Science SEC 3 2023-2024
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Somatosensation
refers to the processing of stimuli like touch, temperature, pain, pressure, and vibration
Vestibular System
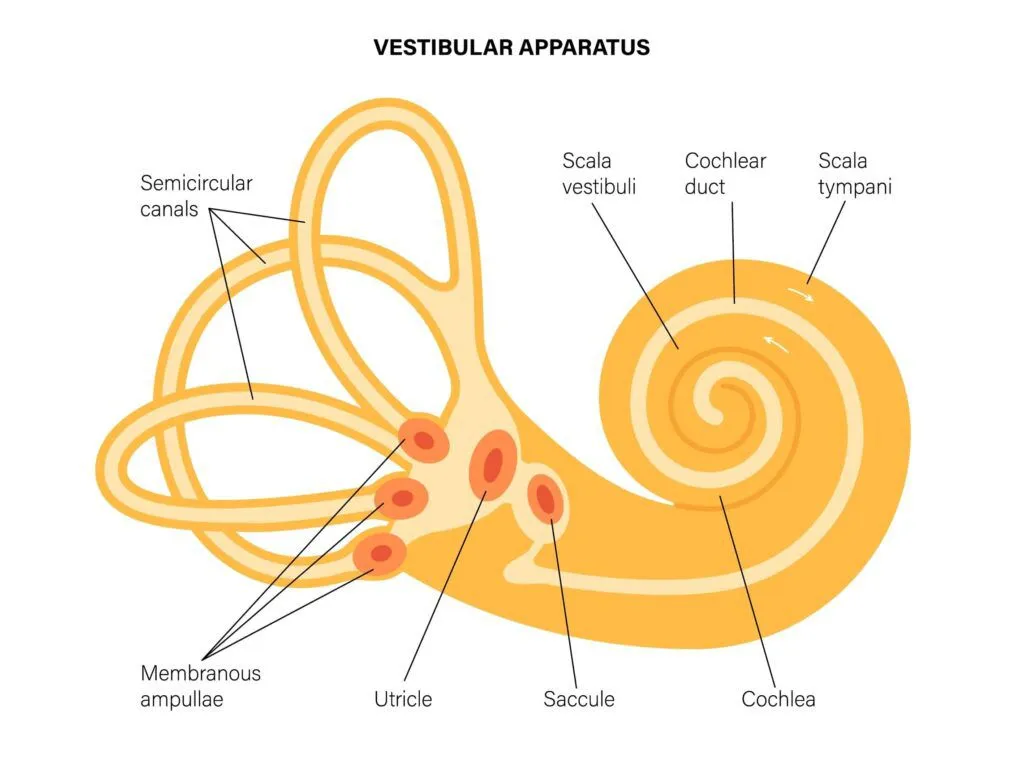
the sensory system comprised of components in the inner ear that provides the brain with information about motion and position; creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation
Proprioception
the sense of where your body is in space; calculated by the stretch and force on your muscles, joints, and tendons
Sensory Transduction
the process of translating sensory stimuli such as light, sound, or pressure on the skin into electrochemical signals via a sensory receptor
Sensory Receptor
a receptor that detects and transduces sensory stimuli like light, sound, and pressure into electrochemical signals that the nervous system and brain can receive, process, and understand
Receptive Field
a specific region in the sensory domain (for vision, a region of visual space; for touch, a region of the skin, etc.) where an appropriate stimulus can evoke a neuronal response
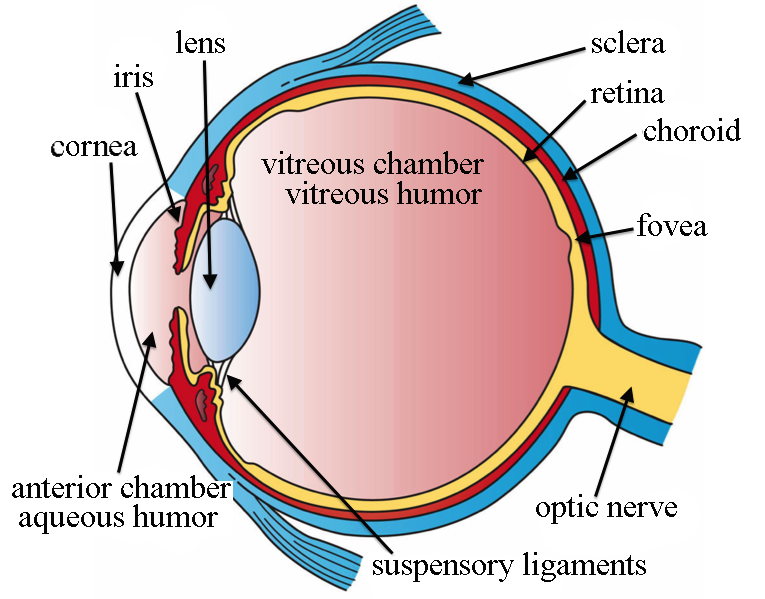
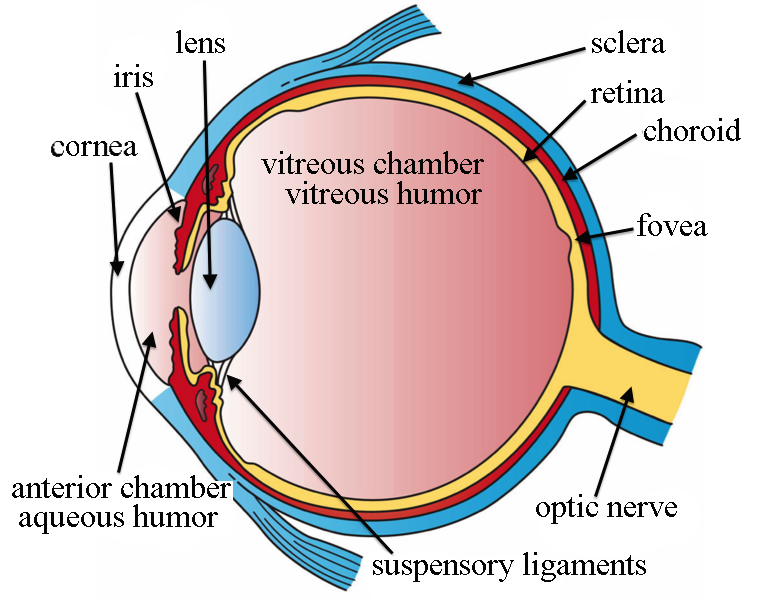
Retina
the thin layer at the back of the eyeball containing cells that are sensitive to light and send nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex
Cornea
the transparent external surface of the eye that is responsible for the majority of the refraction (bending/focusing) of light
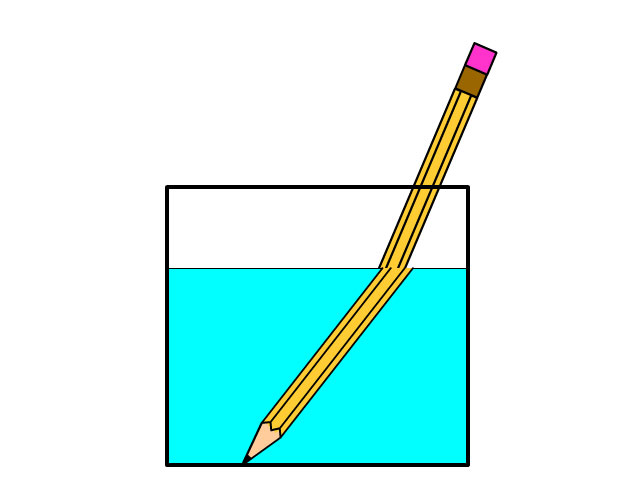
Refraction
the bending of light rays that can occur when the rays travel from one medium to another
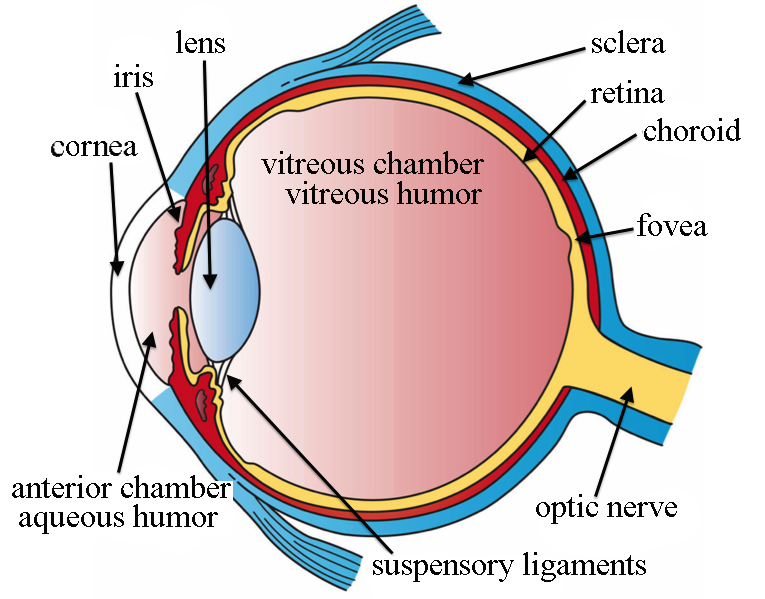
Iris
the circular, pigmented muscle that controls the size of the pupil in the eye
Pupil
the opening that allows light to enter the eye
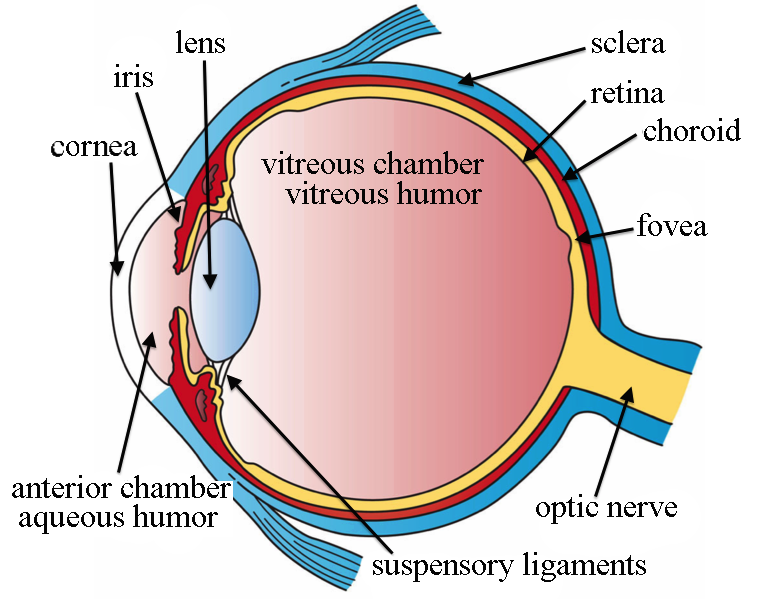
Lens
the dynamic, many-layered, clear structure behind the cornea of the eye that works to further refract light to focus an image on the retina
Visual Field
