Oral Radio
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
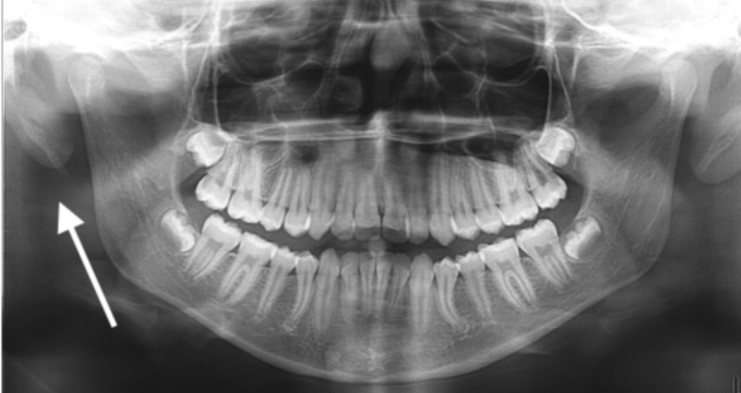
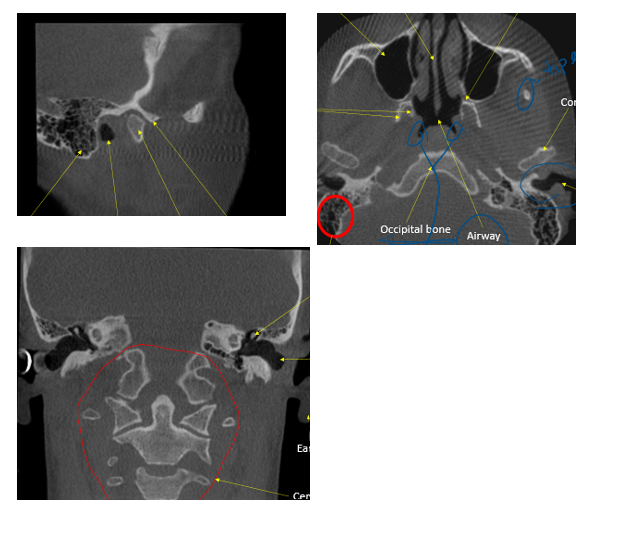
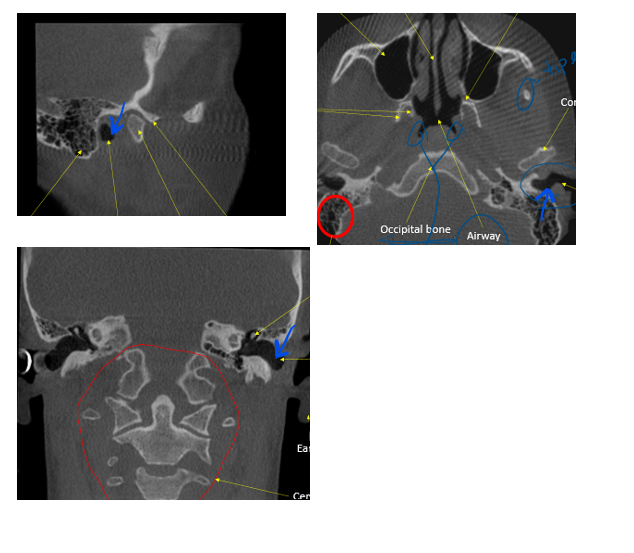
ear

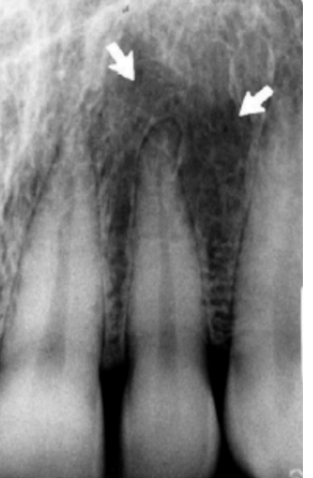
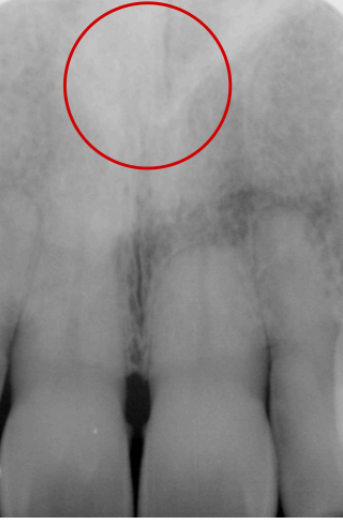
in the circle, indicated by the arrow
styloid process
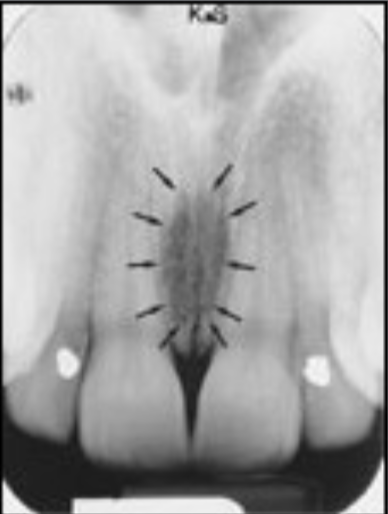
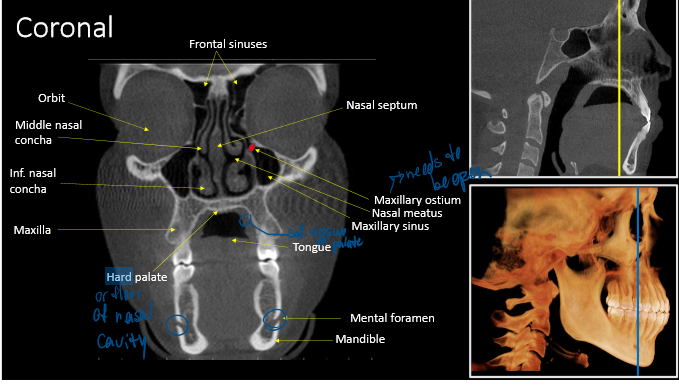
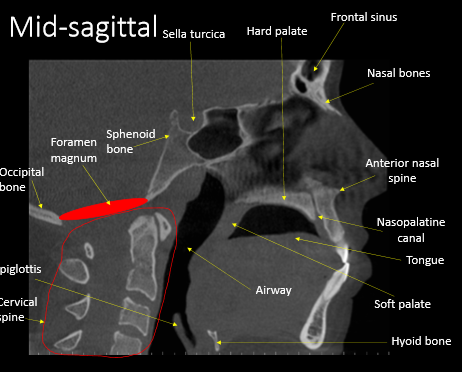
anterior nasal spine
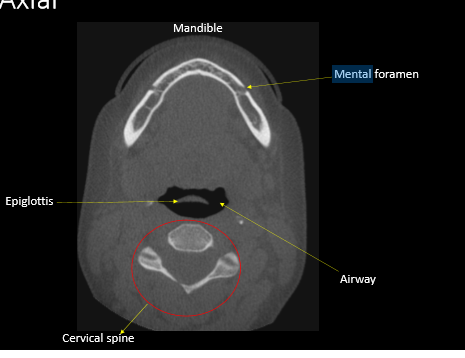
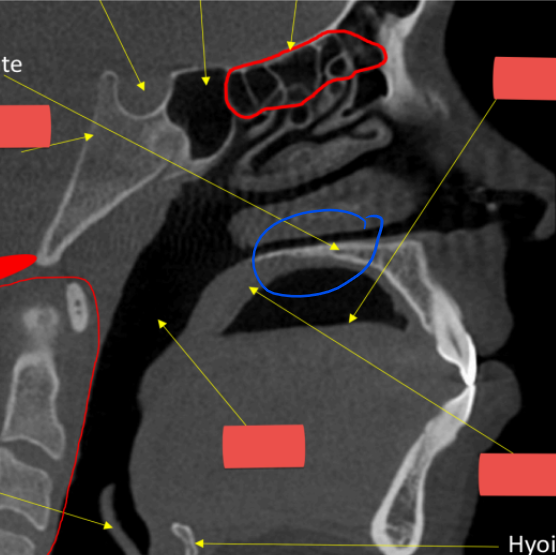
epiglottis
soft palate
