Glaciers Stuff
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What did Milankovitch believe was the most important season/areas for ice ages to occur?
Northern Hemisphere Summer
When was the Quaternary period?
The past 2.5 million years - when there were big ice sheets in both hemispheres reliably
What is the main hypothesis for snowball Earth?
The weathering of silicate rocks from the breaking up of a supercontinent removed carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, allowing cold enough temps for it
When was the Cenozoic Era?
The era that we are in- the past 66 million years
What is the temperature trend in the cenozoic?
temps trending down
What is IRD?
Ice Rafted Debris
When was the Pleistocene Era?
11,700-2.5 million years ago (part of the Quaternary)
When was the Holocene Era?
present-11,700 years ago (part of the Quaternary)
What causes climate to change?
solar output, volcanic and galactic dust, weathering of silicate rocks (CO2 greenhouse effect)
What affects ice growing?
continent location, precipitation, ocean currents, elevation, tectonics
Is it easier for ice to grow on land or water?
land
What are the three things that affect orbital forcing?
Eccentricity, Obliquity, Precession
What is Eccentricity?
Shape of Earth’s orbit, on a 100,000 year cycle
What is Obliquity?
Tilt of Earth’s axis, on a 41,000 year cycle
What is Precession?
Earth’s wobble, on a 19,000-23,000 year cycle. It changes when the seasons fall in each hemisphere
Who was Milankovitch?
the father of orbital forcing, thought that northern hemisphere summer was important
When was the Last Glacial Maximum?
18,000-24,000 years ago
What were the three main ice sheets in North America during the LGM?
Laurentide, cordilleran, inuitin (canada)
What was the biggest ice sheet in north america during the LGM?
Laurentide ice sheet - 70m of sea level change, had 2 domes
What are katabatic winds?
winds that exceed 100mph from a result of cold air building up on an ice sheet/glacier and falling due to gravity
Why didn’t Alaska have ice during the LGM?
it was too dry, no precipitation
What is a marine-based ice sheet?
An ice sheet that rests on land that is below sea level
what is an example of marine based ice sheets?
Kara sea and Barents sea ice sheets
What is the total sea level rise since the LGM?
120 meters
What was the little ice age?
2 waves of increased ice (~1250-1350 AD and ~1550-1870 AD)
What is a trim line?
Clear line where vegetation breaks/stops, due to past glaciation. marks glacier boundaries
What is EAIS
east antarctic ice sheet (land-based, big, ~50m sea level equivalent)
What is WAIS
west antarctic ice sheet (smaller, marine based, ~6m sea level equiv)
Why is marine ice from glaciers/ice sheets unstable?
natural tendency to float, inland sloping bed, accelerated calving, warming ocean, loss of ice shelf, cliff collapse
What is an ice stream?
A body of fast moving ice that is bound or contained by certain boundaries
What is a pinning point?
A high area of the bed that causes glaciers to slow down in their retreat/movement
What controls where glaciers are?
Elevation + latitude (global), precipitation, topography, aspect(sunny/windy sides) (local)
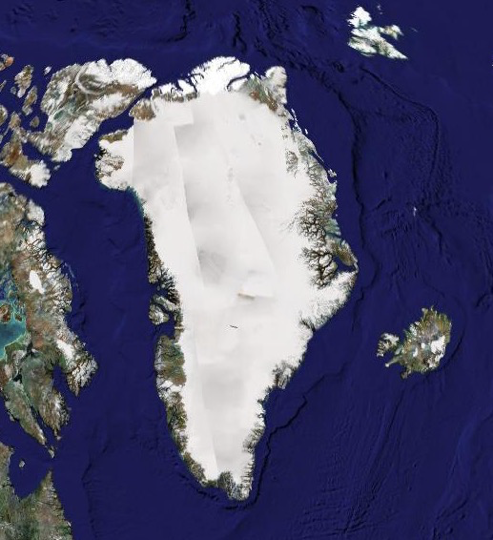