refers to the total area in which objects can be seen in the side (peripheral) vision as the eyes are focused on a central point
Myopia
the inability to see objects far away clearly (nearsightedness)
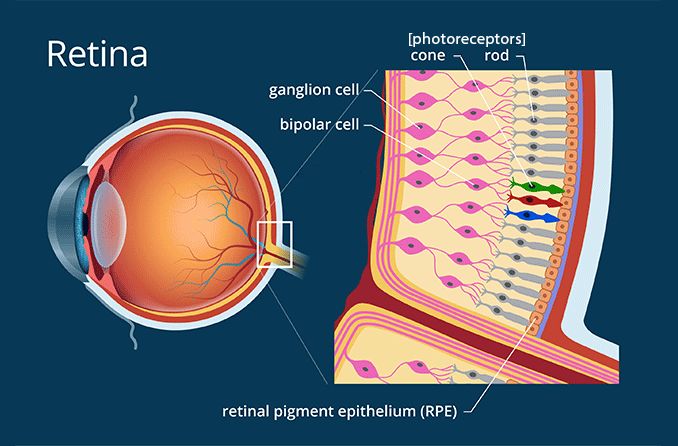
Photoreceptors
cells in the eye’s retina that are responsible for converting light into signals that are sent to the brain
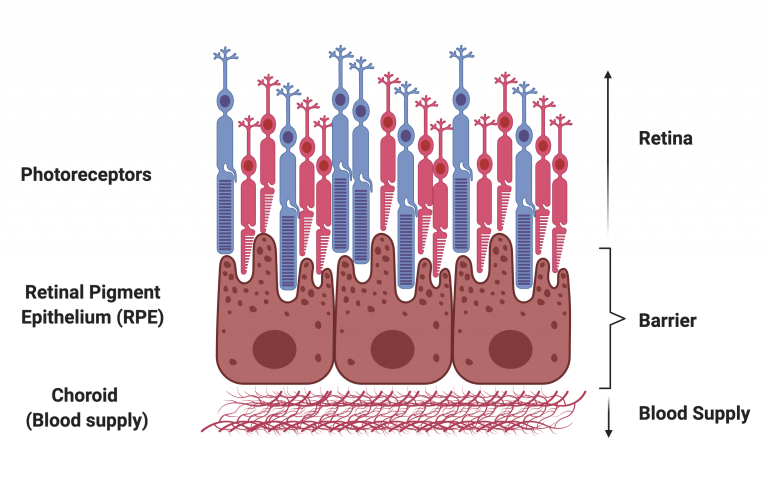
Pigmented Epithelium
a pigmented cell layer just outside the neurosensory retina that works to support the function of photoreceptors in a variety of ways, including absorbing excess light
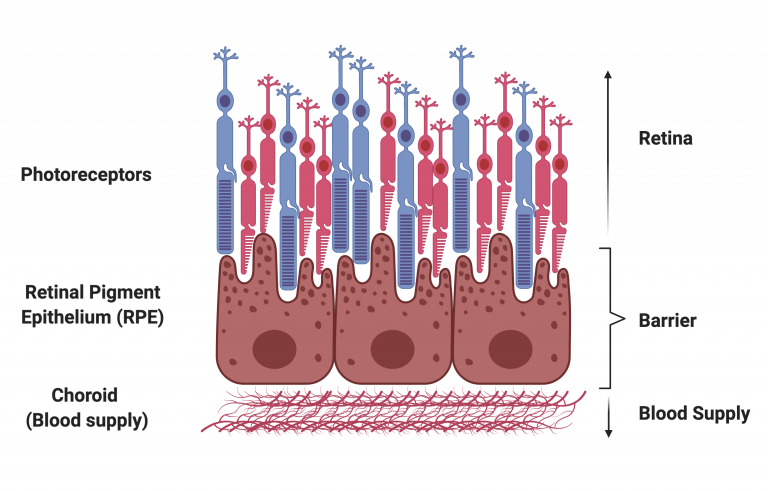
Choroid
a network of blood vessels located between the sclera and the retina; brings oxygen and nutrients to the retina
Fovea
the central portion of the retina, which contains only cone photoreceptors and is specialized for high acuity vision
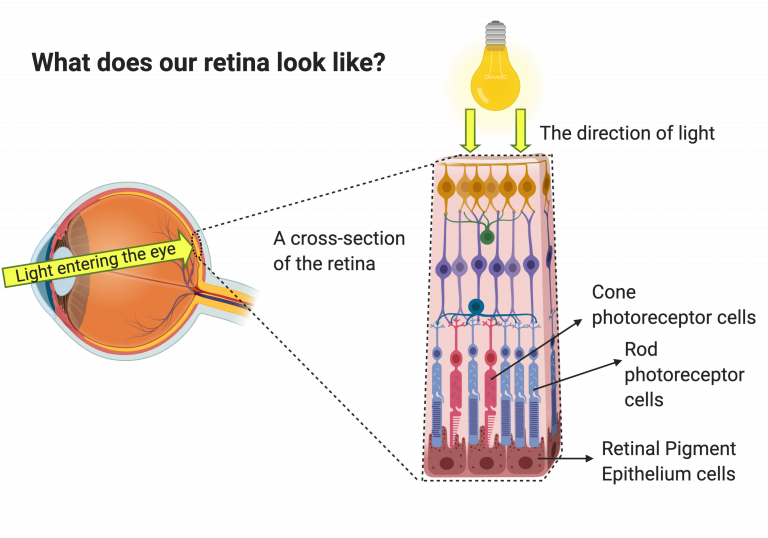
Rod
photoreceptor in the retina specialized for low-light vision; more numerous in the periphery of the retina
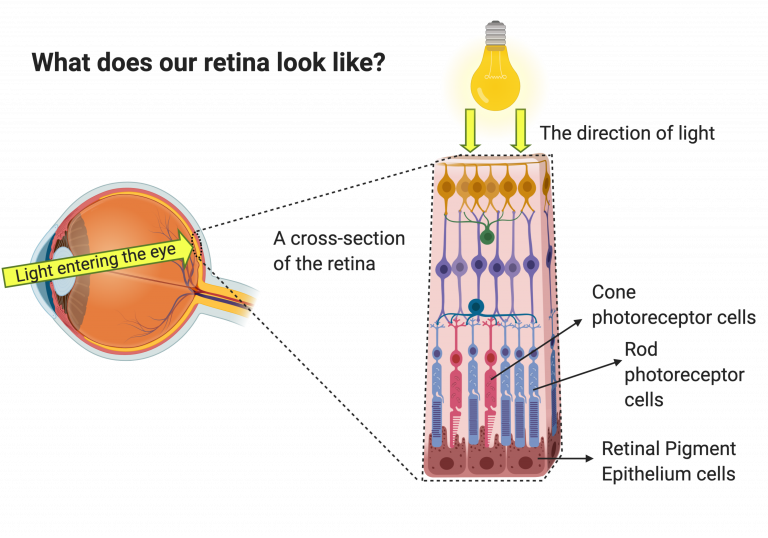
Cones
a photoreceptor type concentrated in the fovea of the retina; specialized for daytime vision and responsible for color vision
Opsin
a light-absorbing pigment; each absorbs a different wavelength or color of light; each type (color) of cone has its own type of opsin, which preferentially absorbs and transduces that one wavelength of light
Rhodopsin
light-sensitive photopigment in rods
Trichromatic
refers to the ability to see colors, mediated by interactions among three types of color-sensing cone cells (red, green, and blue) in the eye

Absorption Spectra
the specific wavelengths of light absorbed by a particular substance; in neuroscience, this refers to the opsins found in cone photoreceptors, each of which absorbs and transduces a different wavelength of light
Bipolar Cells
cells that connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells in the retina
Retinal Ganglion Cells
