Introduction into Anatomy
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
coronal plane
divides body into front and back
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
longitudinal section
cut through the long axis of an organ
-parallel to the long axis
transverse section
a cross section at right angle to long axis
oblique section
cuts made diagonally between the horizontal and the vertical planes
Proximal
Towards the trunk
Closer to the point of attachment
Distal
Away from the trunk or point of attachment
Lateral
away from the midline
Medial
toward the midline
Cephalic/Cranial
toward the head
Caudal
toward the tail
Ventral
Toward the belly
Dorsal
toward the back
Parietal
Toward the wall
-outer layer
Visceral
Away from the wall
-inner layer
Ipsilateral
On the same side of the body
-the right arm and right leg are ipsilateral
Contralateral
On the opposite side of the body
-the right arm and left leg are contralateral
Extension
Increase in angle between body surfaces
-extending down/backwards
Flexion
Decrease in the angle between body surfaces
-flexing up/forward
Hyperextension
Extension beyond what is normal
Smooth Muscle
lines the walls of blood vessels, hollow viscera, and digestive tract
-acts as involuntary, autonomic control
-capable of partial contraction
-capable of peristaltic waves (contraction starts at one end and travels to the other end)
Arteries
carries blood AWAY from the heart
composed of:
-arterioles
-muscular arteries
-elastic arteries (aorta)
Elastic Arteries
contain elastin in the walls
-helps maintain BP between contraction
Muscular Arteries
distributing arteries
-can vasoconstrict to regulate flow to the different parts of the body when needed (controlled by the SNS)
-muscular walls (smooth muscles) contract to propel blood
Arterioles
smallest artery type
-contains thick, smooth muscle walls and a narrow lumen
-regulates arterial pressure
Veins
returns low oxygen blood to the heart (only flows in one direction)
-contains thin walls
-do not pulsate or spurt
venules: smallest; drain capillary beds
Plexuses
collection of veins
venae comitantes
pair of veins around the artery
-acts as a artery pump to help return blood
Vasa Vasorum "Vessels of the Vessels"
some of the largest arteries and veins than contain arteries and veins of their own
Varicose Veins
stretched out veins
-when valves are closed they do not meet in the center causing blood to trickle back down
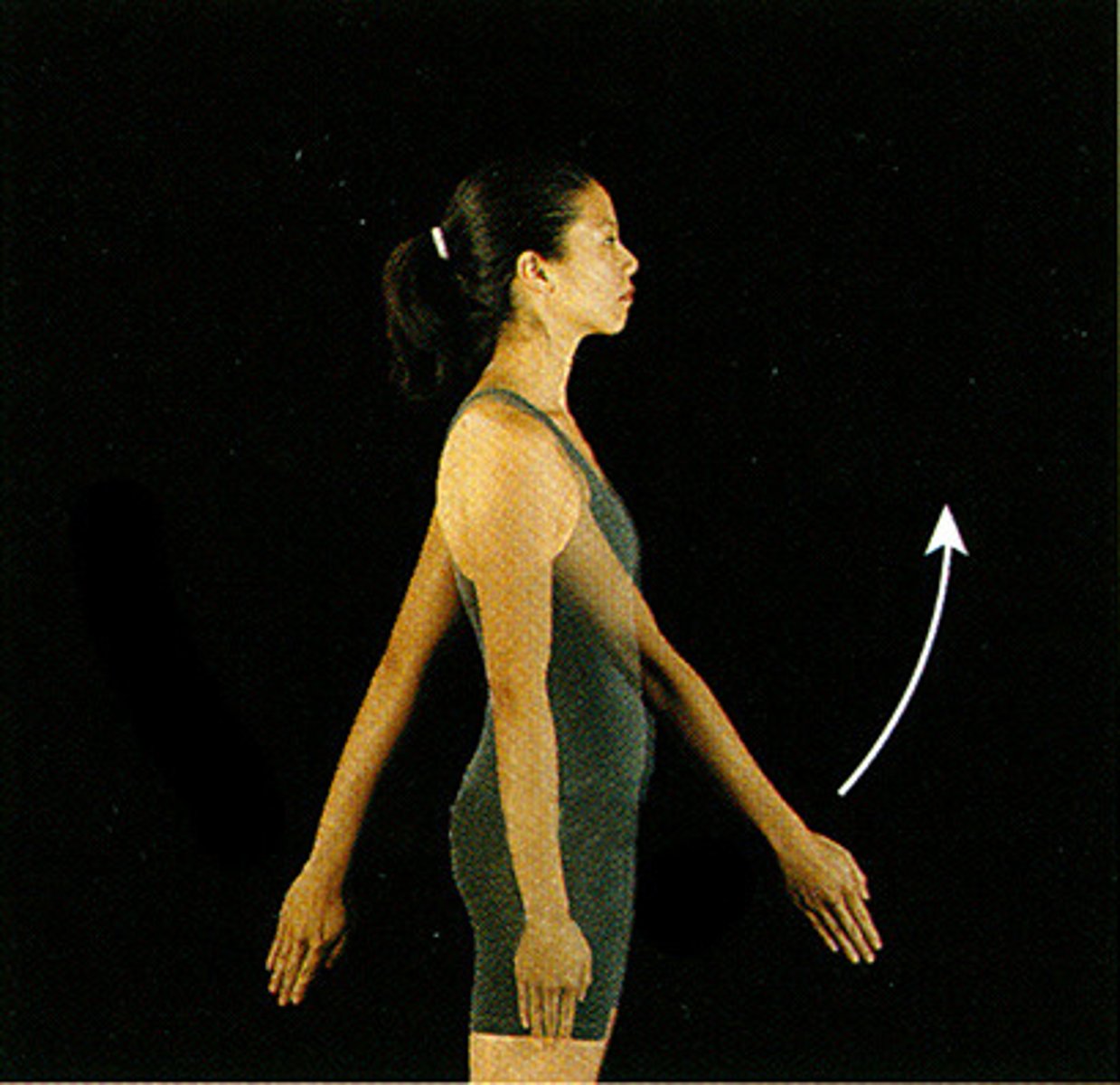
Flexion, if the shoulder is being raised the shoulder is being flexed forward
If a shoulder is being raised up in the supine position, what movement is being made?
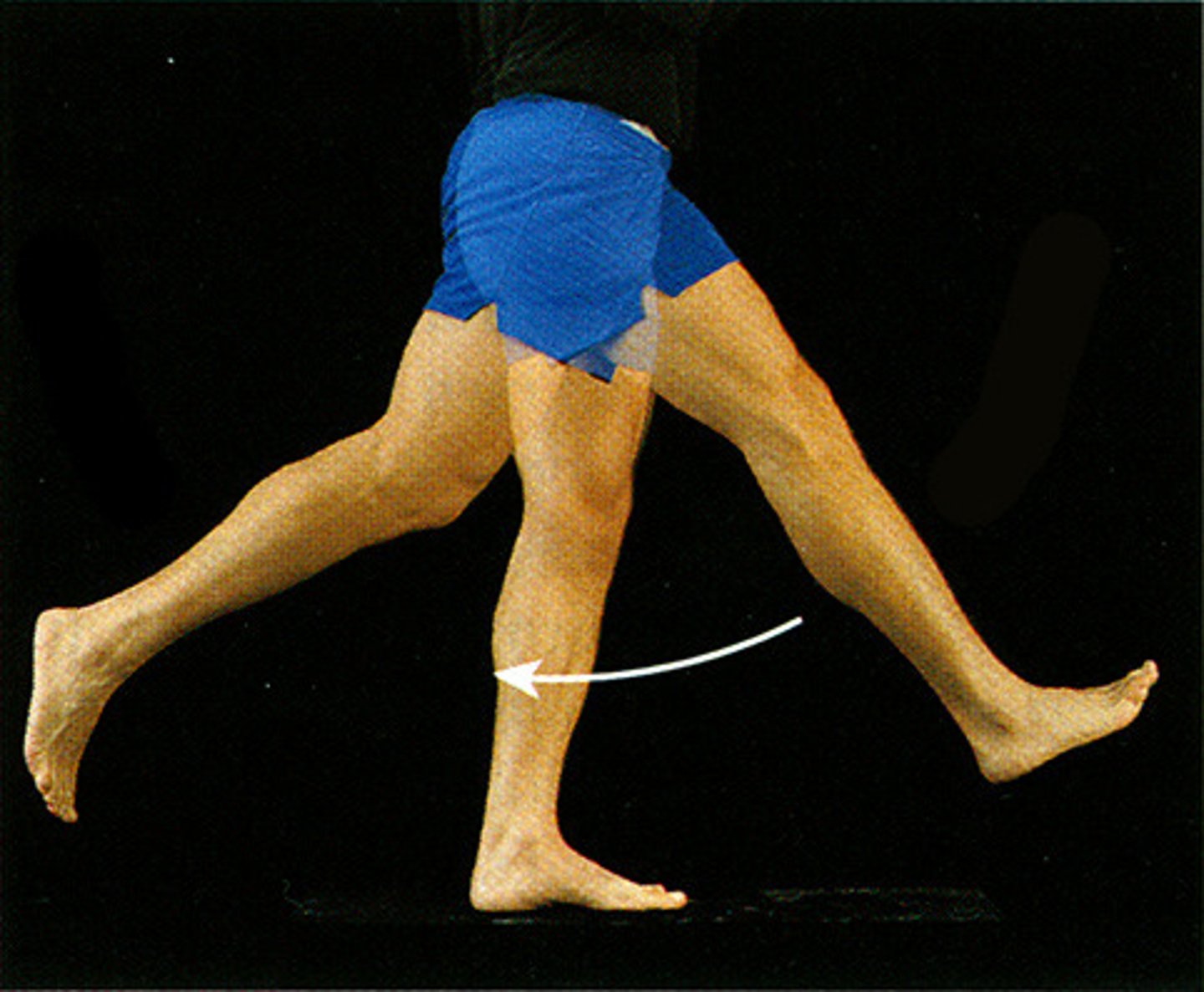
Extension, if the limb is being pulled back the joint is being extended
If a leg is being pulled back via hip joint, what movement is being made?
