Chapter 14: Controlling Microbes in the Body
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Waksman
Antibiotics from Streptomyces
Fleming
Discovered penicillin
Domagk
Discovered sulfanilamide
Ehrlich
Used arsenic compounds as “magic bullets”
Compare natural, semisynthetic, and synthetic antibiotics
Natural: Soil, bacteria
Semisynthetic: Natural but modified (chemical)
Synthetic: Made from chemical
Explain selective toxicity. Why are there more antibiotics effective in killing bacteria than eukaryotic pathogens and viruses?
More targets for bacteria because they are Prokaryotic organisms; Eukaryotic pathogens share many metabolic enzymes and cell structures with humans; virus are more simple particles and don’t have many targets
Describe 6 mechanisms of action for antibiotics and majorr drugs in the category
-Inhibit protein synthesis:
-Inhibit metabolic pathways:
-Inhibits DNA function/synthesis:
-Inhibit cell wall synthesis:
-Inhibit membrane synthesis, components
Never
Let
Monkeys
Eat
Bananas
Neutrophils (60-70%)
Lymphocytes (20-40%)
Monocytes (3-10%)
Eosinophils (1-4%)
Basophils (1%)
The ideal antibiotic should be
One that targets specific organism, effective, safe, does not lead resistance
Compare narrow-spectrum to broad-spectrum antibiotics Is there a disadvantage to using a broad-spectrum antibiotic?
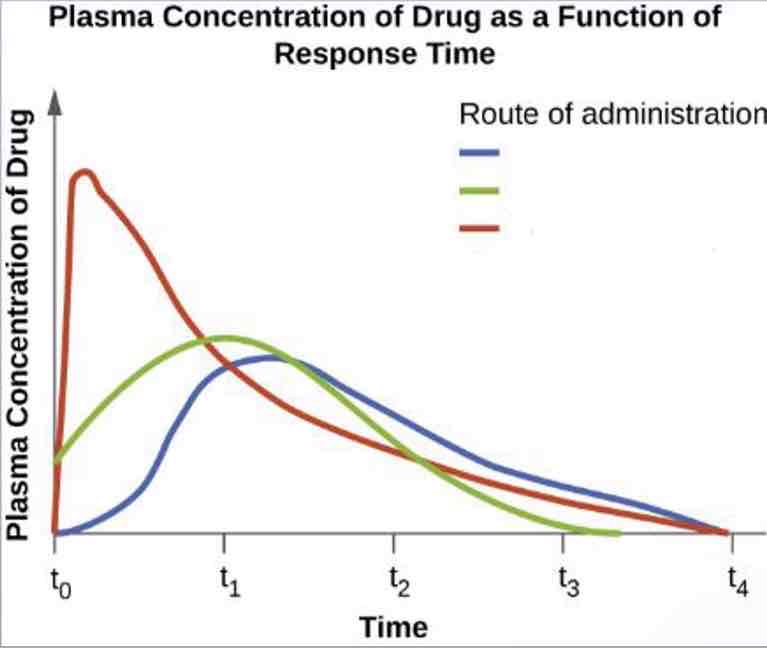
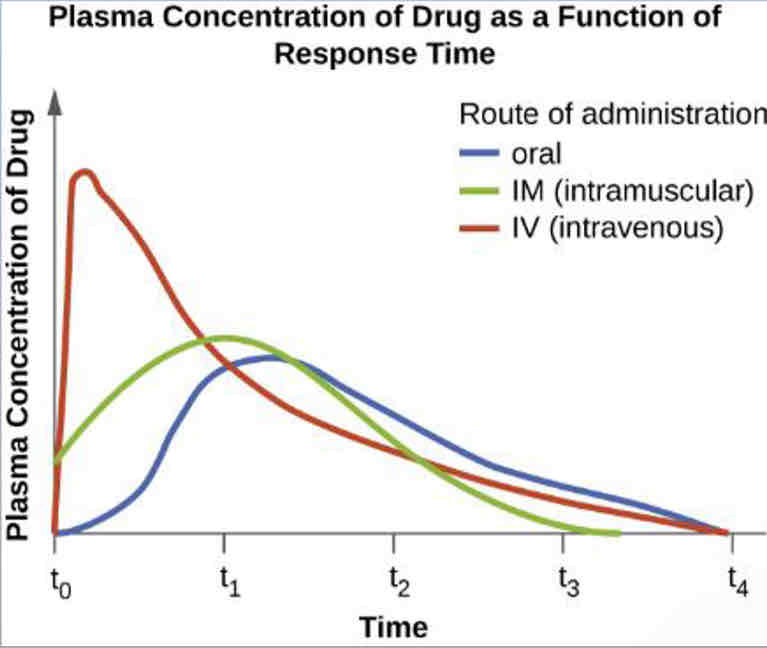
-Oral: took antibiotic by mouth and went through the digestive system (takes awhile)
-IM (intramuscular): Had it in the arm and it got absorbed in the muscle then into the bloodway (2nd to fast reaction)
-IV (intravenous): Straight in the vein(fastest process)
3 examples of how the use of antibiotics causes a patient harmful side effect
Kill good bacteria (microbiota)
Pregnant woman can’t take it
How can microbes become resistant to antibiotics?
-Mutate target enzyme
-Block entrance
-Secretes the antibiotic
-Inactivate the antibiotic
How can we slow down the development of antibiotic resistance? List 5 mechanisms of resistance
Using antibiotics less frequently; use only four bacterial infections