NURS271 - Endocrine Problems
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
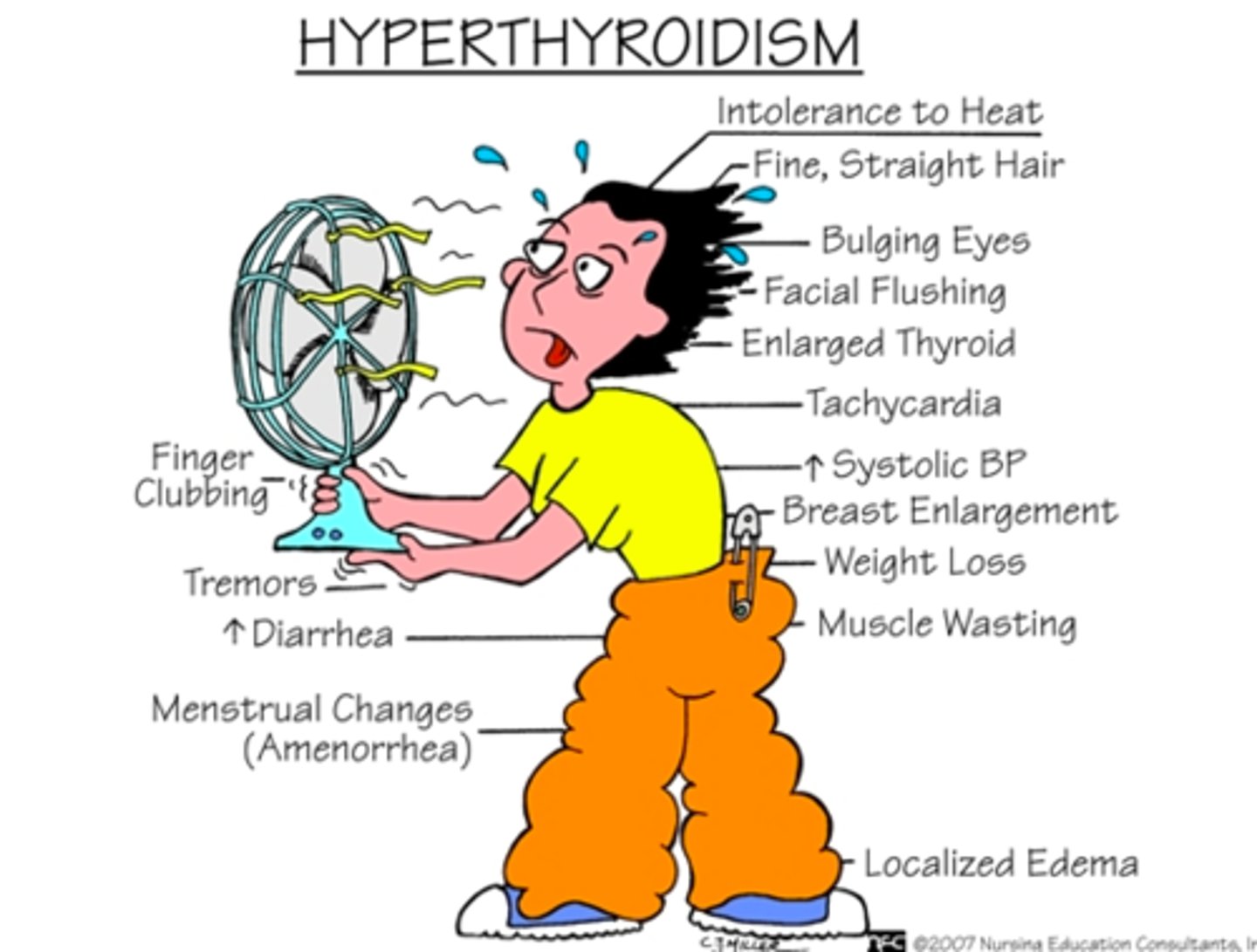
hyperthyroidism
- the production and release of excess thyroid hormones
> T3/Triiodothyronine and T4/Thyroxine
- cause: antibodies stimulate thyroid receptors on gland which decreases TSH, increases T3 and T4
- s/sx: everything is sped up, increased metabolism, increased HR and BP, insulin resistance, resp dysfunction, goiter
graves disease
- autoimmune disorder, most common form of hyperthyroidism
- cause unknown, but likely genetic link
T3 and T4
- controls metabolism
- excessive production in hyperthyroidism
- lack of production in hypothyroidism
thyroid hormones overview
-TRH/Thyroid Releasing Hormone
- TSH/Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
- T3/Triiodothyronine
- T4/Thyroxine
- hypothalamus produces TRH → anterior pituitary gland produces TSH → thyroid gland produces T3/T4
> controls metabolism, excessive production in hyperthyroidism and vice versa
thyrotoxicosis (thyroid storm)
- complication of hyperthyroidism, only occurs if hyperthyroidism is not treated properly
- rare sudden worsening of s/sx due to trauma, stress, and manipulation of the thyroid gland itself during surgery
