Gait Analysis
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
GAIT ANALYSIS - PURPOSE (4)
1. detection of impairment
2. assessment of deviation
3. planning of intervention
4. measure impact of intervention
how do we do movement analysis of gait?
- Observational Gait Assessment (OGA)
- Video Gait Assessment (VOGA)
- Computer Motion Analysis Lab
- Pattern Recognition
- Hypothetic Deductive
- Multiple Branching (ruling out as you go)
- Exhaustive (systematic tools)
what is Pattern Recognition?
based on memory of similar case/presentation
- better presentation of a "cluster of symptoms"
- quickest way
what is the gold standard of gait analysis?
Computer Motion Analysis Lab
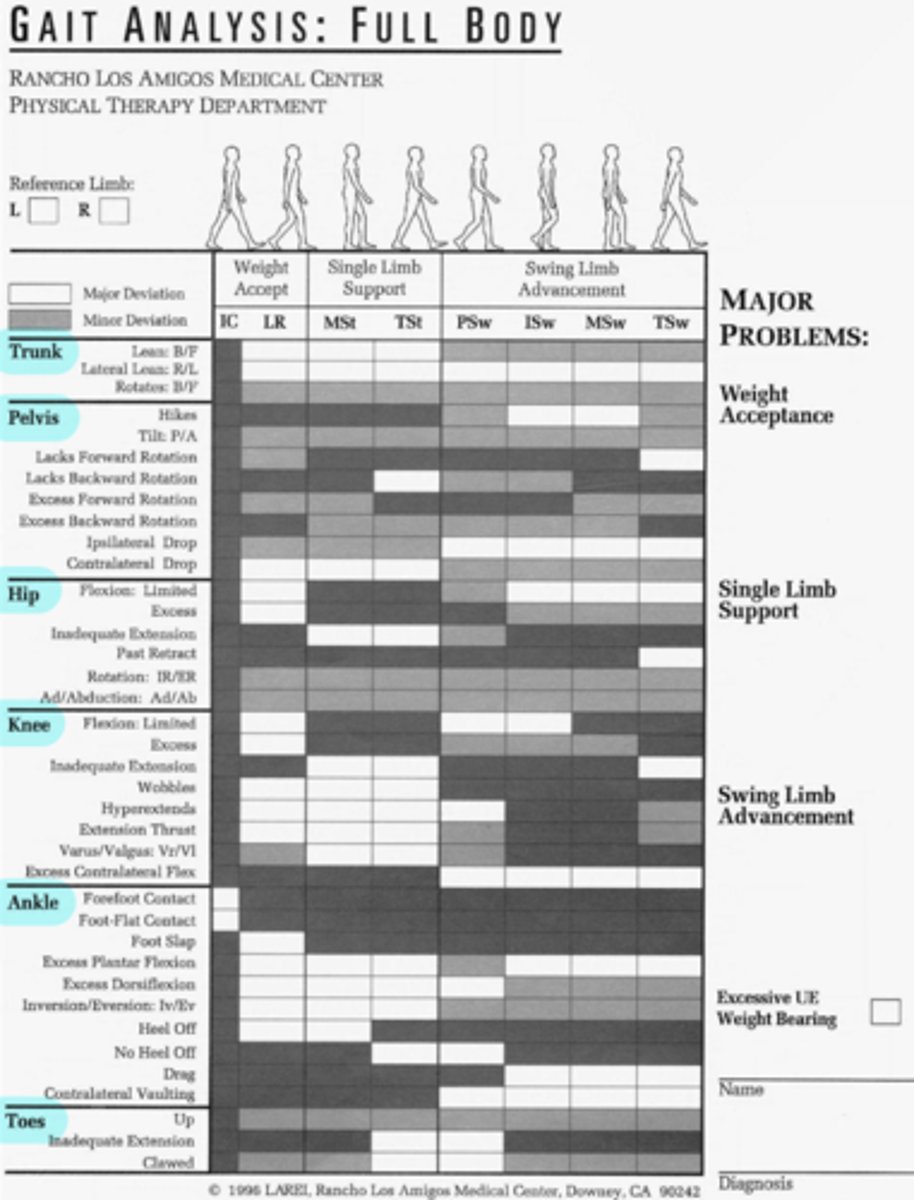
full body gait analysis photo
what is Hypothetic Deductive?
identify a hypothesis and test it
what is Multiple Branching?
several hypothesis
- ruling them out as you go
what should we look for when observing gait?
- Observe from multiple angles
- Uncover joints - feet, knee!
