aortic regurgitation and stenosis
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
predominate AS
80% have coexisting AR (dilated AoV Annulus, Bicuspid/Congenitally Malformed AoV or Endocarditis)
Congenital Leaflet Abnormalities causing AR
AoV is Unicuspid, Bicuspid, Quadracuspid or has a VSD
Acquired Leaflet Abnormalities causing AR
Senile Calcification, Infective Endocarditis, Rheumatic D or Radiation/toxin Induced Valvulopathy
Congenital/Genetic Aortic Root Abnormalities causing AR
Annuloaortic ectasia (enlarged/dilated ascending Ao) or Connective Tissue D
Acquired Aortic Root Abnormalities causing AR
idiopathic aortic root dilation, Aortic Dissection, systemic HTN, Autoimmune D or Aortitis (Syphilitic or Takayasus)
type 1 AR
NORMAL CUSP MOTION with cusp perforation or aortic dilation (STJ enlargement/dilation or SoVA dilation)
dec coronary flow causes
venturi effect (inc velocity but dec P) and inc intramyocardial P
AR causes
dec aortic elasticity/compliance, inc stroke work/wall stress (also from inc LV vol) and inc LV stiffness (LVH)
inc stroke work/wall stress causes
fibrosis
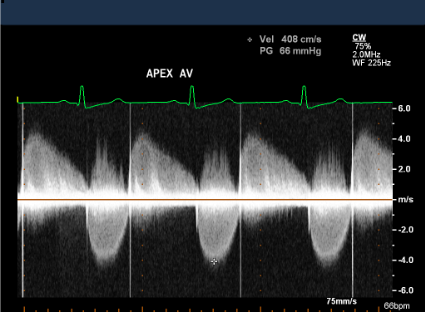
Severe AR PHT
PHT <200 is severe AR
what to look for in AR
Inc Transaortic Flow Velocity, AR Deceleration Slope Signal (PHT) and flow reversal in the Abdominal aorta/Descending thoracic aorta
severe AR jet width
jet width >65% of the LVOT is severe AR
jet width/lvot diameter limitations
underestimates AR eccentric jets but overestimates AR central/transient jets and is affected by LVOT size
severe AR vena contracta width
VC >0.6 is severe AR
jet area/lvot area pitfalls
direction/shape of the jet can over/under estimate the jet area
VC pitfalls
doesnt work with multiple jets or a bicuspid AoV
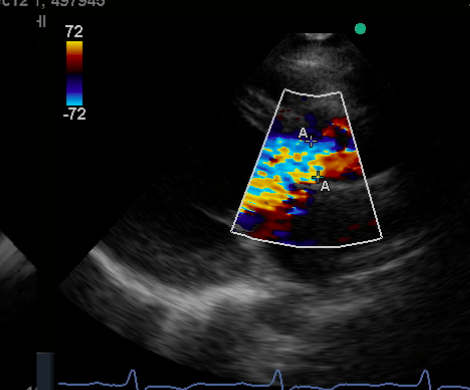
a to a
vena contracta
dilated ascending aorta
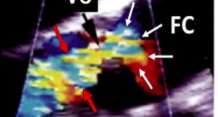
red arrows
jet height
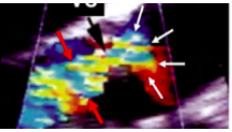
white arrows
flow convergence (FC)
pisa also refers to
flow convergence
normal/Antegrade flow

AR flow
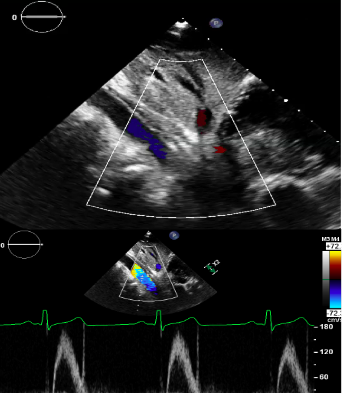
Abdominal Flow Reversal
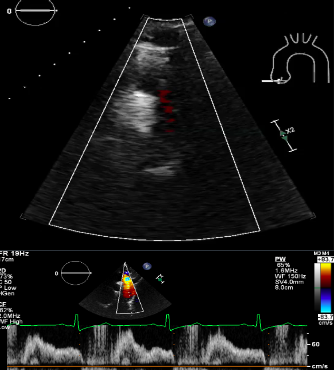
descending Thoracic flow Reversal
Abdominal Flow Reversal
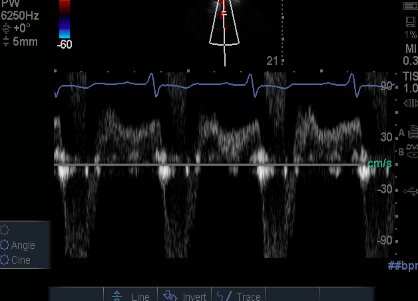
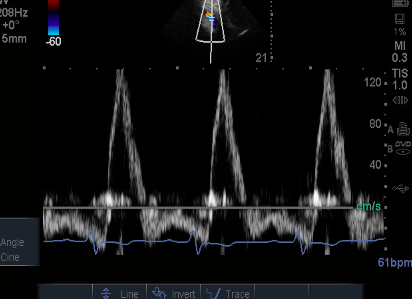
Descending Thoracic Flow Reversal
