L17 Memory (Imported from Quizlet)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Acquisition of information
What is the definition of learning?
Storage of learned information
What is the definition of memory?
Reacquisition of stored information
What is the definition of recall?
Physical embodiment of a memory
What is the definition of the engram?
Ways, regions, pathways
Independent memory systems have different forms of memory stored in different ______/_______/__________ (e.g. playing piano vs passing exams)
Procedural, declarative, implicit, explicit
What are the 4 types of independent memory systems?
Skills and associations largely unavailable to conscious mind
What is procedural memory?
Available to conscious mind, can be encoded in symbols and language
What is declarative memory?
Memory that can be consciously recalled
What is explicit memory?
Memory that cannot be consciously recalled
What is implicit memory?
Procedural memory, classical conditioning, priming (when one stimulus influences the response to subsequent stimuli)
What are the 3 different types of implicit memory?
Immediate memory
Which memory only lasts a few seconds?
Short-term memory (working memory)
Which memory lasts seconds or minutes?
Long-term memory
Which memory lasts days, months, years?
Hallucinations and recollection of past experiences
What can an electrical stimulation of the temporal lobe cause?
Complex sensations and memories
What do epileptic seizures cause?
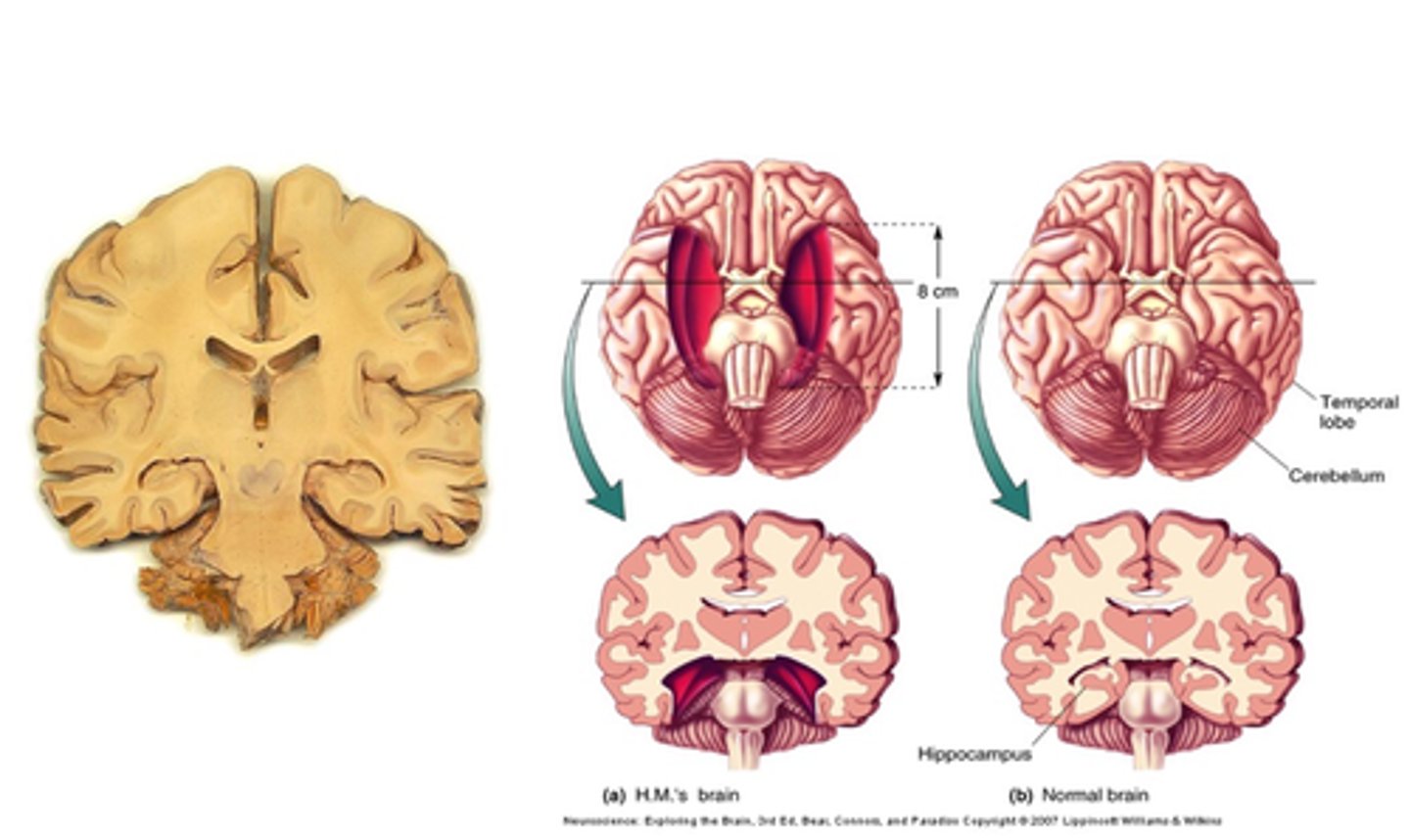
8cm of the medial temporal lobe was removed (epileptic seizures stopped)
Intelligence, personality, etc was intact
Extreme anterograde amnesia (couldn't acquire new memories)
Describe the temporal lobectomy of patient HM
That the temporal lobe in involved in creating long-term memories
The results of the patient HM experiment suggested what?