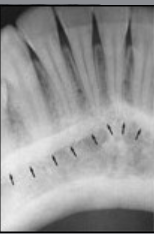
mental ridge
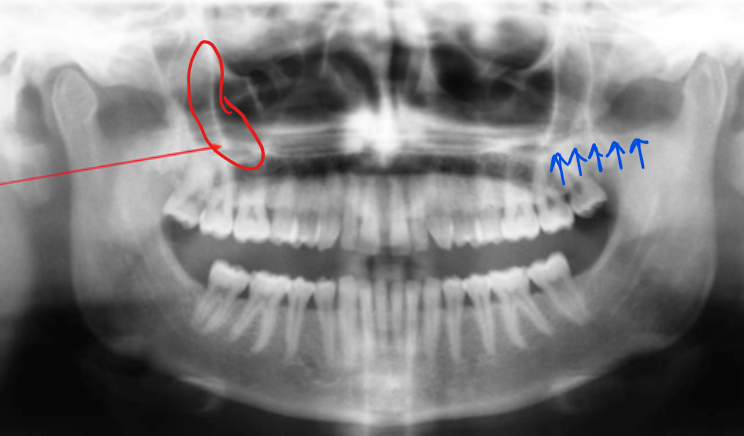
red - zygomatic process of maxilla
blue - zygoma
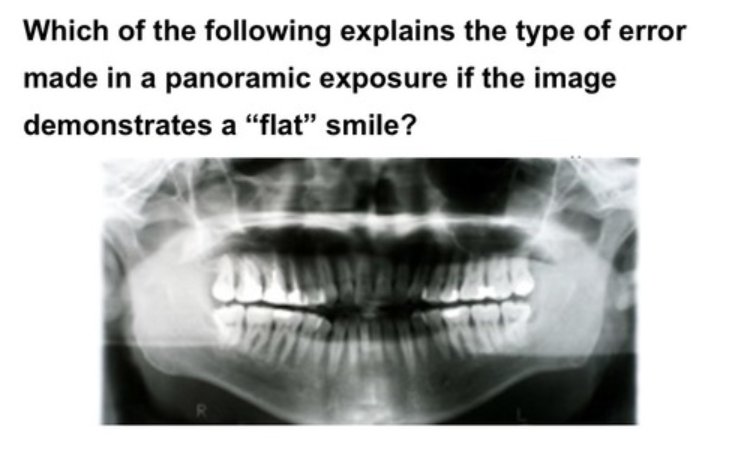
chin up (flat smile, hard palate superimposed)
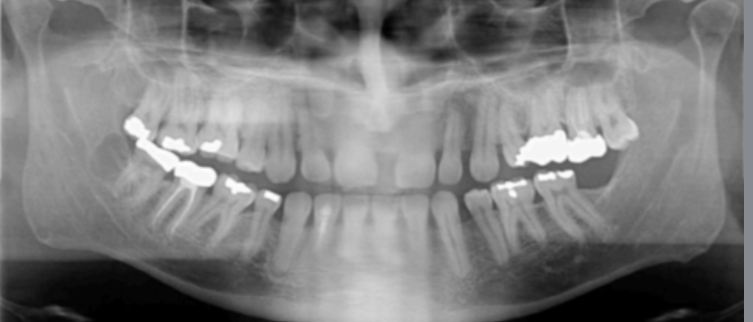
error
Pt too far backward (anteriors are wide/blur, turbinates and meati span across max sinus, condyles thin and on edge of xray)
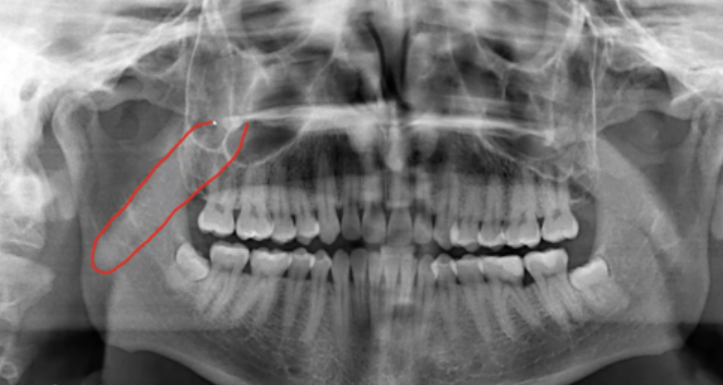
place pin on r or l condyle

ID external auditory meatus
Object between source & center of rotation. What typ eof image would this show?