neurons that connect the input from the retina to the visual processing centers within the brain
Horizontal Cells
a laterally interconnecting cell in the retina of the eye that integrates and regulates input from multiple photoreceptor cells; helps form the center-surround receptive fields
Lateral Inhibition
the capacity of excited neurons to reduce the activity of their neighbors
Center-Surround Receptive Fields
a visual receptive field with a circular center region and a surround region; stimulation of the center produces a response opposite of the response generated by stimulation of the surround
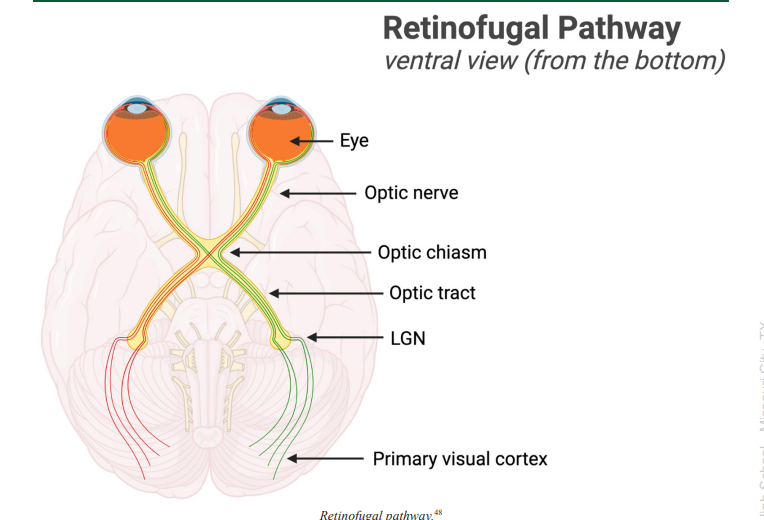
Retinofugal Pathway
connects the retina to the primary visual cortex (V1) through the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
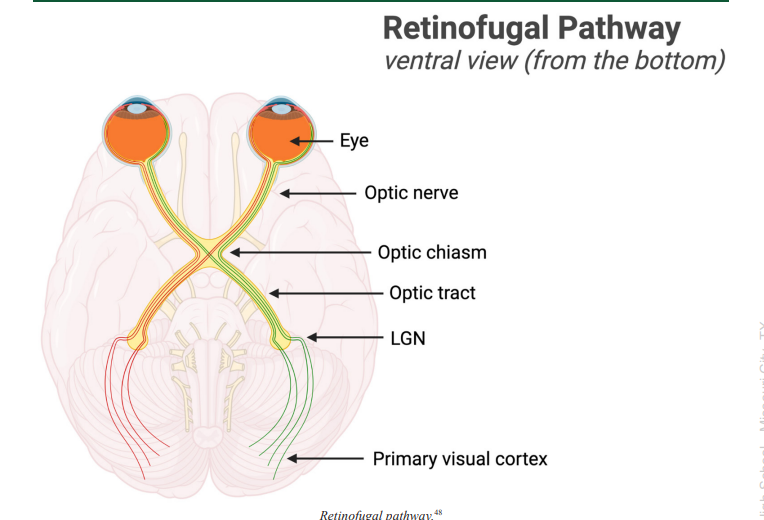
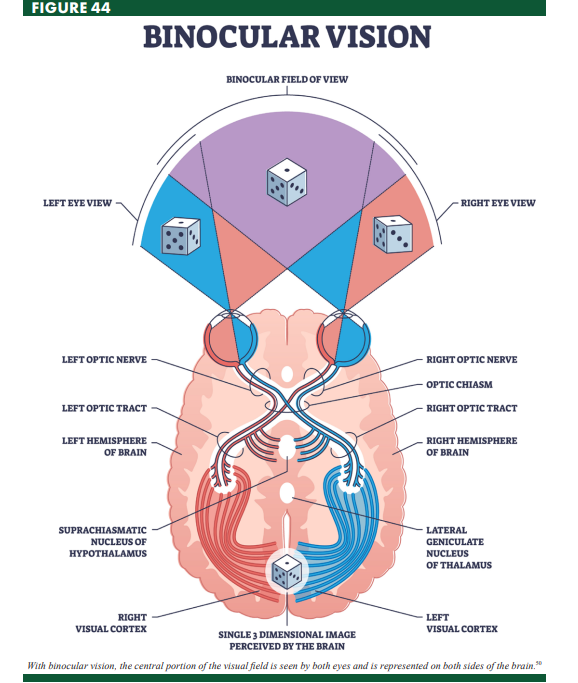
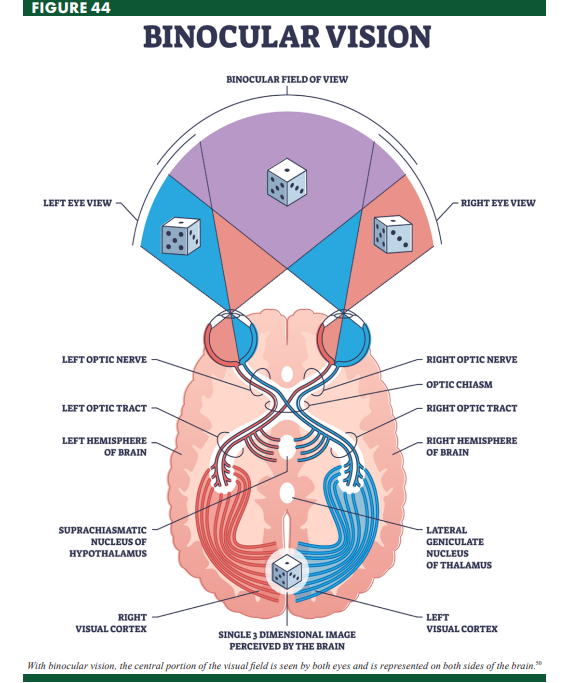
Optic Chiasm
the place in the brain that forms an X-shaped structure where some of the optic nerve fibers coming from one eye cross optic nerve fibers from the other eye
Decussation
the crossing of nerve pathways from one side of the nervous system to the other
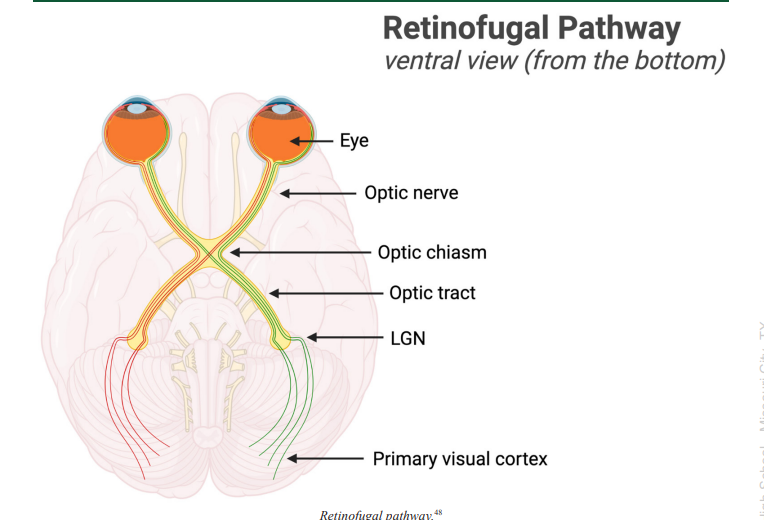
Optic Tract
a bundle of axons that carry visual information from the optic chiasm to the brain, as a continuation of the optic nerve
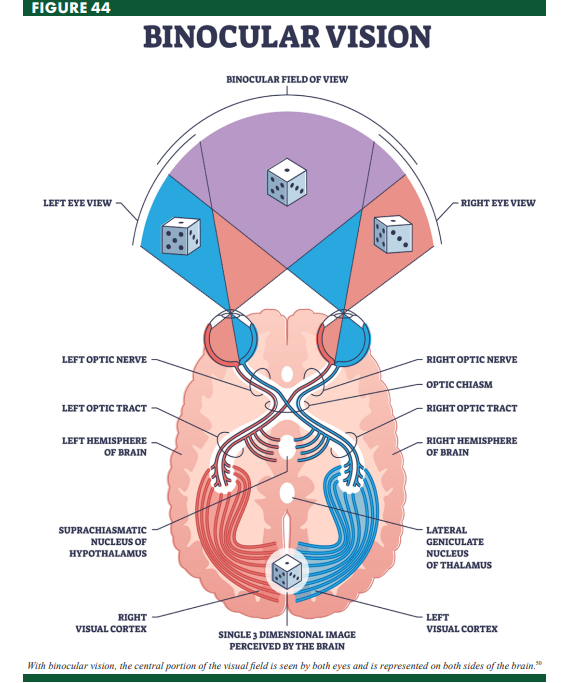
Binocular Vision
vision that incorporates inputs from both eyes into a single image
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
a multilayered structure in the thalamus that processes visual input and regulates the flow and strength of visual information to the visual cortex
Primary Visual Cortex (V1)
the region of the cortex found at the very back of the brain that is specialized for the initial processing of visual input
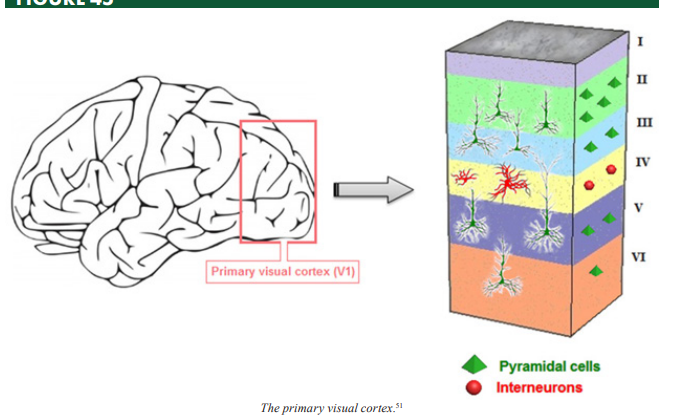
Pyramidal Cells
neurons characterized by a pyramidal-shaped cell body (soma) and two distinct dendritic trees; these are the most prevalent neuronal type in the cerebral cortex