Working memory
What is the pre-frontal cortex responsible for?
Converting short to long term memory
What is the hippocampus essential for?
Declarative memory
What is the hippocampus responsible for?
Multiple, processed sensory inputs (smell)
What happens in the amygdala?
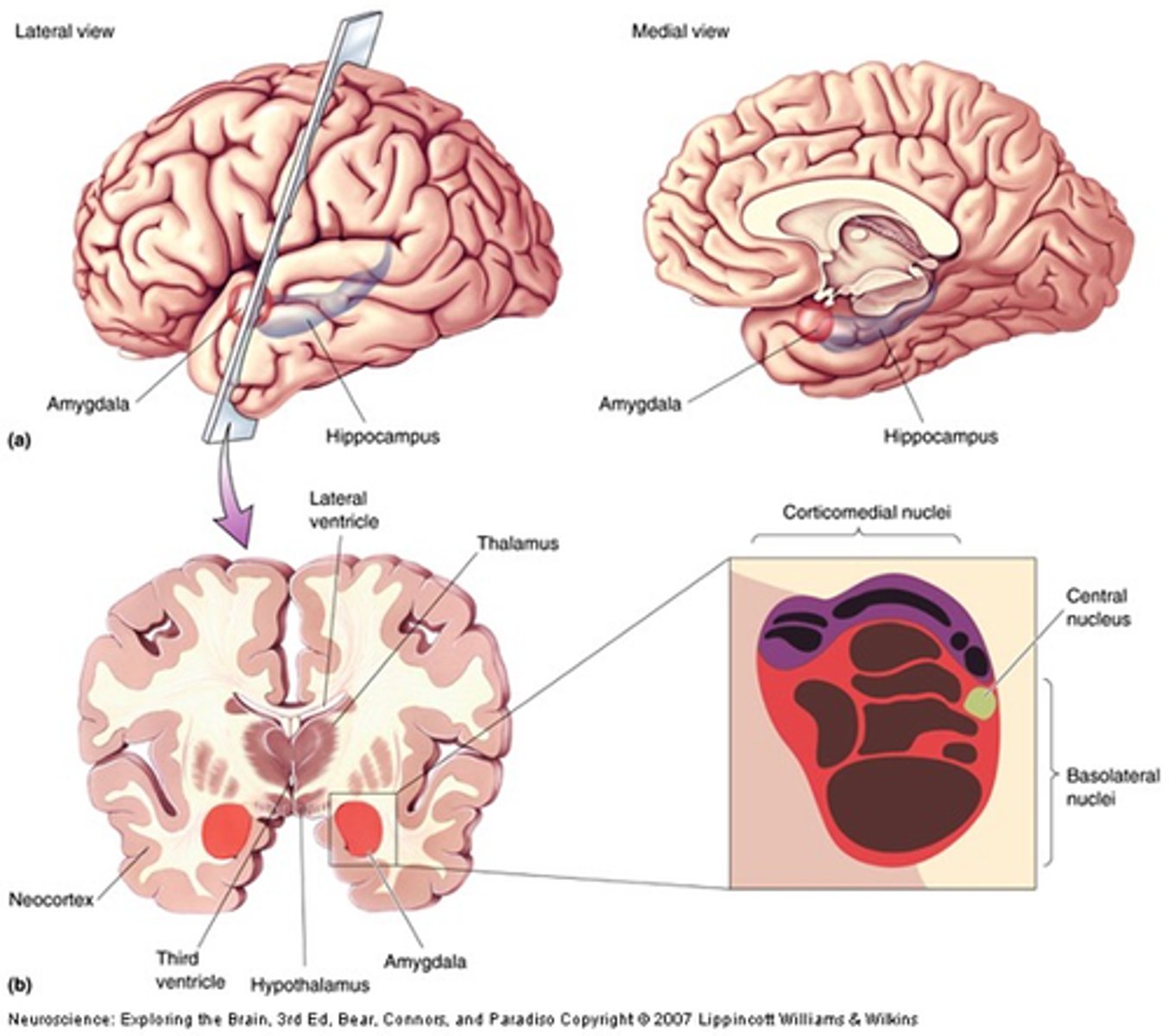
Implicit memories/emotional memories/learnt fear
What is the amygdala responsible for?
Procedural memory
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
Sensorimotors
The cerebellum is involved with ________________
Memory loss
What do hippocampal lesions (elective or accidental) cause?
