Analogue Electronics
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
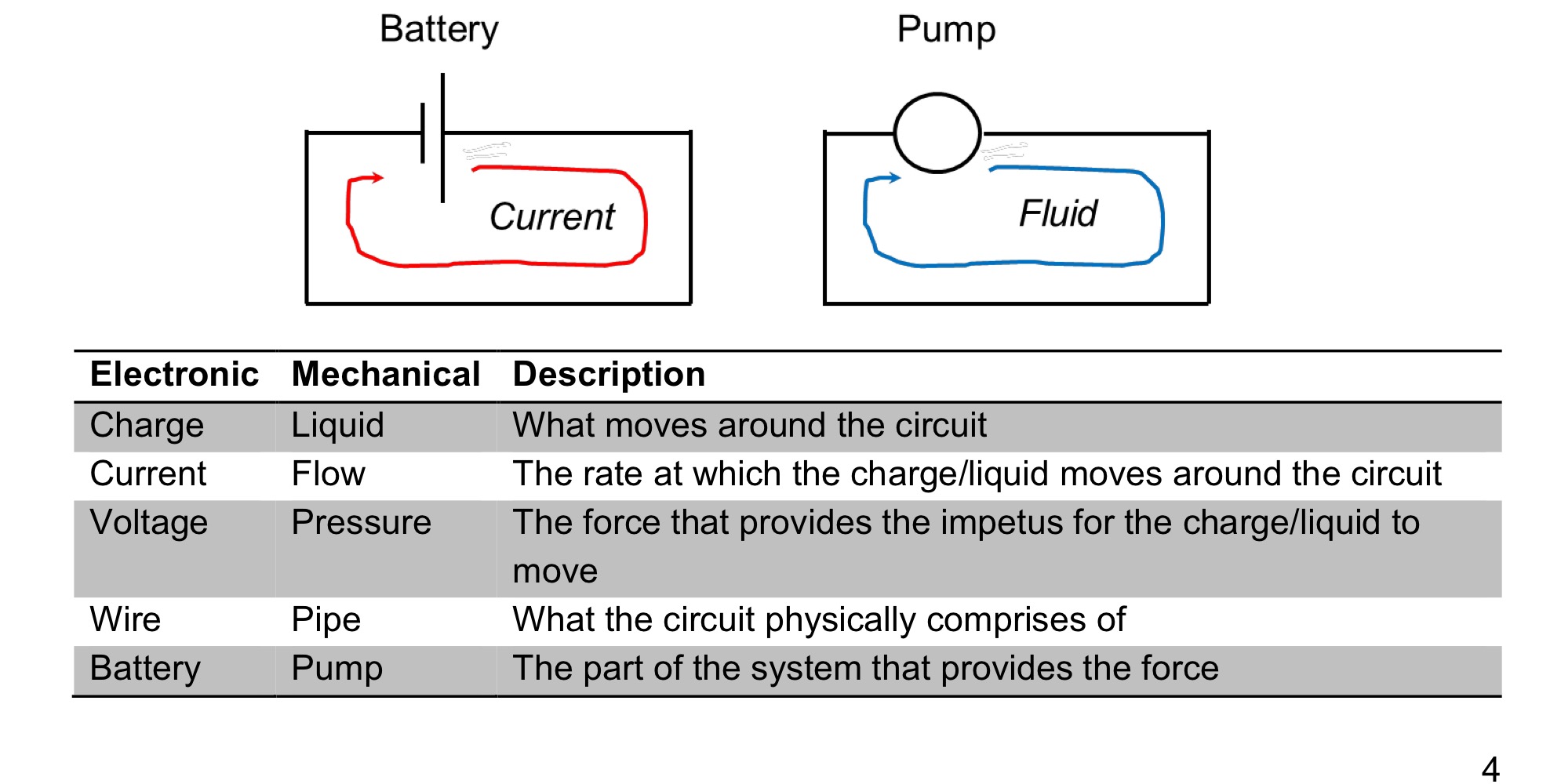
Electrical concepts with mechanical analogues
Electrical Power
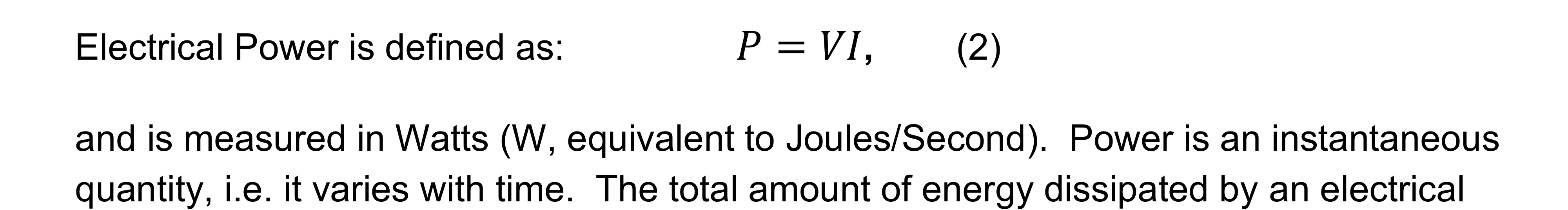
Energy dissipated by an electrical circuit
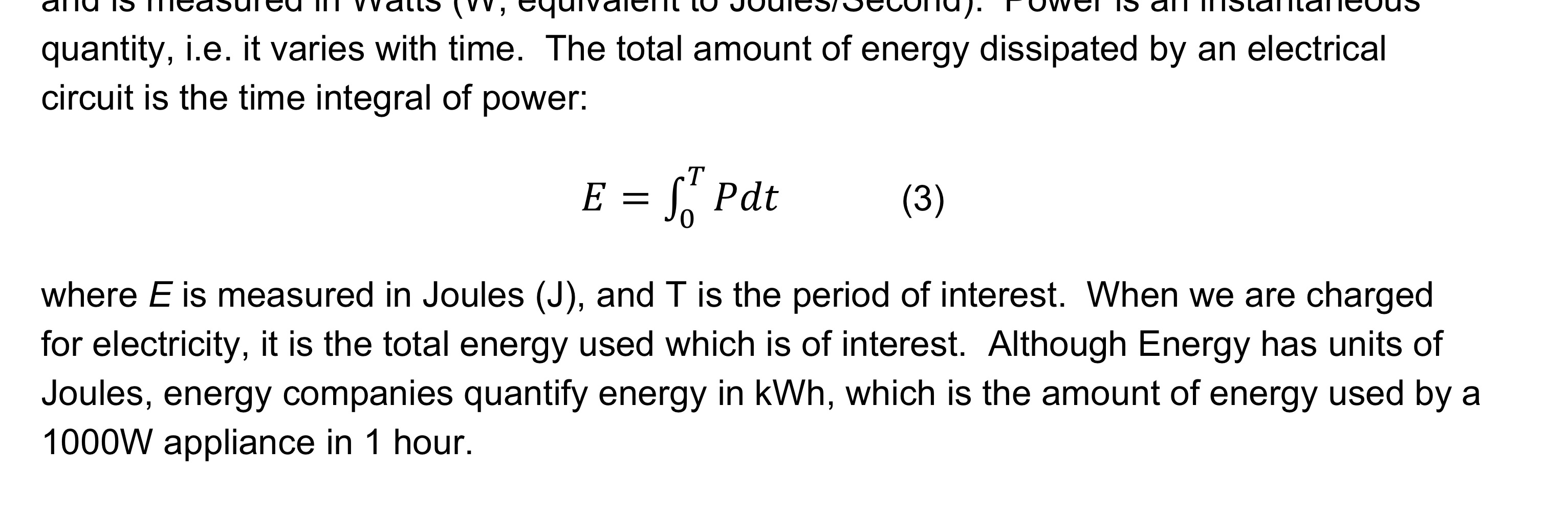
Voltage
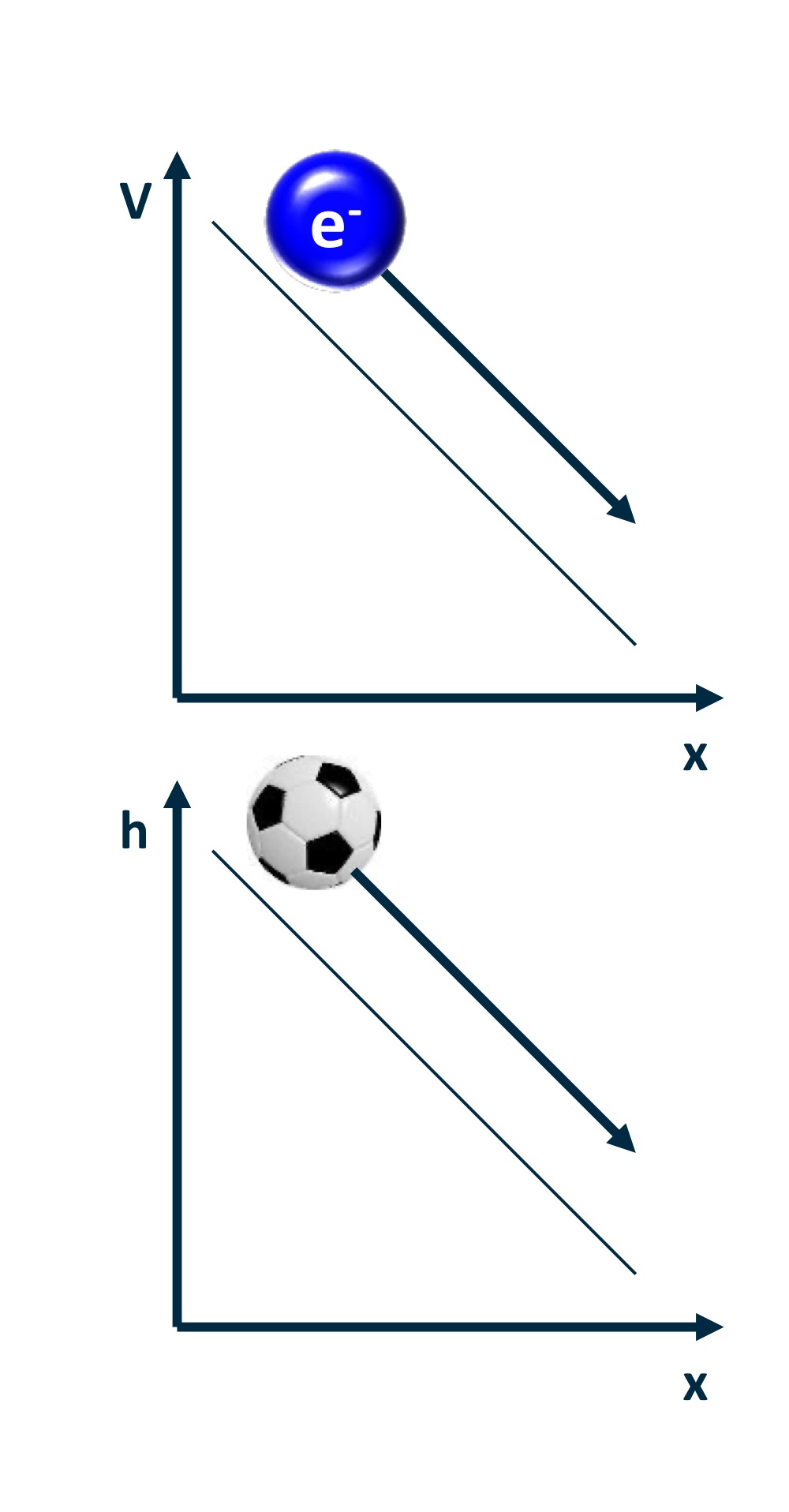
Voltage (V) is the potential energy that pushes
charge around a circuit.
• It is defined as:
“1 Volt provides 1 Joule of energy to each
passing Coulomb of charge”
• A helpful analogy:
Voltage is to an electron in a circuit what height is
to a ball on a hill.
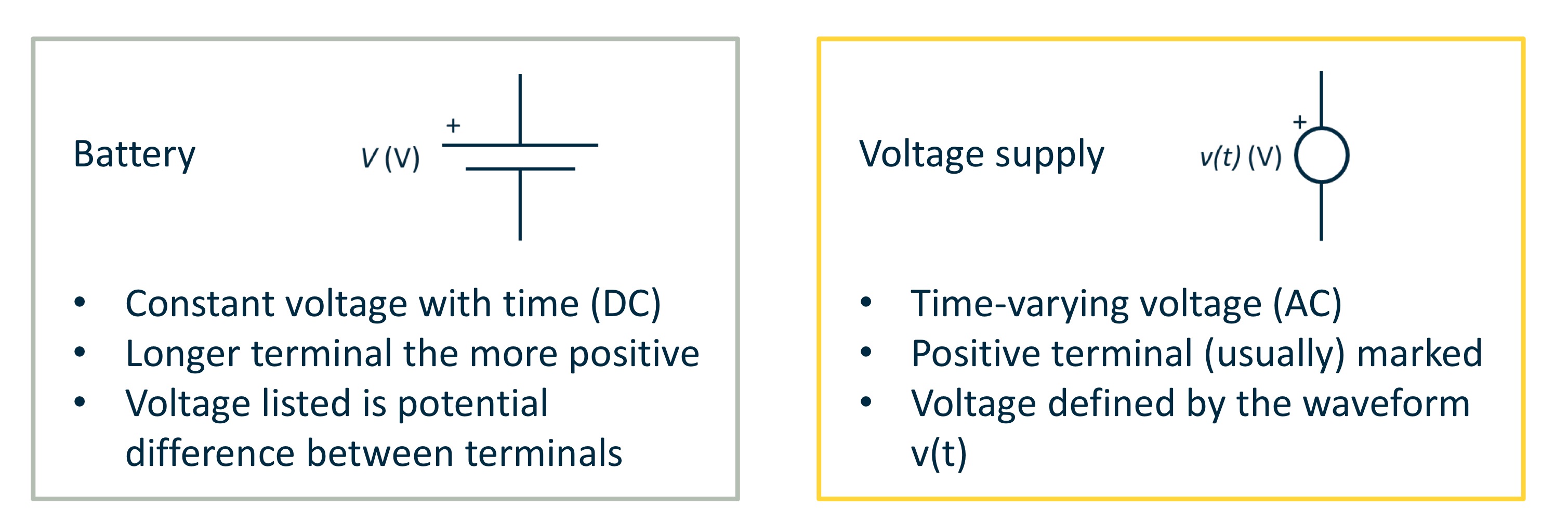
Voltage sources
It is the … between
two parts of a circuit that makes
charges move
It is the potential difference between
two parts of a circuit that makes
charges move
voltage arrow points in the direction
of ...
More positive voltage
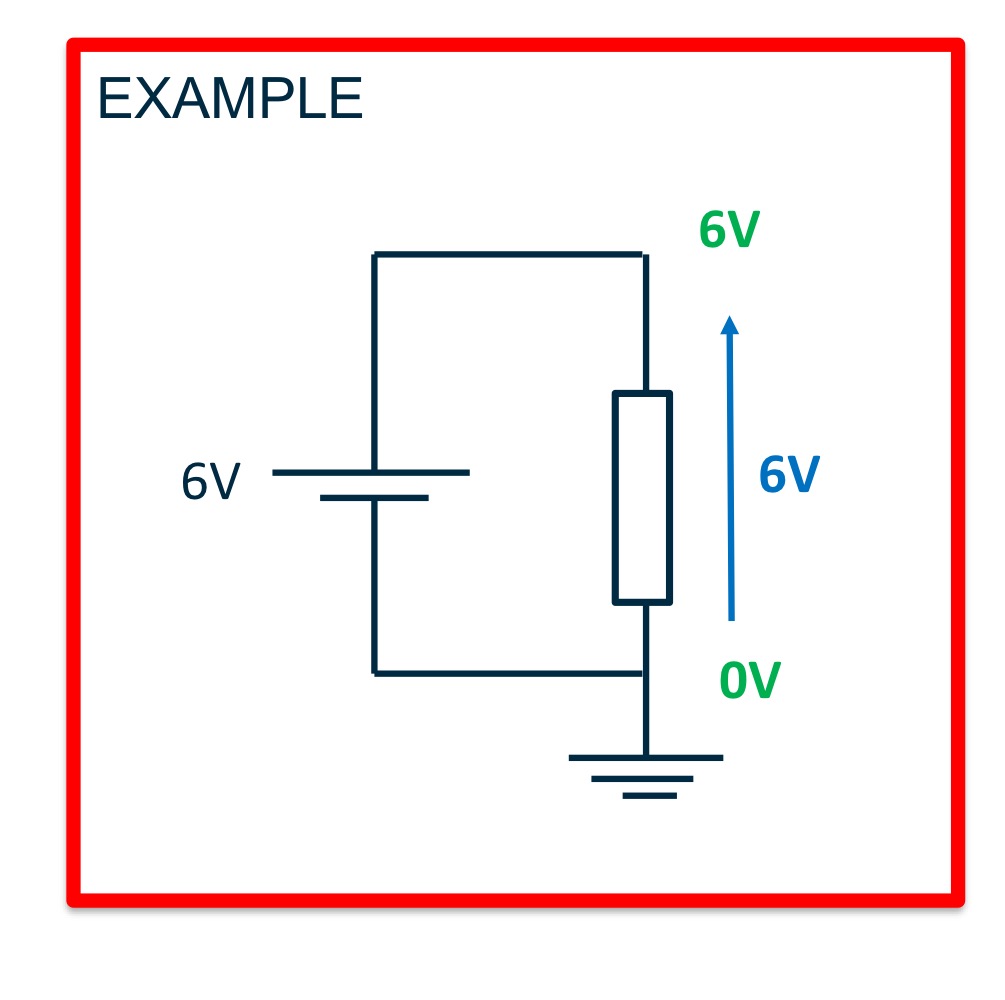
Different parts of a circuit will have
different ….
Different parts of a circuit will have
different absolute voltages.
Ground

Charge, Q
Charge (Q) is the fundamental quantity that means
electrons (holes) react to an electrical potential
difference (voltage)
• A single electron has a charge,
𝑞 = −1.6 × 10−19𝐶
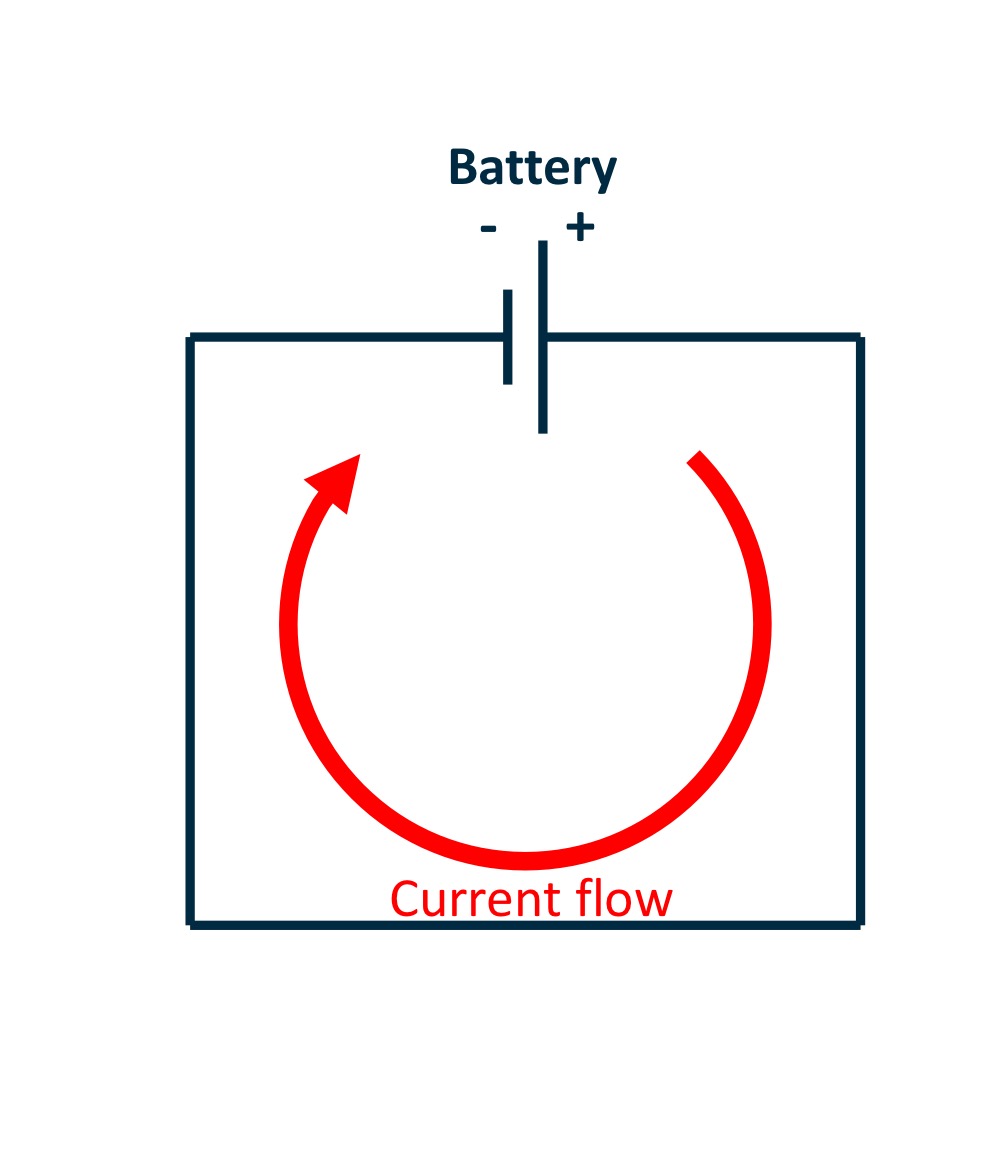
Current, I
Current, I is the flow of discrete charges
𝑰 = 𝒅𝑸/𝒅𝒕
• It has a direction and a magnitude
• Current flows from ‘downwards’ in potential, e.g.
from areas of positive potential to ground


?