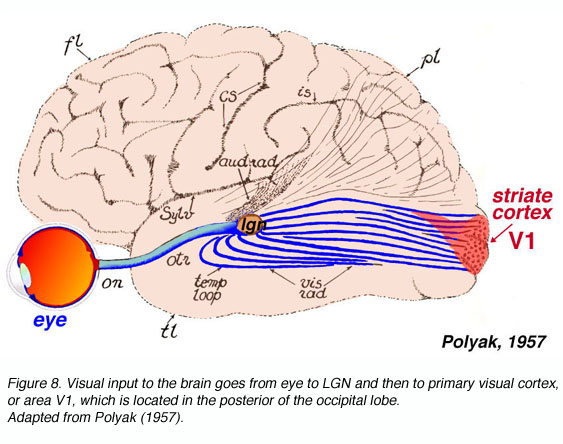
Striate Cortex
the part of the visual cortex that receives most of the visual input and is involved in processing visual information; also known as the primary visual cortex or V1
Monocular
having input from one eye
Retinotopic Map
a map of visual information from the retina onto neurons in the visual cortex
Cortical Magnification
the effect created by the number of neurons in the visual cortex varying as a function of the location of the stimulus in the visual field; items appearing in the central part of the visual field are represented larger in the visual cortex than objects at the edge of the visual field
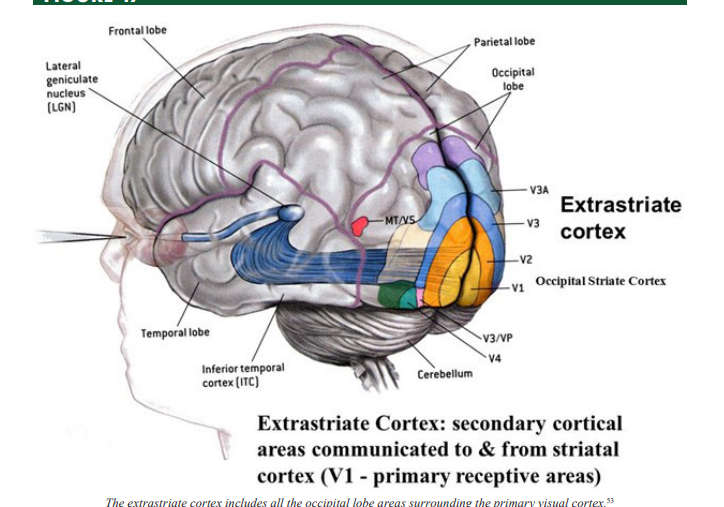
Extrastriate Cortex
a region of the occipital lobe surrounding the primary visual cortex that is involved in high-resolution vision and object recognition
Area MT
a region in the parietal lobe of the cortex that is involved with motion perception
Direction-Selective Neurons
In the visual system, these neurons fire action potentials maximally when they detect movement in a particular direction
Akinetopsia
a condition defined by the inability to detect motion
Visual Agnosia
impairment in recognizing objects
Prosopagnosia
a neurological disorder characterized by the inability to recognize faces
Parallel Processing
the ability of the brain to simultaneously process incoming stimuli, including color, motion, shape, and depth, separately by different cells at all levels of the visual system
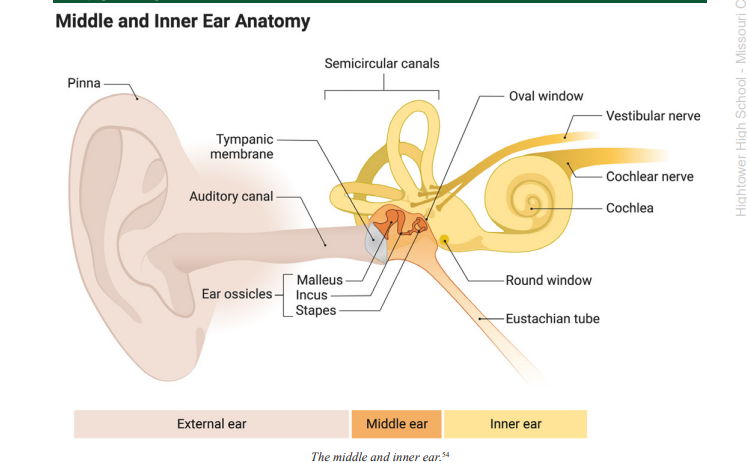
Pinna
the visible, external part of the ear that resides on the outside of the head
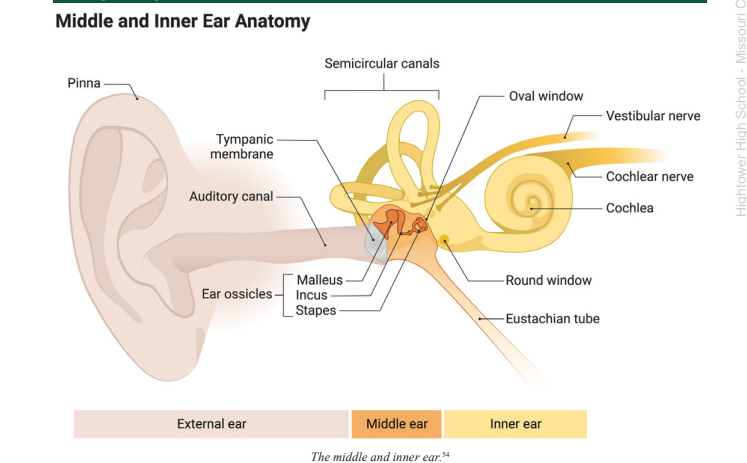
Tympanic Membrane
a membrane at the end of the auditory canal that moves in response to variations in air pressure caused by soundwaves; also called the ear drum
Middle Ear
transfers and magnifies sound waves from the ear canal and ear drum to the inner ear, where the sound waves are transduced
Ossicles
