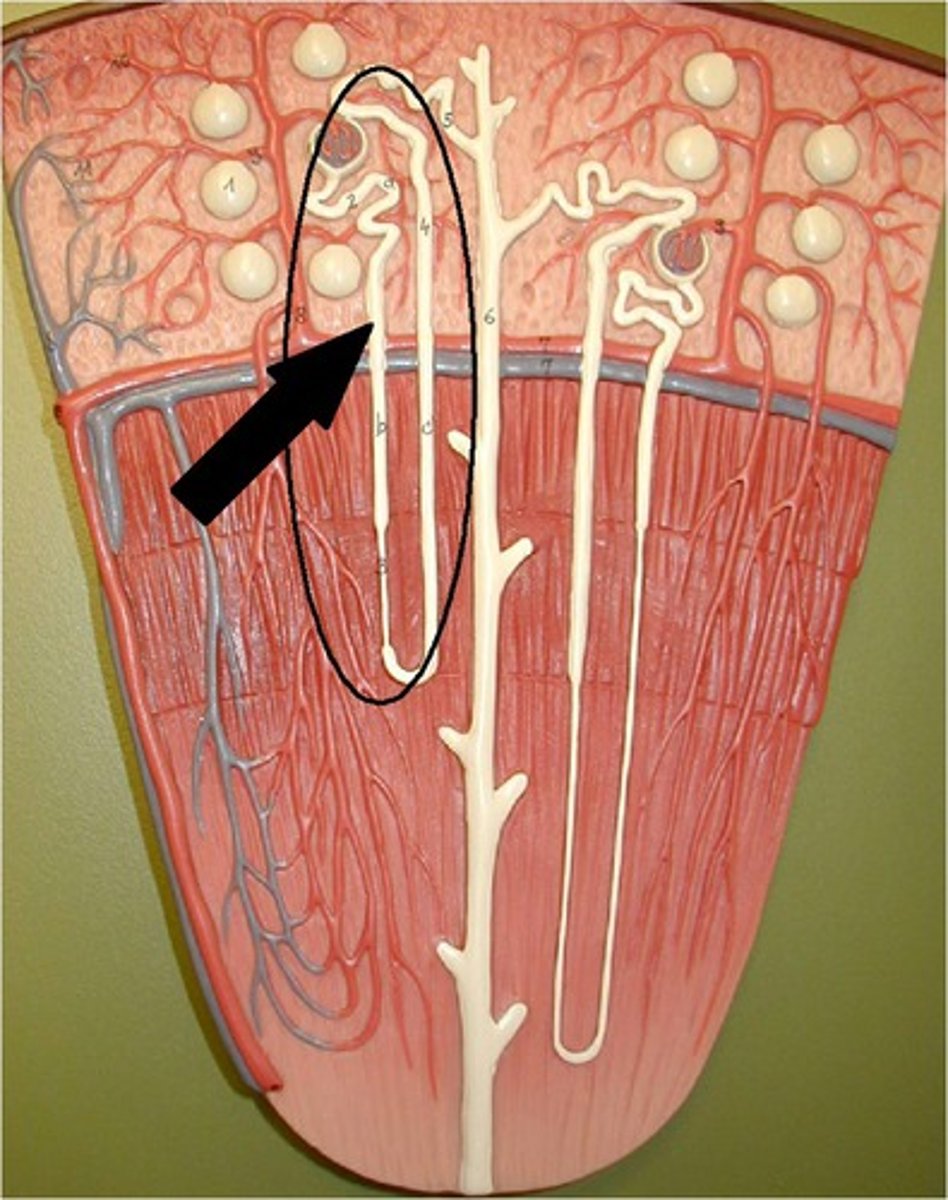
Cortical nephron
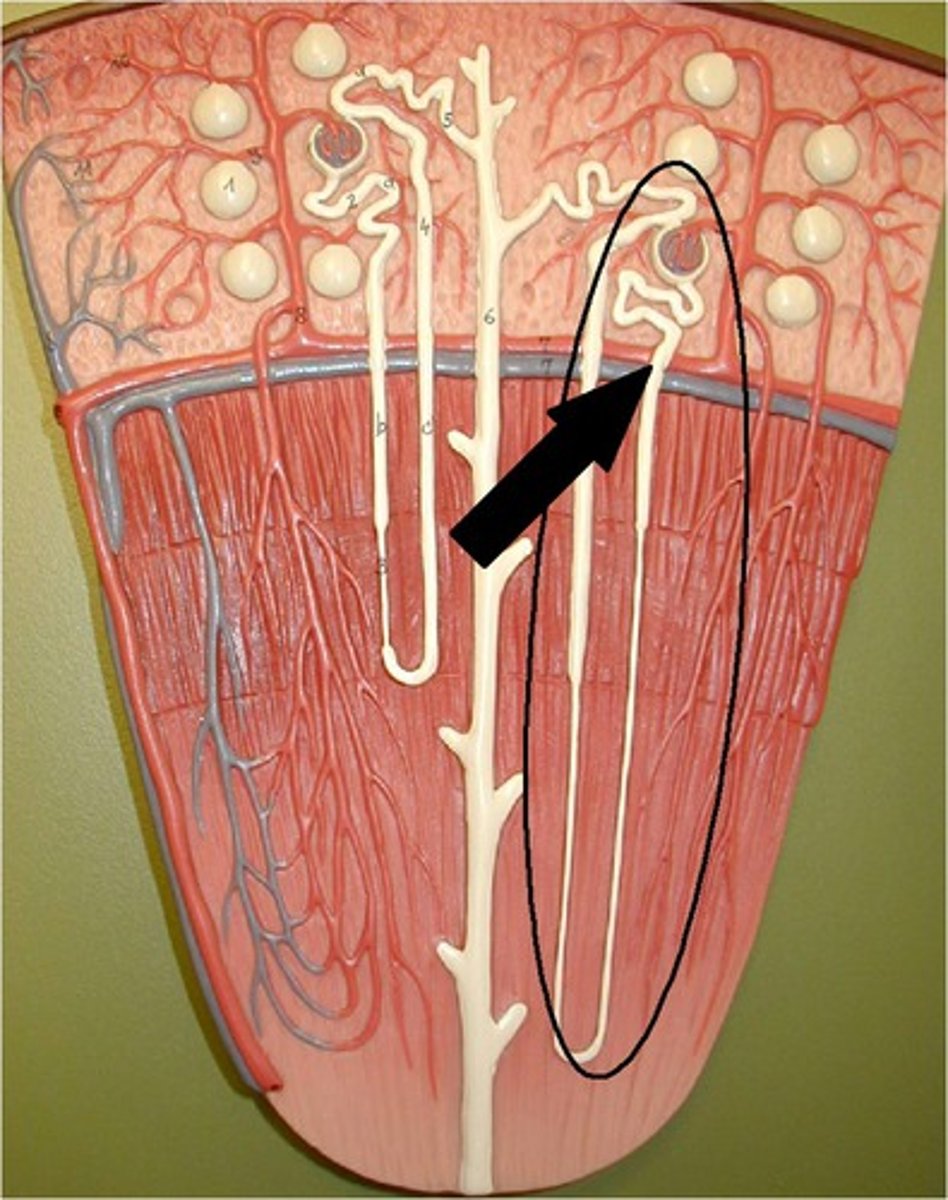
Juxtamedullary nephron
Renal corpuscle
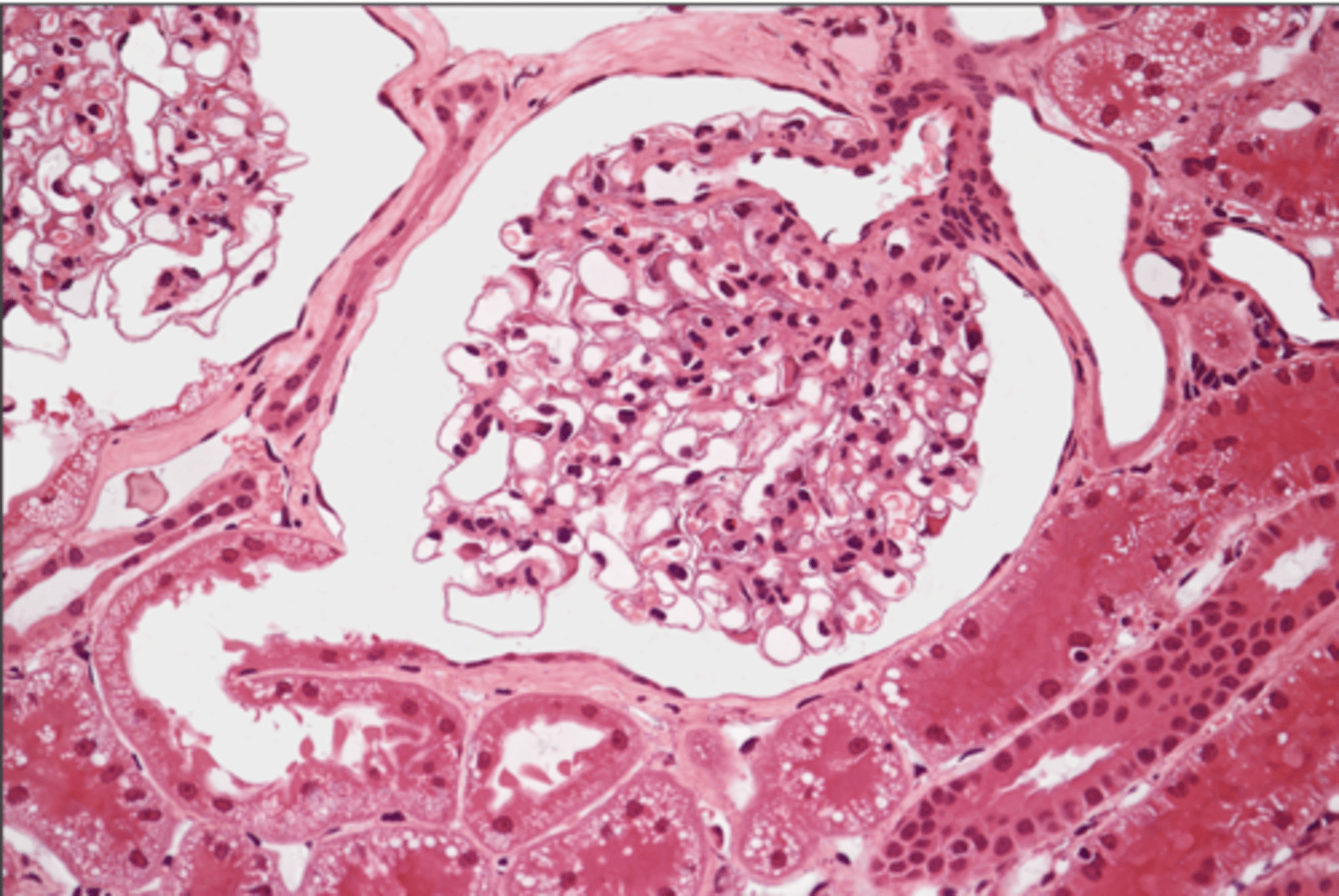
Bowman's capsule
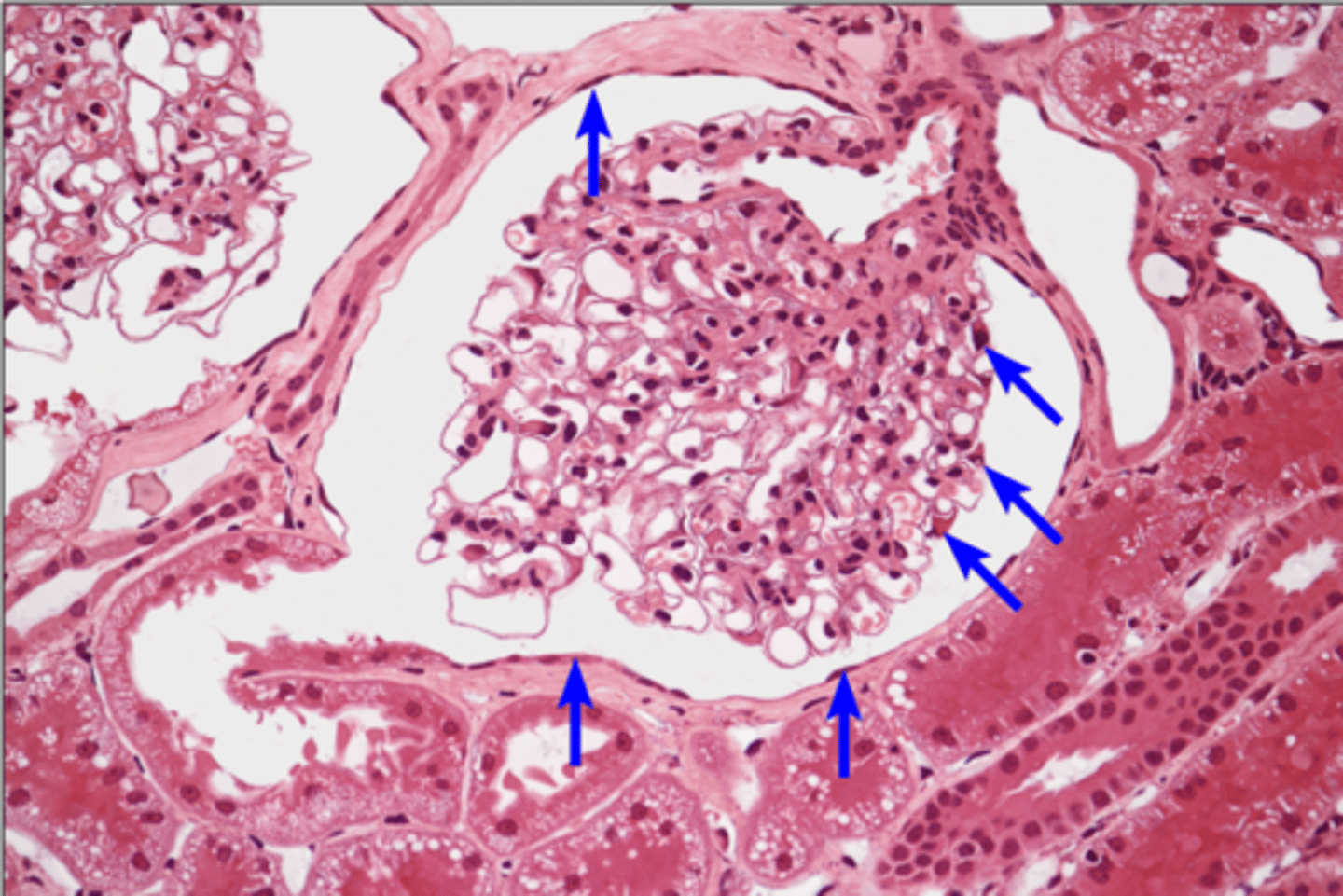
glomerular capsular space
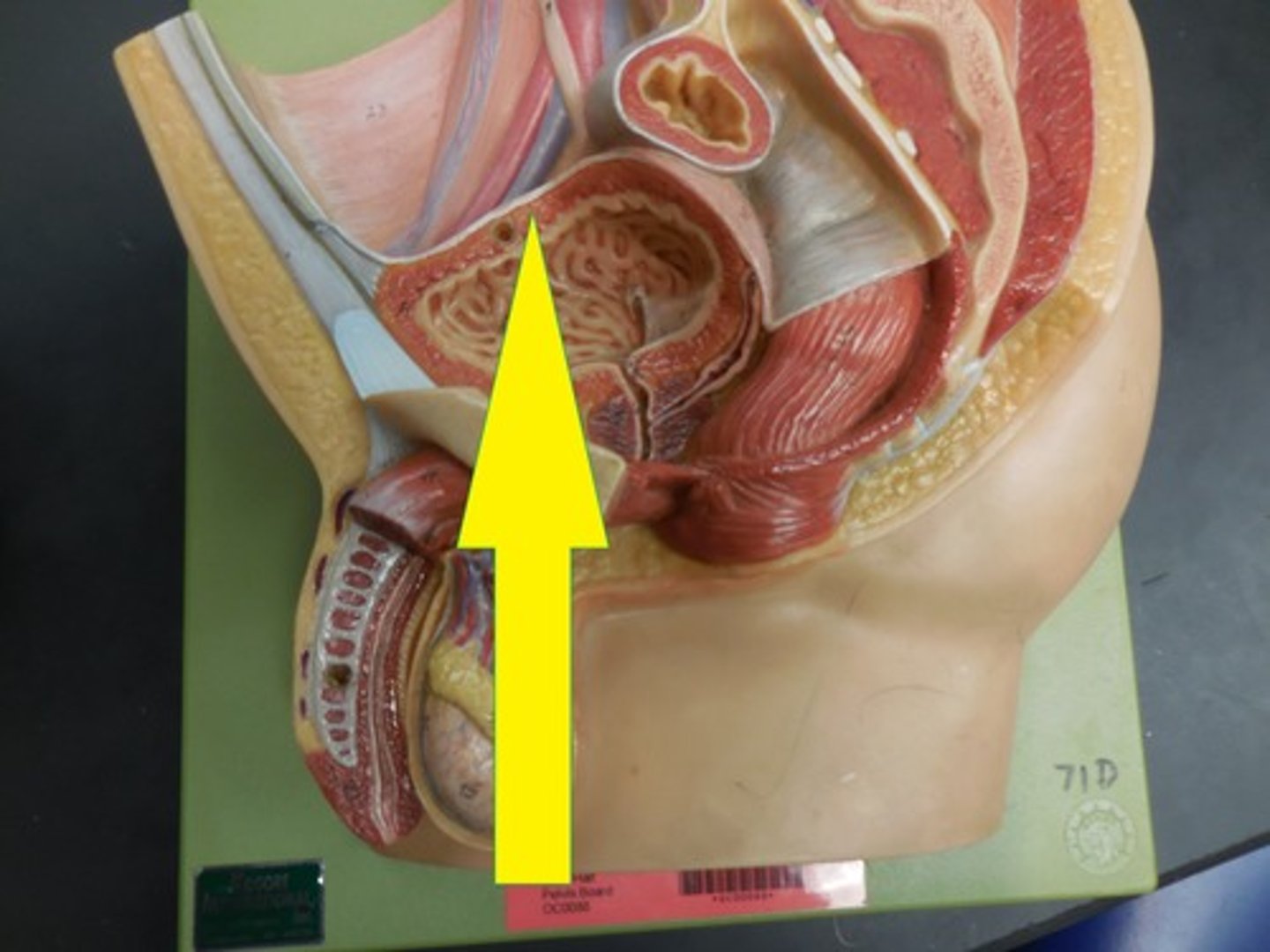
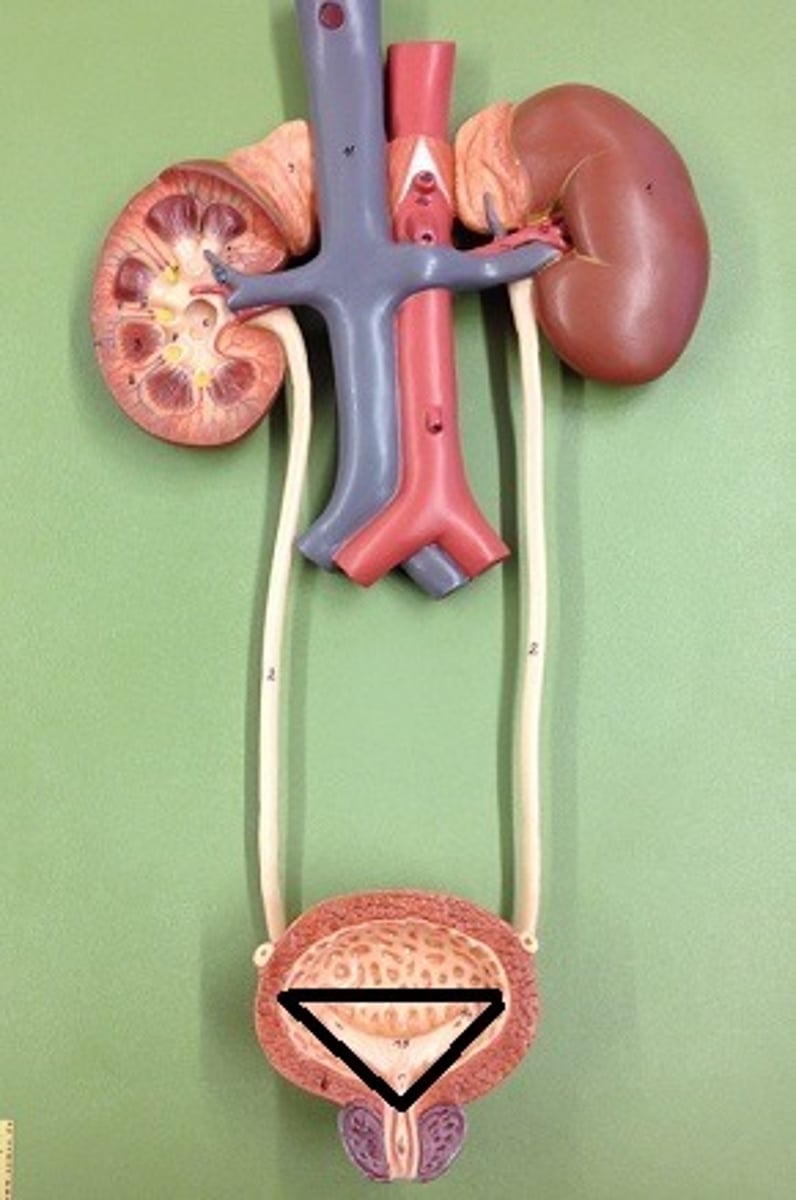
Ureter
Urinary bladder
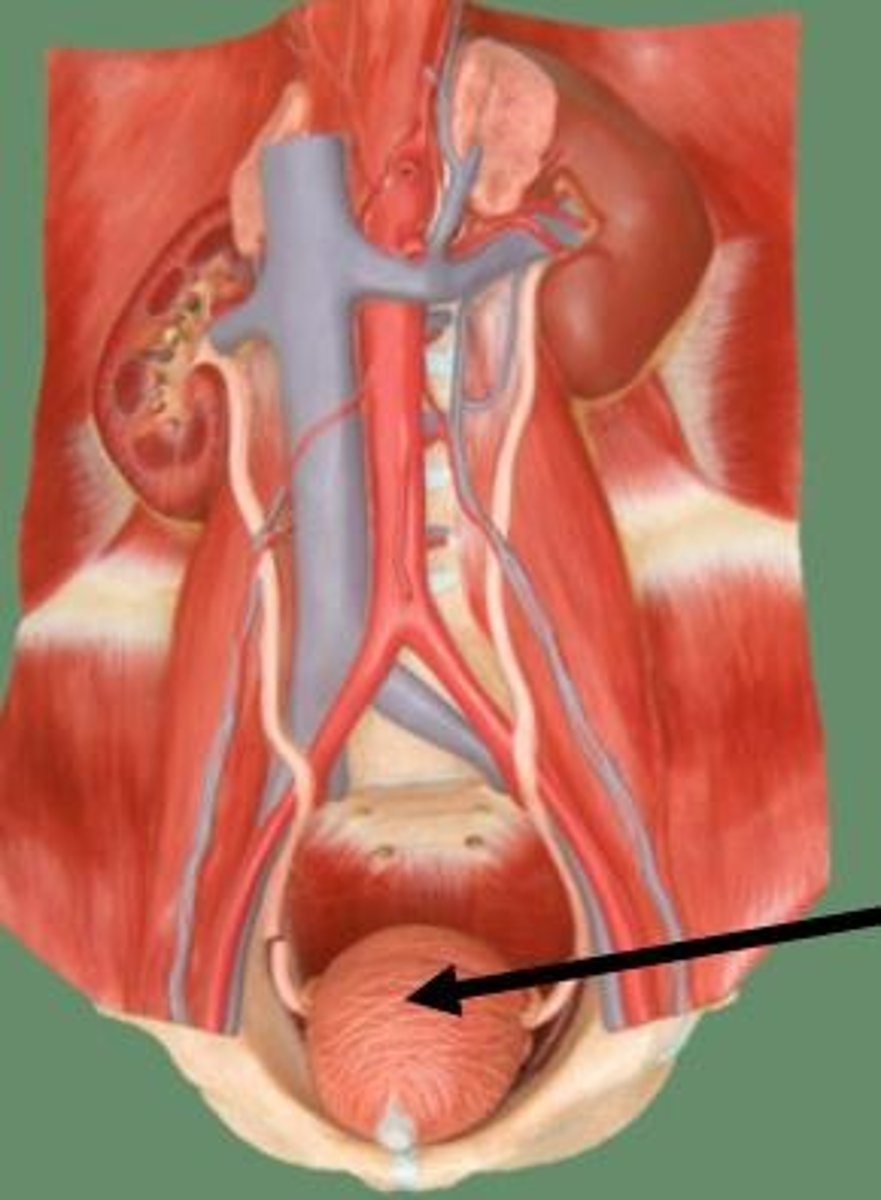
Urinary bladder
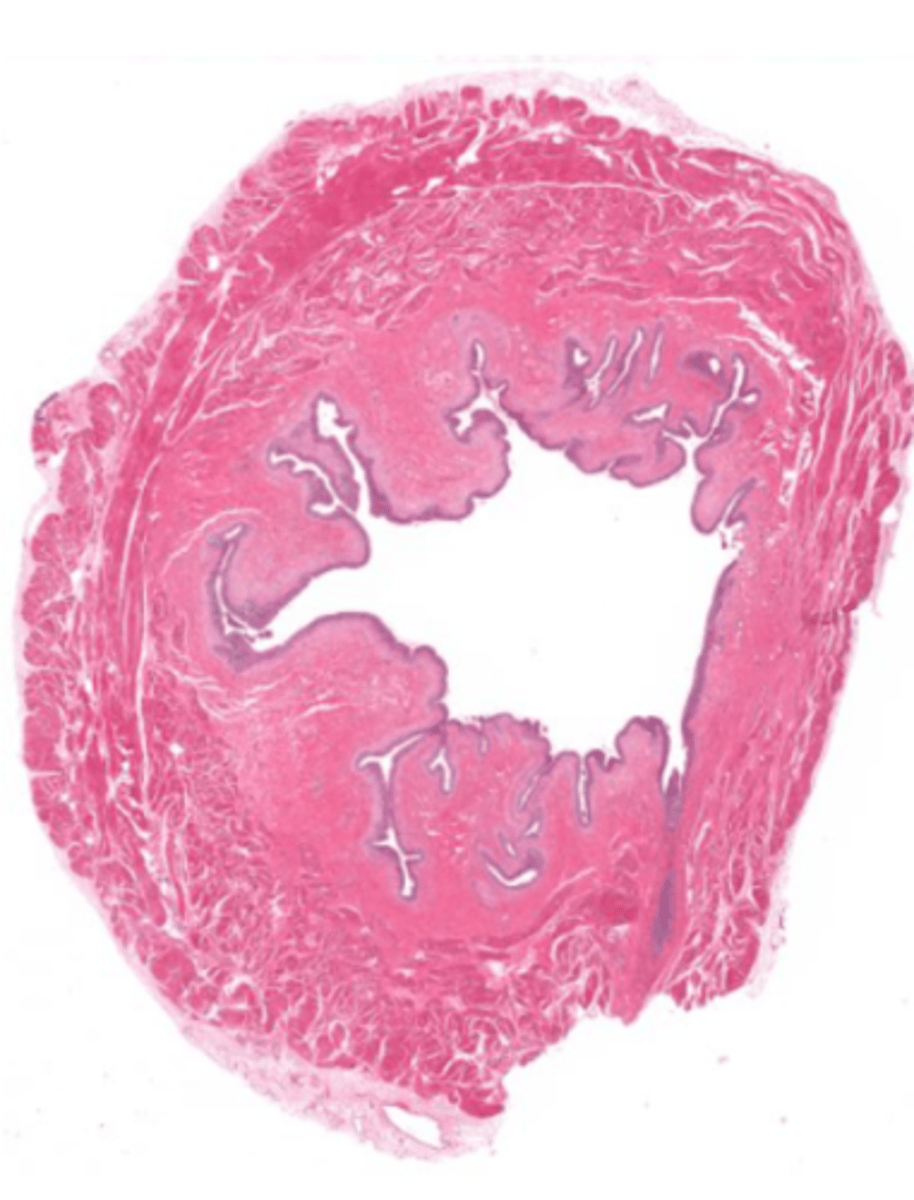
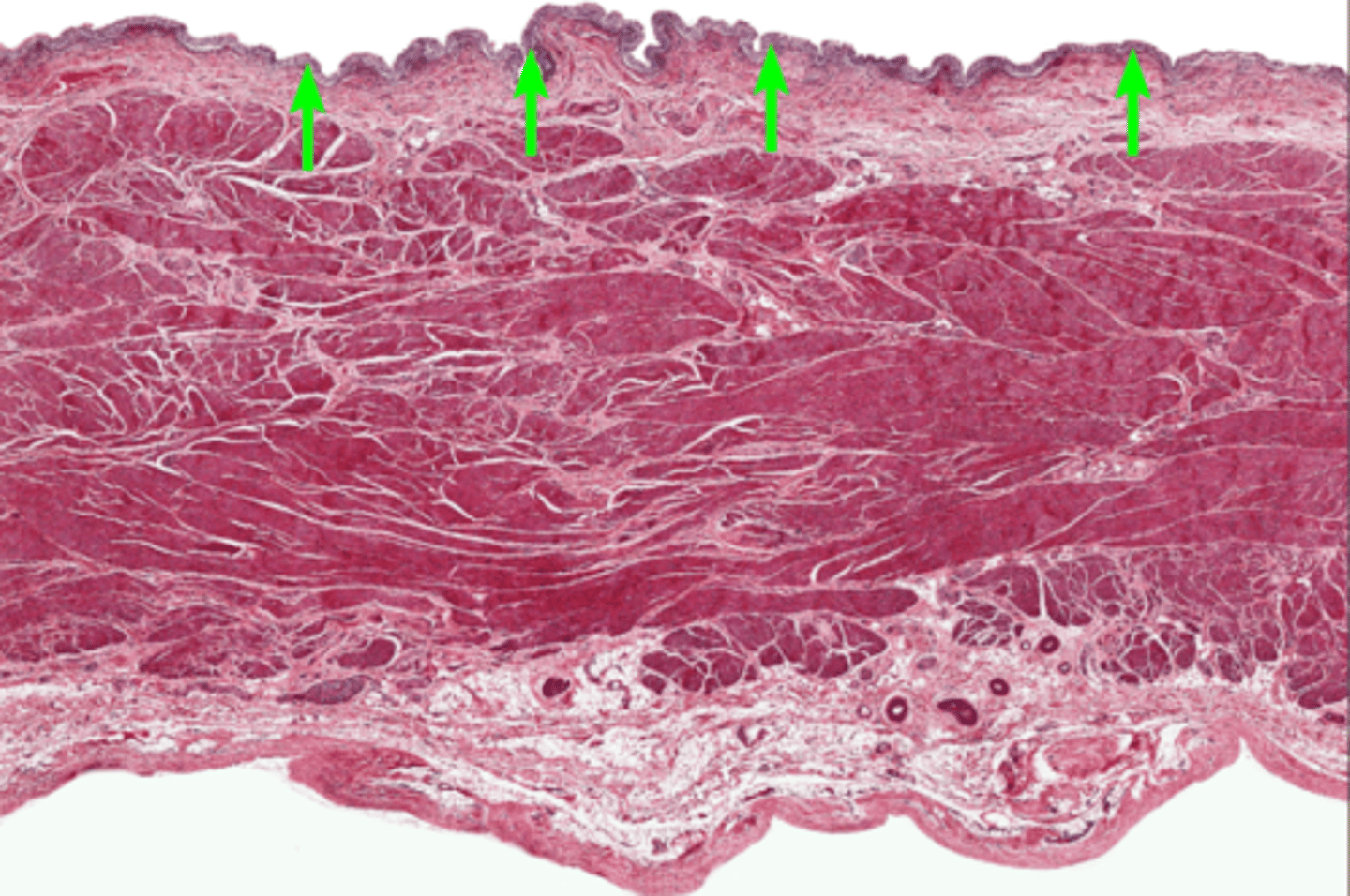
Detrusor muscle
Detrusor muscle
Trigone
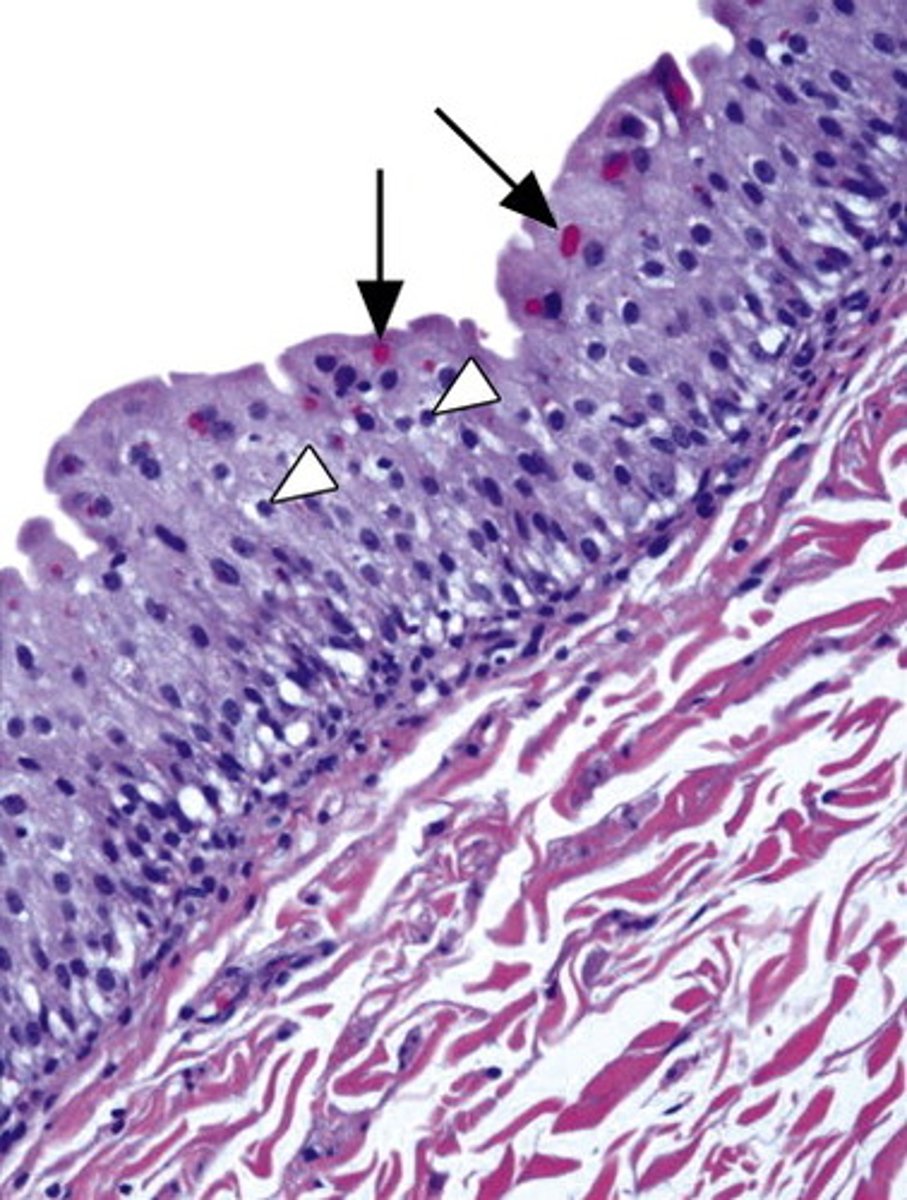
Urothelium
Urothelium
Ureteral orifice
