(Data Types and Compression) A-Level OCR Computer Science
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
primitive data type
Basic data types e.g. integer, real, Boolean, string which are used and supported by computer hardware
real/float data type
positive and negative decimal numbers (but real types can be integers)
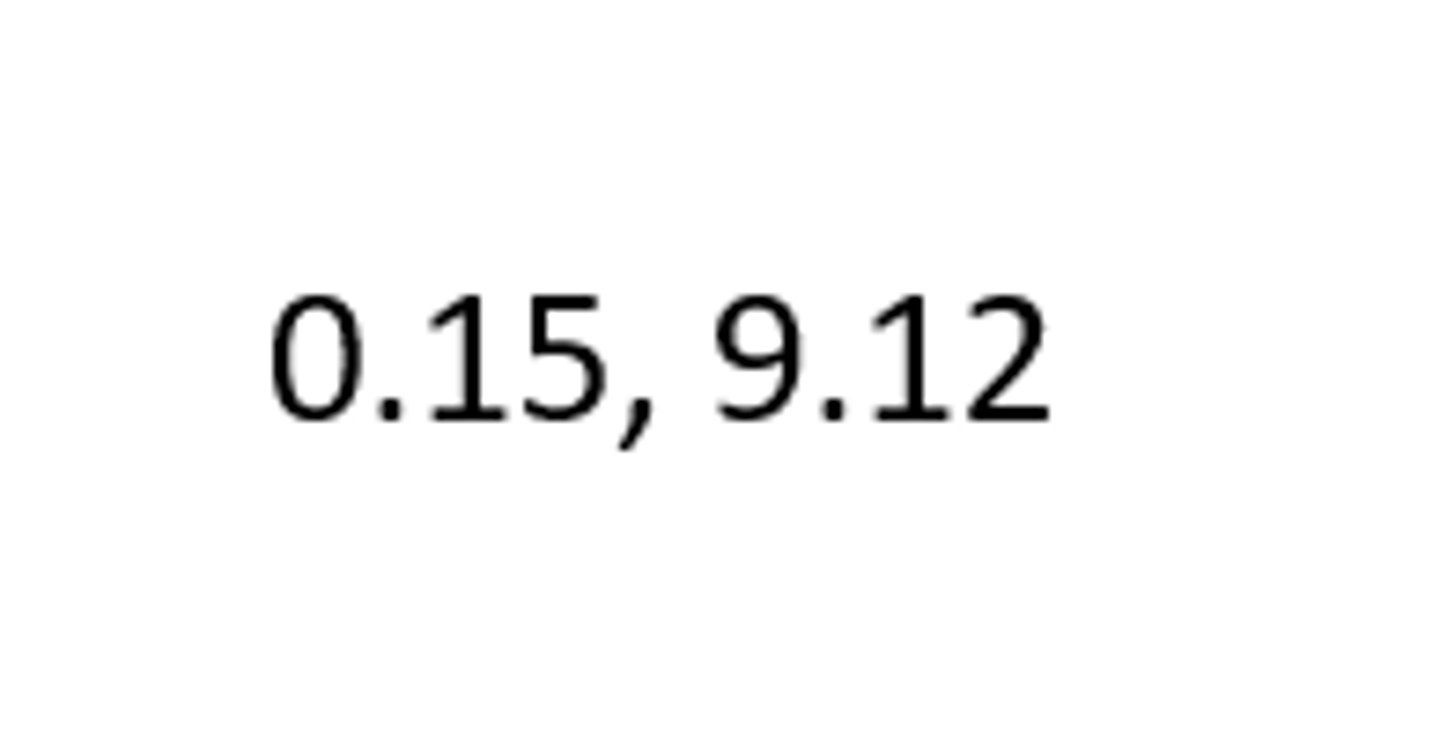
char data type
single letters and symbols
Boolean data type
whether the instance of a string is true or false
why it is important for data to be stored with the right data type
so the right operations can be performed on it
why a phone number should be stored as a string
if it starts with a 0, which numeric data types e.g. integers would cut off, or if it began with a plus sign for a country code
LSB and MSB
LSB of a binary number is furthest to the right, and MSB is furthest to the left
sign and magnitude
The most basic way to represent negative numbers in binary. 0 is positive, 1 is negative
how to make a number negative using sign and magnitude
the MSB (128) becomes the sign bit and no longer represents a weighted value. write the normal number using a 0 or 1 to indicate whether it is positive or negative
two's complement
the MSB becomes negative, then all 1 columns should add to the negative number. Starting form the first 1 column, flip all the bits from right to left (or flip all the bits and add 1)
the largest and smallest number that can be stored by sign and magnitude binary
+127 and -127
disadvantage of sign and magnitude
a bit is lost as the MSB can no longer hold a value
how to subtract in binary
add the negative version of a number (two's complement) to the other
how to convert B7E to denary
(11x16² )+ (7x16) + 14 = 2942
how to convert B7E to binary
convert each hex digit to a binary nibble and combine the nibbles
floating point binary
a method of representing real numbers in binary using a binary point, mantissa and an exponent
why floating point numbers are normalised
to ensure they are as precise as possible in a given number of bits
how to represent positive and negative numbers in floating point binary
starts with 01 for positive numbers, and 10 for negative numbers
Unicode versus ASCII
Unicode uses more bit, so is able to represent more characters for more languages including European symbols, Egyptian hieroglyphics and emojis
a character set
A collection of characters and their unique binary codes which are represented by computers
unsigned binary is used to
represent positive binary numbers
an advantage of sign and magnitude
makes it possible to represent negative numbers
binary borrowing
a method of subtraction to use when x > y
The binary codes of ASCII uppercase letters begin with
01
The binary codes of ASCII lowercase letters begin with
011
The binary codes of ASCII symbols begin with
001
AND bitwise operation
allows you to copy a subset of bits from a binary sequence
Bitwise operations
allows you to check, set, clear and toggle bits
OR bitwise operation
allows you to set a subset of bits in a binary sequence
XOR bitwise operation
allows you to toggle a subset of bits in a binary sequence; where the mask is not applied, bits are copied
ASCII uppercase alphabet
65 to 90
ASCII lowercase alphabet
97 to 122
Why encryption matters
It is used to keep data secure when it is being transmitted
How encryption works
An algorithm is used to scramble data to make it incomprehensible without the use of a key, then this data is transmitted and can be deciphered with the use of the key at its intended destination.