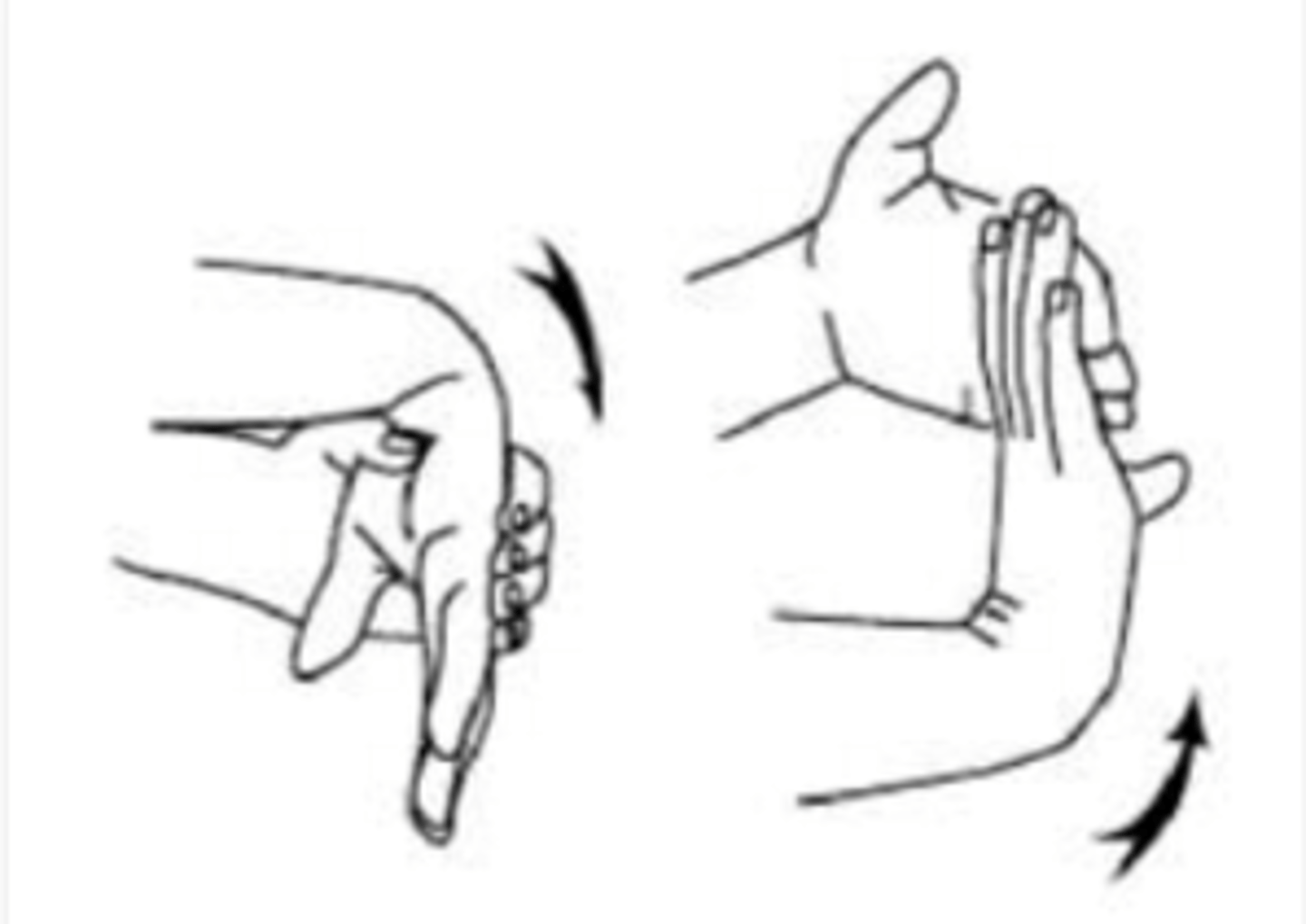
extension is the acting of extending the wrist upwards while flexion is the act of flexing the wrist downward
In which way is the wrist joint being extended and flexed?
Flexion is the contraction of the fingers to form a fist while extension is the extension of fingers while stretched out
In which way does the extension and flexion of digits (fingers occur) at metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints
Abduction
away from the median (going out)
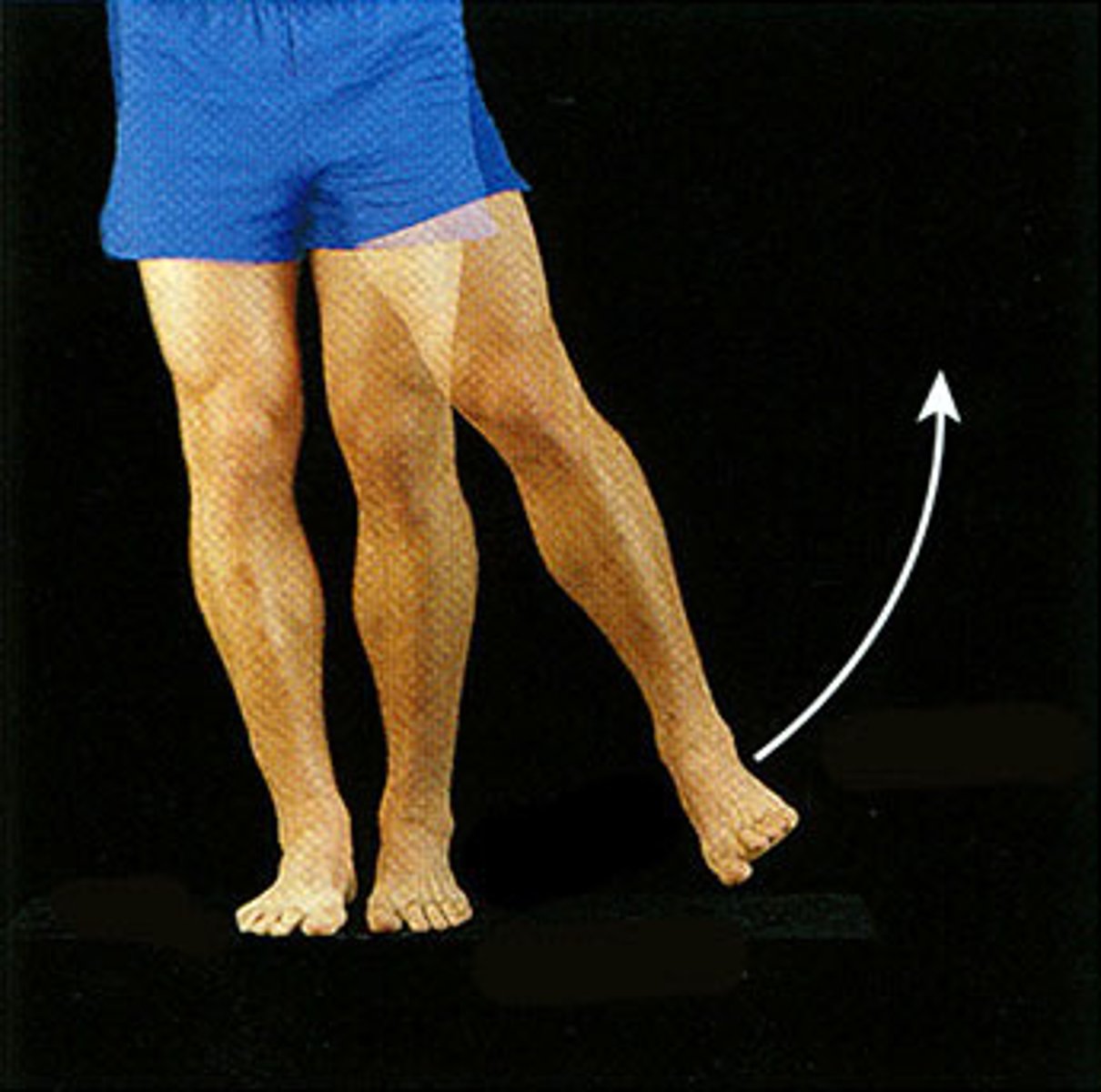