the small bones found in the middle ear that act like a series of levers to transfer and magnify the sound waves from the ear drum to the cochlea of the inner ear
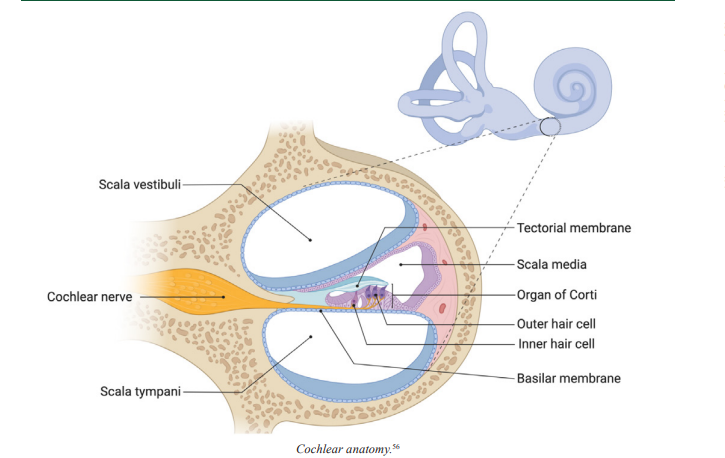
Cochlea
the section of the inner ear where auditory transduction takes place, translating sound waves into electrochemical signals
Semicircular Canals
three tiny, fluid-filled tubes in the inner ear that transduce information about spin and rotation of the head in order to help maintain balance
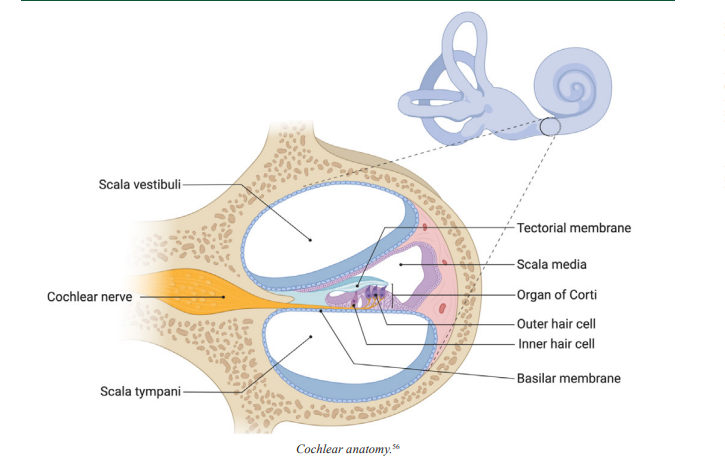
Basilar Membrane
the flexible membrane inside the cochlea where auditory transduction takes place, which encodes the frequency or pitch of a sound based on its position along the membrane
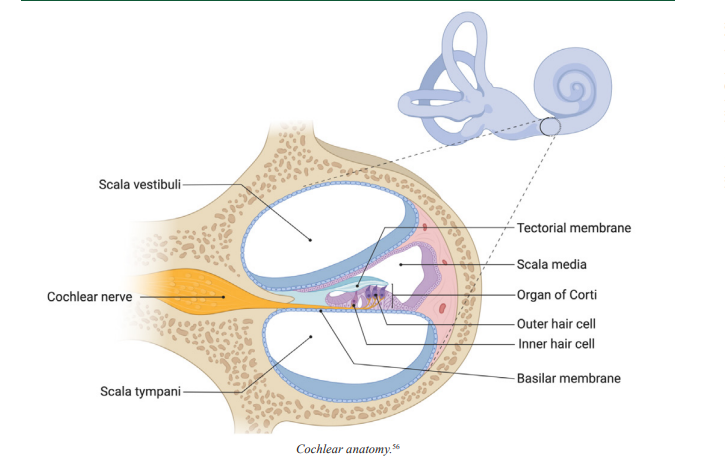
Organ of Corti
the structure in the cochlea of the inner ear in which the hair cells are found
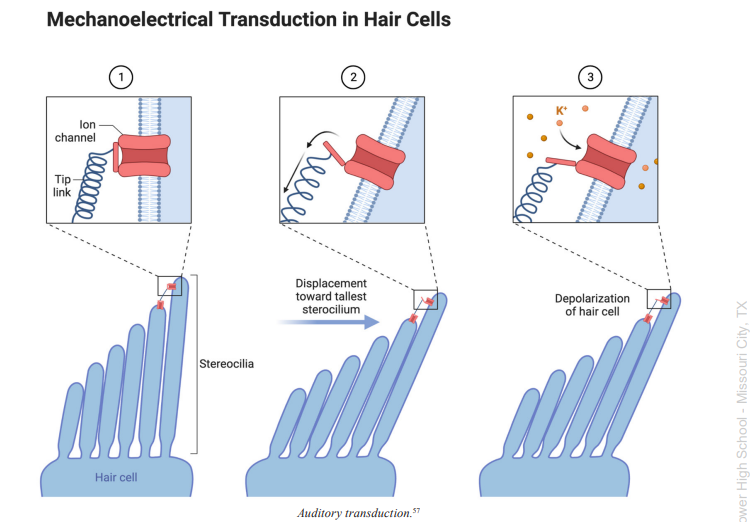
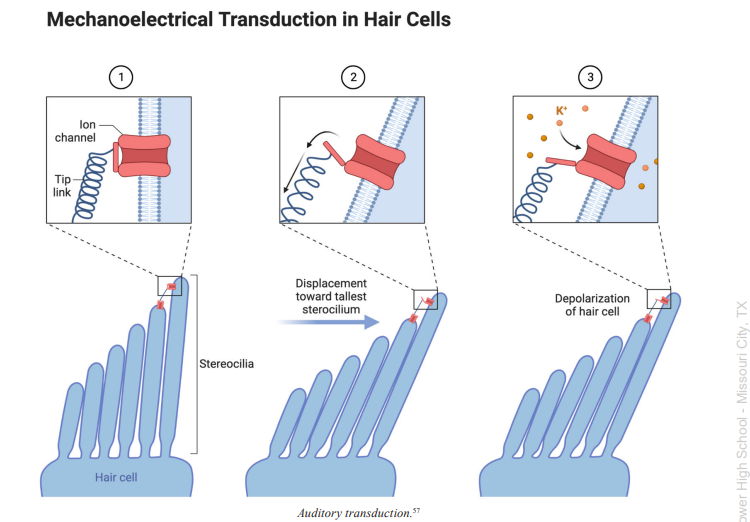
Stereocilia
tiny hair-like protrusions found on the hair cells of the cochlea in the inner ear, which are important for sound transduction
Tectorial Membrane
Located above the organ of Corti in the cochlea, in which the tips of the stereocilia of the hair cells are embedded, this membrane helps them create the back-and-forth movement of the cilia required for sound transduction
Inner Hair Cells
cells of the inner ear featuring stereocilia, which are long hair-like appendages that are moved back and forth by sound waves to transduce sound
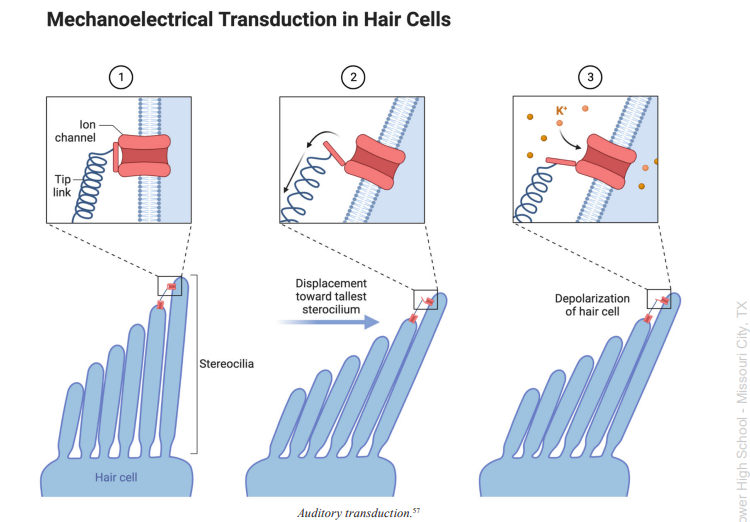
Outer Hair Cells
cells of the inner ear featuring stereocilia, or long hair-like appendages, that can extend or contract to magnify the vibration of the basilar membrane, which helps the cochlea transduce with high sensitivity and accuracy
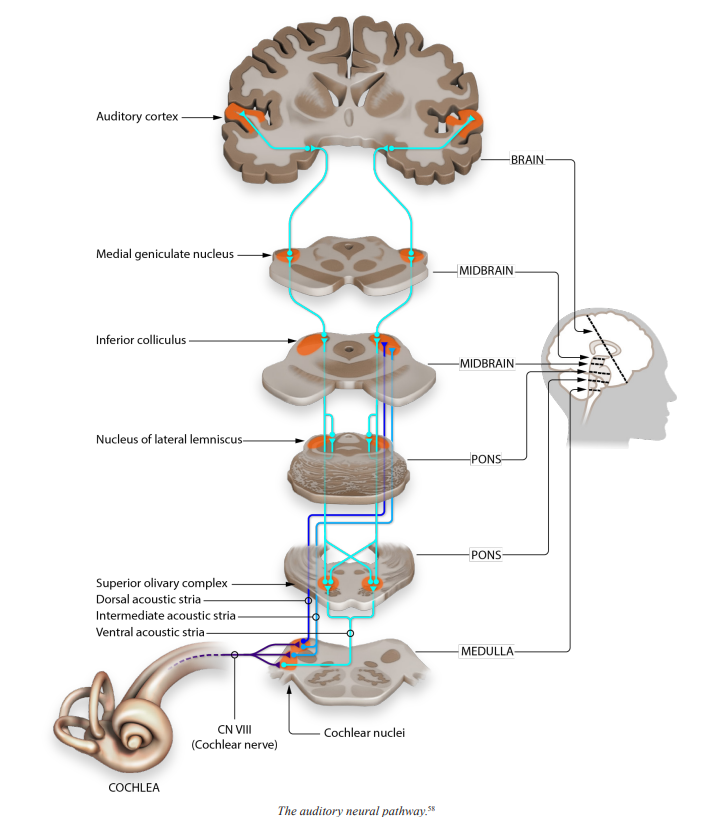
Inferior Colliculus
a cluster of grey matter found in the brainstem that forms an important relay station for auditory information on its way to the brain
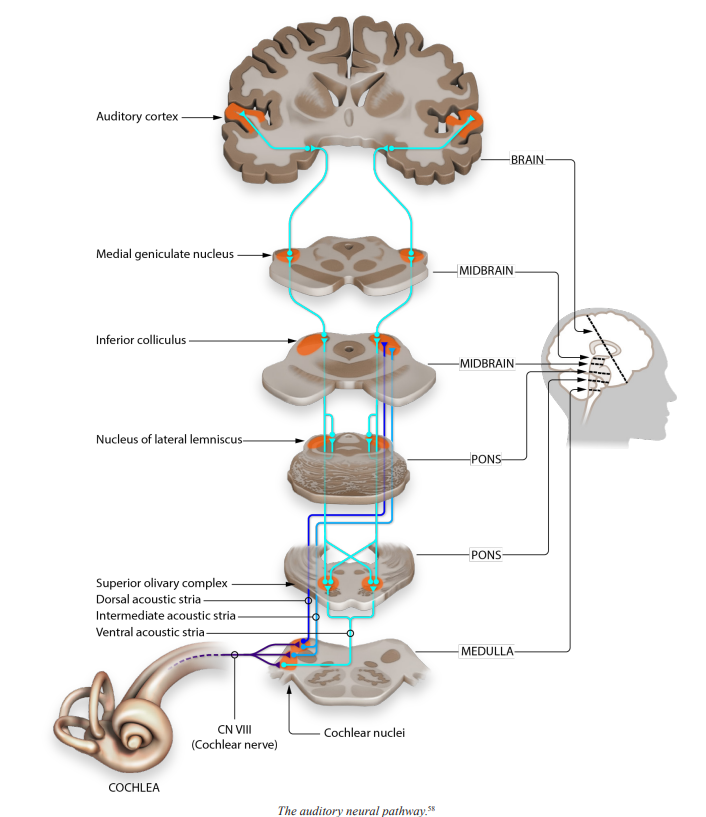
Medial Geniculate Nucleus (MGN)
