L3 Kidney disease Patho
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the vital functions of the kidneys?
Maintain fluid + acid-base balance
Regulating electrolyte concentration
Detoxifying the blood and eliminating wastes (med processing)
Regulating BP
Aiding RBC production (erythropoiesis)
Regulating vitamin D + calcium formation
What are the components of the renal system?
Kidneys
Ureters
Bladder
Urethra
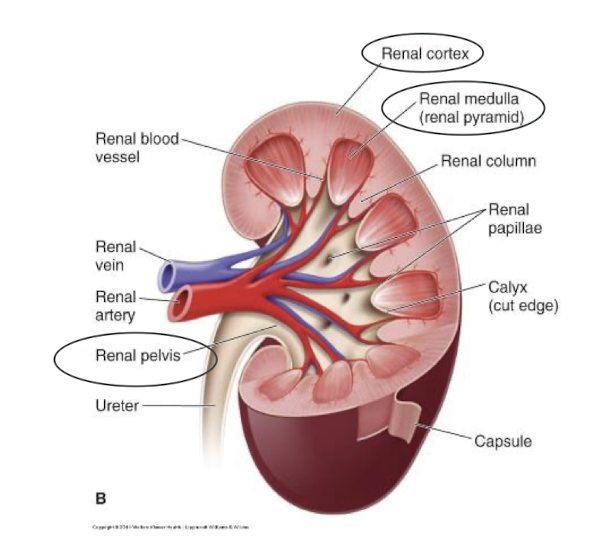
What are the 3 primary sections of the renal system? What does each consist of?
Cortex (outer layer)
Glomeruli
Proximal tubules
Renal corpuscles
Medulla
Pyramids
Distal tubules
Collecting ducts
Pelvis
Urine collection starts
Start of ureter
What is a nephron? Role?
Functional unit of the kidney
Million
Role:
Filters substances from blood
Reabsorb filtered nutrients + water
Secrete waste
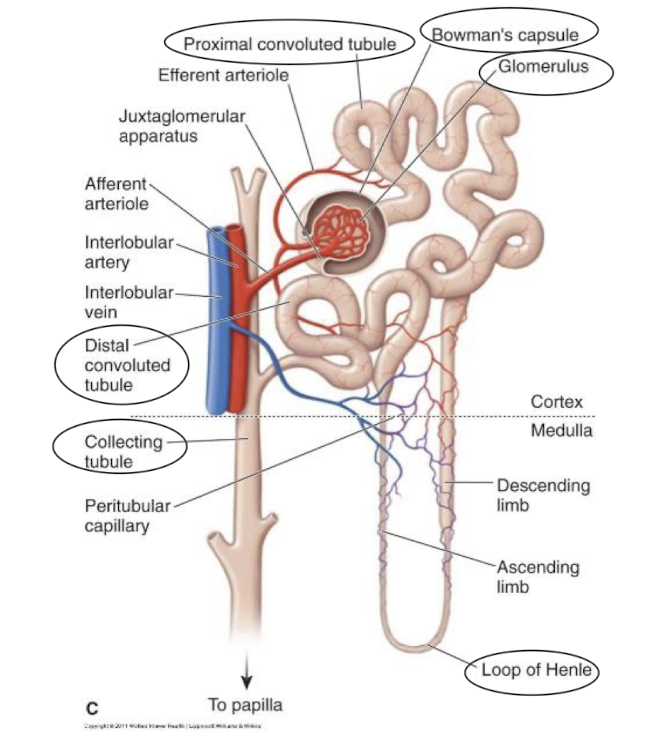
What are the components of a nephron? What is the role of each?
Glomerulus
First filtering stage
Enter under high pressure → Protein + blood + large molecules stay in vessels → Filtrate continues on → Creatinine pulled out here + Never goes back in
Bowman’s capsule
Contains glomerulus
Holding reservoir for filtrate
Proximal tubule
Site of reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, metabolites, electrolytes, and water back into blood
Regulates how much sugar/electrolytes
Loop of Henle
Further reabsorption of water + electrolytes
Descending → High permeability to water, NOT electrolytes
Ascending → High permeability to electrolytes NOT water
Distal tubule
Fine tuning how much water/electrolytes we need to keep/excrete
Collecting tubule/duct
Last piece before leaving
How is urine removed?
Urine first enters the ureters via renal pelvis
Then propelled by ureters into bladder via peristalsis
Bladder activates stretch receptors
Signal stimulates contraction of detrusor muscle via parasympathetic cholinergic motor fibers
Relaxation of internal and external urethral sphincters = micturition (peeing)
Urine characteristics: Color, Total volume, Hourly volume
Yellow → Dark amber can = dehydration, renal/liver disease
Clear → Cloudy may = infection
Total volume = 750 - 2000 mL/day
Kidneys create at least 30mL/hr
What hormones are involved in fluid balance? What are they produced by? What does it do?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Produced by pituitary gland
Alters the collecting tubules permeability to water
Aldosterone
Produced + released by adrenal cortex
Regulates water reabsorption by the distal tubules + Changes urine concentration by increasing sodium reabsorption + Helps control secretion of potassium by the distal tubules
What are some other key hormones of the kidneys? What do they do?