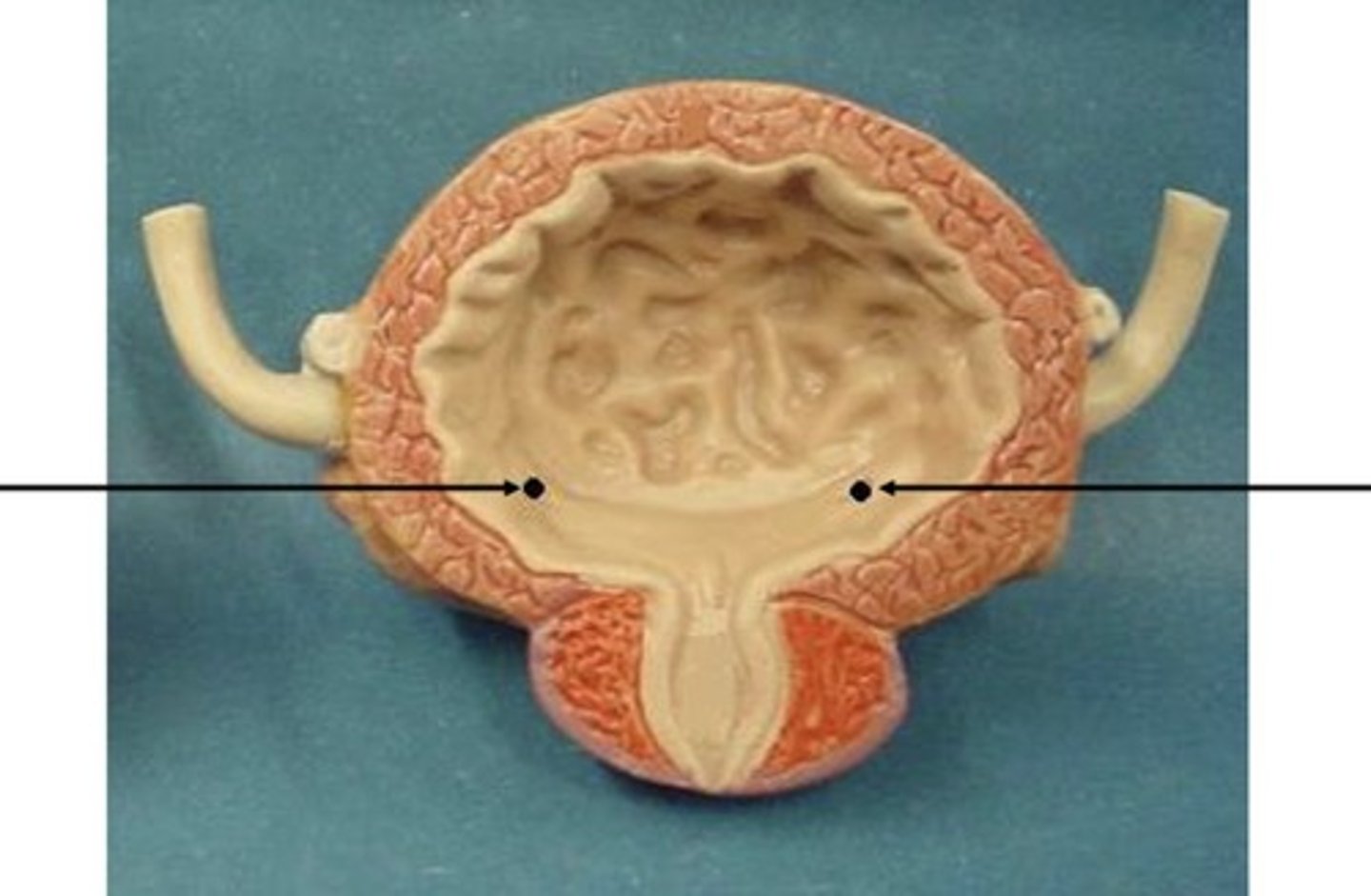
Internal urethral sphincter
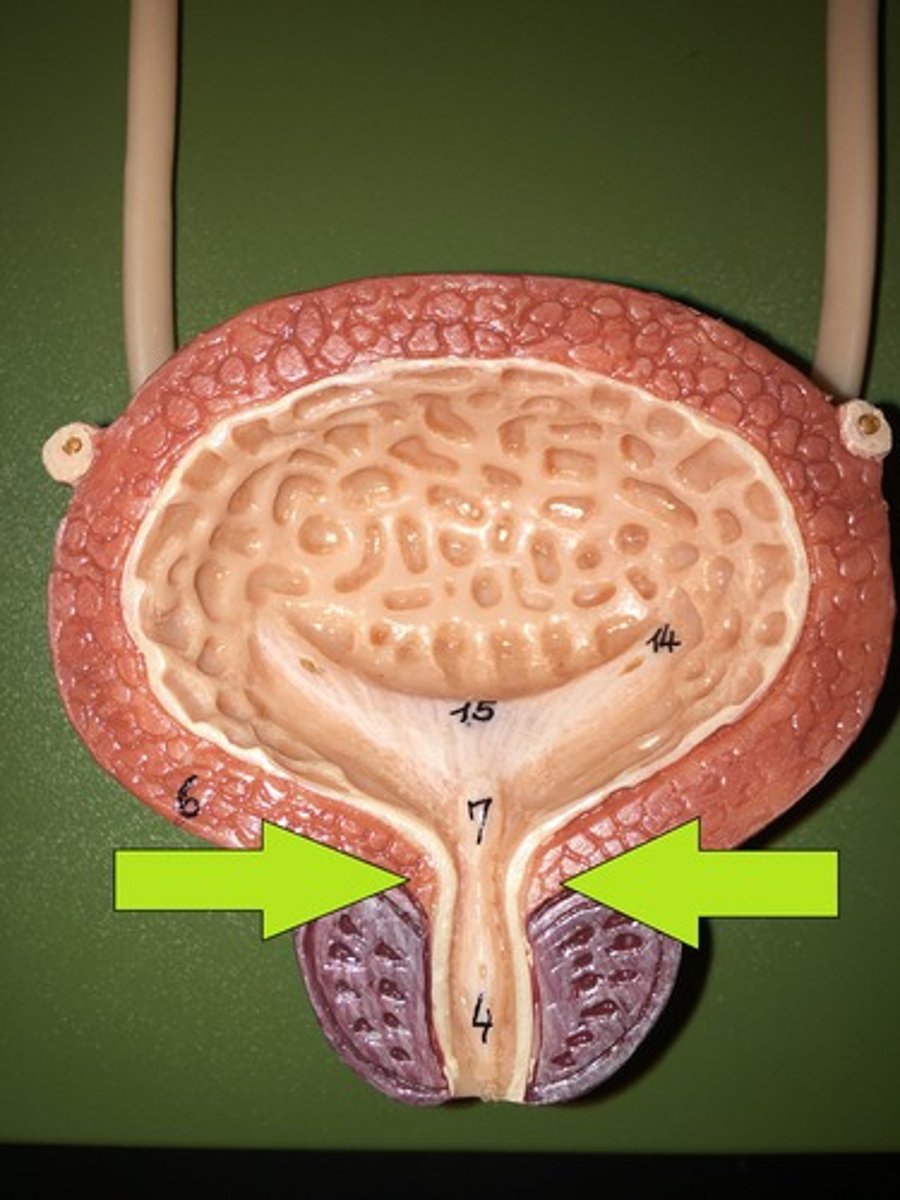
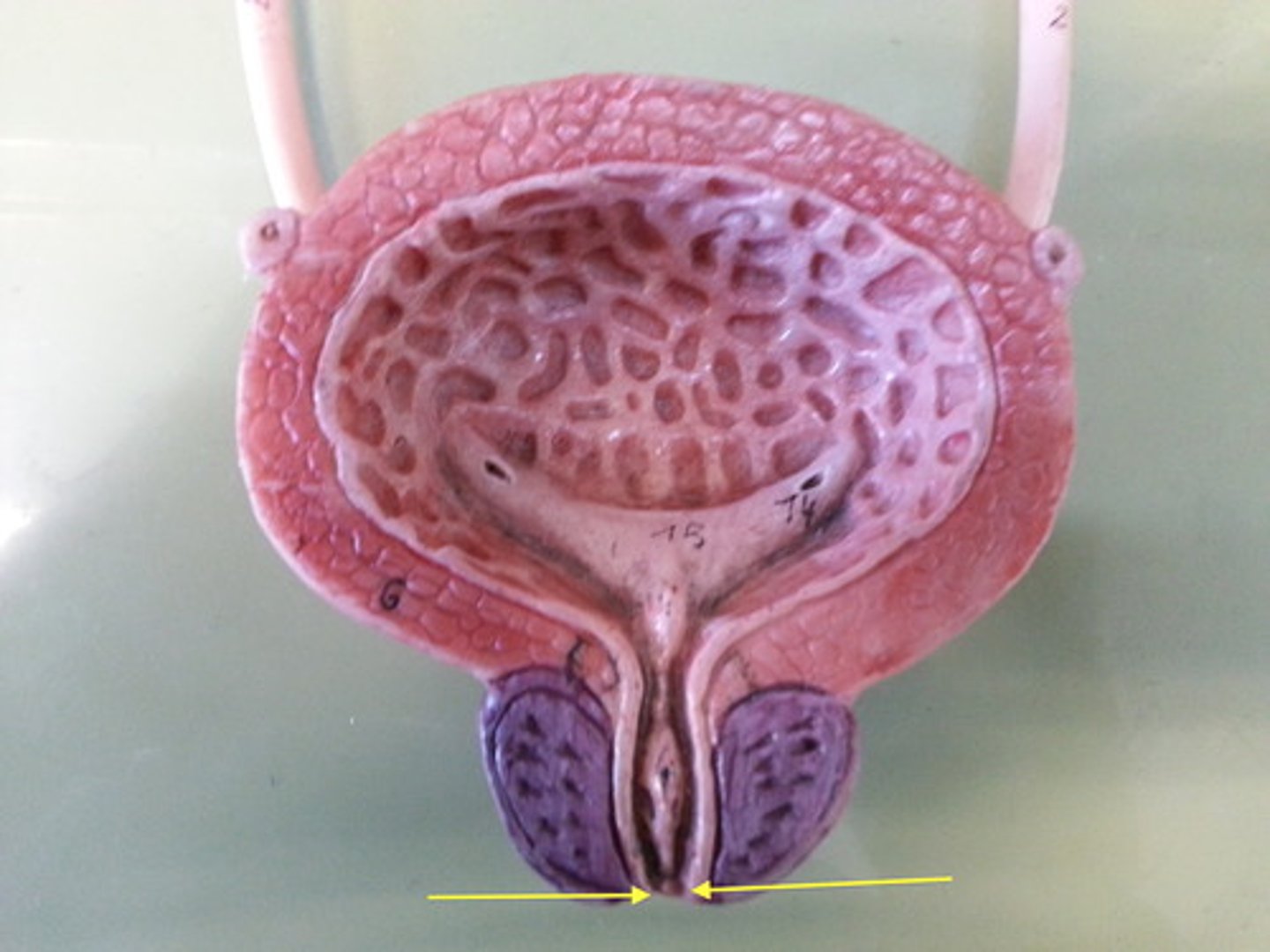
External urethral sphincter
measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution
pH
4.5 - 8.2, usually 6.0
pH range of urine
food/drink consumed, infections, organ dysfunction, medication
Factors that influence urine color
amount of water drank
Factors that influence urine transparency
number and weight of solutes in the urine
Factors that influence urine specific gravity
dehydration, imbalanced diet, genetics, or medications
what causes kidney stones