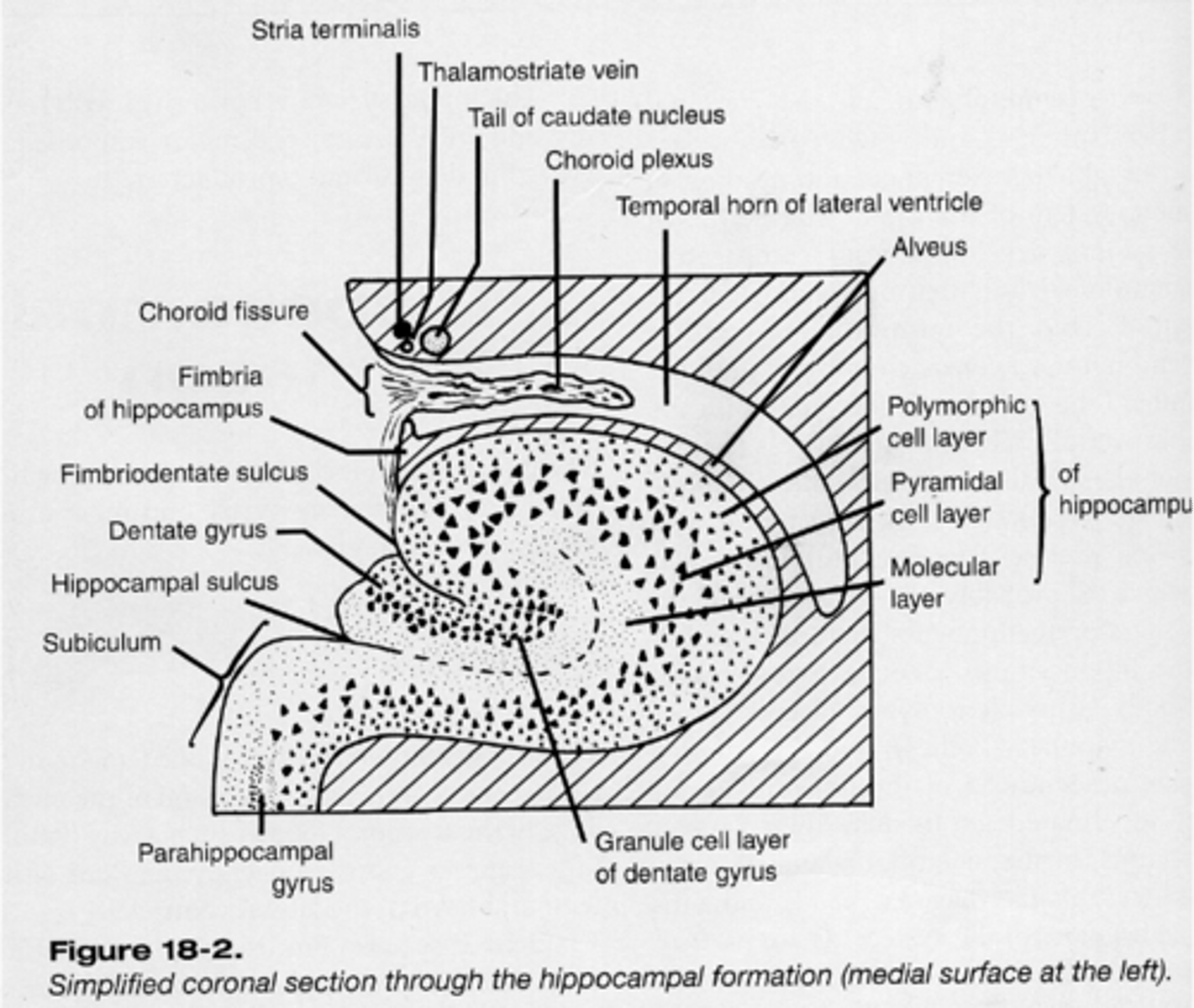
3
How many layers are in the hippocampus?
Entorhinal cortex, many regions
The hippocampus inputs from _____________ _______ and beyond and outputs to _____ _________
Good spatial memory
The hippocampus is enlarged in people whose work requires what?
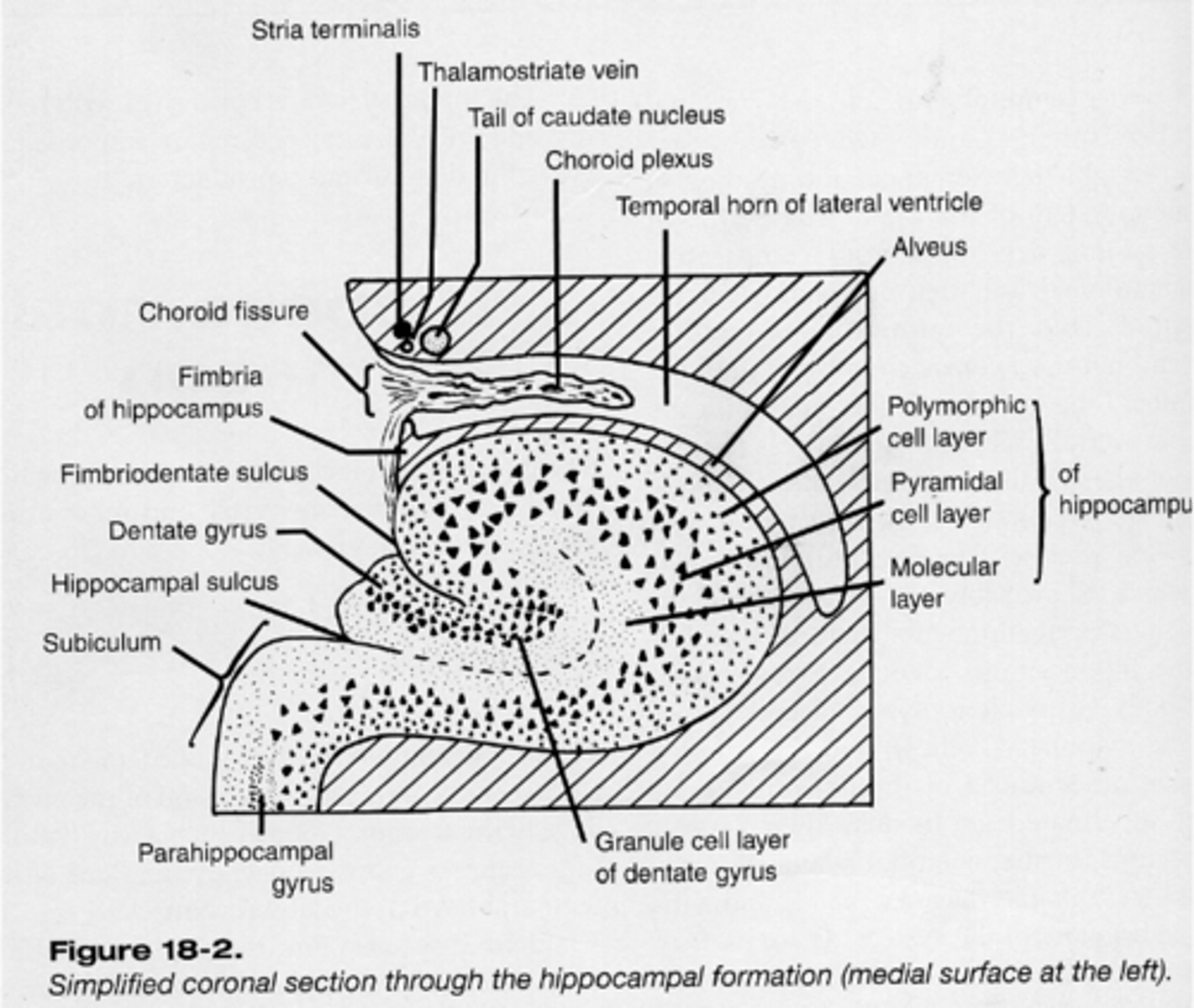
Distributed
Long-term storage of memory seems to be _____________
Reverberating
Mechanisms of memory are an example of _______________ circuits
Change depends on the activity of the neuron
Activity modifiable, plastic synapse