- Use forms to be systematic
- Avoid "quantifying deviation"
- Supplement with other tests and measures
- Ask patient to change their speed, video taping and colleagues all help
THE BARE MINIMUM to watch during gait =
overall gait
Look at Stance phase vs swing phase
Practice and train yourself to look at:
- Early, mid and late stance phase
- Early and late swing phase
- Pelvis and trunk
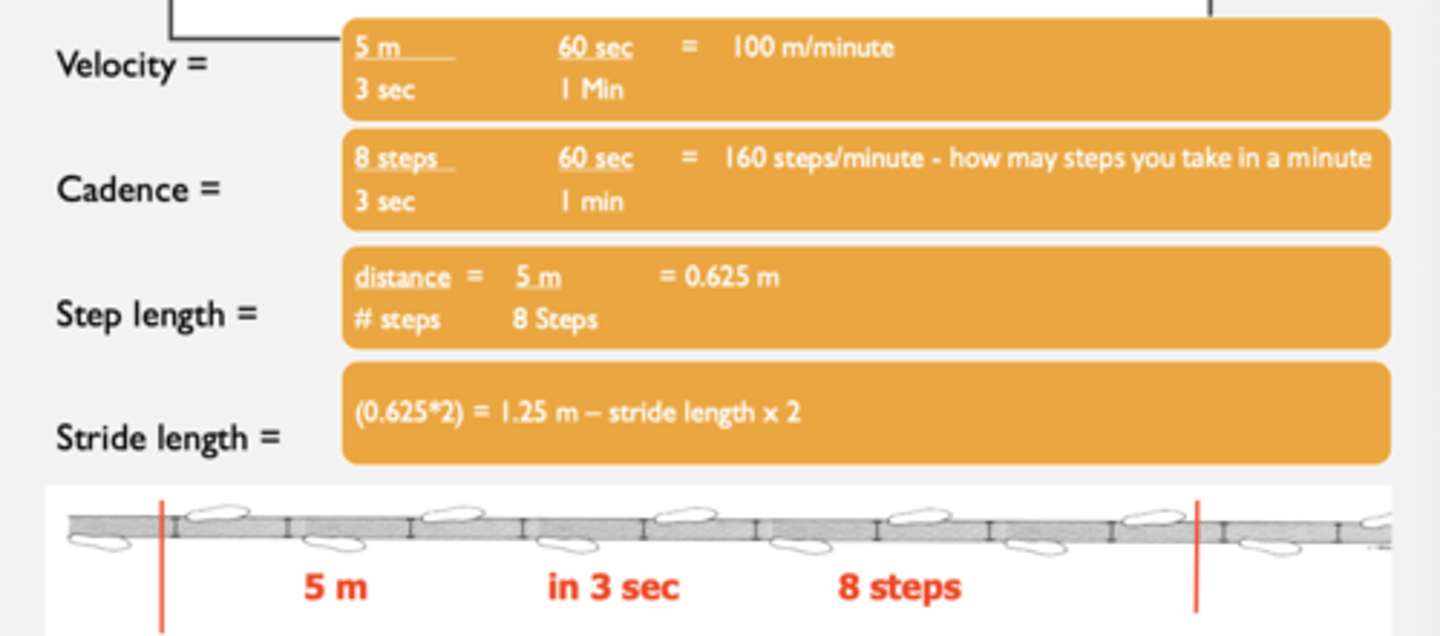
Cadence =
steps per minute
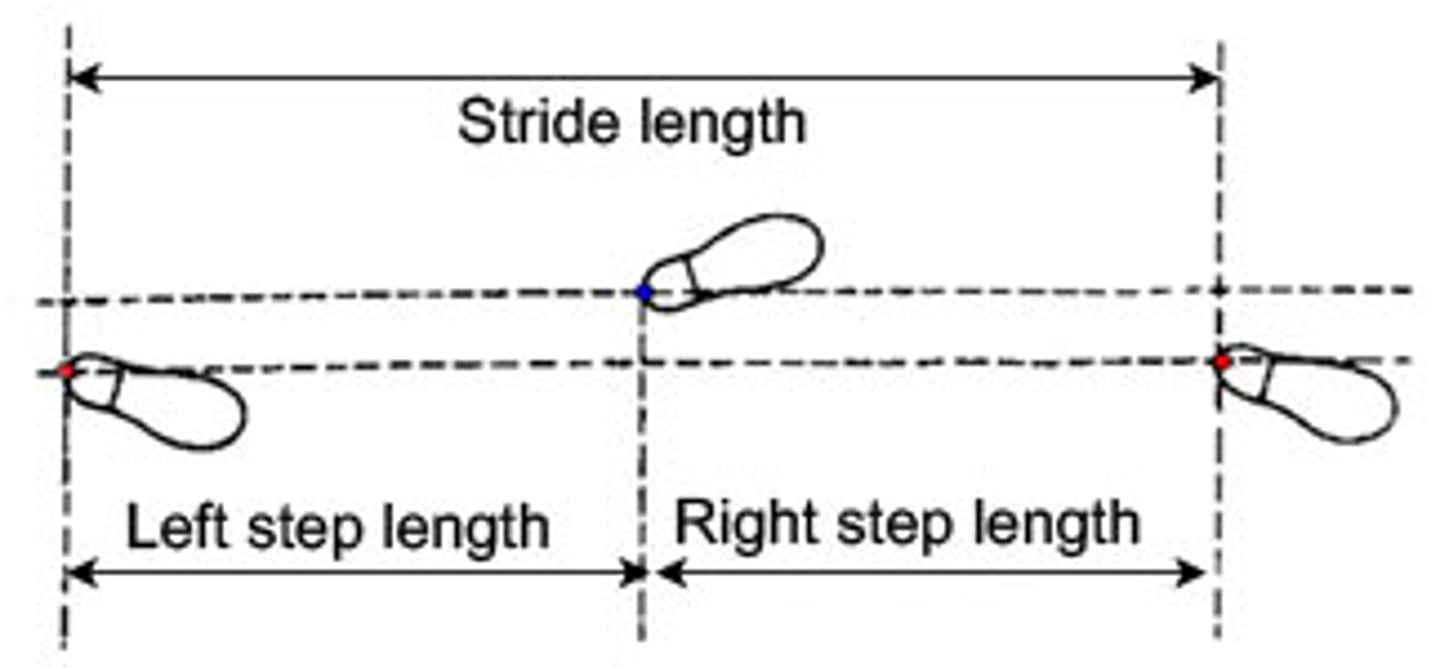
Step Length =
distance between the heel strike of one foot and the heel strike of the other foot
(RHS to LHS)
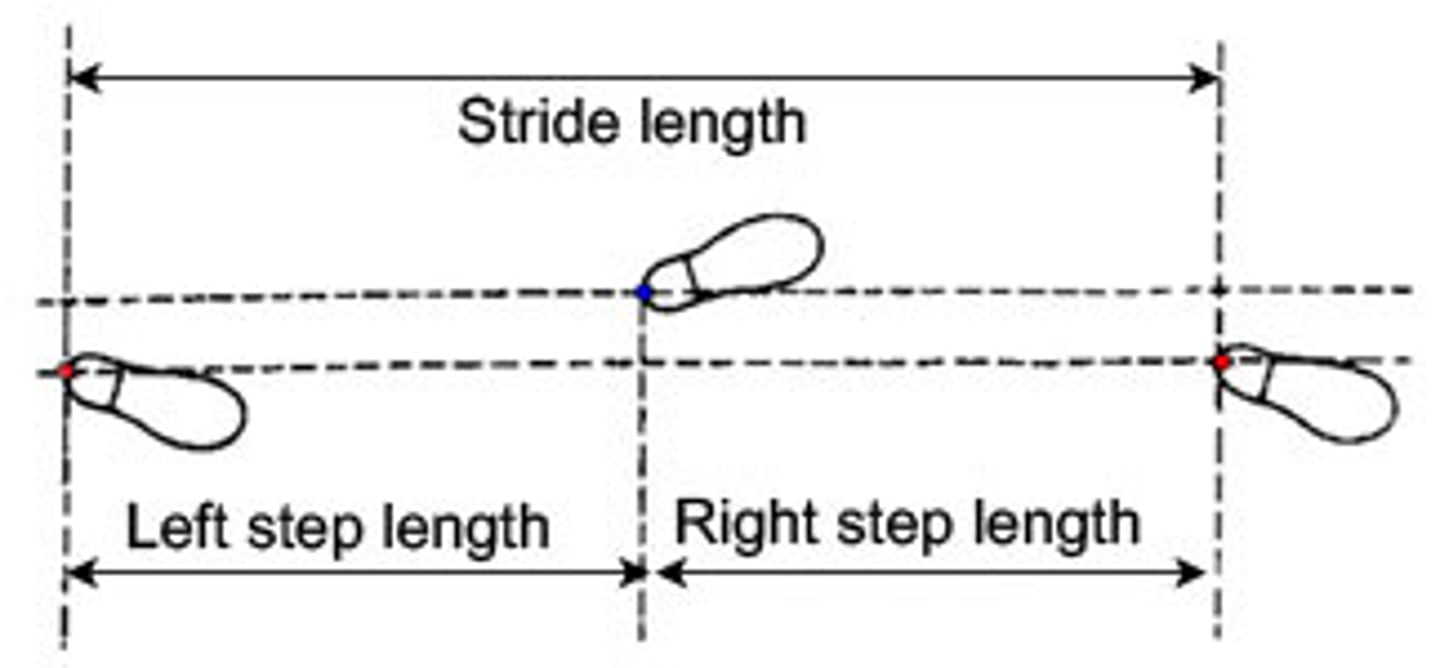
Stride Length =
distance covered with each stride during the gait cycle
(RHS to RHS)
Speed =
distance traveled per unit of time (m/s)
Rhythm and Coordination =
rest of body interacting with the steps
stance is how much percent if the gait cycle?
60%
swing takes up how much percentage?
40%
how many phases are in 1 gait cycle?
8
- initial contact, loading response, mid stance, terminal stance, pre swing, initial swing, mid swing, terminal swing
muscles at initial contact
- eccentric: glut max and med, hams, quads, pretibial muscles
- inactive: iliopsoas, calf muscles
muscles during loading response
- eccentric: glute med, hams, quads, pretibial
- inactive: iliposas, glute max, calf muscles
muscles during mid stance
- eccentric: glute med, calf muscles
- inactive: iliopsoas, glute max, hams, quads, pretibial
muscles during terminal stance
- eccentric: glute med
- inactive: glute max, hams, quads, pretibial
- concentric: iliopsoas, calf
muscles during pre swing