elevated levels of glucose in urine indicates type 1 or 2 diabeties
Glycosuria
elevated proteins in urine indicates kidney disease or immune disorders
Proteinuria
elevated levels of ketones in urine indicates type 1 or 2 diabetes
Ketonuria
blood in the urine indicates kidney damage, UTI, kidney/bladder stones, cancer, or blood disorders
Hematuria
hemoglobin in urine indicates kidney issues or blood disorders
Hemoglobinuria
nitrate in urine indicates UTI
Nitrituria
elevated levels of bilirubin in urine indicates liver disease or blockage of the bile duct
Bilirubinuria
elvated WBCs in urine indicates UTI
Pyuria
Unorganized sediment in acidic urine
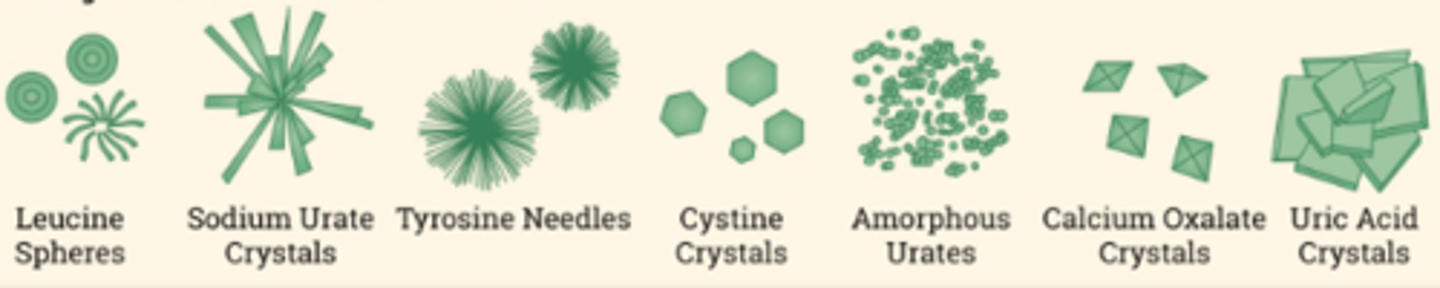
Unorganized sediment in basic urine

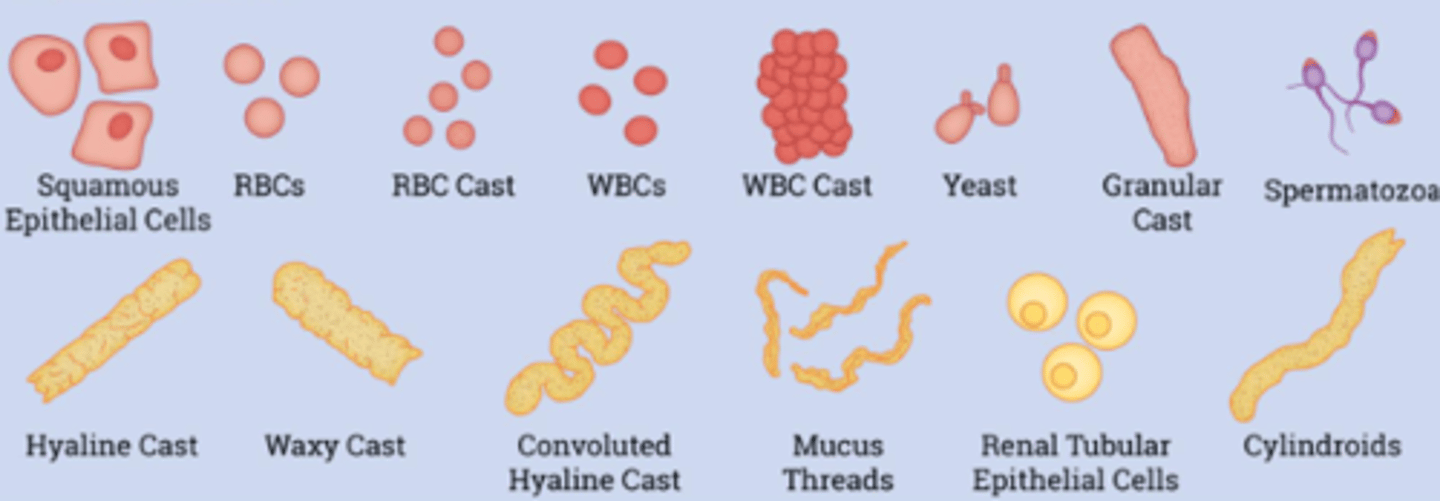
Organized sediment
right ureter
30
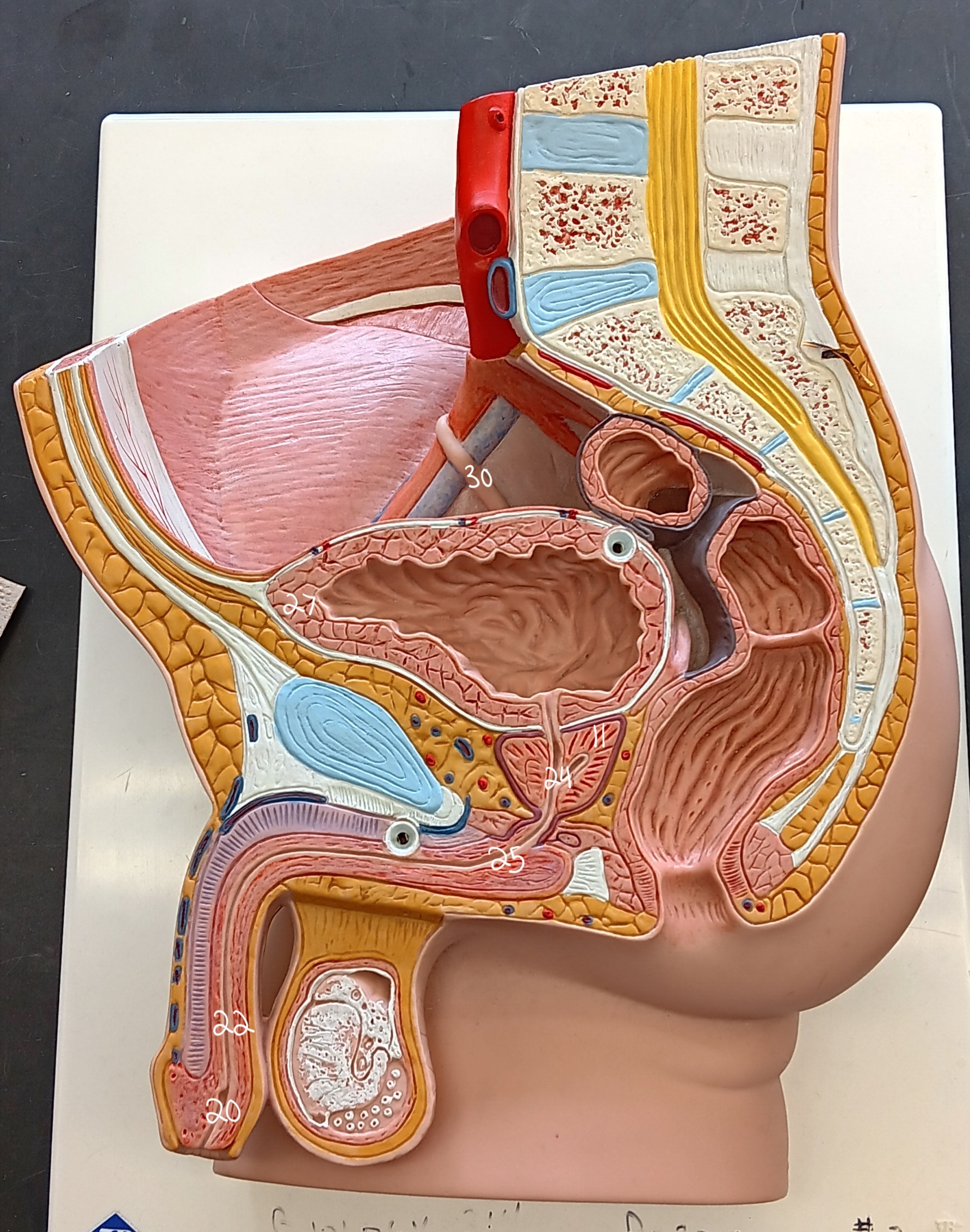
urinary bladder
27
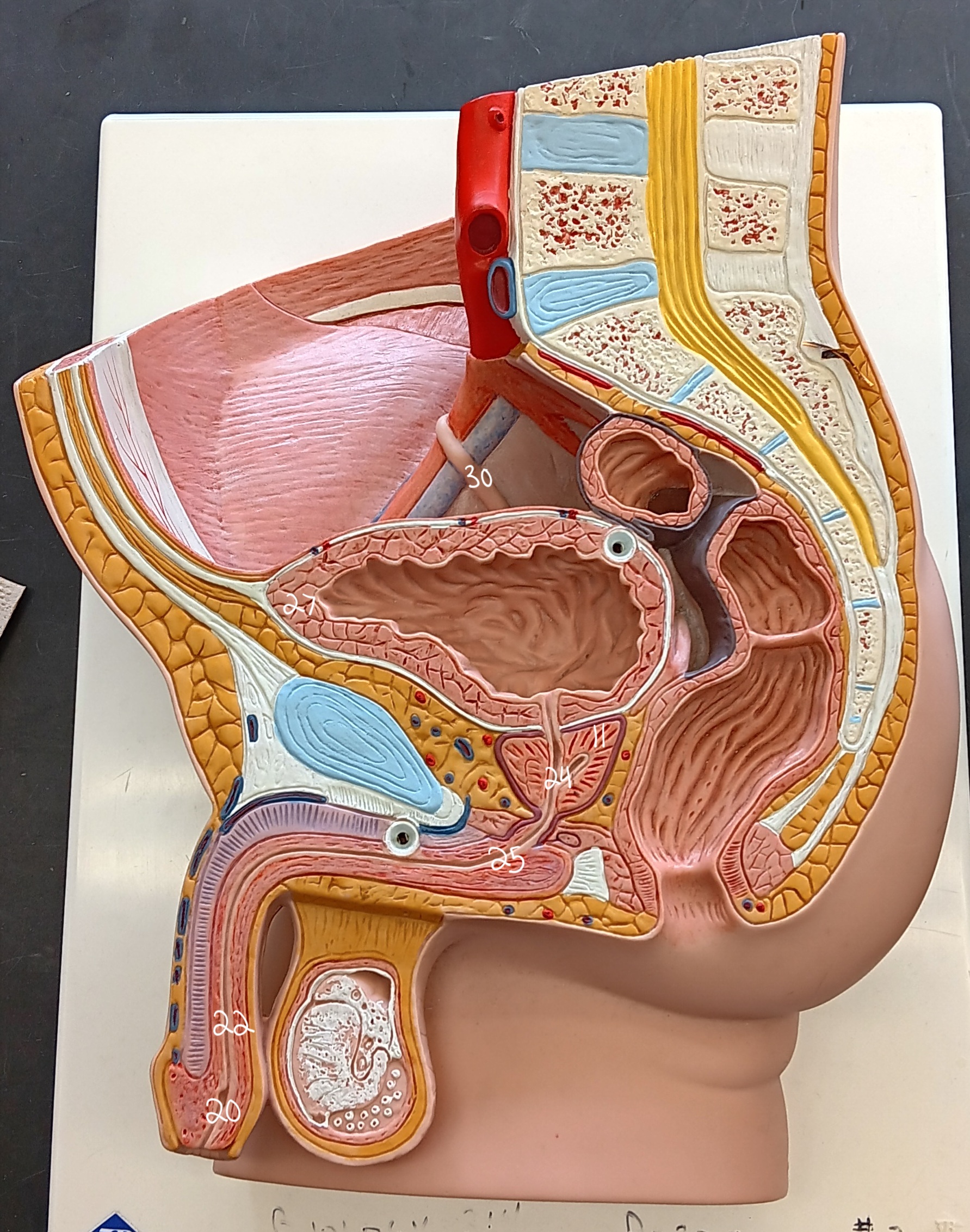
spongy urethra
22
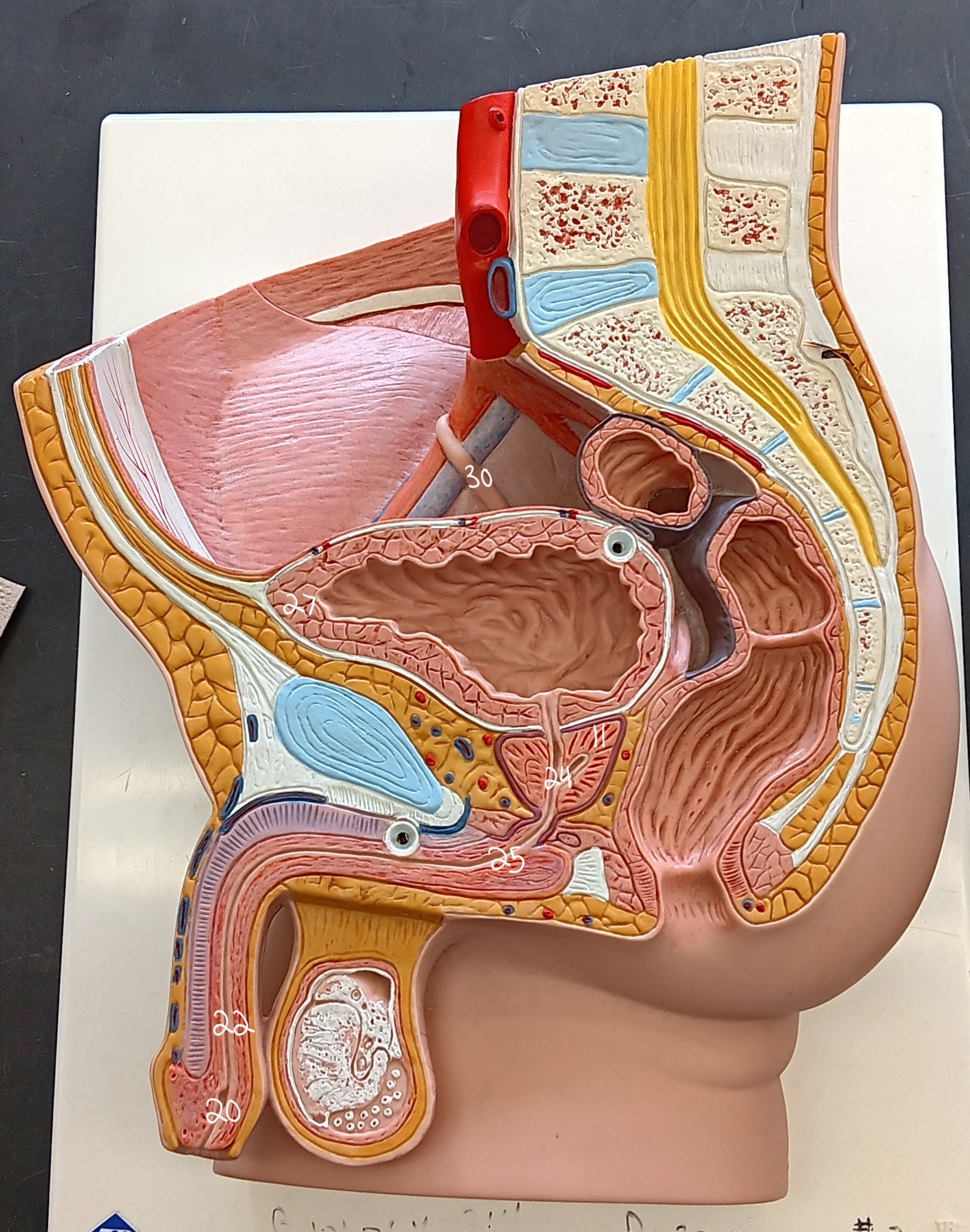
prostatic urethra
24
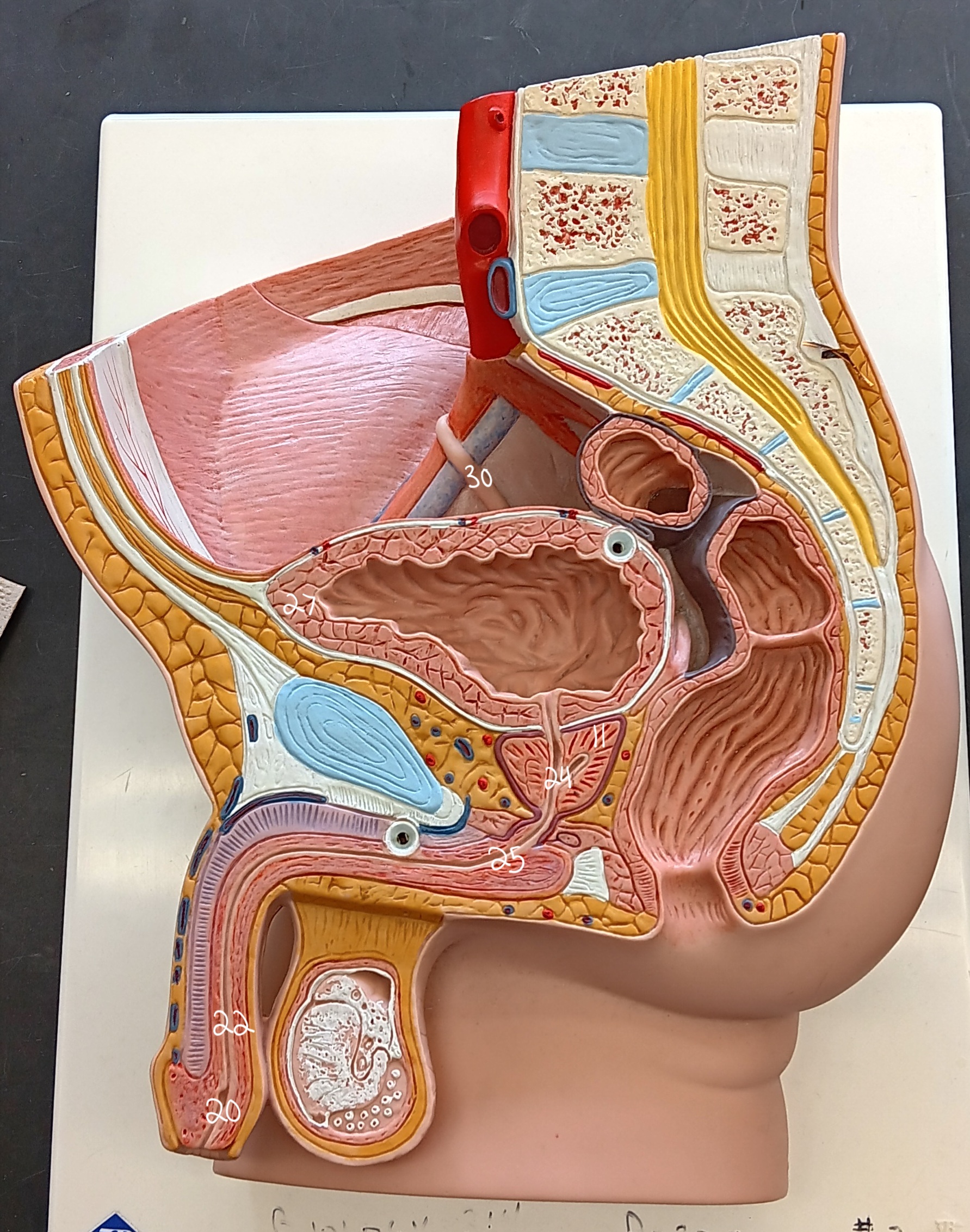
membranous urethra
25
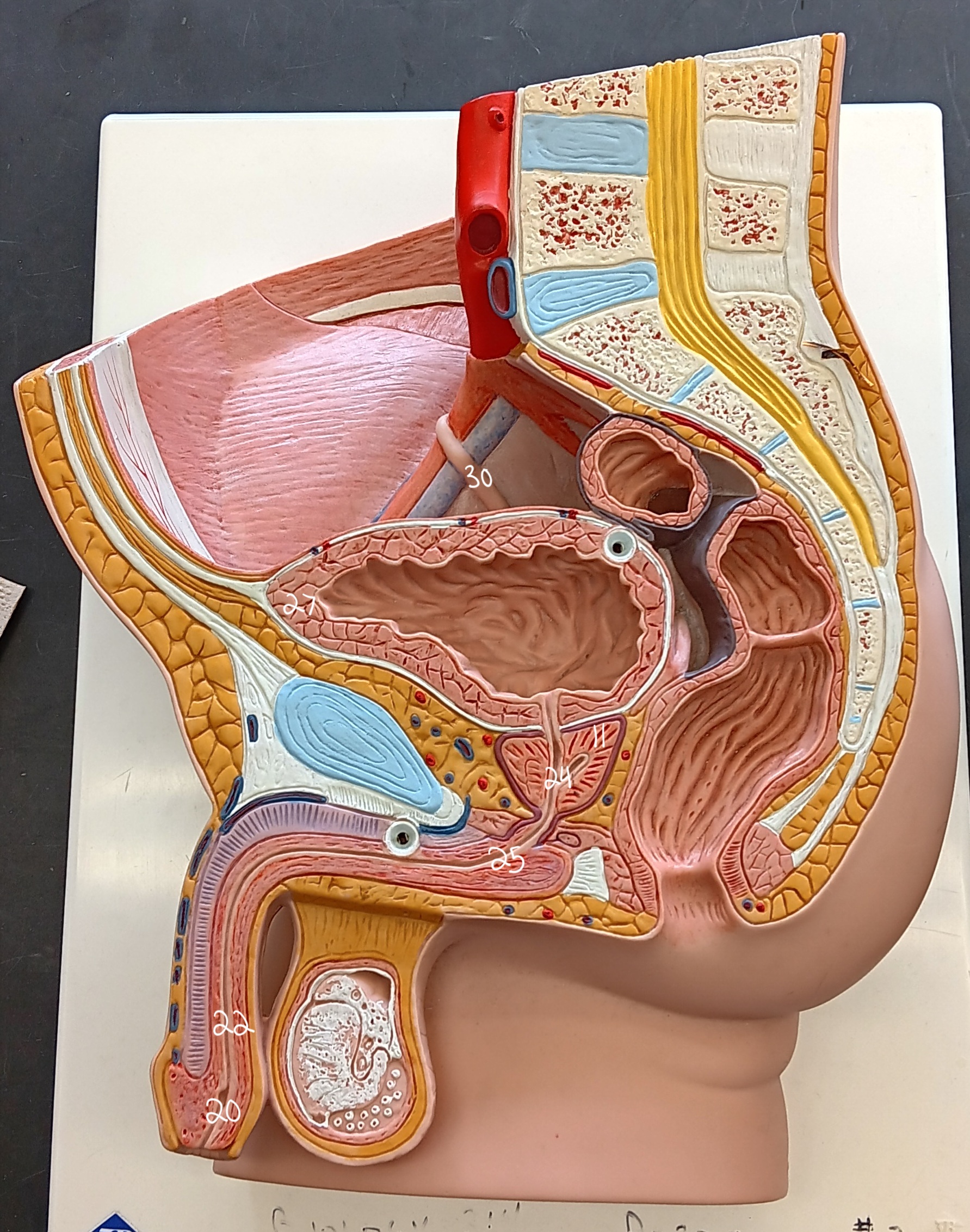
external urethral orifice
20
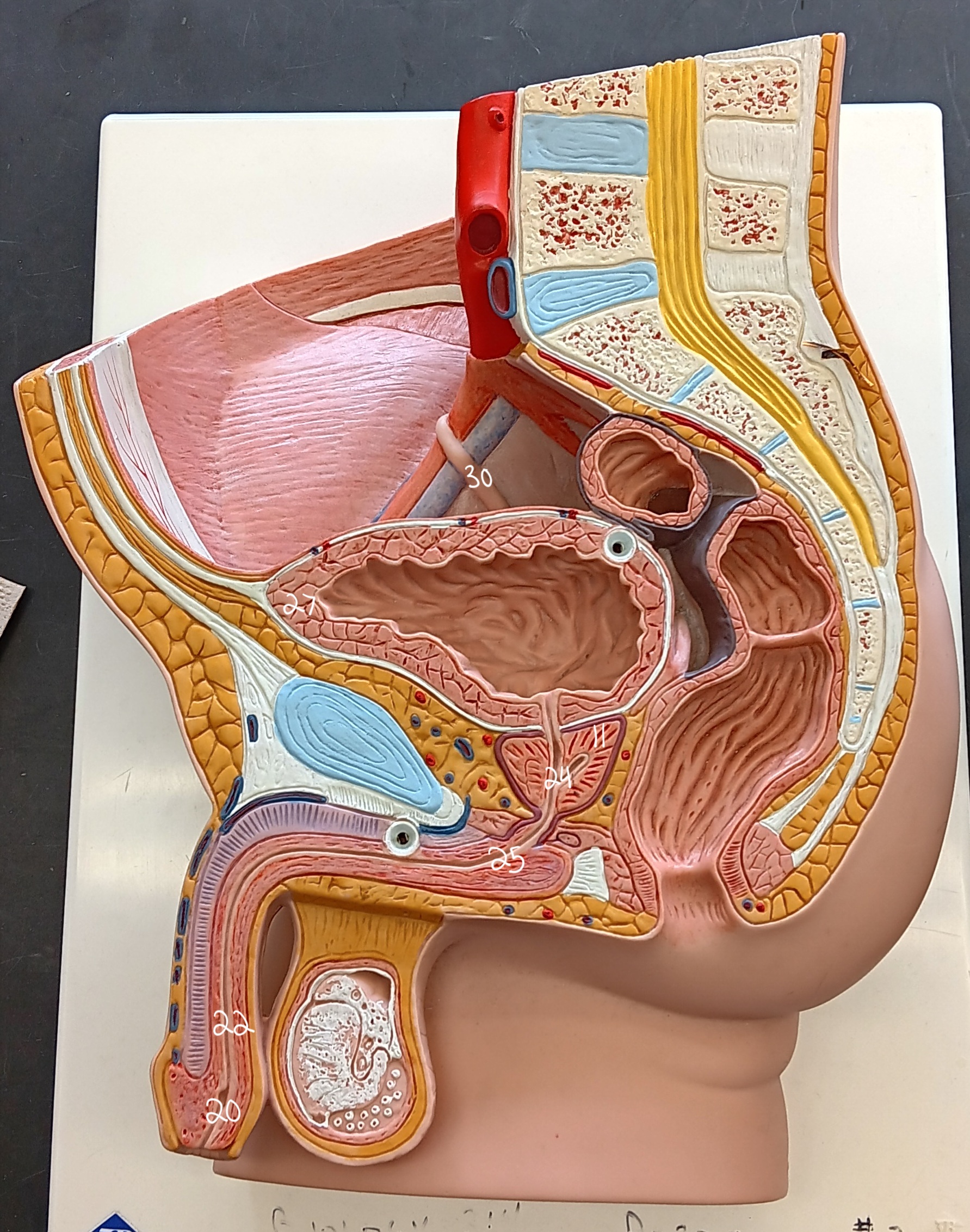
prostate gland
11
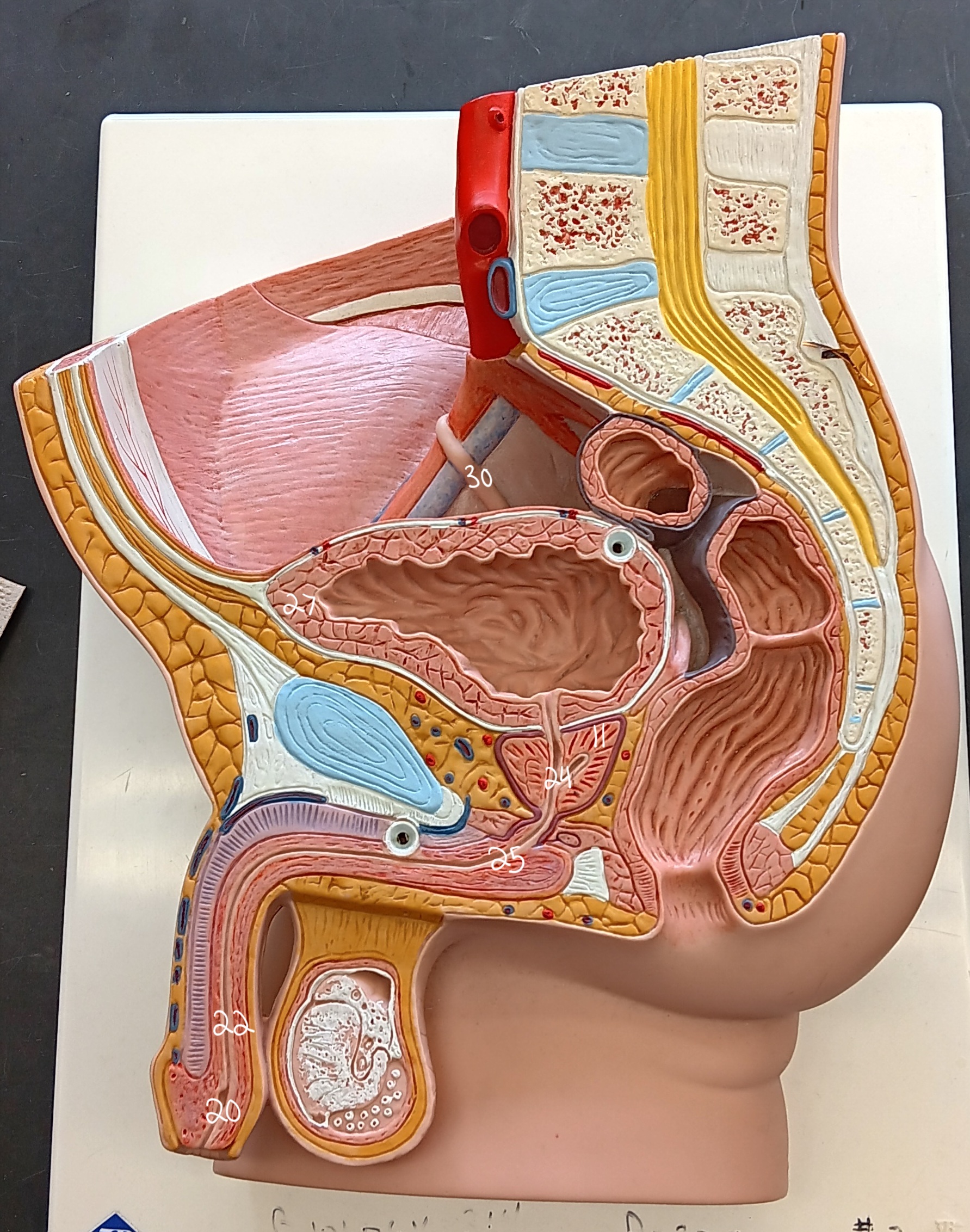
urinary bladder
22
right ureter
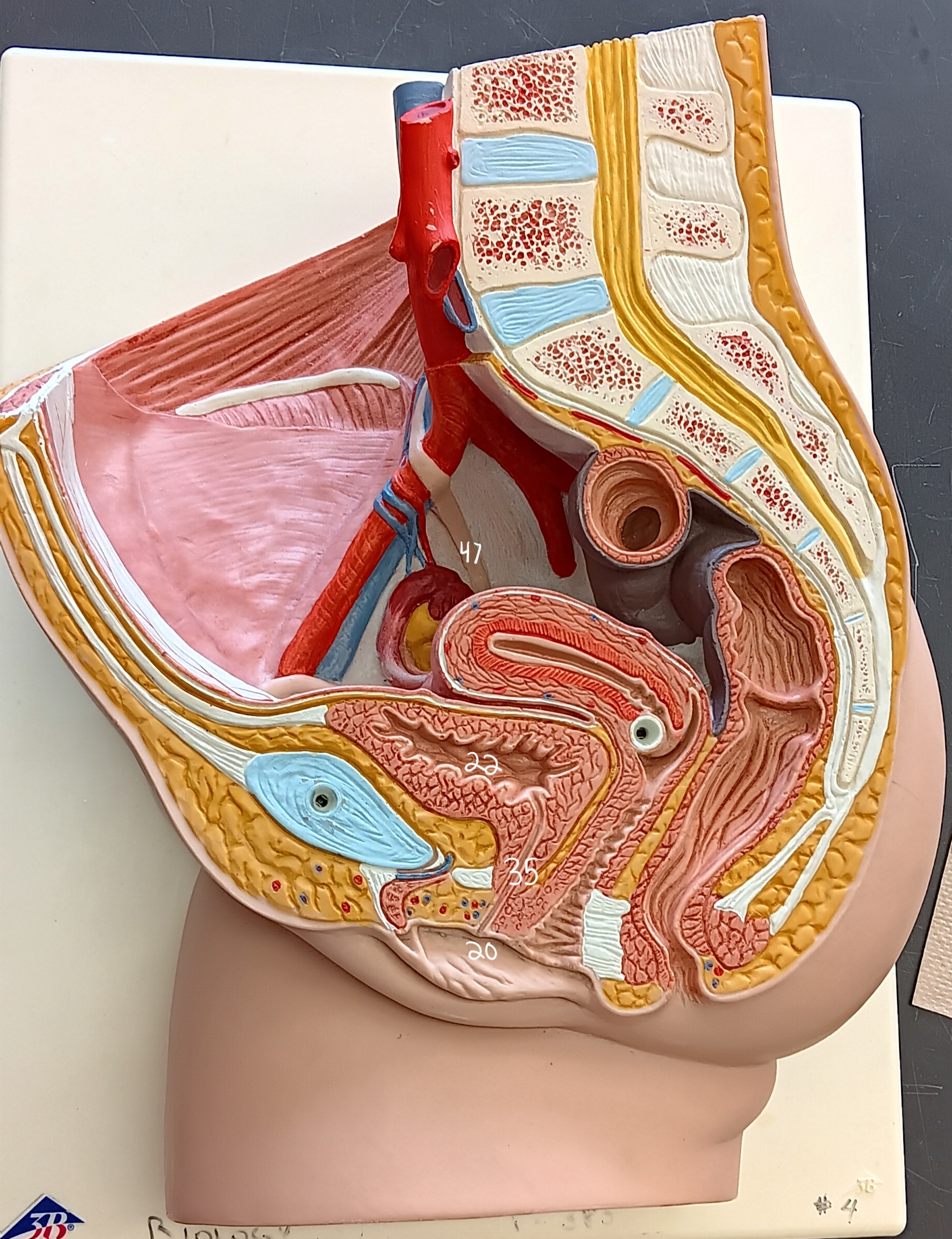