The Hebbian synapse concept - postulates there is a change in the synapse of the neurons
Changes
With memory and synaptic plasticity, synaptic strength _________
Short-term, Ca2+, vesicle
Facilitation/depression is ______-______ (mins/hours) and relies on ____ availability/__________ depletion
Sustained
Long-term facilitation/depression is _________________ (days/weeks+)
LTP in hippocampal slices (and elsewhere)
What does this image show?
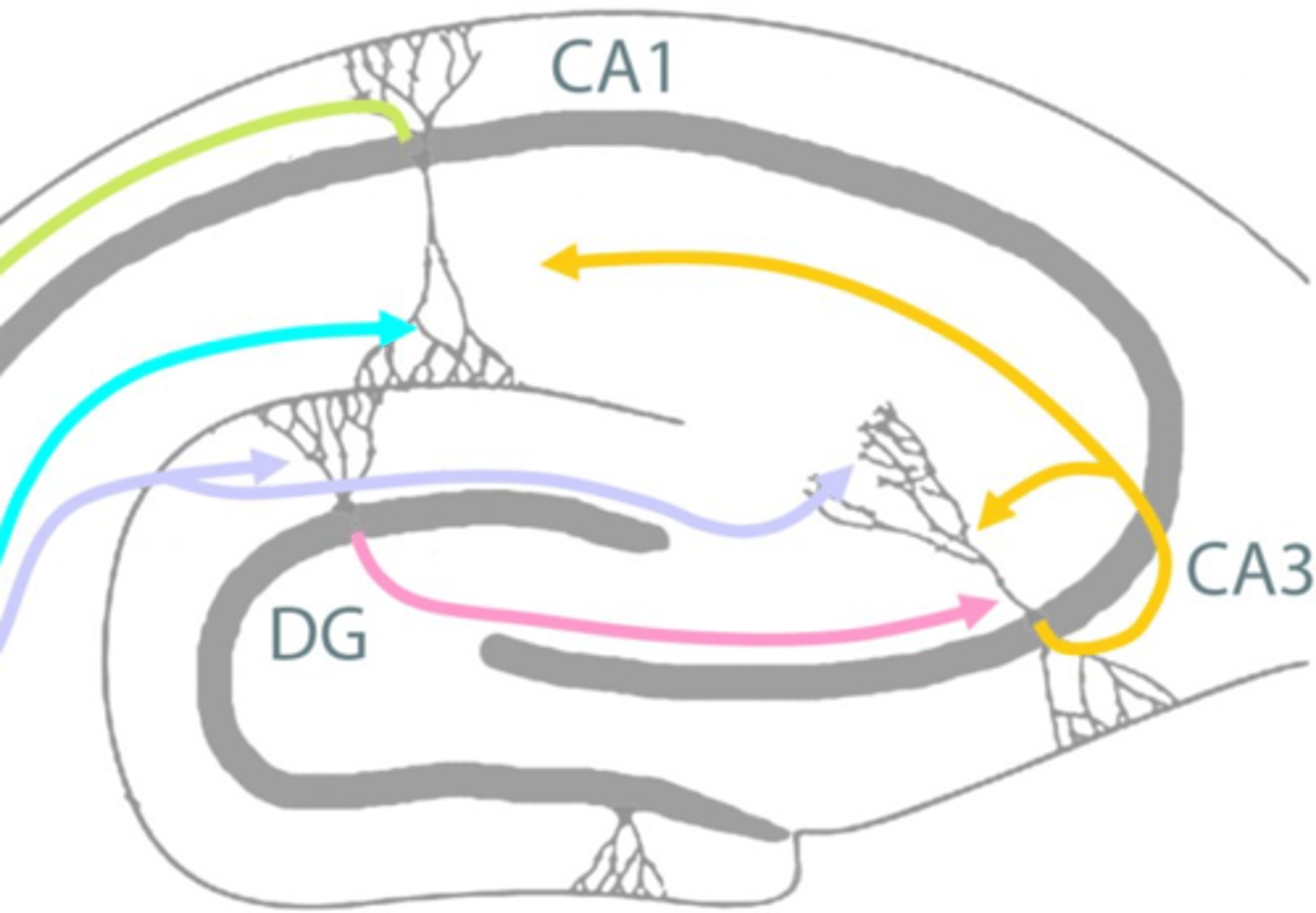
Long term potentiation
What does LTP stand for?