hyperthyroidism/thyrotoxicosis (thyroid storm) s/sx
- tachycardia (HR>200), problematic d/t decreased blood perfusion
- hypertension
- heat intolerance (hallmark), due to increased T4
- exophthalmos (bulging eyeballs)
- diarrhea d/t sped up digestion
- fever d/t heat intolerance
somatotropin (STH)
- growth hormone
- secreted by the anterior pituitary gland
pathophysiology of hyperthyroidism
- types: primary, secondary, tertiary
- thyroid produces T3//T4 (primary)
- pituitary gland produces TSH (secondary)
- hypothalamus produces TRH (tertiary)
primary hyperthyroidism
problem stems from a dysfunctional thyroid gland, increases antibodies trick the thyroid/nodule on gland to increase T3 and T4 secretion
secondary hyperthyroidism
problem stems from an issue with the pituitary gland (such as a tumor on the gland) which causes an increase in TSH and the thyroid gland producing excess T3 and T4
tertiary hyperthyroidism
problem stems from an issue/dysfunction with the hypothalamus, causing an increase in TRH → increased TSH → increased T3 and T4
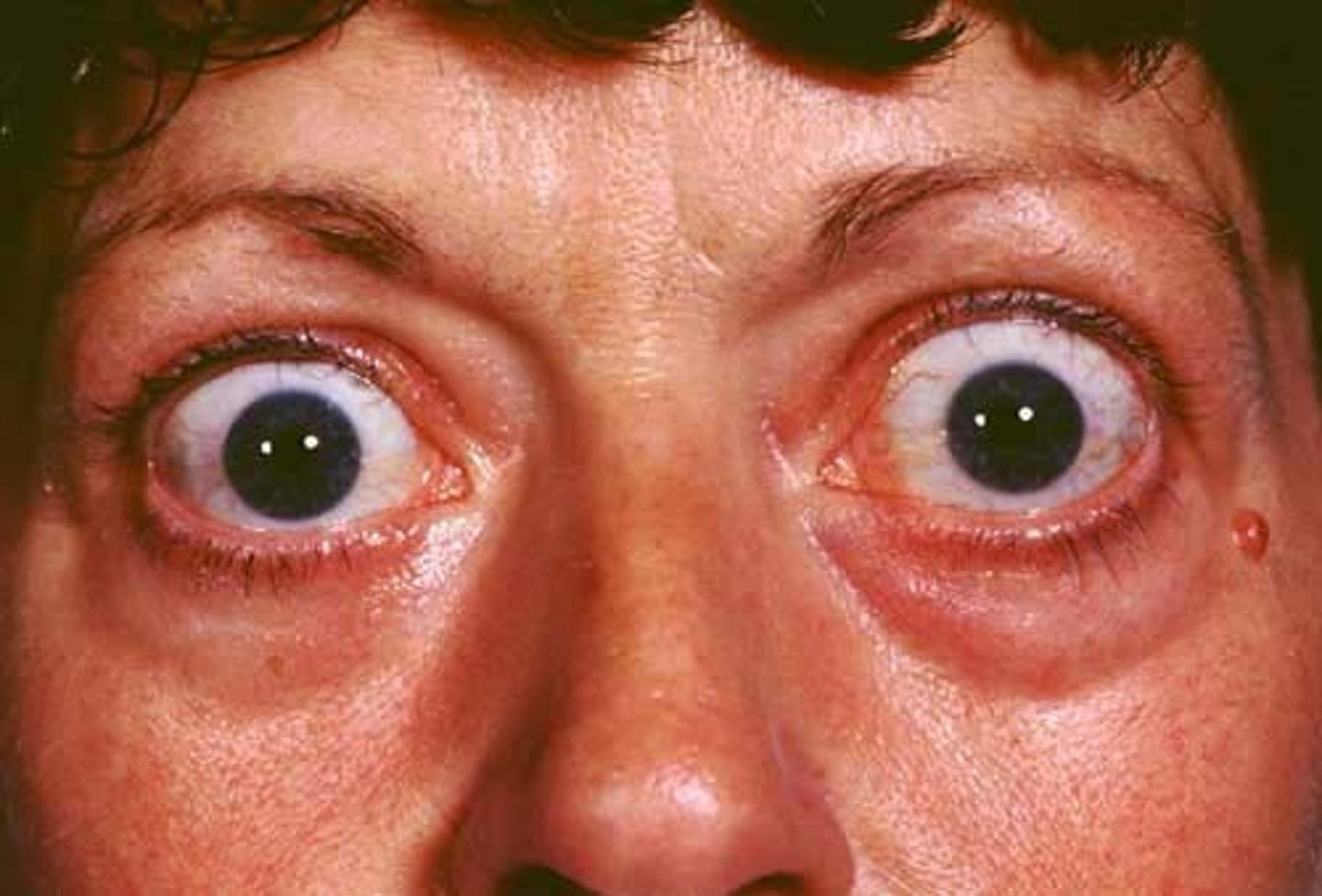
exophthalmos
- caused by edema and accumulation of fatty tissue causing abnormal protrusion of the eyeballs
> common with Graves Disease
- those with it can not see it