47
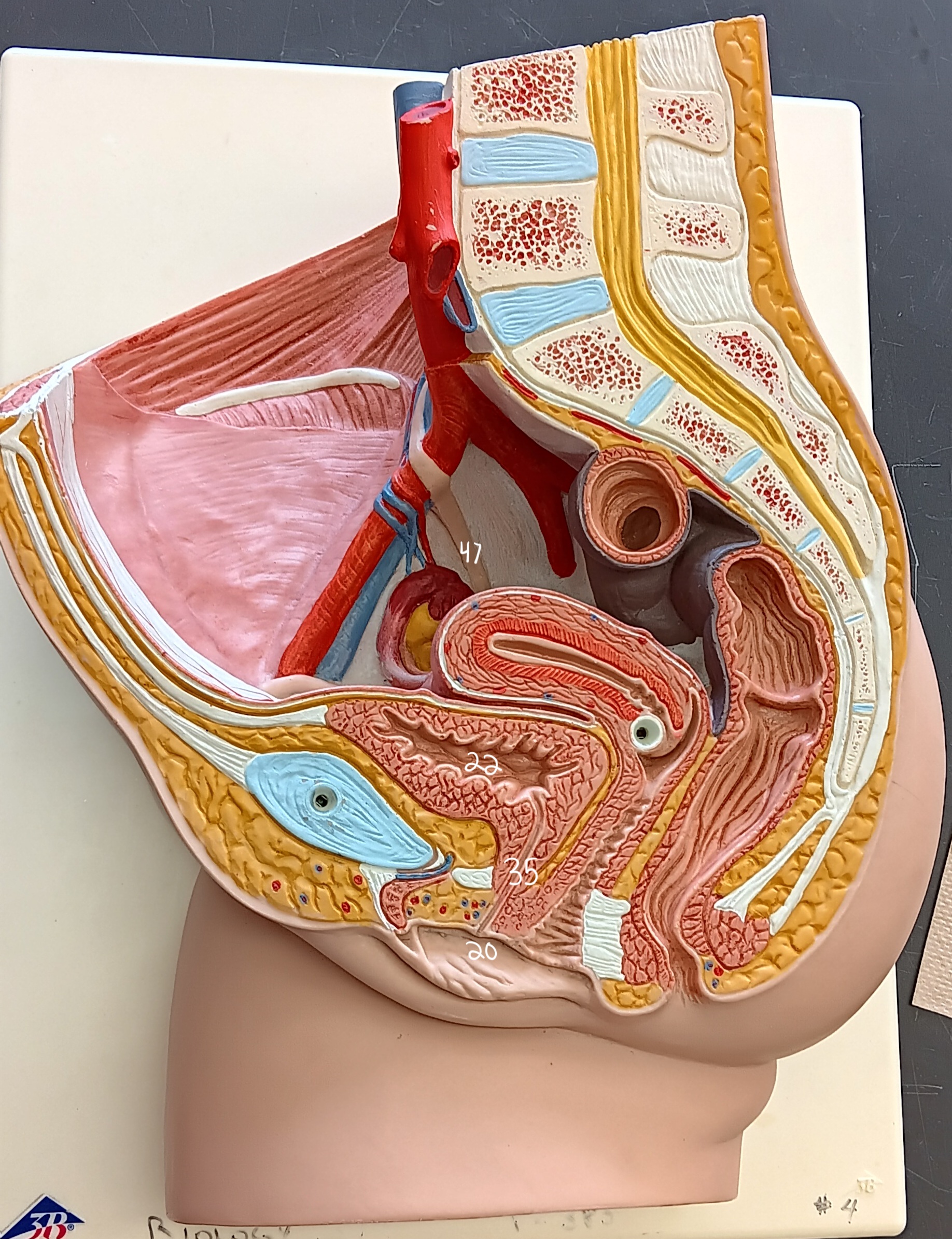
female urethra
35 (specify gender)
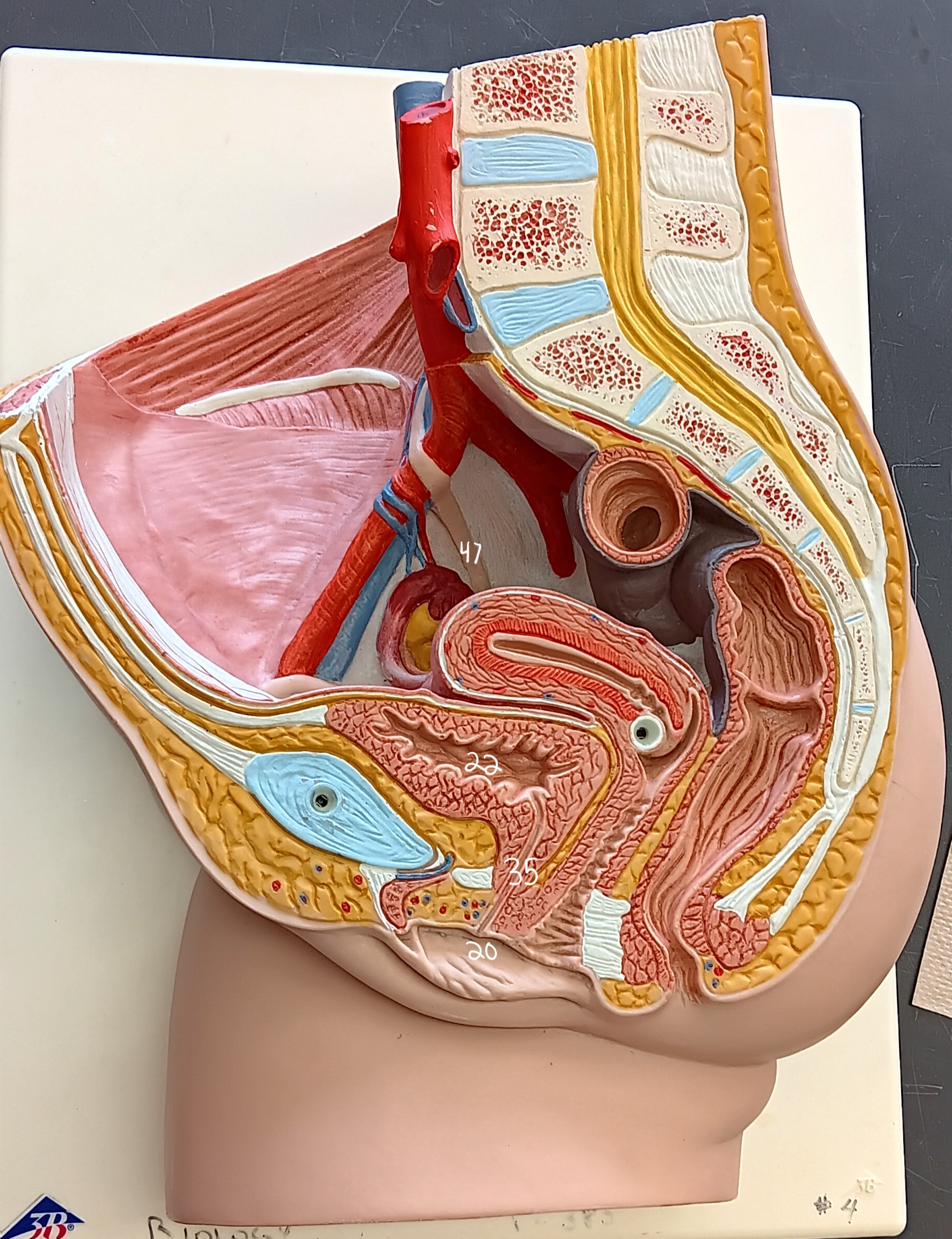
external urethral orifice
20
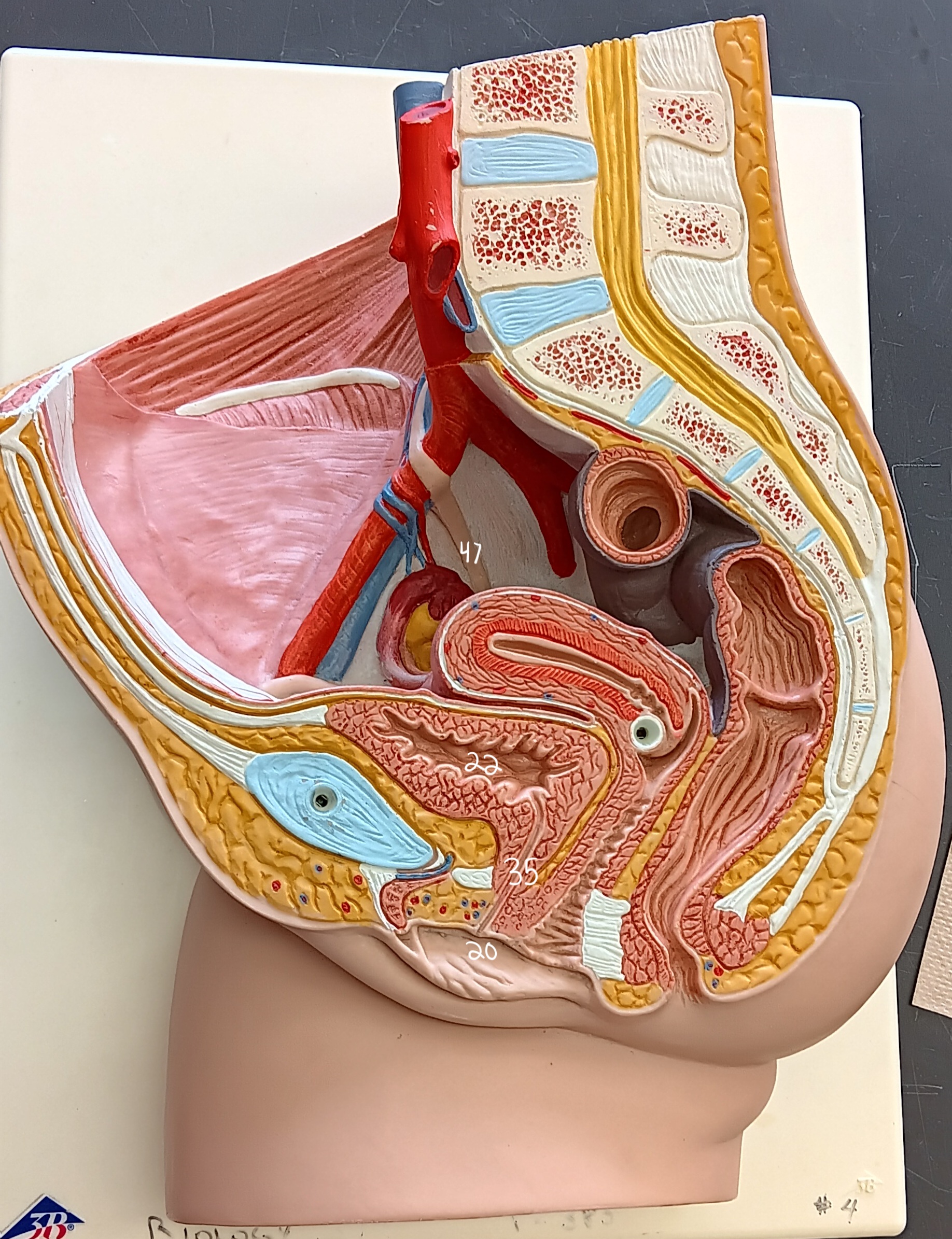
urinary bladder
what organ
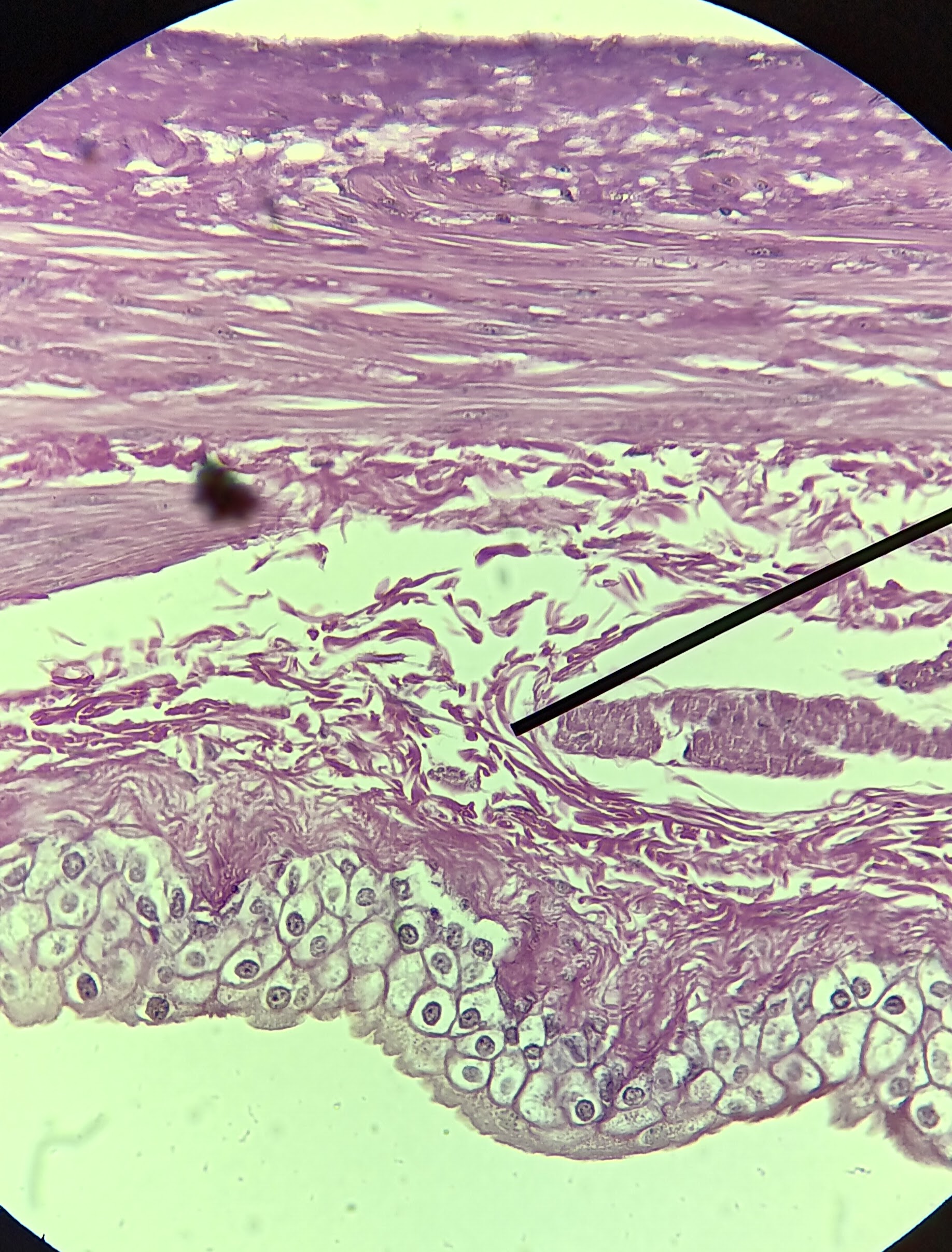
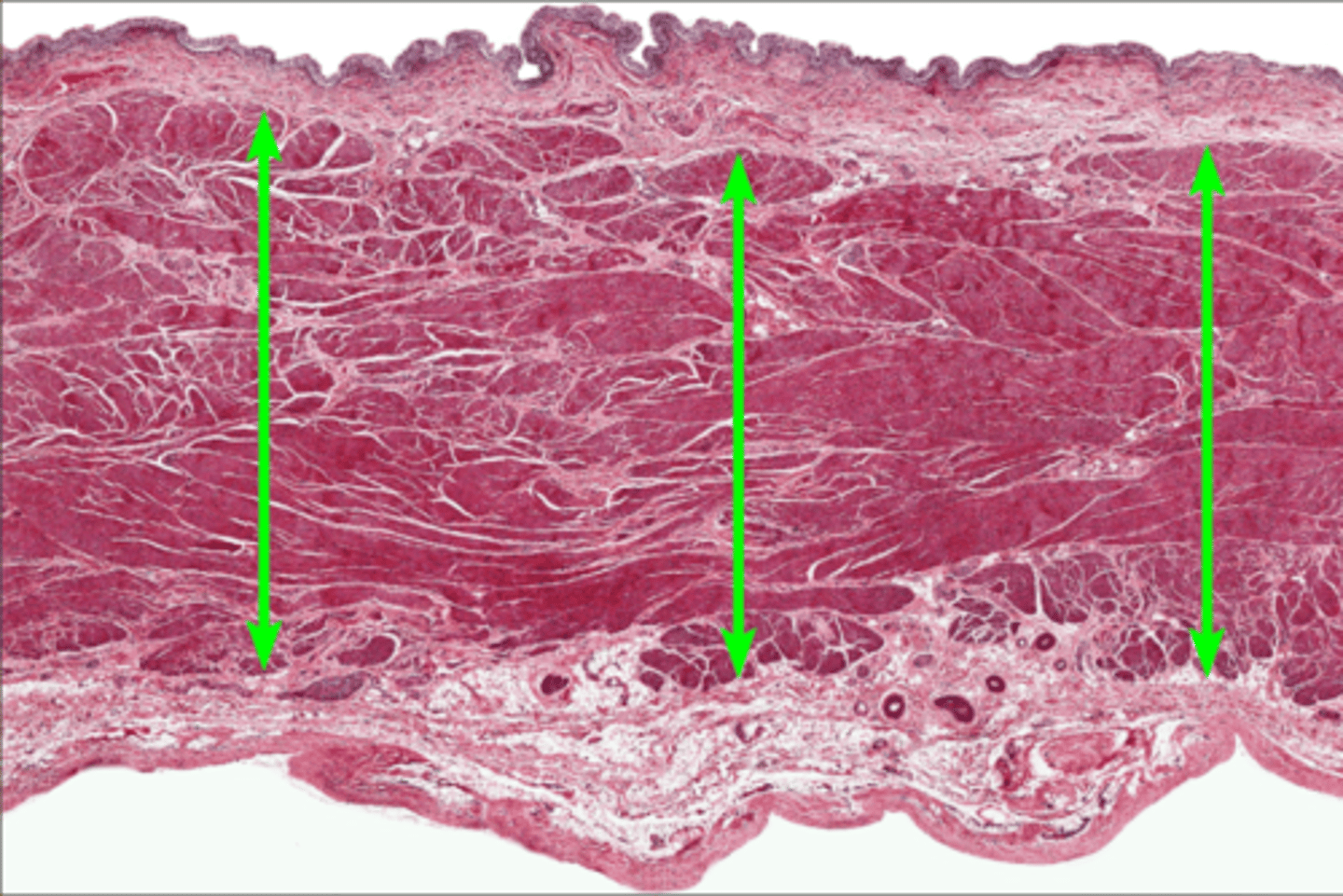
Transitional epithelium
why tissue type/ cells
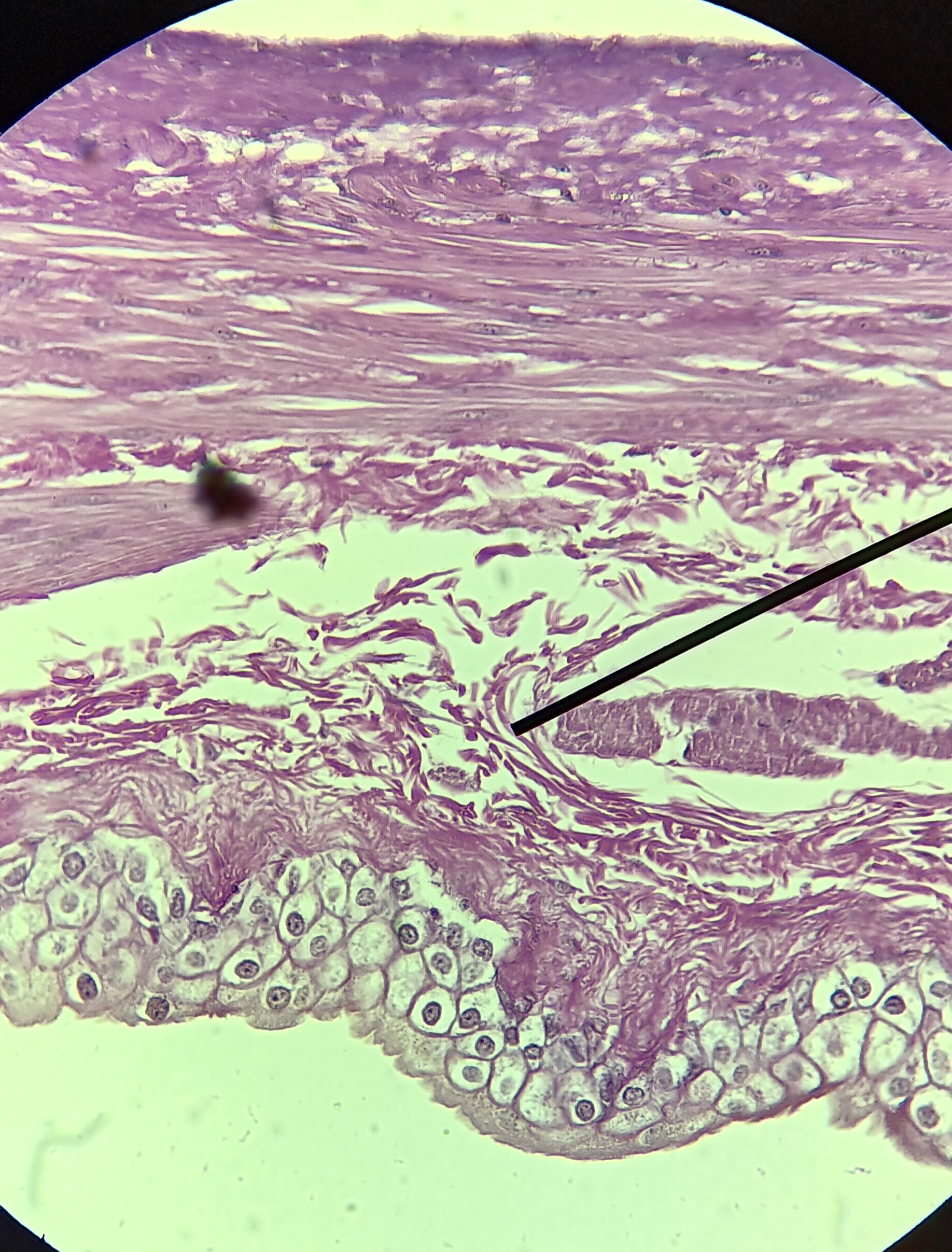
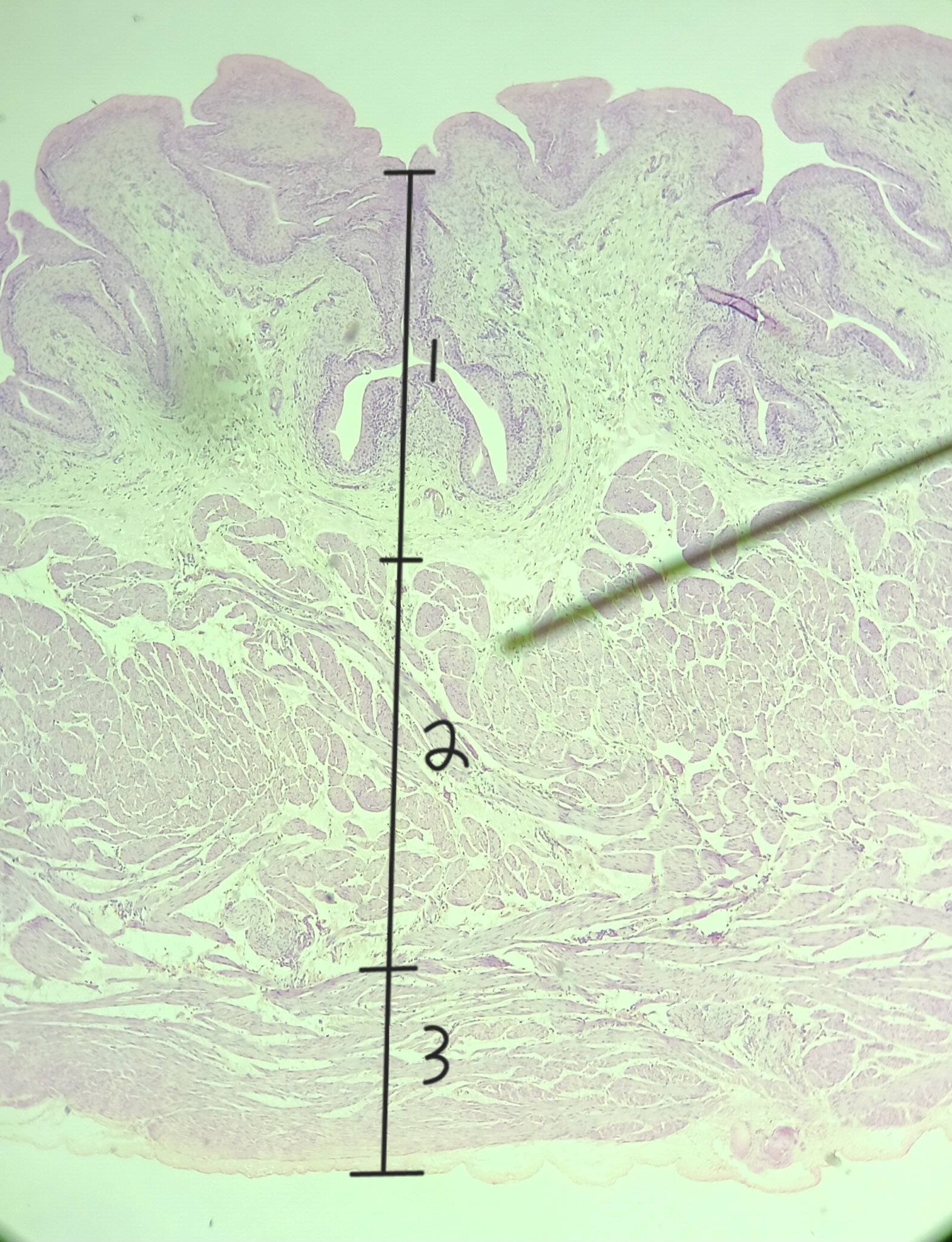
lamina propria
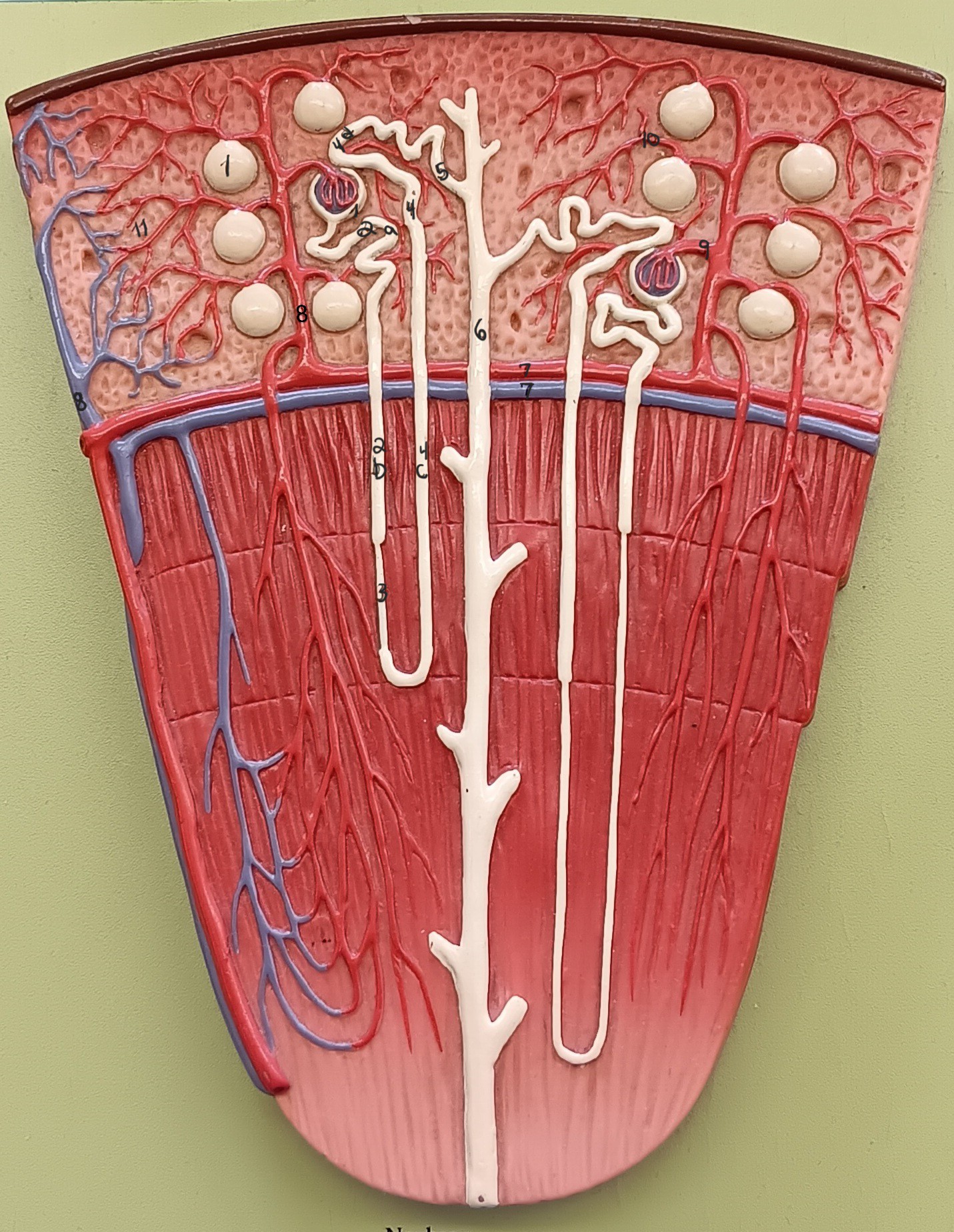
1
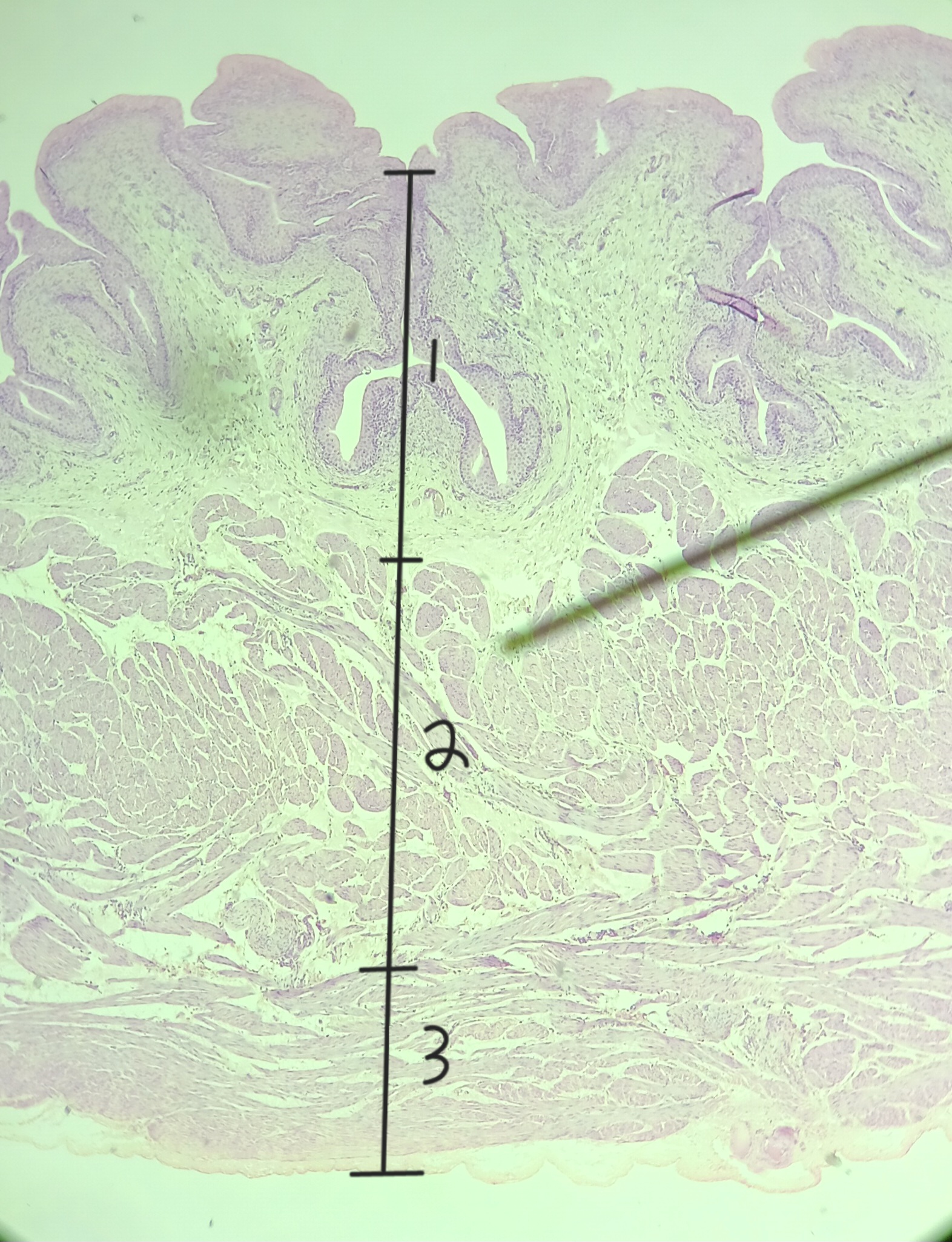
muscularis externa
2
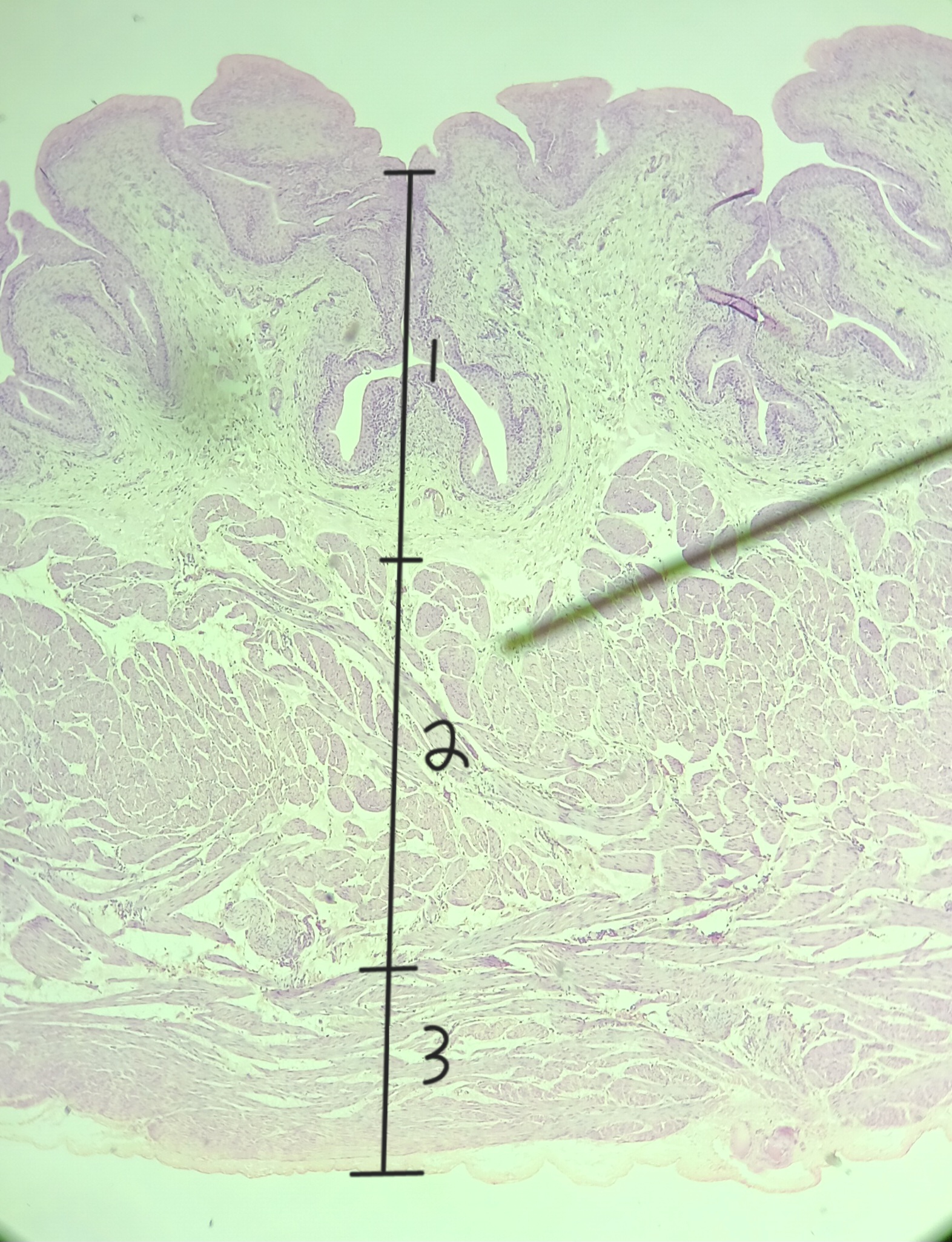
adventitia/ serosa
3
