AP Biology Unit 2: Cell Structure and function
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
All living things are made of cells
cells are the smallest units of life
cells only come from other cells through cell division
Cell Theory
plasma membrane, DNA, cytoplasm, Ribosomes
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic similarities
Nucleoid Region, no membrane bound organelles
prokaryote characteristics
nucleus, membrane bound organelles
Eukaryote characteristics
SA = plasma membrane V= cytoplasm. High SA:V ratio = crammed organelles and faster transport
Why do cells have large SA:V ratio?
low = high concentration of hydrogen ions
high= low concentration of hydrogen ions
pH
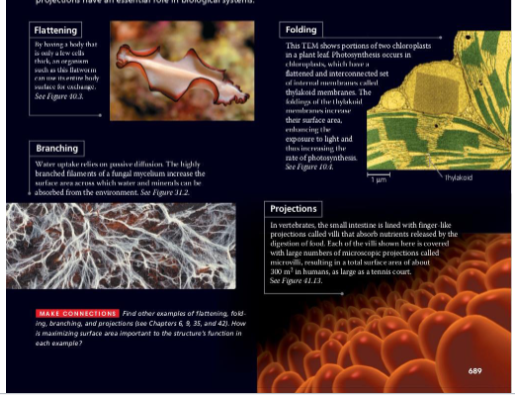
flattening, branching, folding, projections
Adaptation to increase SA:V ratio
increase sa:v ratio and absorb water
role of root hairs
Mutualism: fungus absorbs water + minerals, mycorrhizae gets amino acids and sugars
mycorrhizae and fungi role
threads in intestine that help absorb nutrients
microvilli role in inestines
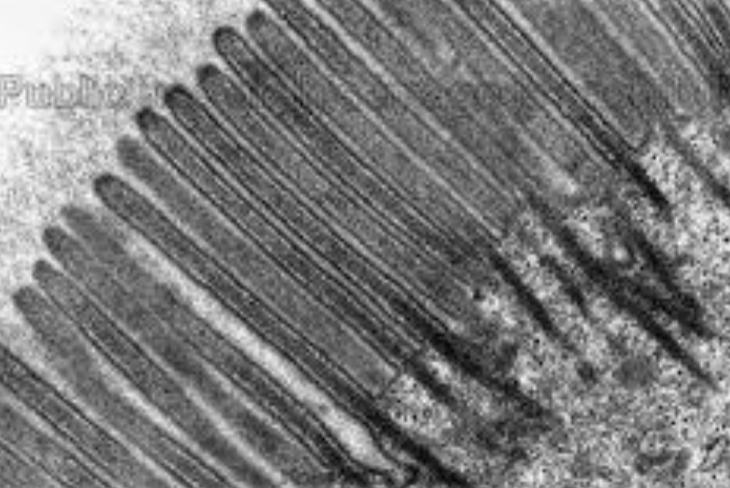
small diameter, folds, microvilli
small intestine adaptations to increase sa:v ratios
membrane bound organelles separate the different jobs, increase efficiency for more complex issues. Small, flat folded and branching cells allow organelles to be squished in max sa:v ratio
why are eukaryotes compartmentalized?