Calcitriol
Assists with converting vitamin D to its active form
Erythropoietin
Stimulates RBC production
Renalase
Affects heart function and BP by metabolizing catecholamines
Renin
Helps regulate BP through angiotensin conversion
What factors influence renal laboratory values?
Age
Gender
Muscle mass
Capillary wall permeability
Vascular and filtration pressure
Hydration status.
What does eGFR measure and what is a normal value?
How much the glomerulus is filtering
Normal is greater than 90.
What is creatinine and how does it relate to GFR?
Creatinine is an indirect marker of GFR
When filtration drops, creatinine rises.
What does BUN measure and how is it affected by filtration?
BUN measures how well the kidneys remove waste
When filtration drops, BUN rises and depends on water reabsorption capacity.
How do we perserve renal function?
Control of BP + glucose levels
Adequate hydration status
Smoking cessation (causes vasoconstriction)
Limit alcohol, caffeine
Limit sodium intake
Caution with nephrotoxic drugs
Renally dose meds based on kidney function (with help from pharmacist!)
What is glomerulonephritis? Pathophysiology? Causes?
Inflammation of the glomerulus
Patho: Injury to glomerulus → Triggers inflammatory reaction at the glomerulus → Causes glomerular filtration membrane to be more permeable → Allows passage of larger particles such as protein / blood through
Causes: Immune relates (SLE lupus), DM, HTN, Infections
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis?
Increased:
Protein
Hematuria
Casts on urine analysis
Labs:
Elevated Creatinine + BUN
Low GFR + Protein in serum
Other:
Oliguria (less than 30mL/hr) or Anuria
HTN
Swelling
Renal failure
Treatment for glomerulonephritis?
Treat cause if possible!
Supportive care
Low salt / phosphorous diet
Limit nephrotoxic drugs
Maintain hydration
What is urolithiasis? Causes? Risk of?
Calculi (kidney stones) form when substances that normally dissolve in the urine precipitate.
Commonly comprised of calcium oxalate / calcium phosphate
Causes:
Urinary stasis
Dehydration
Infection
Elevated urinary levels of salt and minerals
pH changes + Metabolic factors
Diet (high animal protein intake, Na, low fluid)
Risk of renal tubule obstruction
Risk factors of urolithiasis?
Genetics
UTI
Cystic kidney disease
DM
Obesity
Gout
Hyperparathyroidism
Gastric bypass
What does Urolithiasis look like (colic VS noncolic)?
Pain = severe + shooting ; Flank / Costovertebral angle (CVA)
Colic
Distension of collecting system or ureter
Acute, Intermittent, Radiating, Excruciating
Non Colic
Distention of renal calices or pelvis
Dull, Deep w/ varying intensity
How is Urolithiasis diagnosed?
Subjective findings → Hx pain
Xray, CT
Urinalysis / Analysis of calculi composition
Treatment of urolithiasis: Pharmacologic VS Calculi removal
Pharm:
Analgesics
Antimicrobials
Diuretics (prevent urinary stasis)
Removal
Increased fluid intake → If small will pass through micturition
Reduction of calculi size
Surgical removal
Urethral stents
How to prevent urolithiasis?
Diet with foods low in calcium oxalate
Fluids
Management of gout, hyperparathyroidism
What is acute kidney injury (AKI)? What is classification based on?
Sudden decline in kidney function related to decreased blood flow, toxins, or sepsis
Based on location
Progression of AKI?
Initiating event → Prevention still possible
Maintenance (oliguric) phase
Recovery (polyuric) phase
3-12 months
A lot of urine output to catch up from oliguric phase
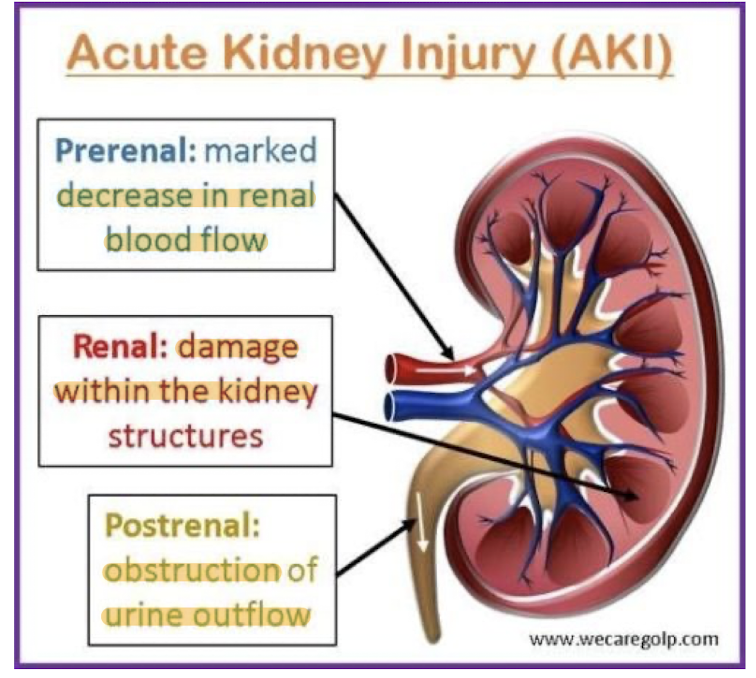
Types of AKI?