Ice Sheet
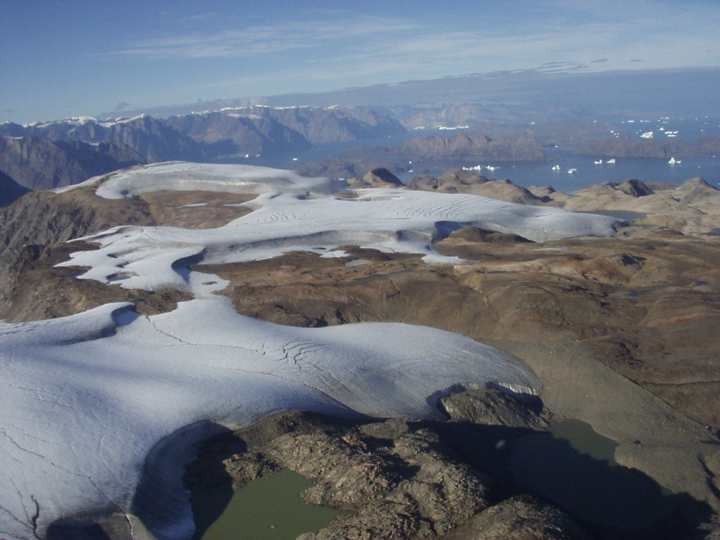

ice caps
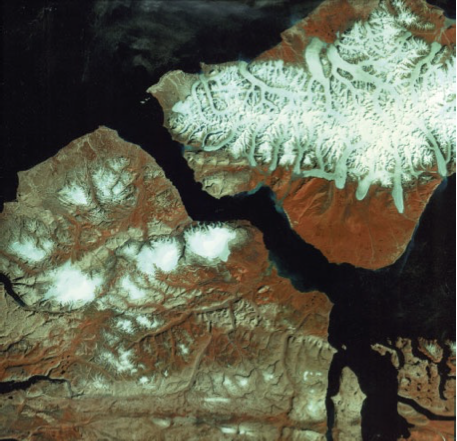

B: Ice field, C: Outlet glaciers, A: ice caps
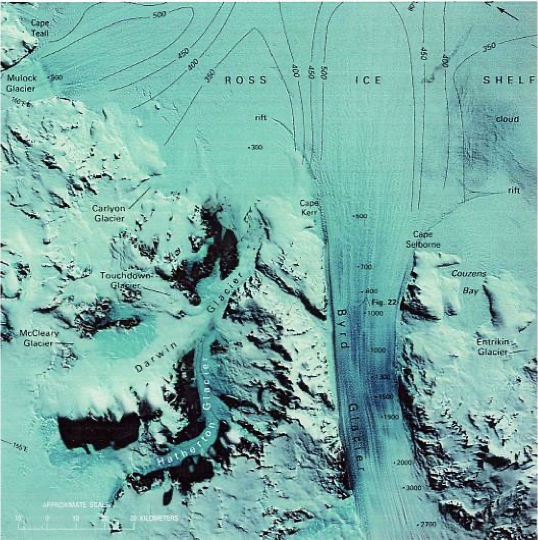
Byrd outlet glacier
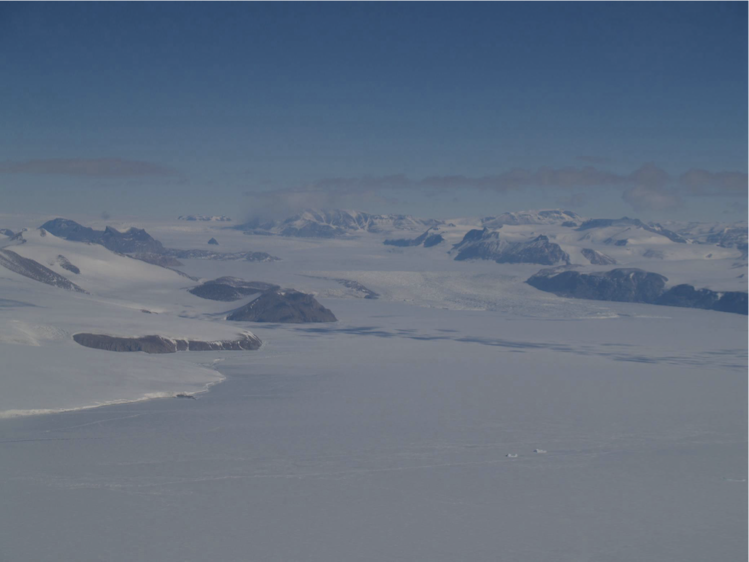

