Thermodynamics and equilibirum and acids/bases
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L2+sime more
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
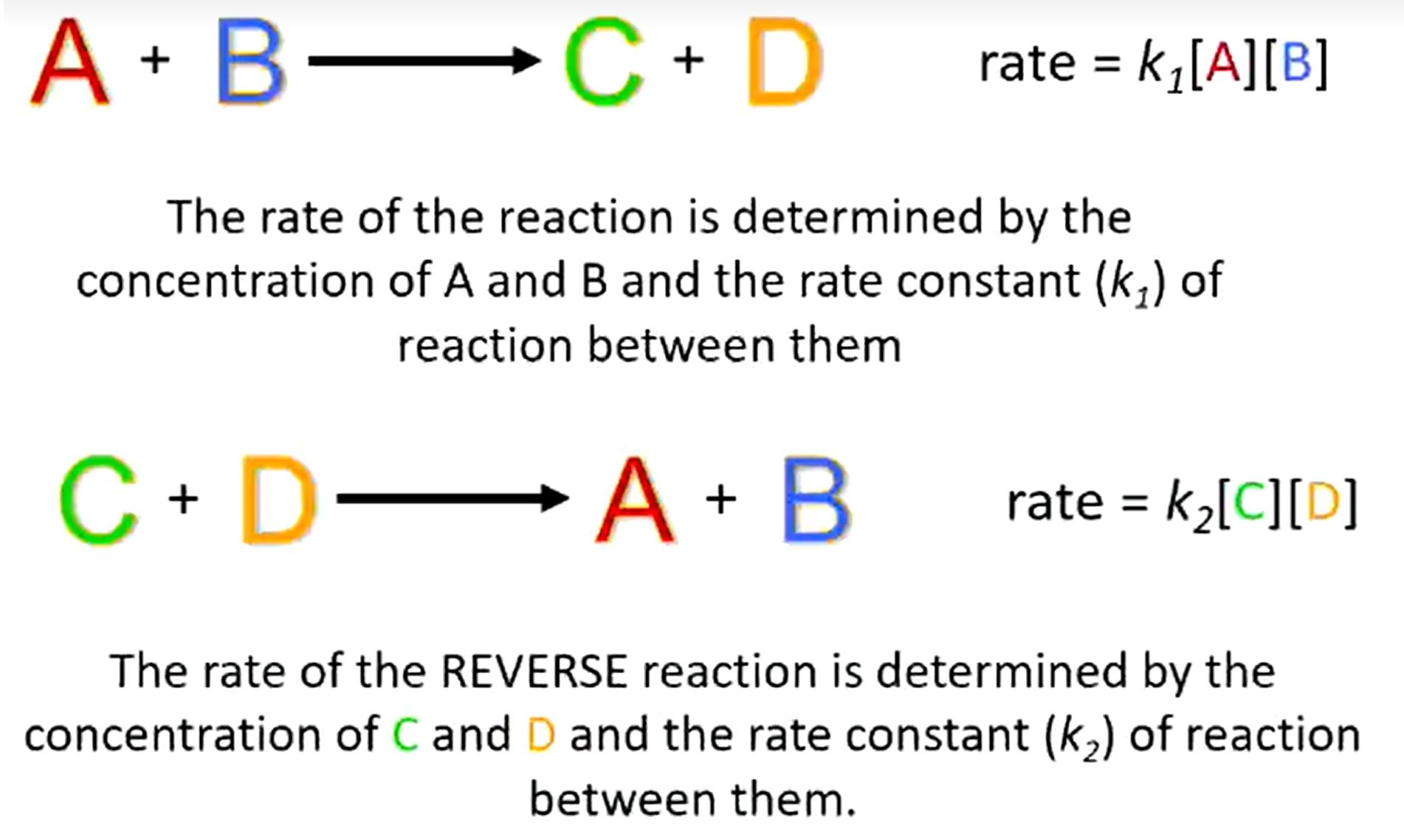