- eccentric: quads
- inactive: glute max, glute med, hams, pretibial
- concentric: iliopsoas, calf muscles
muscles during initial swing
- eccentric: hams, quads
- inactive: glute max and med, calf muscles
- concentric: iliopsoas, pretibial
muscles during mid swing
- eccentric: hams
- inactive: glute max and med, quads, calf
- concentric: iliopsoas, pretibial
muscles during terminal swing
- eccentric: hams
- inactive: iliopsoas, glute max and med, quads, calf
- concentric: pretibial
max amount of pelvis roation needed for gait
5° (forwards and backwards)
- during IC, LR, TSt, PSw, Isw, Tsw
max amount of hip flex needed for gait
25°
- during IC, LR, ISw, MSw, TSw
max amount of hip extension needed for gait
20° (apparently) at TSt
max amount of knee flexion needed for gait
60° at ISw
- 15 at LR
- 40 at PSw
- 25 at MSw
max amount of anke DF needed for gait
10° at TSt
- 5 at MSt
max amount of ankle PF needed for gait
20° at Psw
- 10 at LR and ISw
max ammount of MTP ext needed for gait
60° at PSw
- 20 at TSt
positives of observational gait analysis
- how movement is traditionally analyzed
- solid foundation for understanding normal gait and identifying kinematic differences from normal gait
- especially for people who do not require assistance
negatives of observational gait analysis
- challenging to interpret significance of deficits individually and how they impact the outcome of the gait cycle
- challenging to make a treatment plan
if someone has a foot slap, what is a deviation at the ankle?
weak DF
if someone has toe down at initial contact, what are the deviations at the ankle?