a. Ghost
b. Double
ghost
Radiation weight factor =
equivalent dose ((used to compare biologic effects of various types of radiation))
effective dose definition
modified by biologic tissue weight factor

hyoid
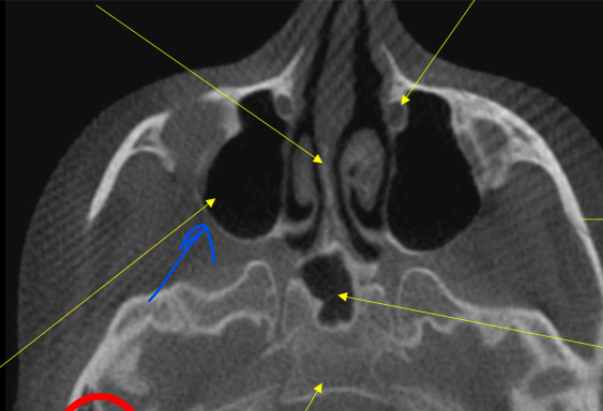
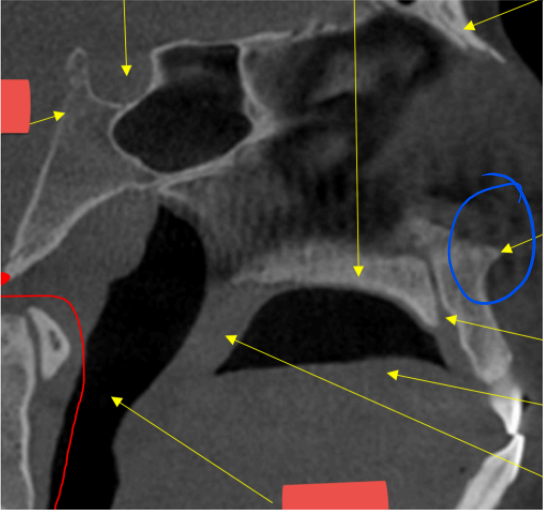
r. max sinus
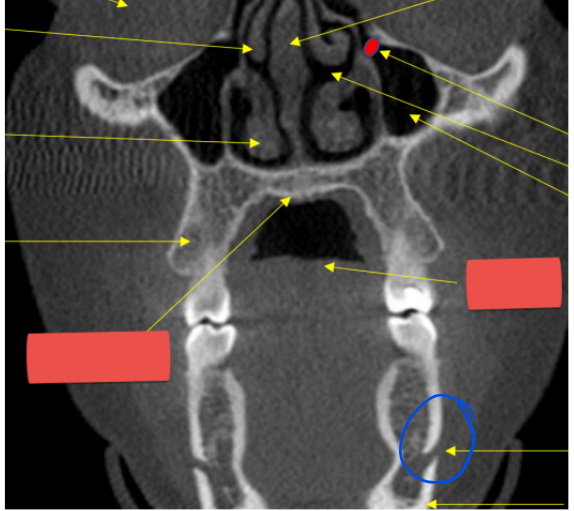
mental foramen
hard palate
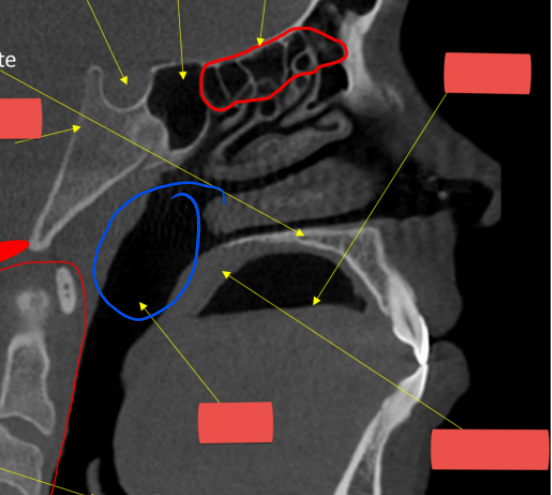
airway
anterior nasal spine
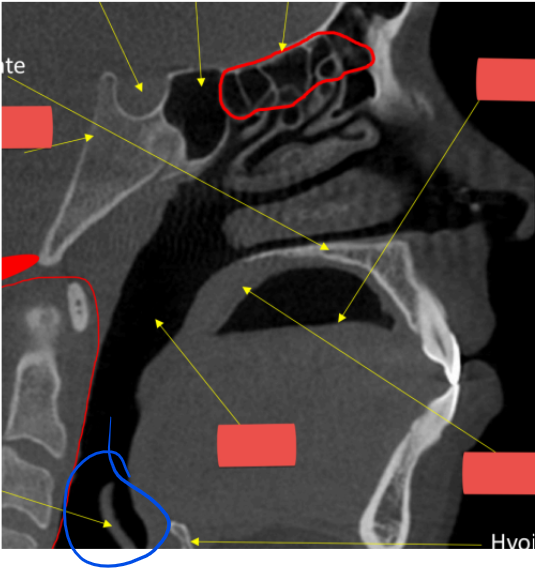
epiglottis
lateral fossa
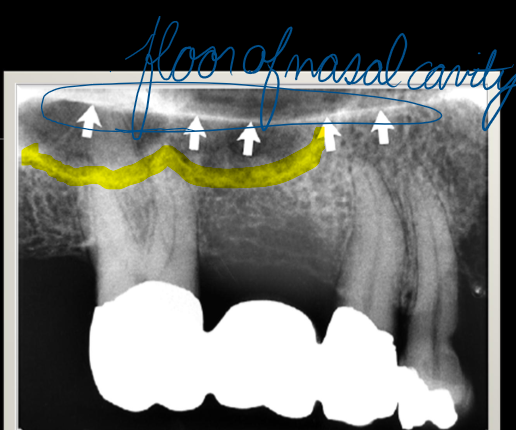
highlight
maxillary sinus
anterior nasal spine
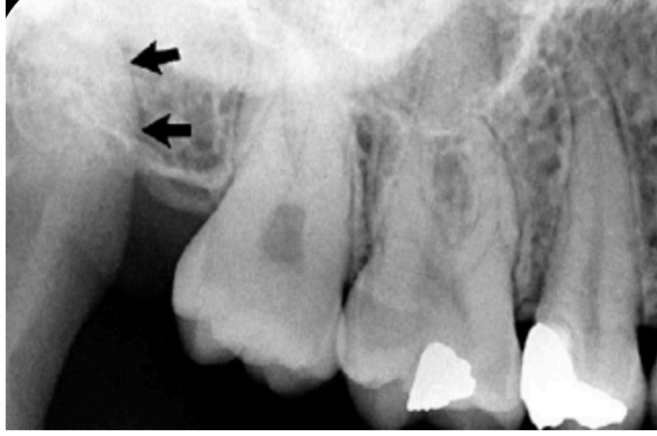
coronoid process
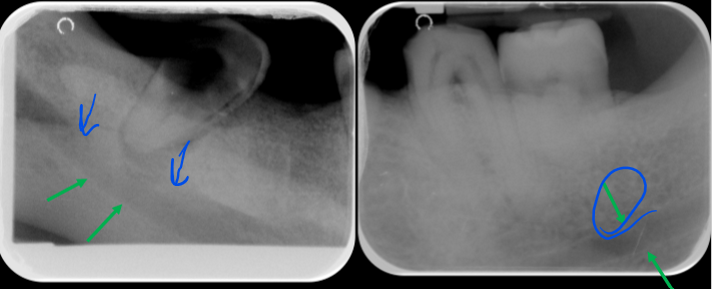
blue