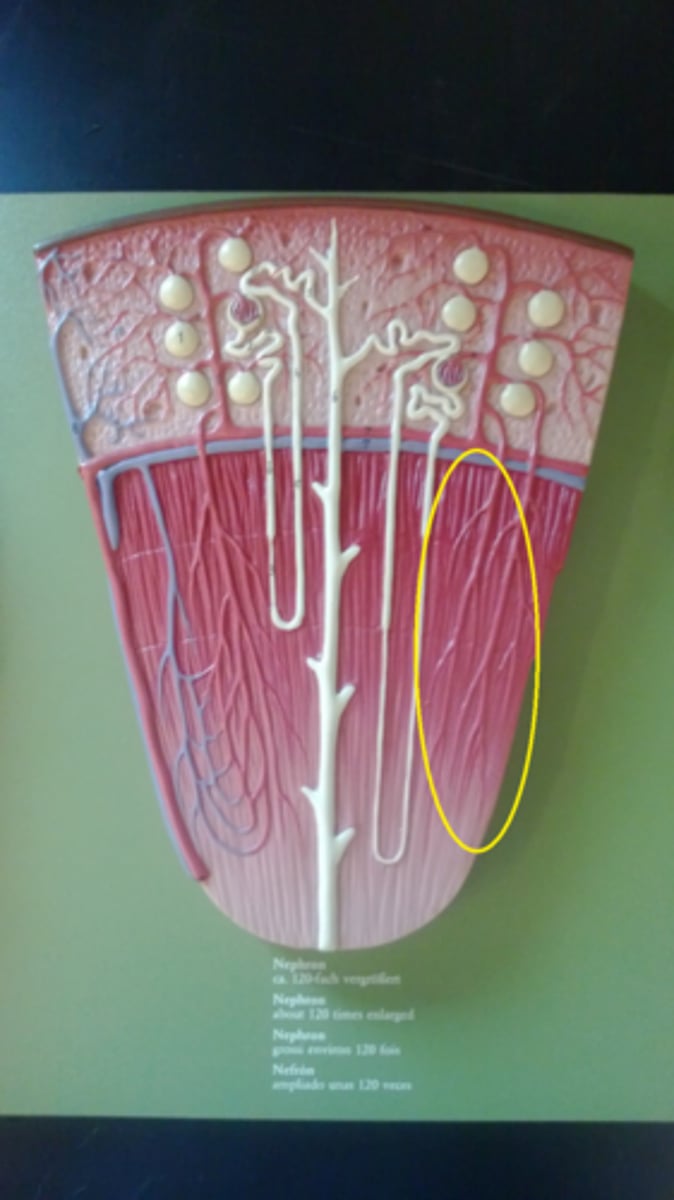
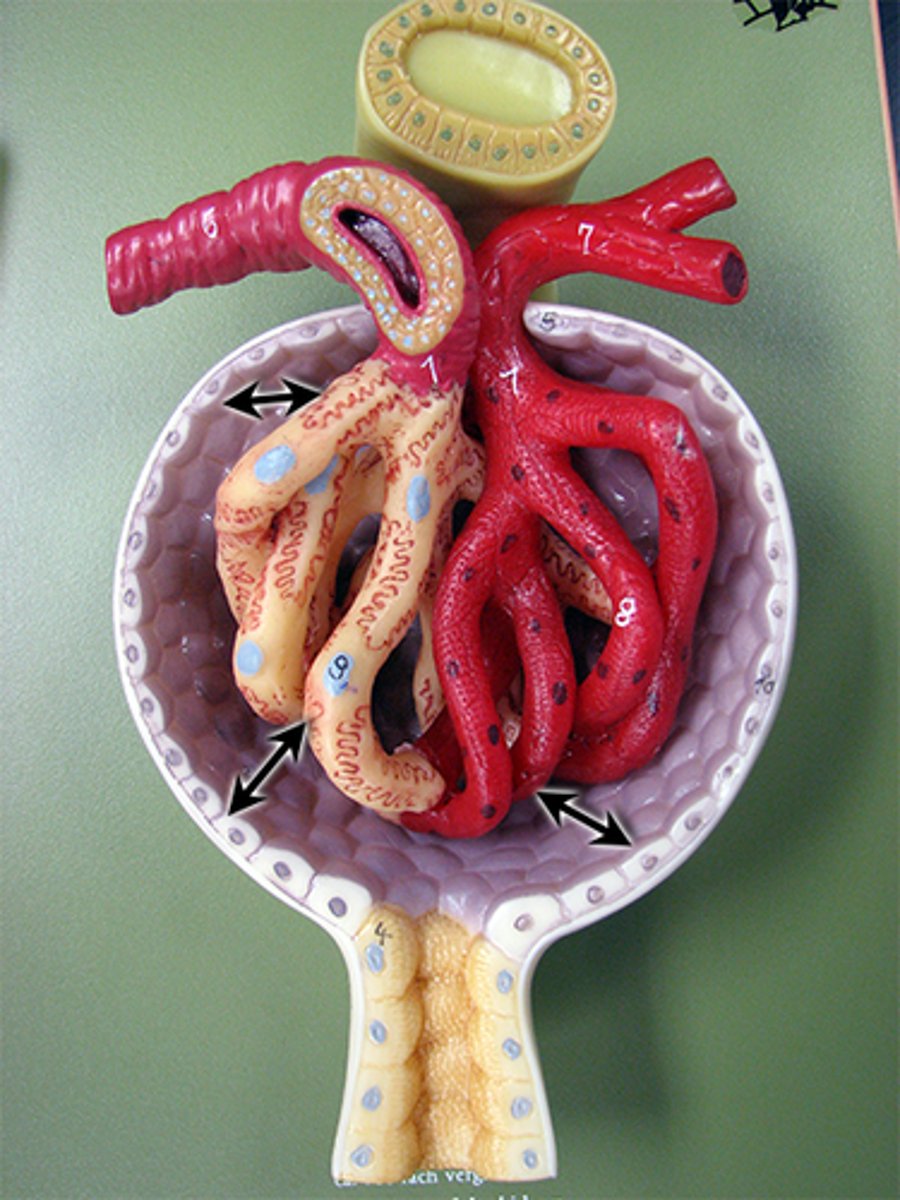
renal corpuscle
1
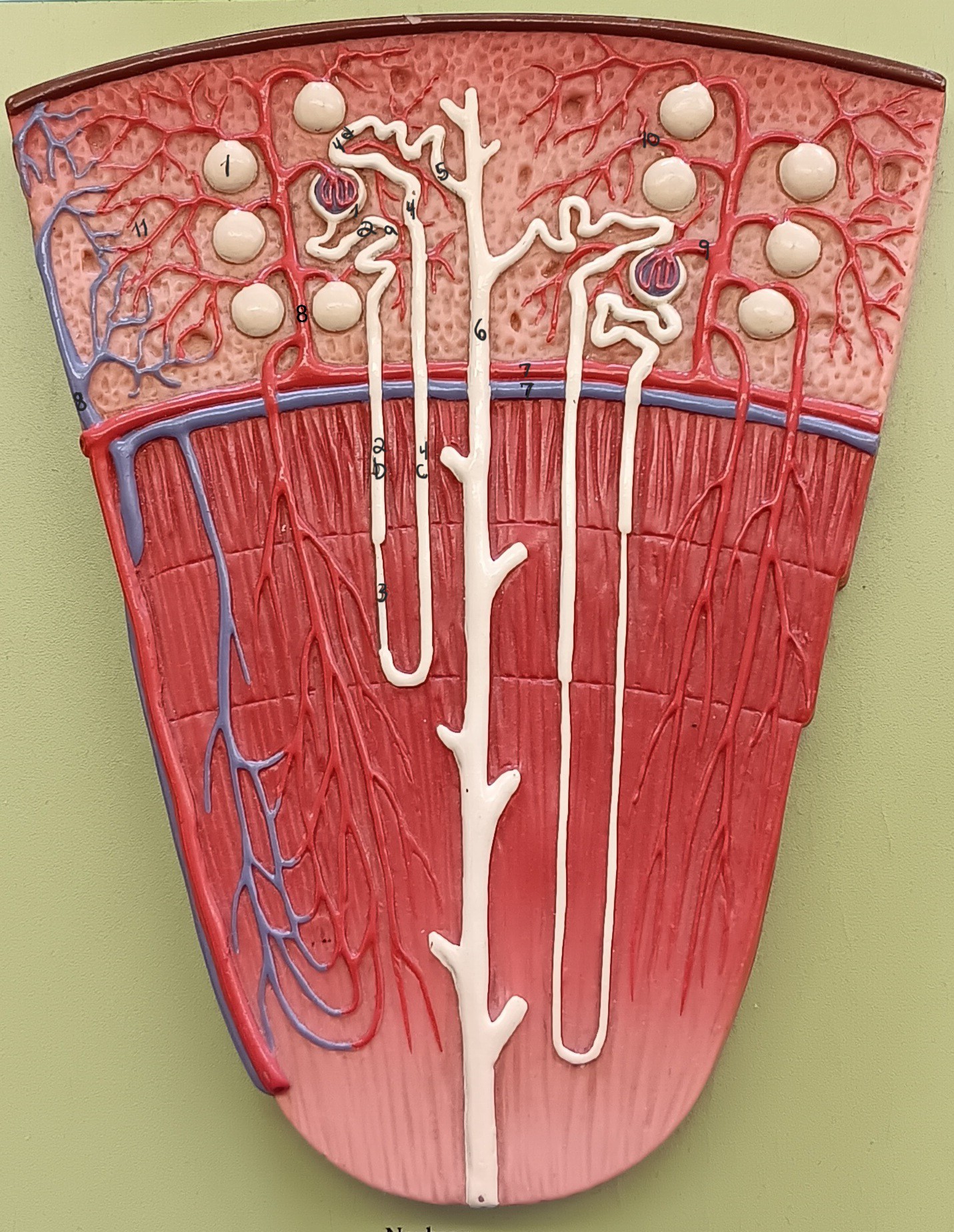
proximal convoluted tubule
2a
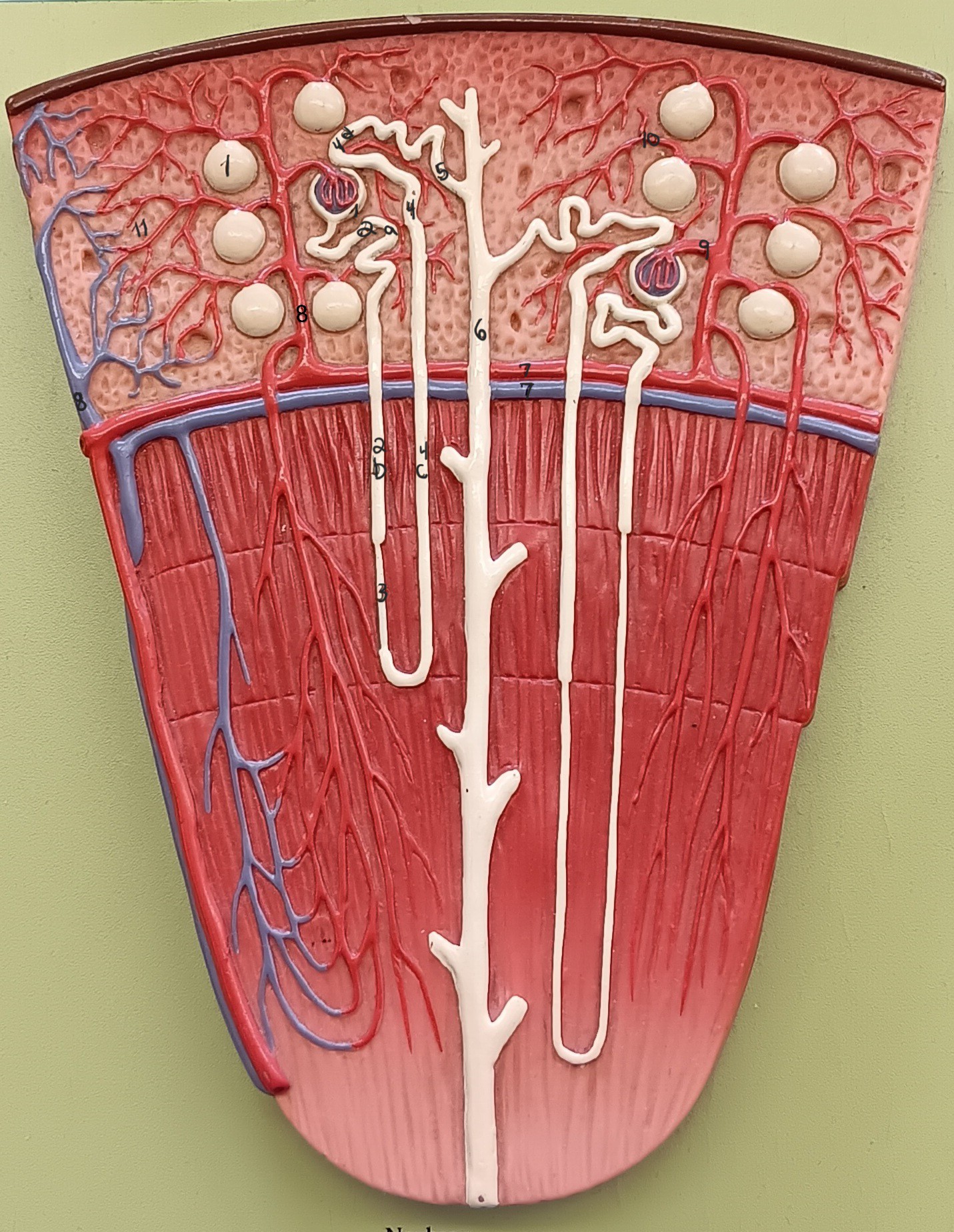
descending loop
2b
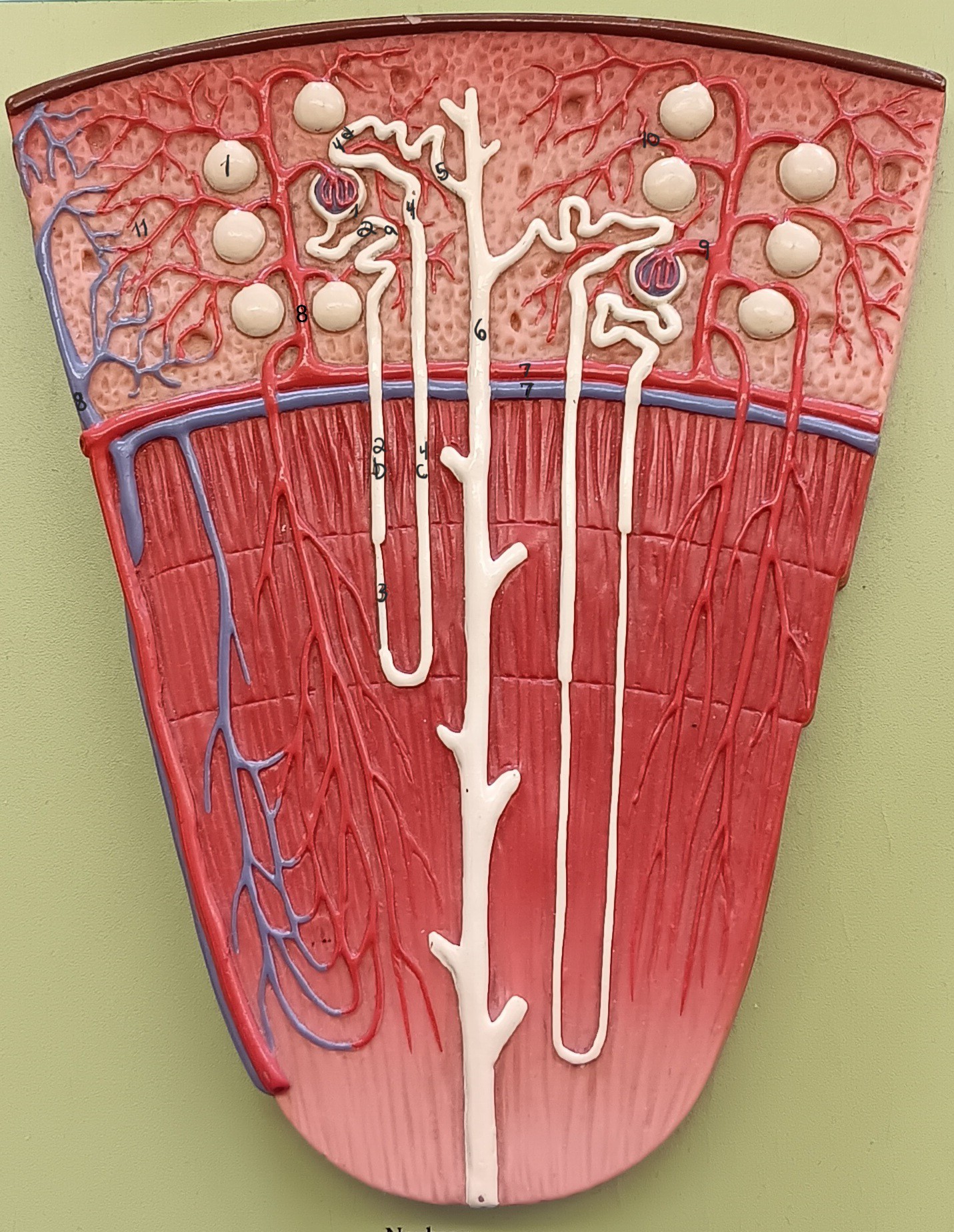
thin segment
3
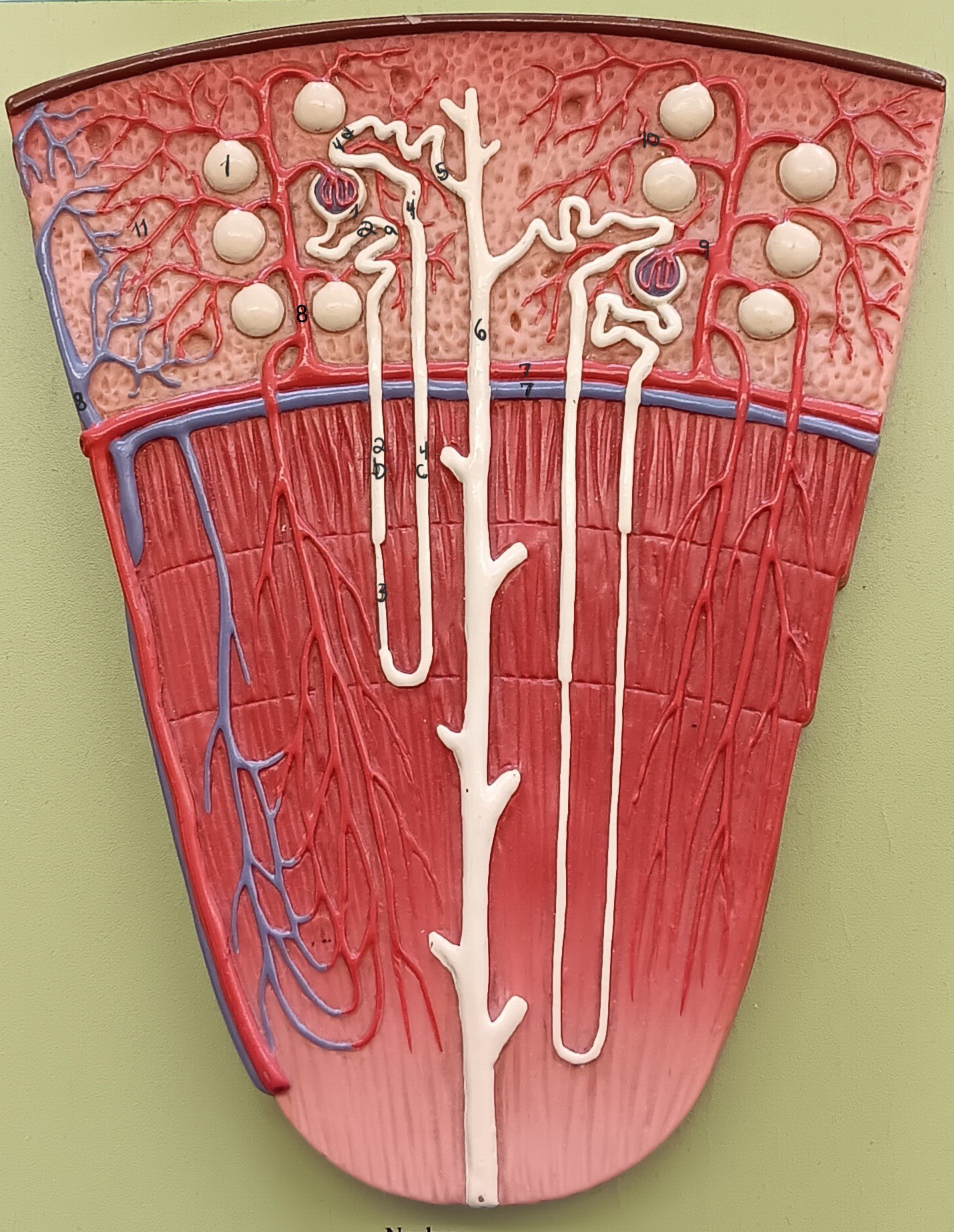
ascending loop
4c
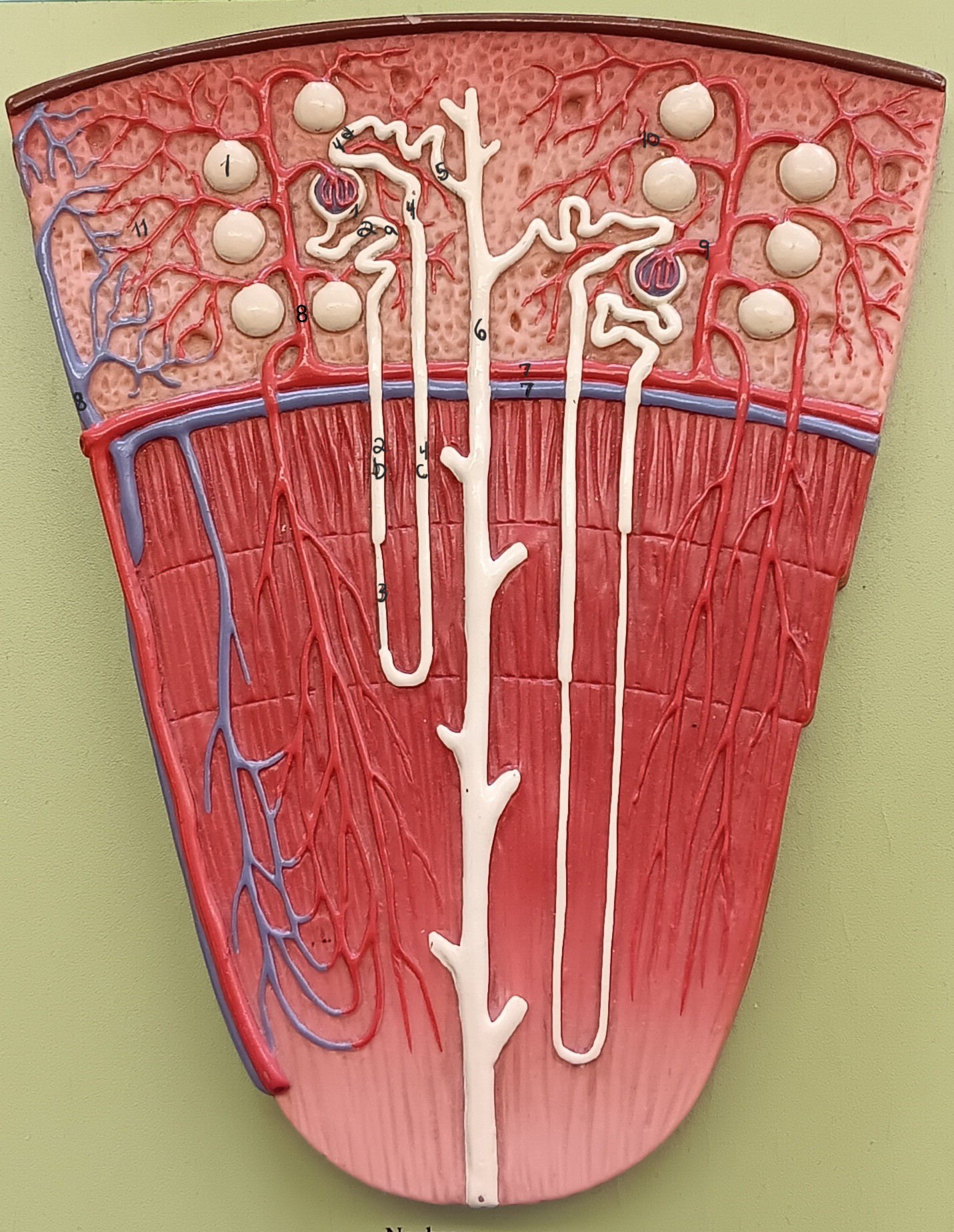
distal convoluted tubule
4d
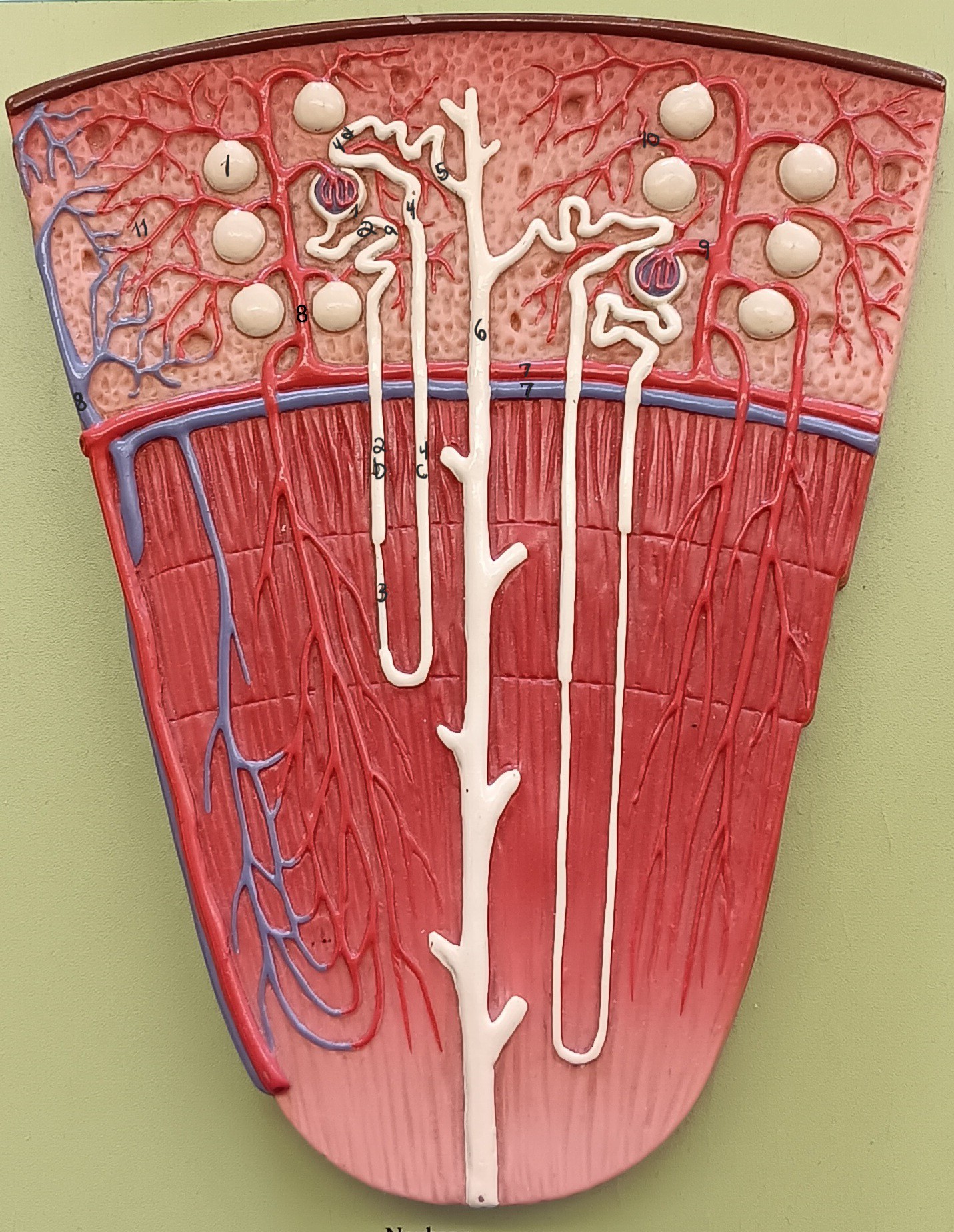
collecting duct
6
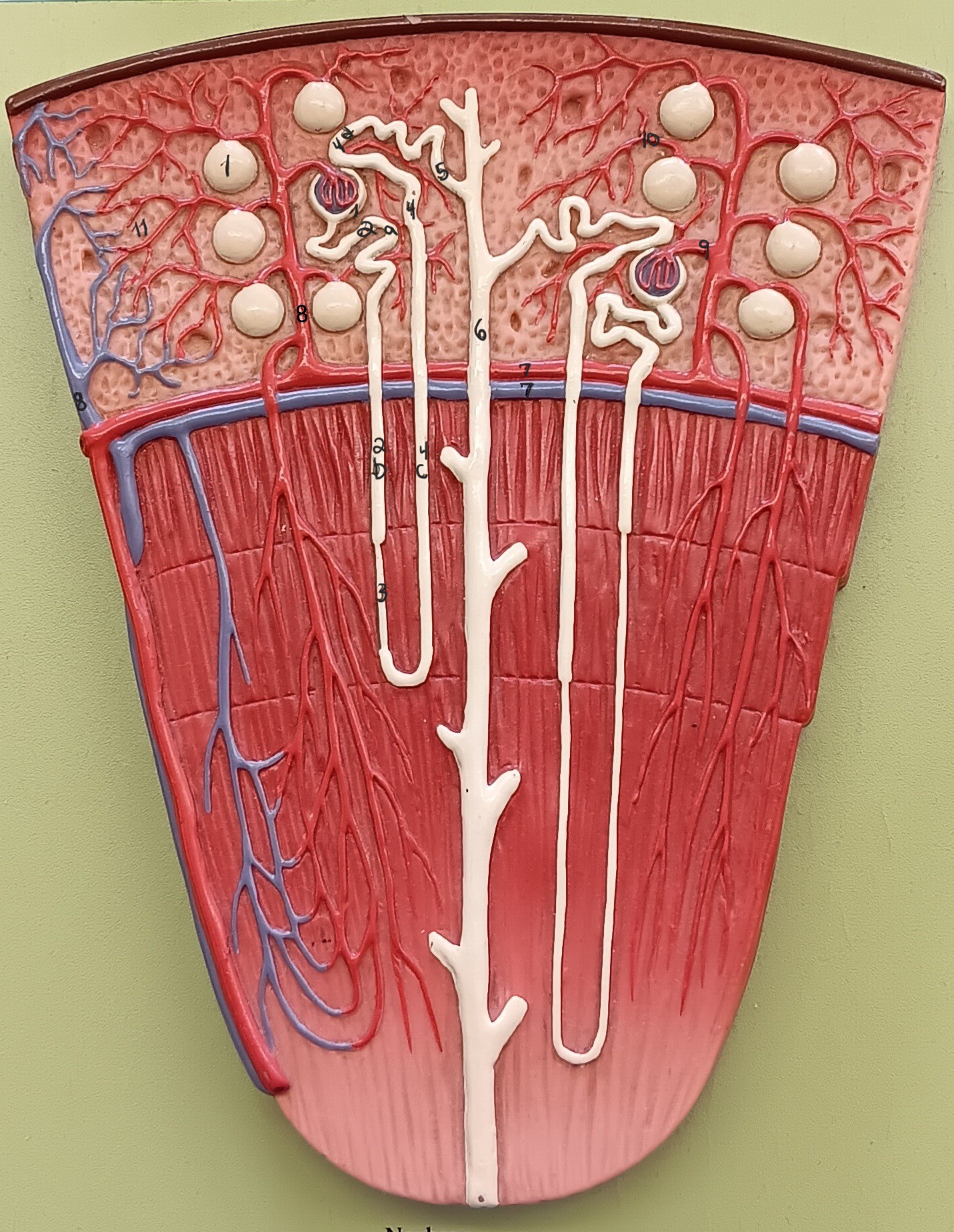
arcuate artery
7 red
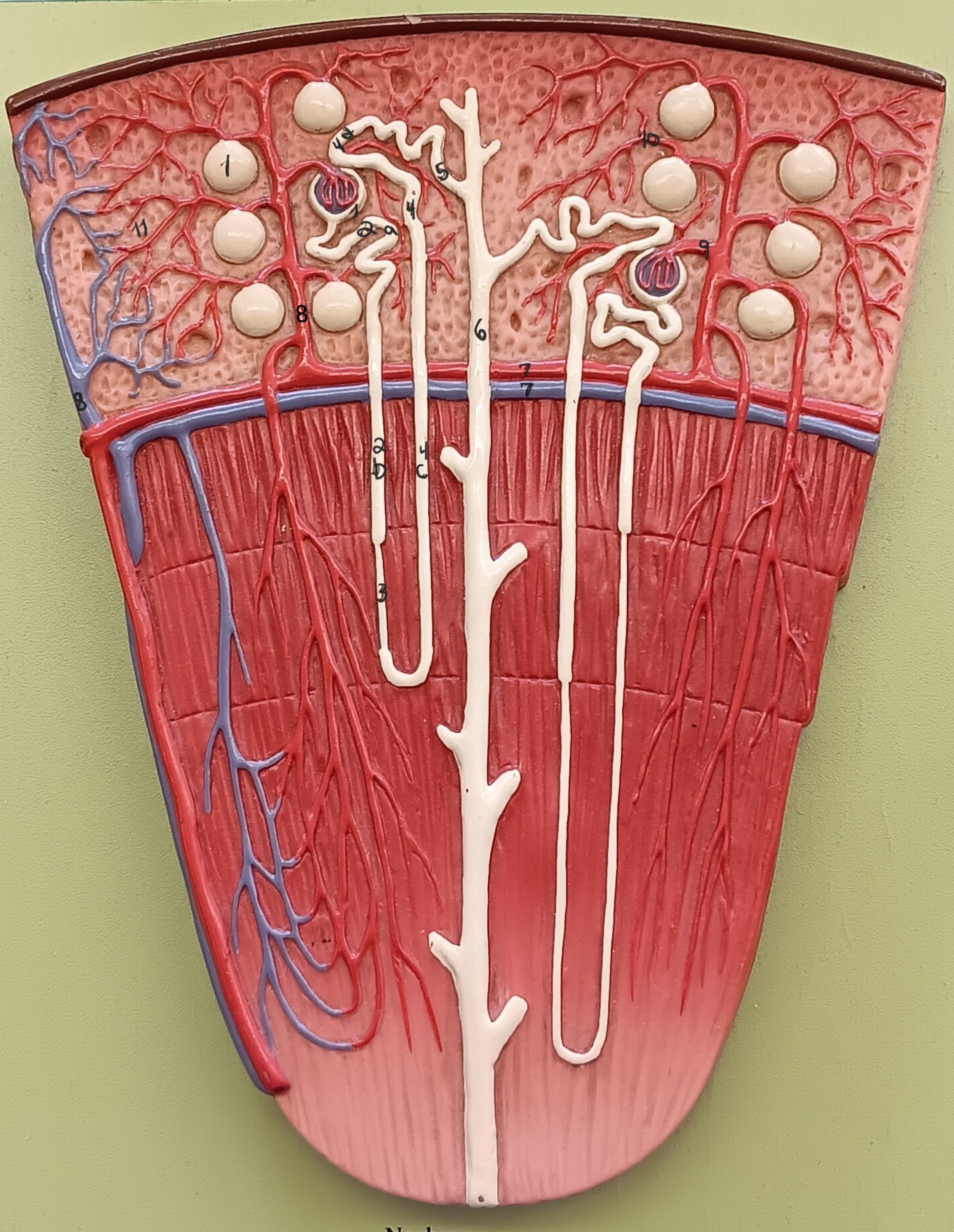
arcuate vein
7 blue
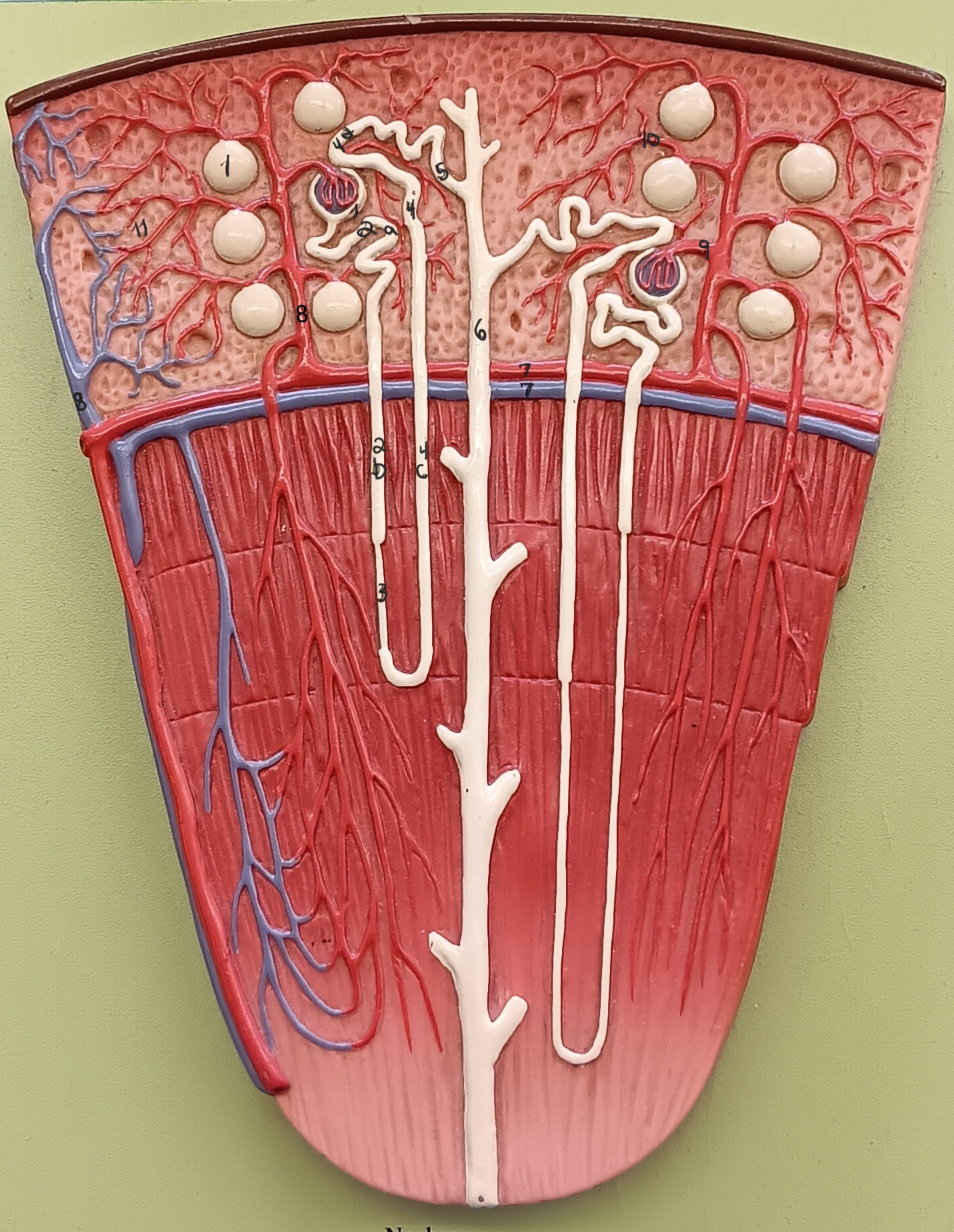
cortical radiate artery