PF spasticity, PF contracture, weak DF, leg length, hindfoot pain
if someone has heel lift during midstance, what are the deviations at the ankle?
insufficient DF range, PF spasticity
if someone has no toe off, what deviation is there?
insufficient PF range
if someone has exaggerated knee flexion at IC, what are possible deviations?
weak quads, hamstring spasticity, limited knee extension ROM
if someone has hyperextension in stance, what are possible deviations?
compensation for weak quads, PF contracture
if someone has knee flexion in terminal stance, what are possible deviations?
knee flexion contracture, hip flexion contracture
if someone has insufficient flexion in swing, what are possible deviations?
knee effusion, quad extension spasticity, PF spasticity, reduced knee flexion ROM
if someone has excessive flexion with swing, what are possible deviations?
flexor withdrawal reflex or synergy
if someone has insufficient hip flexion at initial contact, what are possible deviations?
weak hip flexors, hip extensor spasticity, insufficient hip flexion ROM
if someone has insufficient hip extension in stance, what are possible deviations?
insufficient hip extension ROM, hip flexion contracture, LE flexor synergy
if someone has circumduction during swing, what are possible deviations?
compensation for weak hip flexors, weak DF, or weak hamstrings
if someone has hip hiking during swing, what are possible deviations?
compensation for weak DF, knee flexors or as compensation for extensor synergy pattern
if someone has exaggerated hip flexion during swing, what are possible deviations?
LE flexor synergy, insufficient ankle DF
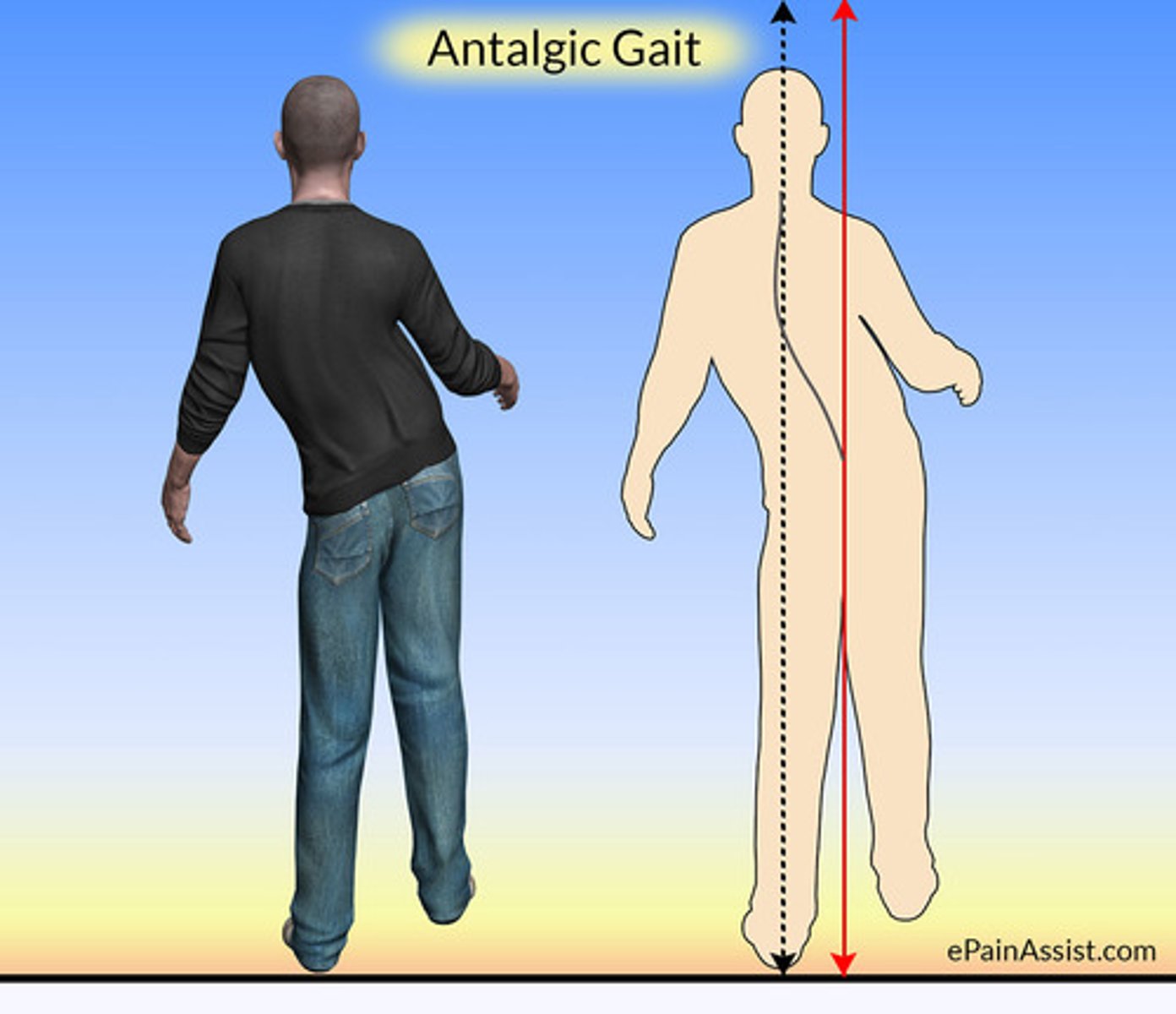
what is an antalgic gait?