superior cortical border of mandibular canal
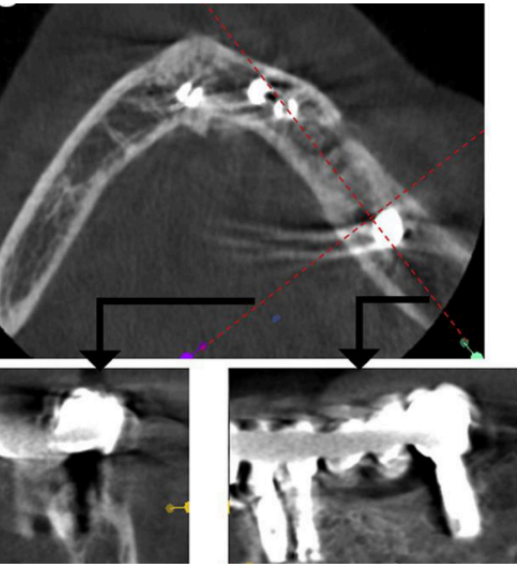
what does this show
beam hardening
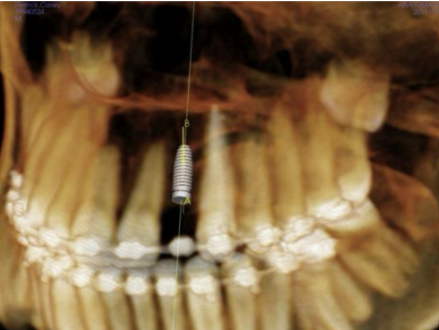
what is this showing for the CBCT
volumetric rendering
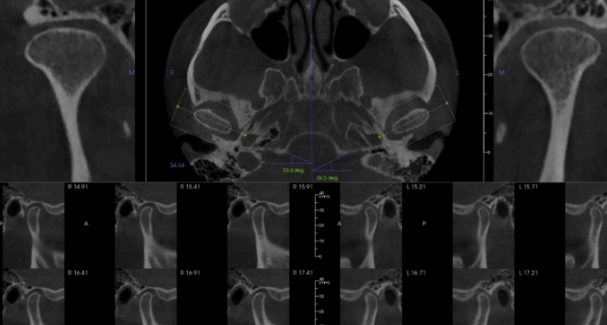
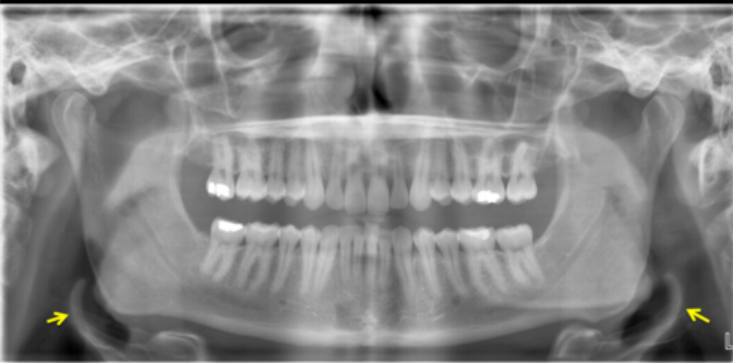
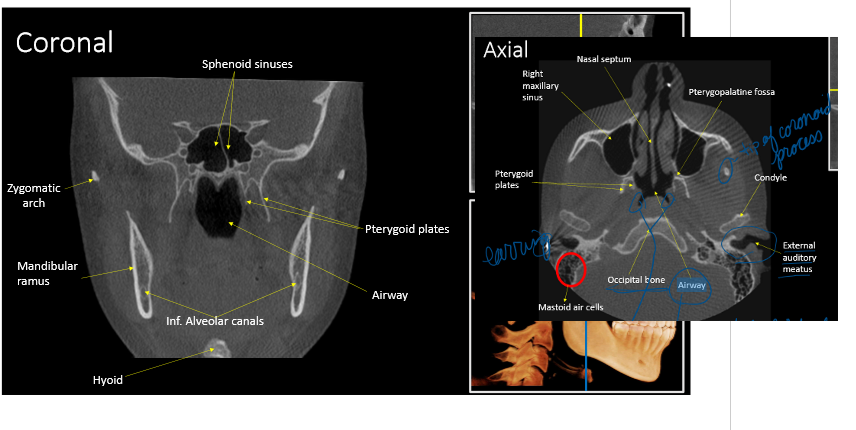
bilateral view of TMJ
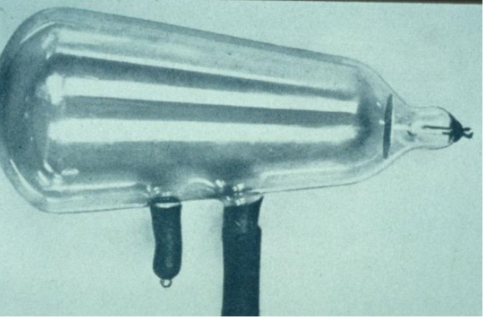
cathode ray bulb
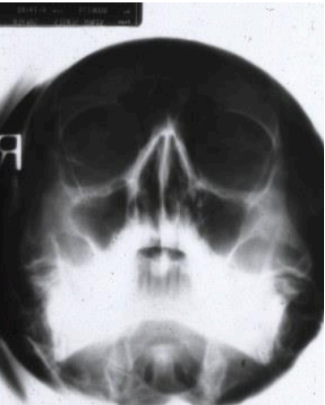
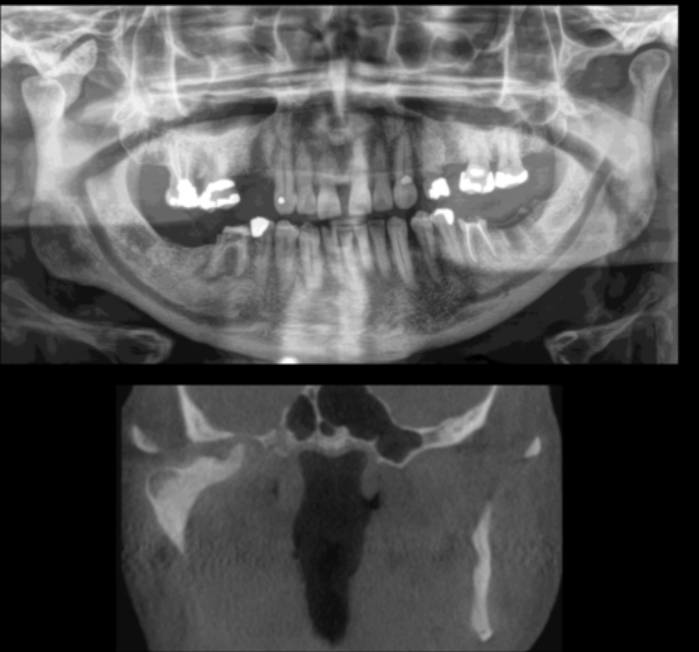
purpose of this radiograph
to view max sinus (waters projection)
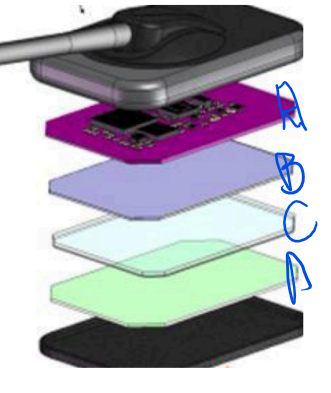
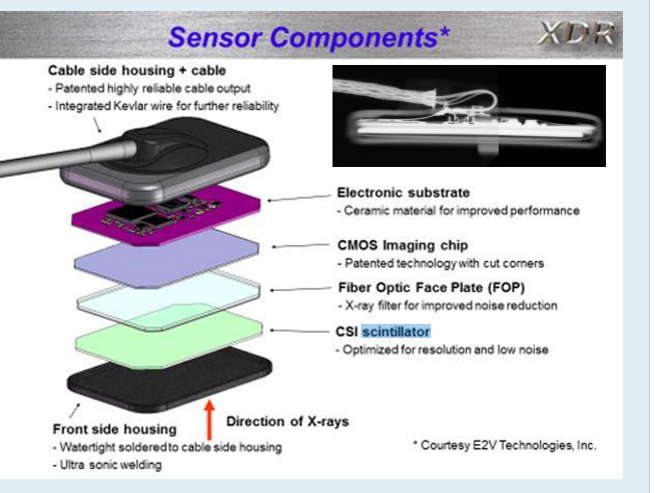
Which of the following is where you would find the scintillator?
D
error
chin up