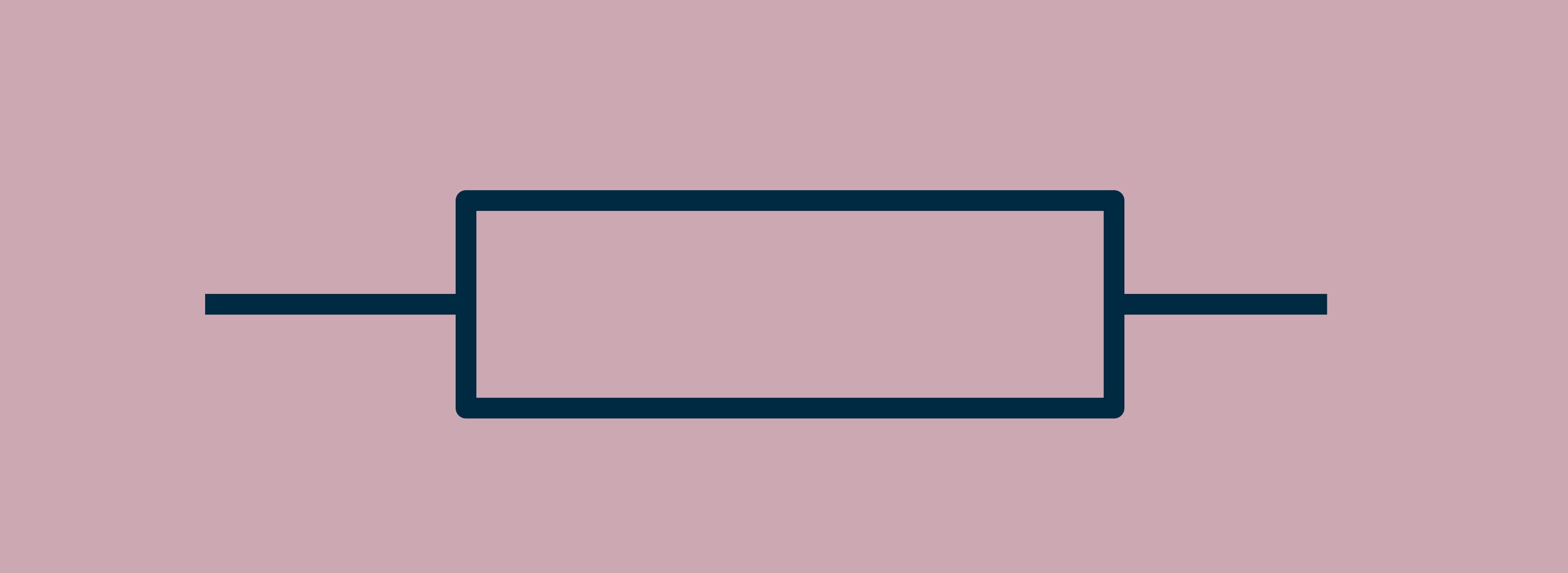
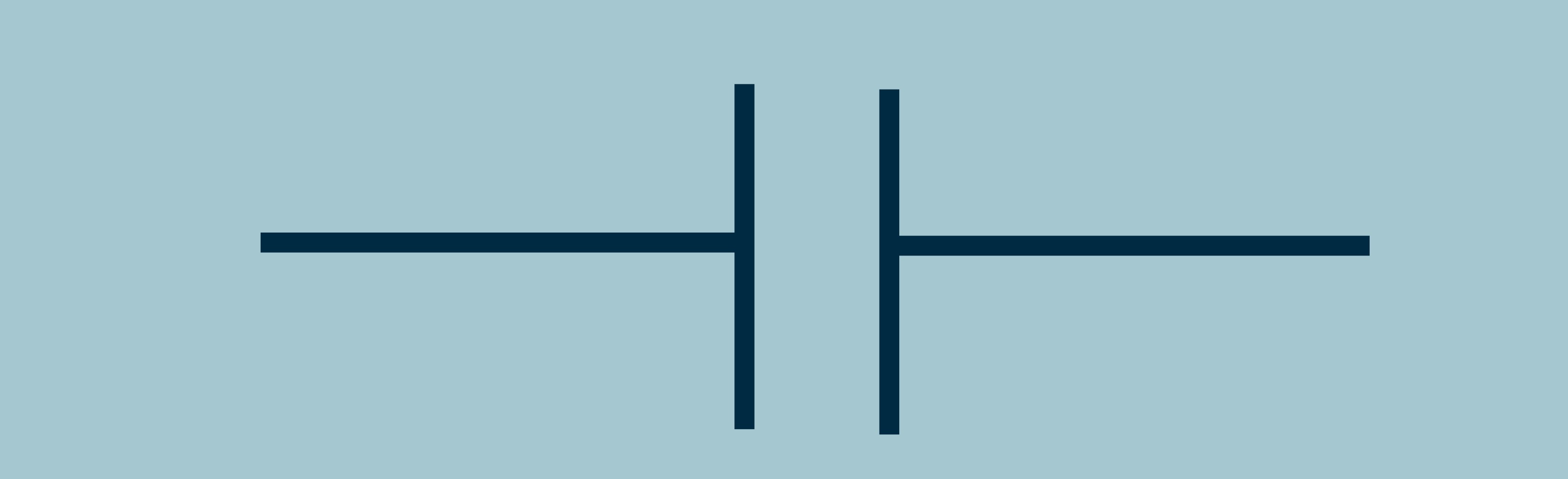
Resistor
?
Capacitor

?
Inductor
?
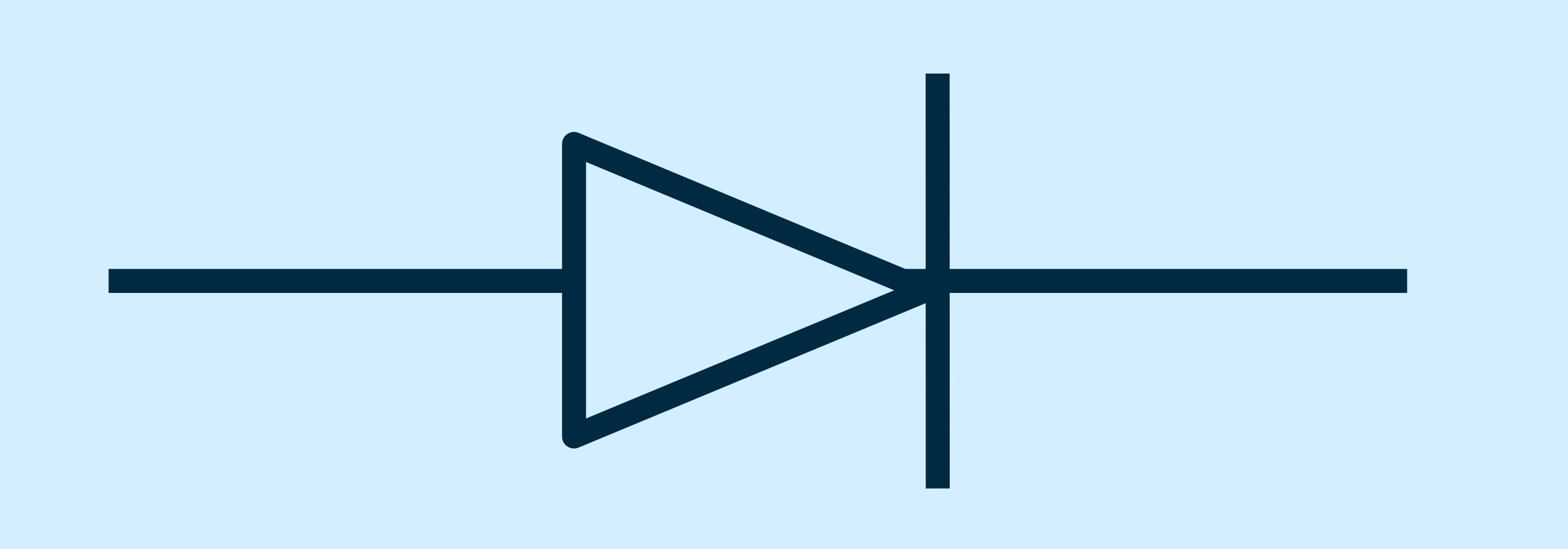
Semiconductors inc. diodes and transistors
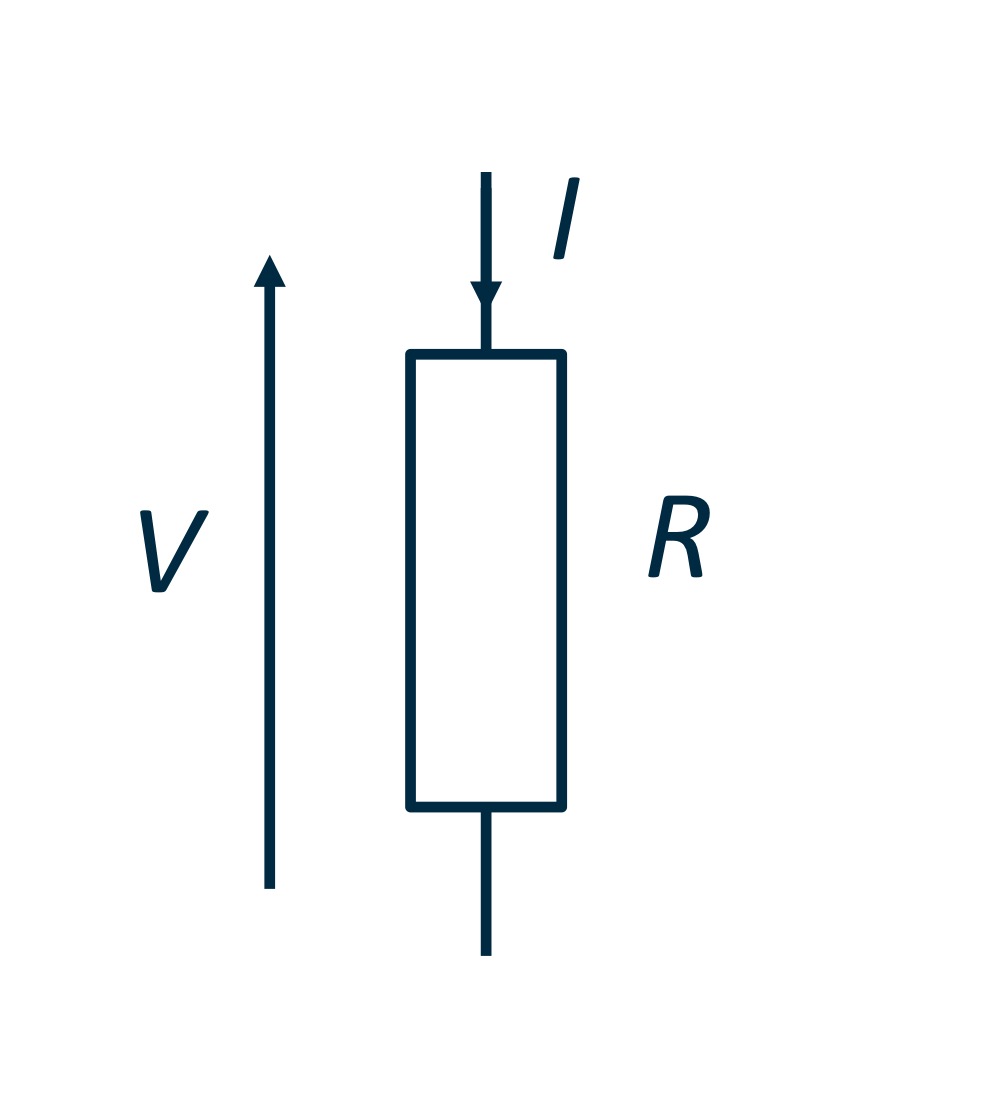
Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s law states that the current flowing through
a conductor (I) is linearly proportional to the
voltage across it (V).
This proportionality constant is the resistance, R
(in Ohms, ). So that we write:
𝑉 = 𝐼𝑅
For materials that obey Ohm’s law, we
can write the power dissipation as:
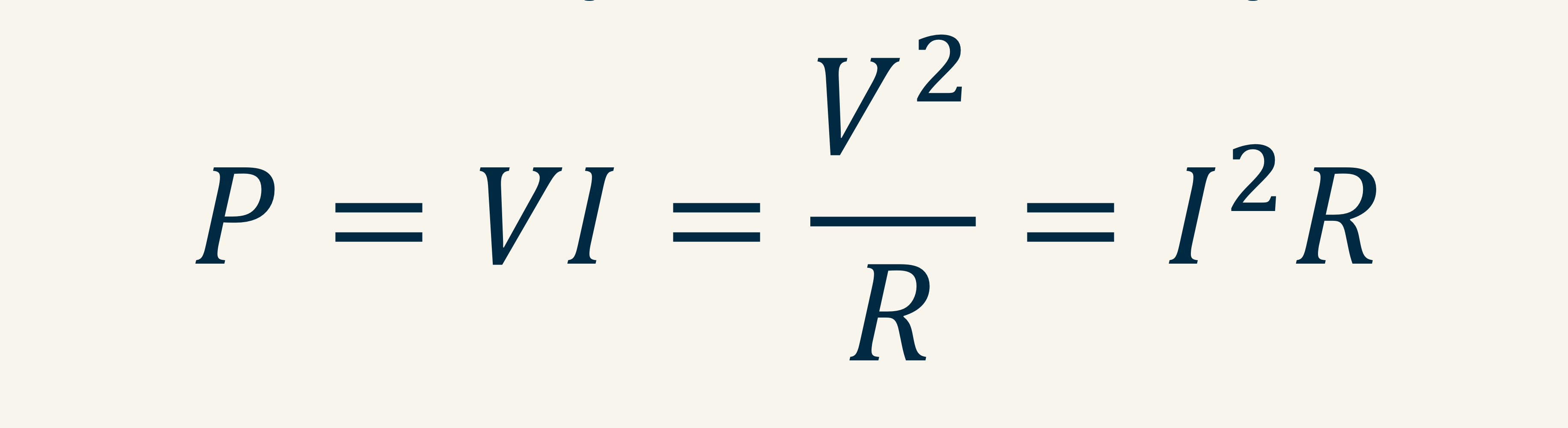
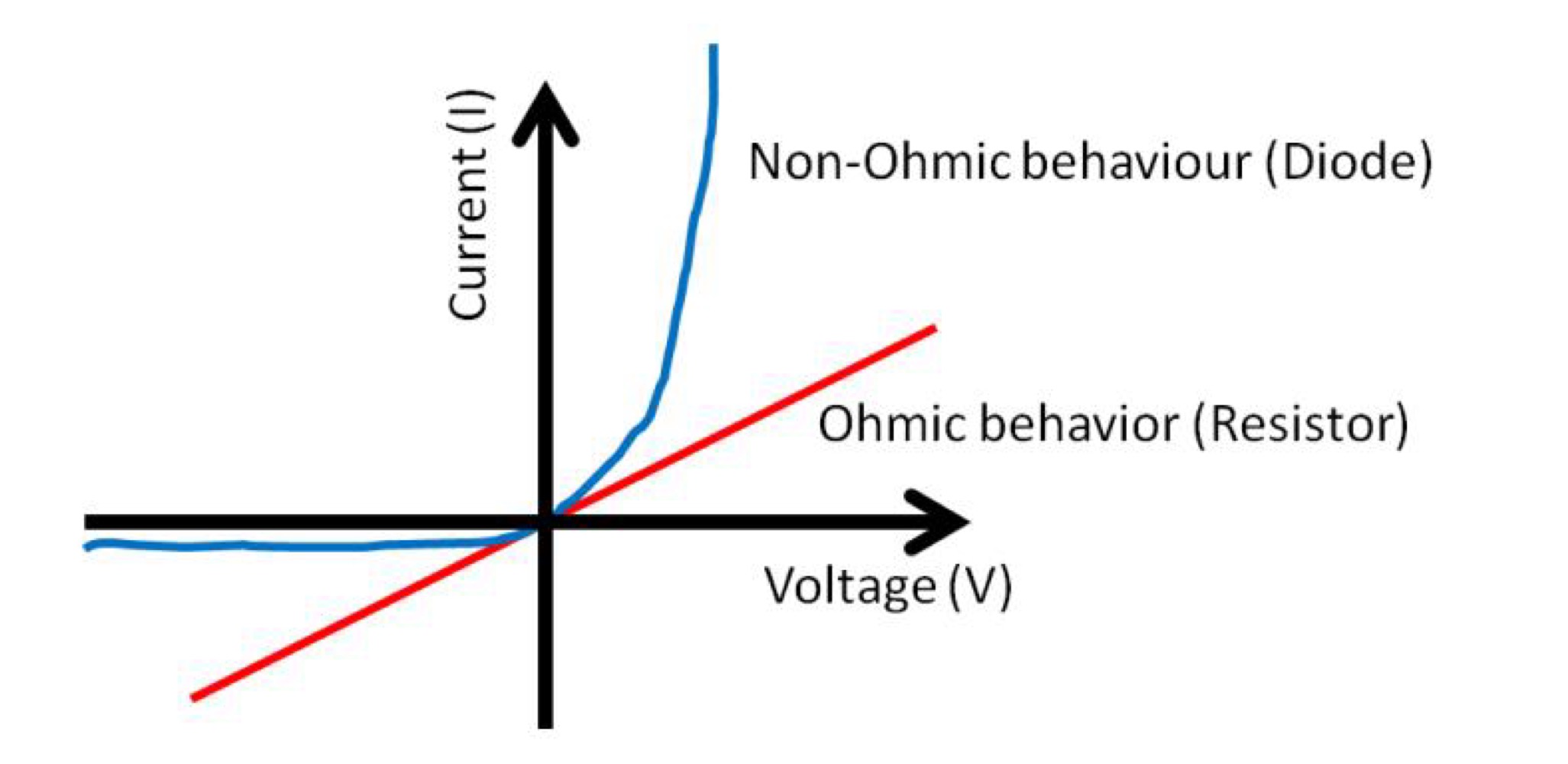
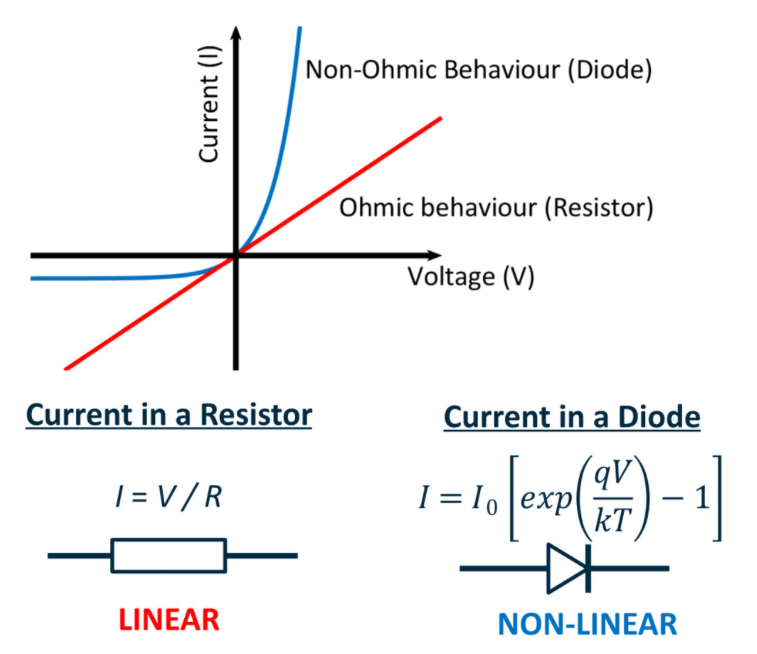
Ohmic conductors
Materials with a linear V-I relationship
are Ohmic conductors, a good example
being metals. Resistors are Ohmic.