8 red
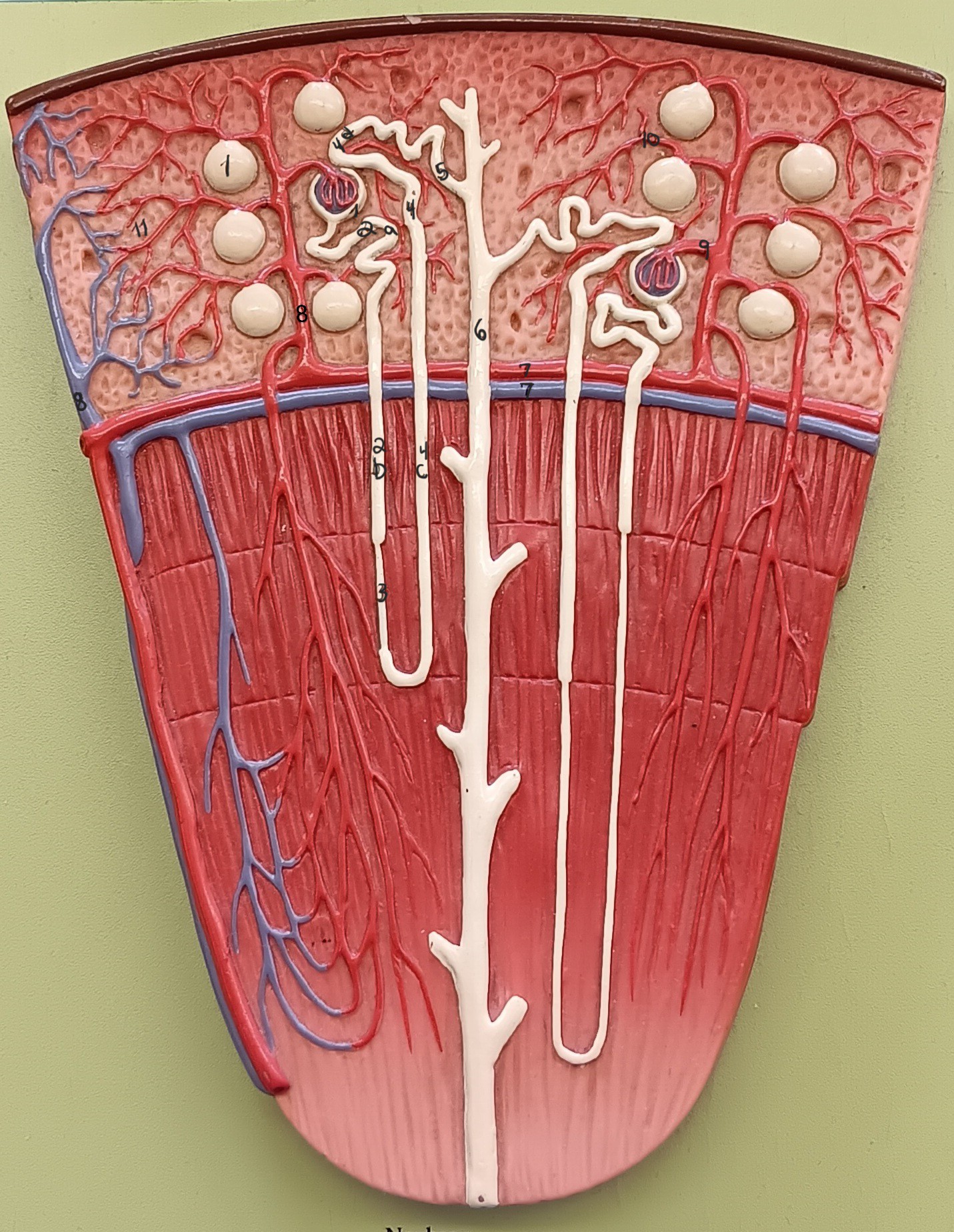
cortical radiate vein
8 blue
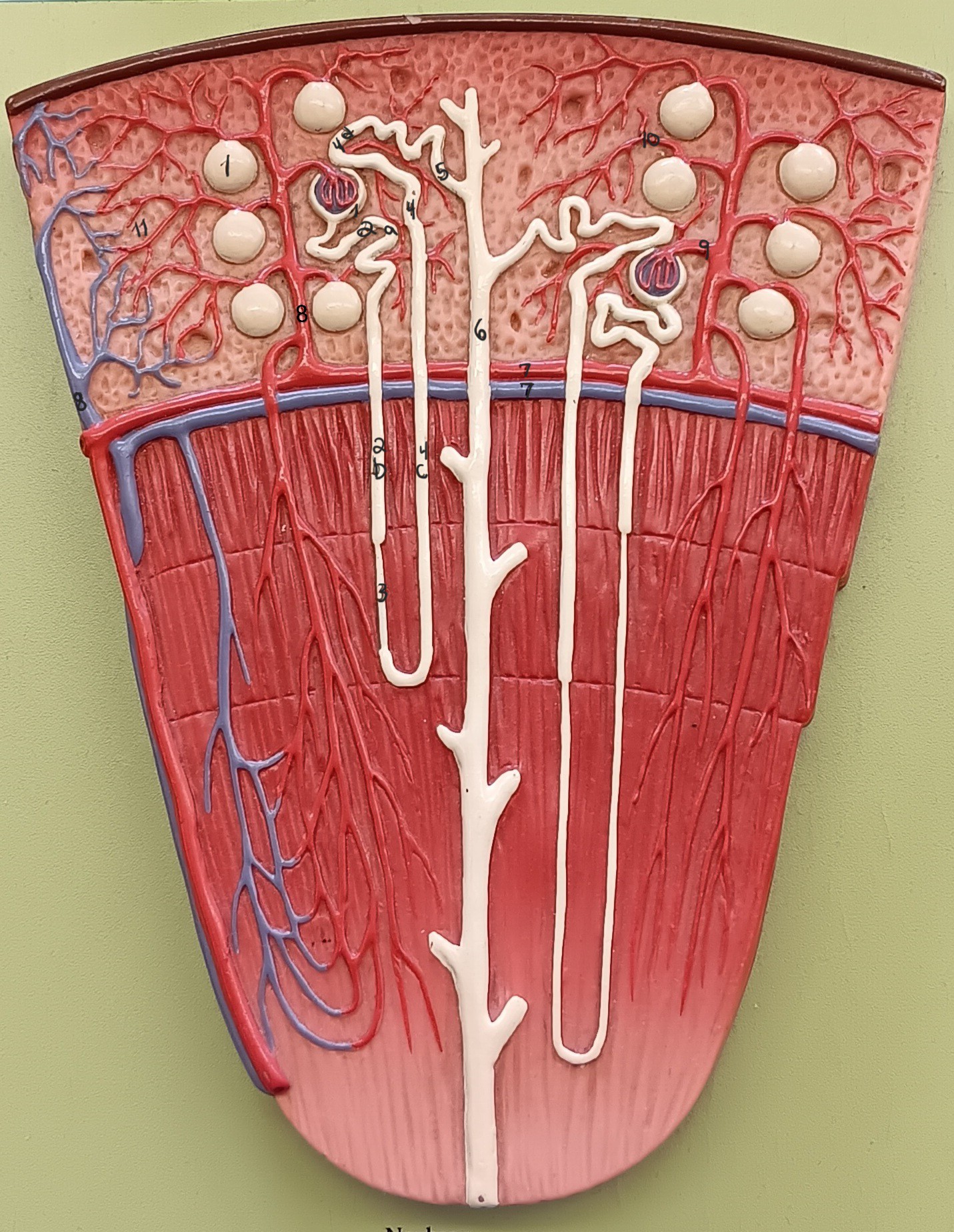
afferent arteriole
9
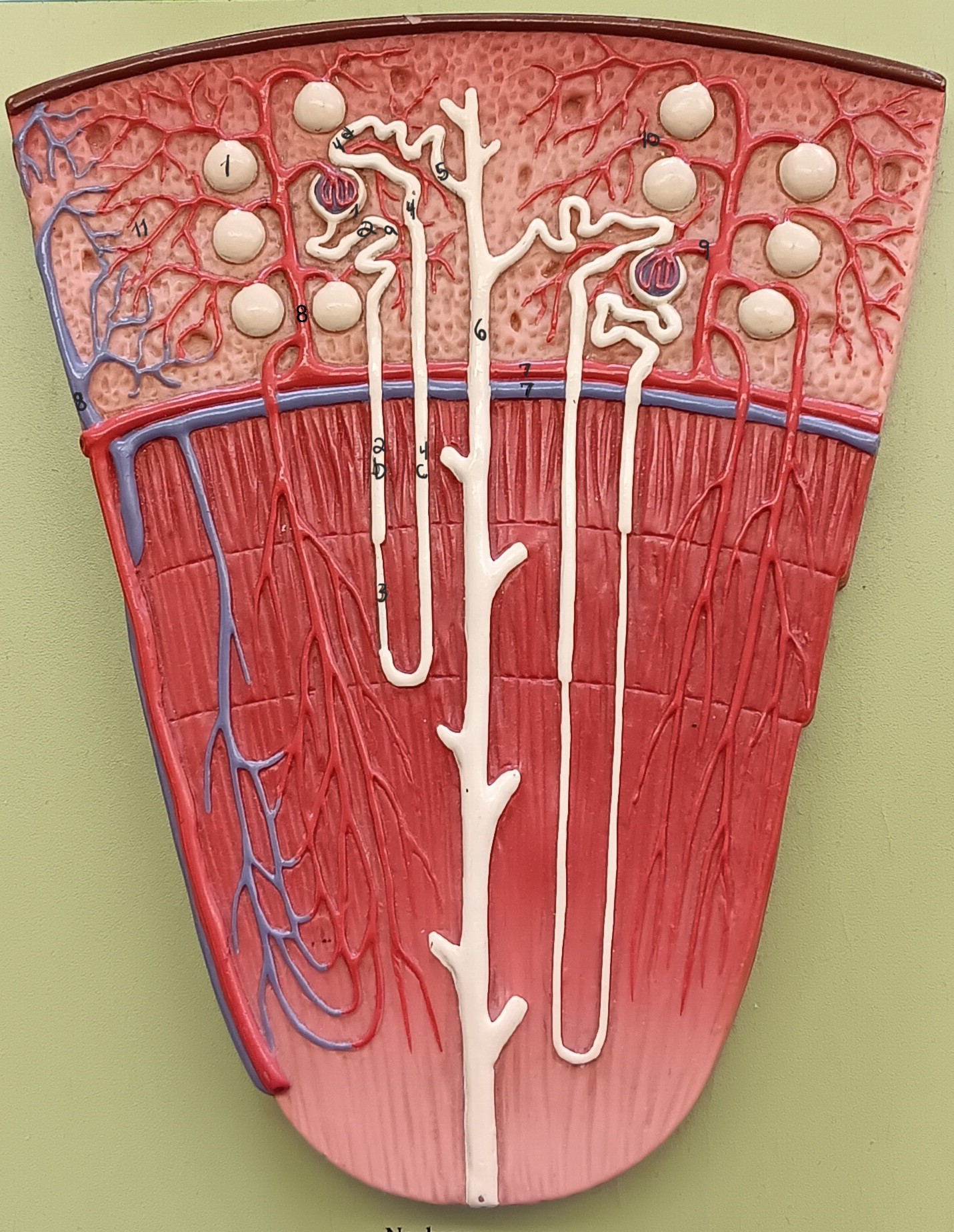
efferent arteriole
10
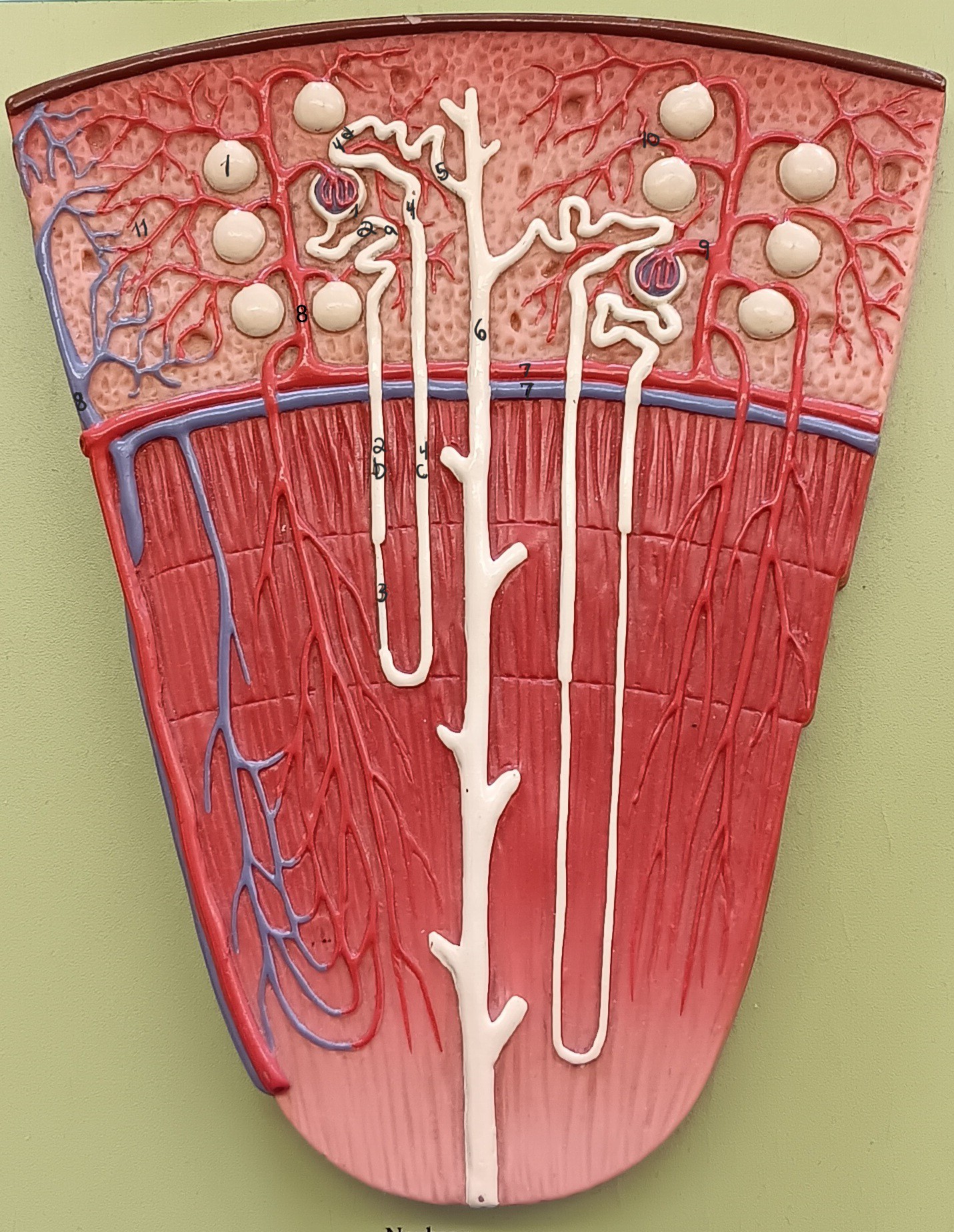
peritubular capillary bed
11
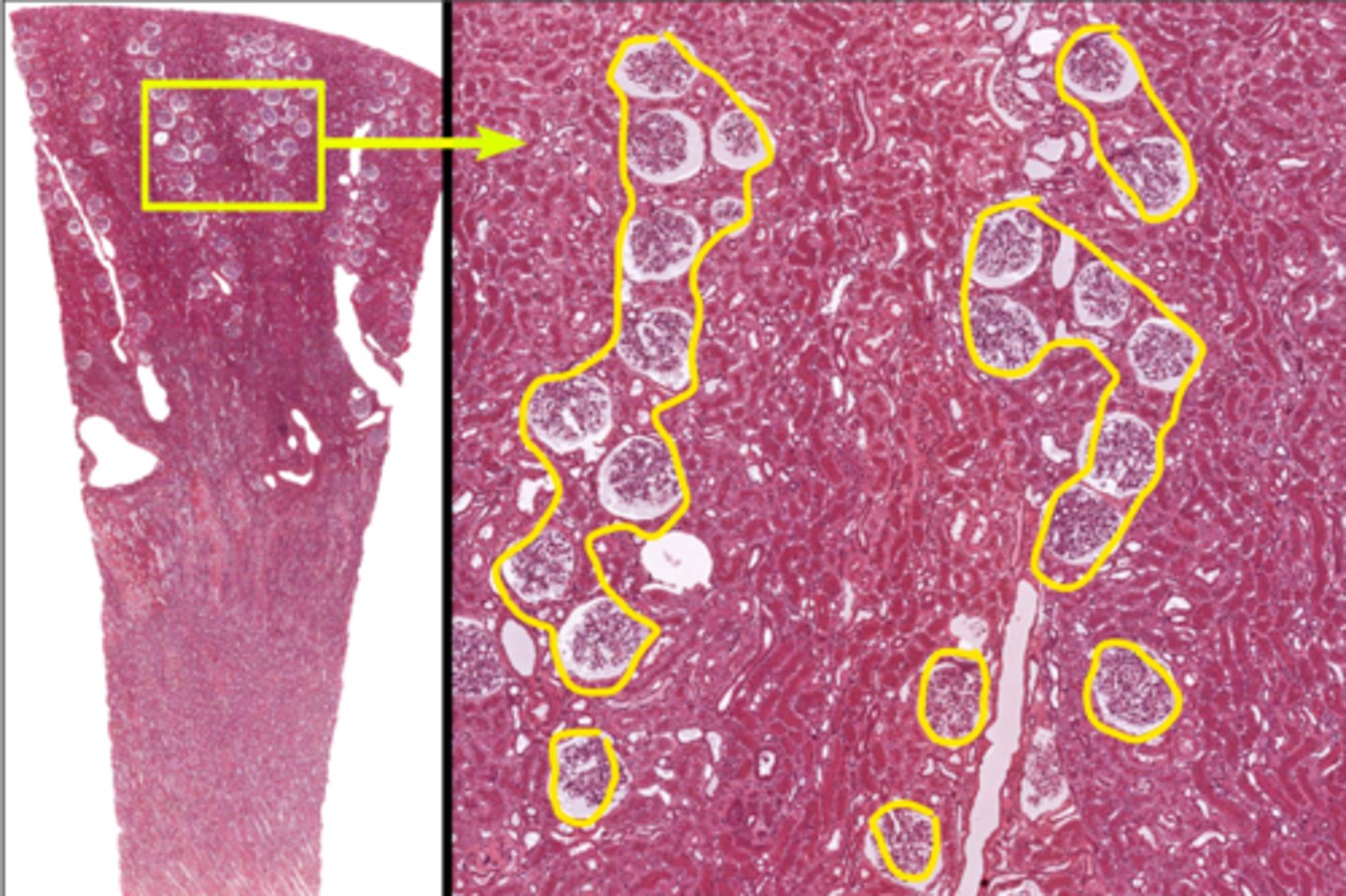
kidney
what organ is this
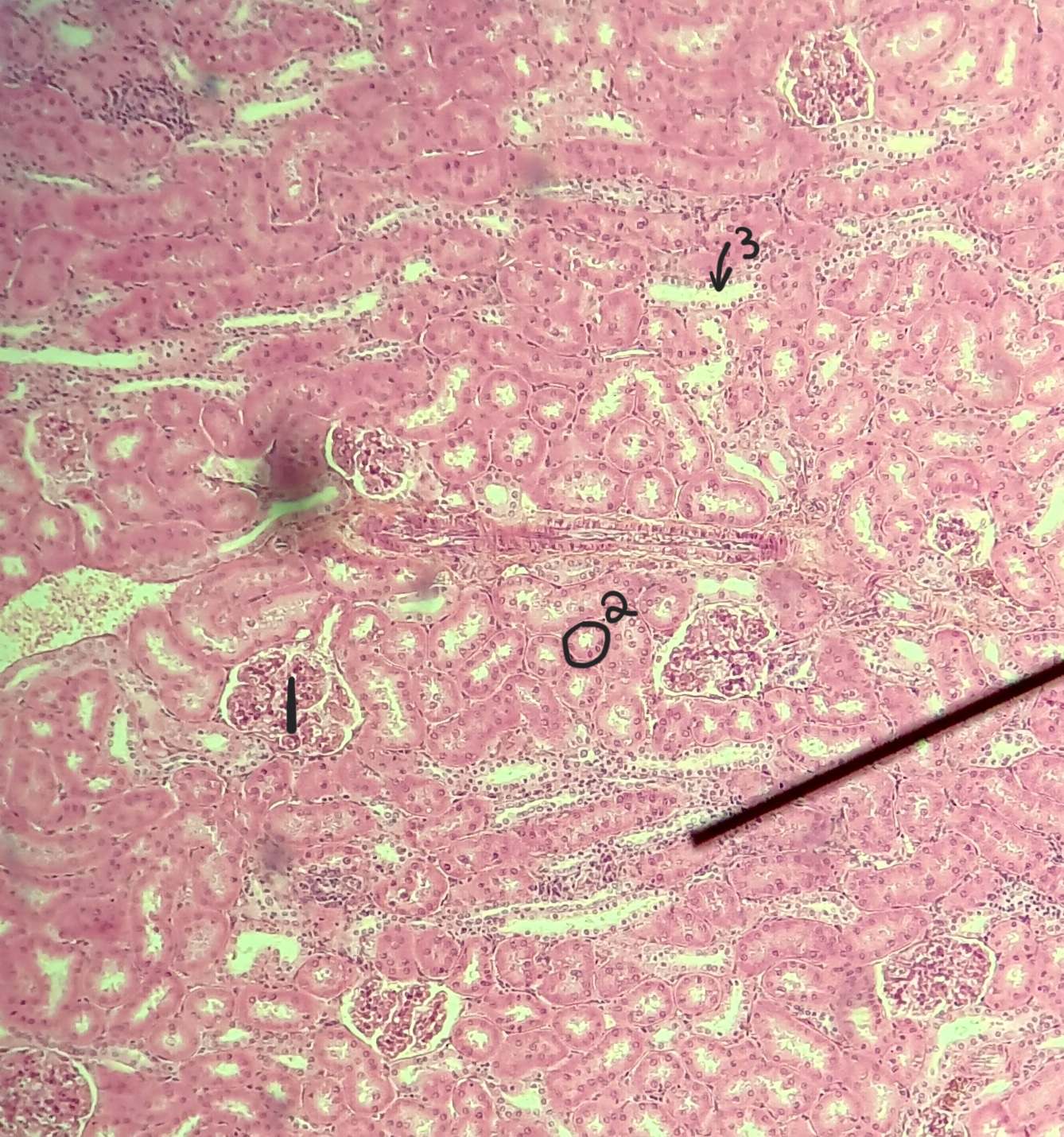
cortex
what region of the kidney
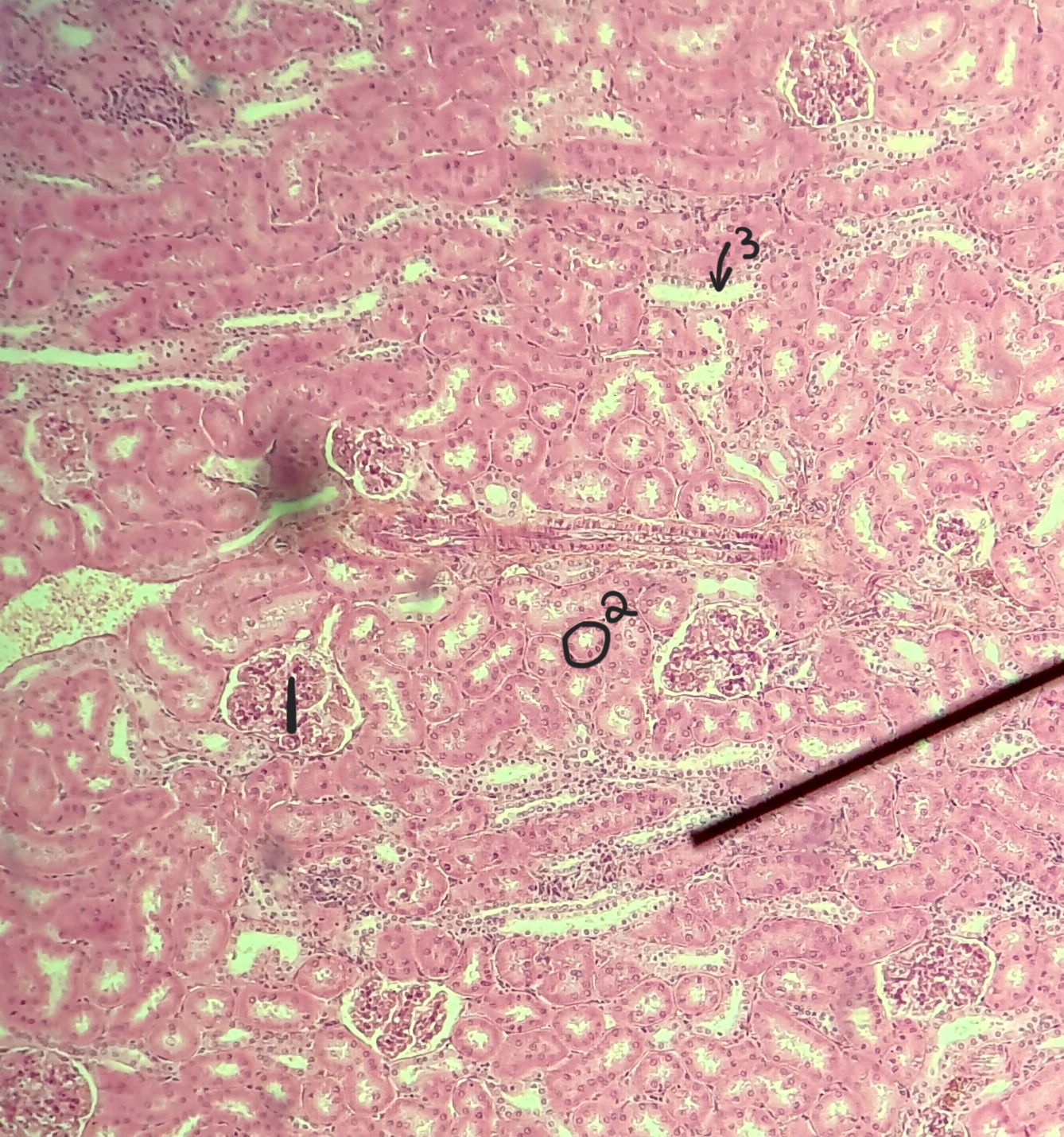
renal corpuscle
1
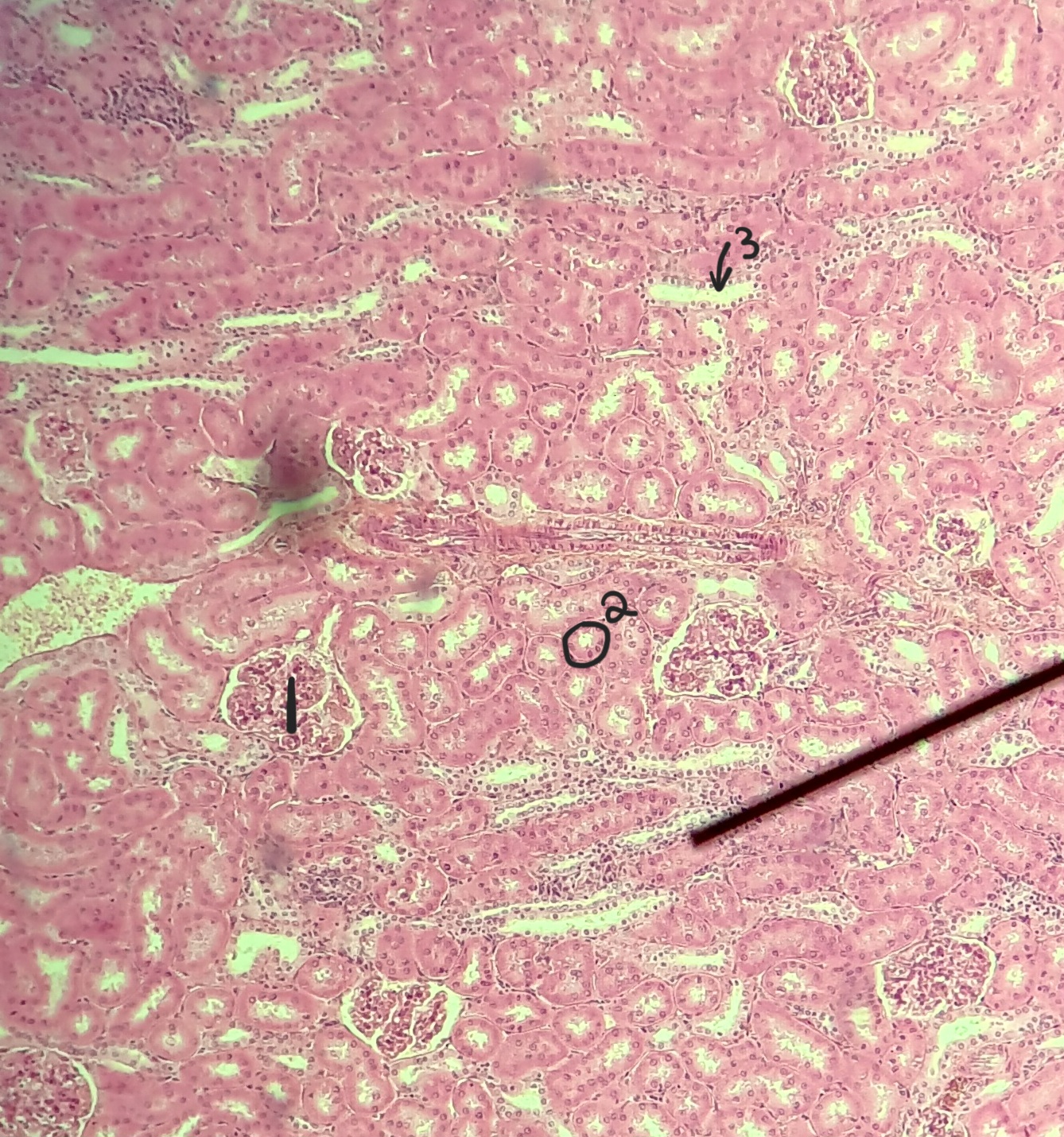
renal tubues
2
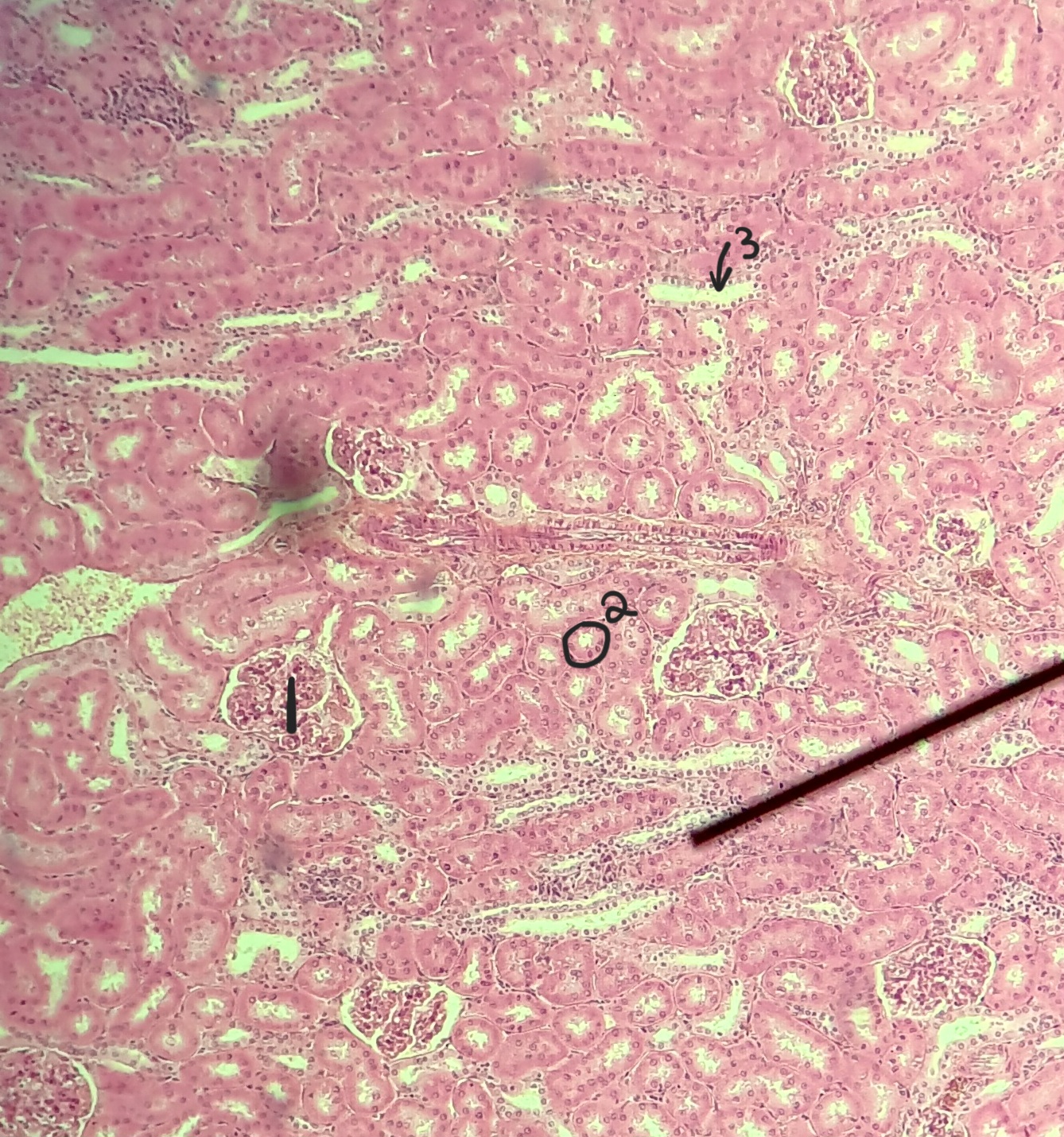
interlobar arteries
3
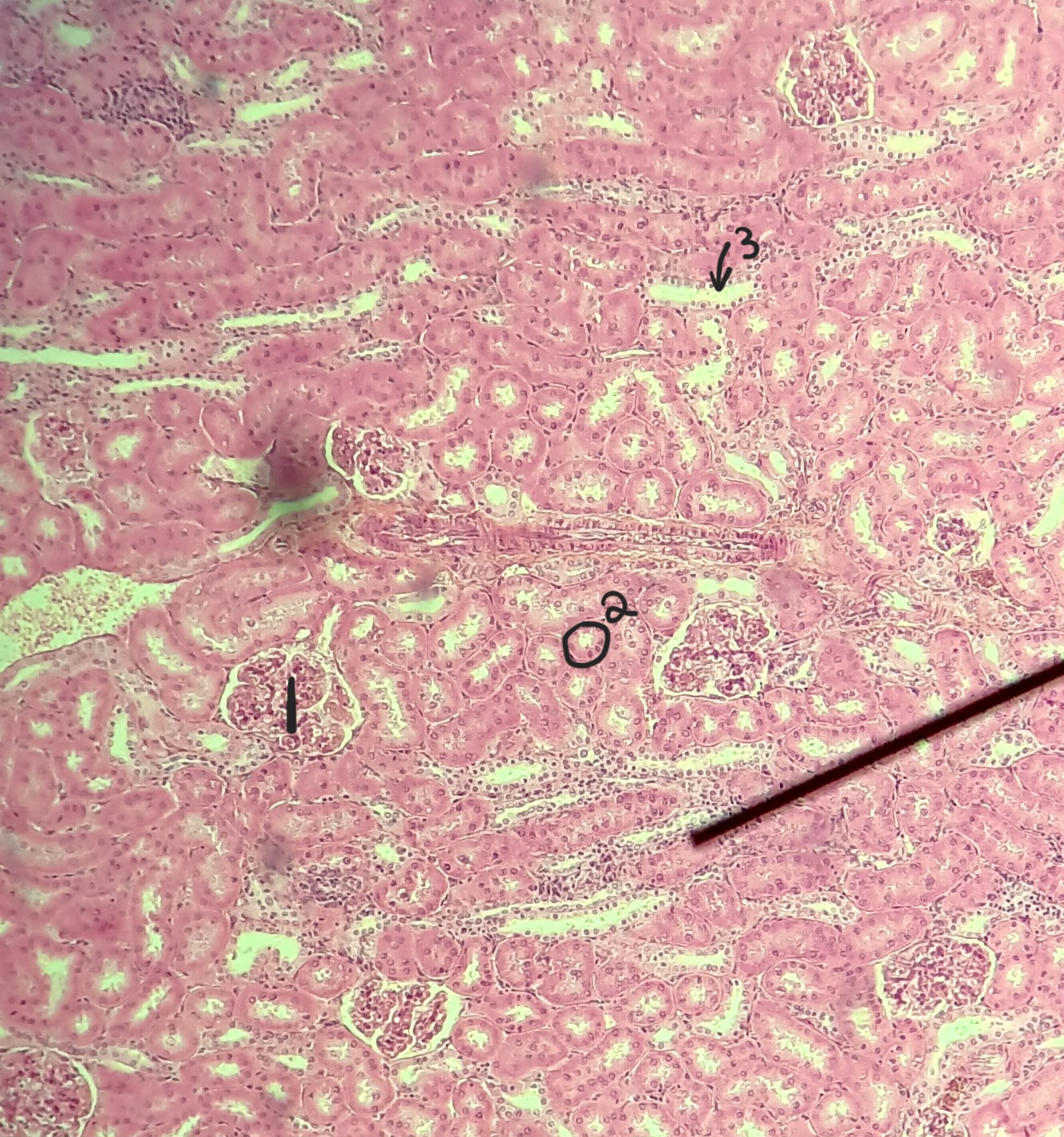
