normal labor and delivery
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
most important hormones involved in labor
-oxytocin
-prostaglandins
oxytocin
-produced in hypothalamus
-released by posterior pituitary
-causes uterine contraction, stimulate the release of milk from the breasts
prostaglandin
-produced by placenta and certix
-help soften and thin cervix
progesterone
-produced by the ovary
-decreases which helps trigger labor
estrogen
-produced by ovaries
-high in pregnancy but opposed by progesterone
dilation
-opening of the cervix during labor
-0-10 cm during labor
effacement
-thinning of the cervix during labor
consistency
-firm non-pregnant, softens or ripens as labor progresses
station
-position of the baby head in the pelvis
0= level of ischial spine
-2= 2cm above ischial spine
+2= 2cm below ischial spine
contraction
-rhythmic tightening of the uterus that help to dilate the cervix and push the baby out of the uterus
progression
-rate at which the cervix dilated and effaces
-normal= 1cm/hr latent and 2cm/hr active
rupture of membranes
-breaking of the amniotic sac
bishop score
-low score ff 1= not going to labor for 3 weeks
-higher score of 10= expected labor in a few days
->8= good chance for vaginal delivery
-<6= lower chance of vaginal delivery
first stage of labor
-longest
Latent phase
-begin when contraction start and become regular and stong
-ends when cervix is dilated to 4 cm
Active phase
-begins when cervix is dilated to 4cm
-ends when cervix is dilated to 10cm
time= 12-19 first time, 10-14 who have children before
second stage of labor
-begins when cervix is fully dilated
-end when delivery of the baby
"push phase"
time= 30-60 min