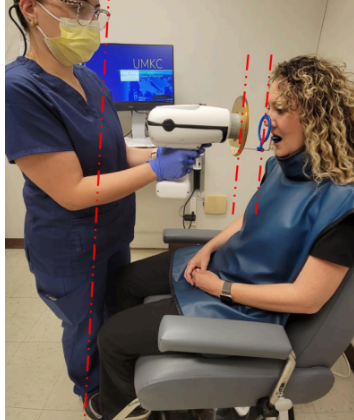
Which of the following describes this operator positioning?
Correct use of the NOMAD to maximize operator safety
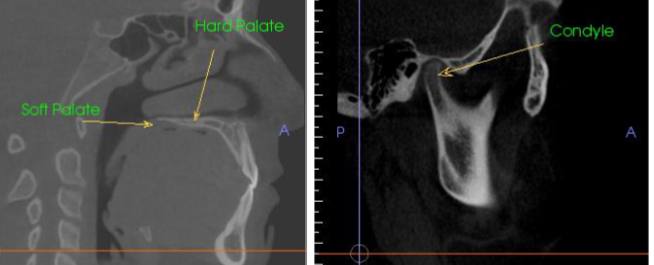
What CBCT view is presented, and what type of contrast is shown on the right ?
sagittal; high
What is the universal language for file formatting for a CBCT?
DICOM
You have a patient that has a CBCT scan sent to your office in a proprietary format. What will you need to do next?
Request for the file to be sent again and converted to DICOM
Who discovered a different form of radiation and received a nobel prize in 1901?
wilhelm roentgan
Who was the dentist to bring about dental radiographs and die from radiation?