respiratory membrane of bacteria; thylakoid membrane acts as a plasma membrane
compartmentalization in prokaryotes
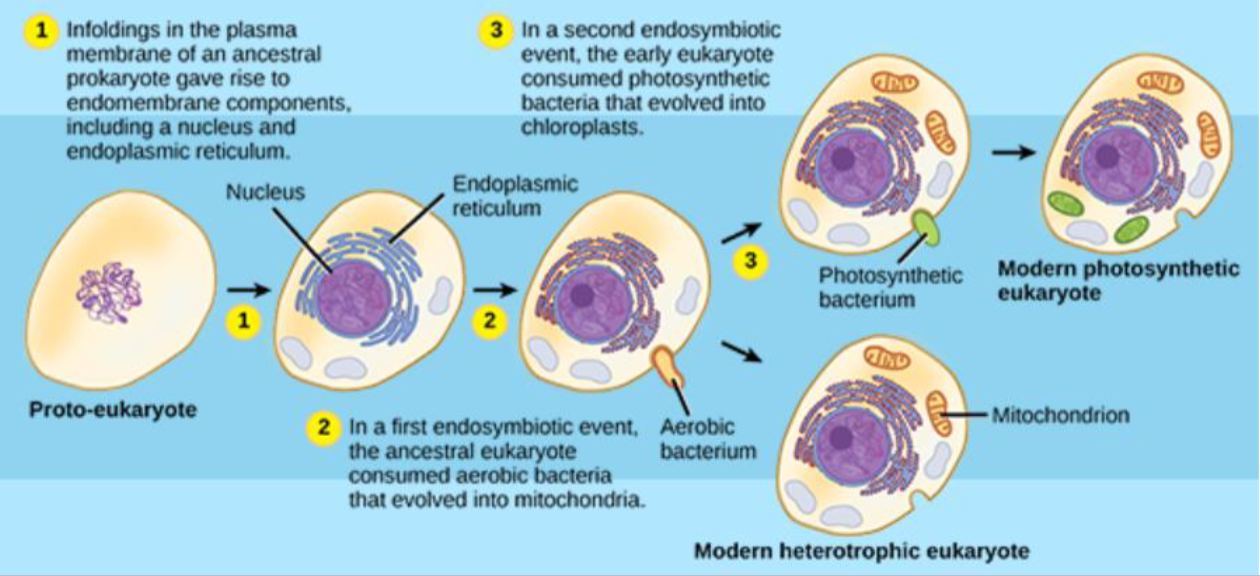
two independent bacteria exist, one engulfs the other and both live and benefit, reproduce together. Mitochondria and chlorplasts.
theory of endosymbiosis

some organelles have double membranes, reproduction occurs like fission, susceptible to antibiotics
evidence of endosymbiosis
hydrolyze/digest stuff within a cell, apoptosis, dissolving tail/webbing, recycles damaged organelles
lysozome roles
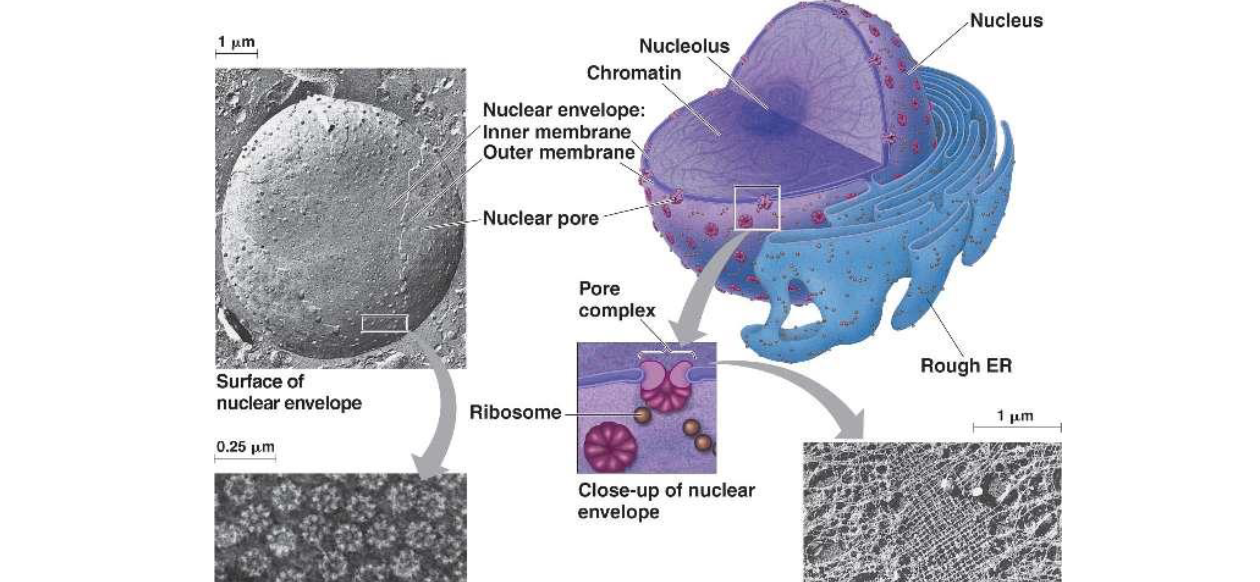
stores DNA
has nuclear envelope with pores to transport large proteins
site of gene expression
nucleus roles
inside nucleus, produces ribosomes
nucleolus
protein synthesis: arrange amino acids
ribosome role
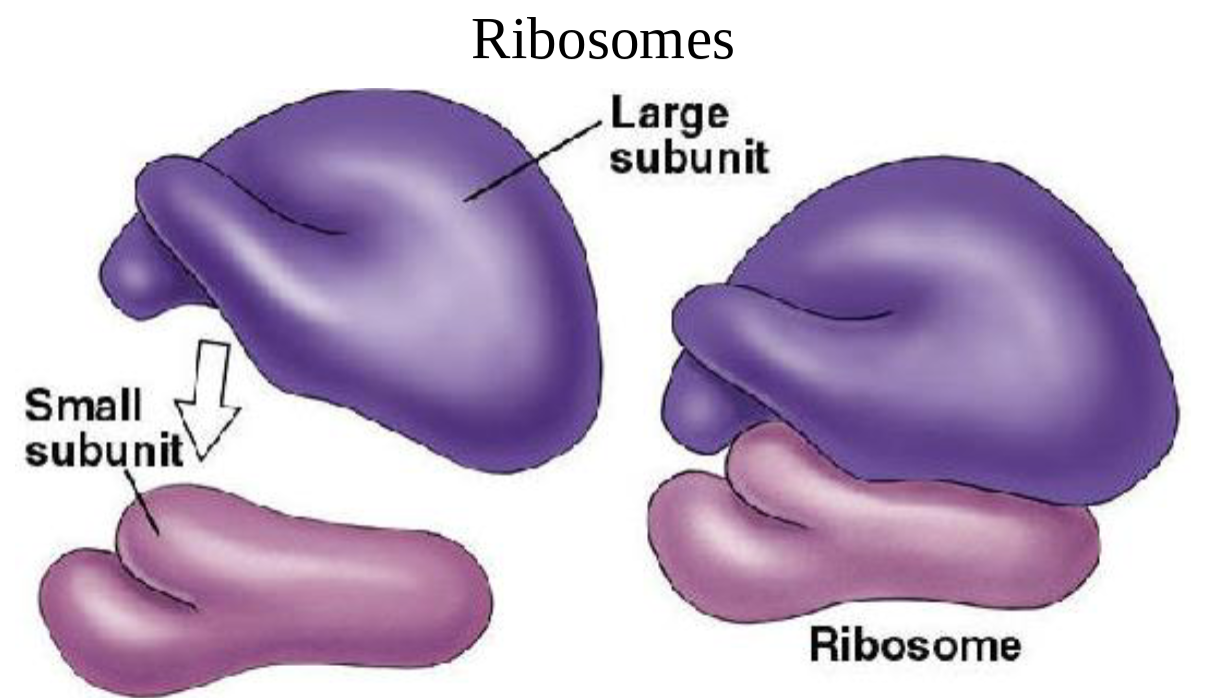
1 large 1 small, made up of rRNA and protein
#of ribosomal subunits and materials needed for synthesis
sythesize secretory proteins, create membrane for transport vesicles
rough er roles
free ribosomes are used in the cytooplasm,
attached ribosomes are attached to rough er and will go to plasma membrane or be secreted out
free vs attached ribosomes
smooth er
lipid synthesis