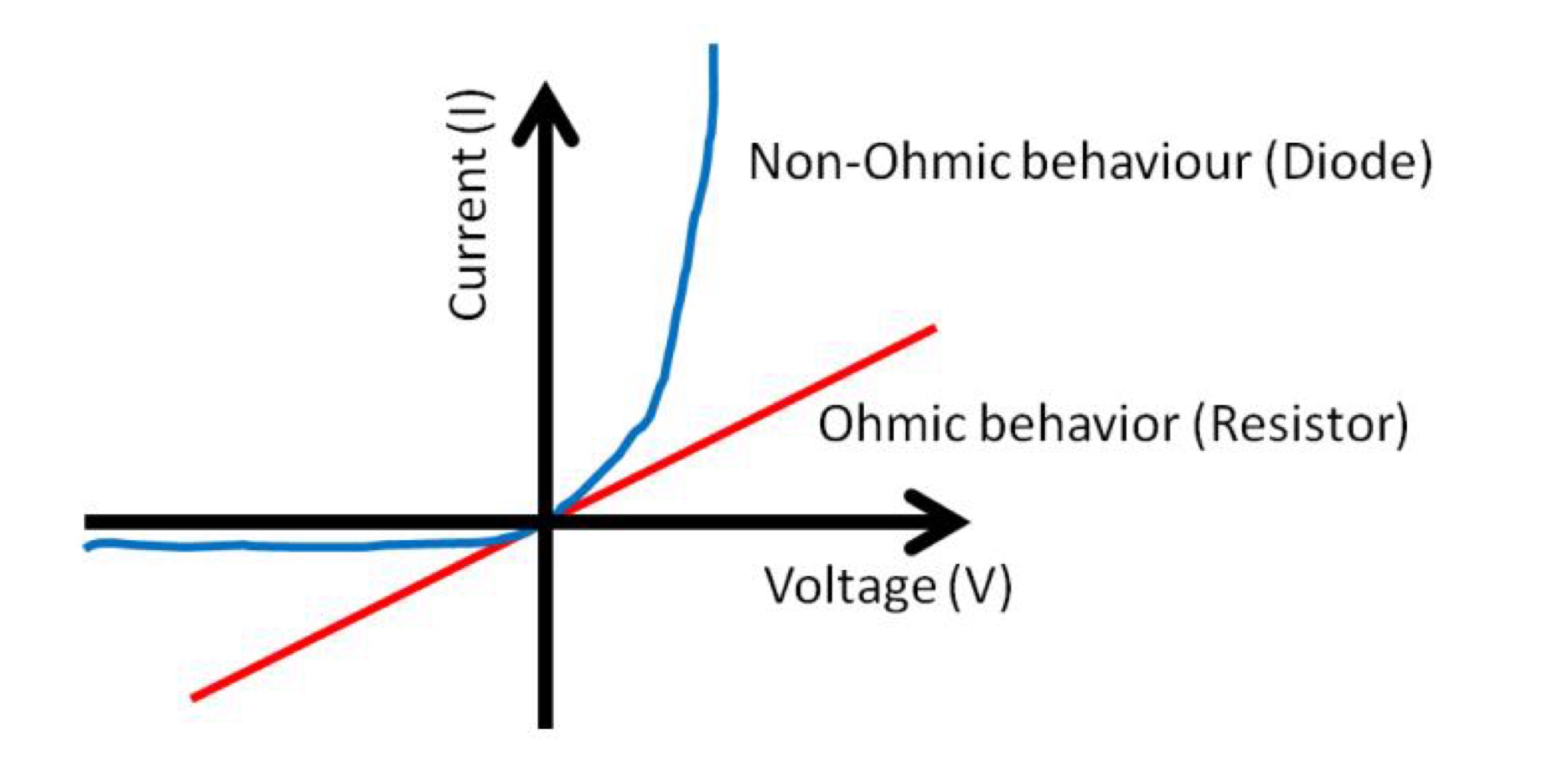
Non-ohmic conductors
Some materials or electronic devices
have non-linear V-I relationships. Many
semiconductor devices, e.g. diodes, are
non-Ohmic.
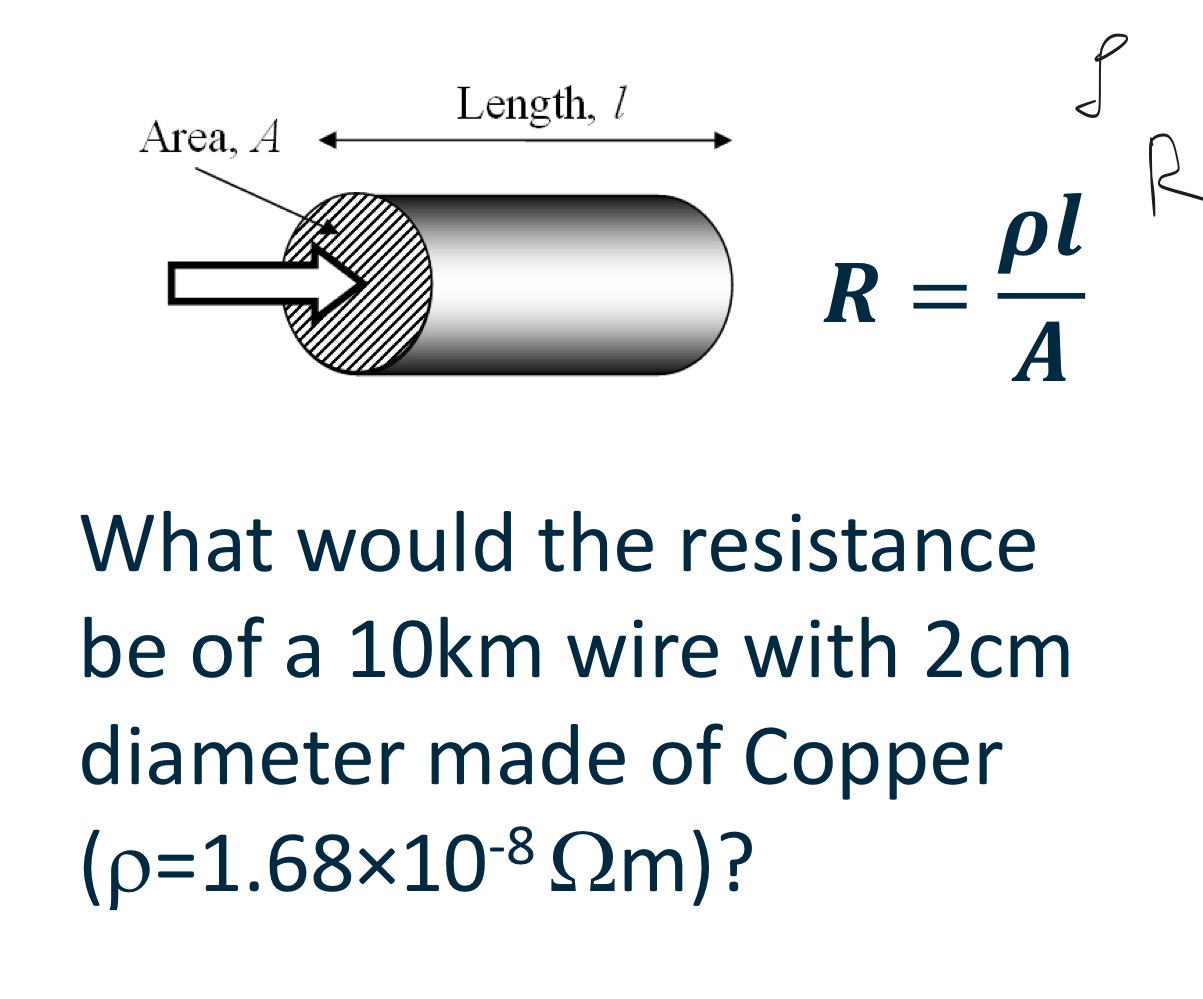
Resistance, R
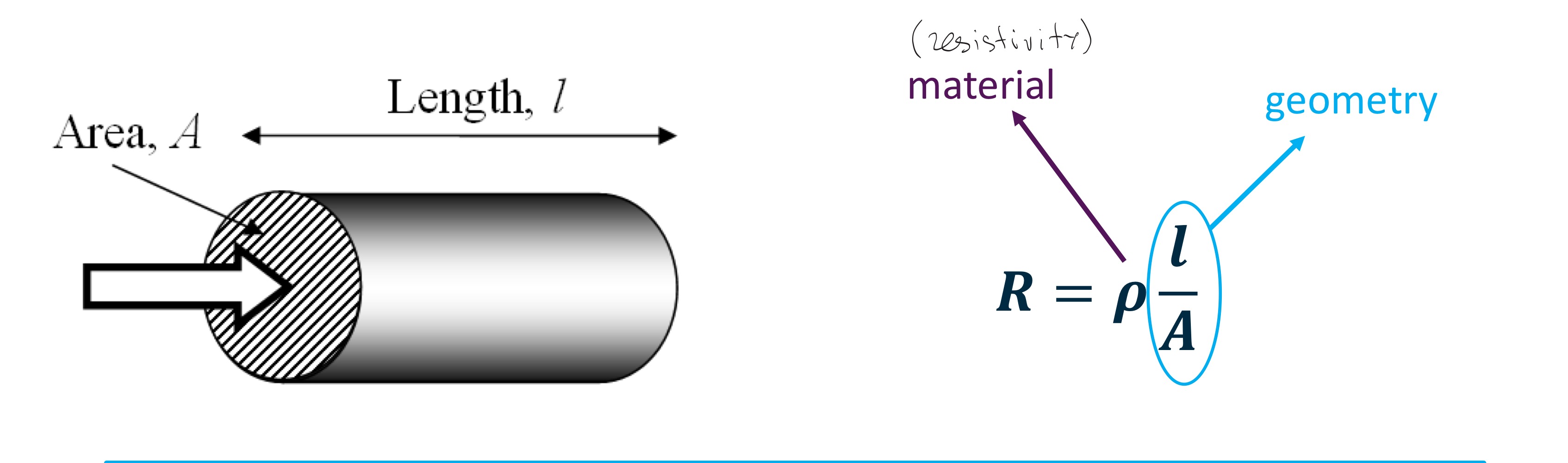
Small resistors that you may have seen inside electronic devices are often made …
Small resistors that you may have seen inside electronic devices are often made Nichrome (‘high’ resistivity) thin films
Wires are often thicker, with high conductivity metals
Resistivity
The resistivity, , is a material property of
the conductor, and is a measure of:
• How many electrons are available…
• How easy it is to move electrons…
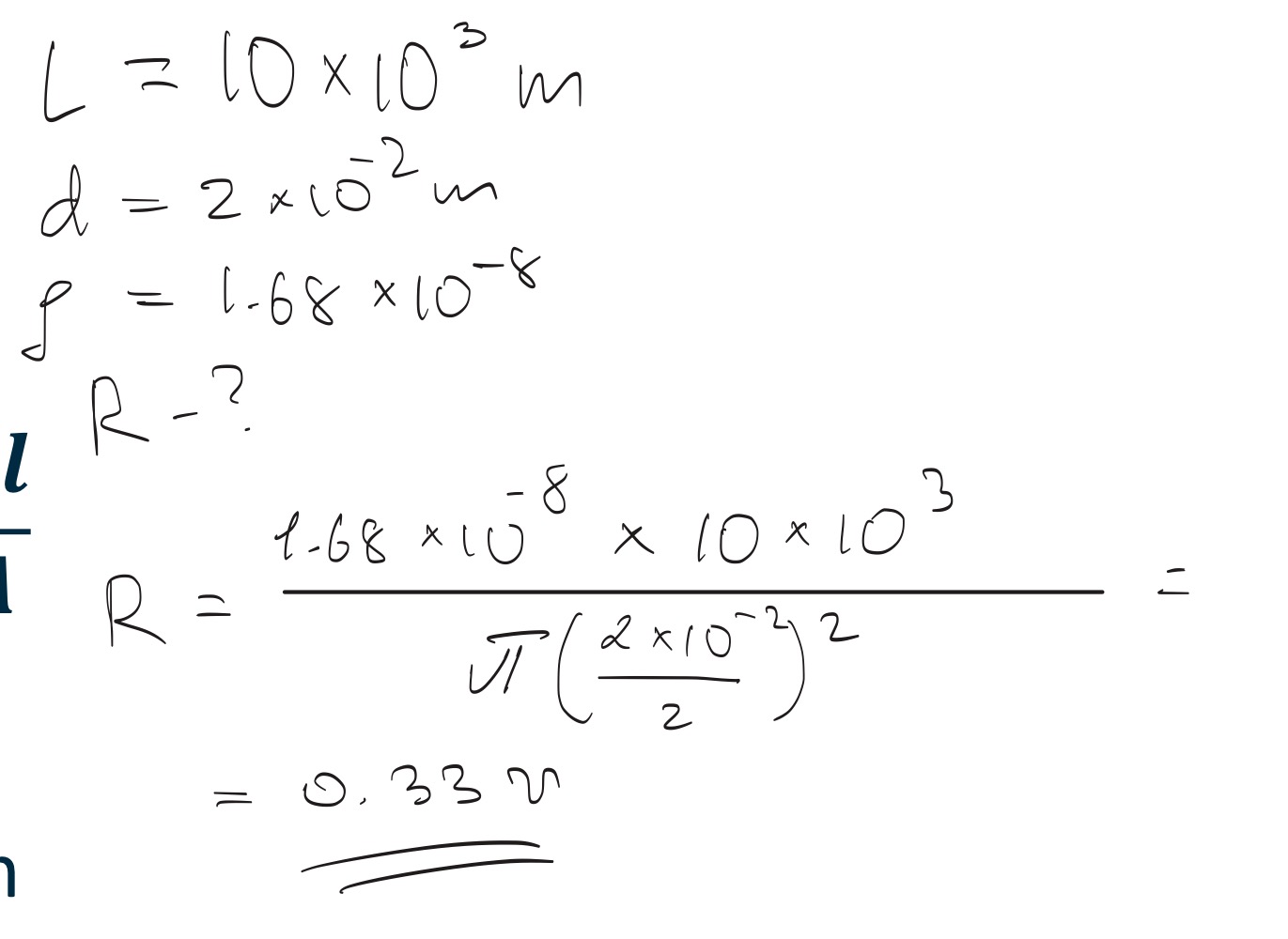
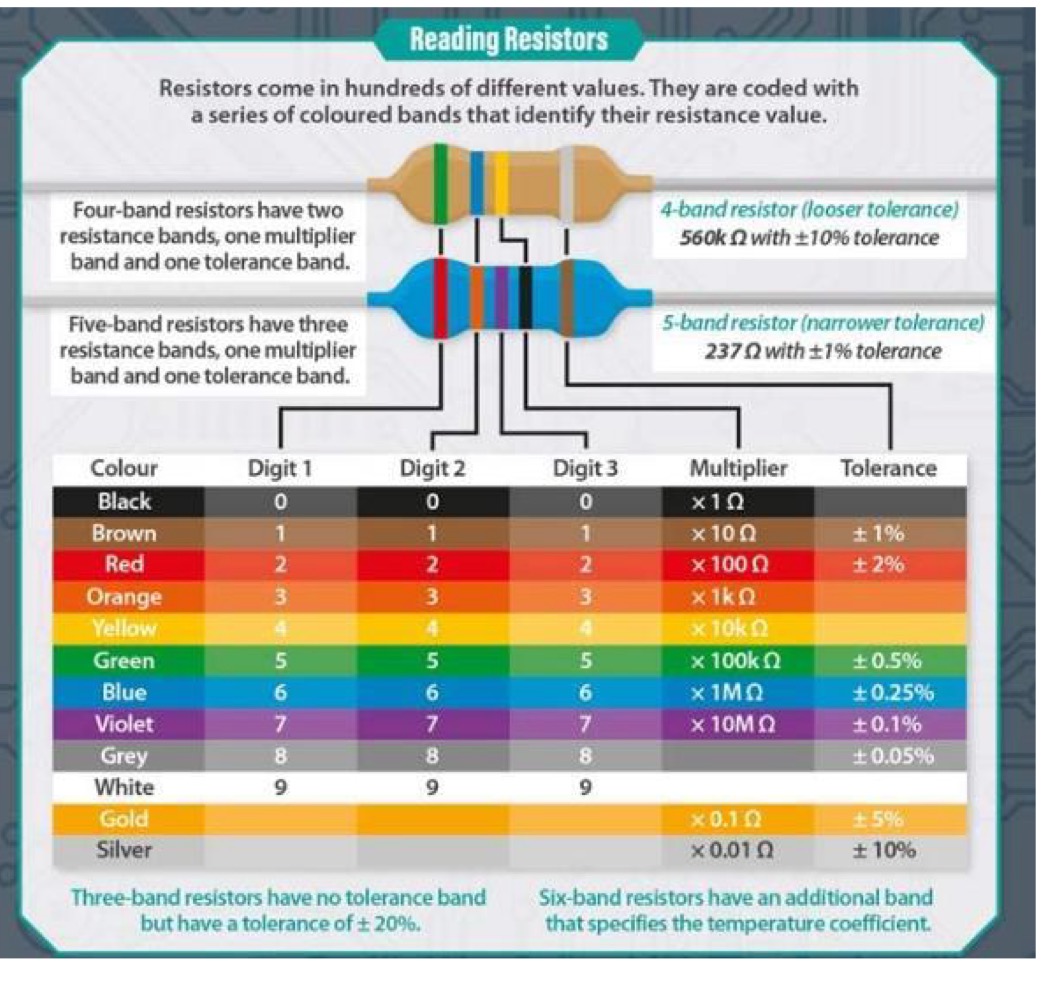
Designs must use
Preferred resistor values
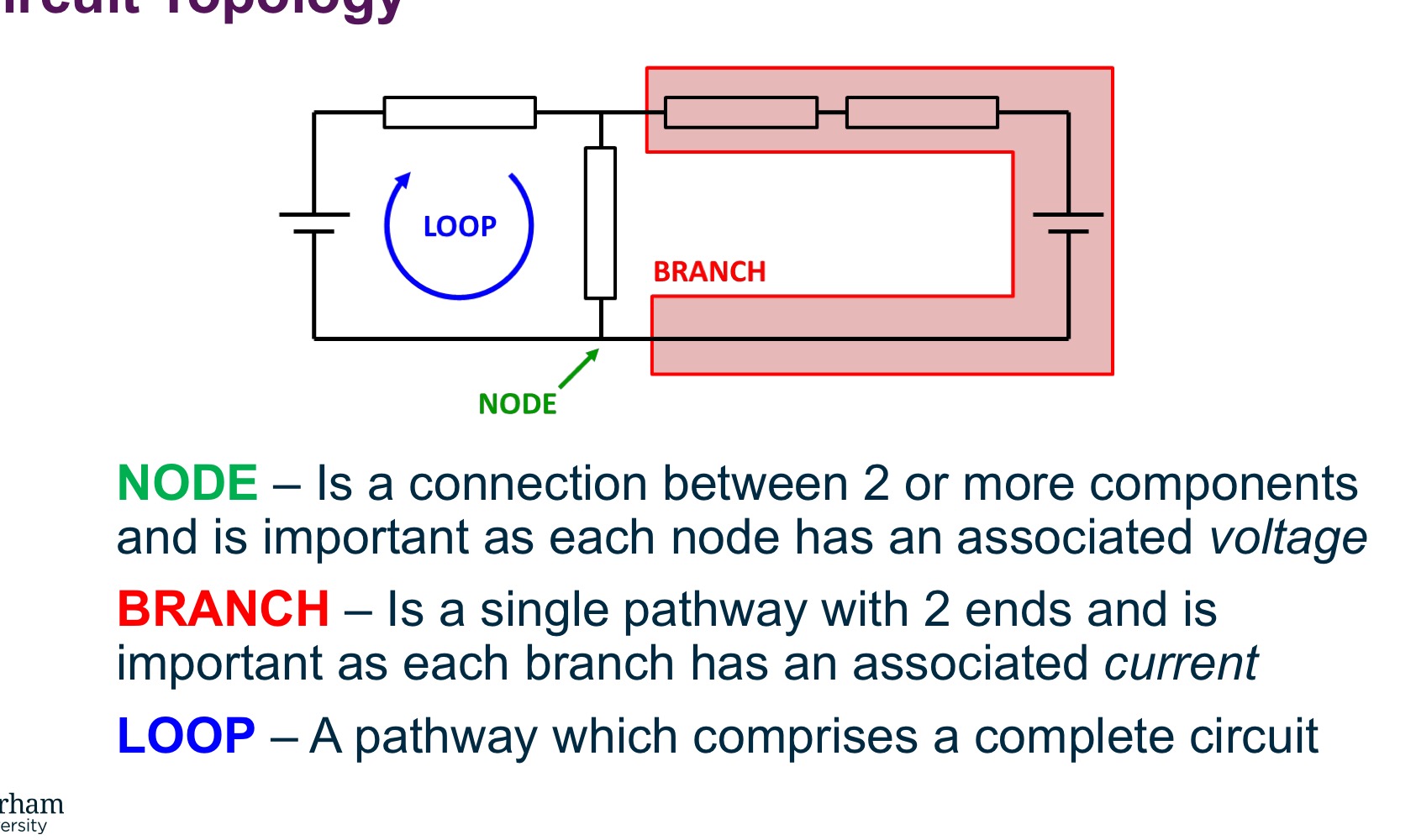
Circuit Topology
Circuit connections
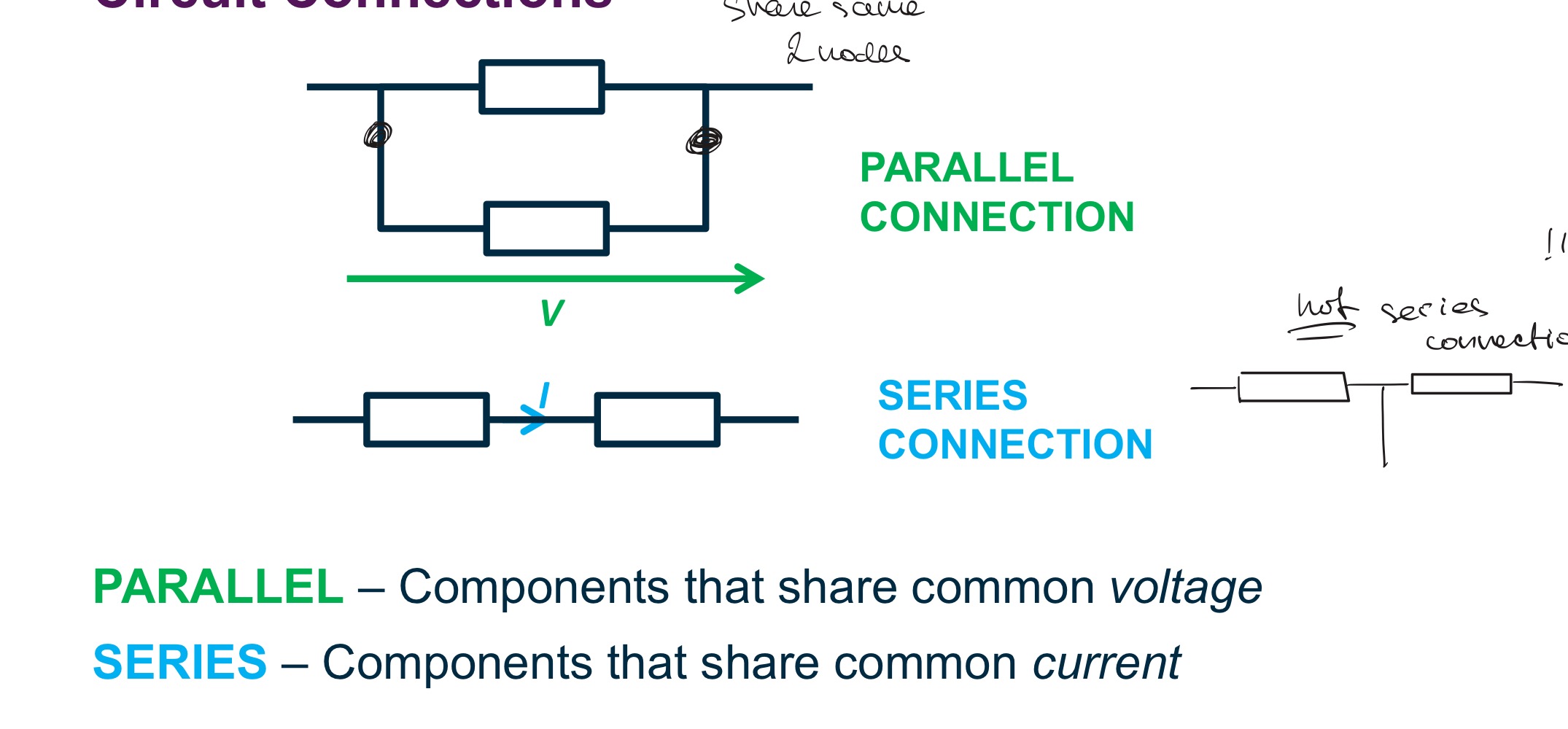
Parallel share common
Voltage
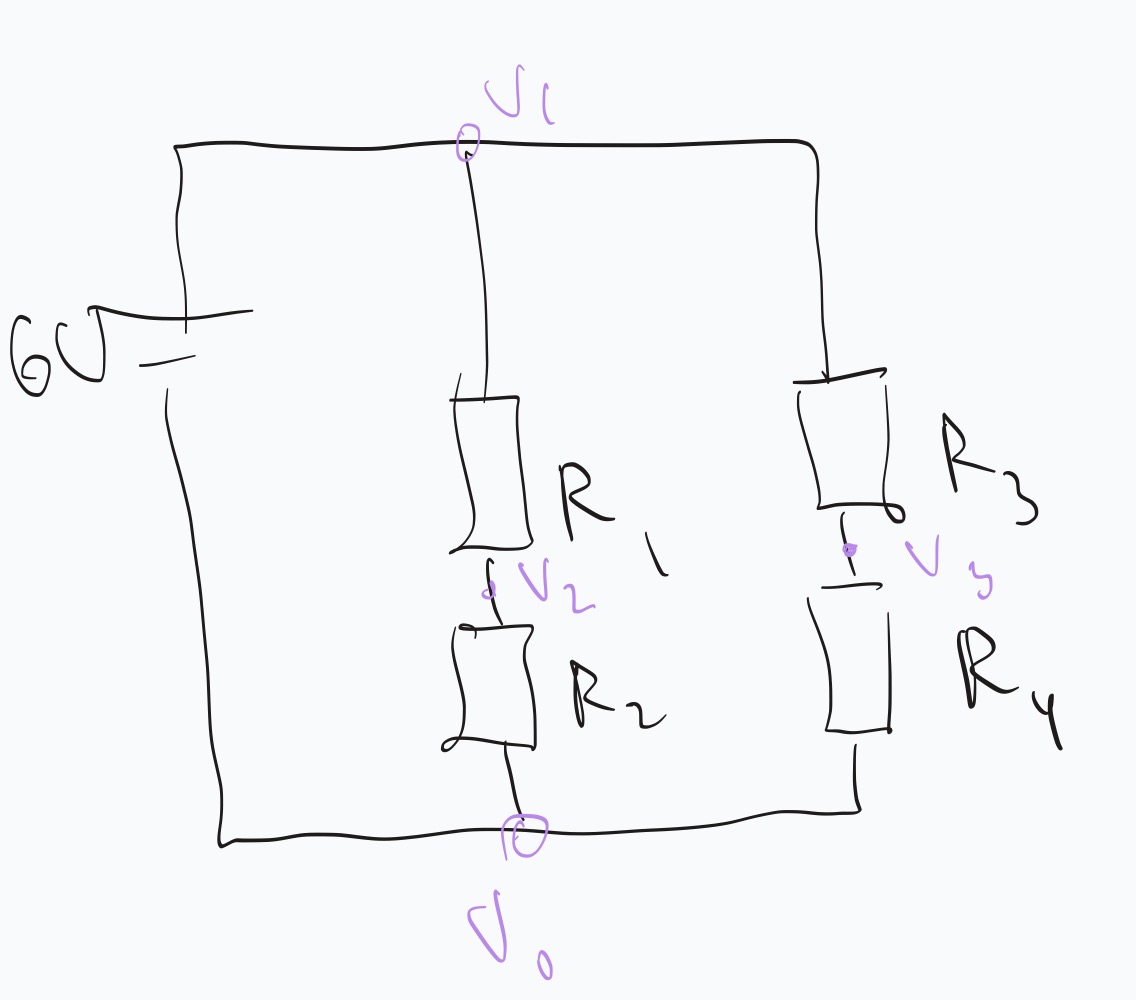
What is parallel with R2?