the region or nucleus of the thalamus used to relay auditory information to the cerebral cortex
Primary Auditory Cortex (A1)
an area of the cerebral cortex found in the upper gyrus of the temporal lobe that is responsible for integrating and processing auditory perception
Umami
the fifth taste, relating to the savory flavor of protein or amino acids
Tastant
a chemical particle in food that can be transduced by taste neurons
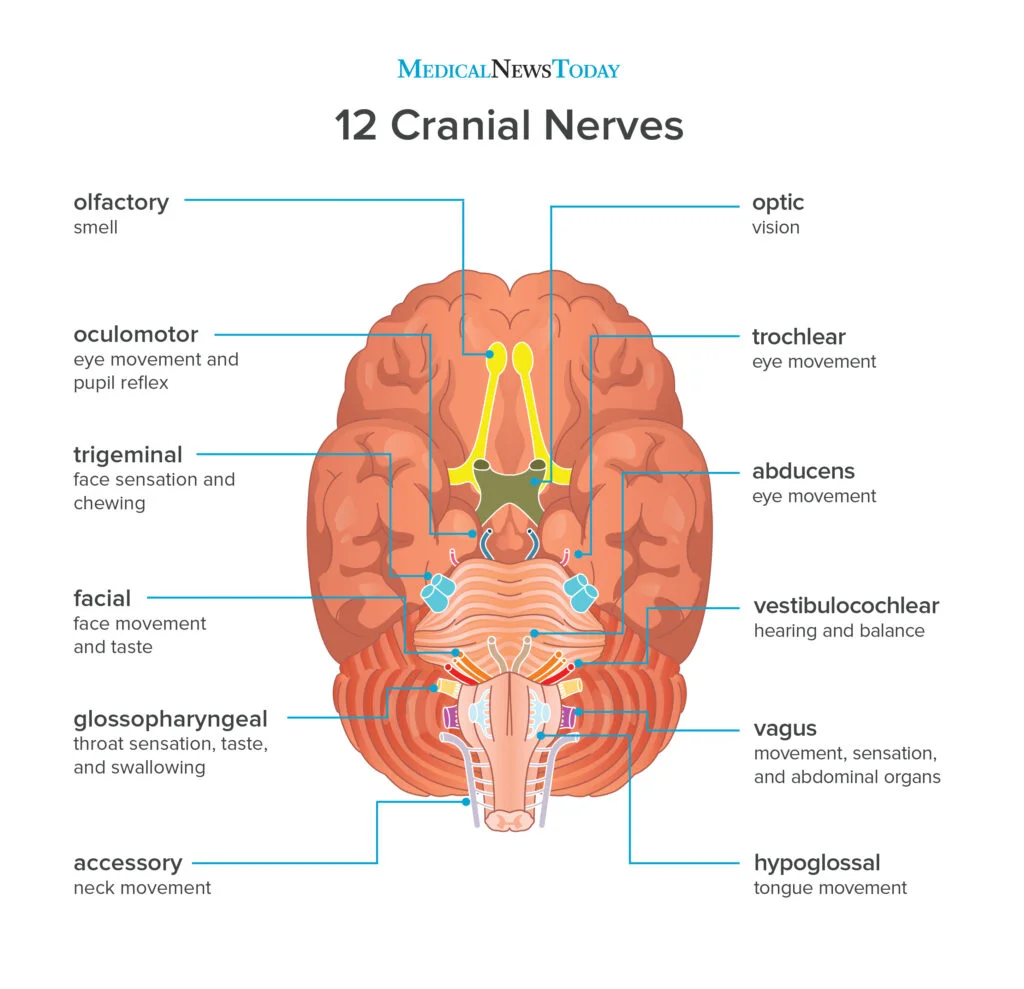
Cranial Nerves
twelve pairs of nerves entering or exiting the brain at the brainstem that connect the central nervous system with the head, face, and neck
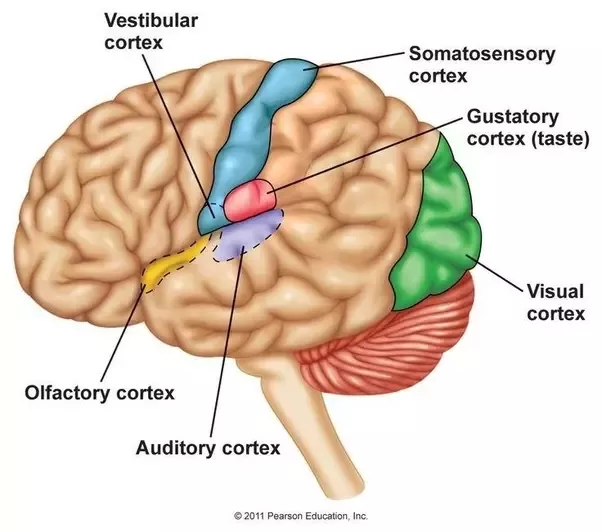
Primary Gustatory Cortex
an area of the cerebral cortex found in the insula that is responsible for flavor and taste perception
Olfactory Epithelium
the specialized tissue found in the nasal cavity or sinuses in which olfactory receptor neurons are found
Odorants
chemical particles in the air that can be transduced by olfactory receptor neurons
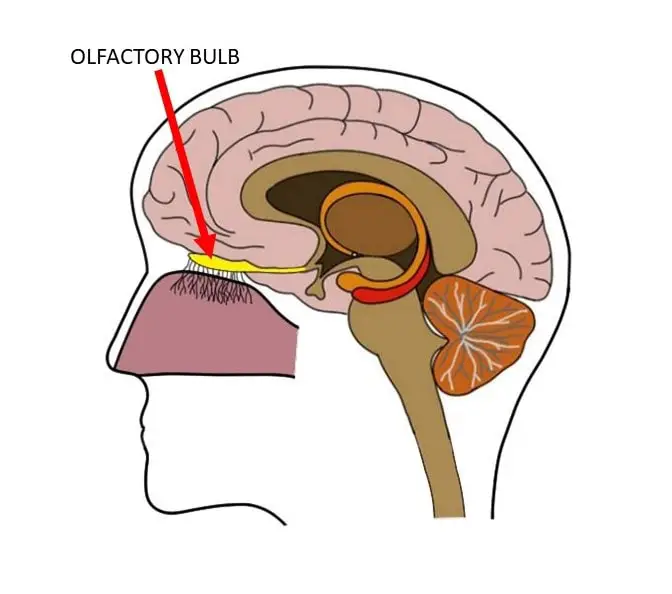
Olfactory Bulb
an extension of the brain that is found below the frontal lobe, which contains several types of nerve cells that are involved in the sense of smell
Cribriform Plate
the part of the skull that divides the brain and olfactory bulb from the sinuses; contains tiny holes for olfactory axons to pass through, carrying smell information to the brain
Glomeruli
the clusters of nerve endings in the olfactory bulb where olfactory receptor neuron terminals meet the next neuron in the olfactory system
Population Coding
a method of representing stimuli by using the coordinated activities of a number of neurons working together
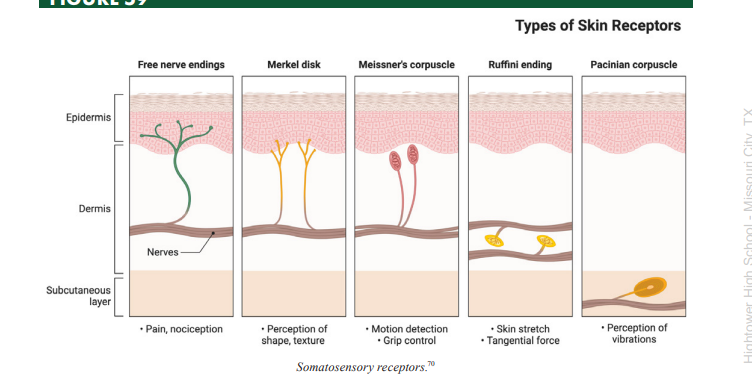
Meissner’s Corpuscles
a type of somatosensory mechanoreceptor used to transduce light fluttering vibration from glabrous skin
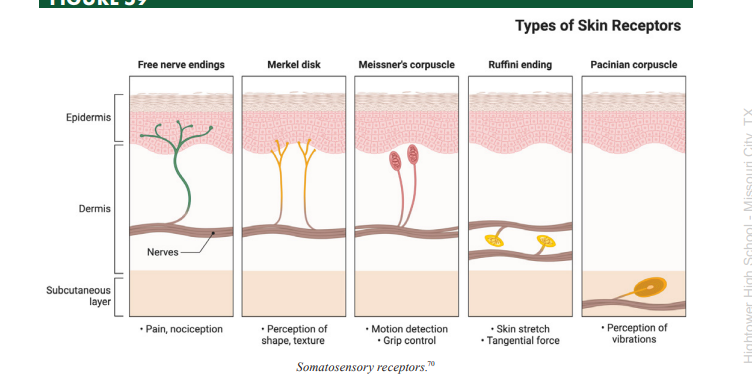
Pacinian Corpuscles
a type of somatosensory mechanoreceptor used to transduce deep vibration information
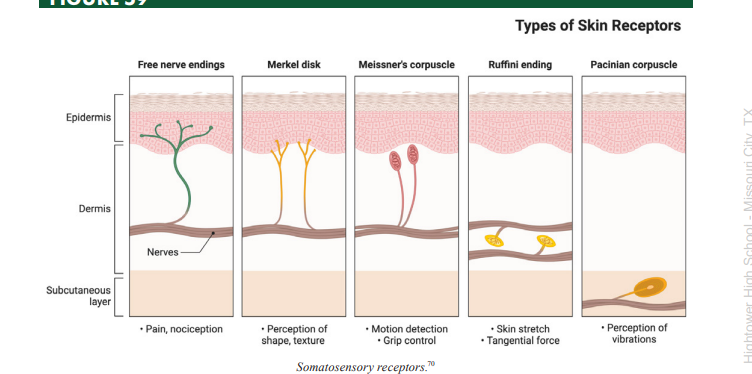