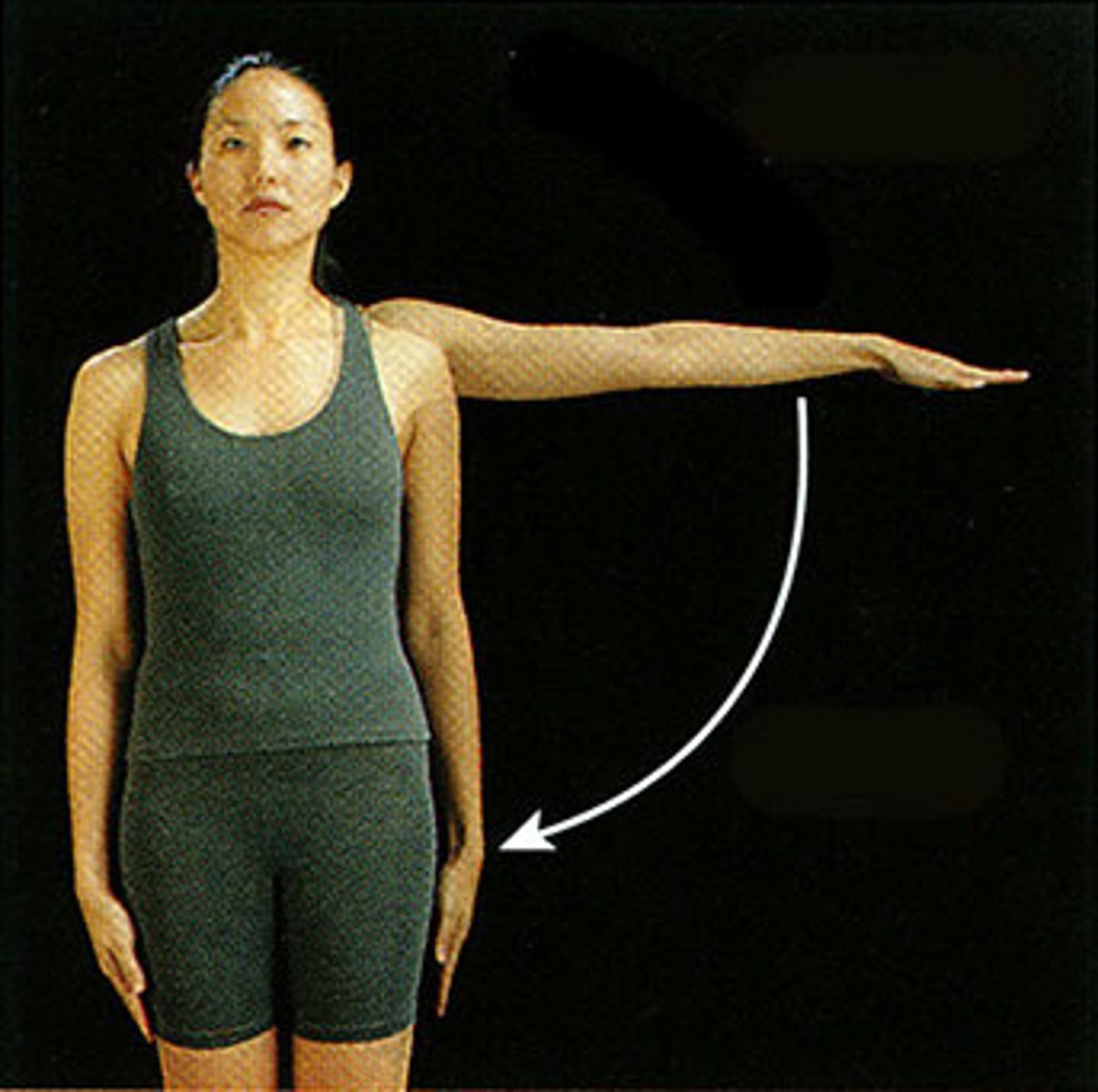
Adduction
towards the median (going in)

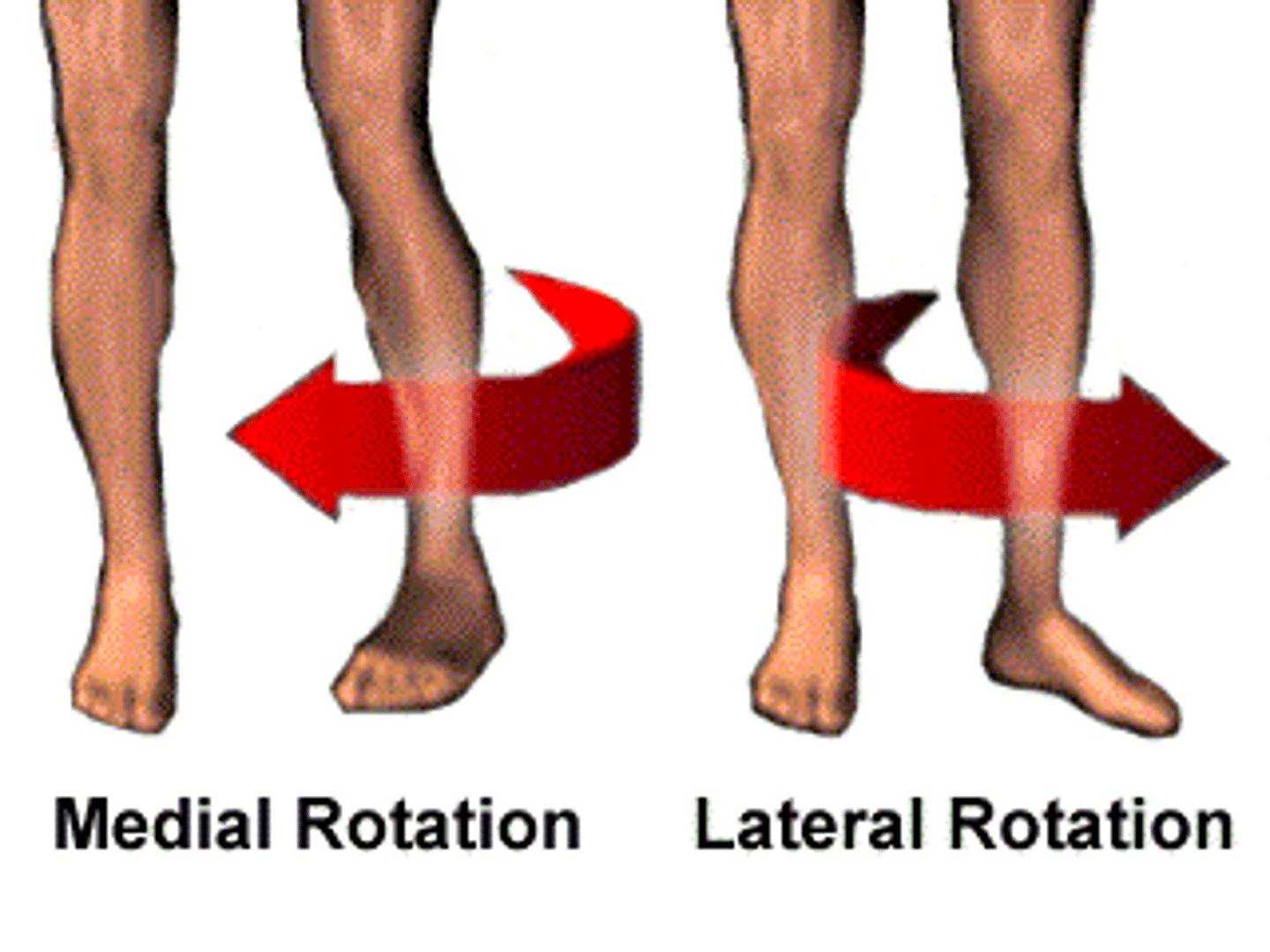
rotation
rotate along the long axis of the part toward (medial) or away (lateral) from the median plane
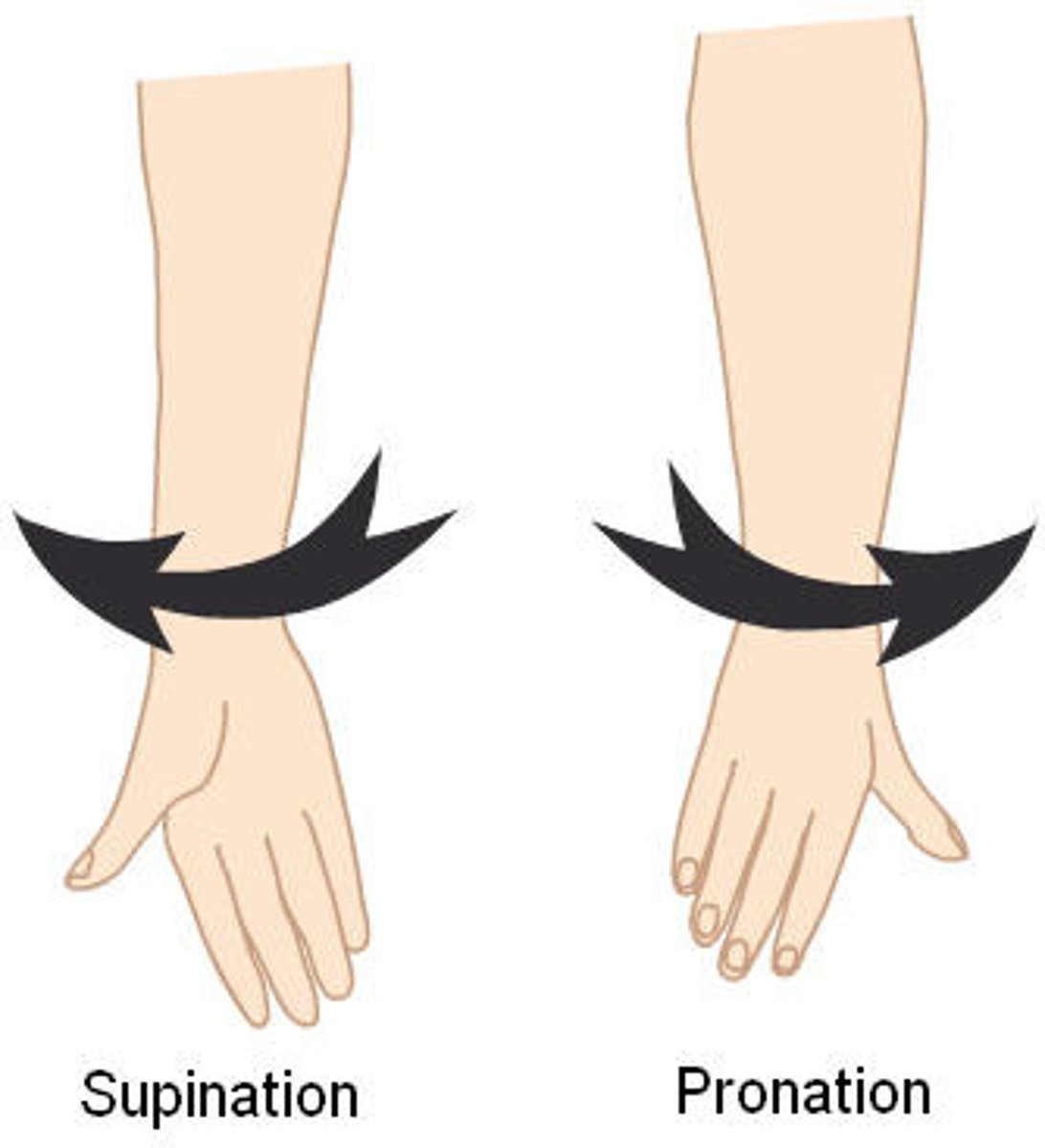
supination
lateral rotation of the forearm/hand so palm faces forward/outward
pronation
medial rotation of the forearm/hand so palm faces down
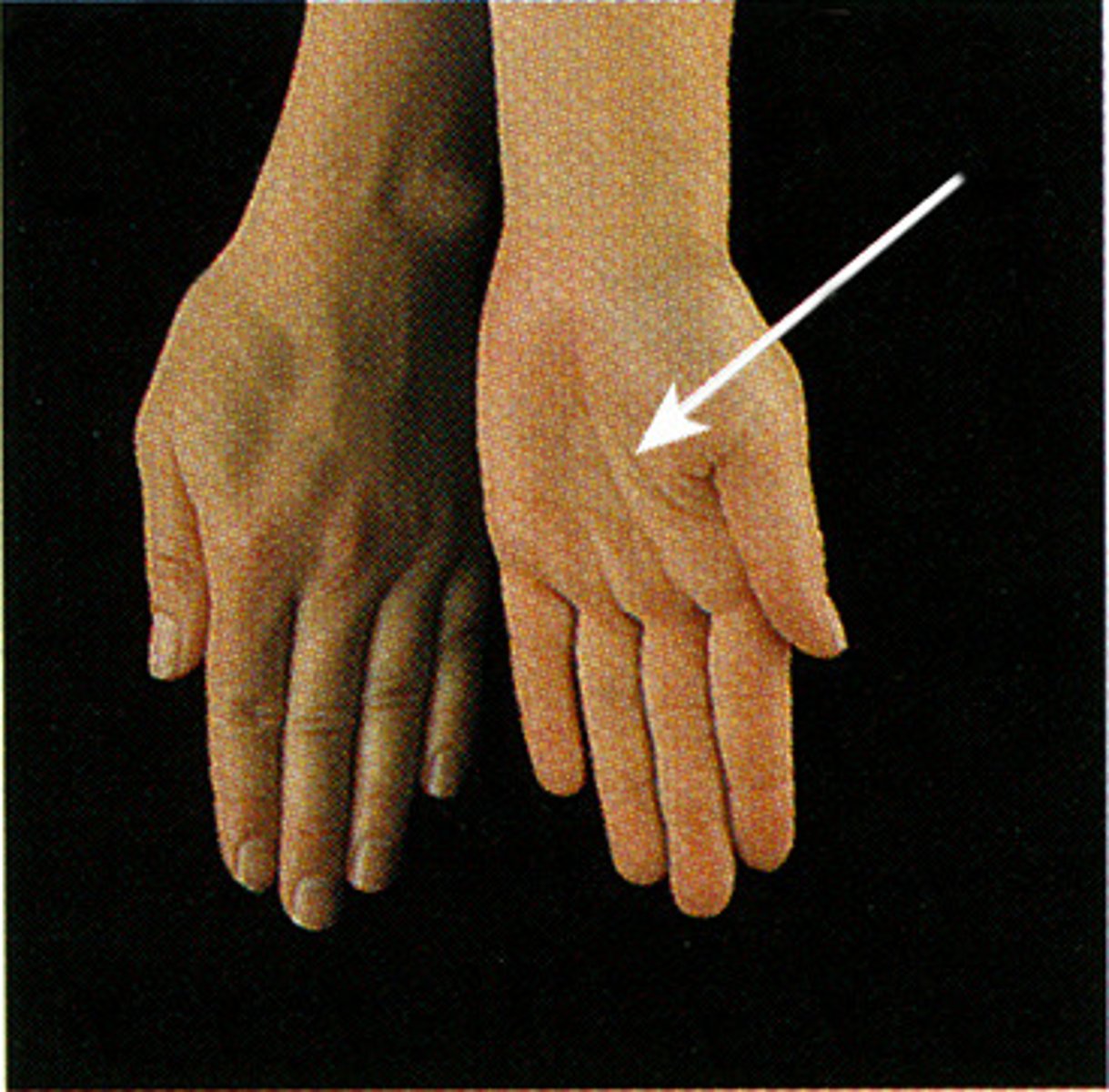
circumduction
combination of flexion, extension, abduction and adduction in a circular movement