- pts may complain of blurred vision, diplopia (double vision), eye pain, photophobia (sensitivity to light), dry eyes, lid lag
lid lag
- the eyelids stay open when a person looks down
- associated with hyperthyroidism
photophobia
eye sensitivity to light
pharmacological tx of hyperthyroidism
- propylthiouracil (PTU) or methimazole (tapazole)
> anti-thyroid drugs
- radioactive iodine therapy
> preferred treatment
> oral intake of radioactive iodine which damages the cells absorb the ioding which damages the cells
- beta-adrenergic blocking drugs (same as beta blockers)
> propranolol (non-selective)
> metoprolol (cardio-selective)
propylthiouracil (PTU) or methimazole (tapazole)
- anti-thyroid drugs to treat hyperthyroidism
- decreases thyroid hormone production
- takes 6-12 weeks to work, taken for >1 yr to correct problem
radioactive iodine therapy
- preferred treatment for hyperthyroidism
- oral intake of radioactive iodine which damages the cells absorb the ioding which damages the cells
> destroys thyroid tissue → decreases T3 and T4
> too much leads to hypothyroidism
> takes 6 months to see affects, Dr monitors levels periodically
beta-adrenergic blocking drugs
- tx for hyperthyroidism
- same as beta blockers
> propranolol (non-selective → can cause bronchoconstriction and decreased RR)