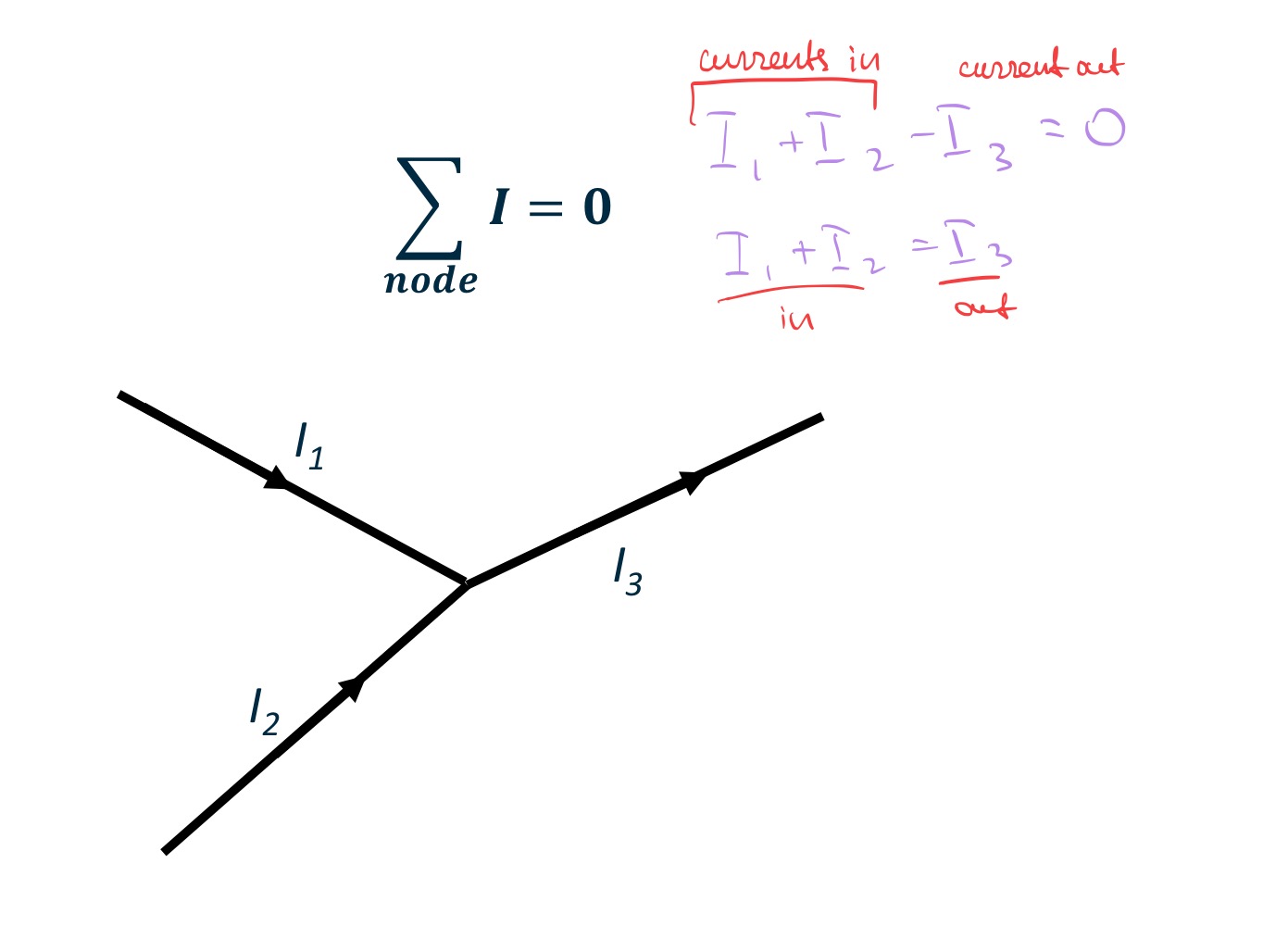
Kirchoff’s Current Law (KCL)
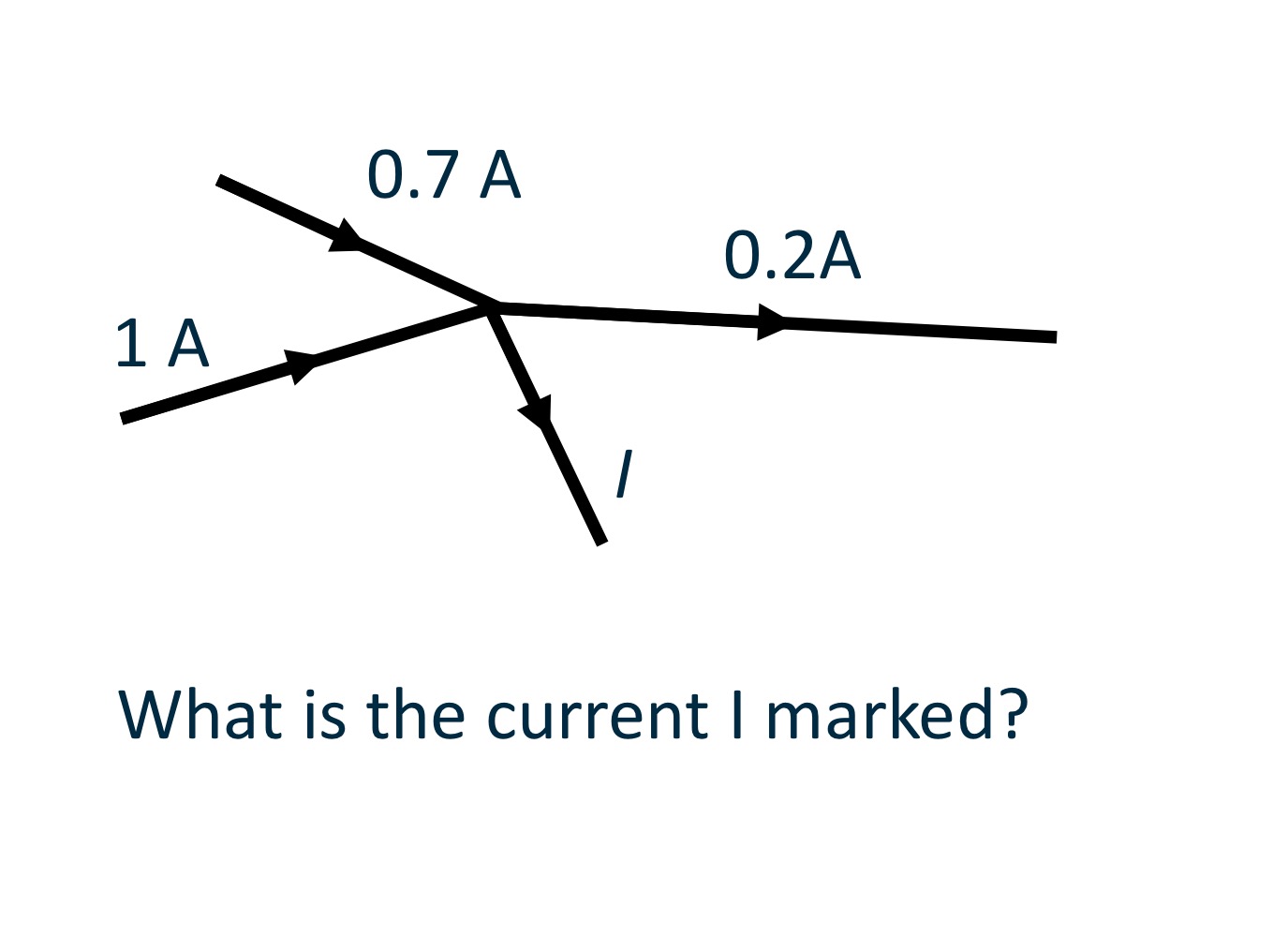
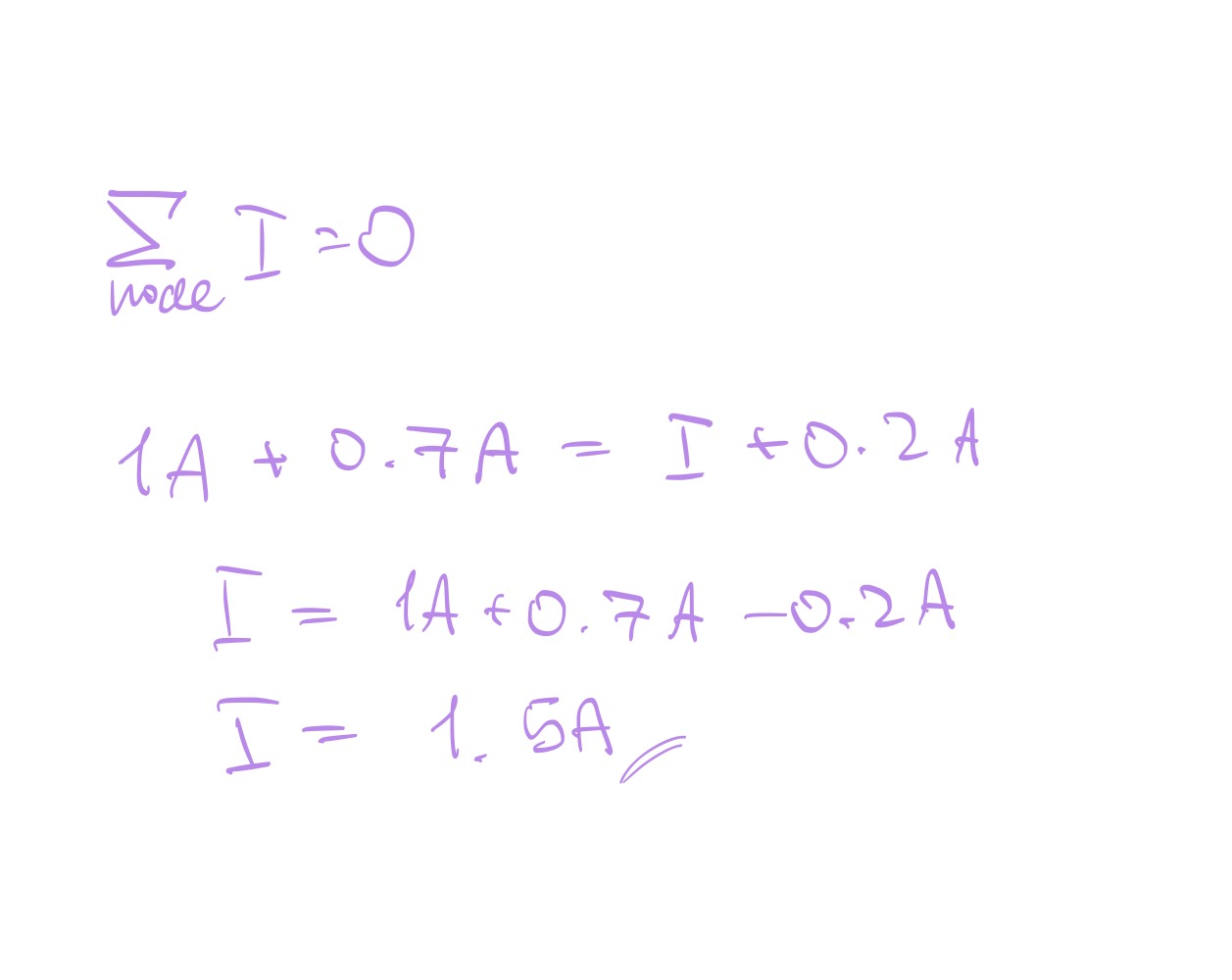
Kirchoff’s Voltage Law (KVL)
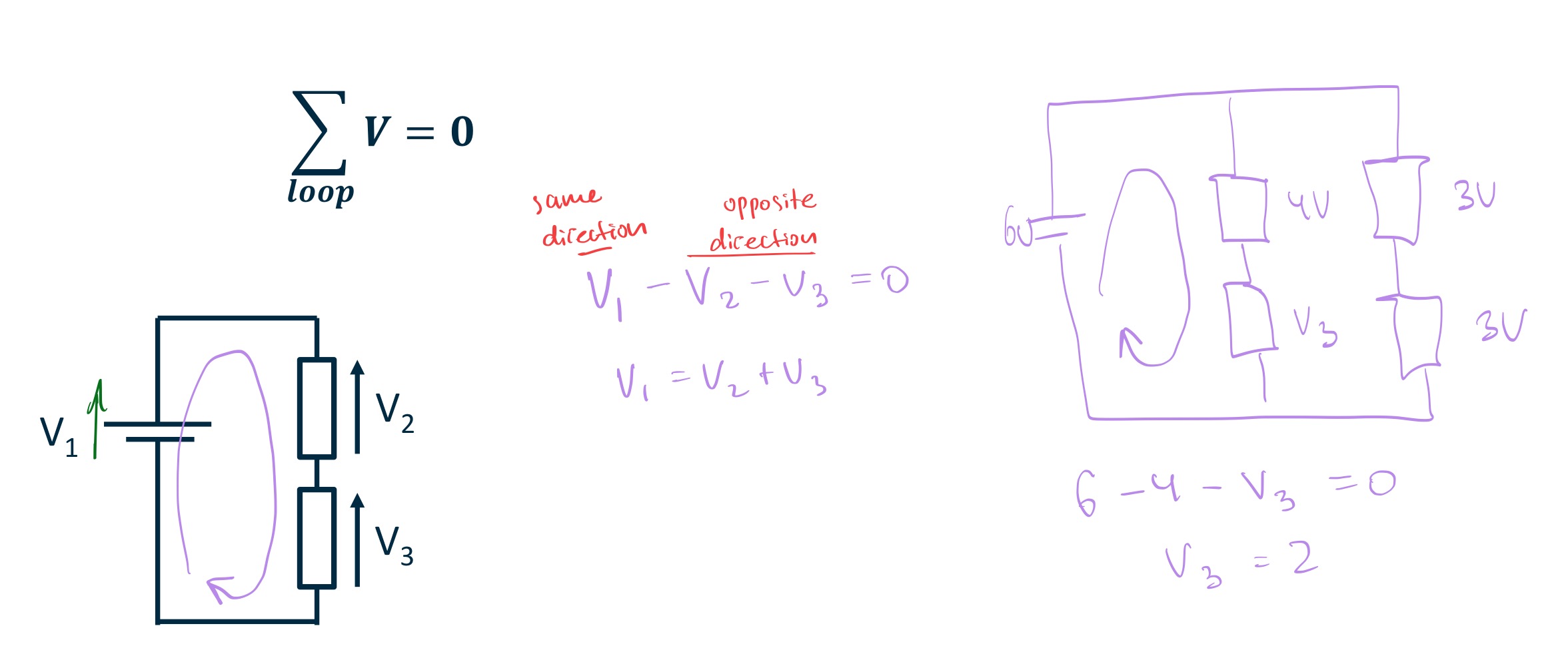
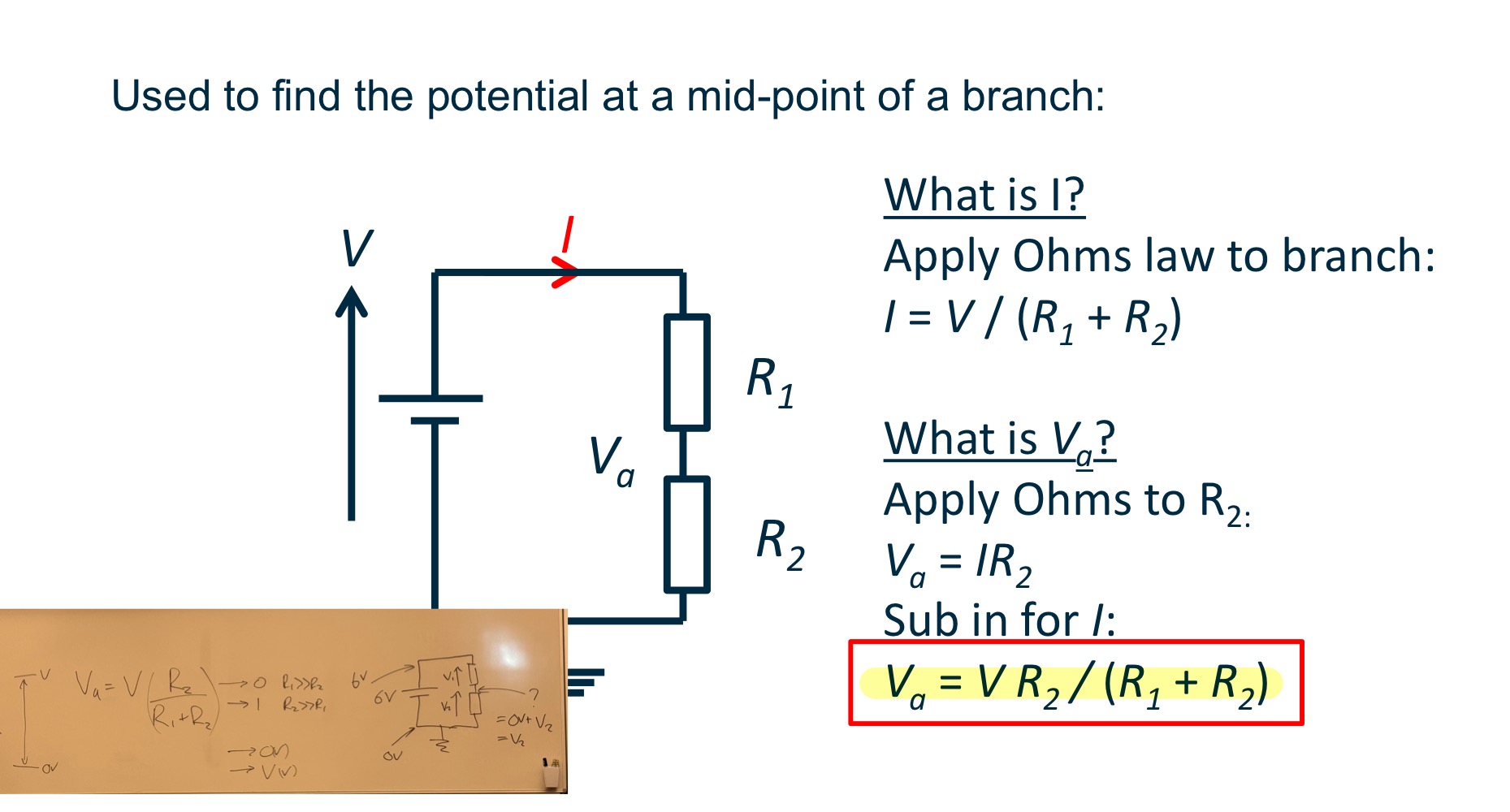
For a resistor, the voltage arrow points….