Merkel’s Disks
a type of somatosensory mechanoreceptor used to transduce light touch information from regions where the sense of touch is highly acute
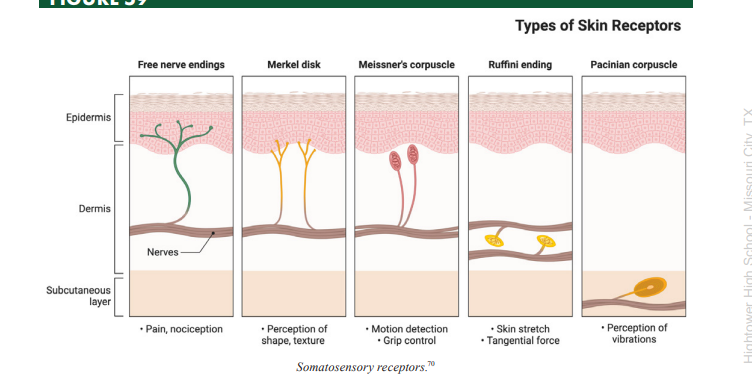
Ruffini’s Corpuscles
a type of somatosensory mechanoreceptor used to transduce stretch sensation information
Mechanoreceptors
a type of somatosensory receptor that transduces touch information through mechanically gated ion channels
Glabrous
describes skin that is hairless, often with a high concentration of sensory receptors for touch
Innervated
a structure is innervated by a region if that region supplies it with information
Dermatome
an area or stripe of skin whose neurons all send their input to the brain via the same spinal nerve and have their cell bodies in the same dorsal root ganglion
Nociception
the sensation or perception of pain
Hyperalgesia
increased sensitivity to pain, often caused by inflammation or related damage
Congenital Analgesia
insensitivity to pain, or pain blindness, present from birth
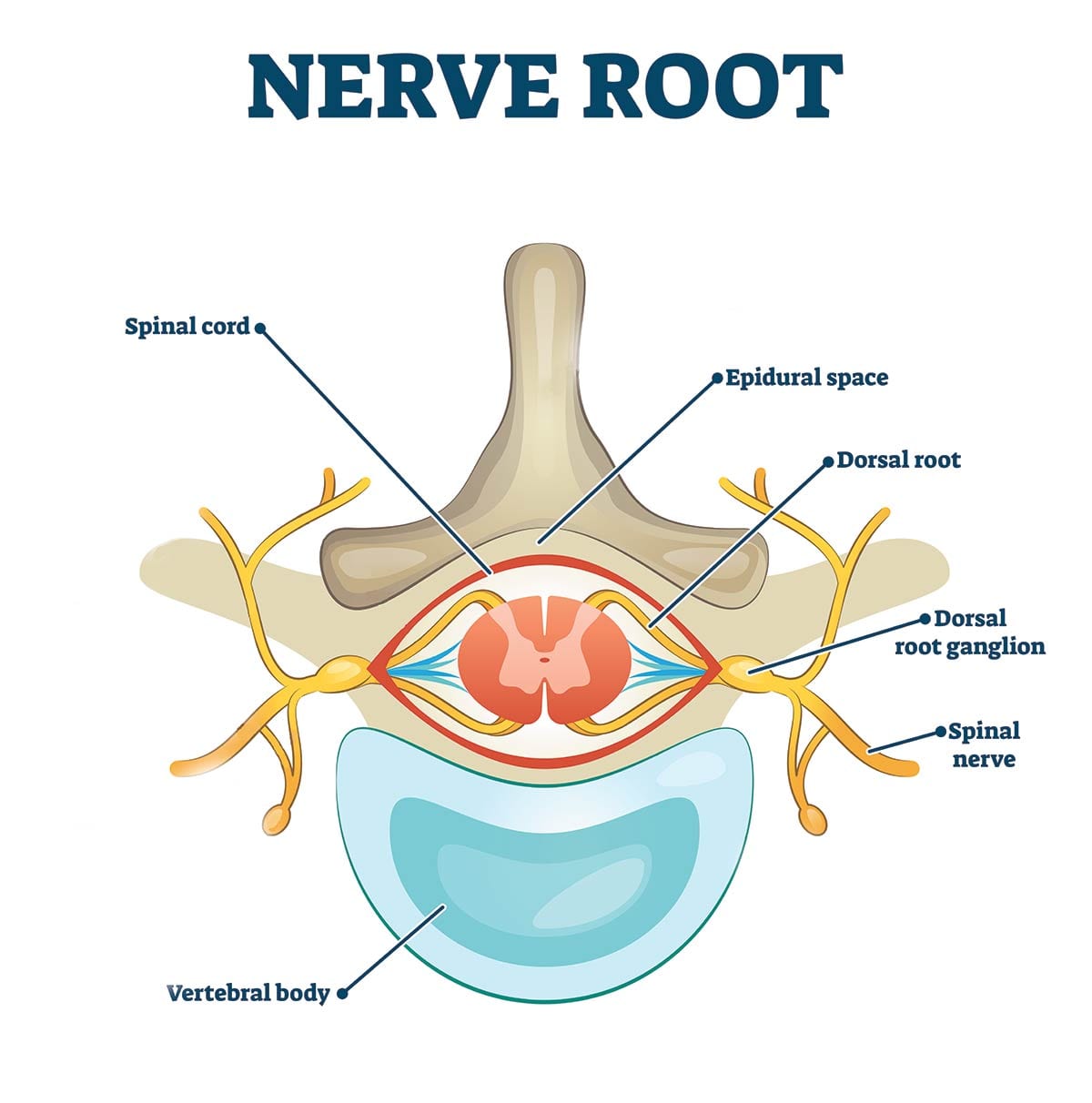
Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG)
the part of the spinal nerves that contains the cell bodies for somatosensory neurons bringing information from the skin and tissues to the brain
Afferent
nerves/axons that bring information to the central nervous system or brain
Efferent
nerves/axons that bring information down from the central nervous system or brain
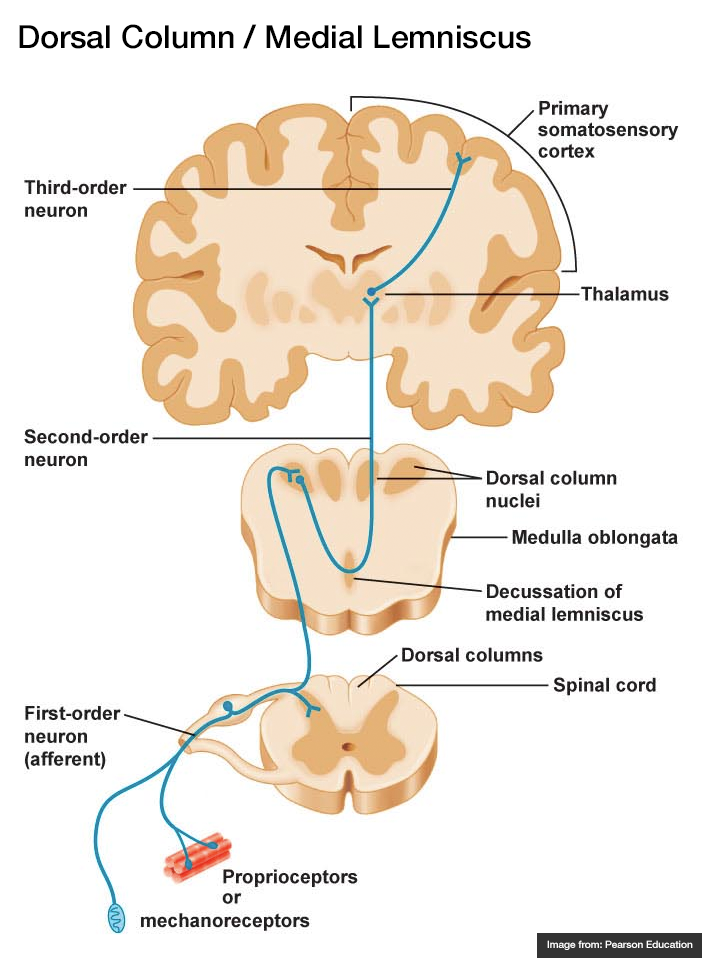
Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscal (DCML) System
one of the ascending systems that brings sensory information from the body to the brain (specifically, fine detailed touch information, vibration, and texture)
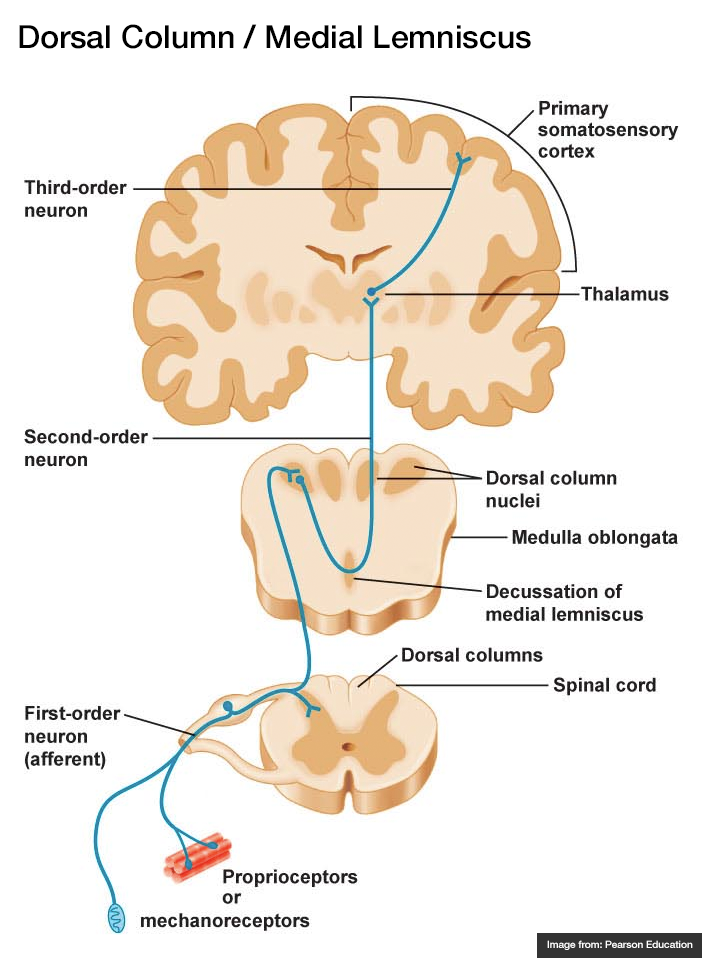
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
an area of the cerebral cortex found at the front of the parietal lobe (next to the motor cortex) that is responsible for integrating and processing touch, pain, and temperature signals from the body
