Systems: macromolecules and subunits
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours) - first part of the digestive systems hyperdoc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Besides oxygen, the other reactant necessary for cellular respiration is ______
Glucose
Chemical formula of Glucose
C₆H₁₂0₆
Formula for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38ATP
Why do we eat? (2 reasons)
Obtain energy from food (mostly glucose for cellular respiration)
Obtain nutrients to build tissues and keep metabolic processes functioning
to make hemoglobin, you need what nutrient in your diet?
Iron
Macromolecules
The 4 main nutrients you need in your diet, they are large molecules and must be digested in their subunits in order to be absorbed
The 4 main macromolecules + examples of sources
Carbohydrates (potatoes, rice, pasta, bread)
Proteins (meat, eggs, cheese, legumes)
Lipids (meat, cheese, nuts)
Nucleic Acid (all foods)
Carbohydrates
The main source of energy for cells
⇨ composed of simple sugars linked together
The various forms of carbohydrates (3)
Monosaccharides: single carbon ring (SIMPLE)
Disaccharides: 2 carbon rings linked together (SIMPLE)
Polysaccharides: hundreds of simple sugars lined up in a chain (COMPLEX)
Examples of Monosaccharides
Glucose, Fructose (same chemical formula as glucose), Galactose
Examples of Disaccharides
Maltose, Sucrose, Lactose
Examples of Polysaccharides
Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen
Starch
Made by plants
Broken down into Glucose by digestive system
Found in fruits, veggies (potatoes), cereals and pasta
Cellulose
Forms the main structure of the cell wall
Not digestible by humans but useful in the intestines as fiber
Cellulose constitutes ___ to ___% of terrestrial plant biomass
35 to 50%
Glycogen
Stored in muscles and liver
Used by animals (and fungi) to store chemical energy
Helps quickly release glucose into the blood
Proteins
building blocks of structural molecules, enzymes, hemoglobin, certain hormones, antibodies, etc
Proteins are made up of subunits called
amino acids
Amino acids are linked together by ____ to form long strands, which make up ___
peptide bonds, proteins
Your cells need a _________ supply of _______ _____ to build all the different protein molecules
regular, amino acids
There are __ total types of amino acids; __ are essential and __ are nonessential
20, 9, 11
Essential vs Nonessential amino acids
Essential = obtained via food
Nonessential = produced by the cells
Lipids (5 uses)
used to store energy⚡
helps absorb fat-soluble vitamins (ADEK) 🐟
builds cell membranes 🔨
produces hormones 💊
provides insulation 🧥
How does the energy provided by lipids compare to sugar?
by mass, lipids provide 2x as much energy as sugar
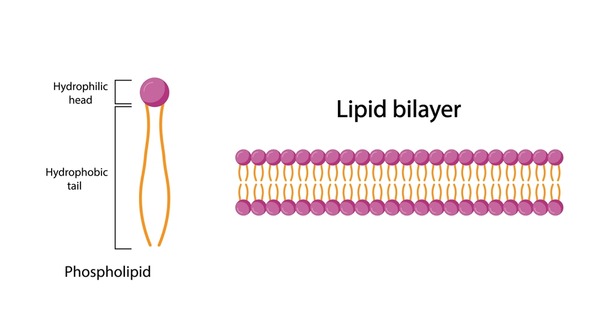
Phospholipids
type of lipid that forms the cell membrane
⇨ composed of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails
Triglycerides
The main type of fat
⇨ composed of 3 fatty acid chains attached to a single glycerol molecule
Saturated vs Unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated: single bonds, straight and tightly packed structure (usually solids)
Unsaturated: double bonds, bent and looser structure (usually liquids)
Nucleic Acids
used in the formation of DNA during Interphase’s S-phase
The subunits of Nucleic Acids are _________, which consist of a sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group
Nucleotide