- Edmund Kells
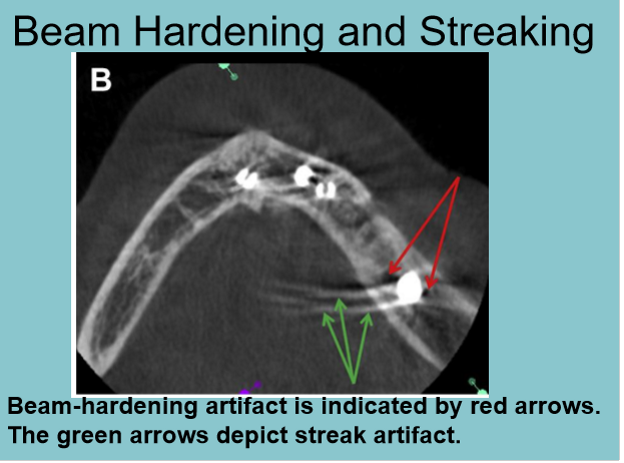
what is it called when a ghost outline or other radiopaque anomaly appear on a CBCT?
streaking
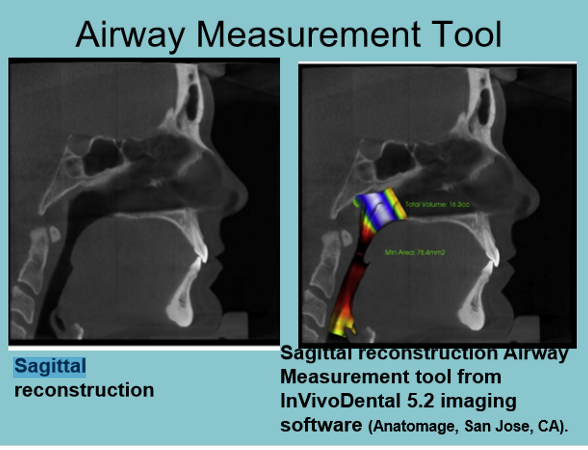
What are some of the advantages to CBCT image reconstruction applications?
measurements
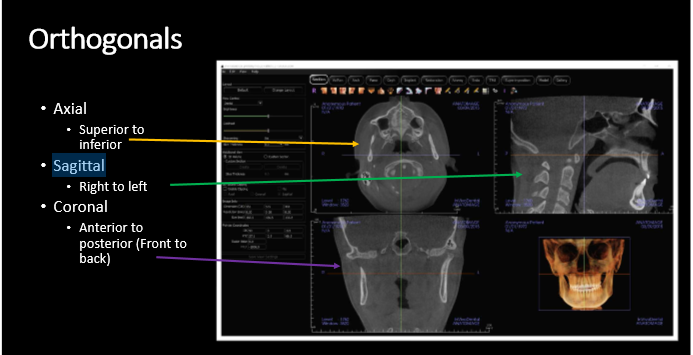
How is a sagittal CBCT reconstruction viewed?
medial to lateral
One of the benefits of cone beam imaging is that there is ____ radiation exposure in comparison to other imaging software such as MDCT.
lower
Smaller voxels will have ____ storage and ____ radiation:
higher and higher

Smaller voxels yield:
Higher resolution, but higher amounts of radiation
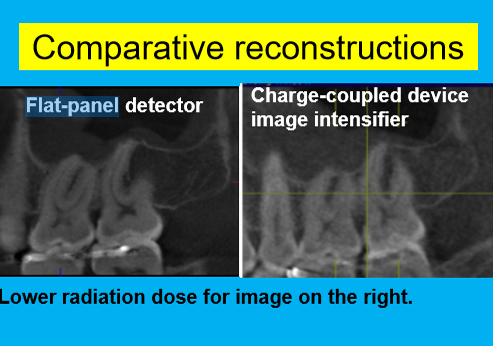
In comparison to the flat panel detector, the image intensifying detector has:
Increased amounts of peripheral image distortion

Which of the following CBCT detectors produces a higher amount of radiation?
flat panel detector
What is defined by its radiation weighting factor?
equivalent dose
Comparing different biological effects from various radiation can be described as?
equivalent dose
This form of ionization interacts with matter allowing for x-ray photons to collide with an inner orbital and lose its energy.
photoelectric effect
Which of the following forms of radiation causes an increase in H2O2?
indirect radiation
Radiation can cause primary damage of fine vasculature, this is described as:
osteoradionecrosis
Which of the following are considered modifying factors that affect x-radiation?
increase in oxygen and decrease in age
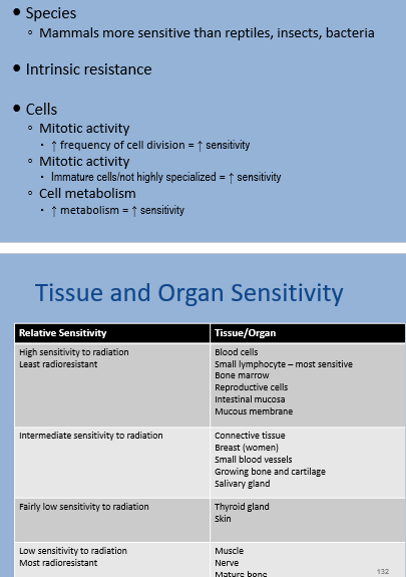
Which of the following has the highest sensitivity to radiation?
blood cells and bone marrow
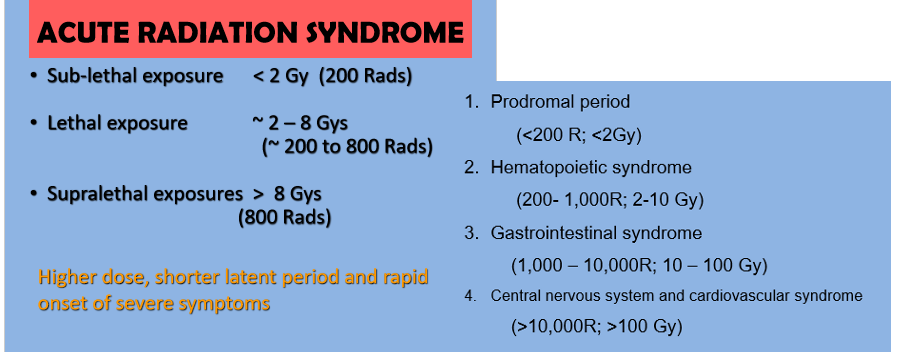
Which of the following produces a sublethal exposure to the body?
prodromal period

Which of the following is a detrimental effect of hematopoietic syndrome?