Post-"tetanic" LTP
High frequency burst
LTP in specific pathway
What does this image show?
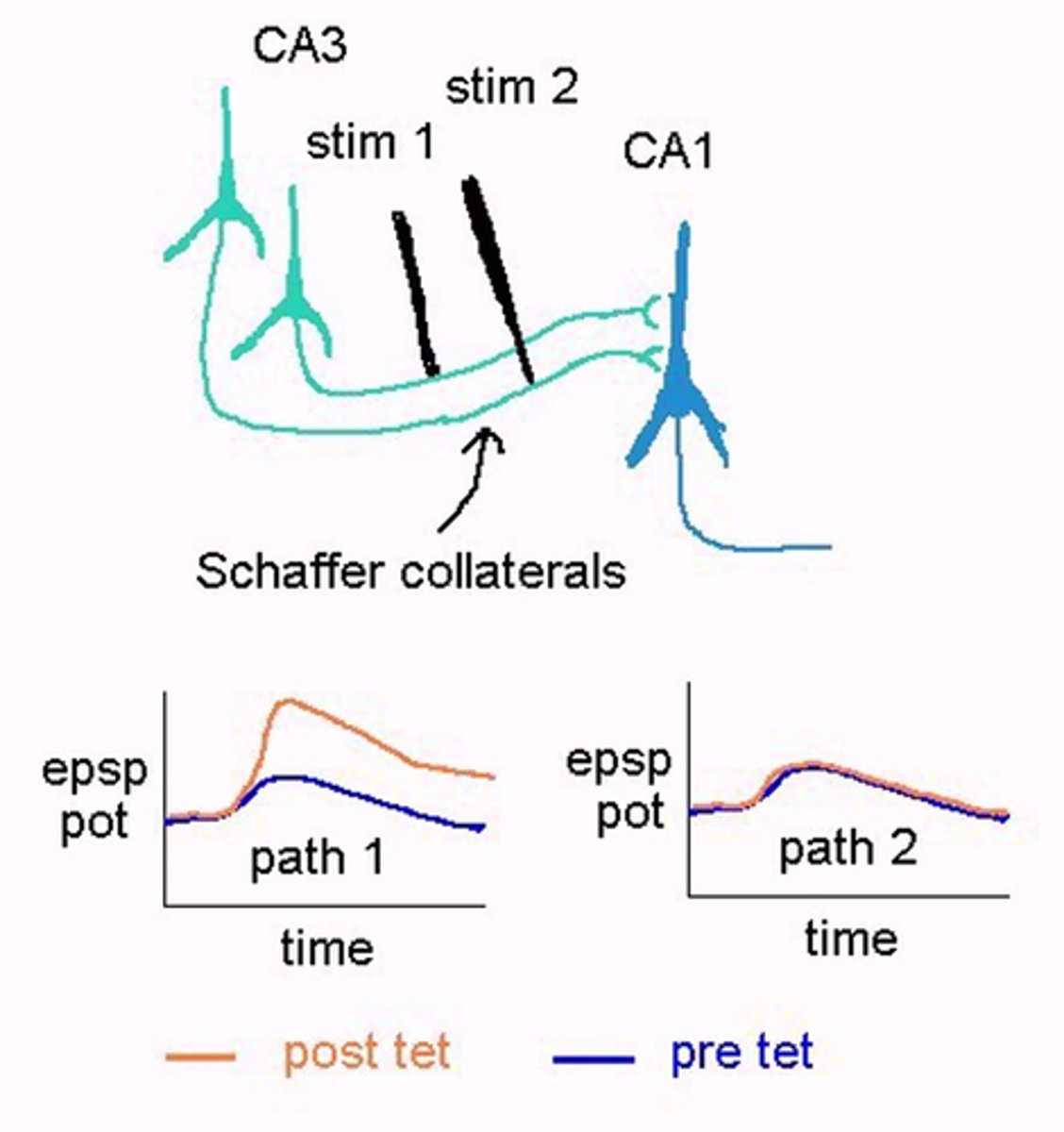
Paired LTP
Coincident stimulus and depolarisation
Associativity
What does this image show?