inversion
sole of the foot towards the median plane (pinky toe)
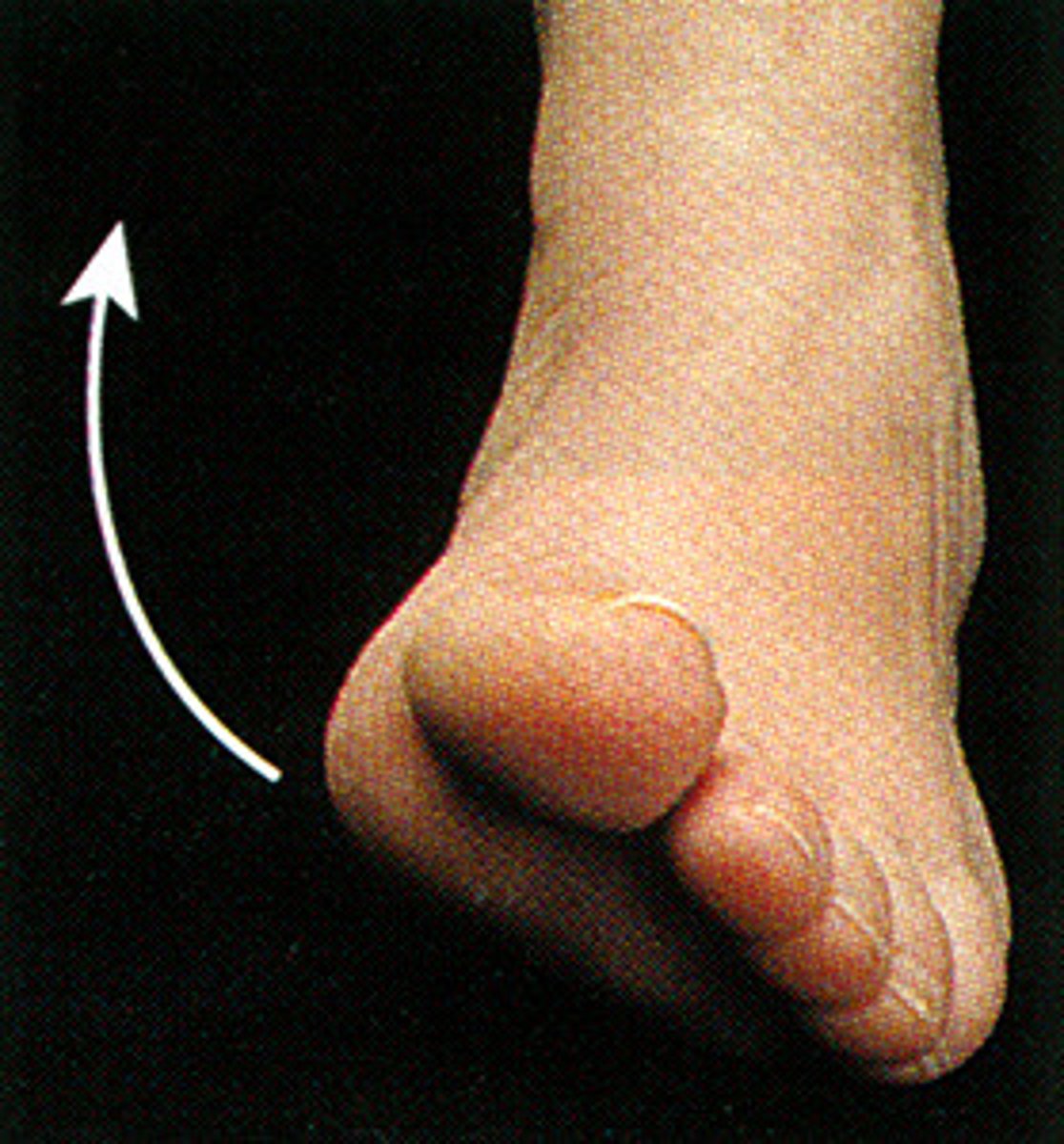
eversion
sole of the foot away from the median plane (big toe)
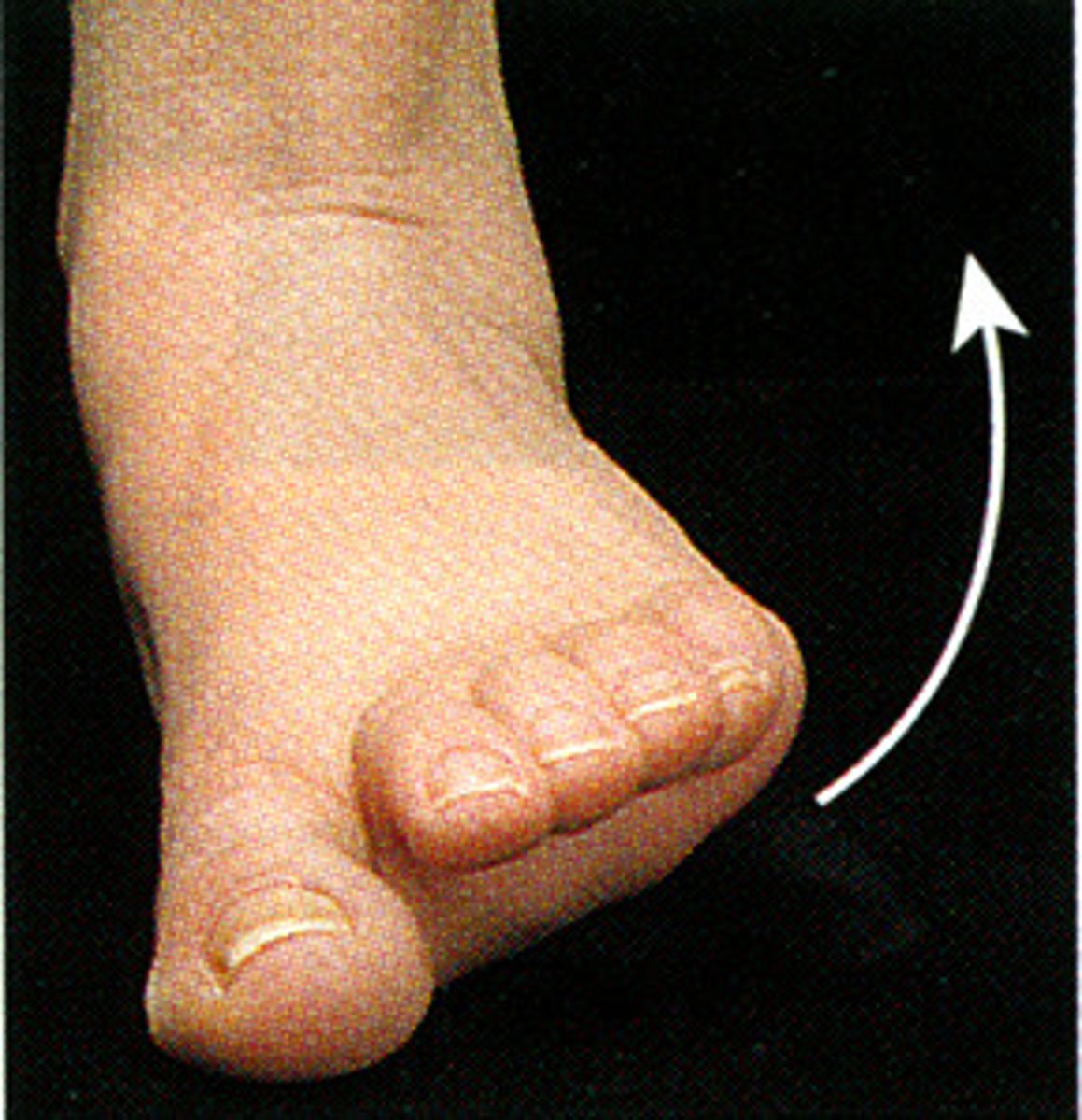
Protection from abrasions, fluid loss, and microorganisms
Containment of tissues/organs, fluids (prevents dehydration)
Heat regulation, evaporation of sweat, dilation/constrict superficial vessels
Sensation from superficial nerves
Vitamin D production and storage
What are the functions of the skin?