Outlet glacier
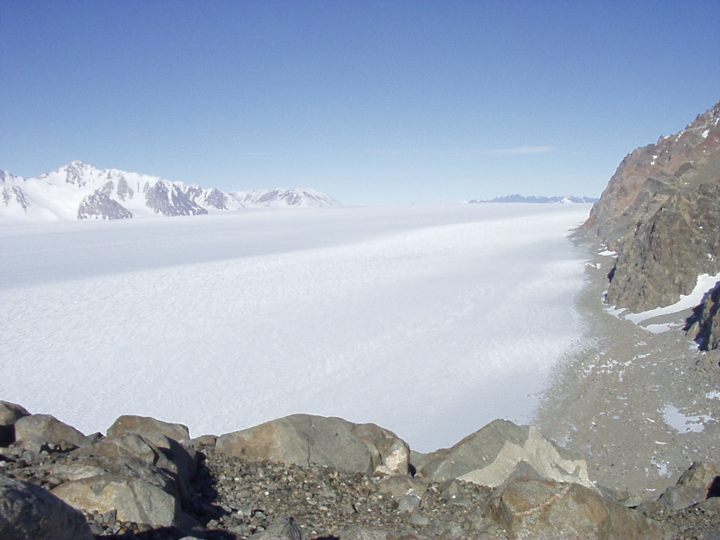

outlet glacier !
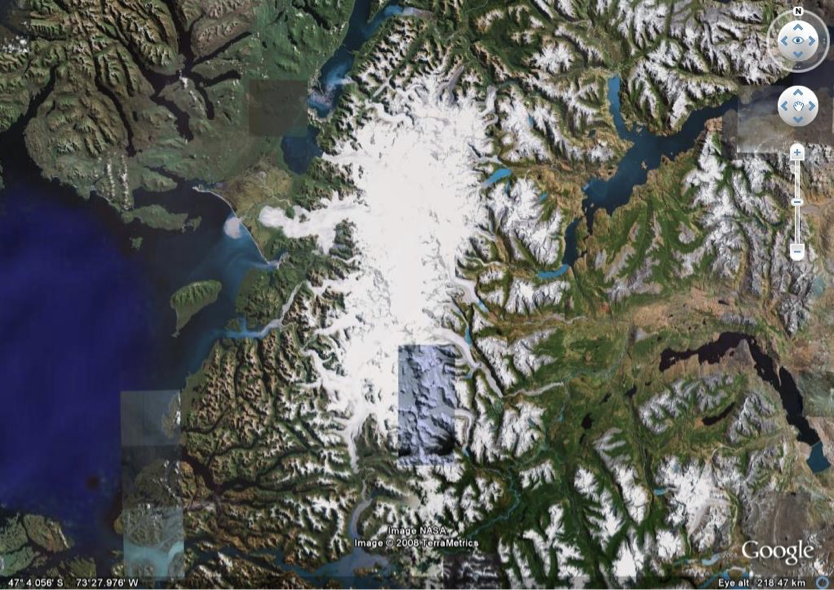
ice field
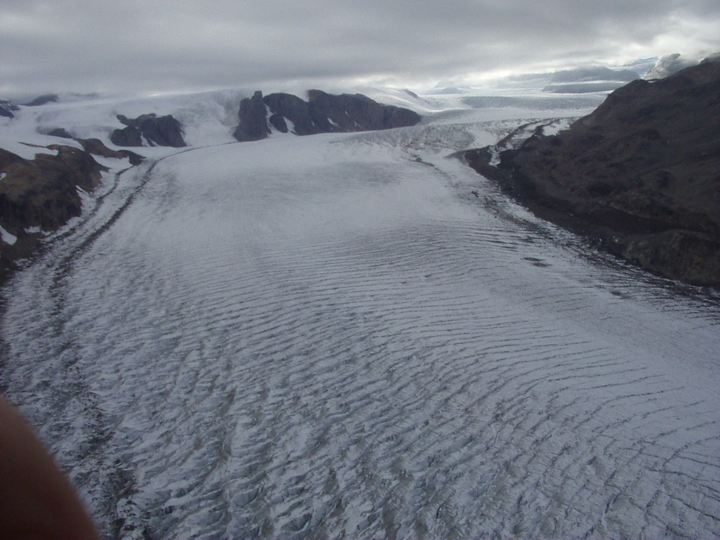