> metoprolol (cardio-selective)
- look at the pts hx to choose correct beta blocker
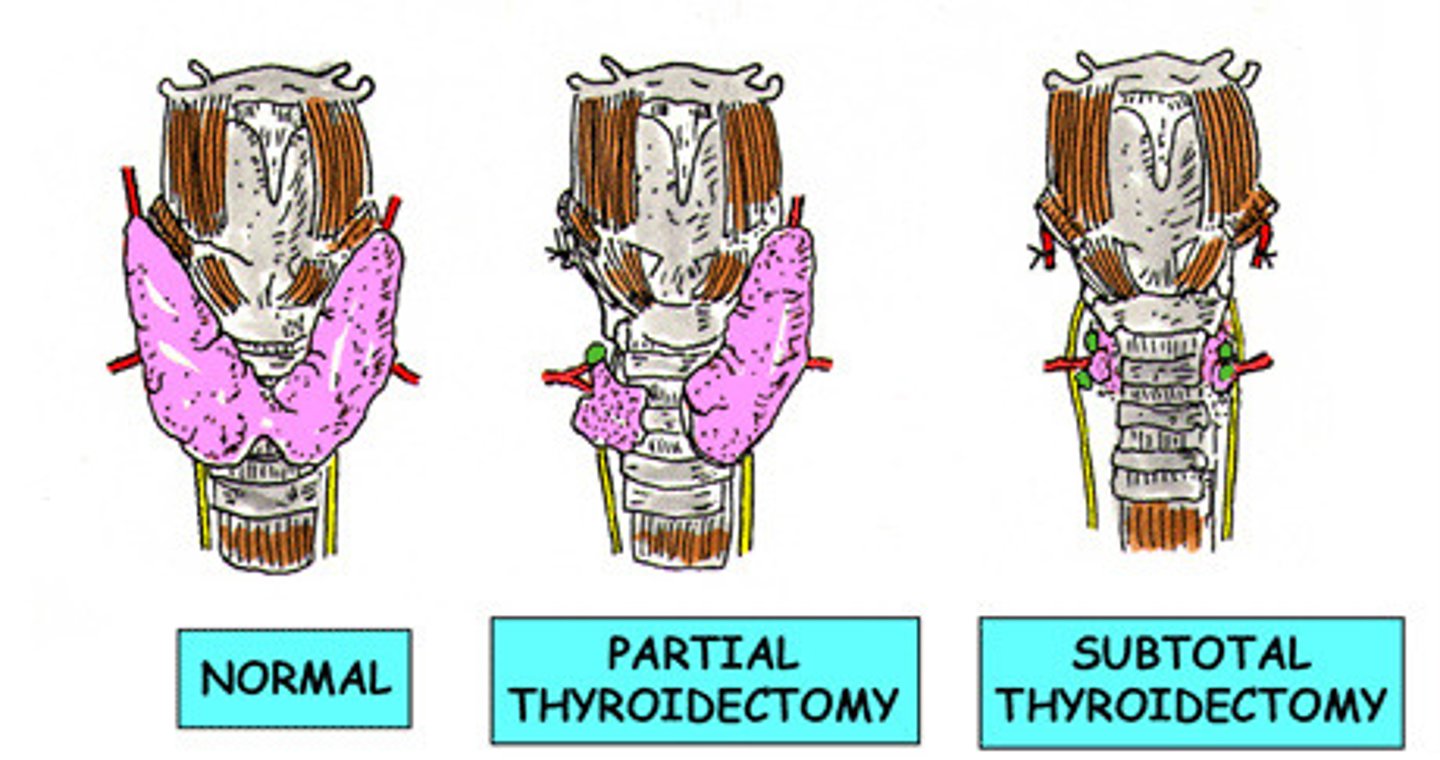
surgical tx for hyperthyroidism
- partial or total thyroidectomy
> total only done if large nodules or thyroid cancer
> may cause hypothyroidism which requires lifelong tx of levothyroxine
- removes part of gland to decrease thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion
> only done if drug tx does not work
hypothyroidism
- extremely decreased production of thyroid hormones
- cause: dysfunctional thyroid, malnutrition (decreased iodine or tyrosine consumption), or thyroidectomy which increases TSH, decreases T3 and T4
- s/sx: decreased metabolism, everything slows down, goiter
- hashimoto thyroiditis, myxedema, myxedema coma
- more common in women, risk increases w/ age
hashimoto thyroiditis (autoimmune thyroiditis)
- most common type of primary hypothyroidism
- immune system attacks the thyroid gland → fibrous tissue grows → inflammation and reduced thyroid hormone production (decreased T3 and T4) → hypothyroidism
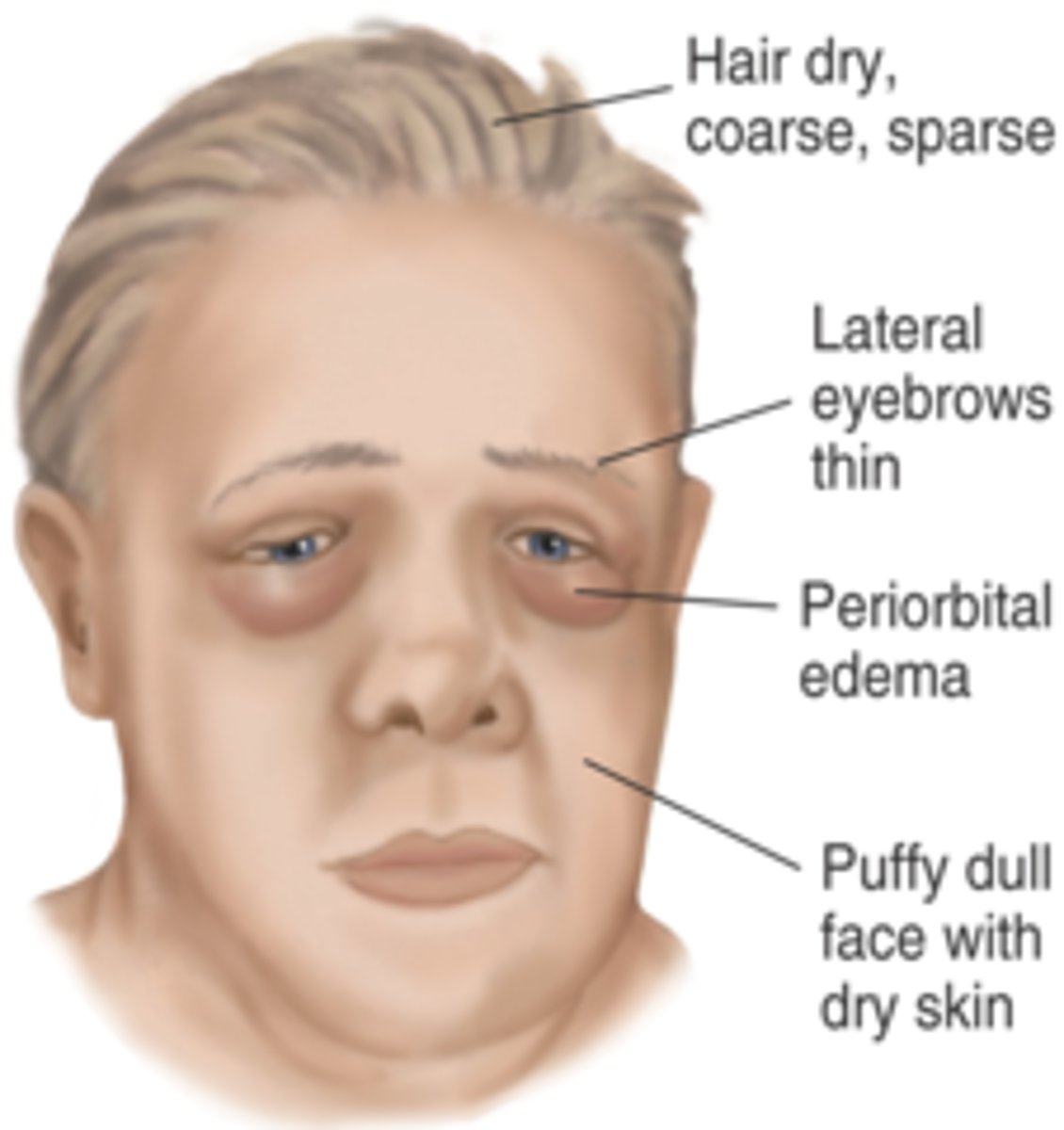
myxedema
- mucus, fluid, and protein build up in the skin and organs due to extreme hypothyroidism
- rare and life threatening
myxedema coma