smooth er
drug detox: filtering blood and detoxing in liver
smooth er
carb metabolism: metabolize glycogen, reduce muscle damage via glucagon hormone
smooth er
calcium ion storage for muscle contractions
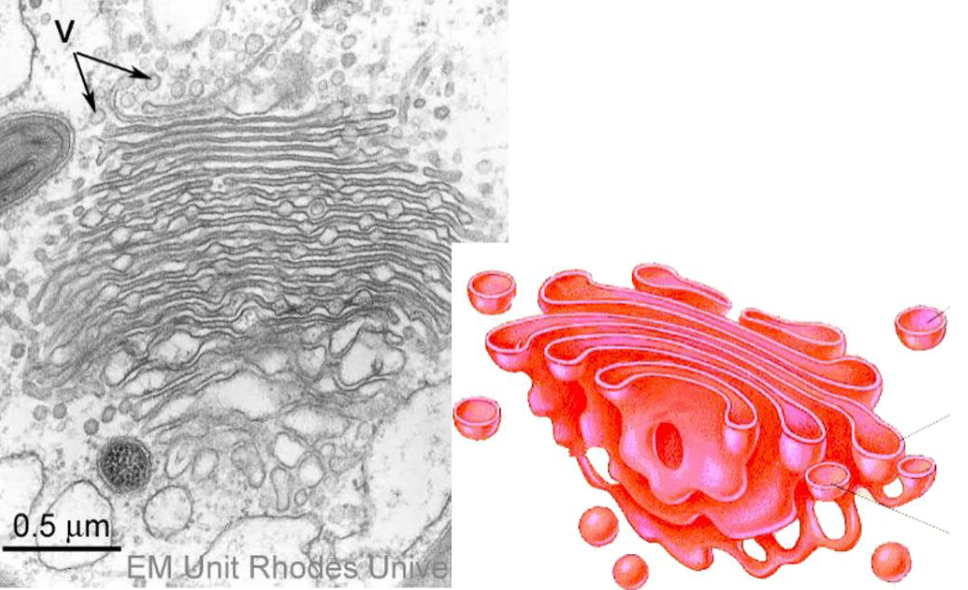
adds functional groups to proteins e.g phosphate group
complete tertiary/quaternary structure
packages carbs to synthesize cellulose on site
think packaging site
golgi apparatus
The central vacuole:
1. stores water to increase turgor pressure and stretch cells
store pigments in petals to attract pollinators
store toxins to repel predators
vacuoles: compartments
increase sa:v ratio
purpose of folded inner membranes within mitochondria and chloroplasts
plants, animals, fungi, protists
4 types of organisms that contain mitochondria
same as the site of cell respiration
enzyme location for cellular respiration
light reactions and calvin cycle
components of photosynthesis
same as where light reactions and calvin cycle take place
where are the enzymes for each step of photosynthesis located?
thylakoid membrane
light dependent reaction location
stroma
calvin cycle location
cytoplasm
glycolysis location
mitochondrial matrix
transition reaction and krebs cycle location
inner membrane (cristae)
chemiosmosis/electron transpport chain location
semipermeable
cell wall permeability in plants
plasmodesmata
holes in cell wall that allow for fast exchange of water, minerals, sugars, and other macromolecules between two cells
chitin, semi permeable
chemical composition of fungi cell walls, permeability
septa
partially formed cell wall in fungi that helps transport all polymers except for Dna and Rna
peptidoglycon = AA+sugar combo, semipermeable
chemical composition of bacterial cell walls, permeability
Fluid Mosaic Model
model of cell membranes characterized as dynamic, flexible, and always changing composition. Made up of a ____ of components
laterally
direction that membrane components move
sidedness
referring to how the cytosol and extracellular stuff are different, stuff on either side of the membrane is different
regulate fluidity
cholesterol role in cell membranes
hydrophilic, hydrophobic
phospholipid heads are ____, phospholipid tails are____
false
true or false, the membranes within each organelle and species have the same chemical composition and structure
Too rigid= not enough transport, too fluid= too much transport
how does fluidity influence transport?
