Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Functions
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Source: Burton's
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
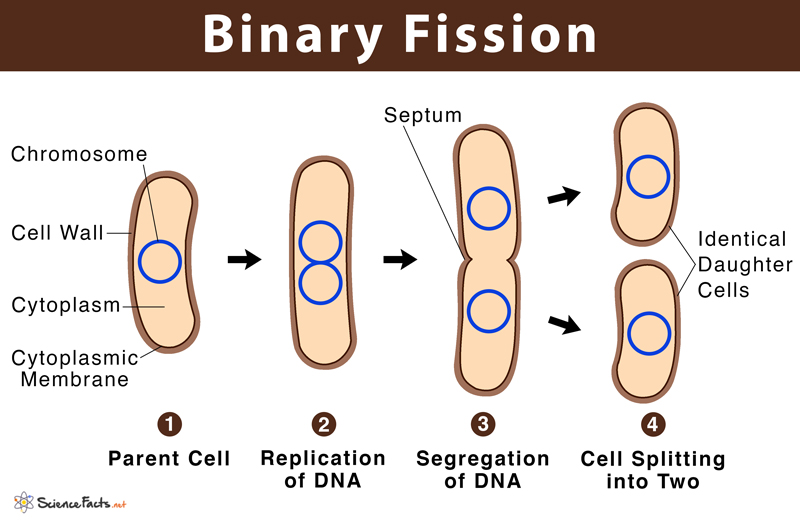
Binary fission
Reproduction of prokaryotic cells — the simple division of one cell into two cells, after DNA replication and the formation of a separating membrane and cell wall.
Chromosome, ribosomes, and other cytoplasmic particles
Embedded within the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells
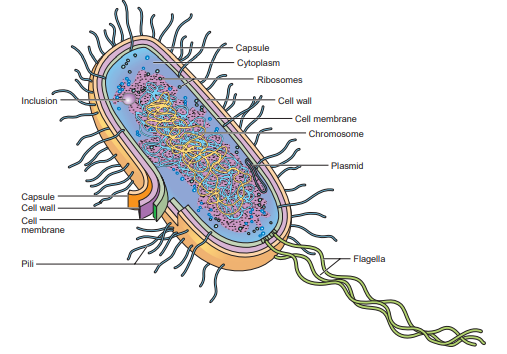
Cell Membrane
Enclosed the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cell. This membrane is similar in structure and function to the eukaryotic cell membrane.
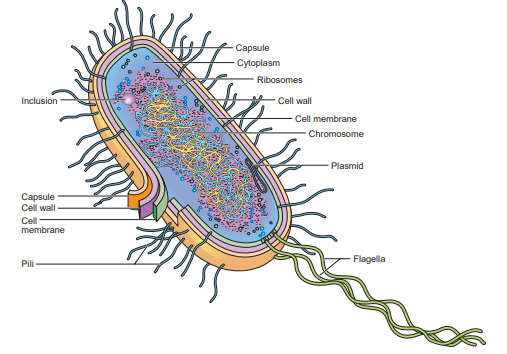
Prokaryotic cells
Does not contain any membrane-bound organelles or vesicles.
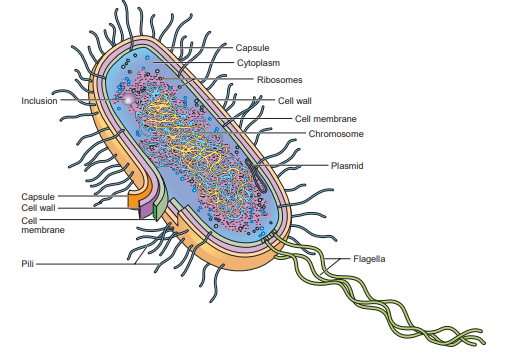
Chromosomes (Prokaryote)
Suspended or embedded in the cytoplasm. It is capable of duplicating itself, guiding cell division, and directing cellular activities.
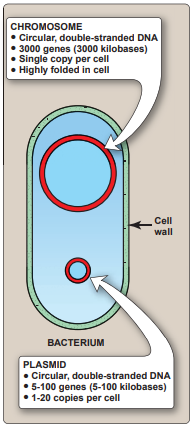
Plasmid
A small, circular molecule of doublestranded DNA. It is referred to as extrachromosomal DNA because it is not part of the chromosome. Plasmids are found in most bacteria.
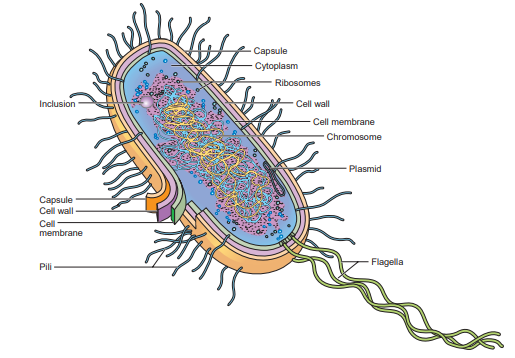
Cytoplasm (Prokaryotic)
consists of water, enzymes, dissolved oxygen (in some bacteria), waste products, essential nutrients, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids—a complex mixture of all the materials required by the cell for its metabolic functions.