- rare/extreme complication of hypothyroidism when it is poorly or completely untreated
> triggered by illness or trauma
- decreased cardiac output → decreased tissue perfusion → brain and organ depletion → multi-organ failure → death
goiter
- enlargement of the thyroid gland due to abnormality
> most common cause: iodine deficiency
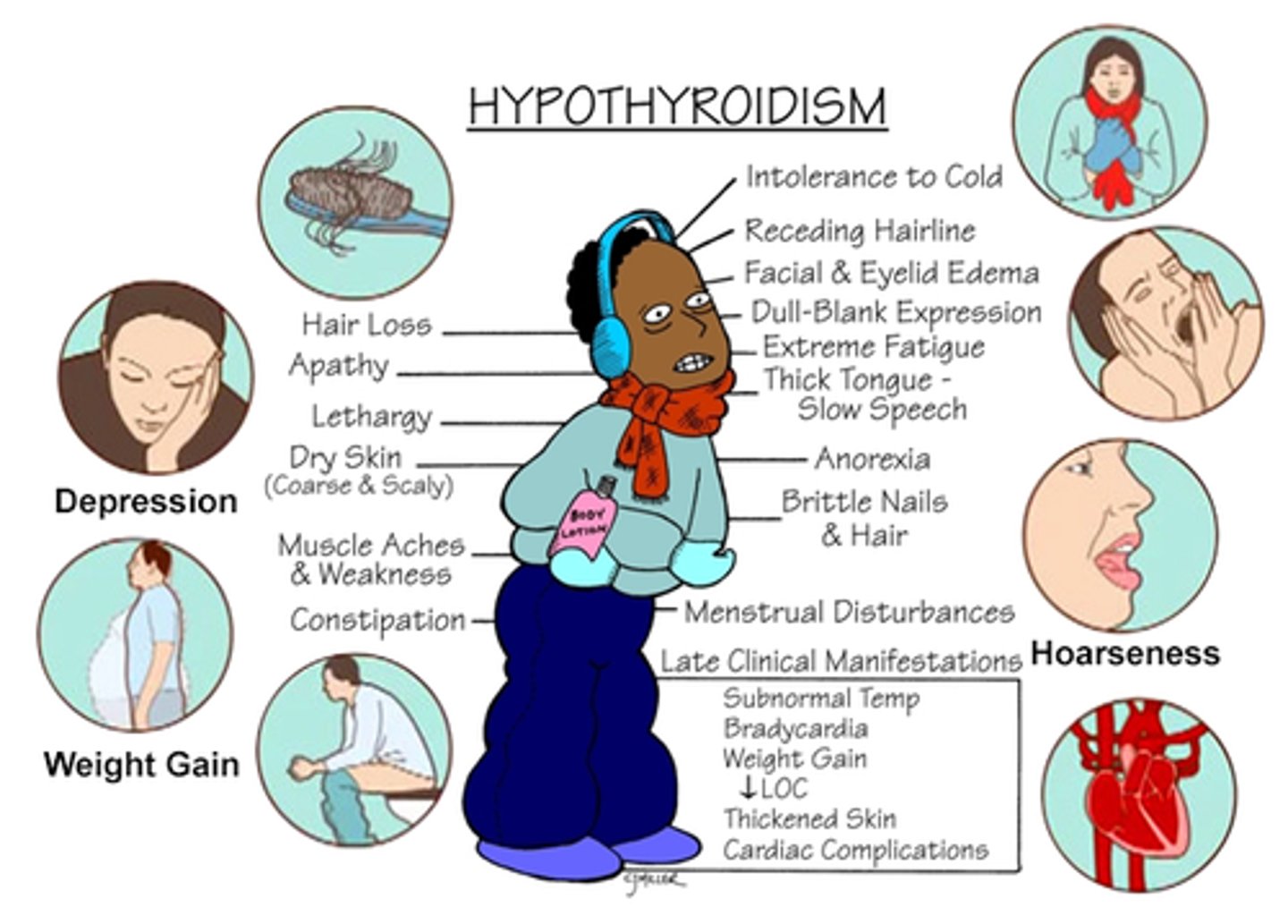
hypothyroidism s/sx
- decreased metabolism
- cold intolerance
- extreme fatigue (hallmark)
- constipation
- bradycardia
- weight gain
- mental challenges/deficiencies
- decreased growth
pharmacological tx of hypothyroidism
- levothyroxine (synthroid)
> one pill for the rest of your life
> best taken in the morning on an empty stomach
levothyroxine (synthroid) side effects
- decreases the ability of insulin or anti-diabetic meds to function in pts w/ diabetes
> dosage of insulin or anti-diabetic rugs may need to be adjusted
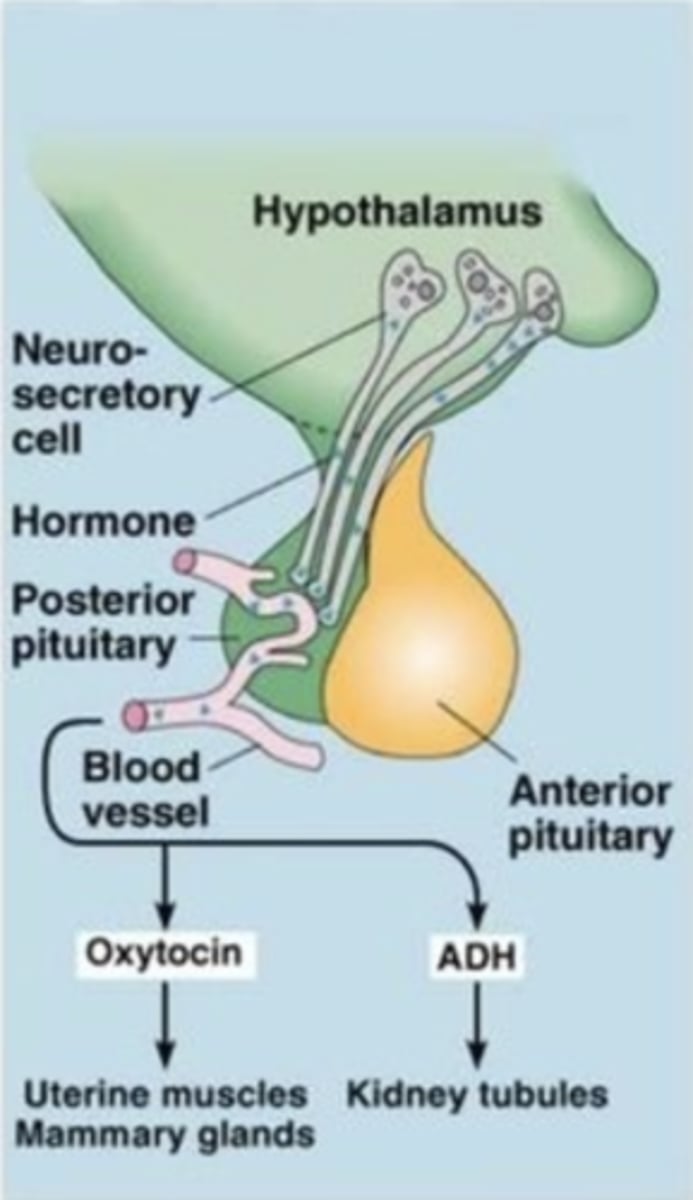
hypothalamus
- a neural structure lying below the thalamus
- directs eating, drinking, body temperature, and is linked to emotion
- controls the pituitary gland through hormones secreted by neurosecretory cells
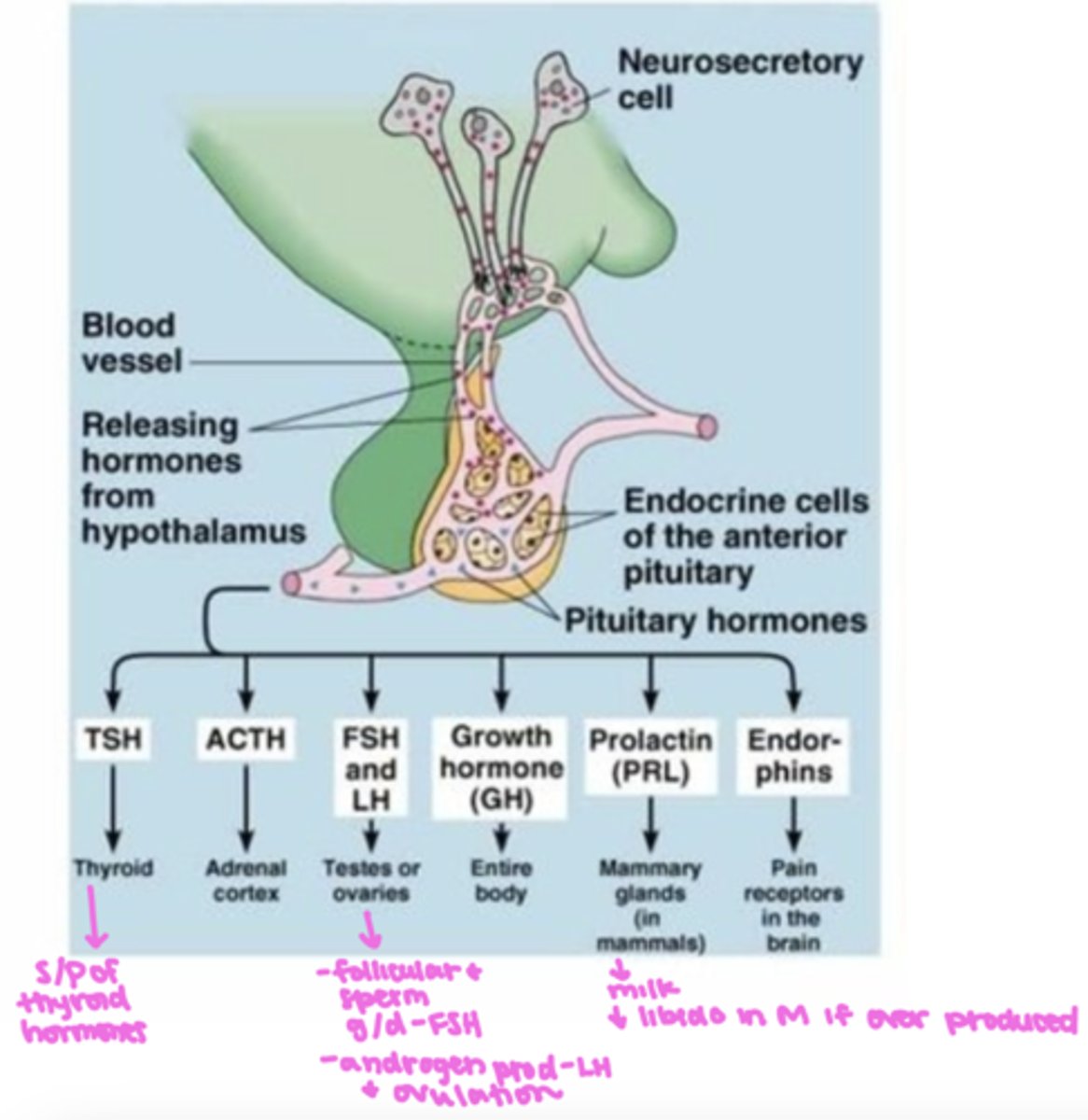
anterior pituitary gland
- an endocrine gland whose secretions are controlled by hypothalamic hormones
- secretes six different hormones: TSH, ACTH, FSH/LH, Growth hormone (GH), Prolactin (PRL), endorphins
anterior pituitary gland disorders
- primary pituitary dysfunction
- secondary pituitary dysfunction
- pituitary hypofunction
- pituitary hyperfunction
primary pituitary dysfunction
problems with the anterior pituitary gland itself
secondary pituitary dysfunction
problem with the hypothalamus that causes anterior pituitary gland dysfunction
pituitary hypofunction
- decreased secretion and production of anterior pituitary gland hormones
- can be caused by trauma, circulatory disturbances, congenital malformations, or tumors
- tx: hormone replacement therapy
pituitary hyperfunction
- excessive secretion and production of anterior pituitary gland hormones
- often presents as acromegaly or gigantism
cause of hypopituitarism
- benign or malignant tumors compress and destroy pituitary tissue
- anorexia nervosa → malnourished → rapid tissue loss
- shock or severe hypertension → decreased blood flow to PG → hypoxia → pituitary infarction
- Sheehan's syndrome
- postpartum hemorrhage
Sheehan's syndrome
- hypopituitarism caused by uterine hemorrhage during childbirth
- pituitary gland is unable to function due to blood loss.