Partial Skin Thickness
Composed of the epidermis (superficial cell layer) and dermis (layers of collagen and elastic fibers- connective tissue layer- that provides toughness to the skin
contains:
-hair follicles
-arrector pili muscles (goose bumps)
-sebaceous glands (secrete oil)
-sweat glands (evaporation of sweat to help cool body)
-generates wrinkles depending on the toughness of skin
Superficial Fascia
subcutaneous tissue located between the skin and the deep fascia
- lose fatty connective tissue (stores fat)
-retains heat (thermal regulation), provides padding between skin and bony prominences
-contains sweat glands, blood vessels, lymphatic and cutaneous nerves
-skin ligaments (retinaculum cutis): fibrous bands through subcutaneous to the dermis (determines mobility of the skin)
Deep Fascia
dense organized connective tissue
-covers the muscles
-forms fascial compartments (groups of muscles with similar function and same nerve supply)
helps make the muscle action more efficient by limiting the outward expansion with contraction*
Prime movers
main muscle responsible for producing specific movements of the body
-synergists: assist in producing that same movement
-antagonist: opposes the movement of another muscle
-fixators: steadies proximal part of the limb through isometric contraction while movement occurs distally
True, the fixator muscle does not produce movement by itself, rather it stabilizes the origin of the primer mover so that it can act efficiently
example: muscles attaching the shoulder gridle to the truck contract to fix shoulder gridle, allowing deltoid muscle to move the shoulder joint
True or false: the fixator muscle does not move itself
cardiac muscle
involuntary muscle, under autonomic control
-myocardium: wall of the heart
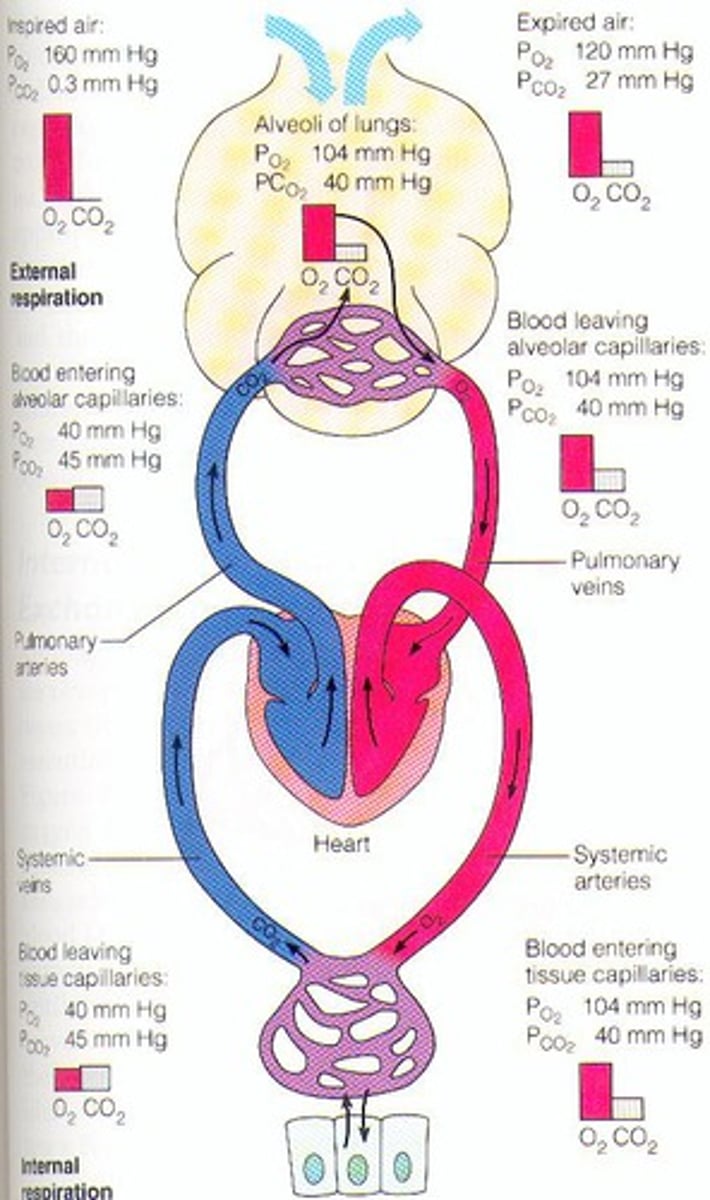
Capillaries
endothelial tubes that connect arterioles to venules (nutrient exchange between blood and tissues)
-AV shut (direct connection between arterioles and venules) to conserve heat/energy
Arteries-Arterioles-Capillaries-Venules-Veins
What is the typical exchange of blood throughout the body?
Lymph
tissue fluid ( plasma proteins and material from tissue cells) that enters lymph capillaries
-gets returned back to vascular system
Lymph nodes
small mass of lymphatic tissue along the path of the lymphatic vessels that filter lymph on its way to the venous system
-each node filters out 90% of bad stuff
Drainage and filtration of tissue fluid
Defense mechanisms of the body
Absorption and drainage of fat
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct (located on the left) drain lymph back into the venous system at the junction of the internal jugular vein and the subclavian vein
How do lymphatic ducts function?
Central Nervous System
composed of the brain and spinal cord and is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and meninges
integrates and coordinates incoming/outgoing signals
works to perform higher mental functions
-composed of dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
-CSF is located between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater
dura mater
epidural space: superficial to the dura mater
subdural space: between the dura and the arachnoid mater
Peripheral Nervous System
cranial and spinal nerves (nerve fibers and cell bodies outside the CNS, conduct impulses to or away from the CNS)
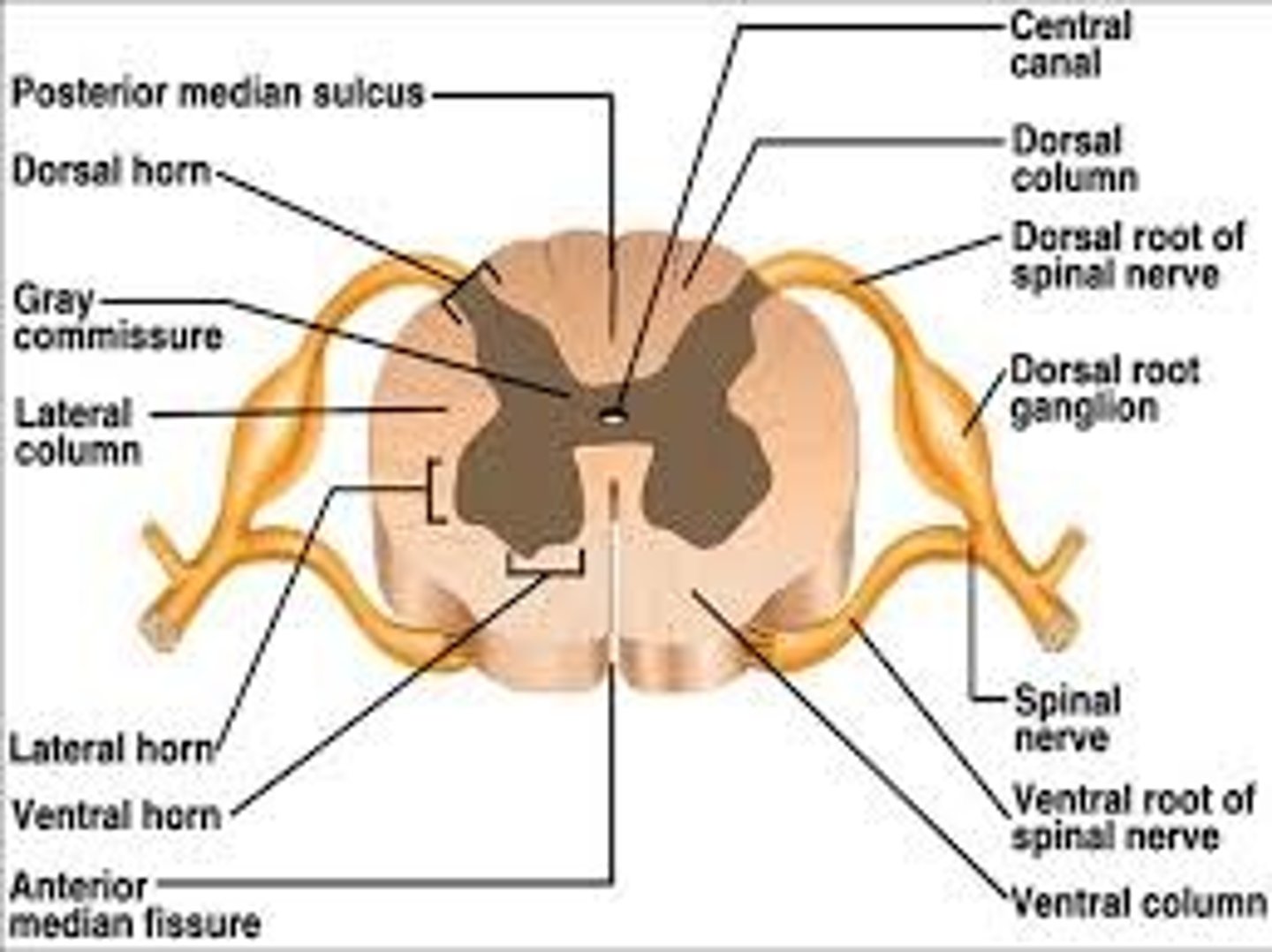
Spinal Nerve
contains a ventral root (motor or efferent) and a dorsal root (sensory or afferent)
divides into dorsal ramus (innervates deep/intrinsic muscles of back, facet joints and skin) and ventral ramus (innervates all limbs and anterolateral trunk
Spongy bones (cancellous, trabecular)
in medullary cavity, contains air spaces
-has both red and yellow bone marrow (makes blood cells/platelets)
Compact (dense) bones
hard, no spaces, surrounds the spongy bone and provides the strength of the bone
-located in all bones
Osteoblasts (organic)
the breakdown of calcium and phosphate (inorganic) in bones
Osteoclasts (organic)
the formation of calcium and phosphate (inorganic) in bones
Osteoporosis
decrease of organic and inorganic components therefore causing a decrease in the quantity of the bone
Osteomalacia
bones become soft due to Vitamin D deficiency (Vitamin D helps you form calcium)
-bone is breaking down faster than it can form
Rickets, the child form of osteomalacia
What is the condition known as a decrease in calcium in kids?