For a resistor, the voltage arrow points towards the
node where the current enters.
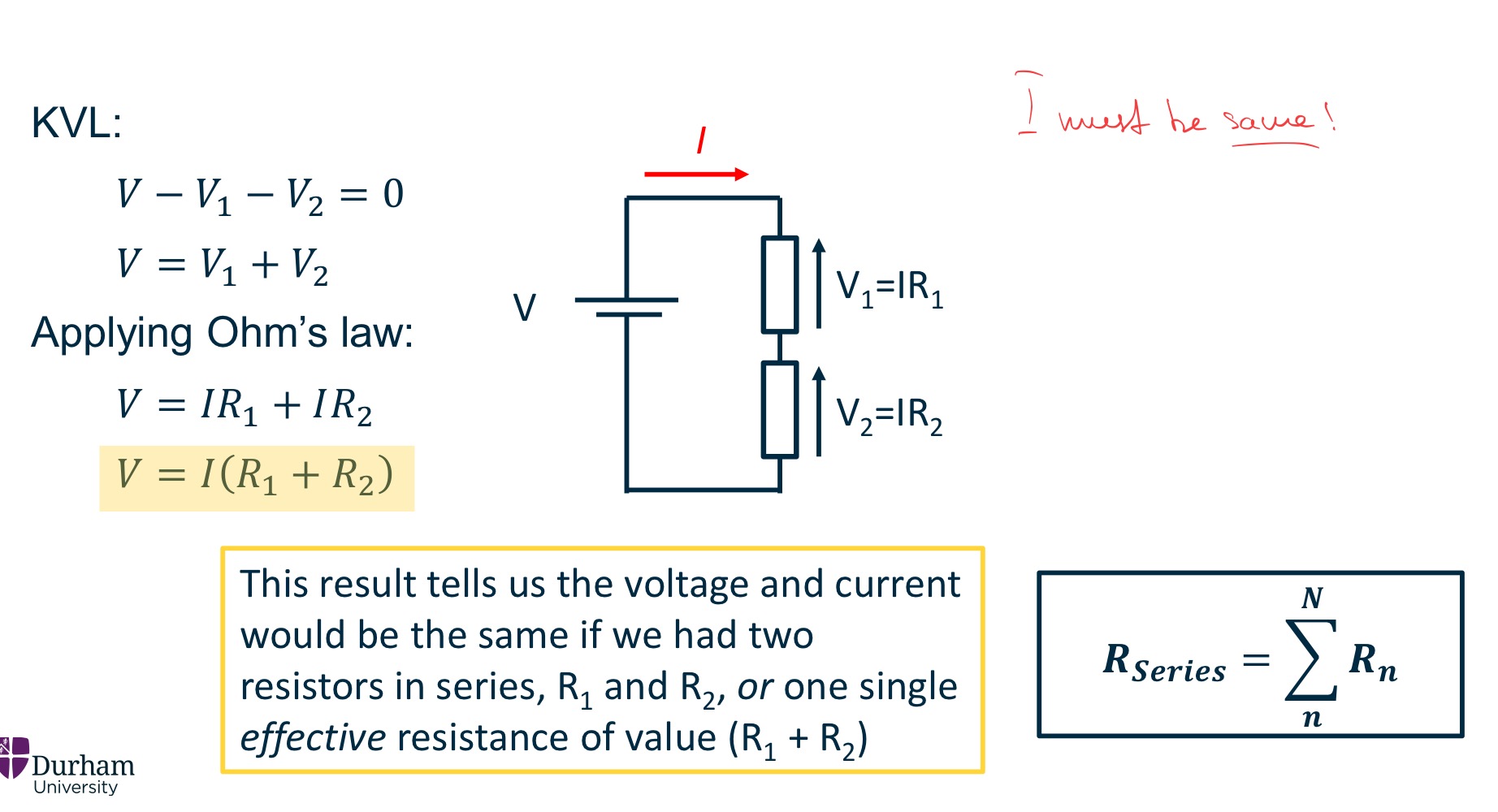
Combining resistors in series
Combining resistors in parallel
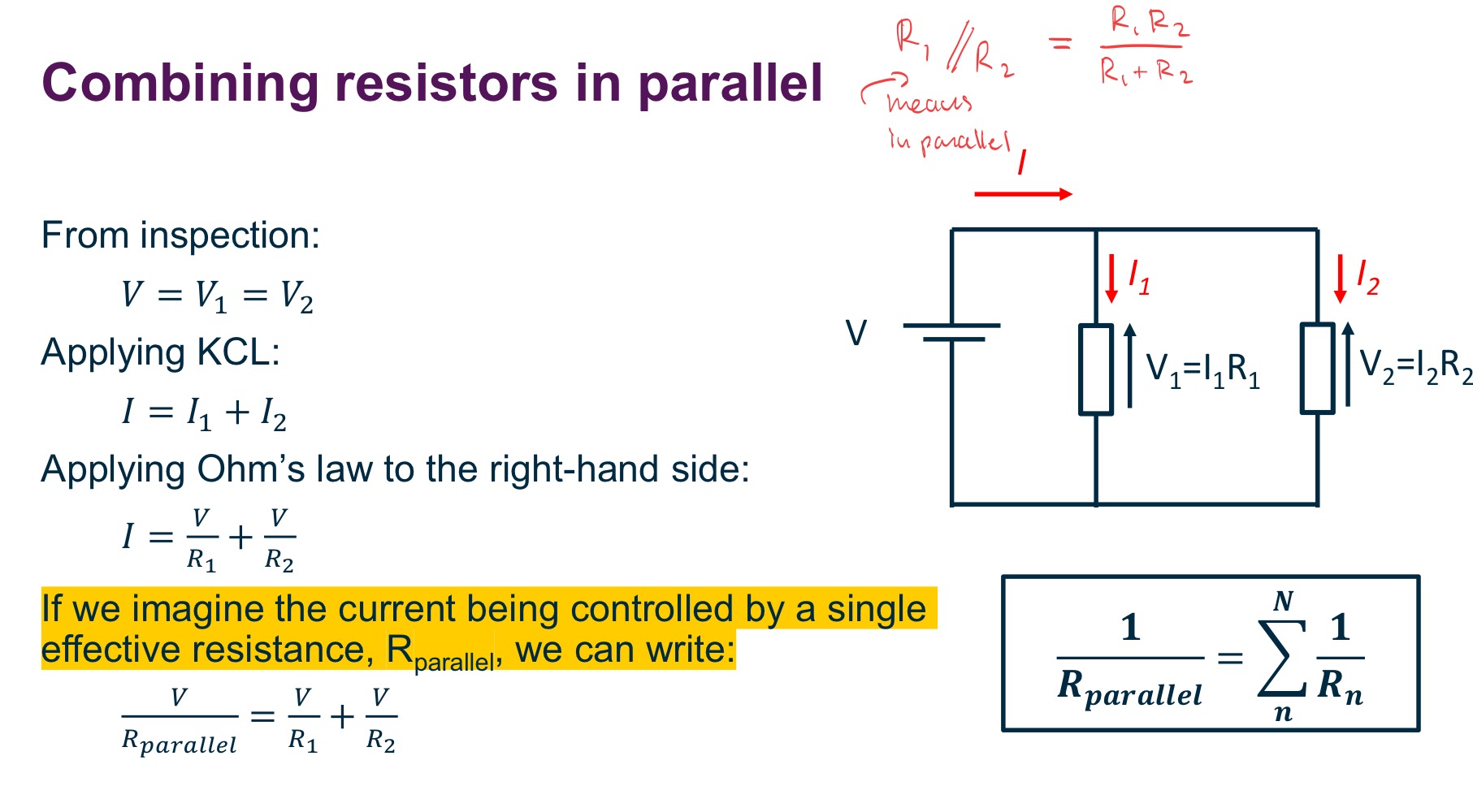
How do we write “parallel resistors”
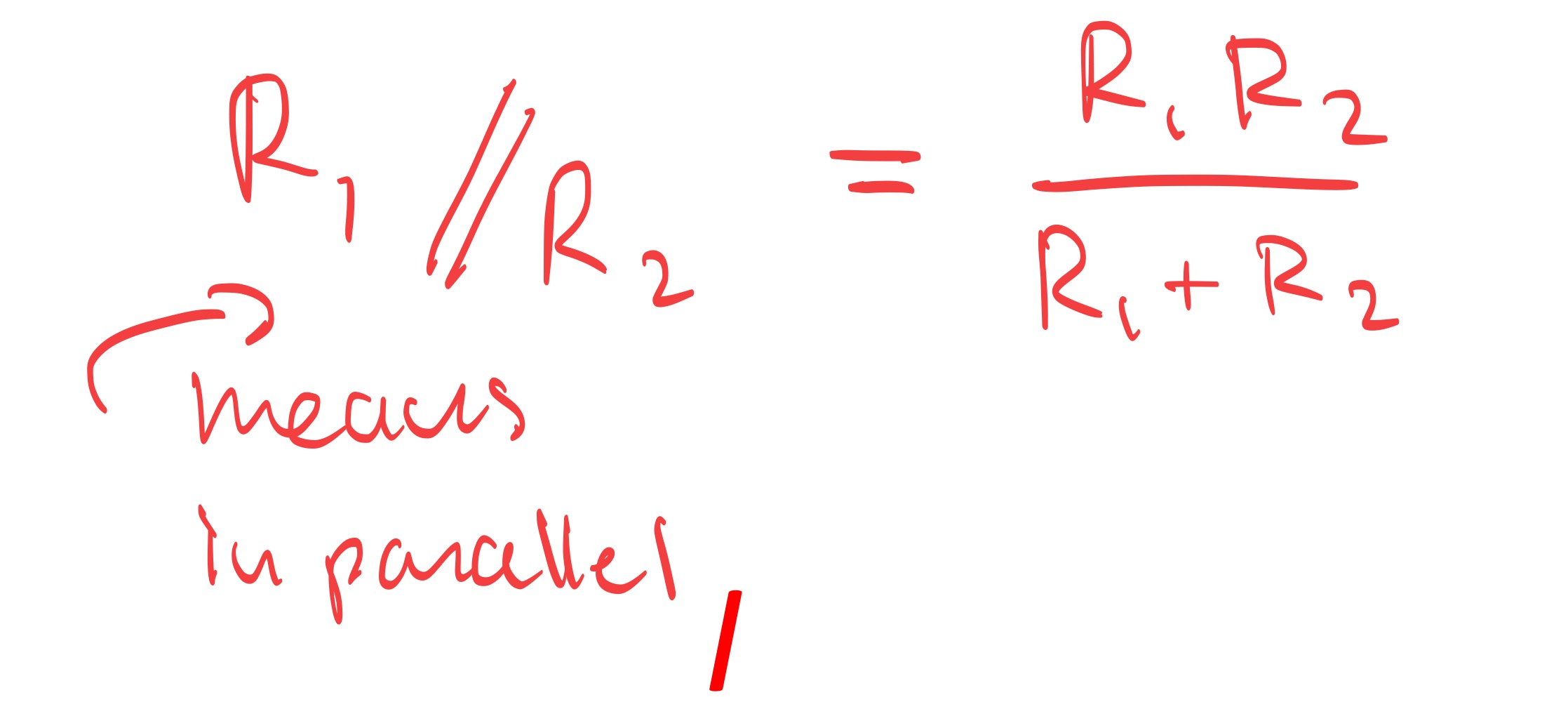
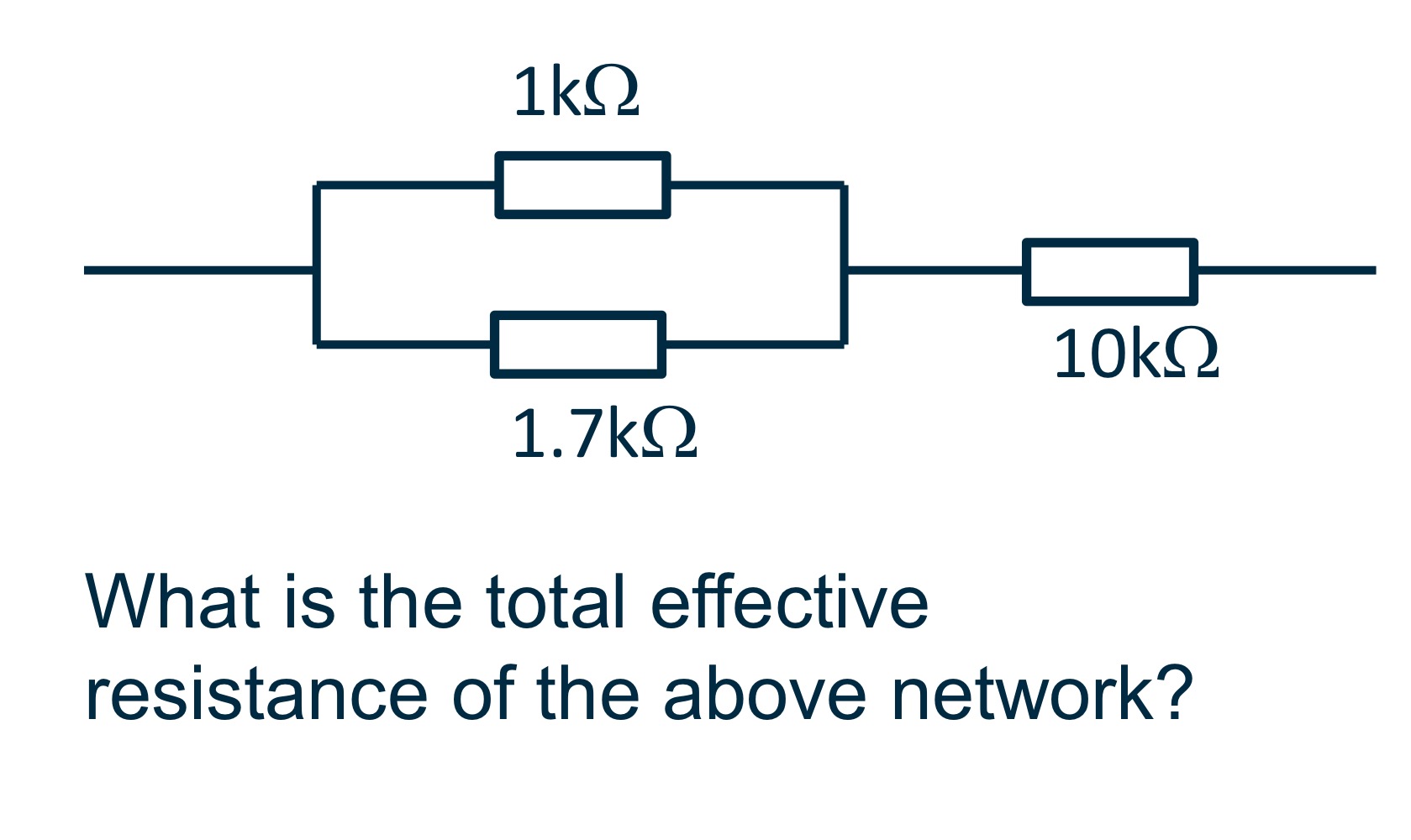
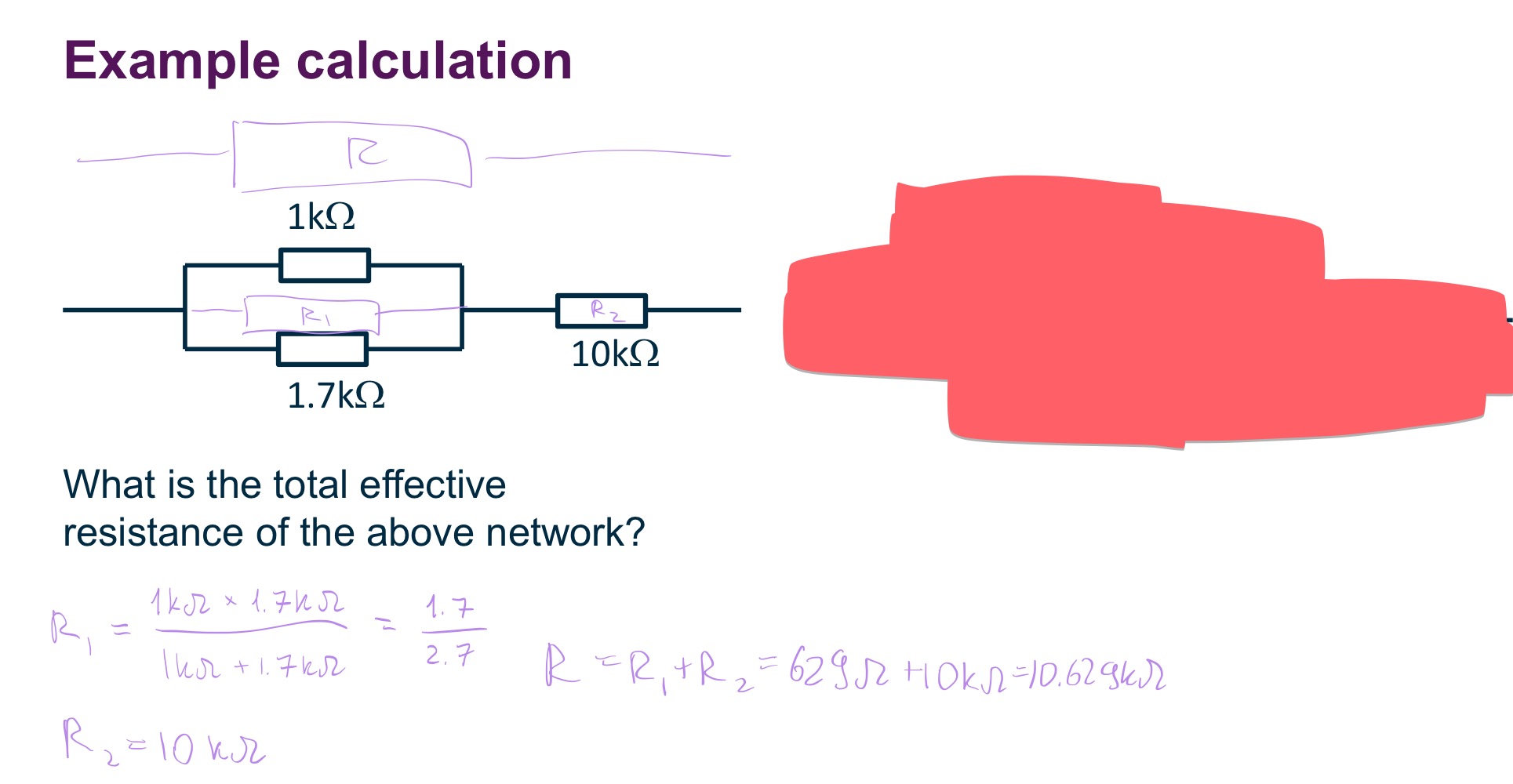
Potential Divider
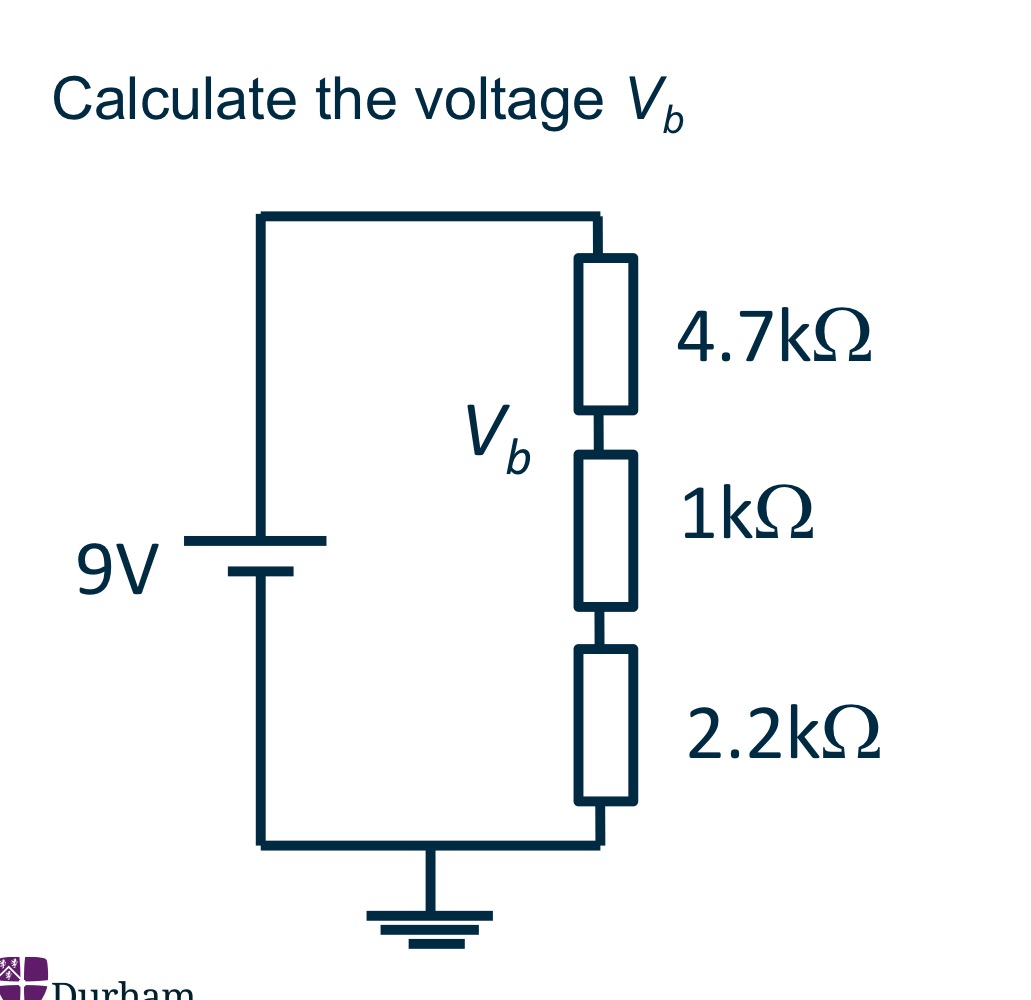
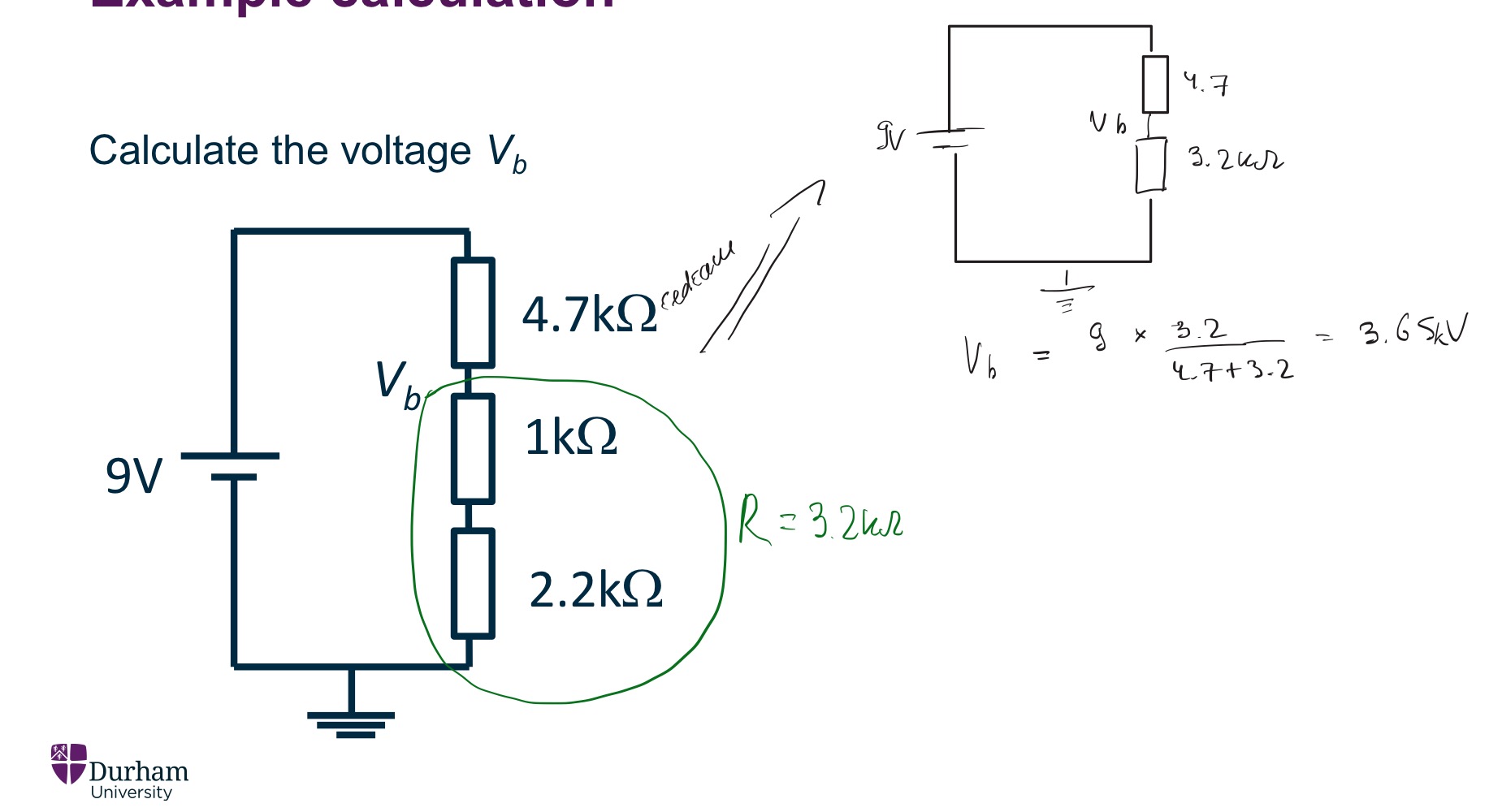
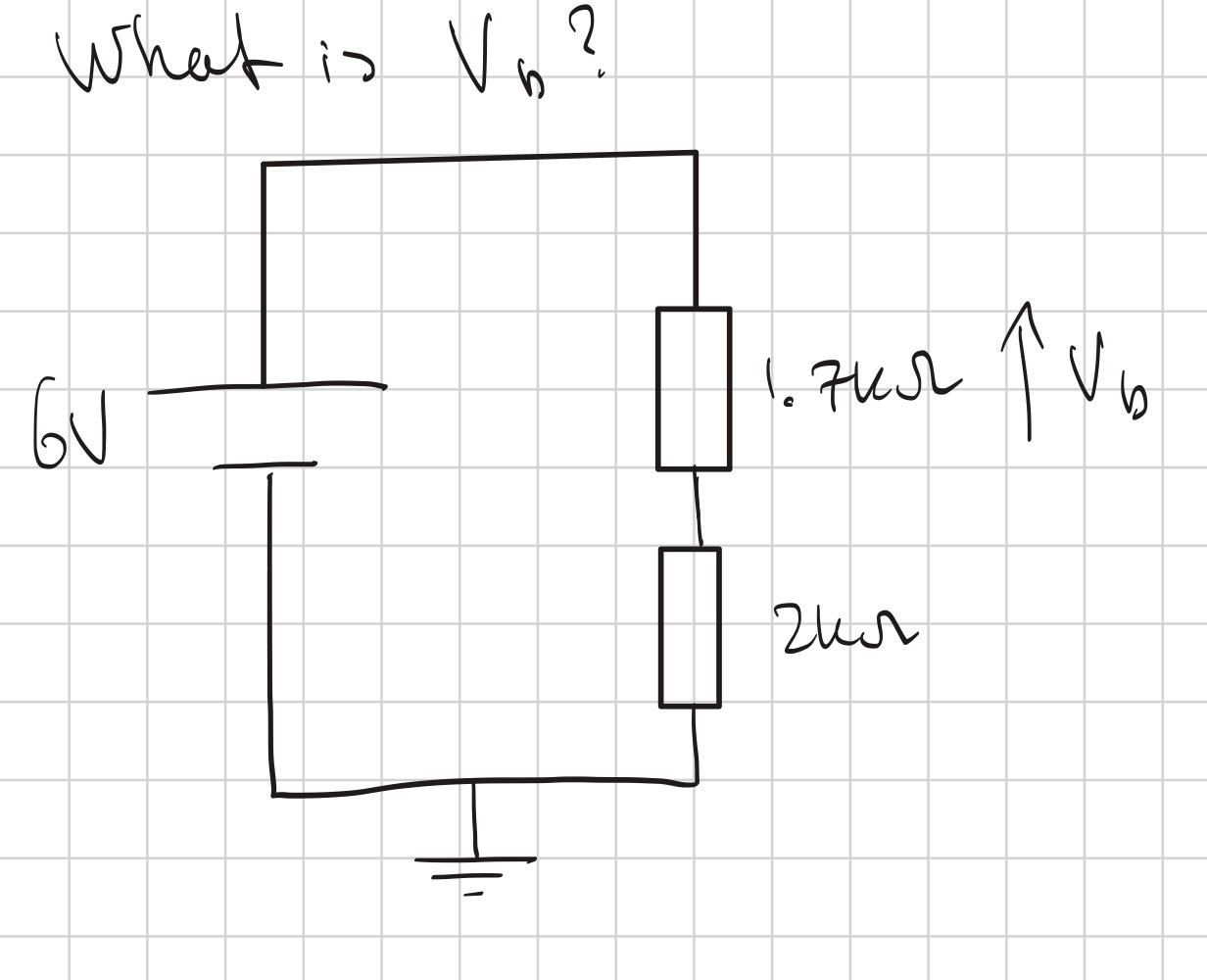