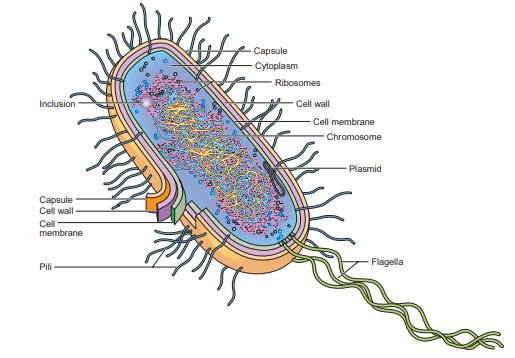
Cytoplasmic particles
Most of these are ribosomes, often occurring in clusters called polyribosomes or polysomes. The granules may consist of starch, lipids, sulfur, iron, or other stored substances.
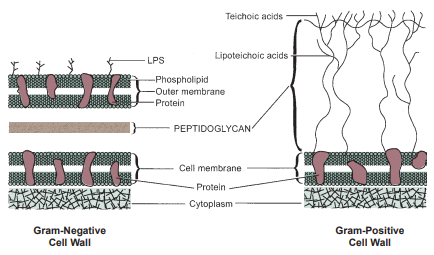
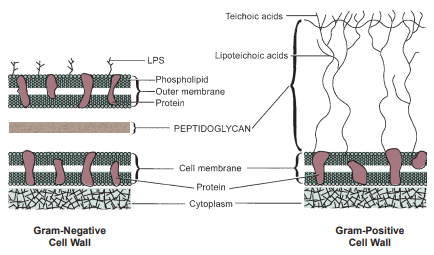
Difference of Gram negative cell wall to positive
The relatively thin Gram-negative cell wall contains a thin layer of peptidoglycan, an outer membrane, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The thicker Gram-positive cell wall contains a thick layer of peptidoglycan and teichoic and lipoteichoic acids.
Bacterial cell wall
Providing rigidity, strength, and protection. The main constituent is a complex macromolecular polymer known as peptidoglycan (murein)
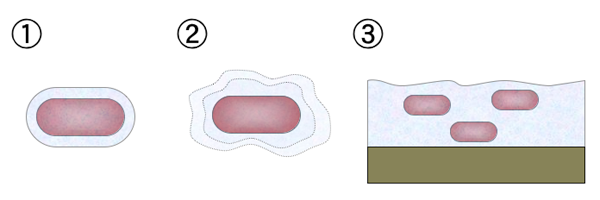
Glycocalyx
slimy, gelatinous material produced by the cell membrane and secreted outside of the cell wall.
Capsule and slime layer
Two types of Glycocalyx
Glycocalyx (Function)
enables certain bacteria to resist phagocytic engulfment by white blood cells in the body or protozoans in soil and water.
Flagella (Prokaryotic)
threadlike, protein appendages that enable bacteria to move.
Peritrichous Bacteria
Bacteria possessing flagella over their entire surface
lophotrichous bacteria
Bacteria with a tuft of flagella at one end
amphitrichous bacteria
having one or more flagella at each end
monotrichous bacteria
Bacteria possessing a single polar flagellum
spirochetes (spiral-shaped bacteria)
have two flagella-like fibrils called axial filaments
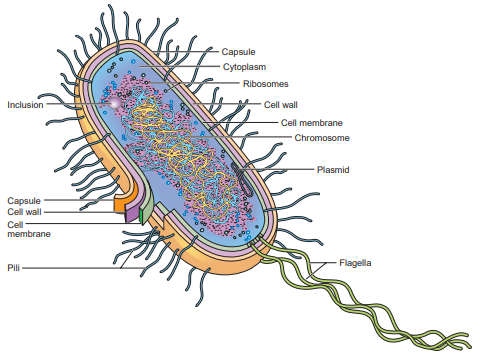
Pili (or fimbriae) (function and structure)
are hairlike structures, most often observed on Gram-negative bacteria. Not associated with motility. They serve different roles in cell motility, adhesion and host invasion, protein and DNA secretion and uptake, conductance, or cellular encapsulation.
Conjugation
Process of transferring through hollow sex pilus from the donor cell to the recipient cell.
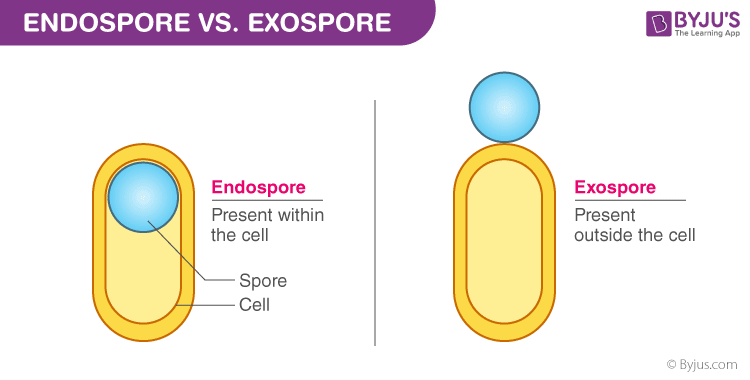
Endospores
enable bacteria to survive adverse conditions, such as temperature extremes, desiccation, and lack of nutrients