third stage of labor
-begins after the baby is born
-ends with delivery of placenta
time= 5-15 min
signs and symptoms of normal labor
-contraction should be 4 min apart each contraction lasting 1 min and this pattern lasting 1 hr = come to hospital
-bloody show= cervix is starting to dilate
-water breaking= rupture of amniotic sac
-pelvic pressure= due to descending baby
-diarrhea= cause by hormones
if there is a rupture of membrane during labor
-if the present is not fixed into the pelvis, the umbilical cord can prolapse and become compresses
-labor is likely to begin soon
-delivery is delayed after rupture, intrauterine and neonatal infection is more likely as the time interval lengthens
rupture membrane diagnosis
-amniotic fluid pool in the posterior fornix or clear fluid flows onto the speculum
-check pH >7
-microscope= fern pattern
labs that are checked in labor
-hematocrit and hemoglobin
-type and antibody screen
-some do syphilis, hep B, HIV
-urine sample
non-stress test (NST)
-measures the baby heart rate
-measures strength and frequency of the contraction
biophysical profile (BPP)
-ultrasound
-fetal breath movement
-fetal movement
-fetal tone
-amniotic fluid volume
pain management
-relaxation
-water tub
-ambulation
-epidural IV or IM: blocks pain in particular region of the body, often delivered with opioid
NPO
-hold food during active labor due to delayed gastric emptying and aspiration risk
bladder management
-empty bladder regularly to prevent obstruction of fetal descent and reduce infection risk
at the start of uterine contraction
-patient is instructed to exert downward pressure
-not encouraged to push beyond completion of contraction
-several positions
power