patient assessment for hypopituitarism
- M/F s/sx: changes in peripheral vision, vision loss, diplopia, blurred vision, infertility, impotence, headache,stress/irritation
- LH and FSH deficiencies → change/loss of secondary sex characteristics
- Females: amenorrhea, painful sex, difficulty conceiving, decreased hair in armpits
- Males: decreased body hair, impotence, decreased libido
hypopituitarism tx
- replace deficient hormones, lifelong therapy
- androgen (testosterone), decreases LH for M, impacts reproduction for M/F
> preferred route: gel
>> cost effective, convenient, good at stabalizing hormones, libido, mood & energy
acromegaly
- hypersecretion of growth hormone (GH, secreted by APG) after puberty
- most common cause is pituitary adenoma
> tumor grows on APG, causing over secretion of GH
- increase in size of bones in hands and feet, bone deformities, splenomegaly, hypertrophy of skin
- no change in height
- takes years to develop, by the time people notice the damage to organs is already done
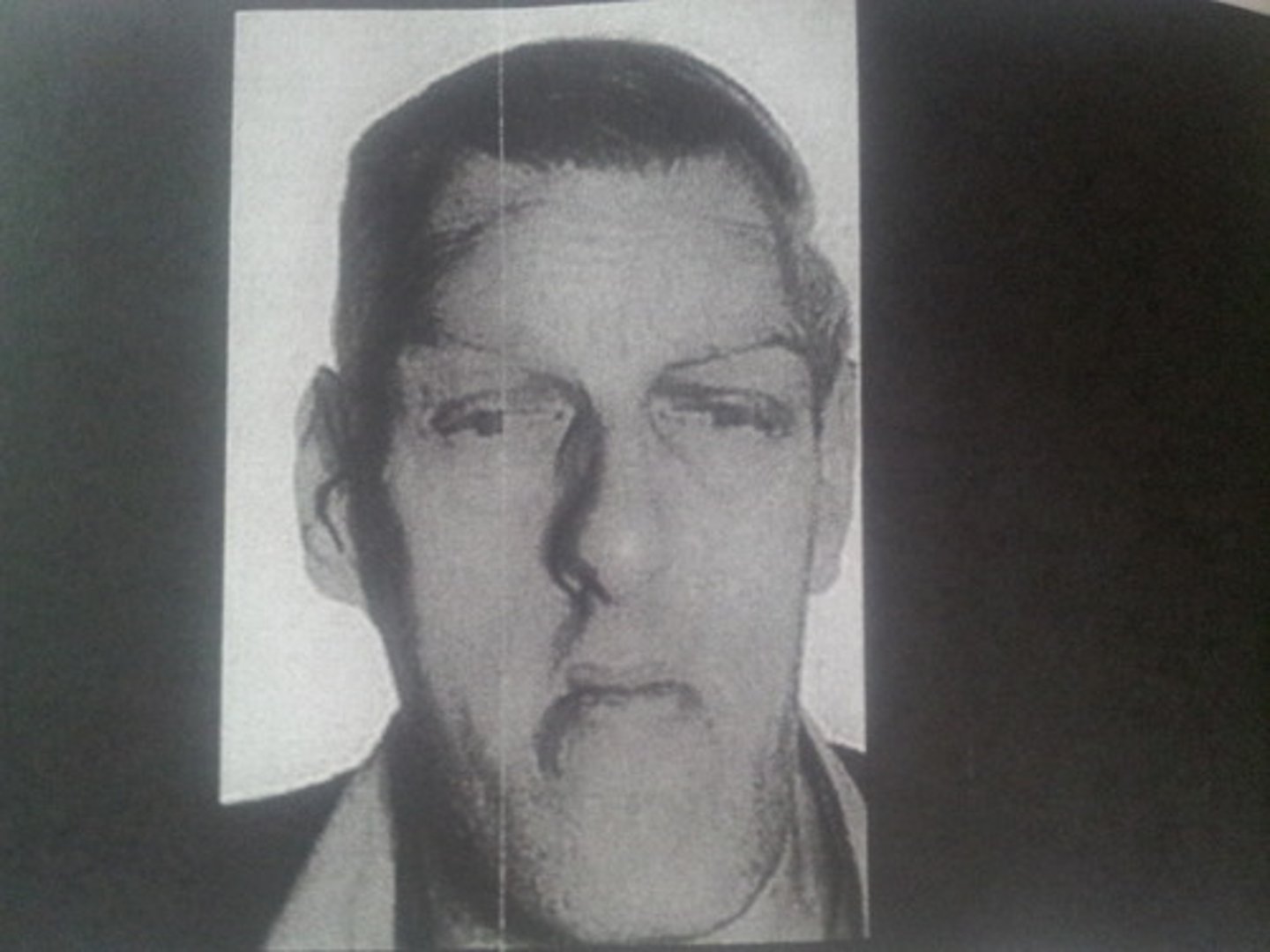
gigantism
hypersecretion of GH from the APG (usually a tumor) before puberty, leading to abnormal overgrowth of body tissues, especially long bones

pituitary tumor drug tx
- dopamine agonist → decrease tumor size
- cabergoline (dostinex)
> preferred tx
> taken 1-2x weekly, longer lasting, better tolerated
- bromocriptine (parlodel)
> more side effects, taken daily
dopamine agonist
- mimic dopamine by binding to D2 receptors on the tumor cells
- decrease prolactin production
- reduce pituitary tumor size
- restore normal gonadal function
preferred pharmacological tx for pituitary tumors?