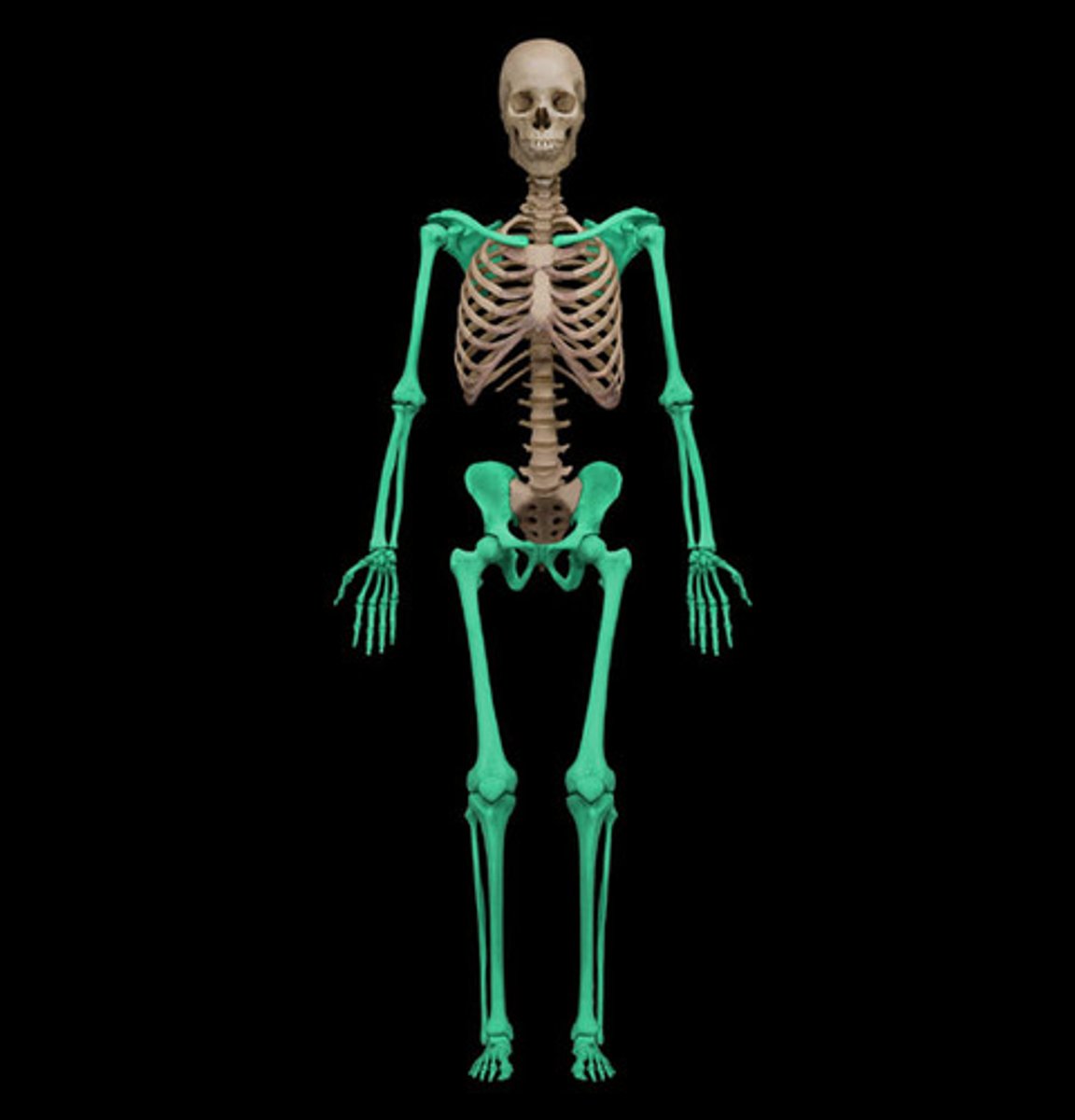
Skull, Spine, Sternum, and Ribs (midline)
What composes the axial skeleton?
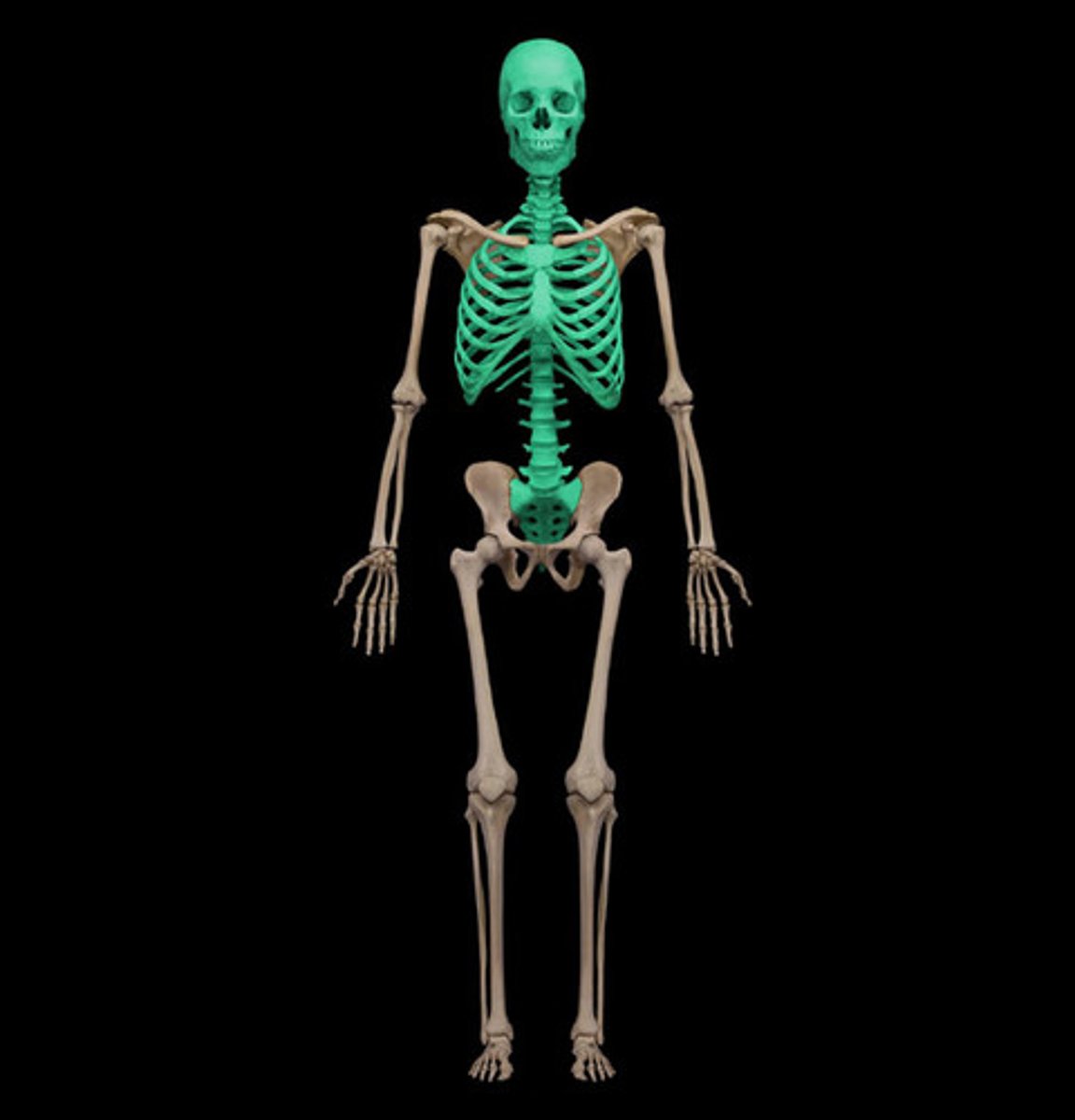
Pelvic gridle and bones of the lower extremities
Shoulder gridle and bones of the upper extremities
What composes the appendicular skeleton?