usually for warm temps, makes membrane more rigid
how do the presence of saturated phospholipids impact membrane fluidity?
usually for cold temps, makes membrane more fluid
how do the presence of unsaturated phospholipids impact membrane fluidity?
more cholesterol + unsaturated fats bc of cold, increase fluidity
what would the membrane structure of a fish living in very cold waters look like?
conifers have more saturated fats= adjusting temps
what would the membrane structure of a tree living in changing temps look like?
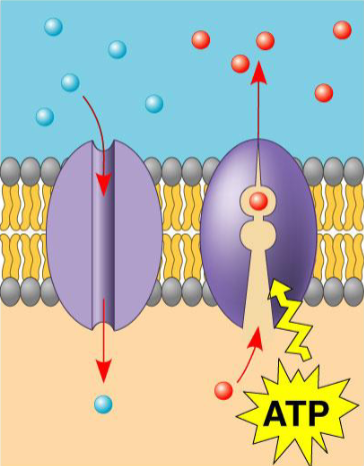
Transport proteins: send substances in and out of cells
what protein, what purpose?
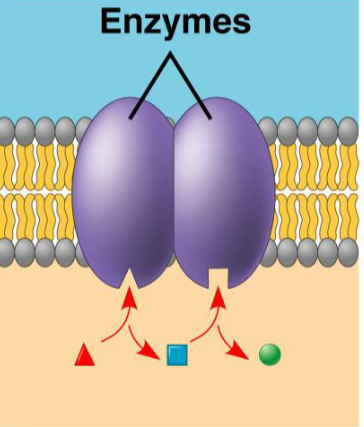
Enzymatic Proteins: make cellulose, ATP, chloroplasts
what protein, what purpose?
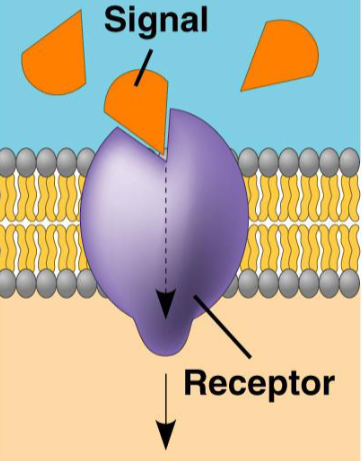
Signal Transduction Proteins: cell communications with transmitters and receivers, think insulin
what protein, what purpose?
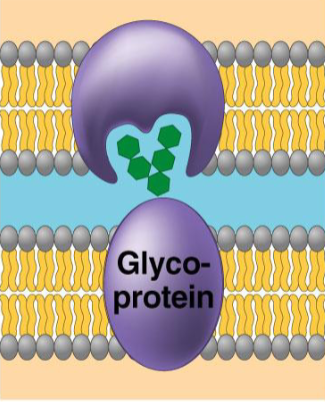
Glycolipids/Glycoproteins: cell marking/identification, think immune response, blood transfusions, tissue/organ transplants
what protein, what purpose?
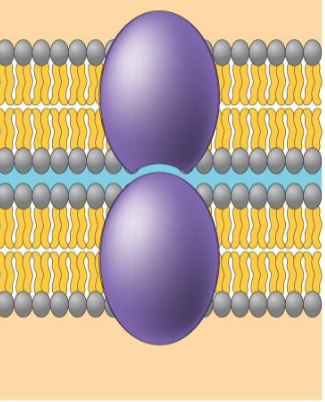
Intercellular joining: skin
what protein, what purpose?