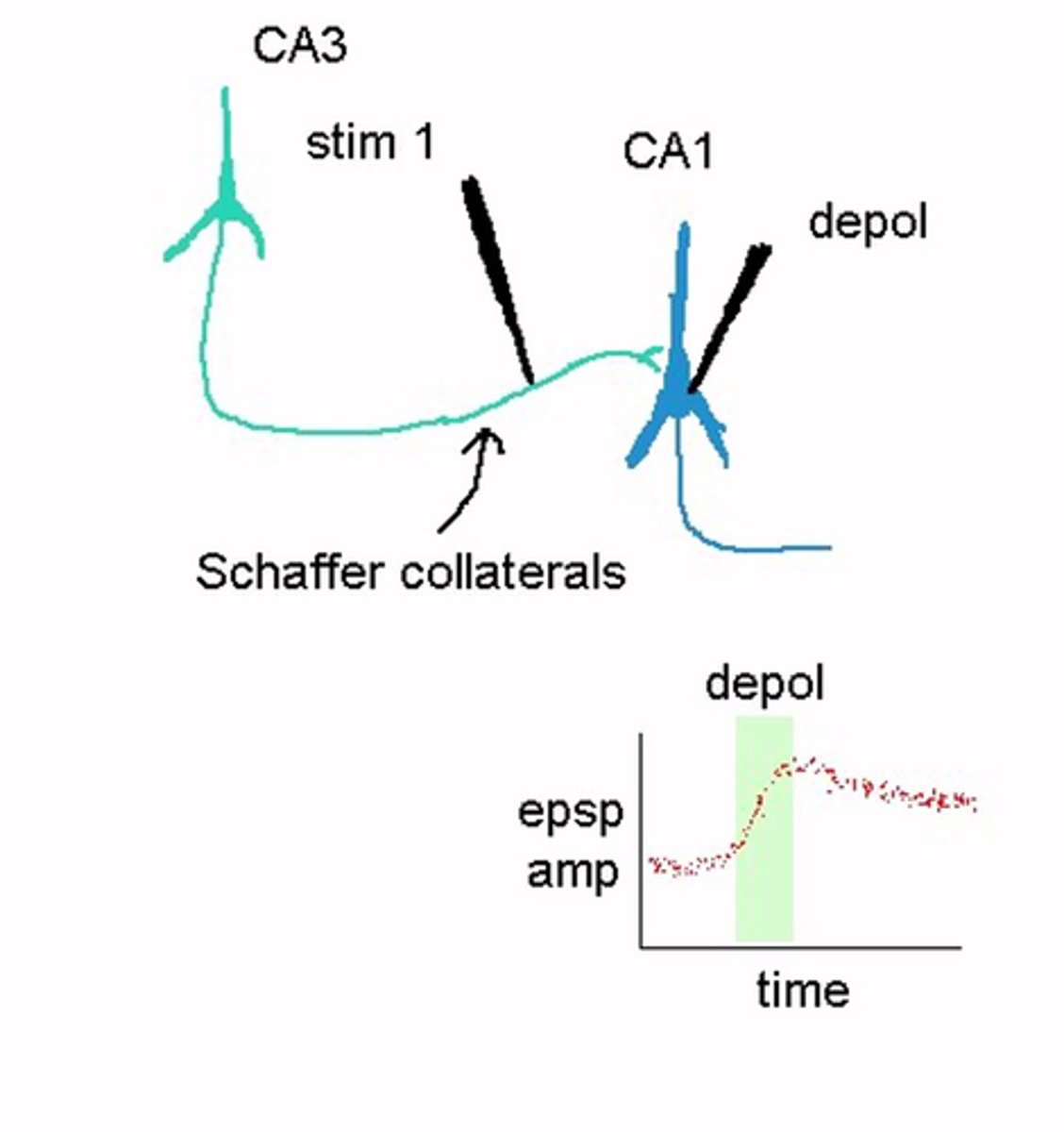
Long term depression
What does LTD stand for?