valley glacier
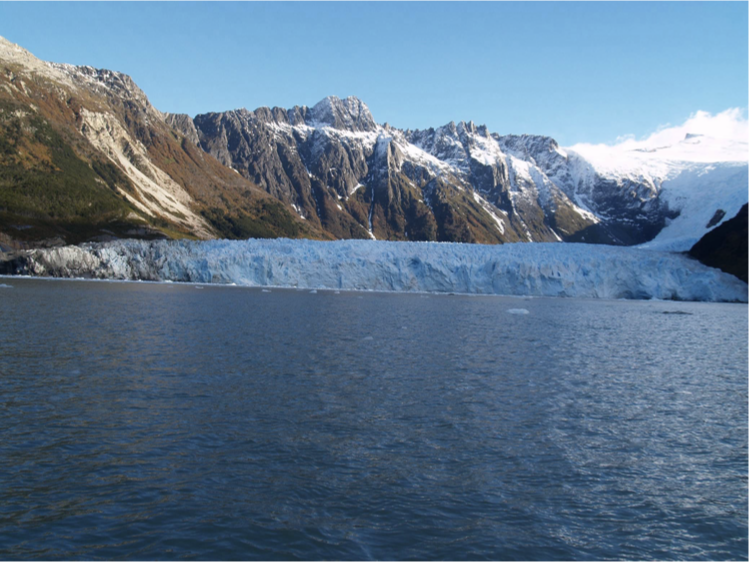

fjord or tidewater glacier
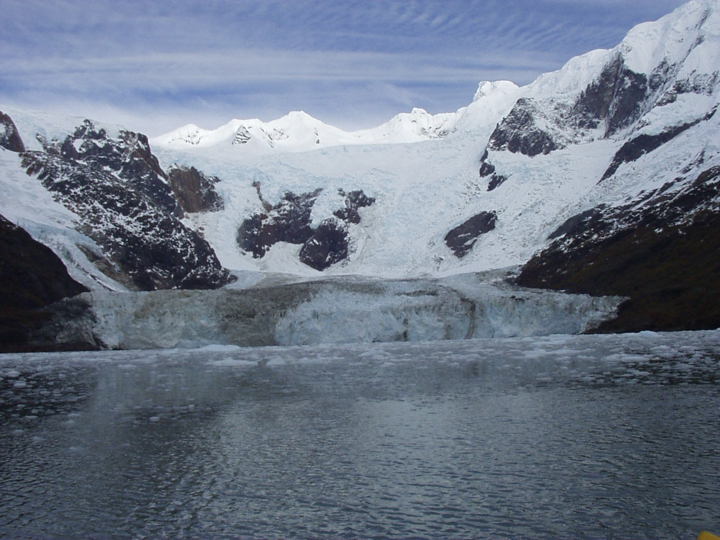

Fjord/tidewater glacier
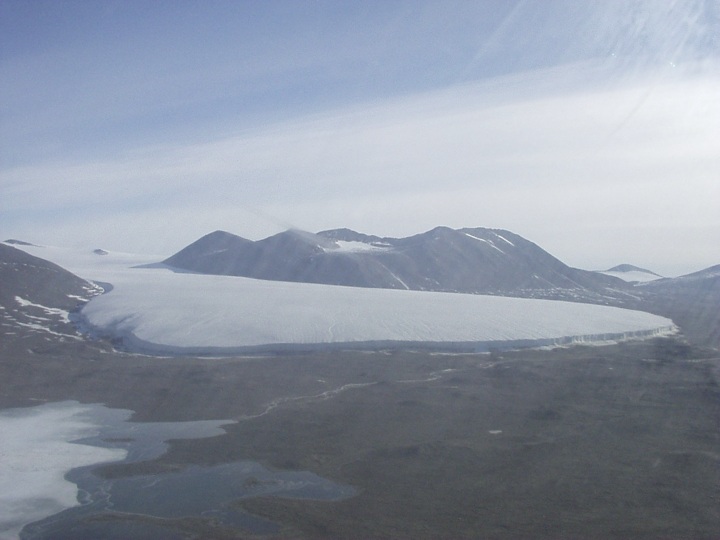

piedmont glacier - come out from a narrow valley and spread out in a large lobe like pancake batter
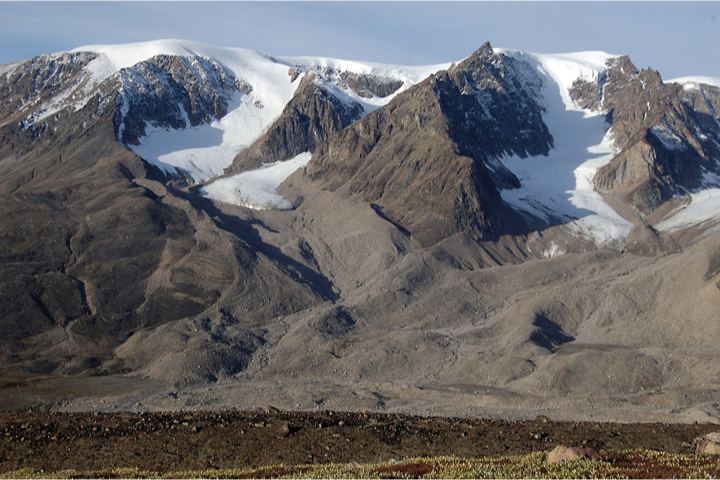