Rate of reaction in a reversible and irreversible reaction
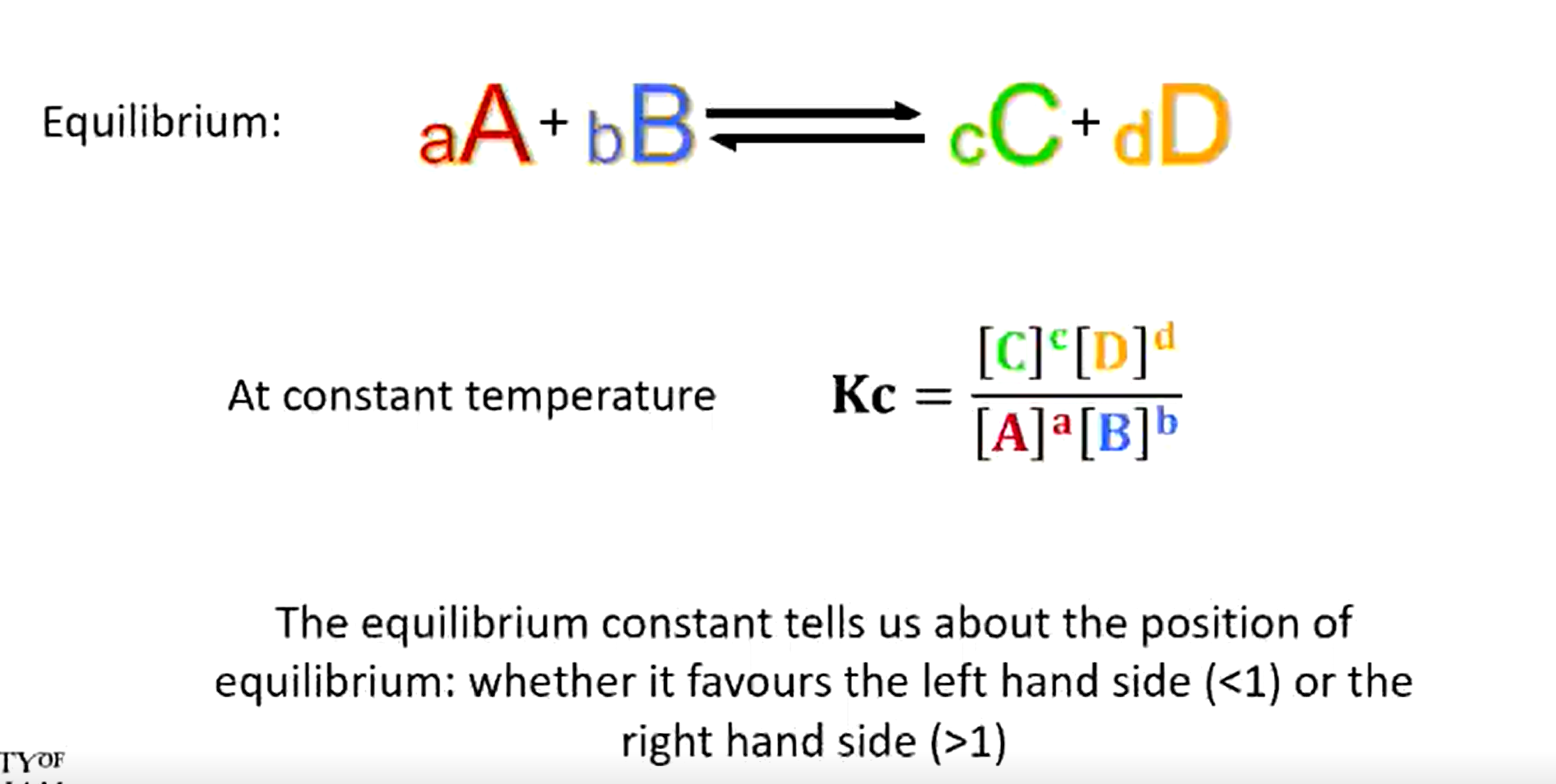
Does an equilibrium constant >1 favour the forward or backwards reaction?