long bones
tubular in shape
ex: humorous and femur
short bones
cuboidal in shape
ex: bones in ankle and wrist
flat bones
bone that usually serves as a protective function in the body
ex: ribs, sternum
irregular bones
bones that come in various shapes depending on the person
ex: cranium, vertebrae
sesamoid bones
bones that develop in some tendons where they cross ends of bones
ex: patella
-protects tendons from excessive wear and can change the angle of tendons as they pass their attachment
Mesenchyme
embryonic connective tissue/membrane that is turned into bone via intramembranous ossification or intracartilaginous ossification (endochondral bone formation)
intramembranous ossification
process by which bone forms directly from mesenchymal tissue
-occurs with the skull, mandible, and clavices
intracartilaginous ossification
the process of replacing mesenchymal tissue with cartilage which then turns to bone
contains:
-primary ossification centers: center of future shaft known as diaphysis; prenatal and by birth it reaches the end
-secondary ossification centers (epiphyses): form after birth via ossification
-metaphysis: part of the diaphysis closest to the epiphysis (separates the diaphysis from the epiphysis so they don't fuse during growth of bones)
For females, cartilage at plates is totally replaced by bones usually by 18
For males, it usually takes longer depending on their height
When do bones stop growing for both men and women?
Bones contain periosteal arteries which supply rich nerve supply to the periosteum of the bone
As well, bones contain metaphyseal and epiphyseal arteries and veins
What is the vascular supply in bones?
periosteal nerves
serves as the pain sensor
-the periosteum (the outer covering of bones) is very sensitive
Fractures hurt due to the sensitivity of the periosteum which contains the periosteal nerve that stimulates pain in the bones
Why do fractures hurt?
Protection (ex: ribs protect the lungs
Support (ex: the skull supports the brain)
Movement (ex: bones act as a lever for movement)
Blood Cells (ex: bone marrow makes blood)
Storage (ex: the bones store calcium and phosphate)
What are the 5 main functions of bones?
fibrous joints (synarthrosis)
bones are connected by strands of collagen fibers
-suture: contains short fibers with layer of fibrous tissue (found in the skull)
-syndesmosis contains one sheet of fibrous tissue (connective tissue between the radius and the ulna)
-gomphosis: serves as a socket in the mouth that allow the tooth to be anchored by a ligament into the jaw
cartilaginous joints
bones held together by hyaline or fibrocartilage
Synchondrosis (hyaline) found in epiphyseal plates, 1st sternocostal joints