alpine glaciers
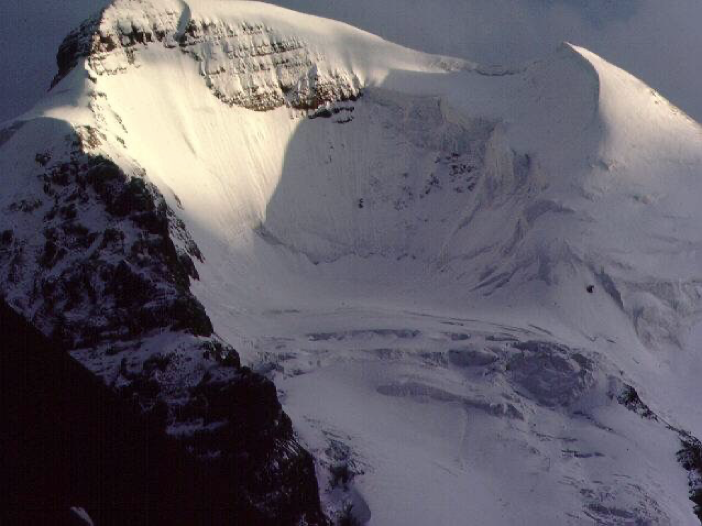

cirque glacier

reconstructed glacier
What is a nunatak?
stone/bedrock “islands” surrounded completely by ice
What is a distributary lobe?
A side portion of a glacier that intrudes into another area
What is sastrugi?
parallel wave-like ridges caused by winds on the surface of hard snow, especially in polar regions.
What is rime ice?
Ice that forms on a surface due to moisture from the air
What is a polynya?
permanently or semi-permanently area of open water surrounded by sea ice - caused by katabatic winds pushing sea ice away
What are the two types of unconstrained glaciers?
Ice sheets and ice caps
What is regelation?
The re-freezing of ice in a cavity on the base of a glacier, due to pressure melting
What is superimposed ice?
Ice formed on the surface of a glacier due to meltwater
What is mass balance?
Accumulation - ablation = mass balance
What is the ELA?
equilibrium line altitude, its normally at 0 degrees celsius. its changing location can tell us about past climate
What is AAR?
Accumulation Area Ratio, measured in percentages. Tells us what percent of the glacier is the accumulation zone
What is MELM
maximum elevation of lateral morraines (morraines end where the ablation zone ends)
Who was Max Demorest?
The first guy to say something about internal glacier flow, proposed extrusion flow theory in the 1940s (not correct)
How does glacier flow velocity change with depth?
The velocity of a glacier decreases as depth increases. (slower on the bottom)
What is a moulin?
A shaft in a glacier kept open by running water
What is a melange?
a mixture of frozen sea ice surrounding other types of ice
What is the equation for the stress on a glacier that causes it to move?
T = pghsinx (T=stress, p=density of ice, g=acceleration due to gravity, h=ice thickness (m), x=surface slope of glacier). Pete got his son a xylephone!!!