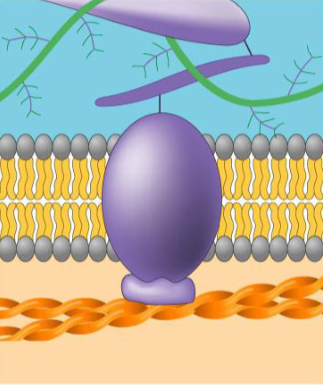
Cytoskeleton connection to extra cellular matrix: environment and cytosol are connected via proteins
what protein, what purpose?
Smooth er makes lipids
Rough er makes proteins
Golgi packages lipids and proteins
where are cell emmbranes built and modified?
transport large ions through facilitated diffusion
transport protein purpose
true
true or false: transport proteins are specific to an ion
Transport proteins can only work so fast, rate increases than plateaus with a limited number of transport proteins, more proteins = more transport
transport protein saturation
moving a nutrient from high to low concentration, no energy
passive transport
different concentration on either side of a membrane vs same concentration
concentration gradient vs equuilibrium
high to low
water flows from ___ to ___ water potentials
decreases, decreases
as solute concentration increases, solute potential _____ which ____ water potential
lipid soluble vitamins, proteins
what will diffuse fastest across a membrane?
their own
each nutrient diffuses down ____ concentration gradient
gases like O2, N2, CO2, small uncharged/nonpolar molecules
what molecules can pass through the lipid bilayer through diffusion, without a transport protein?
an organism’s ability to regulate internal water, e.g kidneys, skin, and large intestine help absorb water and get rid of excess
osmoregulation
water moving from high to low solute concentrations or through facilitated diffusion with transport protein
osmosis
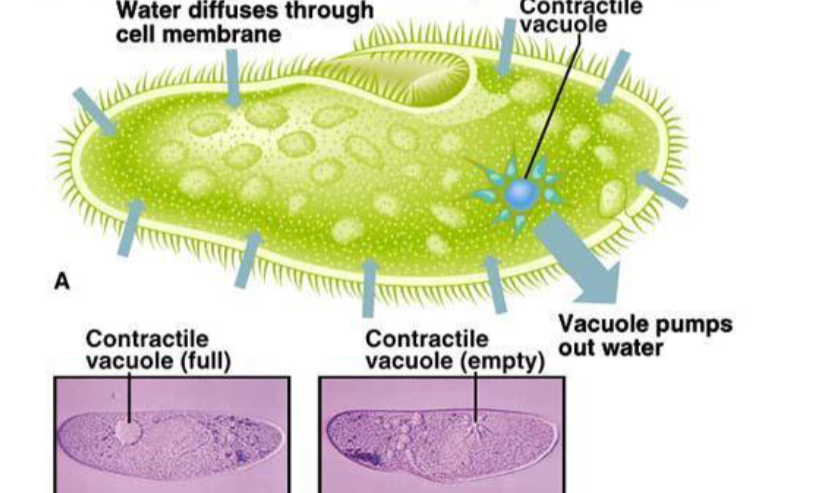
help osmoregulation by allowing freshwater to diffuse into the cell but then being pumped out by vacuole to reduce water pressure. Pumps from low to high.