glomerulus
1
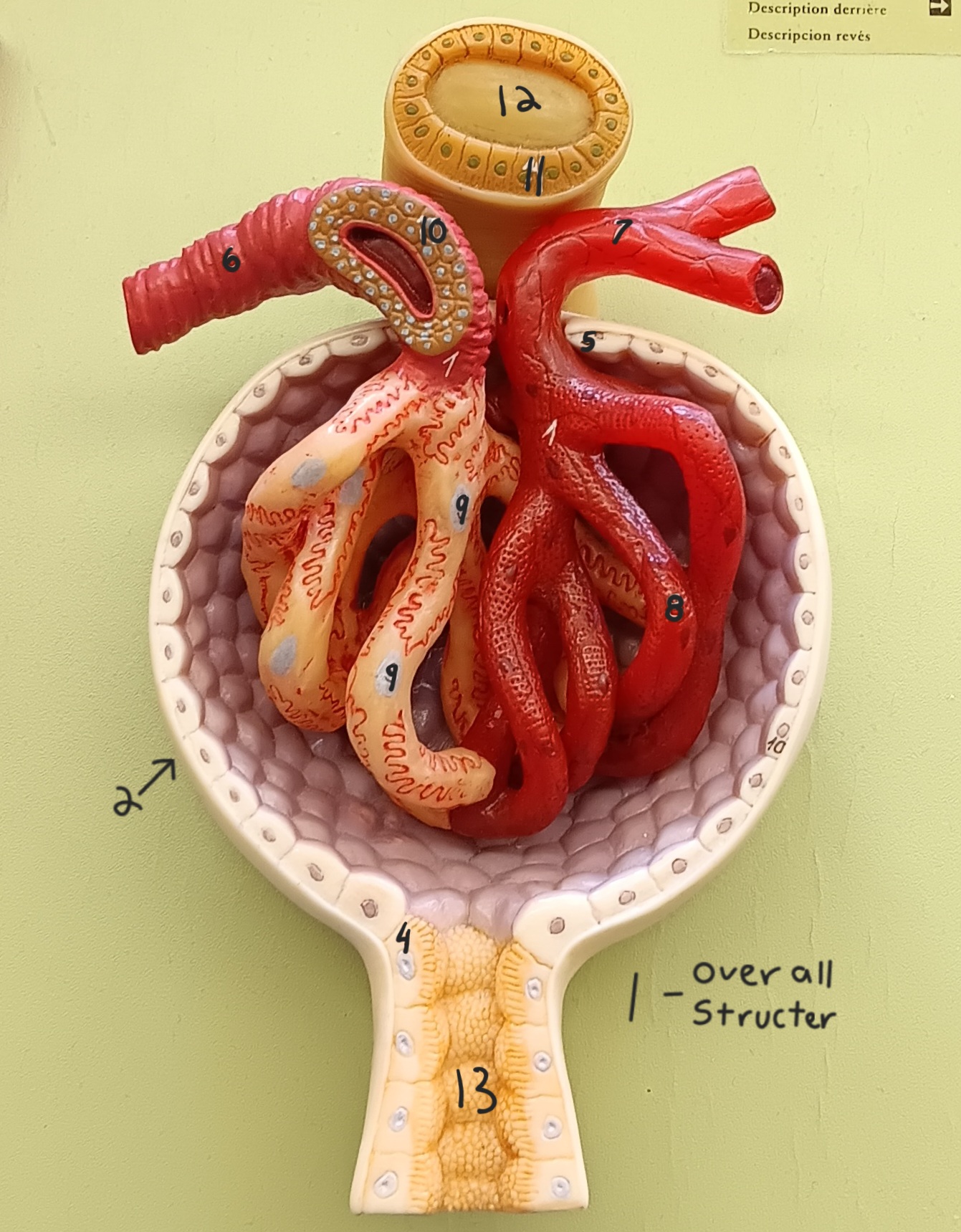
glomerular capsule
2
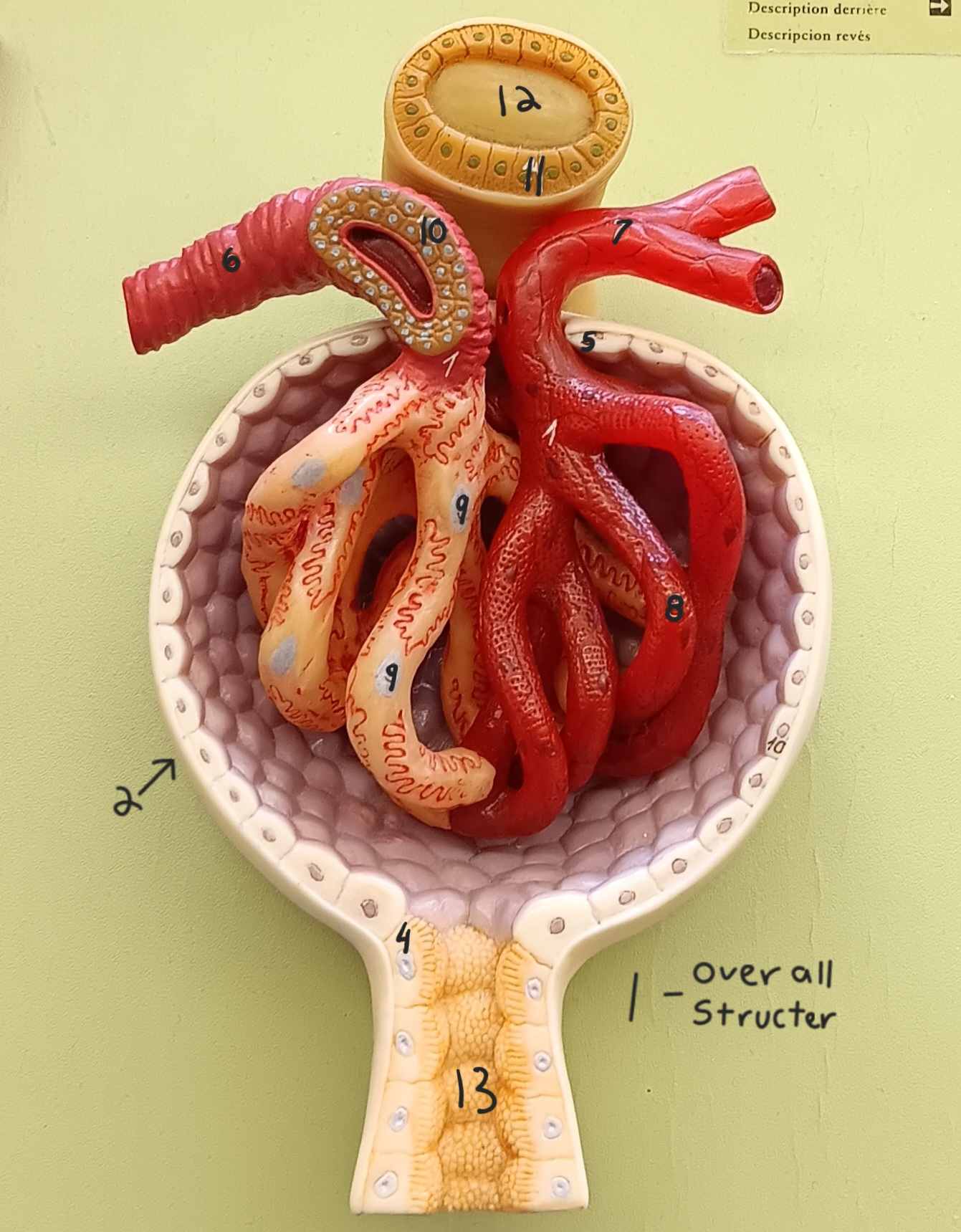
afferent arteriole
6
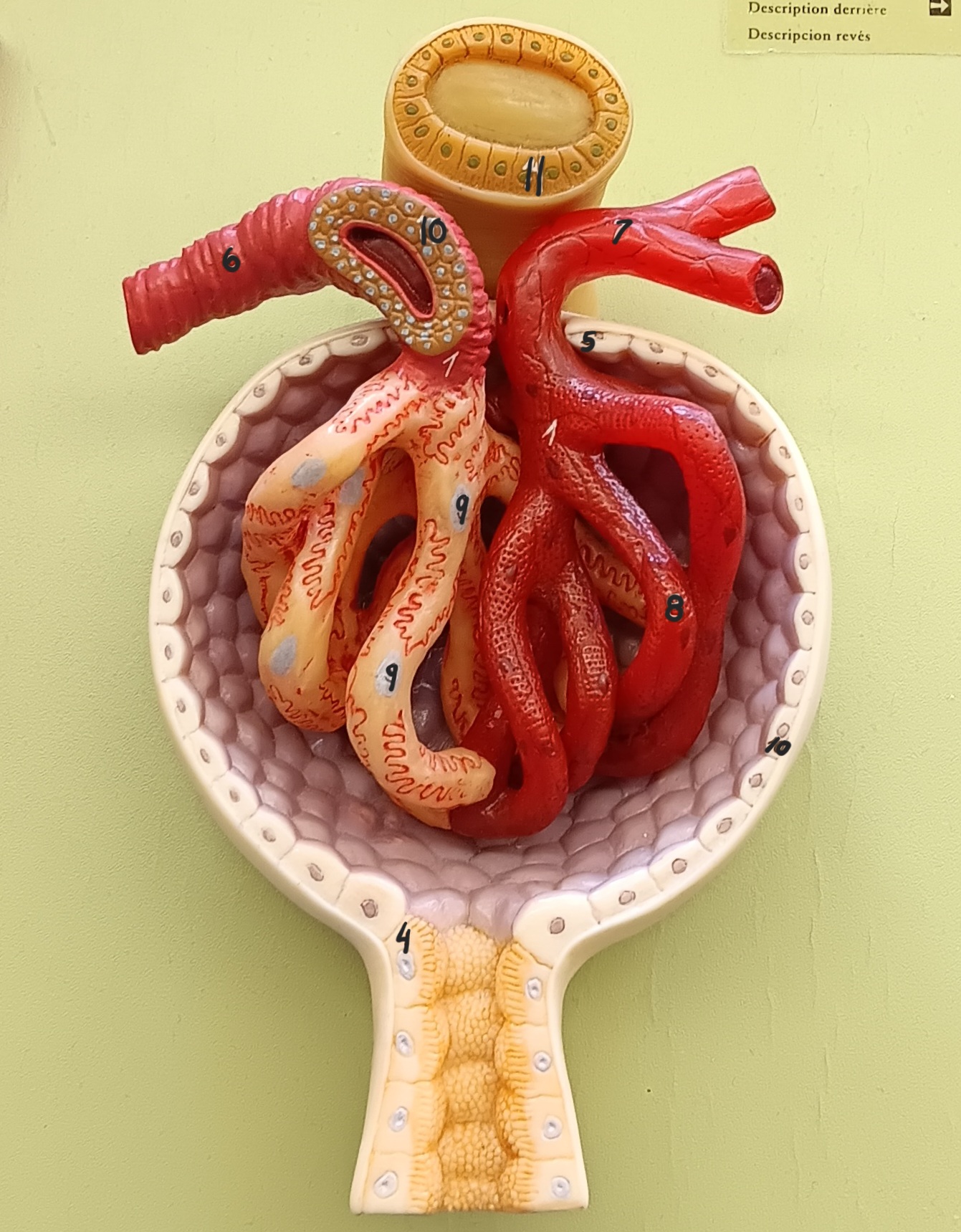
efferent arteriole
7
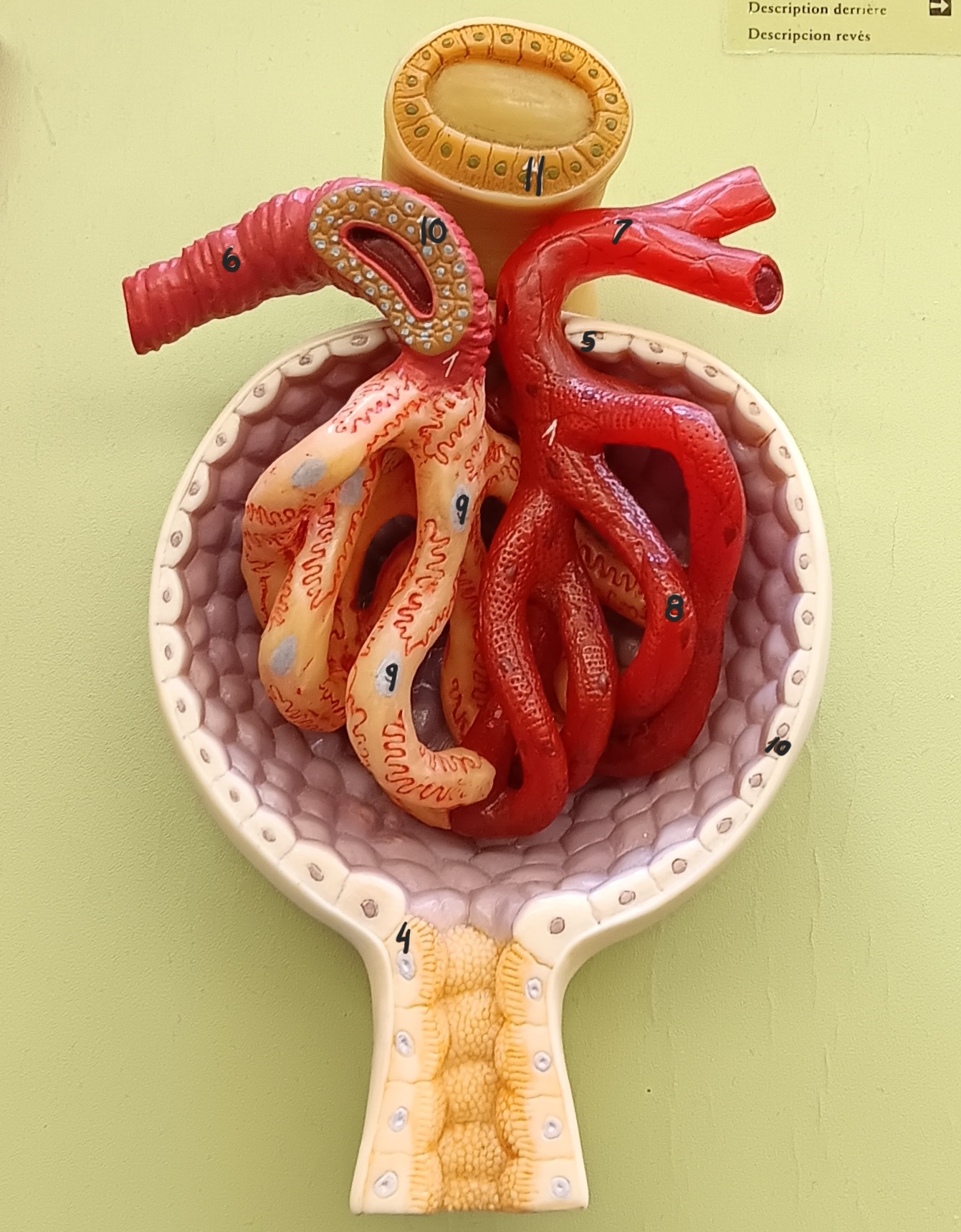
podocyte
9
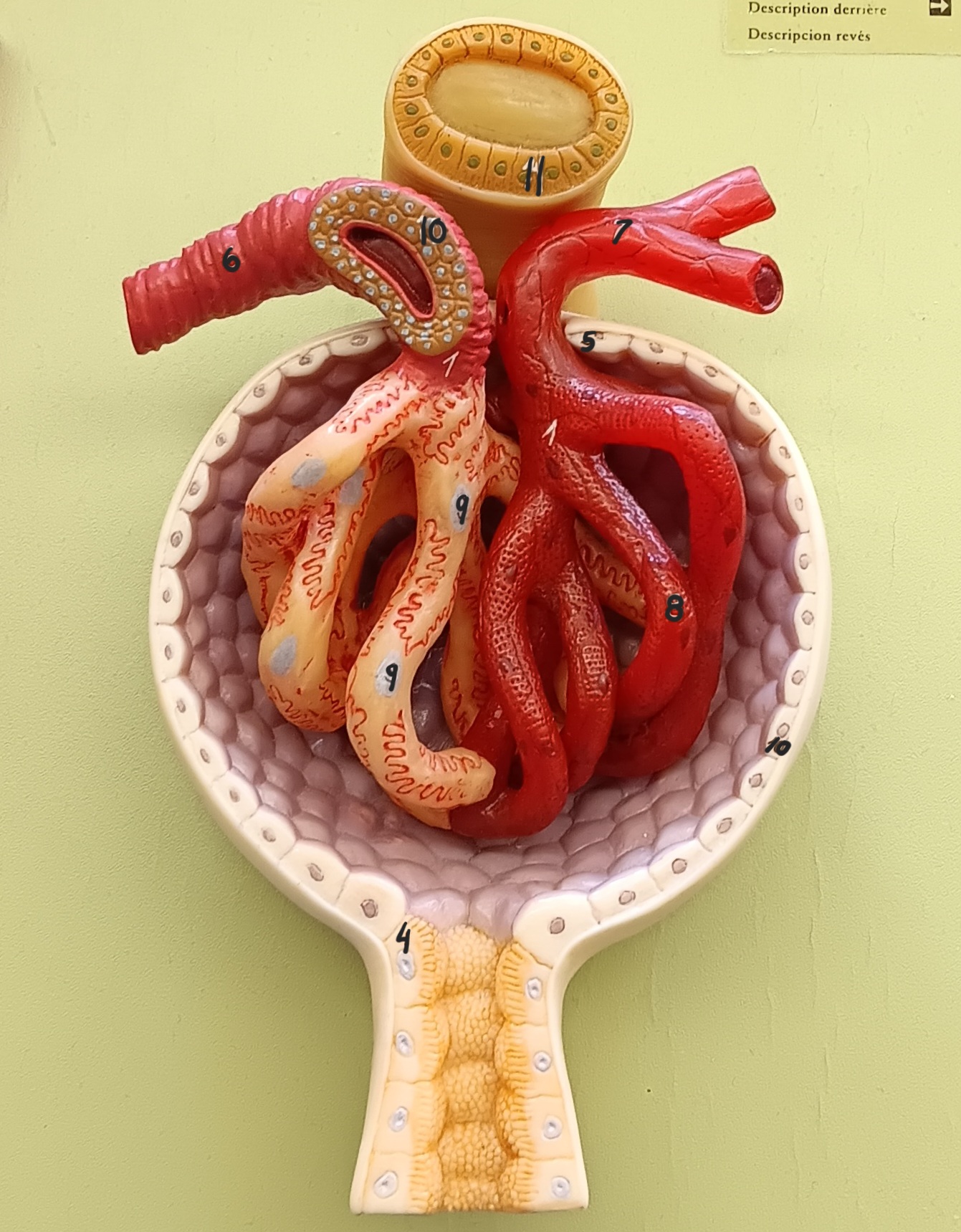
juxtaglomerular cells
10
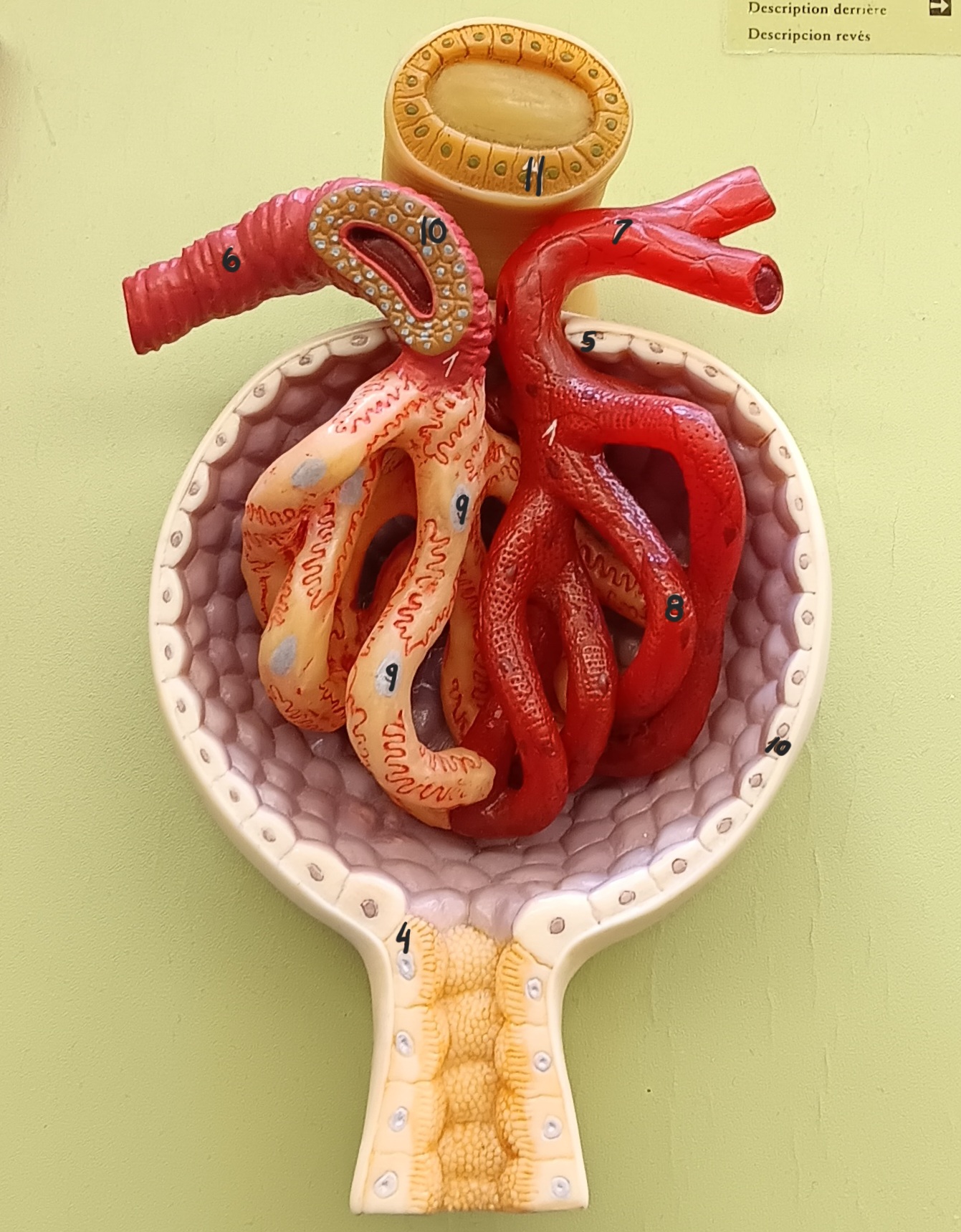
macula densa
11
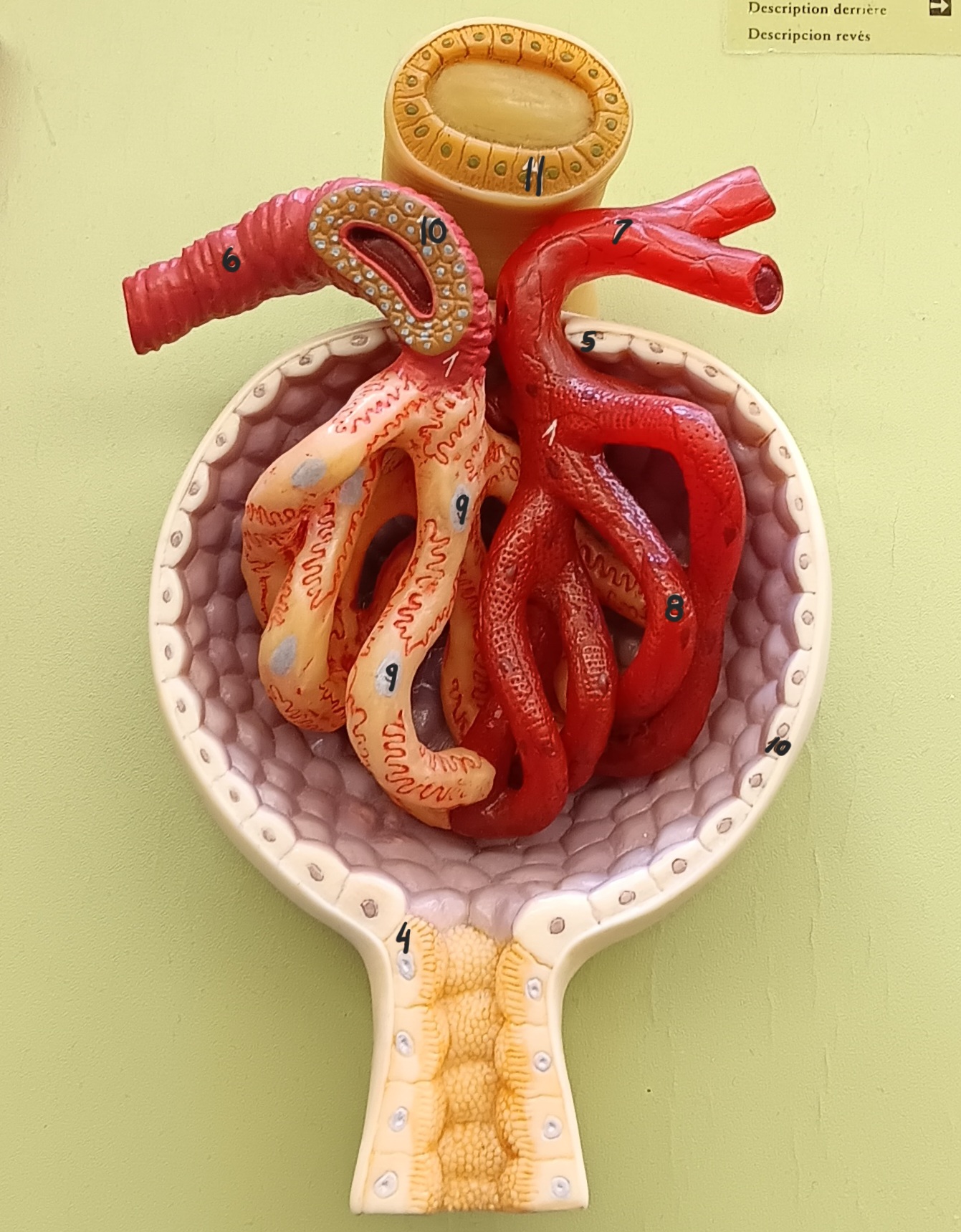
distal convoluted tubule
12
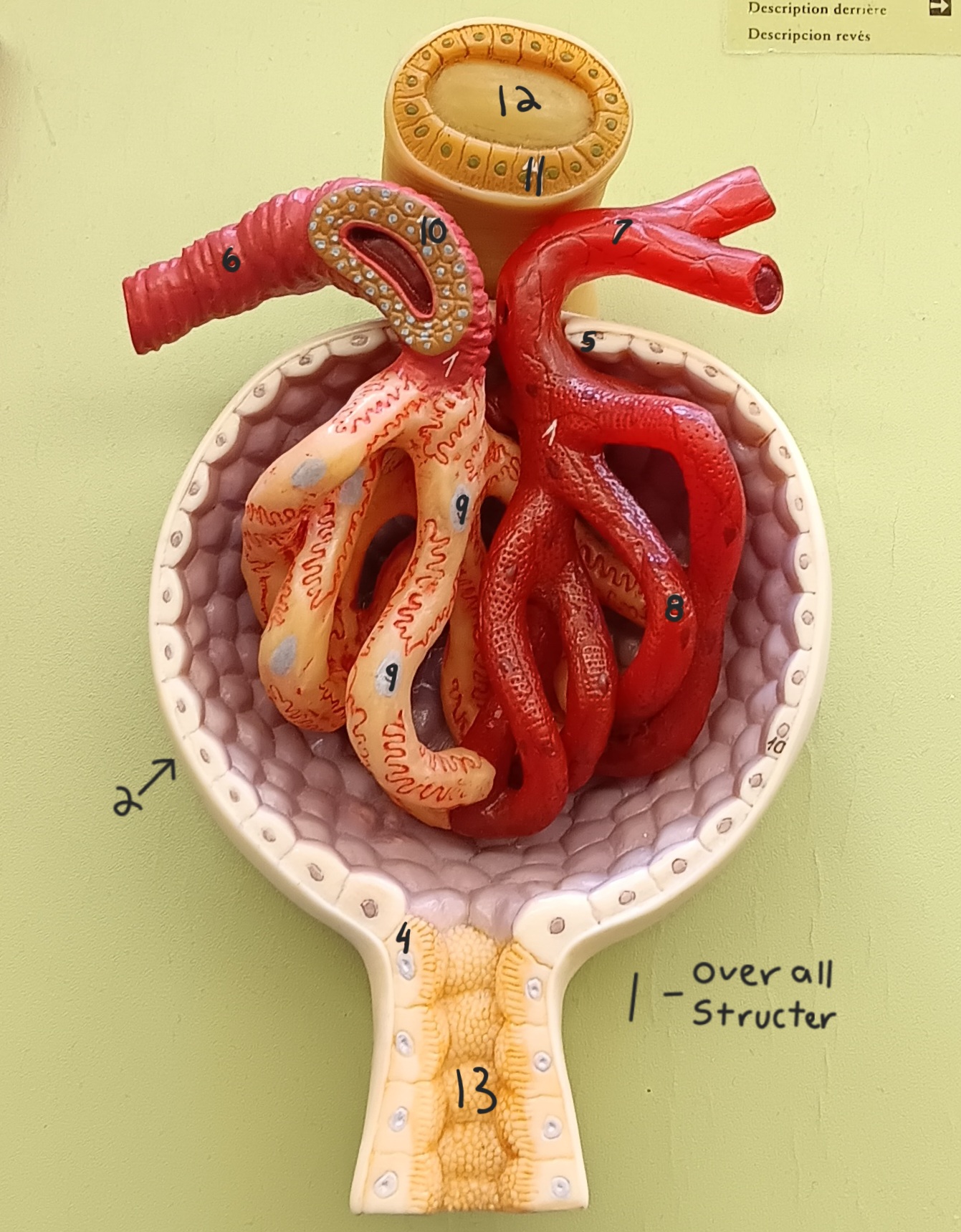
proximal convoluted tubule
13
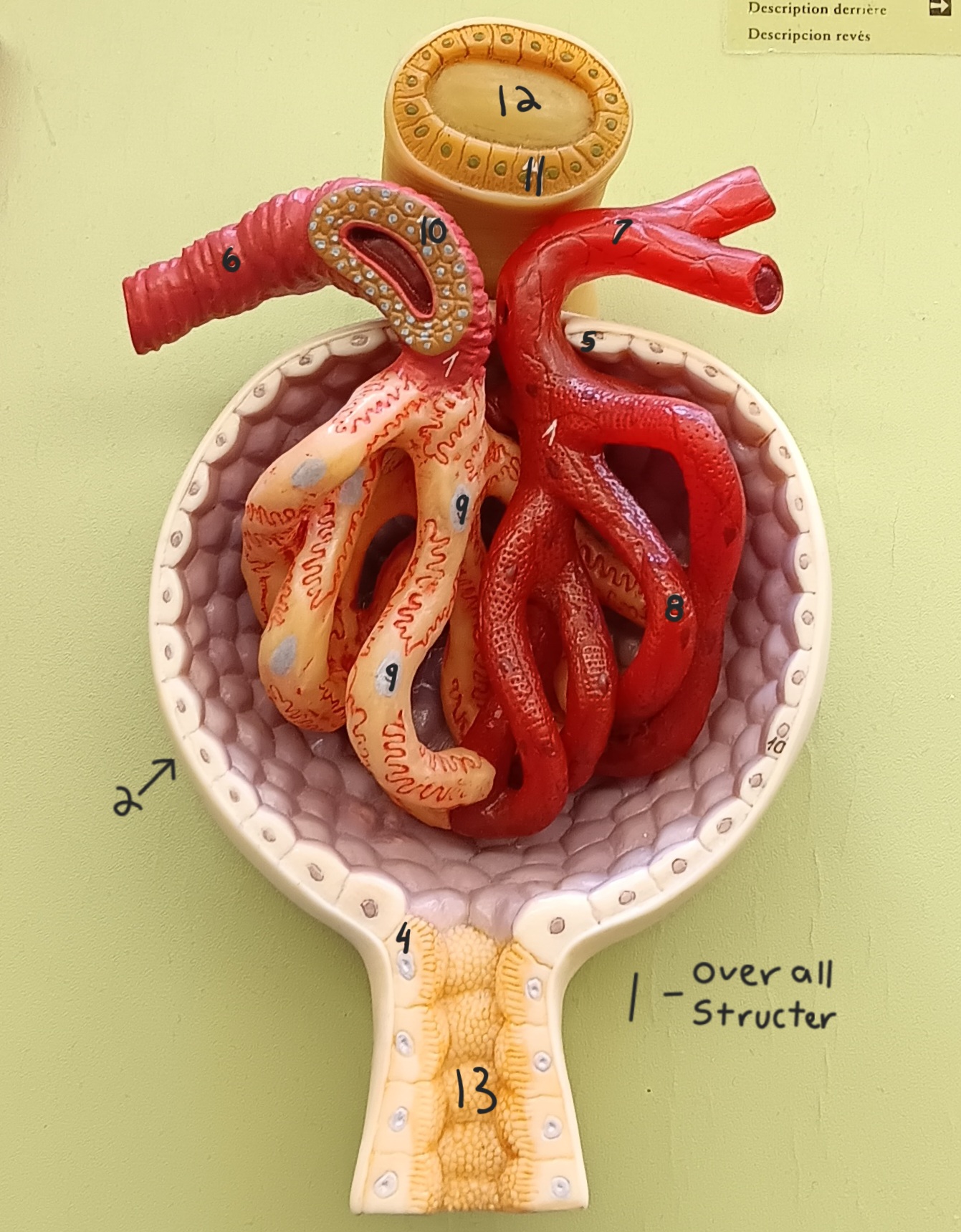
renal column
a
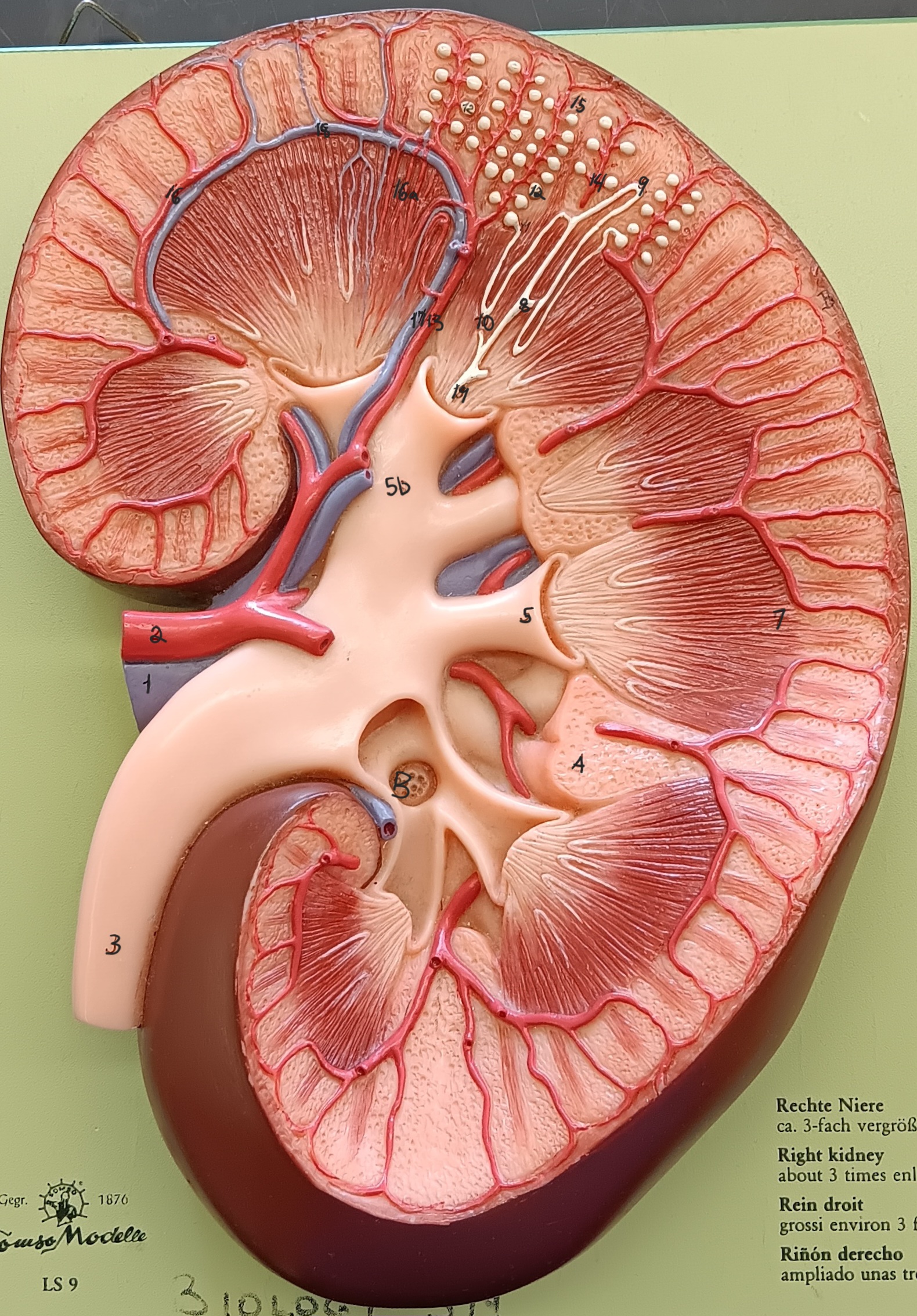
renal cortex
b