What type of relationship does ice thickness and surface slope have?
an inverse relationship
What is Glen’s Flow Law equation?
E = BT^n (E=creep rate, B=constant based on ice hardness, T=stress, n=creep exponent (3)). ed bought tree nuts!!
What can small changes in stress cause?
large changes in creep rate/deformation
What is enhanced creep?
When creep rate accelerates due to increased pressure/stress as a result of interaction with an obstacle (boulder, mountain, etc.)
What is the pressure melting point? PMP
The temperature at which ice melts under a certain amount of pressure. Ice has a lower melting point with increased pressure.
What is a temperate glacier?
A glacier where water and ice coexist throughout its entirety. At the PMP throughout and wet based. On diagram, PMP and temp gradient are the same
What is a polar glacier?
A glacier with no water throughout. Cold-based, but can have wet-based patches. On diagram, PMP goes from right to left going down, while temp gradient goes left to right doing down. If lines intersect, water is created
Draw a diagram for a glacier that spans across maine and arctic canada. Add labels.
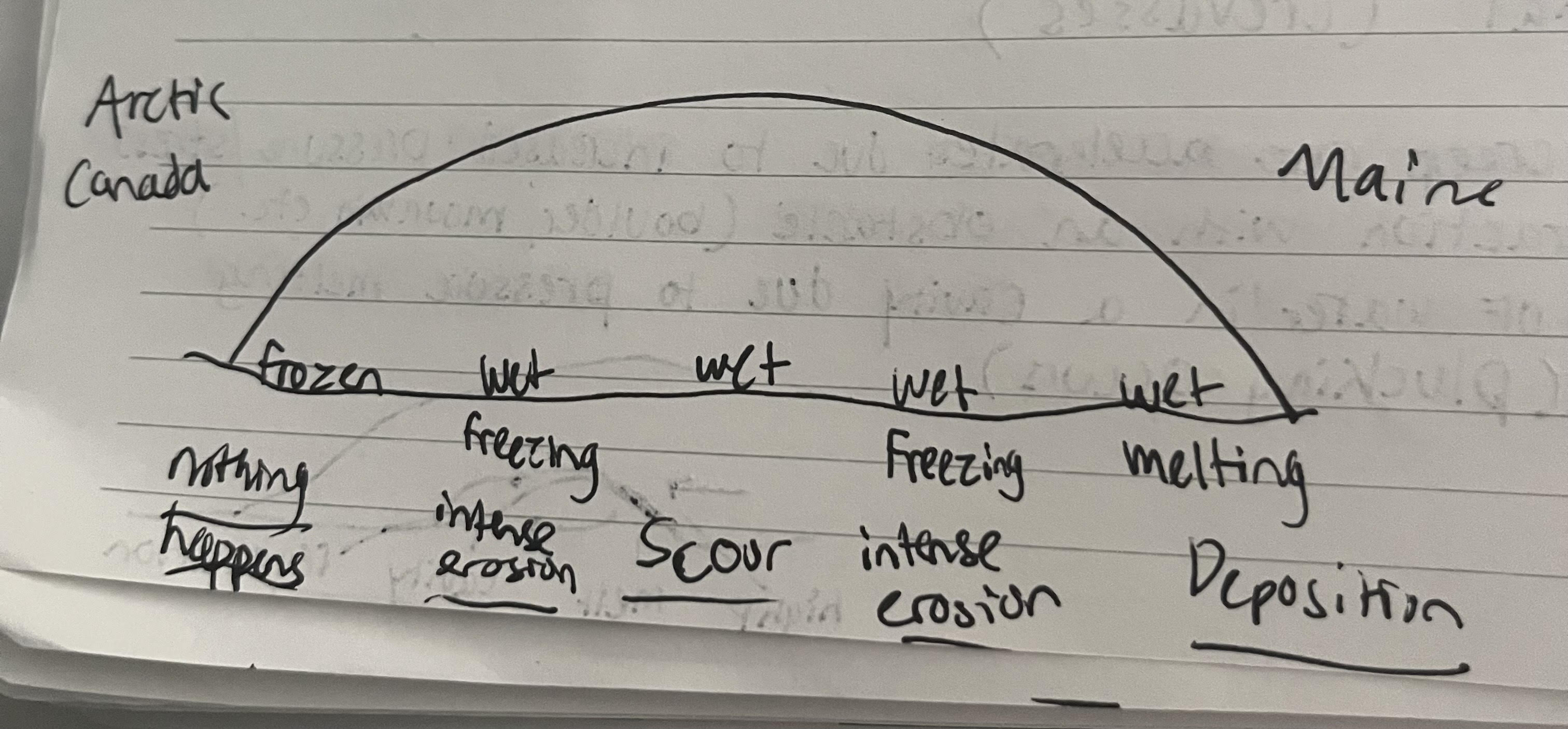
What is supraglacial water?
Water on top of the glacier in the ablation zone
what are cryoconitic holes?
Holes in the ice caused by sediment being blown onto surface.
What are a glacier’s primary water sources?
SURFACE MELT (most important), basal water, precipitation, runoff
What is an N-channel?
A tunnel/channel in the rock/bedrock below the ice. Subglacial
What is an R-channel?
A tunnel/channel created in the ice. These are how/where eskers form.
What does englacial mean?
situated, occurring, or formed inside a glacier.
What is a subcrustal setting?
just below the surface of a glacier, melting can occur. Think turkey/christmas story