sepsis

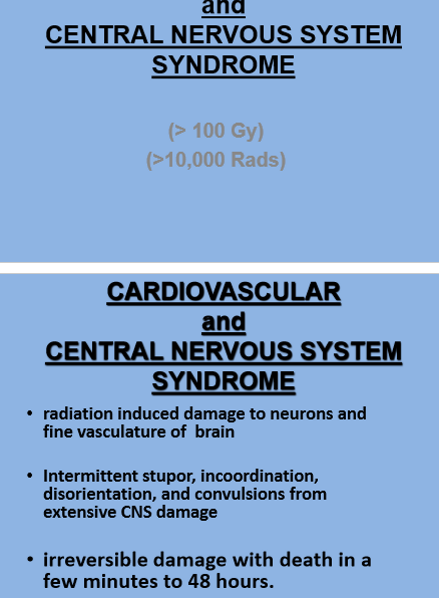
Which of the following steps related to radiation dosage is the most lethal?
Central nervous system/cardiovascular syndrome
You have a recall pt. that comes into your office, they are at a high risk for caries. How often is it suggested by the ADA to take radiographs on this patient?
12-18 months (even though its supposed to be 6 to 18)
Which of the following electron shells has the most energy?
k shell
What is the definition of the Wave Theory?
The explanation of propagation of radiation
The exposure button and indicator light are mandated by:
a. Federal law
b. Missouri state law
a. federal
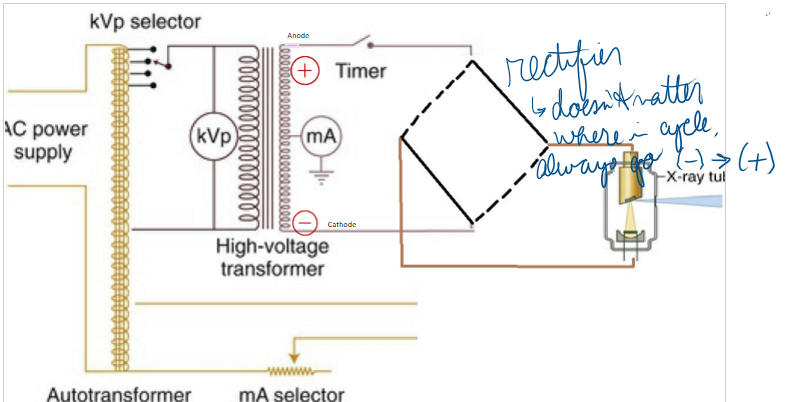
Which of the following is controlled by the step down transformer?
mA (kVp step up) (supplies energy to the filament)
The distinguishing factors for Bremsstrahlung’s Radiation are:
Heterogenous, maximum energy released
Factors that impact an x-ray beam intensity related to voltage:
increases in quality and quantity
Quality of an image is related to:
density
Which of the following controls quantity?
kVp
What is the relationship for kVp if an image has high amounts of contrast?
low kVp
If an object is closer to the source, what will occur?
less sharpness
What are the units for binding energy?
eV
Why does a ghost image of the cervical spine occur when taking a pano?
patient is slumped
An anatomical structure that is closer to the source will project ____ in comparison to a
structure further away?
higher
Where do you place the lead apron prior to taking a pano?
higher in the front; lower in the back
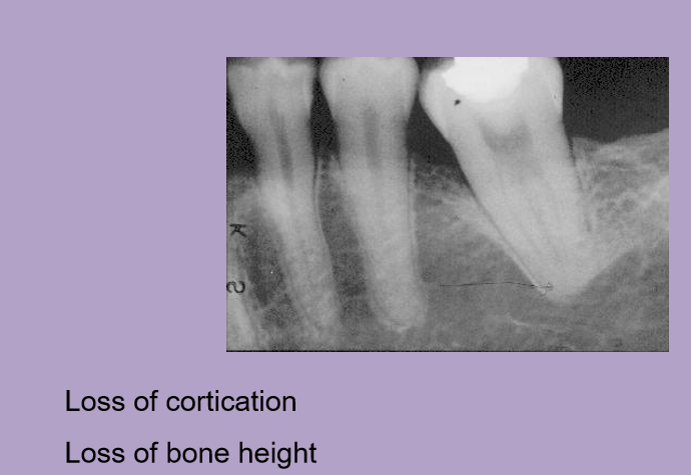
list 3 things that show the periodontal status of a tooth
crown:root ratio
verticla bone loss
horizontal bone loss
Which of the following has a negative impact on the periodontal status of a tooth?
conical root and embrasure space loss
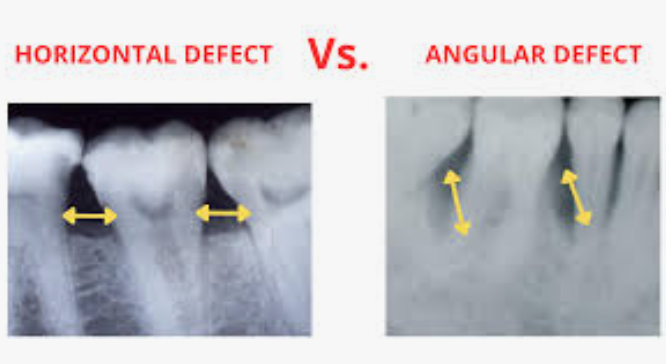
what type
HBL
It is acceptable to take radiographs on a pregnant patient when:
Only when the patient is experiencing acute pain that needs immediate
attention
In order to maximize sharpness, which of the following would you need?
a longer cone head attachment
Which form of radiation has the most biological effects?
compton scatter
Which of the following errors can occur when the central beam is perpendicular to the
tooth?
elongation
What is the difference between CCD and CMOS?