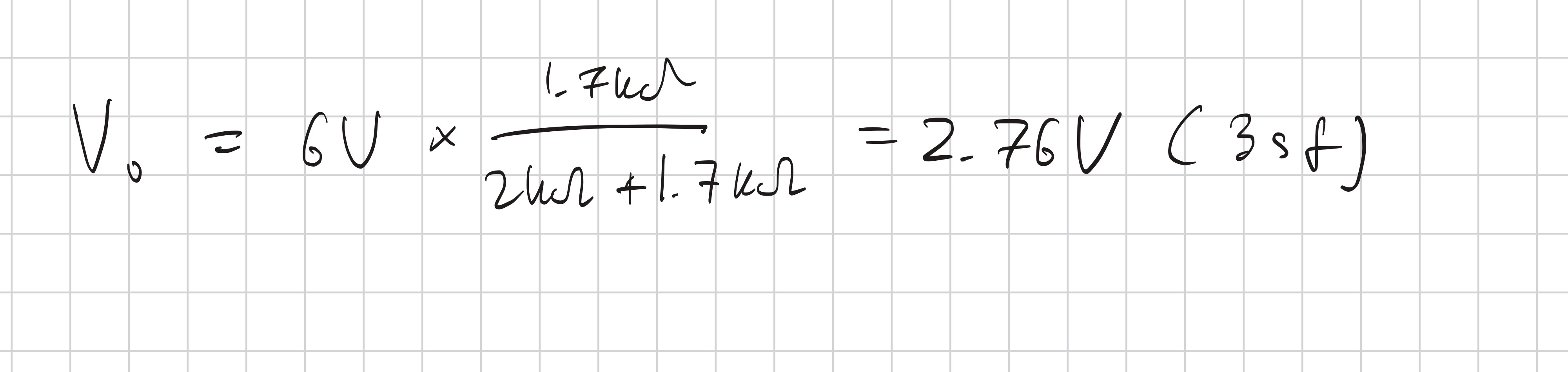
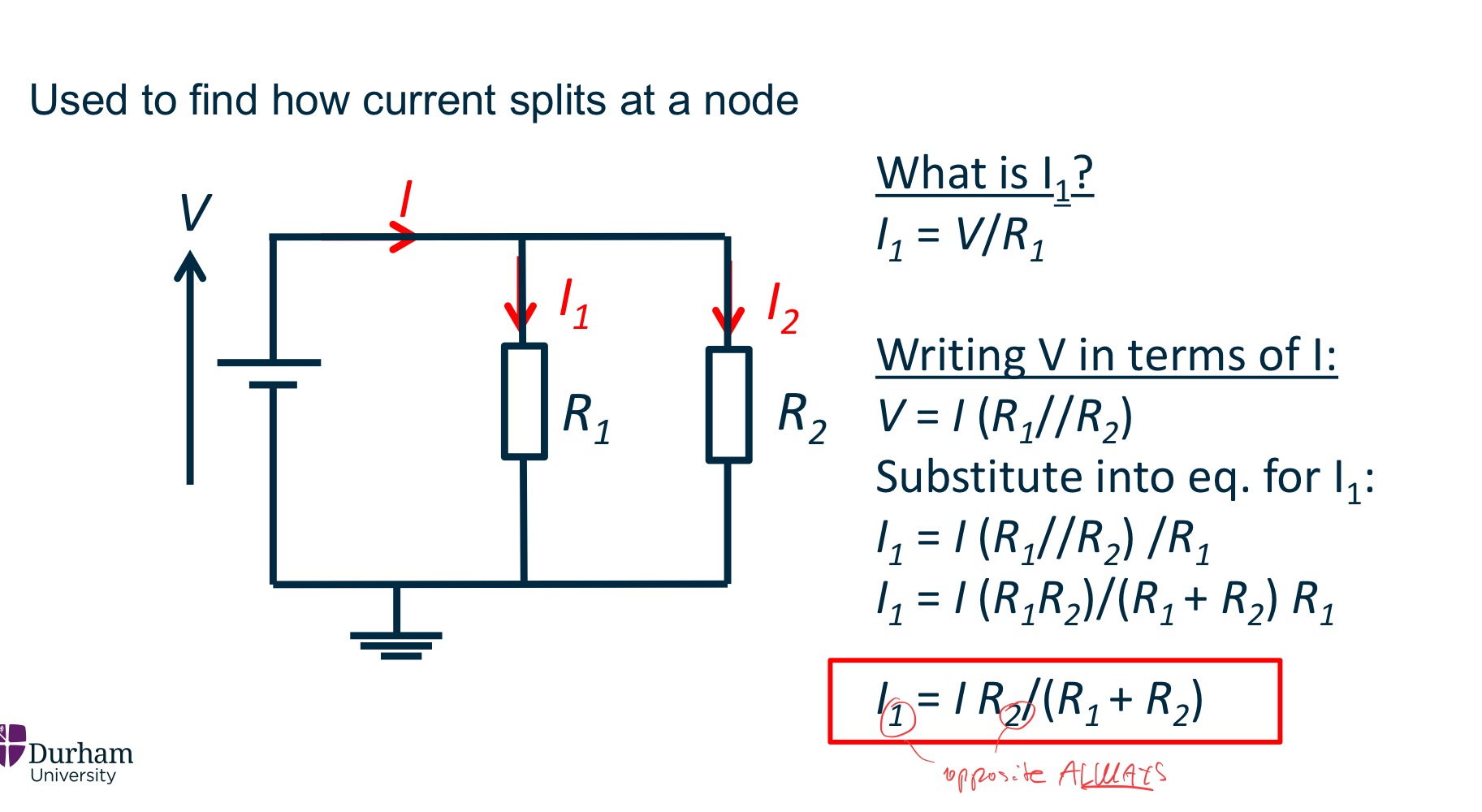
Current Divider method
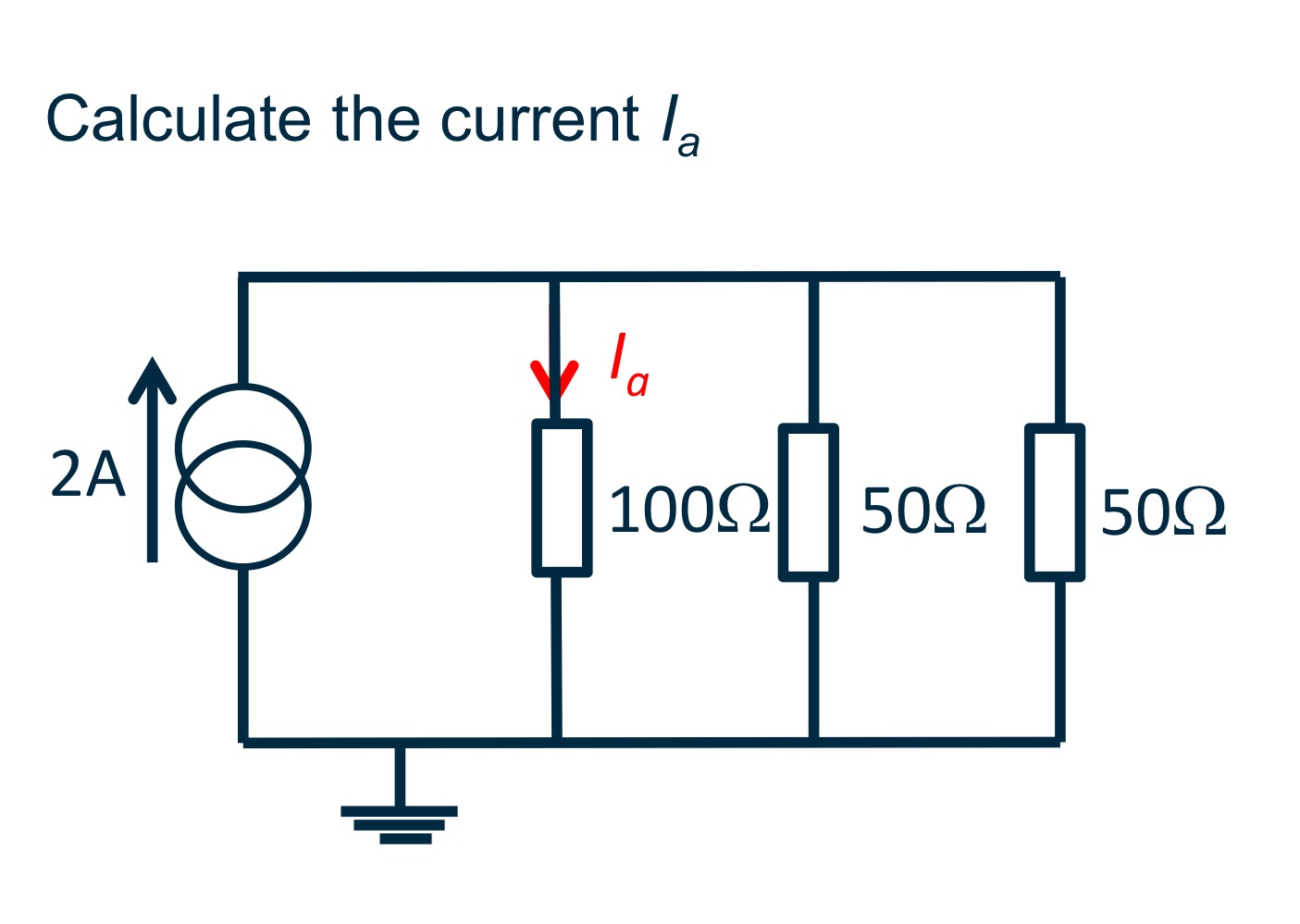
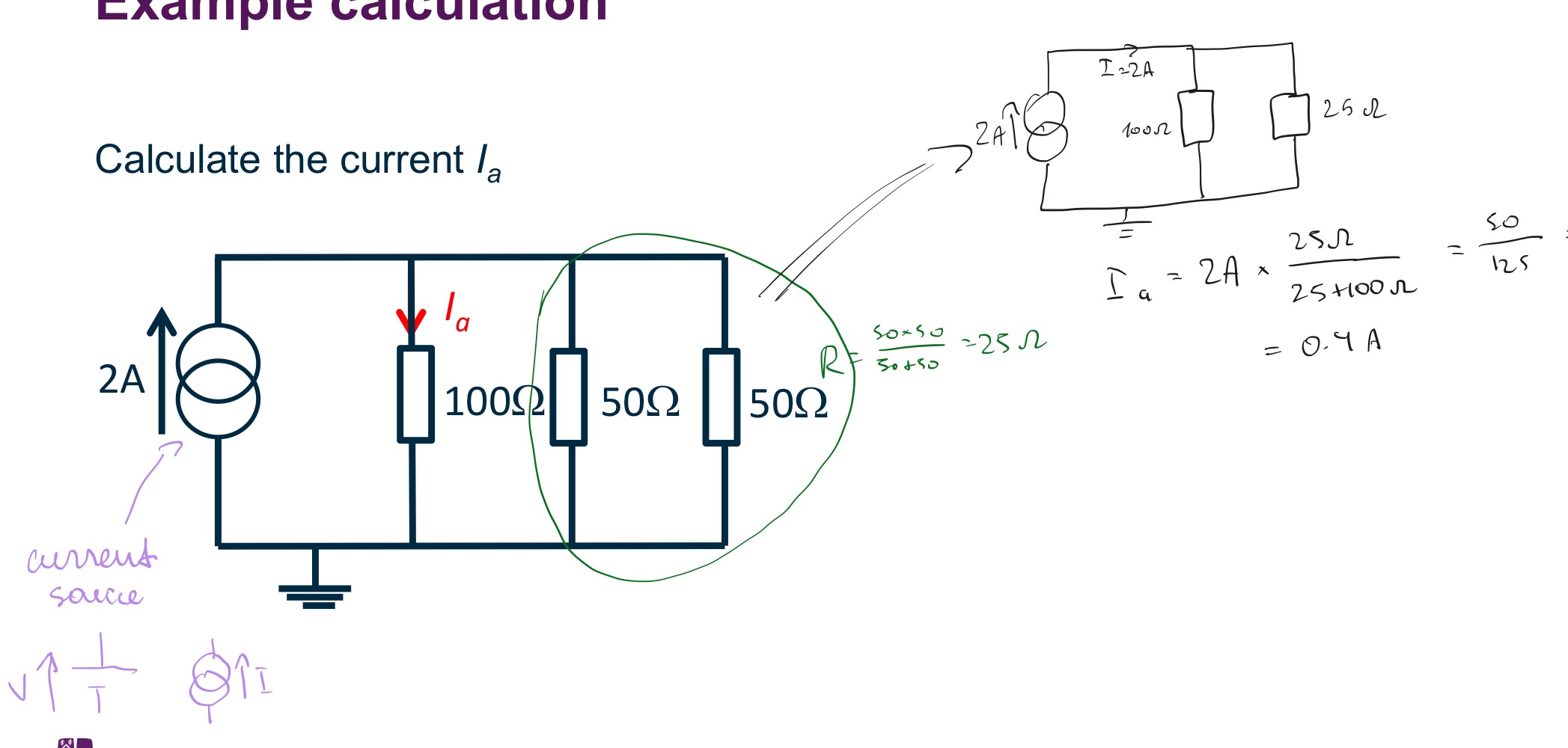
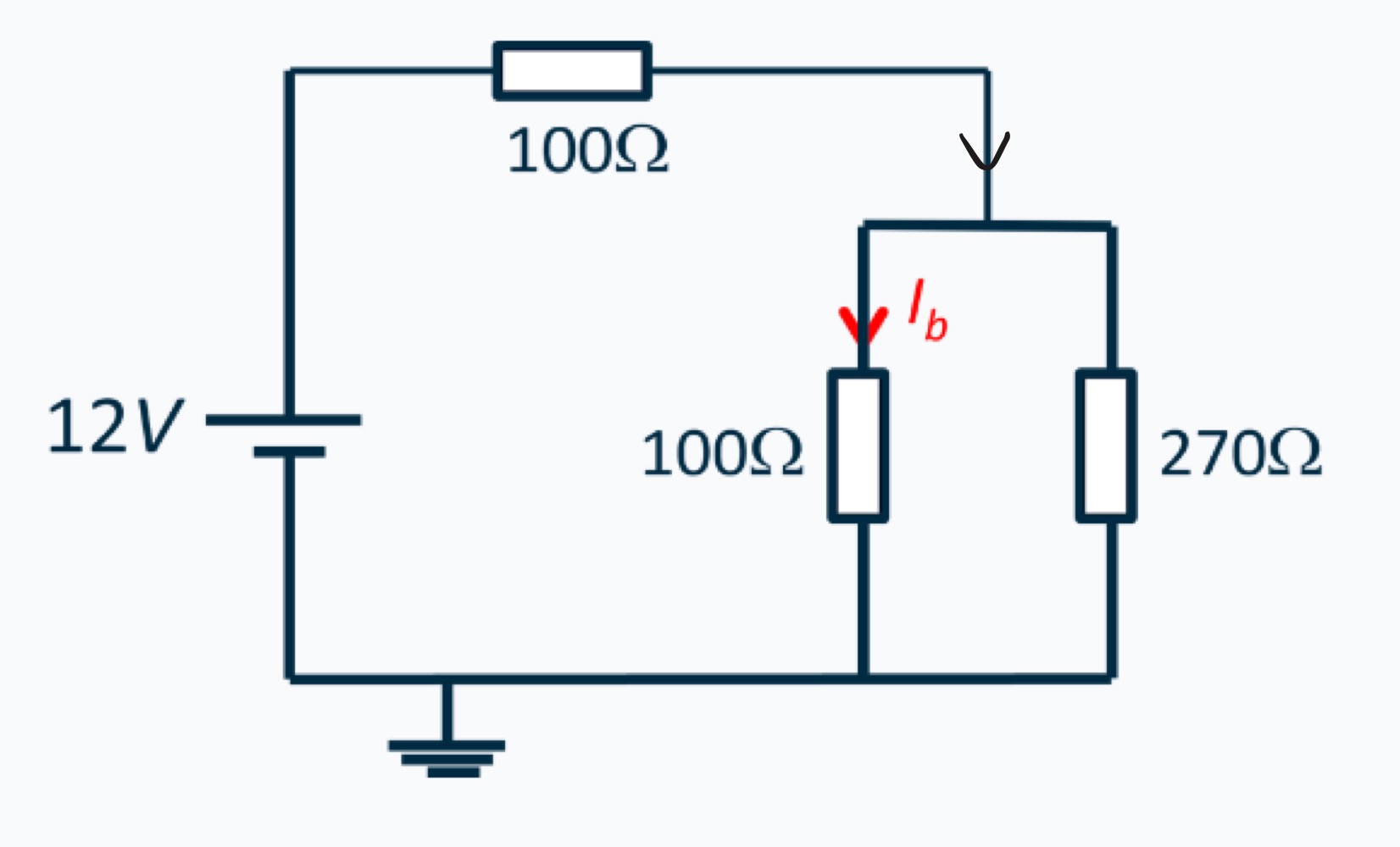
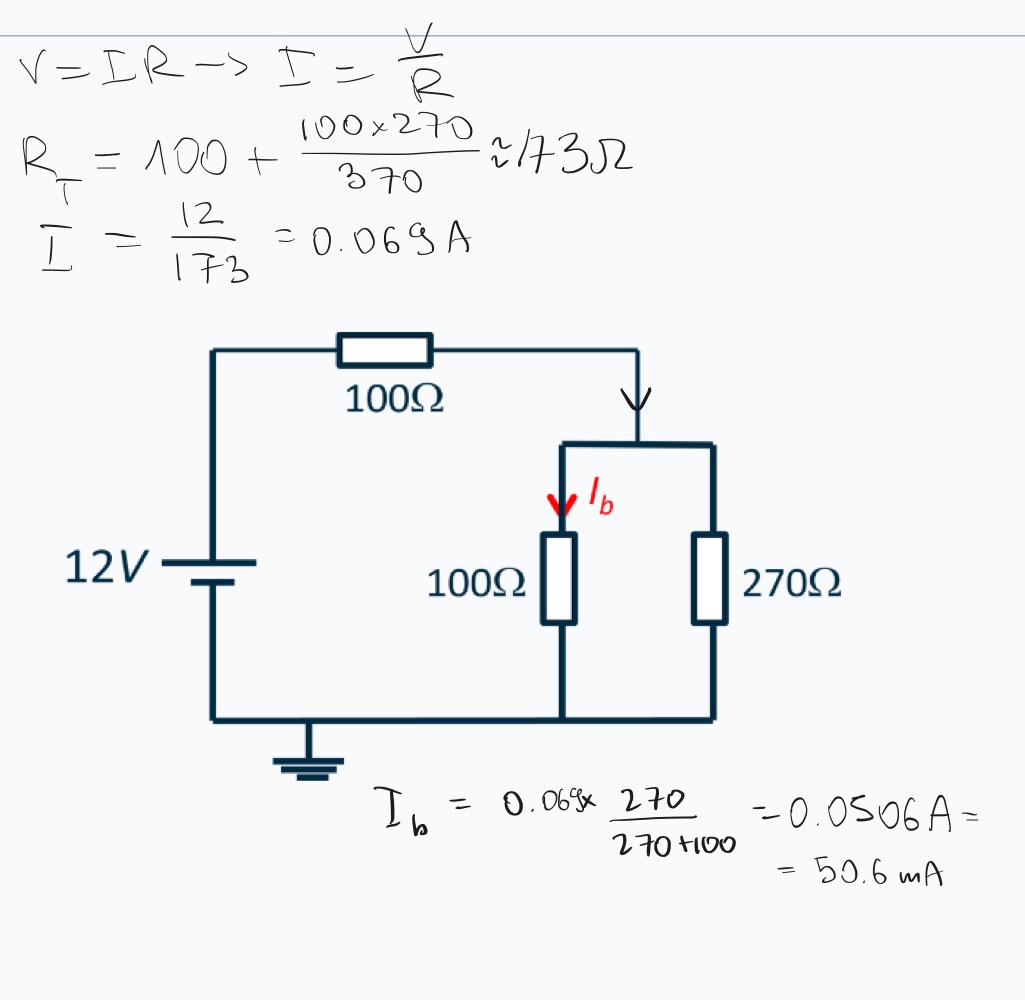
What is the current Ib?
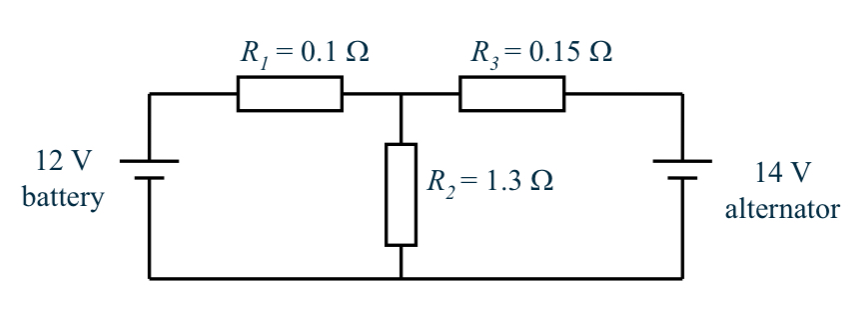
Steps of loop analysis
Steps are:
1. Identify a set of loops to allow solution of the currents of interest
2. Sketch voltages from loop currents
3. Apply KVL
4. Solve set of simultaneous equations