The hippocampus
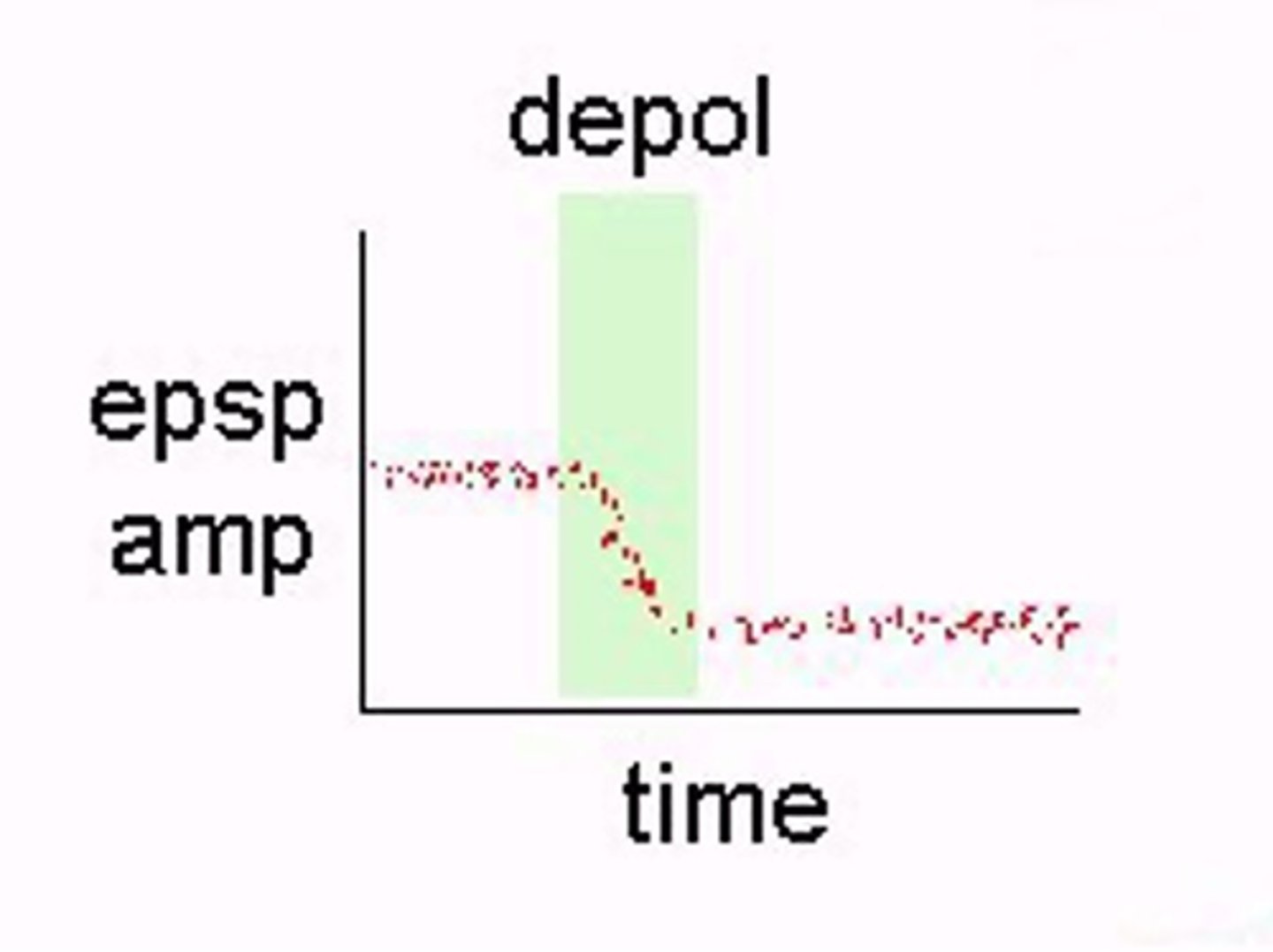
Where do you get LTD?
EPSP amp decreases with time and will stay like that for hours/days/weeks
What happens in LTD?
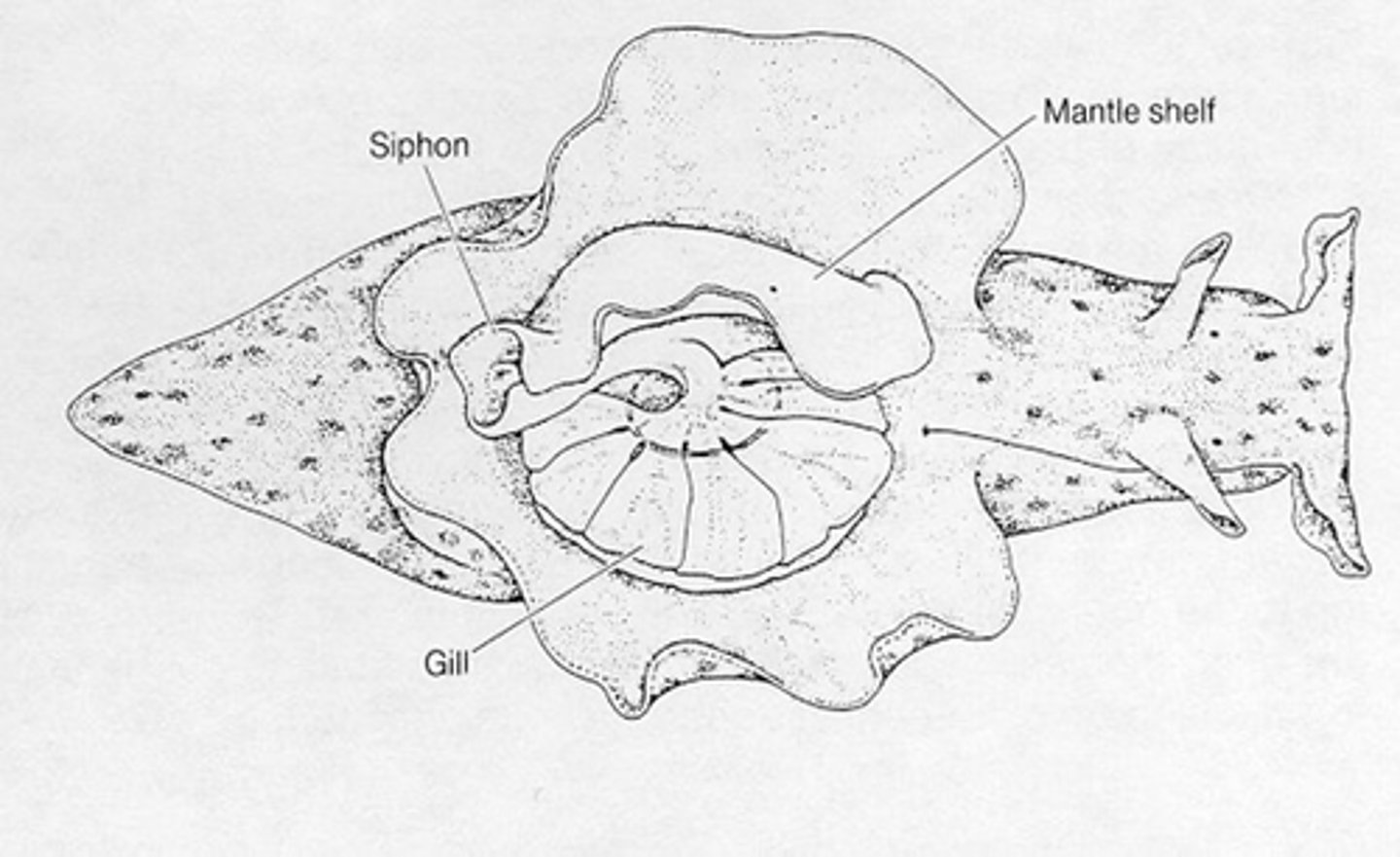
Neurons, Gill withdrawal
Aplysia Californica has a small number of _________ and a ___ ___________ reflex
Reduced gill withdrawal (habituation)
Repeated gentle stimuli to siphon causes what?