CMOS is faster to digitize
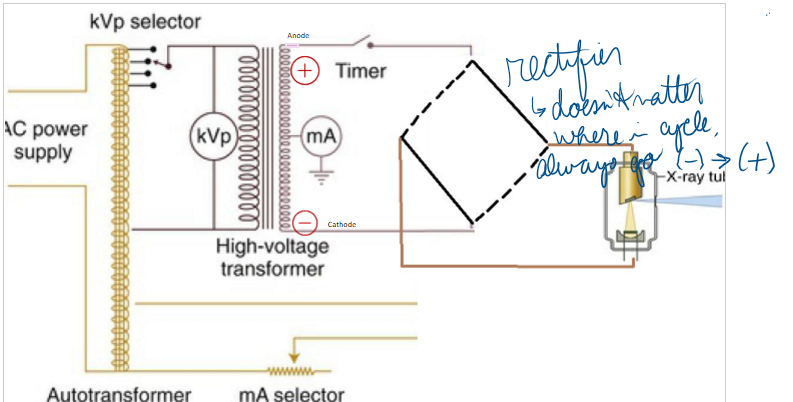
step down transformer heats of the tungsten filament, this process is known as:
thermionic emission
An electron to nucleus interaction with fast moving electrons that either slow down or
stop when contacting the nucleus to transmit energy as x-rays.
Bremsstrahlung radiation
Why will an object appear wider on a radiograph?
Object is lingual in the focal trough
How many viewpoints does a CBCT have?
100s to 1000s
Which of the following views are MPR reconstructions?
axial and whatever else the image shows
What will happen on a CBCT when you have 120 kVp -----------------
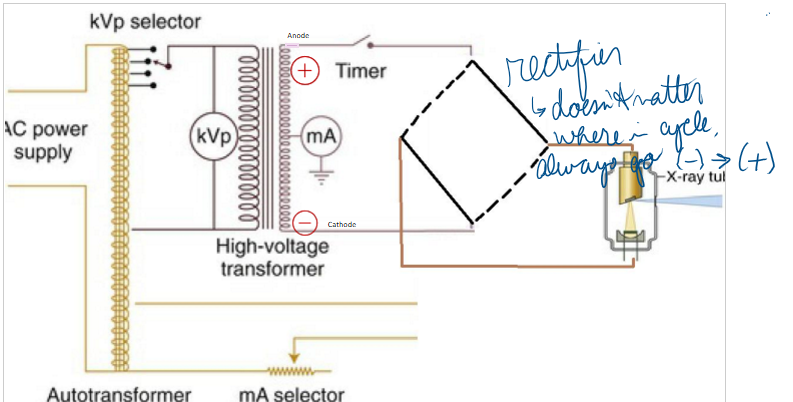
Select true statement about charge and component of tubehead
a. Negative cathode
b. Positive cathode
c. Negative anode
a. negative cathode
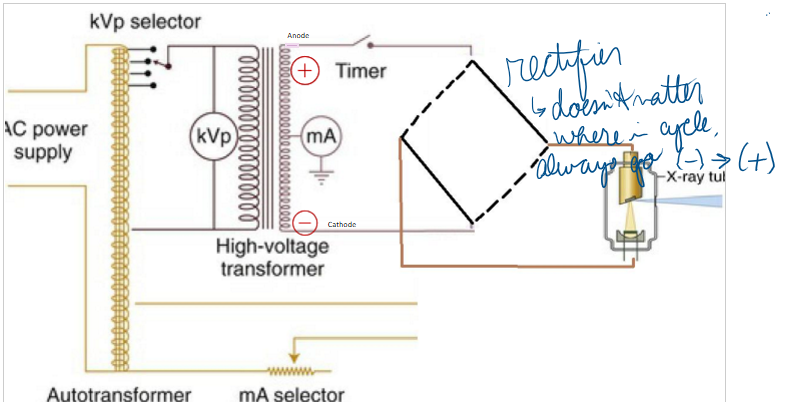
What has a cesium iodide scintillator
a. Solid state sensor
b. PSP
a. solid state sensor
What happened if you change short cone to long cone
a. Increase sharpness
b. Increase magnification
increase sharpness
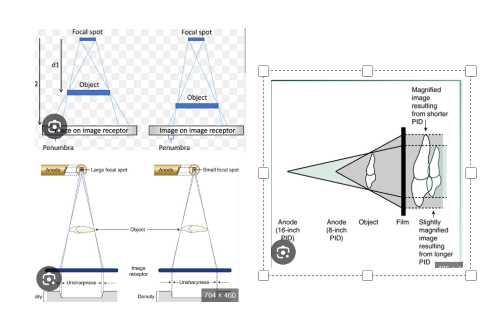
. advantage of CBCT
a. Visualize anatomy of hard tissue
Topographical vs standard cross sectional
a. Change in vertical angulation
b. Change in horizontal angulation
a. Change in vertical angulation
Negative angulation of pano x-ray source results in objects appearing
Higher
Bc of occipital bone
What is true about CBCT
a. 2-3 minutes exposure
b. Can be reconstructed in more than three planes
c. DICOM can be used with 3rd party
b and c
exposure is 5 to 40 seconds usually
MBCT vs CBCT
Dosimetry is less for CBCT
90 kVp is
a. Higher mean energy than 60 kVp
b. Lower mean energy than 120 kVp
a. a. Higher mean energy than 60 kVp
The unit of binding energy
a. mA
b. eV
c. Second
d. kVp
b. eV
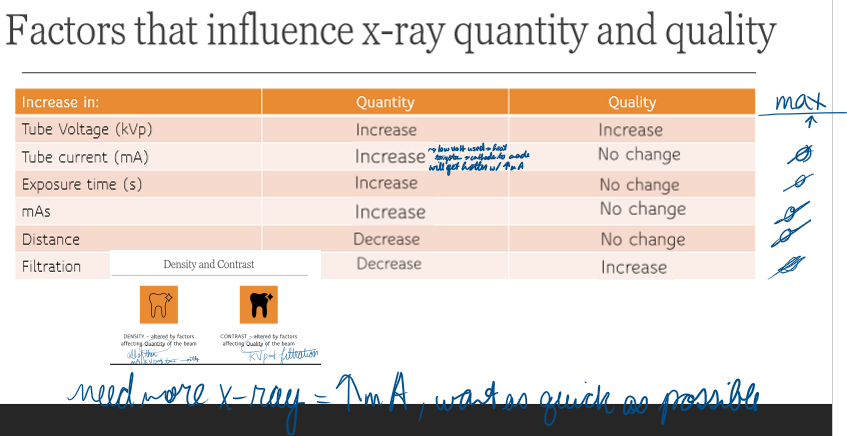
Filtration decreases what?
Quantity