patio week 5 lecture - fluid and electrolytes
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What is the role of sodium in fluid balance?
Sodium helps regulate fluid balance by controlling the movement of water in and out of cells.
What is a hypertonic solution?
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solutes outside the cell, causing water to move out and the cell to shrink.
What is a hypotonic solution?
A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes outside the cell, causing water to move in and the cell to swell.
What is the effect of hypertonic solutions on bacterial cells?
Hypertonic solutions can shrink bacterial cells by drawing water out of them.
What is the significance of calcium in the body?
Calcium is essential for muscle contraction, nerve function, and blood clotting.
What can cause increased thirst?
Increased thirst can be caused by dehydration, high sodium intake, or certain medical conditions.
What is the relationship between potassium and fluid balance?
Potassium helps maintain fluid balance and is crucial for proper muscle and nerve function.
What is the role of Vitamin D in calcium regulation?
Vitamin D enhances calcium absorption in the intestines and helps maintain calcium levels in the blood.
What is respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis occurs when the lungs cannot remove enough carbon dioxide, leading to increased acidity in the blood.
What are the symptoms of dehydration?
Symptoms of dehydration include decreased thirst, dry mouth, fatigue, and dark-colored urine.
What is the function of the renin-angiotensin system?
The renin-angiotensin system regulates blood pressure and fluid balance by controlling sodium and water retention.
What is the effect of alkalosis on the body?
Alkalosis can cause muscle twitching, hand tremors, and confusion due to decreased acidity in the blood.
What is the significance of bicarbonate in the body?
Bicarbonate acts as a buffer to maintain pH balance in the blood and neutralize acids.
What is the normal pH range for human blood?
The normal pH range for human blood is approximately 7.35 to 7.45.
functions of body fluids
- Transport gases, nutrients, and wastes
- Help generate the electrical activity needed to power body functions
- Take part in the transforming of food into energy
- Maintain the overall function of the body
intracellular compartment (ICF)
1) fluid within cells
2) ~2/3 of body water
3) site of ↑ K+, moderate amounts of Mg2+
Extracellular Compartment (ECF)
-Contains the remaining one third of body water
-Contains all the fluids outside the cells, including that in the interstitial or tissue spaces and blood vessels
-High concentration of Na+
composition of ECF
-large amounts of sodium and chloride
-reasonable large amounts of bicarbonate ions
-small amounts of potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate, and organic acid ions
BABY W/ CHLORIDE AND CALCIUM EARS AND SODIUM AND BICARBONATE HAIR
composition of ICF
-almost no calcium
-small amounts of sodium, chloride, bicarbonate, and phosphorus
-moderate amounts of magnesium
-large amounts of potassium
ADULT WITH EYES MADE OF POTASSIUM AND PHOSPHORUS AND MAGNESIUM MOUTH
potassium concentration is highest inside of or outside of the cell?
Inside
sodium concentration is highest inside of or outside of the cell?
outside
which ion is in the highest concentration in the ICF
potassium
concentration gradient
difference in concentration over a distance
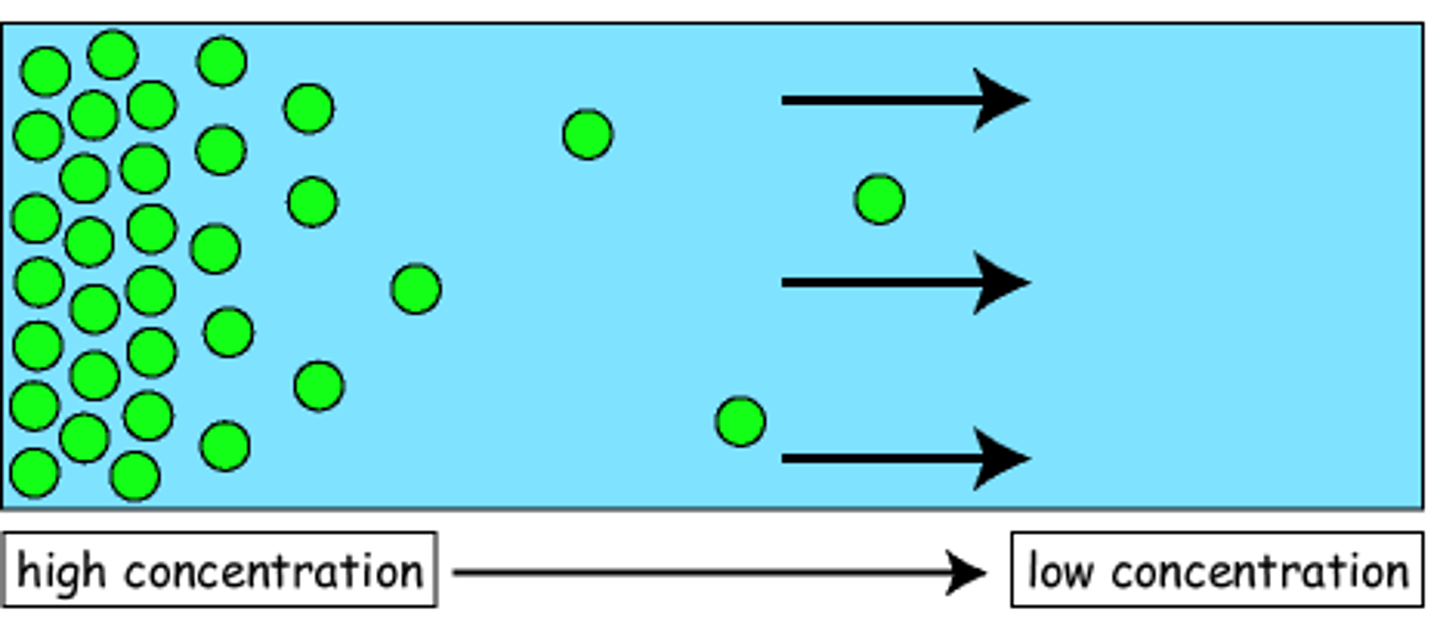