Re-establish siphon reflex, short term ~60min+
If you pair single tail pinch (aversive) with siphon touch, what happens and is it long term or short term?
Long, habituating
Repeated pairing of siphon touch and tail pinch - _____-term, non-_____________ siphon/gill reflex
Activation
LTP, LTD and Aplysia require receptor ______________ (glutamate/serotonin)
Synaptic
LTP, LTD and Aplysia have altered __________ responsivity
Second messengers (Ca2+/cAMP)
What is LTP, LTD and Aplysia mediated by?
Protein phosphorylation
In early stages, what does LTP, LTD and Aplysia require?
Protein synthesis
In late stages, what does LTP, LTD and Aplysia require?
Biochemical, structural
LTP, LTD and Aplysia involve ____________ and ____________ pre and post-synaptic changes
Evidence suggests often a post-synaptic event
Most indicates a critical role for Ca2+
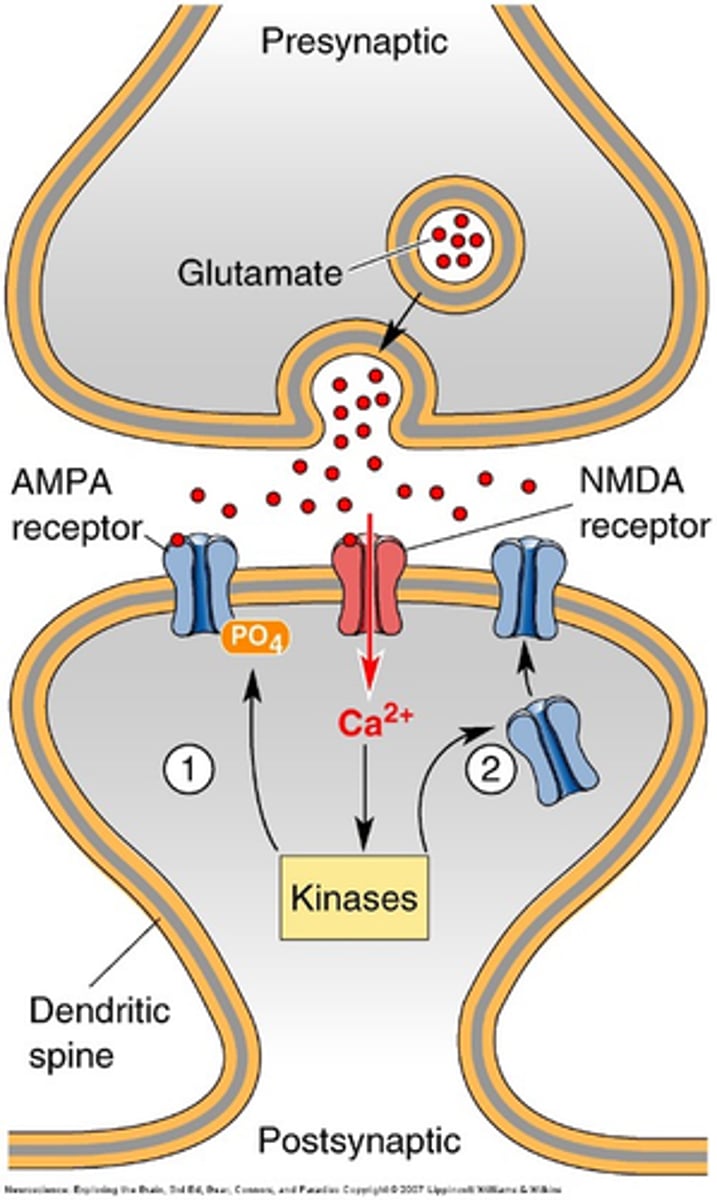
Involves trafficking of AMPA receptors to the postsynaptic membrane
How does LTP occur?