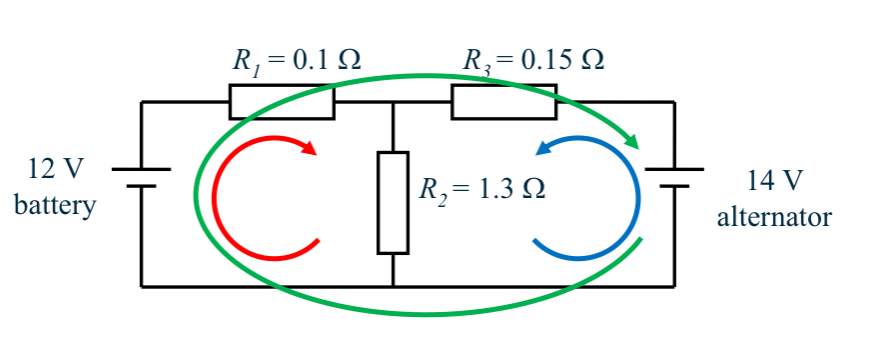
Identify loops
What if you get negative current when doing loop analysis?
It only means that the direction of current is opposite of what we guessed. Direction of loops really doesn’t matter
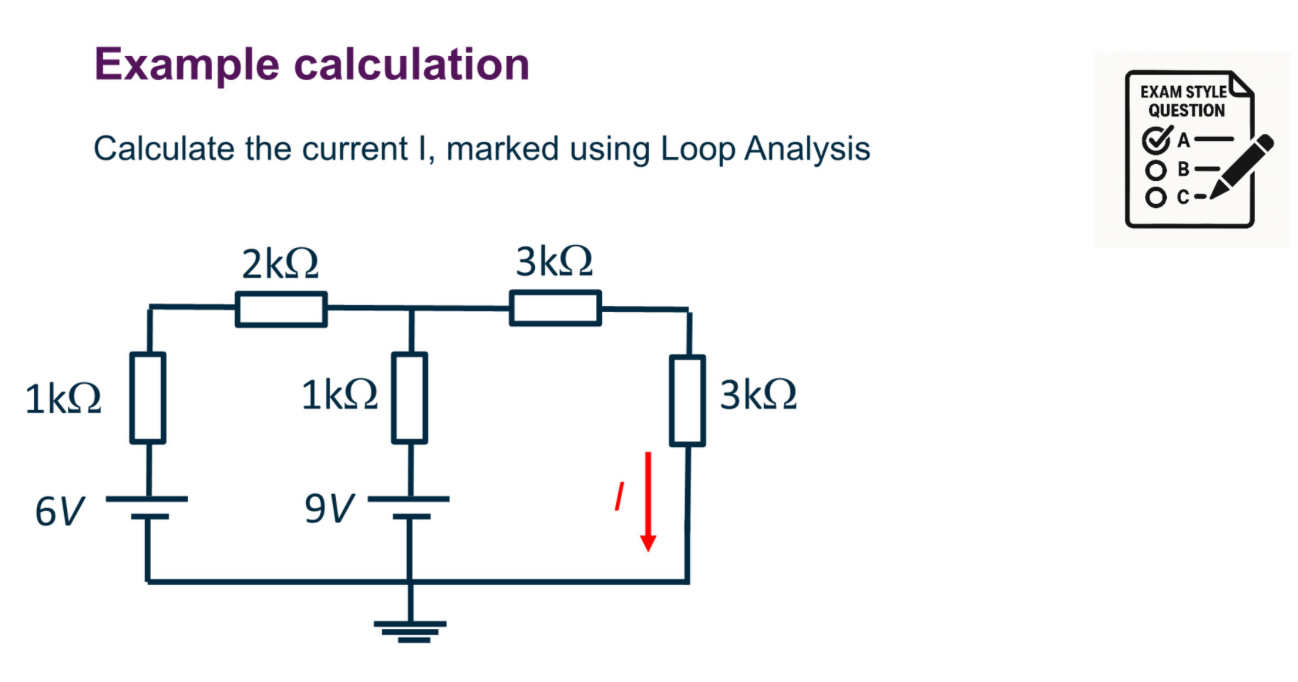
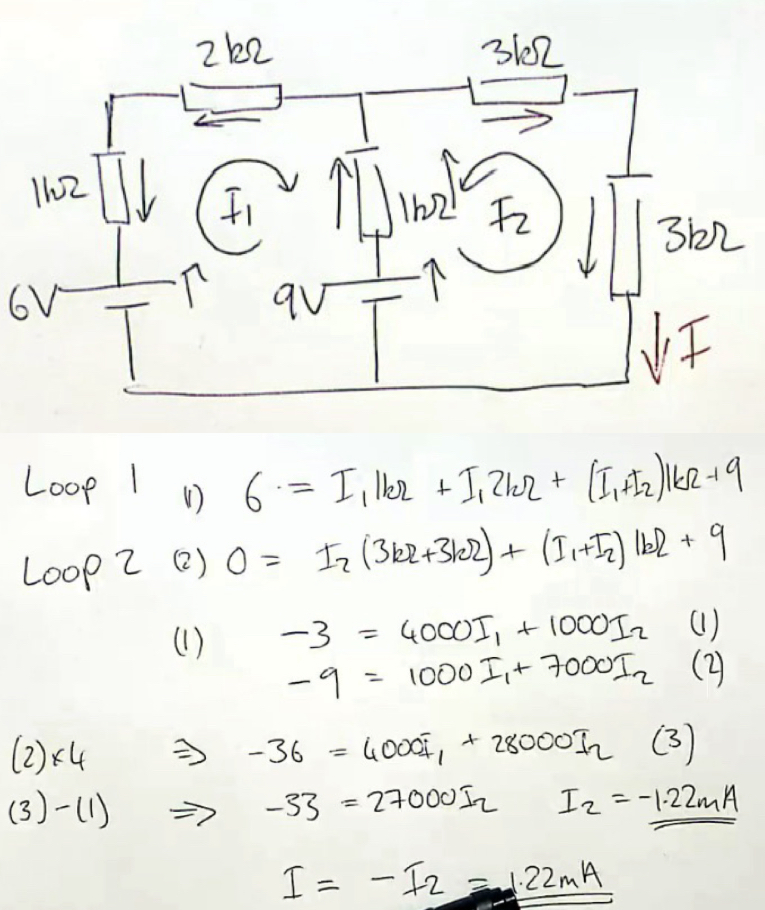
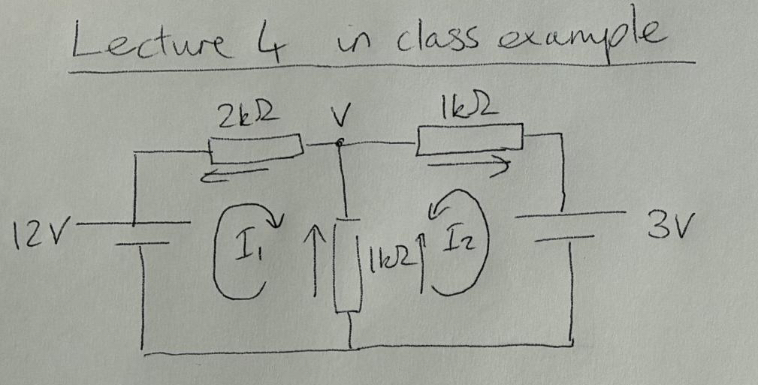
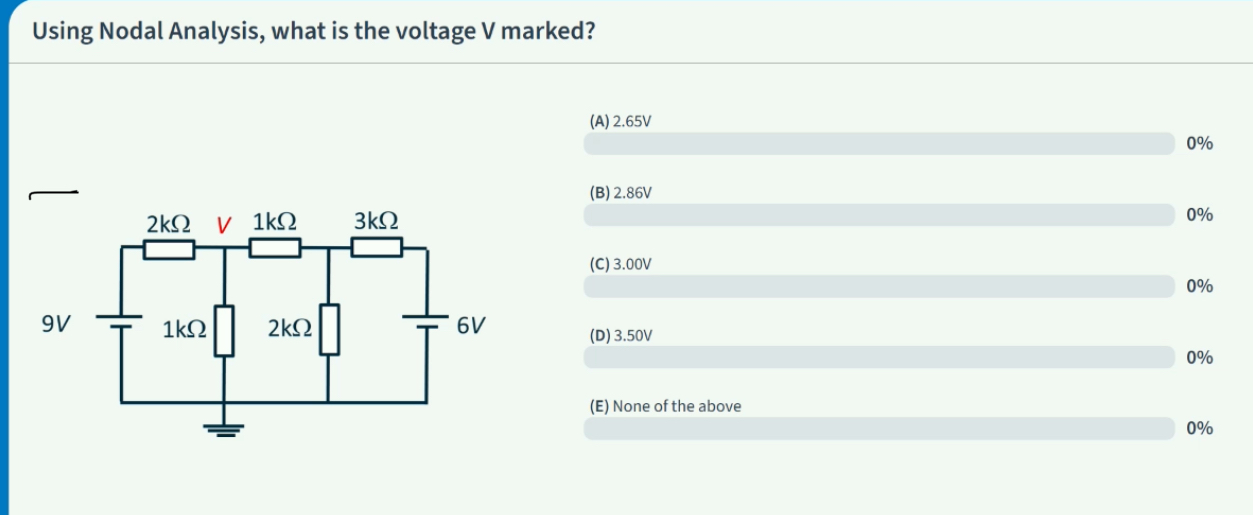
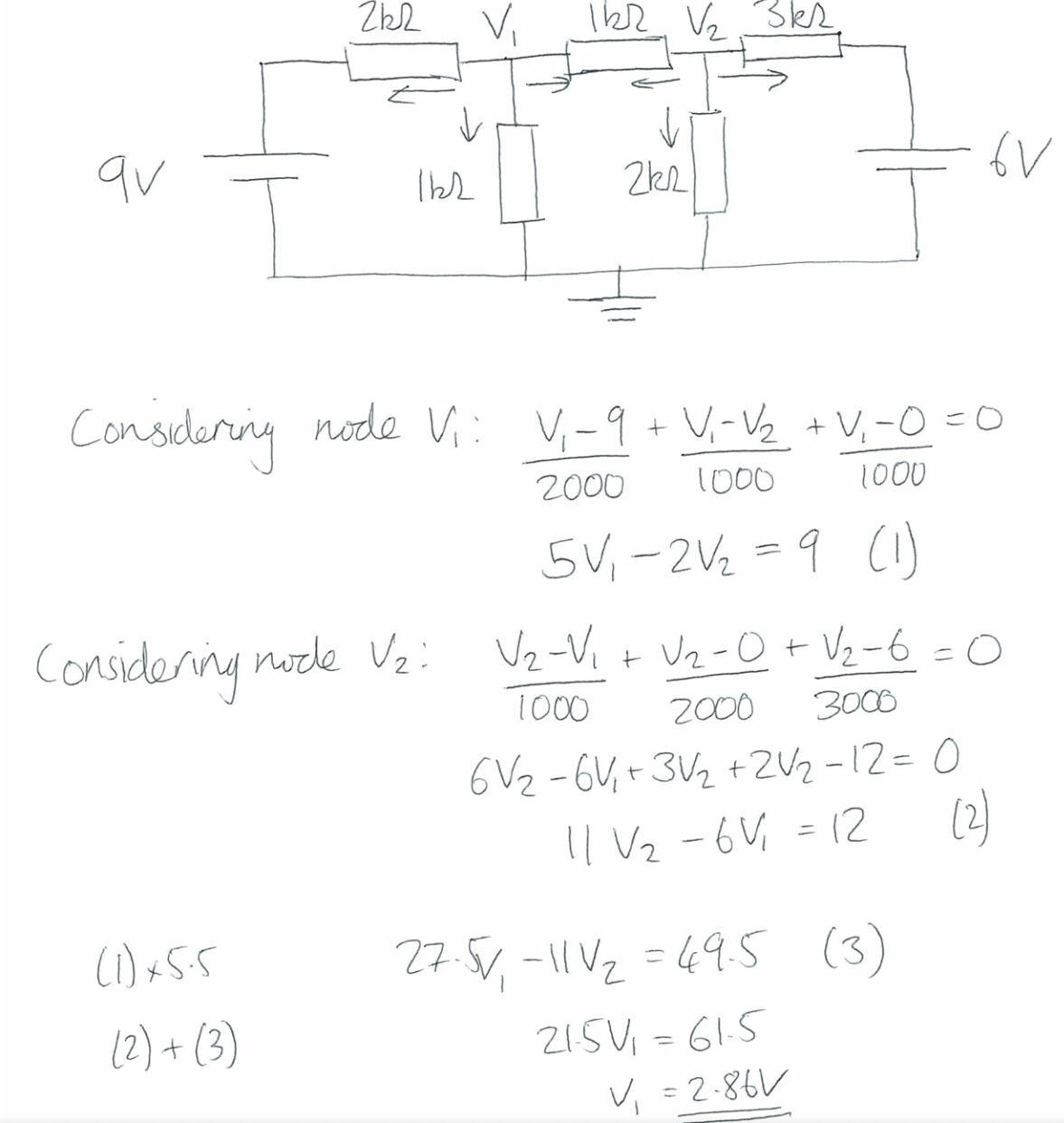
Identify V
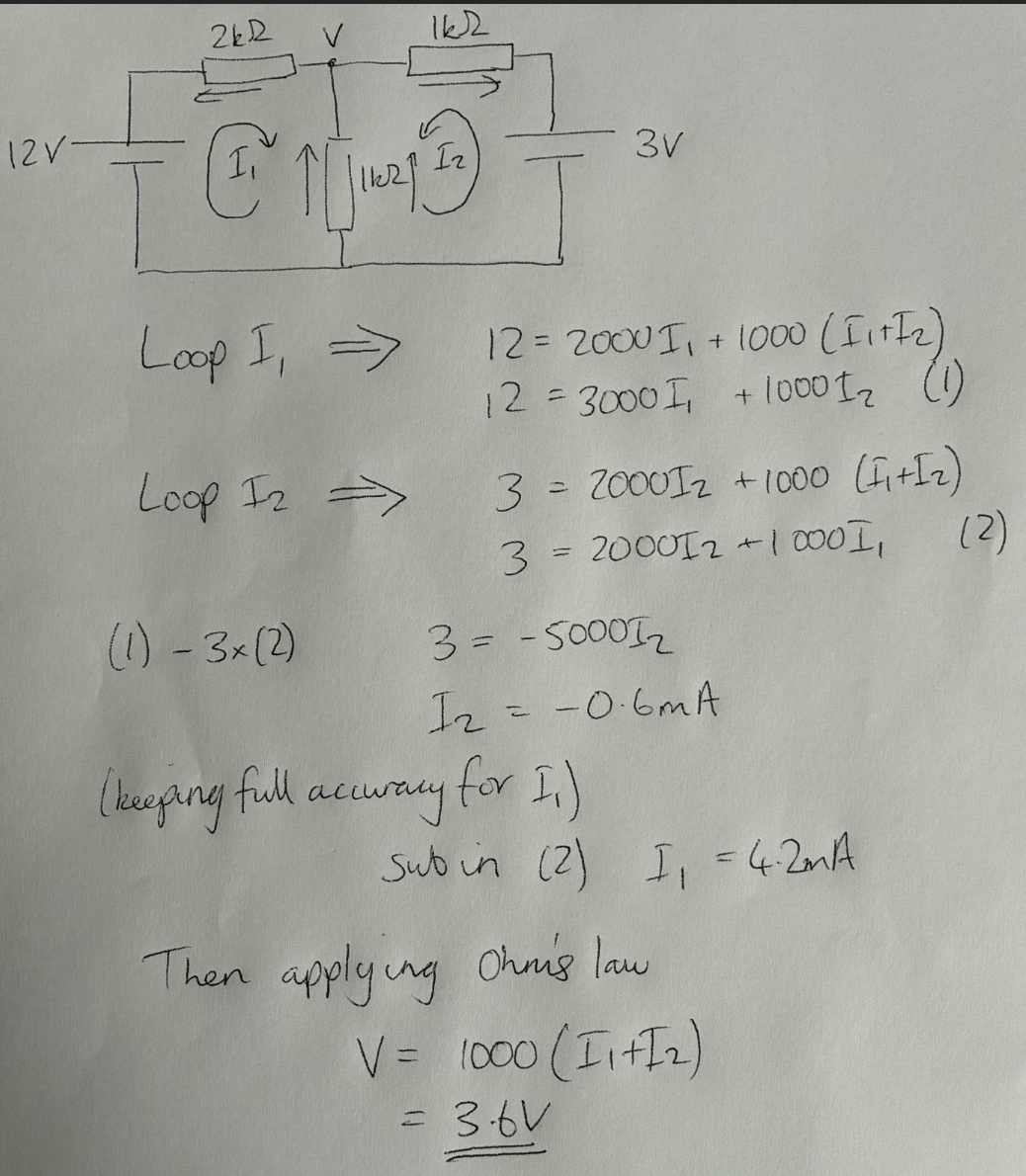
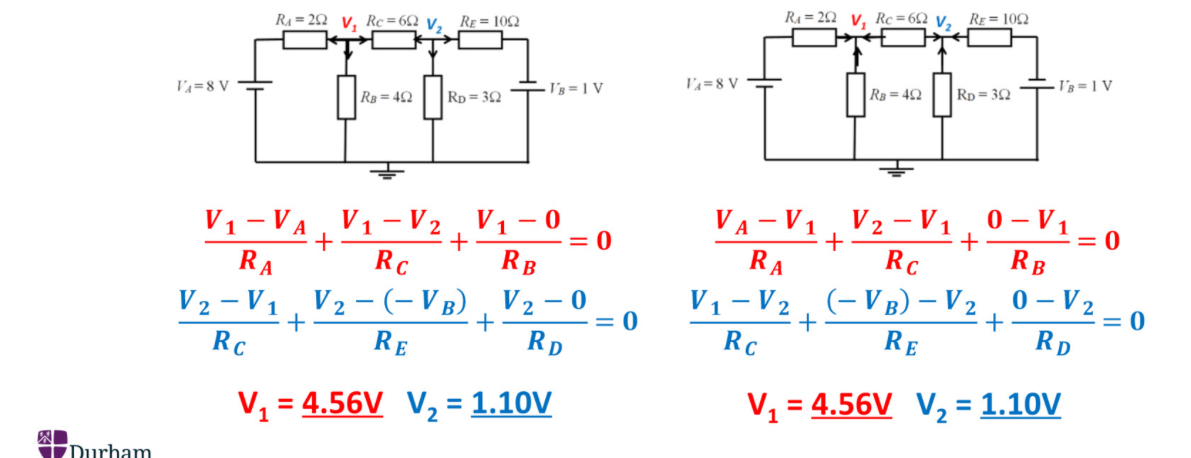