gait pattern that develops as a way to avoid pain while walking (good leg moves faster)
- "limping'
what is an ataxic gait?
unsteady, uncoordinated walk, employing a wide base and the feet thrown out (drunken sailor)
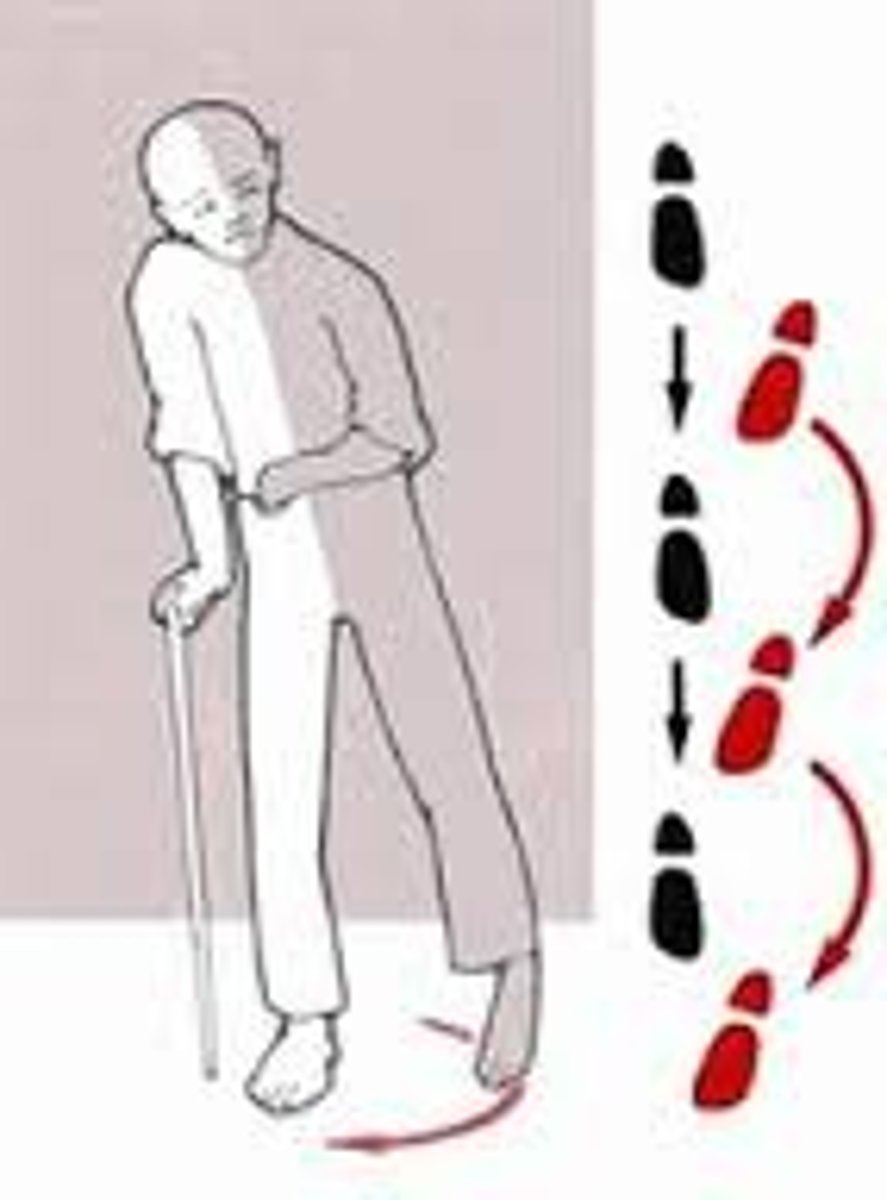
what is a hemiplegic/circumduction gait?
strength or ROM issue that forces the bad leg to circumduct to advance
- upper body still shifted to the side
- antalgic gait - but not a pain issue
what is a parkinsonian/festinating gait?