Forward reaction
Equation for a dynamic equilibrium
Small numbers are the mole counts (big numbers next to a formula e.g. 3 in 3H₂O)
What is an acid
A molecule that can donate a proton
What is a base
A molecule that can accept a proton
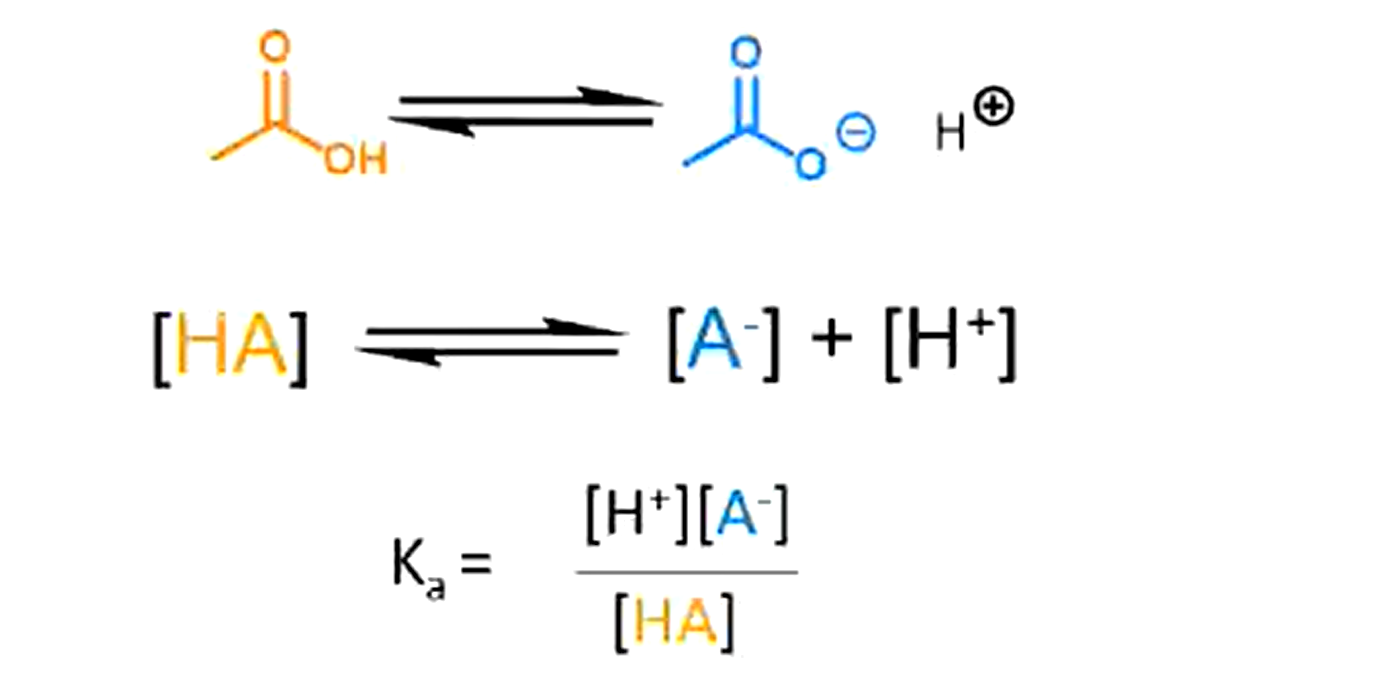
What is Ka
Degree of dissociation of an acid - i.e. how much of the acid is in the ionised form
What is an equivalent (eq)?
A quantity that is calculated by moles * valence
What is a normal (N)
A unit of concentration calculated by
N = eq/L
OR
N = M * Valence
Equation to convert [H+] to pH
10^[H+] (concentration usually in M)
Calculation for pOH in a strong base
14-pH = pOH
What is C in the data sheet equation pH = ½ pKa - ½ logC and the use of the equation
C = [HA] in a weak acid when you know degree of ionisation