Symmetric encryption
The faster one
The key used in symmetric encryption
The same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the data
Public and private keys are
Mathematically linked
Compression is used to reduce file size
So they are quicker to transfer, so more can be transferred in a given time
Compression is used to reduce bandwidth in order to
make the best use of available bandwidth for data transfers and streaming over the internet
Compression is used to reduce storage requirements
as more files can be stored with the same amount of storage space
Compression is used to reduce download times
as downloading a compressed version of a file is faster than downloading the full version , as the file size is smaller
Compression
The process used to reduce the storage space required by a file, meaning you can store more files with the same amount of storage space
Lossy compression
The size of the file is reduced through the loss of information which cannot be recovered upon decompression
Effects of lossy compression in an image
Grouping similar colours in an image could result in a more pixelated image. This is noticeable
Effects of lossy compression in a video
Loss of similar frames. Not noticeable
Effects of lossy compression in a n audio file
Loss of frequencies in the sound which humans cannot hear. Not noticeable
Lossless compression
The size of the file is reduced through the simplification of information which can be recovered upon decompression
Lossy standards
JPEG, MPEG, MP3
The importance of lossy compression
Test files, executable programs need to have all information recovered upon decompression to be understood
total number of bits
available bits x characters = total number of bits
Lossless standards
ZIP, PNG, GIF
A loss of data results in a
reduction of quality
Run Length Encoding (RLE)
A compression algorithm that represents an image in terms of the length of runs of contiguous and identical pixels
A disadvantage of RLE
it relies on consecutive pieces of data being the same so if there's little repetition, does not offer a great reduction in file size.
Compress AAAAAABBBBBCCC using RLE frequency/data pairs
A6B5C3
Dictionary encoding
Frequently occurring pieces of data are replaced with an index, and compressed data is stored alongside a dictionary which matches this data to an index.
Why the compressed data must be sent alongside the dictionary
So the original data can be restored
How dictionary encoding reduces file size
Any occurrence of the data stored in the dictionary is replaced with its index which reduces the size of the original passage
fixed point binary
a way to represent fractional numbers using a fixed number of bits (the position of the binary point is defined in a fixed position)
the exponent in floating point binary
determines where the position of the binary point will be
the mantissa in floating point binary
the main number, which contains the binary point after the MSB
- it can represent a wide range of numbers, including fractions and integers which is good if you don't know what the range of your calculation results will be
- it can represent both very large and very small numbers by adjusting the binary point
Why floating point is better than fixed
an increased number of bits allocated to the mantissa means
greater precision of the number
an increased number of bits allocated to the exponent means
a larger range of numbers can be represented
when the exponent is negative, the point is moved to the ______ and spaced are infilled with _______
left, spaces are infilled with 1s
when the exponent is positive, the point is moved to the ______ and spaced are infilled with _______
right, spaces are infilled with 0s
salts are used only for
password systems
metadata and hash value
this information affects the hash value that is generated
lossless compression and streaming
it causes buffering and decreases bandwidth as the file size is larger
the sign but does not
affect the original number
the main problem with symmetric encryption
it uses the same key between sender and recipient, and it is this same key that is transmitted over the internet. it also must be kept secure, alongside encrypted data.
the disadvantages of asymmetric encryption
it is computationally expensive, and takes longer
how asymmetric/symmetric encryption can be used together (SSL/TLS)
asymmetric encryption is used to establish a secure session between a client and a server, and then symmetric encryption is used to exchange data within that session.
asymmetric encryption is used to
securely exchange keys
symmetric encryption is used to
encrypt and decrypt data
Not studied (75)
You haven't studied these terms yet.