contractile vacuoles in freshwater paramecium
tonicity
how solutes influence osmosis
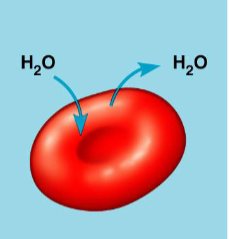
normal, red blood cells, body tissues
animal cells in an isotonic solution, examples
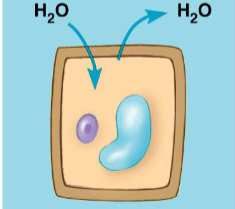
flaccid, guard cells close stoma to stop water loss
plant cells in an isotonic solution, examples
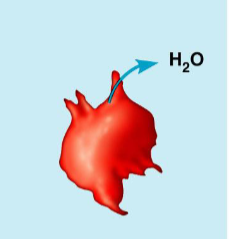
crenation (shrivel), high salt concentration in blood draws water from body tissues, increasing blood pressure
animal cells in hypertonic solution, examples
plasmolyzed (large gap between cell membrane and cell wall), excess fertilizer dehydrating lants
plant cells in hypertonic solution, examples
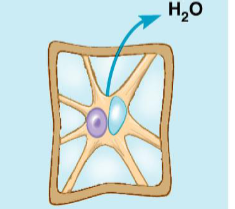
lysed, large intestine epithelium, capillaries designed to absorb water, without regulation it leads to dysentery
animal cells in a hypotonic solution, examples
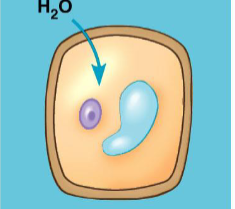
turgid, root hairs, guard cells open stoma to let water in
plant cells in a hypotonic solution, examples
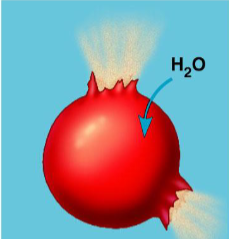
hypertonic
water moves towards the ____ solute concentration
using transport and carrier proteins to move large molecules from high to low concentration, no energy
facilitated diffusion
channel proteins
funnel ions from one side of a membrane to another, can open and close, used in passive transport
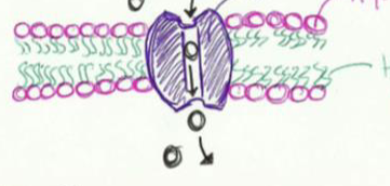
carrier proteins
changes shape to dump ions on other side of membrane, used in active transport
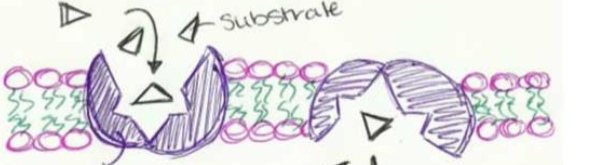
water through aquaporins
fructoose through channels in small intestine epithelium
glucose through muscle,liver, or fat cell channels
examples of substances that diffuse through transport proteins