observe if
LVESDI <20 and LVEF >60%
opperate if
LVESDI >25 and LVEF <55%
mild AR characteristics
normal LV size with small/no flow convergence
Moderate Grade 2 AR
Rvol 30-44, RF 30-39% and EROA 0.1-0.19
Moderate Grade 3 AR
Rvol 45-59, RF 40-49% and EROA 0.2-0.29. if all 3 then severe AR
specific criteria for mild AR
VC width <0.3, central jet width <25% of the LVOT, PHT >500, RVOL <30, RF <30% and EROA <0.1
specific criteria for severe AR
VC width >0.6, central jet width >65% of the LVOT, PHT <200, RVOL >60, RF >50% and EROA >0.3
Severe AR characteristics
flail valve, large flow convergence and an enlarged LV with normal function
Pulse Pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic P
Pulse Pressure AR
wide pulse P in AR and a Bounding/bifid arterial pulse
Pulse Pressure AS
narrow pulse P in AS
Bicuspid Aortic Valve
(PSAX systole) appears football shaped and is domed/tethered. eccentric closure on M Mode
Bicuspid Aortic Valve might have coexisting
aortic coarctation, stenotic dilation or LVH
for AoV peak velocity
use CW pedof
views for peak AoV velocity
AP, subcostal, ssn, RCL and RPS
AVA
depends on LVOT^2 so a large LVOT measurement can underestimate AS
Peak Pressure Gradient
Peak PG is the same as the Peak Instantaneous Gradient
Mean Pressure Gradient correlates with
Mean PG correlates with Cath Peak to Peak Gradient
VTI
Velocity Time Integral
VTI is good for
patients with poor LV function or who have moderate to severe AI
in VTI
trace the waveform
Dimensionless Index (DI)
ratio of LVOT and AS velocities or VTI
use DI for when
LVOT diameter cant be accurately measured or if LV dysfunction is present
Aortic Stenosis in the Cath Lab
peak instantaneous P is obtained with Doppler and echo gradients are usually higher than cath gradients
AR murmur
Diastolic blowing murmur thats high pitched at the
left sternal border (LSB)
AR symptoms
CHF, DOE, angina and syncope
Severe acute AR
causes premature MV closure FROM ELEVATED LVEDP
AR can cause
PRE SYSTOLIC OPENING of the aortic leaflets and HYPERDYNAMIC (for acute) or HYPODYNAMIC (for chronic) LV contractility
TEE
TEE is best for diagnosing aortic dissection
AR can also cause
LV dilation
Ao P ½ Time
time it takes for the initial AoV PG (during diastole) to dec by half
PHT grading
steeper waveform = more severe