posture is forward
- reduced arm swing
- shuffling legs, no hs, small steps
- freezing
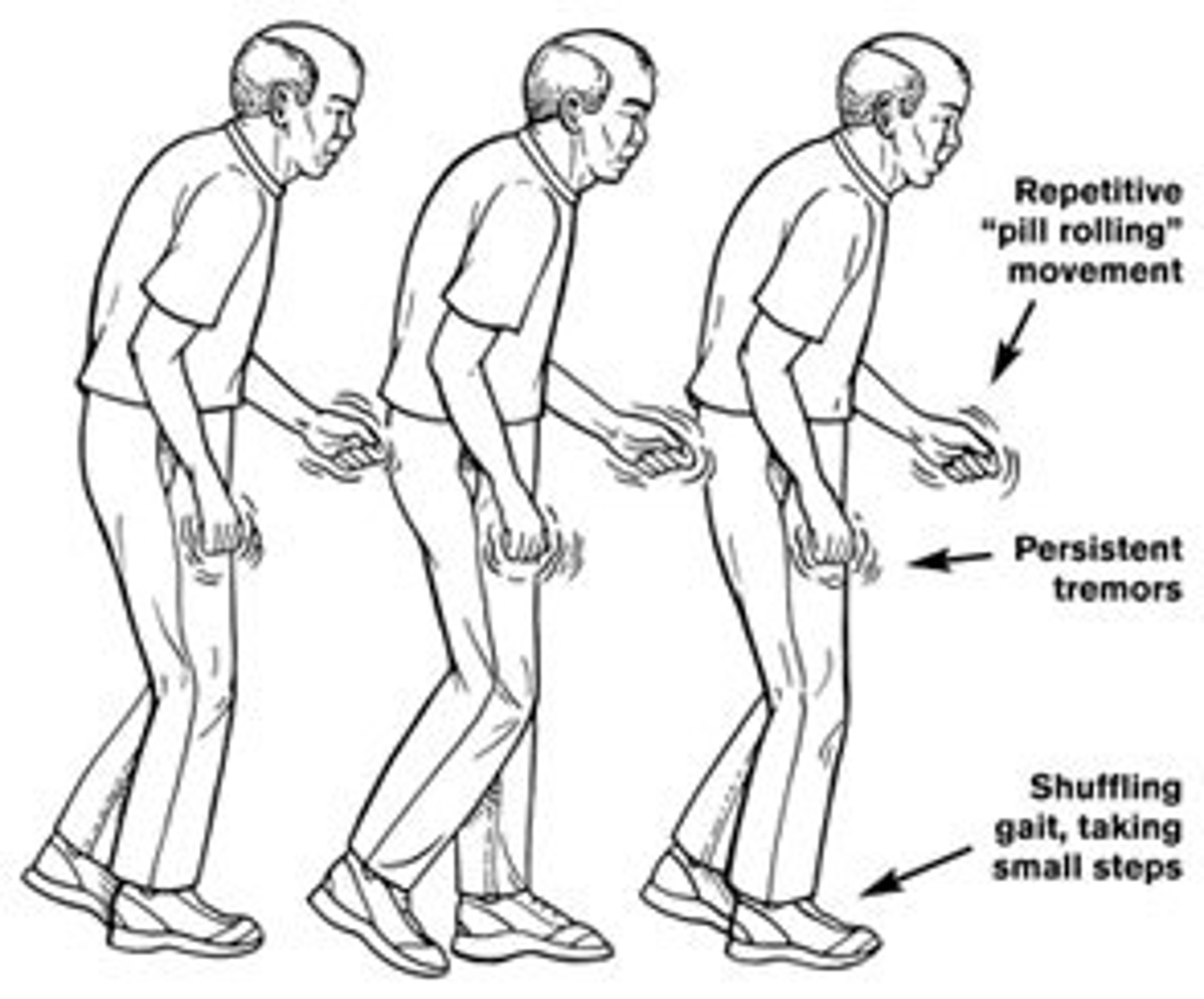
what is freezing in parkinsonian gait?
a sudden, temporary inability to move the feet while walking, often described as feeling "glued to the ground"
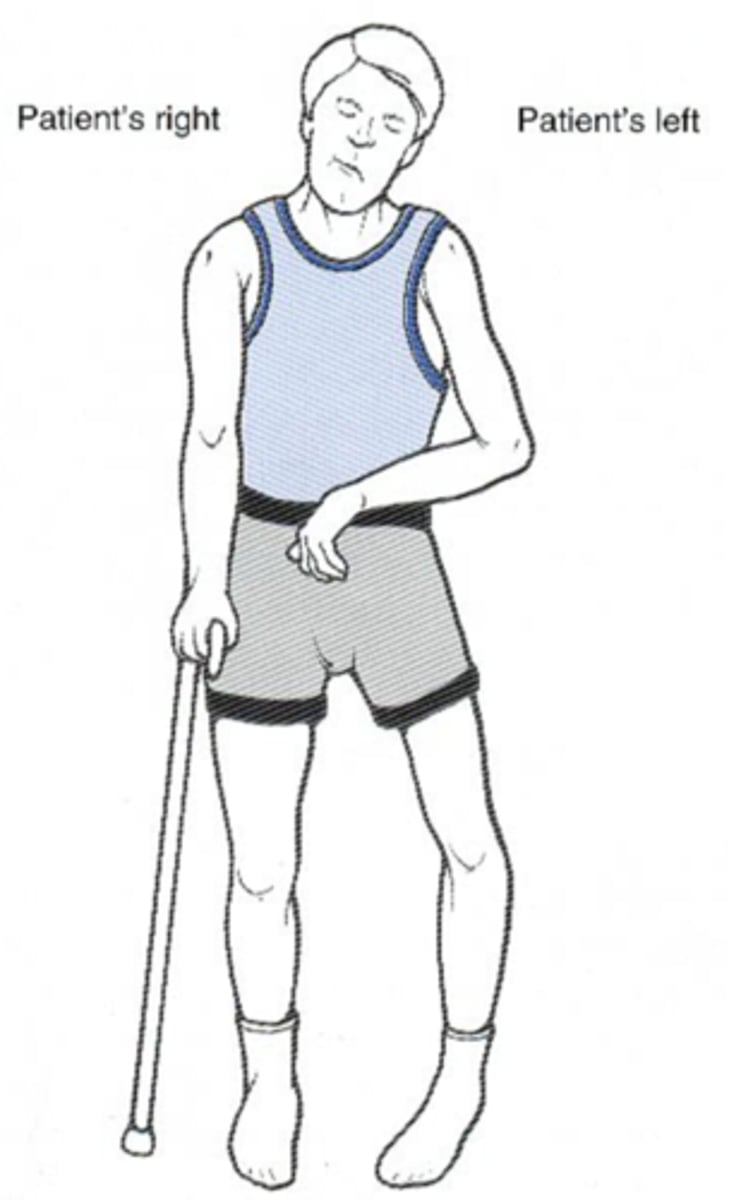
what is a spastic gait?
A gait pattern with stiff movement, toes seeming to catch and drag, legs held together, hip and knee joints slightly flexed. Commonly seen in spastic paraplegia.