using a transport protein to pump large substances from low to high concentrations, requires energy supplied by ATP
active transport
Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) ion pumps used in neurons
Proton pumps in mitochondria and chloroplasts
examples of active transport
charges of the cytosol and extracellular fluid can impact diffusion
membrane potential
negative, positive
the cytoplasm is usually ___ and the extracellular fluid is usually ___
true
true or false: if a nutrient has a charge it is impacted by membrane potential
sodium potassium pump in neurons
proton pump in in mitochondria and chloroplasts in plants, fungi, and bacteria
examples of membrane potentials
no concentration gradient
why is energy used for bulk transport, though it is not considered active transport?
a vesicle produced and packaged at the golgi goes to plasma membrane, fuses and dumps nutrients SECRETE
exocytosis
SECRETE
pancreas secreting insulin
White blood cells secreting antibodies
small intestine epithelium secreting enzymes
exocytosis examples
phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor mediated endocytosis
types of endocytosis
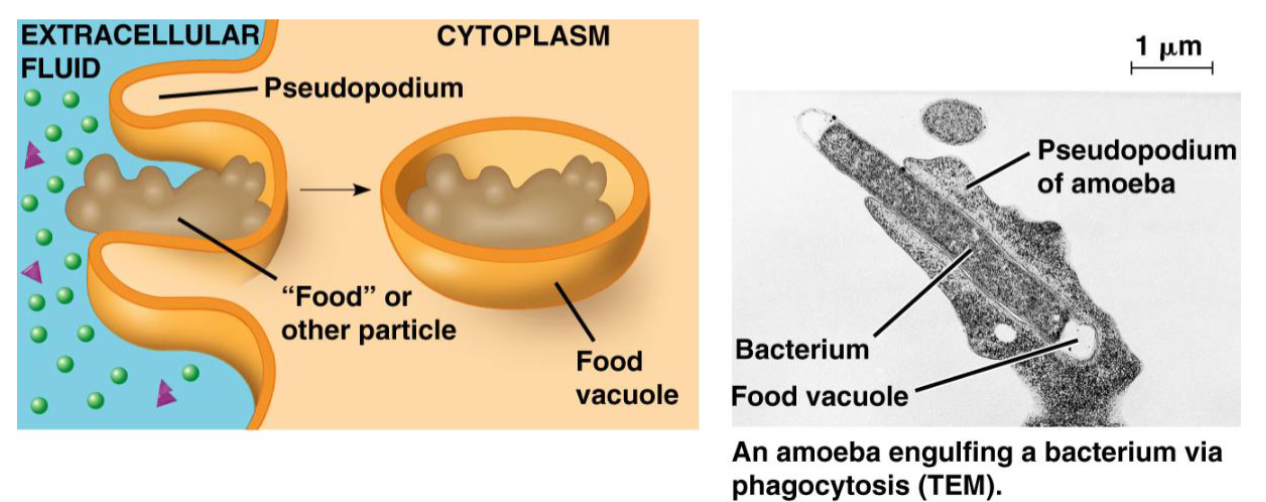
englufing food particles and creating food vacuoles.
lysozomes
White blood cell engulfing a virus
Amoeba engulfing a bacterium
phagocytosis, examples
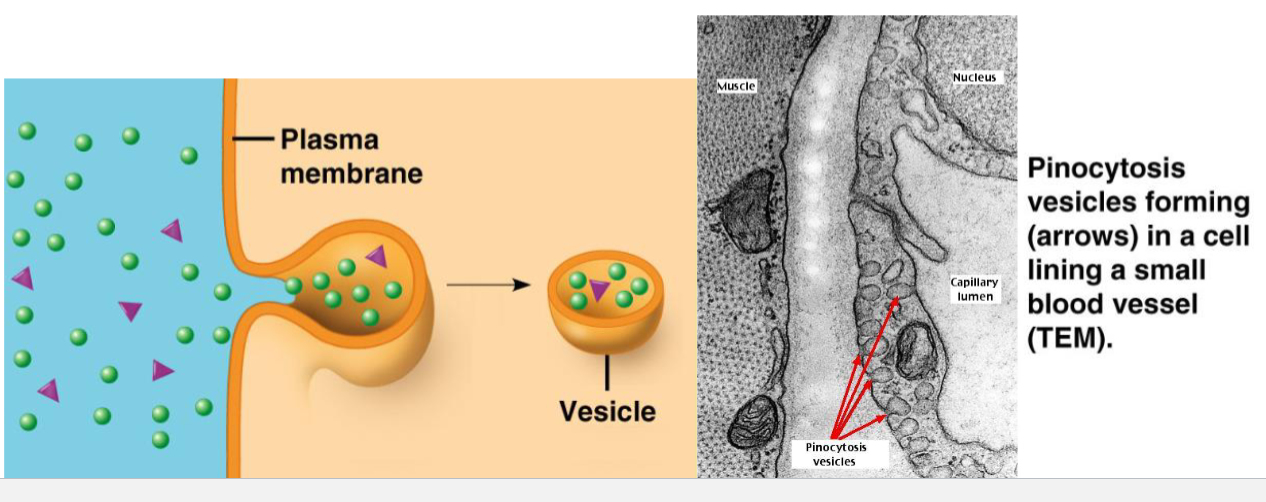
using transport vesicles to move fluids into cell. WITHIN EVERY CELL
epithelial cells taking in plasma (water minerals and biomolecules of blood)
pinocytosis, examples
target molecule binds to receptor protein
Liver cells removing cholesterol from blood, if receptor protein doesn’t work liver will make more cholesterol resulting in hypercholesterolemia
receptor mediated endocytosis, examples
loss of pressure = water is leaving cell
loss of turgidity