-force of uterine contractions
passenger
-refers to the fetus
-fetal size, estimated fetal weight
-fetal lie
-presentation
-position and station
passage
-refersto the bony pelvic and soft tissue of the birth canal
braxton hicks contractions
-irregular, painless uterine contractions
-before 37 weeks distinguish form preterm labor
fetal lie
-more than 99 percent of of labor at term, the fetal is longitudinal
-ethier head or breech
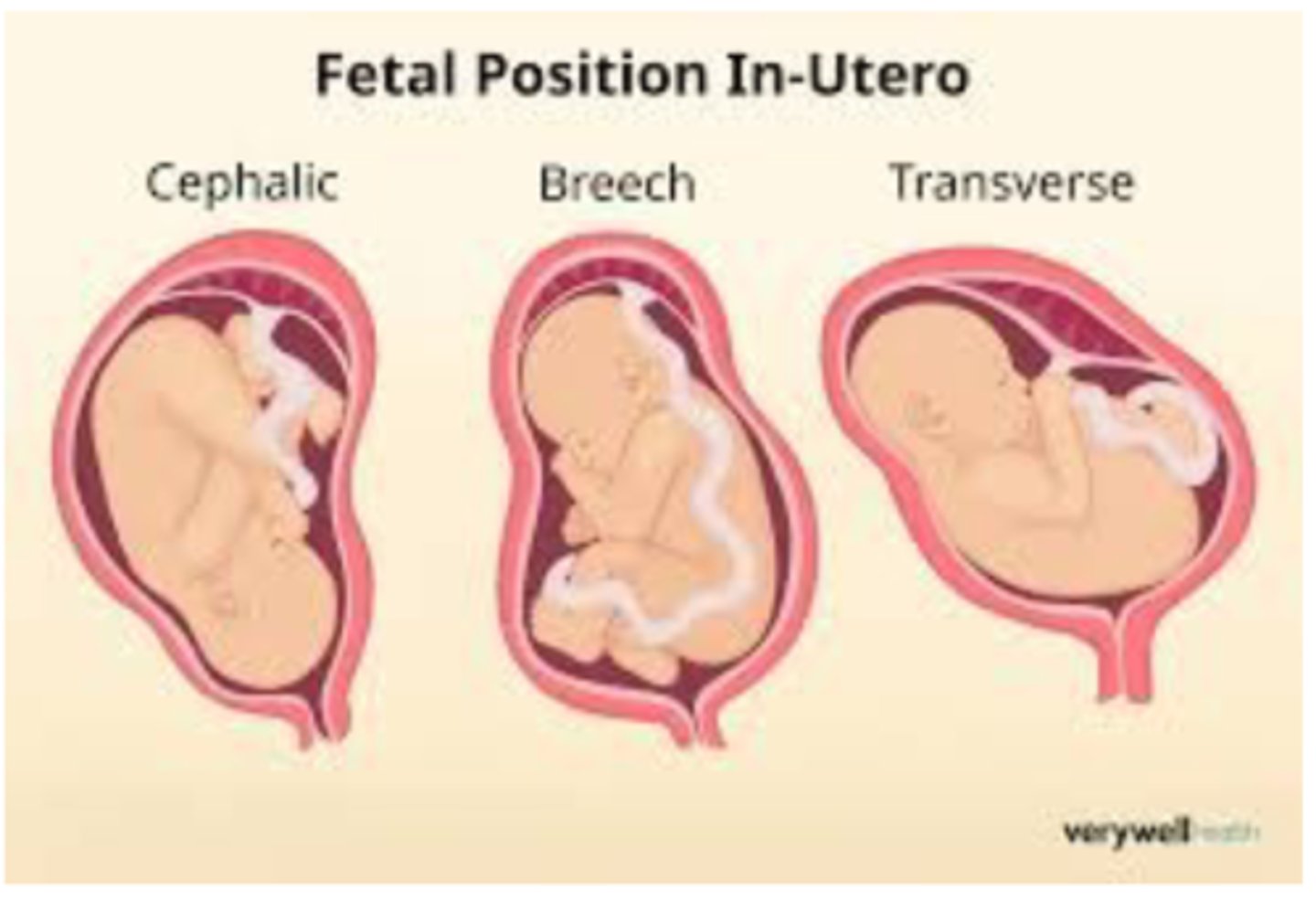
cephalic presentation
-want right or left occiput anterior
engagement
-head is sitting in pelvic inlet
-happens in last 2 weeks
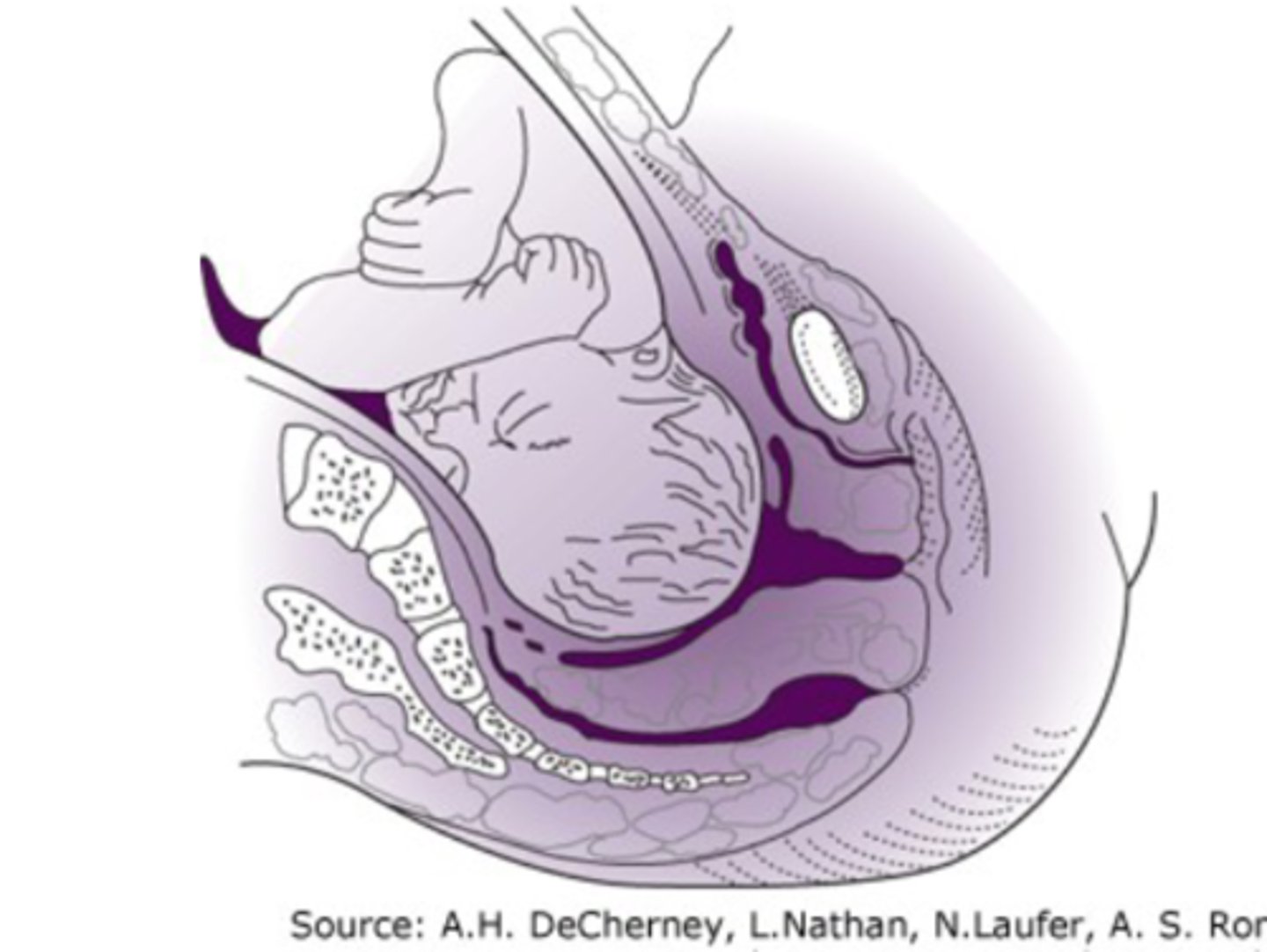
descent
-present part passing through the pelvis
-continues till the fetus is delivered
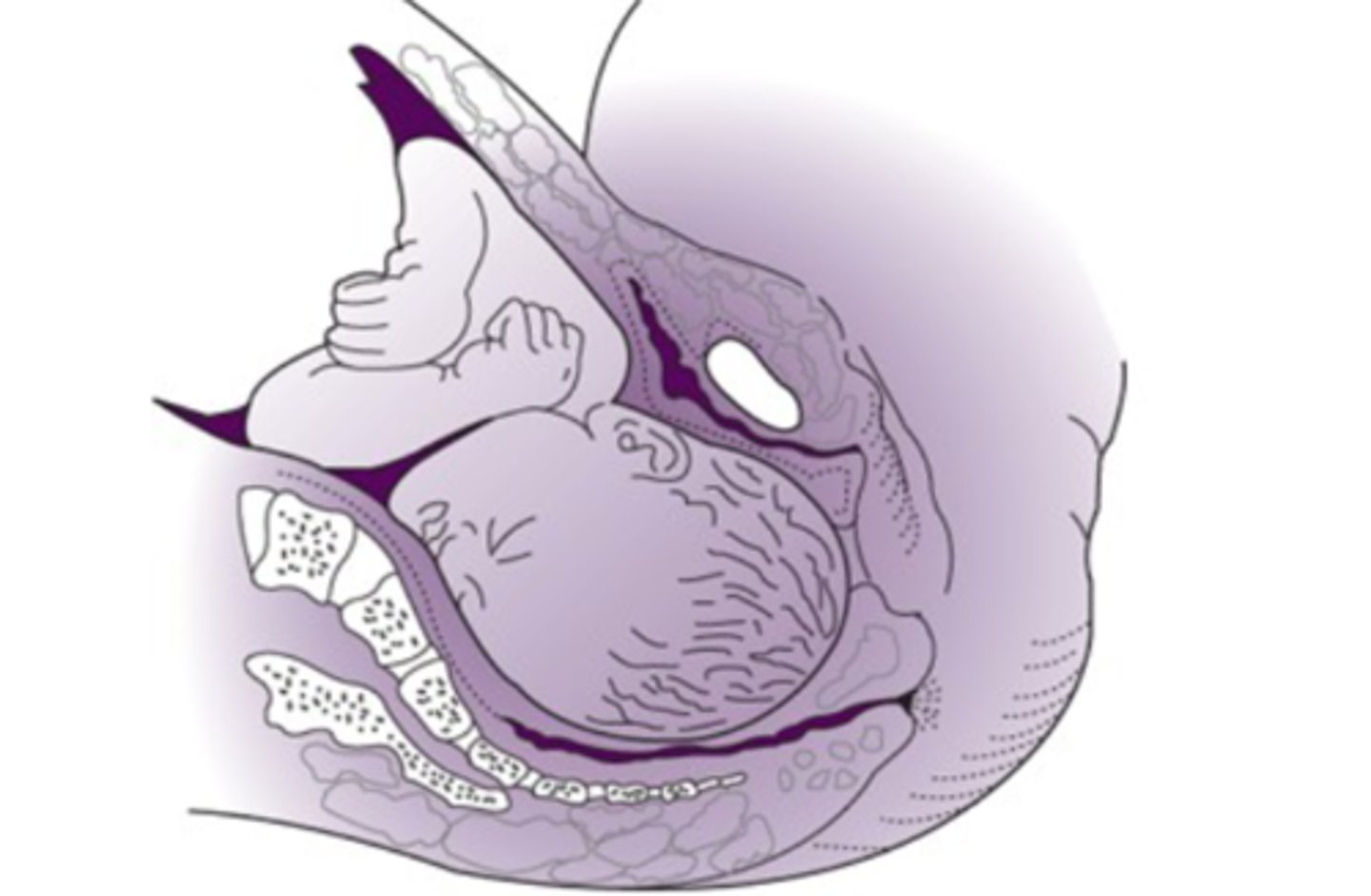
flexion
-due to shape of bony pelvis the fetal head passively undergoes flexion to present is smallest diameter