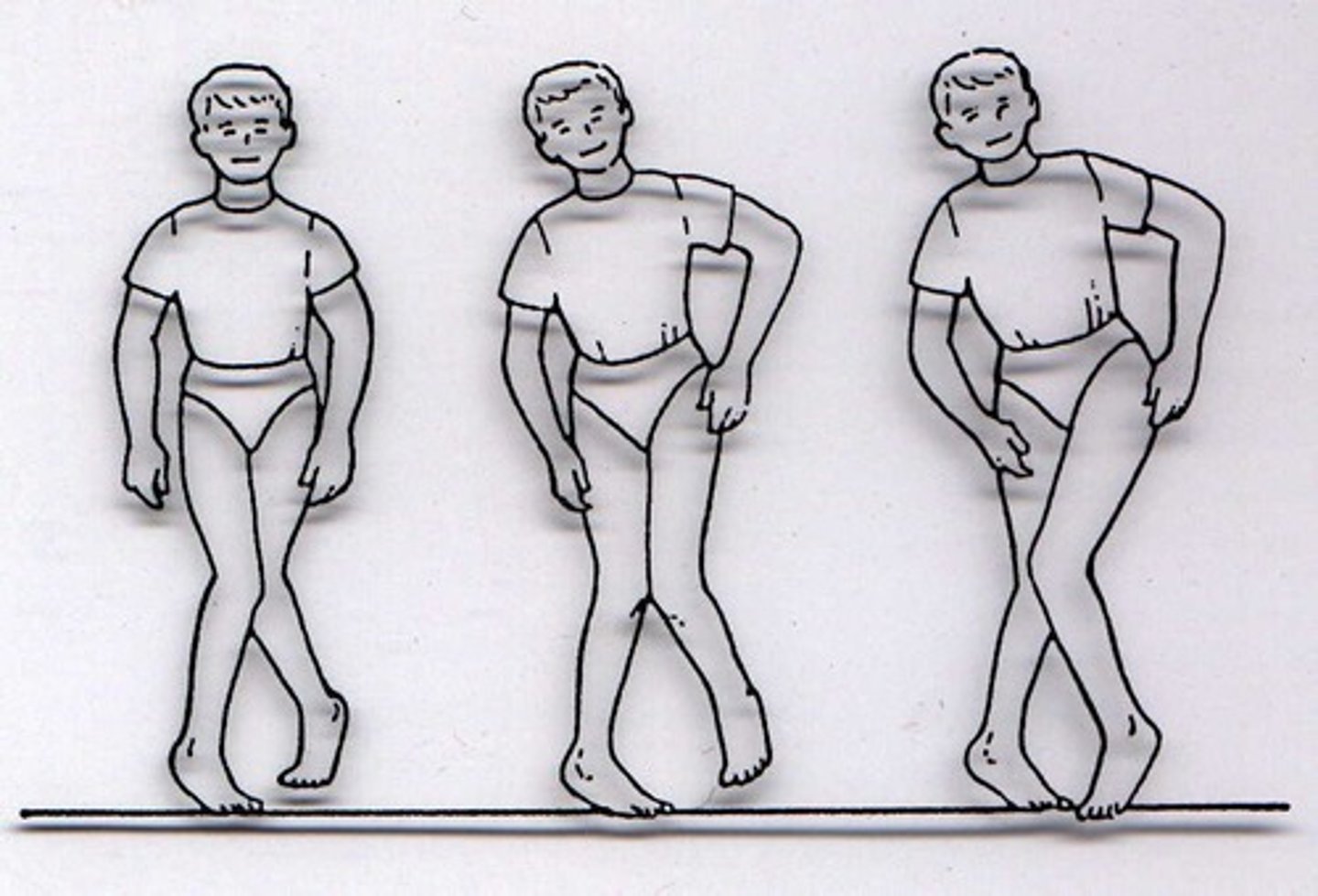
what is a scissoring gait?
the legs cross or meet in a scissors-like motion
- in kids alot of the time
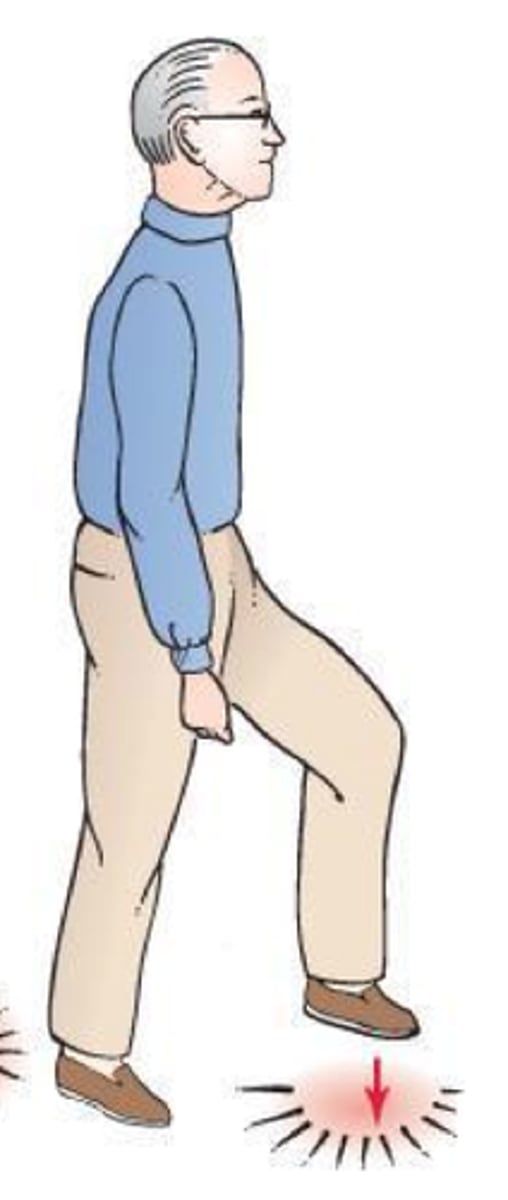
what is a steppage/equine gait?
