ochem 2 - carboxylic acids & derivatives
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
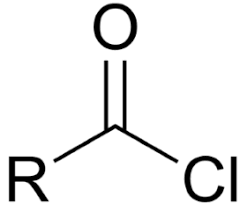
derivative - acid chloride
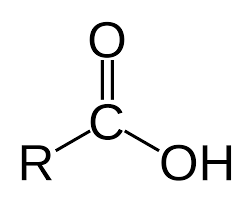
carboxylic acid
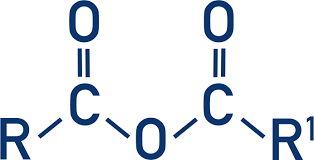
derivative - acid anhydride
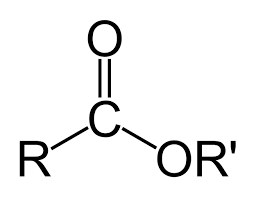
derivative - ester
derivative - amide
rank the derivates from most to least reactive and state why
most reactive - acid chloride (Cl is very electronegative)
acid anhydride - (good LG and resonance stabilized)
ester - (O is more electronegative)
least reactive - amide (N is least electronegative - electron donating)
if the carbonyl carbon is negative, and the nucleophile is strong…
there will be a direct attack on the carbonyl carbon, resulting in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate.
if the nucleophile is weak…
the carbonyl carbon has to be activated - oxygen will first attack the electrophile to form a protonated carbonyl, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
acid esterification *draw mechanism*
reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, resulting in the formation of an ester and water.
Williamson ester synthesis *draw mechanism*
A method for synthesizing esters by reacting an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide, facilitating the formation of an ester bond.
diazomethane esterification *draw mechanism*
A chemical reaction that involves the conversion of carboxylic acids into esters using diazomethane as a reagent, involves alkoxide intermediate
conversion of carboxylic acid to acid chlorides *draw mechanism*
reaction of carboxylic acid with SOCl2 and pyridine to form an acid chloride (can also be done with PBr3 to form acid bromide)
conversion of carboxylic acid to acid anhydrides
reaction of carboxylic acid and P2O5
conversion of acid chloride/bromide to carboxylic acid *draw mechanism*
reaction of acid chloride/bromide with H2O, NaOH or pyridine may be added to quench HCl byproduct
conversion of acid chloride/bromide to ester
reaction of acid chloride/bromide with an alcohol and pyridine - if more than one alcohol is present, the least sterically hindered alcohol will react first
conversion of acid chloride/bromides to amide
reaction of acid chloride/bromide with NH3 - does not work with a 3° amine, only 1° or 2°
reaction of acid chloride/bromide with gringards reagent *draw mechanism*
acid chloride/bromide reacted with 1) R’-MgBr, /\o/\ 2) H2O, HCl to form a tertiary alcohol
reaction of acid chloride/bromide with organocuprates
acid chloride/bromide reacted with 1) R’-CuLi 2) H2O to form a ketone
reduction of acid chloride/bromide to alkene *draw mechanism*
acid chloride/bromide reacted with 1) LiAlH4, THF 2) H2O , forms a primary. alcohol
reduction of acid chloride/bromide to aldehydes
acid chloride/bromide reacted with 1) LiAlH(O-tbu)3, /\o/\ 2) H2O - a weaker reducing agent is needed so that it will not react further with the aldehyde
conversion of ester to carboxylic acid in basic conditions *draw mechanism*
ester reacted with 1) NaOH, OH 2) HCl, H2O
conversion of ester to carboxylic acid in acidic conditions *draw mechanism*
ester reacted with HCl, H2O
conversion of ester to amides
ester reacted with NH3, /\o/\
2 ways to reduce an ester
A) 1) LiAlH4 , /\o/\ 2) HCl, H2O - will reduce to a primary alcohol
B) 1) DIBAL, toluene, -78°C 2) HCl, H2O - will stop reducing at the aldehyde
acidic hydrolysis of amides *draw mechanism*
amide is reacted with HCl, H2O, heat to form carboxylic acid
basic hydrolysis of amides *draw mechanism*
amide reacted with 1) NaOH, H2O 2) HCl, H2O to form a carboxylic acid
reduction of amides
amide reacted with 1) LiAlH4, /\o/\ 2) H2O to form a primary amine