Anterolateral Spinothalamic System
one of the ascending systems that brings sensory information from the body to the brain (specifically, pain and temperature)
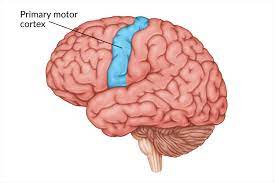
Primary Motor Cortex (M1)
an area of the cerebral cortex found at the very back of the frontal lobe that is responsible for issuing motor commands to the muscles of the body
Sensory Homunculus
a topographical representation of the body found in the cerebral cortex, mapping out which sensory signals come from which parts of the body
Lower Motor Neurons
neurons with cell bodies in the grey matter of the spinal cord that synapse directly onto muscles, telling them to contract or relax to create movement
Upper Motor Neurons
neurons with cell bodies in motor regions of the brain that carry motor commands down to the body and synapse onto lower motor neurons
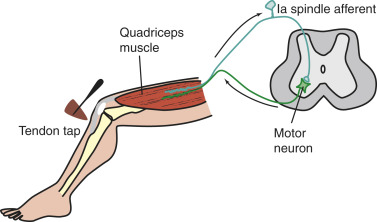
Myotatic Reflex
also known as the knee jerk reflex, in which the muscle of the front thigh contracts in response to the stretching of the tendon attaching the muscle to the knee
Muscle Spindle
stretch receptors buried in skeletal muscle that detect the length of a muscle and report this to the brain for proprioception, or body position perception
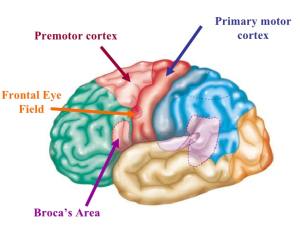
Premotor Cortex
an area of the cerebral cortex found in the back of the frontal lobe where motor commands are planned out before they are executed
Rubrospinal Tract
one of the descending motor pathways bringing motor information down from the brain to the muscles (specifically, voluntary movement relating to maintaining muscle tone)
Corticospinal Tract
one of the descending motor pathways bringing motor information down from the brain to the muscles (specifically, voluntary movement commands for most parts of the body, including limbs and digits)
Vestibulospinal Tract
one of the descending motor pathways bringing motor information down from the brain to the muscles (specifically, to maintain balance)