diffusion
the movement of charged or uncharged particles along the concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration
osmosis
the movement of water access a semipermeable membrane from the side of the membrane with the lesser number of particles and greater concentration of water to the side with the greater number of particles and lesser concentration of water
tonicity
The tension or effect that the effective osmotic pressure of a solution with impermeable solutes exerts on cell size because of water movement across the cell membrane
isotonic
fluid balance equal
neither shrink or swell
hypotonic
less particles outside the cell so water flows into the cell
SWELLS
hypertonic
more particles outside the cell, fluid leaves the cell
shrinks
lyse
when a cell bursts from too much water (hypotonic)
3rd spacing
loss or trapping of ECF in the transcellular space
examples: pericardial sac, peritoneal cavity, pleural cavity
contributes to body weight but nit fluid reserve
causes of 3rd spacing
leaky capillary syndrome (pancreatitis)
liver failure
intestinal obstruction
crush injury
burns
edema
increase cap filtration pressure and permeability
decrease capillary osmotic pressure
obstructs lymph flow
body water is ?% of body weight
60
physiologic mechanisms assisting in regulation of body water
thirst (primary)
ADH (regulates water output)
both respond to changes in ec osmolaty and volume
hypodipsia
Decrease in the ability to sense thirst associated with cerebral lesions in the hypothalamus.
can lead to: stroke, confusion, sensory deficits, motor disturbances
polydipsia
symptomatic/true thirst
false thirst
compulsive thirst
symptomatic/true thirst
due to loss of body water; resolved when water is replaced
false thirst
from increased angiotensin (CHF< DM< CKD) or anticholinergic drugs
compulsive water drinking
psychogenic polydipsia, most common in schizophrenic patients. Some antipsychotic drugs (and cigarettes) can increase antidiuretic hormone, but still mysterious. Could lead to water intoxication
baroreceptors
regulate effective volume
how kidneys control PH
main regulator of sodium
monitors arterial pressure (retains sodium when decreased and eliminates it when increased)
rate coordinated by sympathetic nervous systems and RAAS
ANP may also regulate sodium excretion by kidney
how lungs control PH
Via carbonic acid concentration, PCO2
RAAS
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
diabetes insipidus
antidiuretic hormone is not secreted adequately, or the kidney is resistant to its effect leading to large concentrations of urine output (very light colored)
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)
fails to use the negative feedback system that regulates the release and inhibition of ADH
decreased urine production, very darl
assessment of body fluid loss
heart rate (thready/fast, or bounding/slow)
BP low
fluid volume deficit
inadequate eintake
GI loss (vomit, diarrhea)
renal
skin
3rd spacing
fluid volume excess
excessive fluid and/or sodium intake
inadequate elimination: renal, hear, liver failure, corticosteroid excess
water intoxication
causes lysis of cells which can lead to death
very important to follow directions for baby formula
potassium distribution and regulation
Body stores: depend on body size & muscle mass
Source: dietary intake
Regulation:
Renal mechanisms → conserve or excrete K⁺
Transcellular shifts → movement between ICF & ECF
ICF K+ concentration
140-150 mEq/L
ECF K+ concentration
3.5-5.5 mEq/L