Symphysis (fibrocartilage) found in intervertebral disc, pubic symphysis, and manubrium to sternum
synovial joints
contains a cavity with synovial fluid, hyaline cartilage (no nerves or blood), and a capsule lined by synovial membrane
-usually contains intrinsic (thickenings of the joint capsule) and extrinsic (outside of the joint capsule) ligaments
-may contain discs as well (ex: meniscus in the knee)
Pivot joints: a round bone that fits into bony ligamentous socket allowing for rotation (ex: neck)
Ball and Socket joints: a rounded head fits into a concavity permitting movement of several axes, most mobile form (ex: hip)
Plane joints: permit gliding or sliding movements (ex: clavicle)
Hinge joints: permit flexion and extension only (ex: elbow joint)
Saddle joint: each surface is convex in one direction (ex: wrist to thumb attachment)
Condyloid joint: one surface is concave while the other is convex (ex: finger bones against on another)
What are the different types of Synovial Joints?
Hilton's Law
nerves supplying a joint also supply the muscles moving the joint and the skin covering their distal attachments
-pain and proprioception from articular nerves that supply the joint
Articular arteries get the blood supply from surrounding joints and brings it into the joint
Anastomoses branch from different blood vessels to connect with each other and form a network
Veins accompany the arteries to pump unoxygenated blood back to the heart
How is blood supplied to the joint both in capsule and synovial membranes?
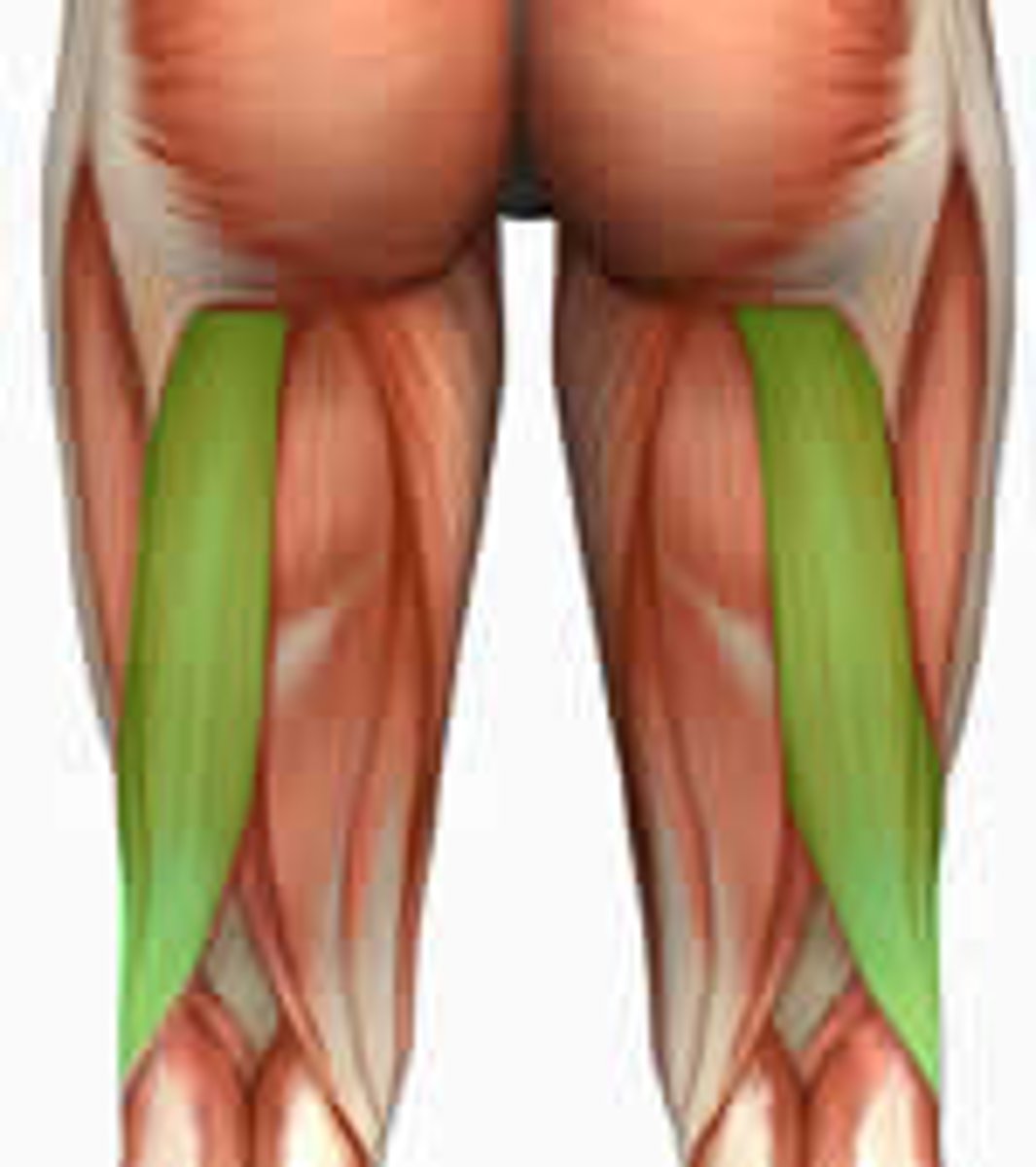
longitudianal muscles
fibers parallel to the force that is generated
ex: hamstring
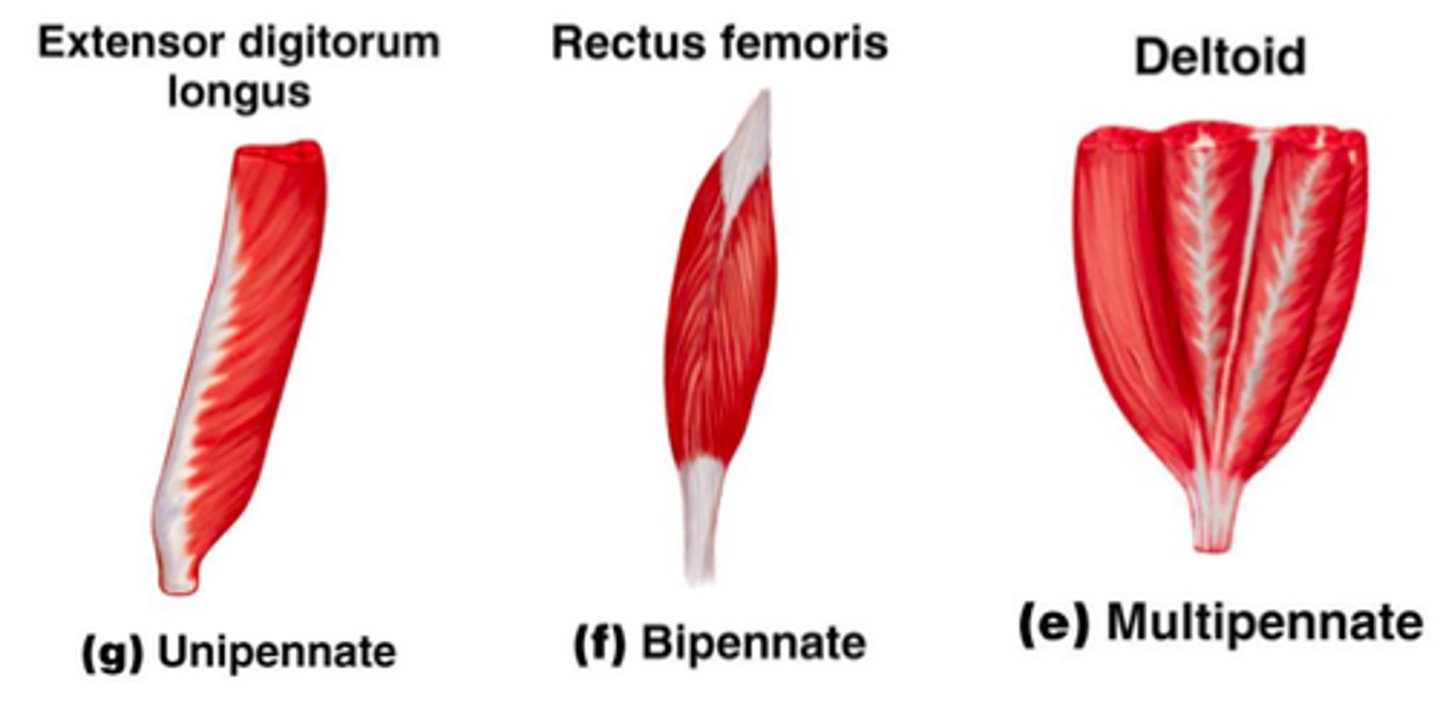
unipennate, bipennate, multipennate muscles
muscles arranged from one angle to allow more fibers to be packed in to save space and generate more force
-multi: arranged at several angles relative to force direction
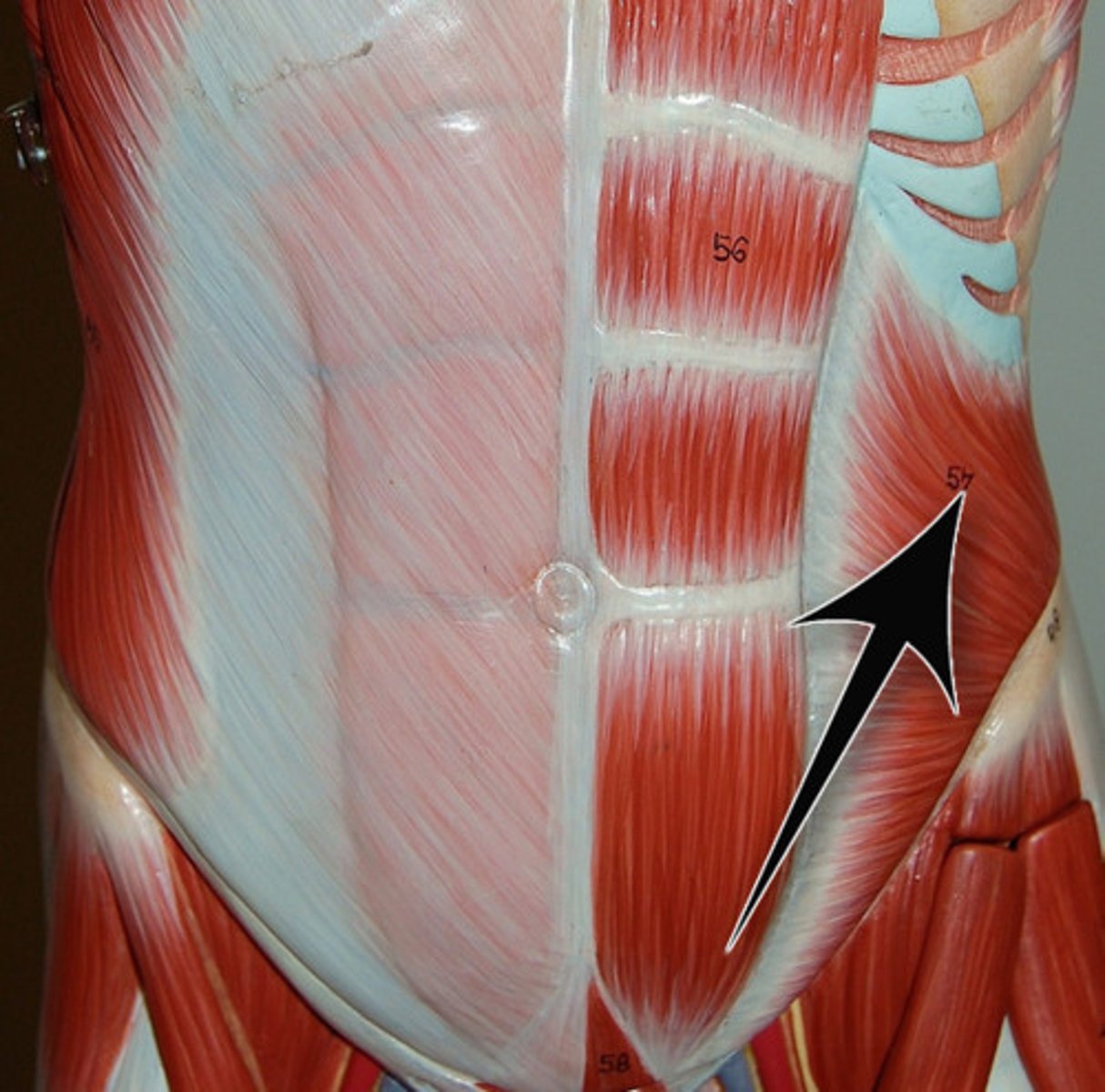
flat muscles
Parallel fibers often having aponeurosis (flat tendons)
ex: external oblique
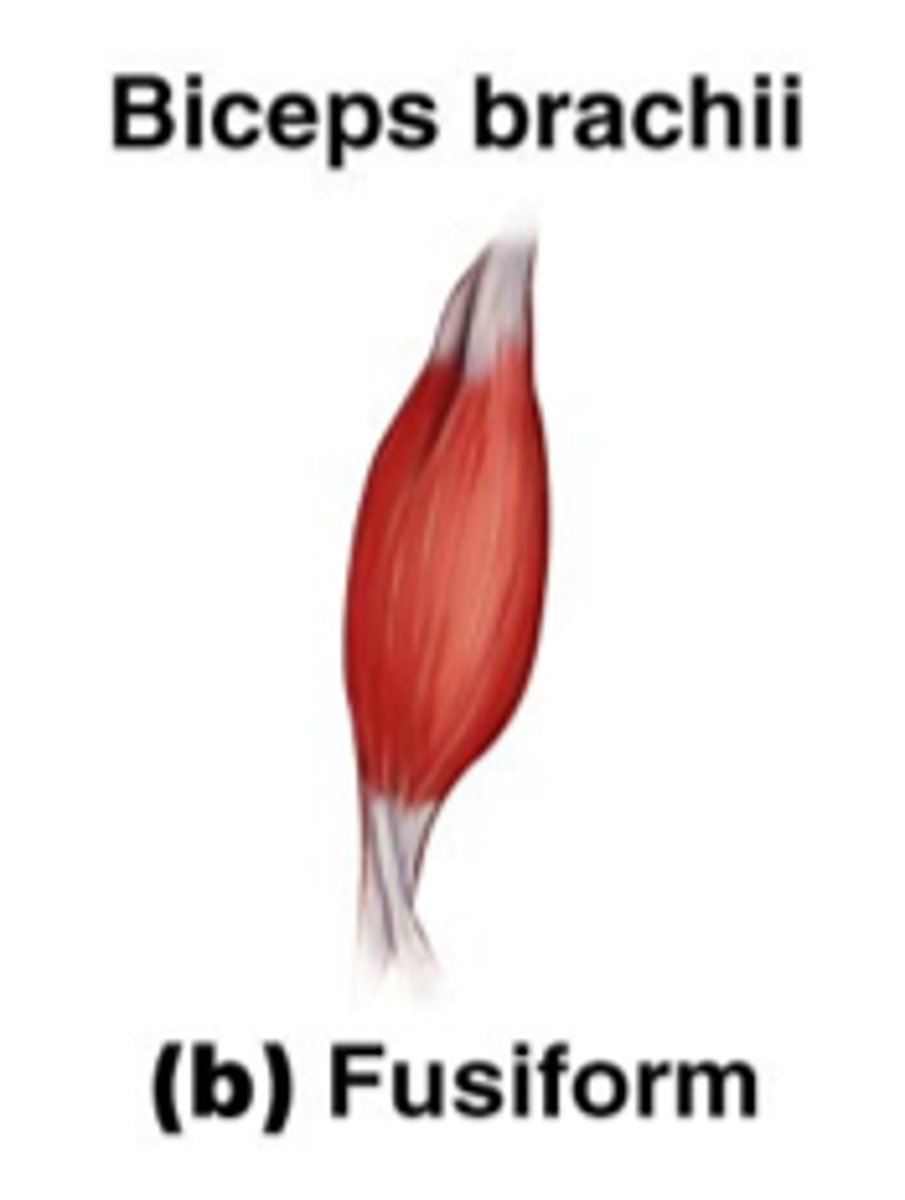
fusiform muscles
spindle-shaped muscle with a central belly that tapers to tendons on each end
allows them to focus their power onto small, bony targets
Ex. brachialis, biceps brachii
quadrate muscles
muscle has four equal sides
ex: pronator quadratus, quadratus lumborum
circular muscles (sphincters)
form rings around body openings
-constricts the opening when the muscle contracts
origin/insertion vs. proximal/distal attachments (attachment of muscles)
when a muscle contracts, one of its attachments is usually fixed while the other is moving (the origin is not always the one that is fixed)
-occurs via tendon, aponeurosis, fascia, skin, or mucous membrane