a high-stepping walk where the foot is lifted excessively at the hip and knee to clear the ground
- horse like
what is a sensory/tabetic gait?
type of unsteady walk, or sensory ataxia, caused by poor proprioception (sense of one's body in space)
- stomping, need to feel the ground because they dont know where it is
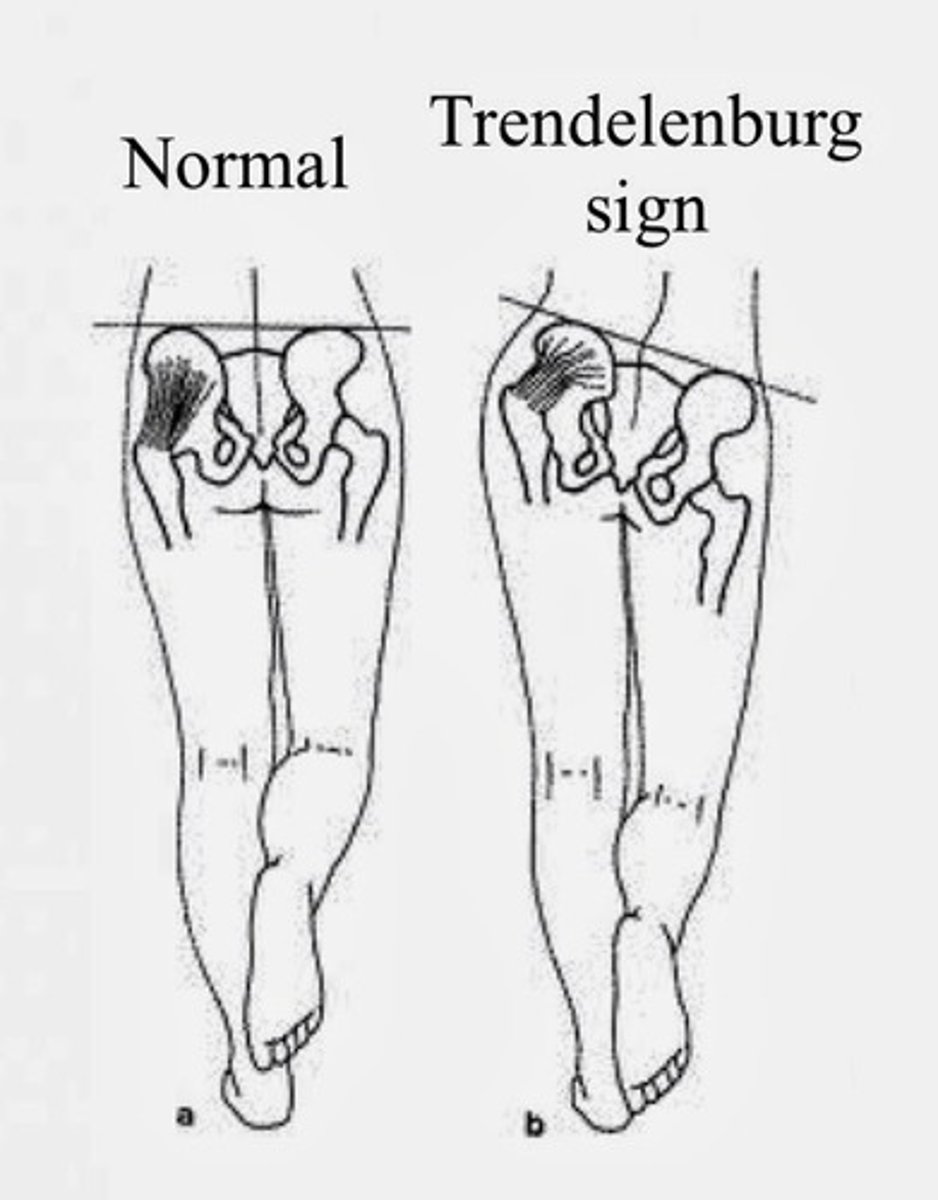
what is a trendelenburg gait?
pelvis drops on the side opposite to the leg that is bearing weight, resulting in a waddling or lurching motion
what is a vaulting gait?
rising up on the toes of the stance leg to create extra clearance for the swing leg
4 main categories to assess according to moss-magee
1. knee stance stability
2. trunk upright
3. limb advancement
4. dynamic balance
according to moss-magee, what do you want to reduce?
compensatory strategies (bracing and AD)
if assistance is needed during gait, what 3 things does moss-magee say
- providing it yourself allows you to grade
- can modify to determine response
- when assessing one aspect of walking, try to compensate for other aspects, but NOT the one being assessed
treatment planning according to moss-magee
- IF my patient has a deficit in a particular aspect of walking... THEN, I need to facilitate PRACTICE WALKING
- MUST have an appropriate level to challenge that particular aspect of walking with appropriate feedback, intensity, dosage
what are 4 other key components of walking?
1. stance control
2. limb advancement
3. propulsion
4. postural stability
goals during gait assessment
- safety first!
- measurable and relatable
math for gait