hypokalemia
Low potassium levels in the blood (below 3.5)
d/t inadequate intake, excessive loss, or redistribution between ICF and ECF
hyperkalemia
high levels of potassium in the blood (greater than 5)
d/t decreased renal elimination
rapid administration
movement from ICF to ECF
diagnoses of potassium disorder
exam: muscle weakness, signs of volume depletion
labs: potassium an ECG
treatment of potassium disorder
Calcium: stabilizes membranes
NaHCO₃: shifts K⁺ → ICF
Insulin: lowers ECF K⁺
Other: ↓ intake/absorption, ↑ renal excretion, ↑ cellular uptake
Hypokalemia signs
flat/inverted t waves
polyuria
alkalosis
hyperkalemia signs
peaked t waves
oliguria or anuria
acidosis
calcitonin
acts on the kidney and bone to remove calcium from the ECF
PTH and Vitamin D
stimulate calcium absorption
calcium lab value
8.5-10.5 mg/dL
hypocalcemia
hypoparathyroidism
vit d deficiency
abnormal calcium loss
increased protein binding
soft tissue sequestration
hypocalcemia tx
IV calcium gluconate o chloride Ca supplement
hypercalcemia
increased intestinal absorption
increased bone reabsorption
decreased elimination
hypercalcemia tx
fluid replacement (NaCl)
diuretics
biphosphonates
hypocalcemia signs
C - Convulsions
A- Arrhythmias
T - Tetany
S - Spasms and stridor
heart failure
muscle cramps
hypercalcemia signs
decreased concentration
increased sleep
depression
confusion and coma
death
arrhythmia and bradycardia
muscle weakness
alterations in_____ result in hypercalcemia?
vitamin d
role of phosphate
-bone formation
-atp formation
-nucleic acid formation
- delivery of o2 to rbc
-normal function of other blood cells
phosphate and calcium have an ______ relationship?
inverse
hypermagnesia causes
Renal insufficiency, excessive consumption or IV administration
hypomagnesia causes
prolonged fasting or starvation, chronic alcoholism, diuretics
hypermagnesia s/s
lethargy
n/v
loss of reflexes
respiratory and cardiac arrest
hypomagnesia s/s
confusion
hyperactive reflexes
tremors
seizures
cardia dysrhythmias
hypermagnesia tx
Dialysis if severe, restrict magnesium in diet, increase fluids
hypomagnesia tx
Oral, IV or IM magnesium
increase consumption of green veggies, nuts, banana, oranges, peanut butter, chocolate
PH levels
7.35-7.45
acidic
less than 7.35
basic
more than 7.45
regulation of PH
concentration of metabolic acids and bicarbonate base is regulated but he kidney
CO2 concentration is regulated by respiratory system
PH lab tests
arteriole blood gasses and pH
CO2 and bicarbonate levels
base excess or deficit
anion gap
increased CO2
acidosis
decreased CO2
alkalosis
respiratory acidosis
increased pCO2 levels
raised by impaired alveolar ventilation (medulla impairment, lung disease, chest injury, weakness of respiratory muscles, airway obstruction)
respiratory alkalosis
caused by conditions that cause hyperventilation and reduction of pCO2 levels
anxiety, hypoxia, lung disease, stimulation of respiratory center, mechanical ventilation
losing acid (vomit)
m alkalosis
losing base (diarrhea)
m acidosis
metabolic acidosis
decrease in HCO3 and hP caused by
excess production/accumulation acid
diarrhea, ostomy, keto/lactic acidosis
metabolic alkalosis
high pH, high HCO3
caused by H+ ion loss or HCO# ion gain
NG tube, vomiting, OD of bicarbonate. or antiacids
HCO3 levels
22-26 mEq/L
kussmauls breathing
hyperventilation that accompanies metabolic acidosis in which the body attempts to compensate (give off excess body acids) by blowing off carbon dioxide through deep and rapid breathing
PCO2 lab
35-45