Steps of nodal analysis

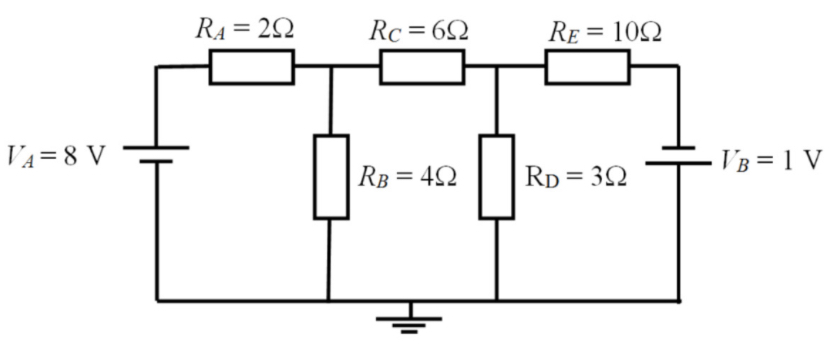
Find unknown voltages in nodes
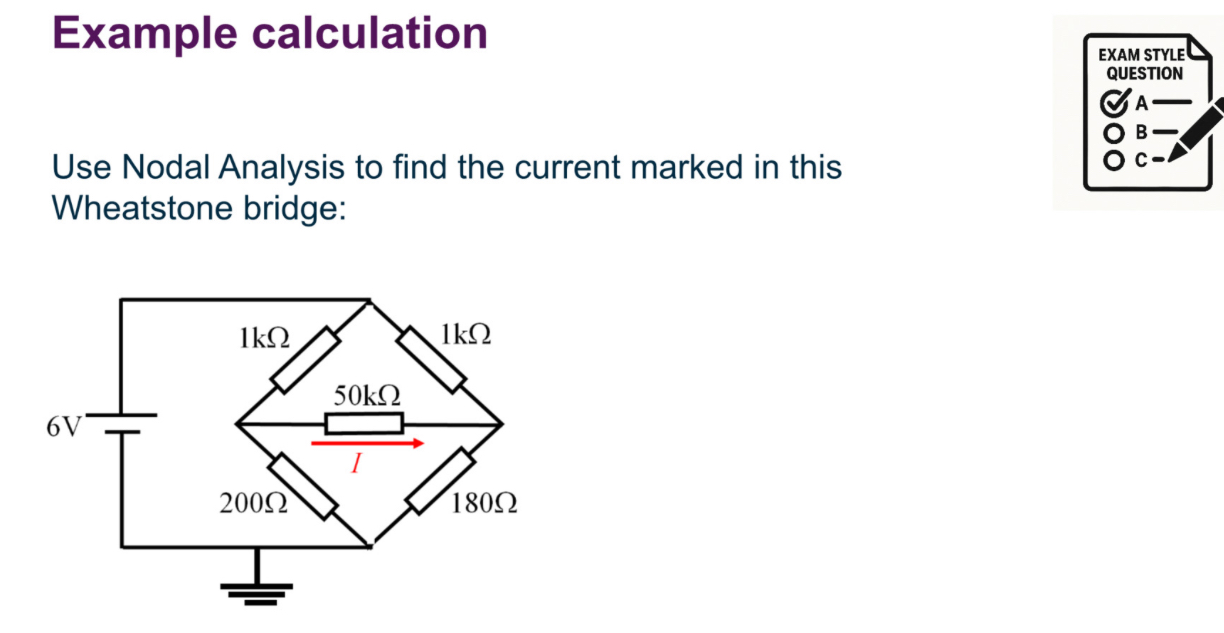
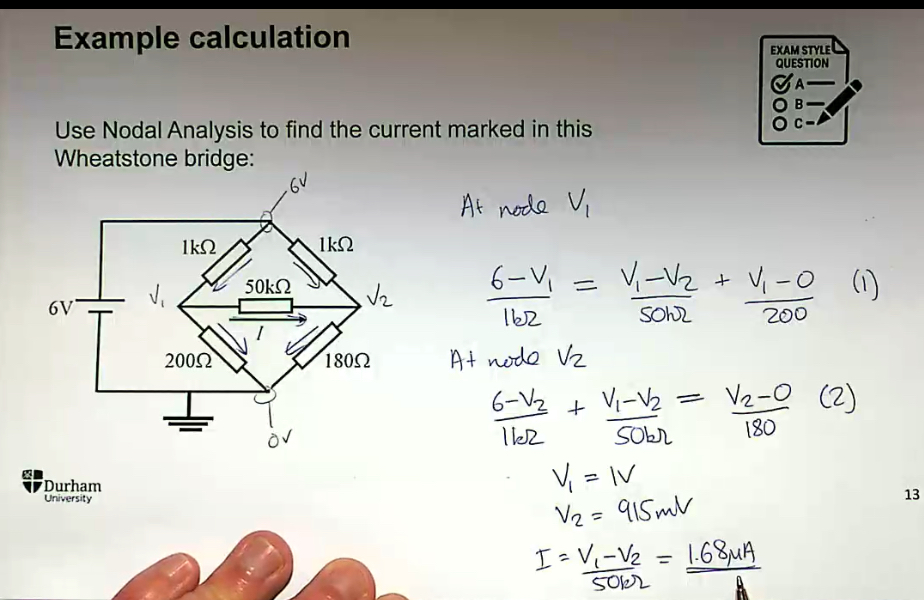
A system is said to be linear when


When the above is satisfied, it is said

Graph of current against voltage of ohmic (linear) and non-ohmic (non-linear) behaviour
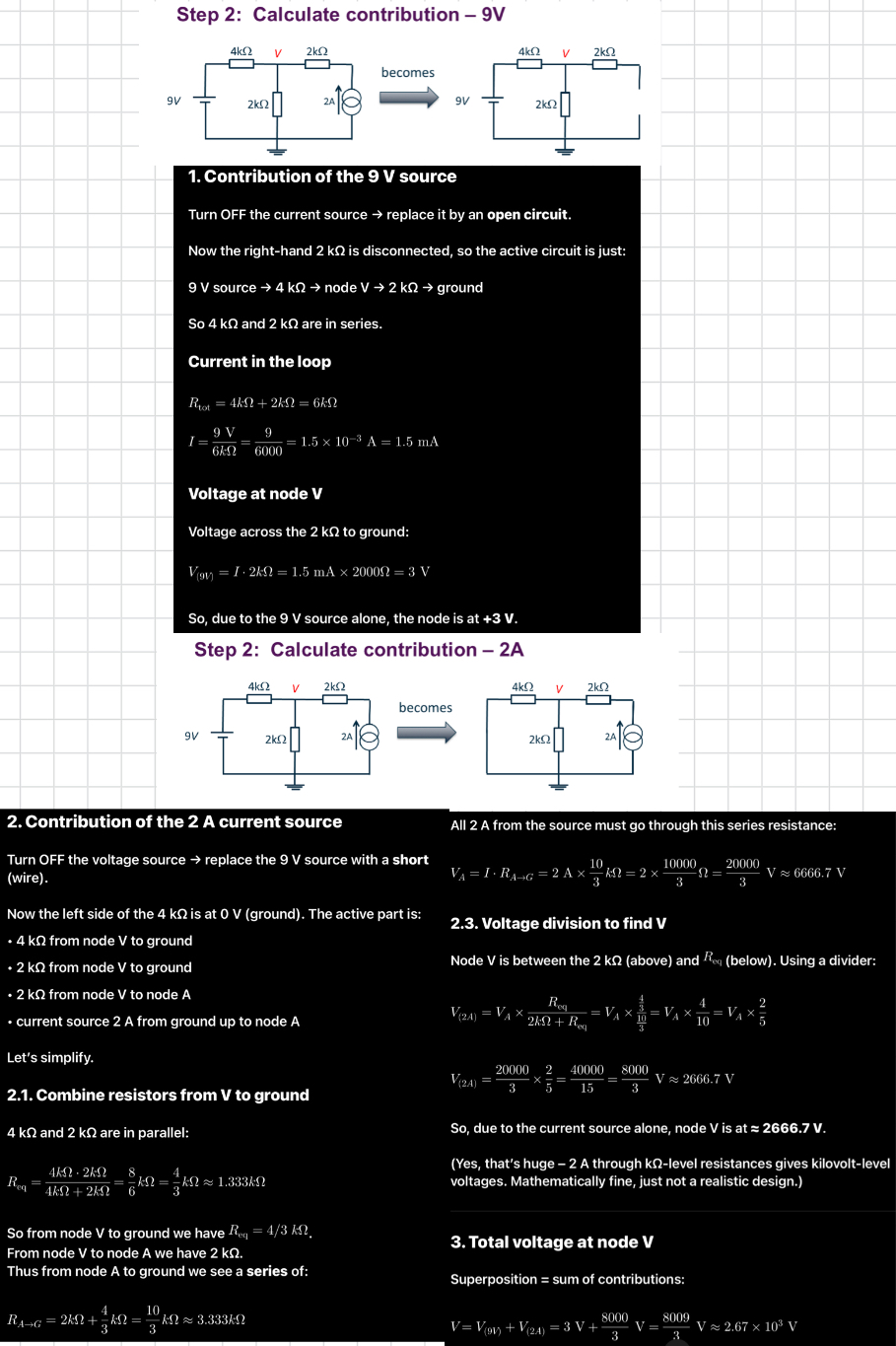
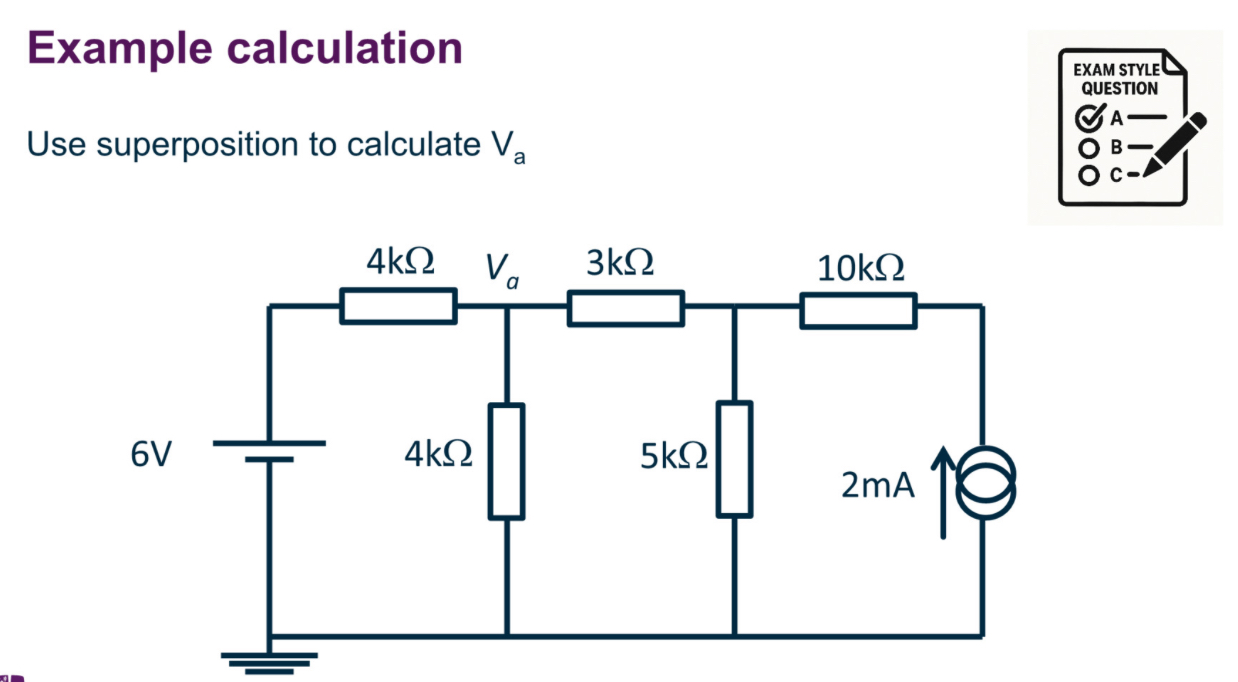
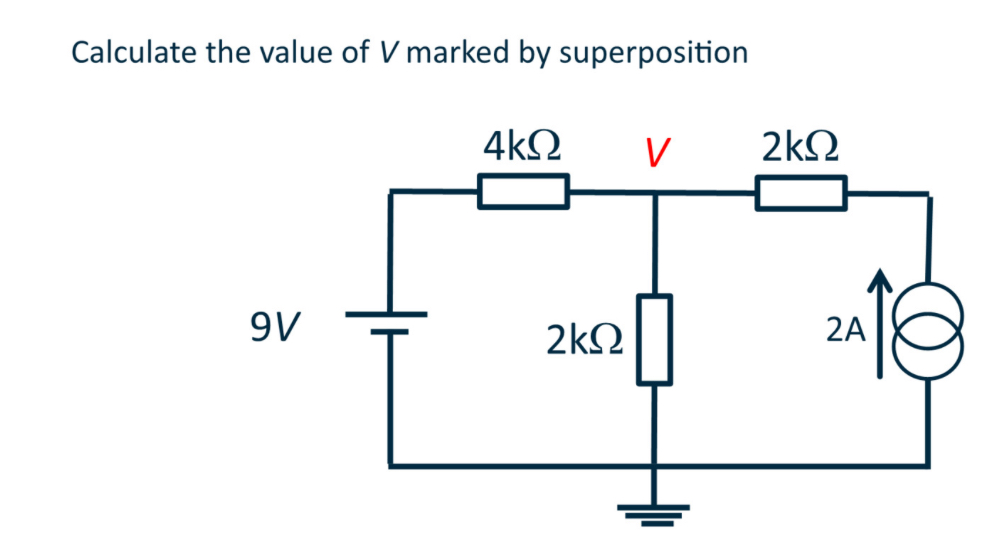
Superposition is used to

Steps of superposition

Linear
Found two sources