-essential for engagement and descent
internal rotation
-head goes from original position, gradually moving anteriorly toward the symphysis pubis
-descent of the head mid pelvis
extension
-fetus has descended to the introitus and then deflexes
-ring of fire
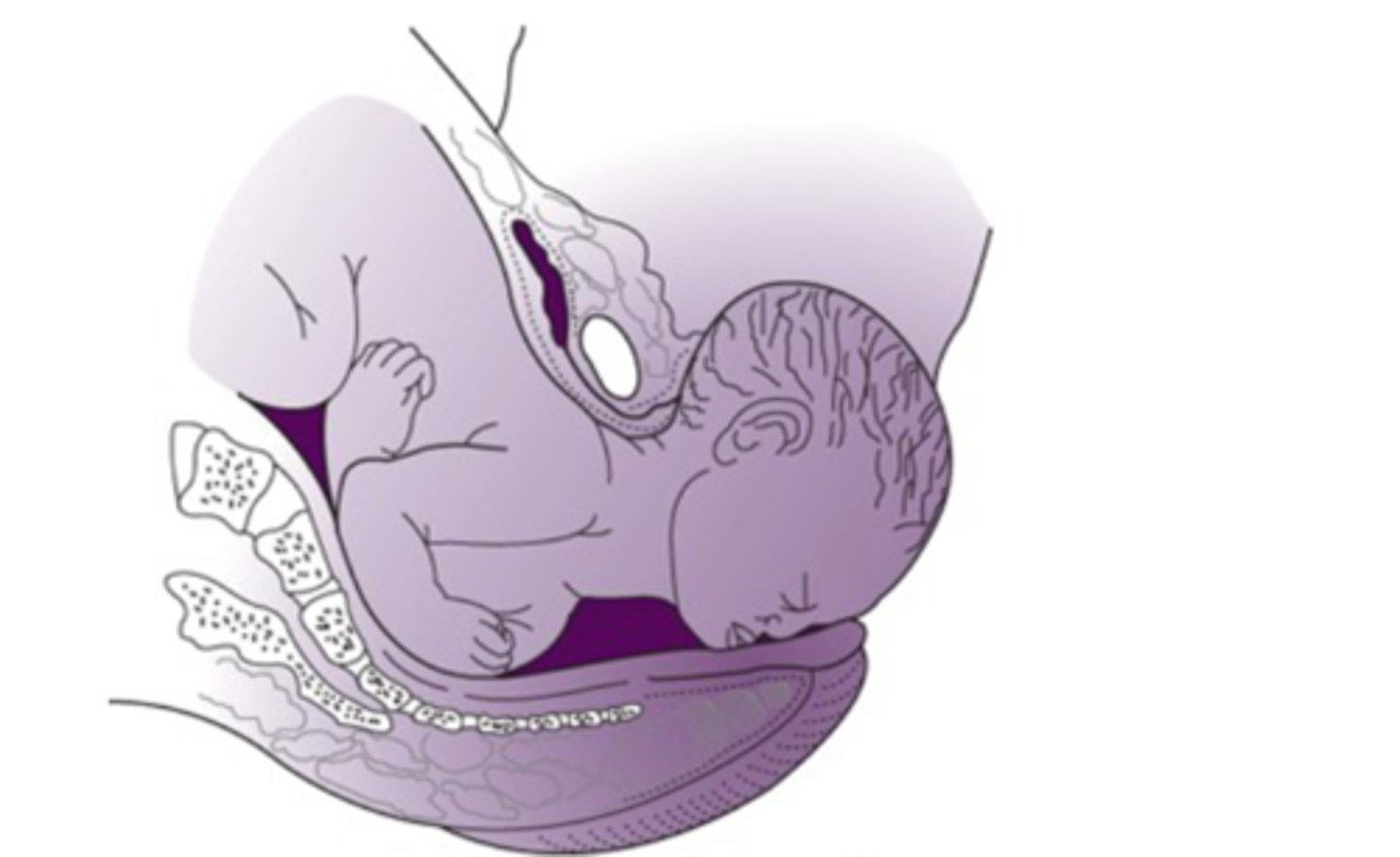
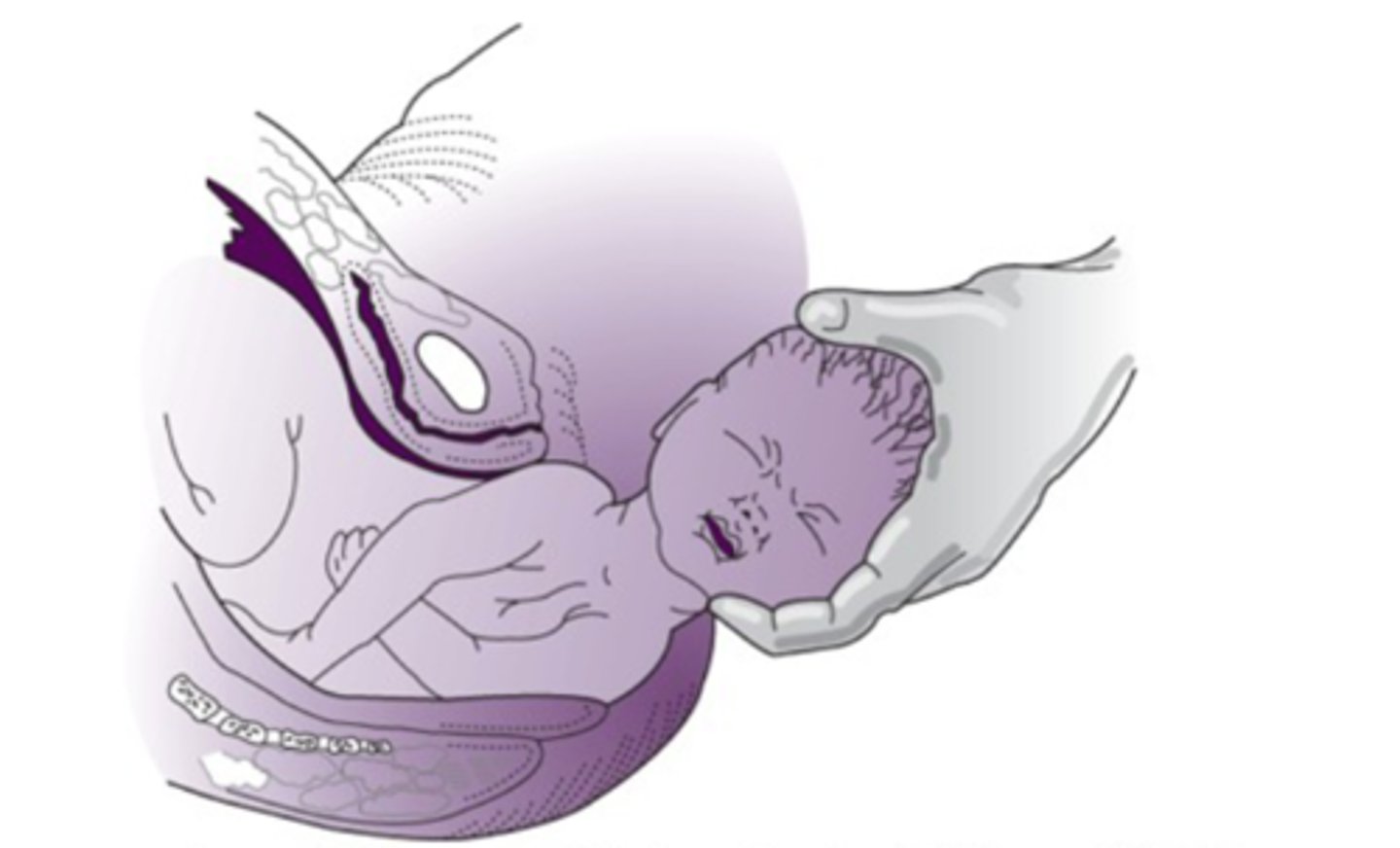
external rotation
-passive rotation of the fetal head back to anatomical position
-anterior shoulder rotates under the symphysis pubis
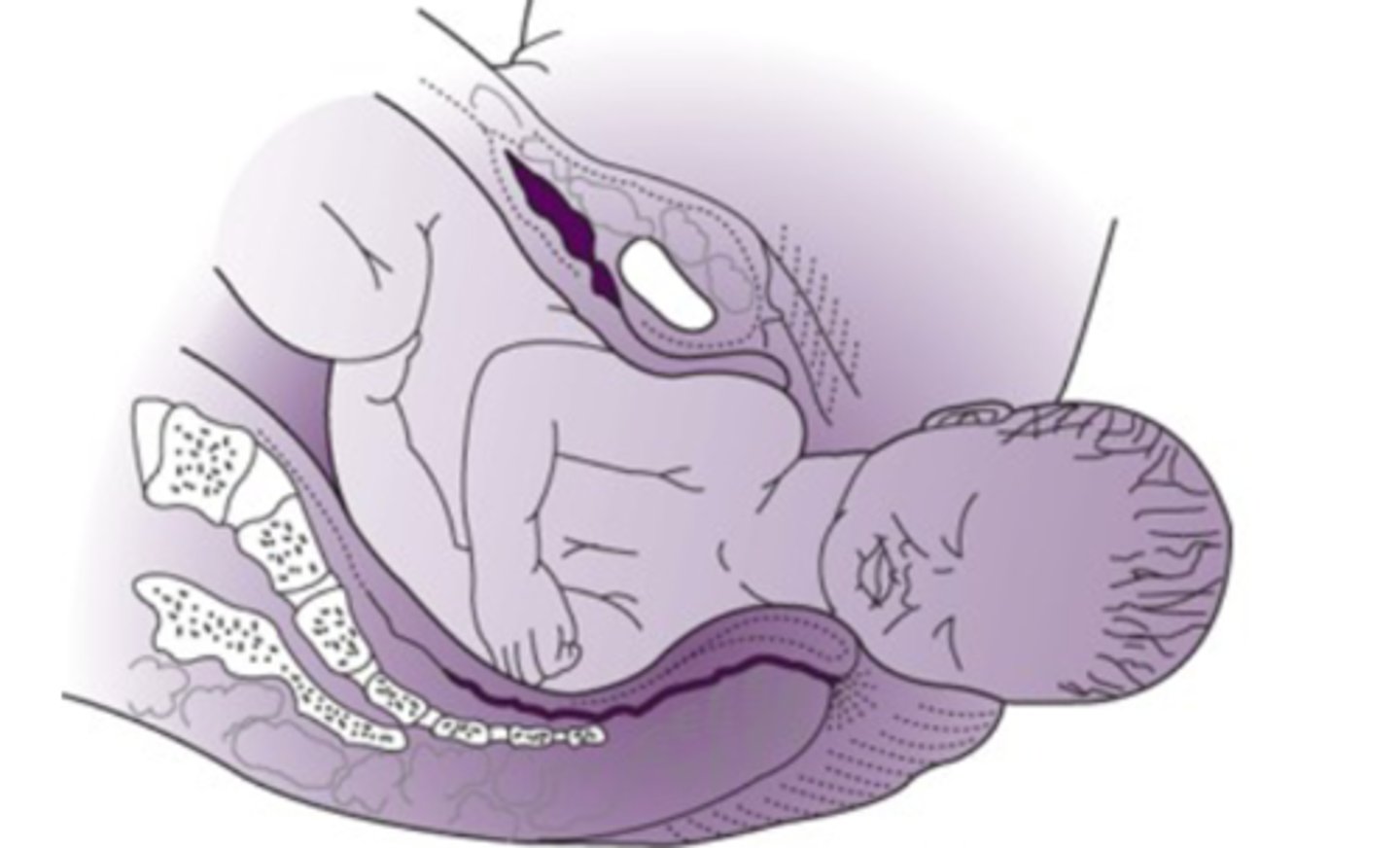
expulsion
-delivery of the entire fetus
clamping the cord
-wating 30-60 seconds associated with high hemoglobin levels after delivery and greater iron stores
skin to skin
-results in optimal warmth for the newborn
-earl maternal neonatal bonding and facilitation of early breastfeeding
postpartum care of the mother
-laceration are repaired
-uterine tone and perineum frequently evaluated
-Bp and pulse noted immediately after delivery ever 15 min for 2 hours
-temperature q4 during first 8 hours, then q8 after
preparation for C section
-patient is aware of indication, alternative, risks
-IV 18 gauge needle should be place
-patient given antacid
-foley catheter
-abdomen is preped
abdominal incision
-transverse incision with or without transection of rectal muscles
-15cm
-if emergency midline vertical suprapubic incision is preferred
once baby is delivered C section
-blood loss can be minimized by massaging the uterus
-oxytocin continued in dilute IV solution
-uterine cavity is wiped clean to remove any retained membrane
closure of incision
-entire of the uterine thickness of myometrium should be closed
-should be closed in 2 layers