cabergoline (dostinex)
transsphenoidal adenomectomy (TA)
- removal of a pituitary tumor through the sphenoid sinus
> most common s/sx for women is amenorrhea
- clip off tumor through nose, takes ~45 min
- if tumor is too large → open skull (rare)
- post-anesthesia recovery, post op-unit for a day
postoperative care for TA
- monitor neurologic response
- assess for postnasal drip
> monitor for presence of CSF/halo sign, indicates increased intracranial pressure
- HOB elevated, bed rest
- assess nasal drainage
- avoid bending
- avoid straining
diabetes insipidus (DI)
- damage to the APG or hypothalamus usually d/t tumor or manipulation
- ADH deficiency causes H2O metabolism problem → renal tubules can't reabsorb any water → large amts of urine secreted (polyuria) → rapid dehydration
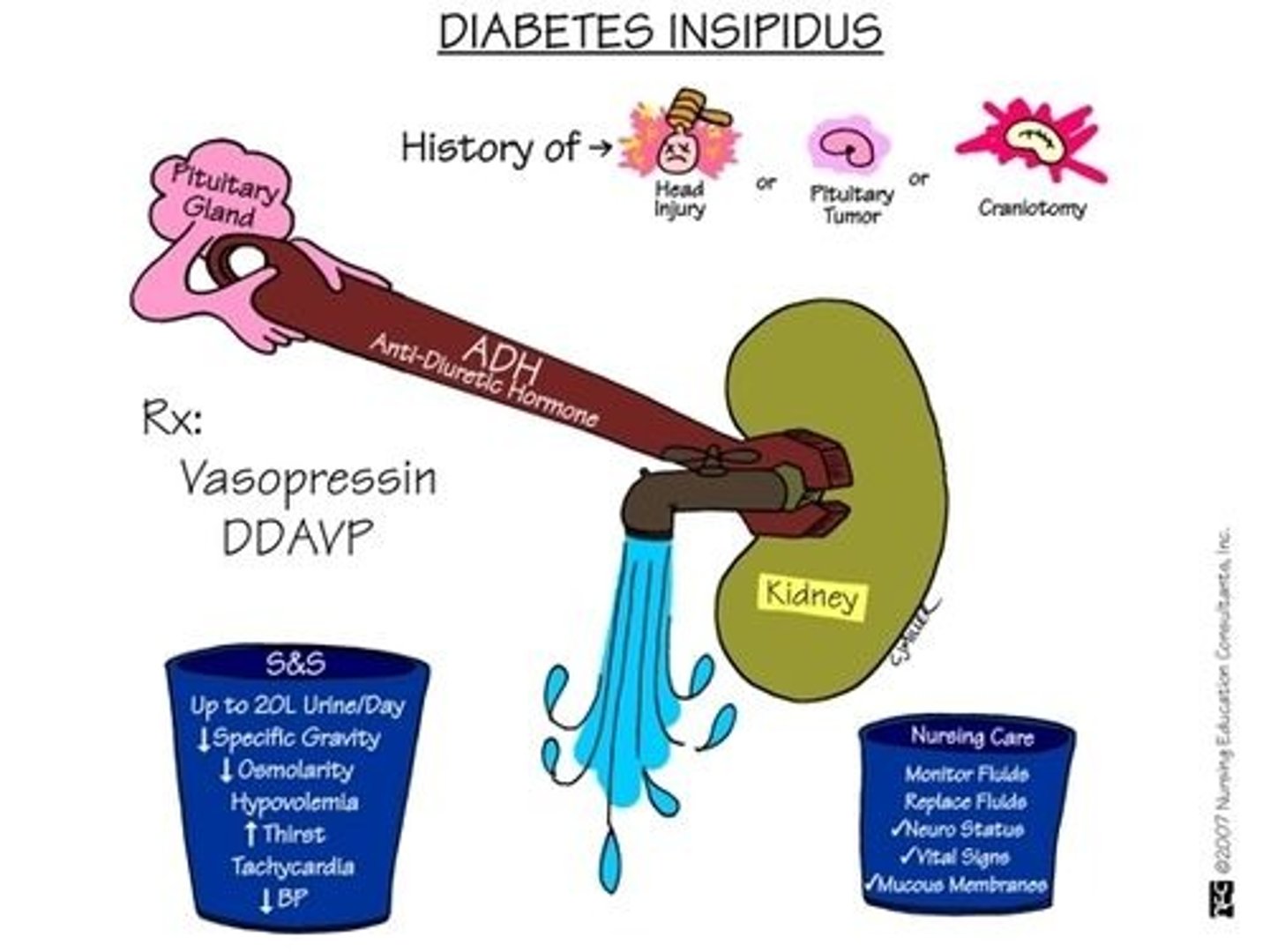
DI drug tx
- desmopressin acetate (DDAVP)
- replaces vasopressin, works w/in an hour
- can be given PO, nasal, or IV
vasopressin
hormone normally produced in body to help balance amount of water and salt
diabetes insipidus s/sx
- DRY INSIDE
- up to 20L urine/day
- decreased specific gravity
- decreased osmolarity
- hypovolemia
- increased thirst
- tachycardia
- decreased BP
- edema, jugular distention, increased weight
- neurological issues, confusion, disorientation
syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
- over secretion of ADH/vasopressin, even when plasma osmolarity is low or normal
- feedback mechanisms do not function properly
- water is retained, resulting in hyponatremia
> dilutional hyponatremia
- soaked inside
causes of SIADH
- heart failure
- diseased hypothalamus
- lung cancers
- pneumonia
- tuberculosis
SIADH nursing interventions
- fluid restriction
- furosemide (lasix), loop diuretics to excrete water with solvents, NOT free water
- 3%NS, hypertonic saline to increase Na
- drug tx: vaptans
vaptans
- tolvaptan (samsca)
- vasopressin antagonist
> block V2 receptors and prevents vasopressin from exerting its effect
> blocks water reabsorption
> increases free water excretion
> results in increased serum concentration correcting hyponatremia