Prerenal
Intrarenal
Postrenal
Prerenal: Cause, Urine output, Urine osmolality, Urine sodium
Most common!
Caused by hypovolemia
Low urine output
High urine osmolality
Low urine sodium
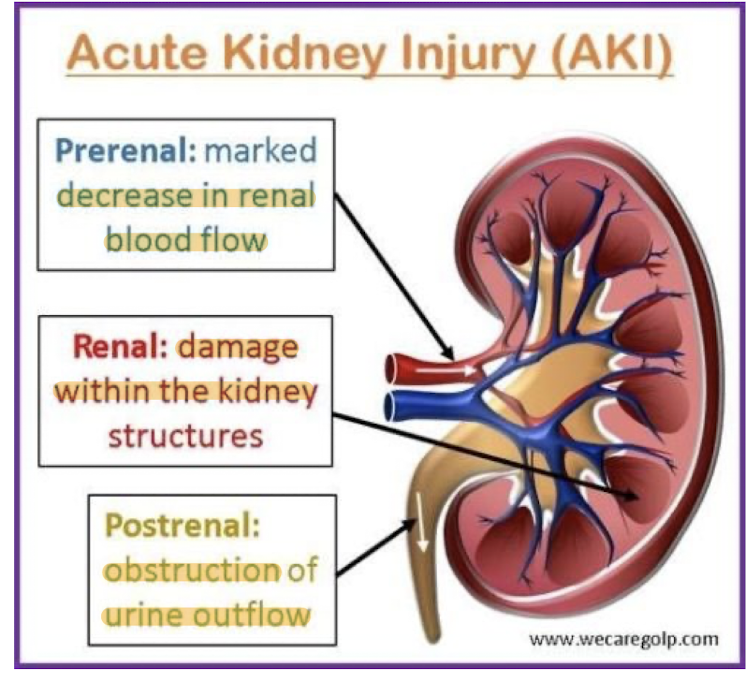
Intrarenal: Cause, Urine output, Urine osmolality, Urine sodium
Typically caused by tubular necrosis
Can also be caused by toxins, Contrast media, heavy metals, myoglobin from crush injuries
Low urine output
Low urine osmolality
High urine sodium
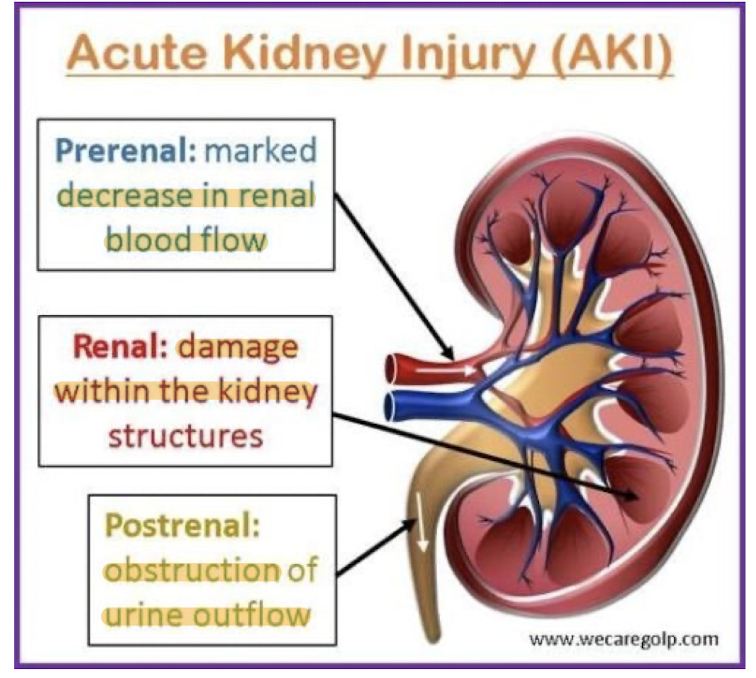
Postrenal: Cause, Urine output, Pain
Rare!
Caused by obstruction in urinary tract
No urine output
Hours of flank pain
RIFLE criteria for acute kidney dysfunction/failure
Risk
Increased creatinine x 1.5 / GFR decreased by 25%
Urine output <0.5mL/kg/hr → 6hr
Injury
Increased creatinine x 2 / GFR decreased by 50%
Urine output <0.5mL/kg/hr → 12hr
Failure
Increased creatinine x 3 / GFR decreased by 75%
Urine output <0.5mL/kg/hr → 24hr / anuria x 12hr
Loss
Persistent acute renal failure >4 weeks
Some sort of intervention done to keep pt. alive
ESKD
End stage kidney disease
> 3 months
Less than 10% kidney function
Supportive treatment of AKI?
Manage potassium / electrolyte levels
Limit sodium / phosphorous intake
Balance fluid intake
Avoid / reduce nephrotoxic drugs
Short term dialysis in severe cases
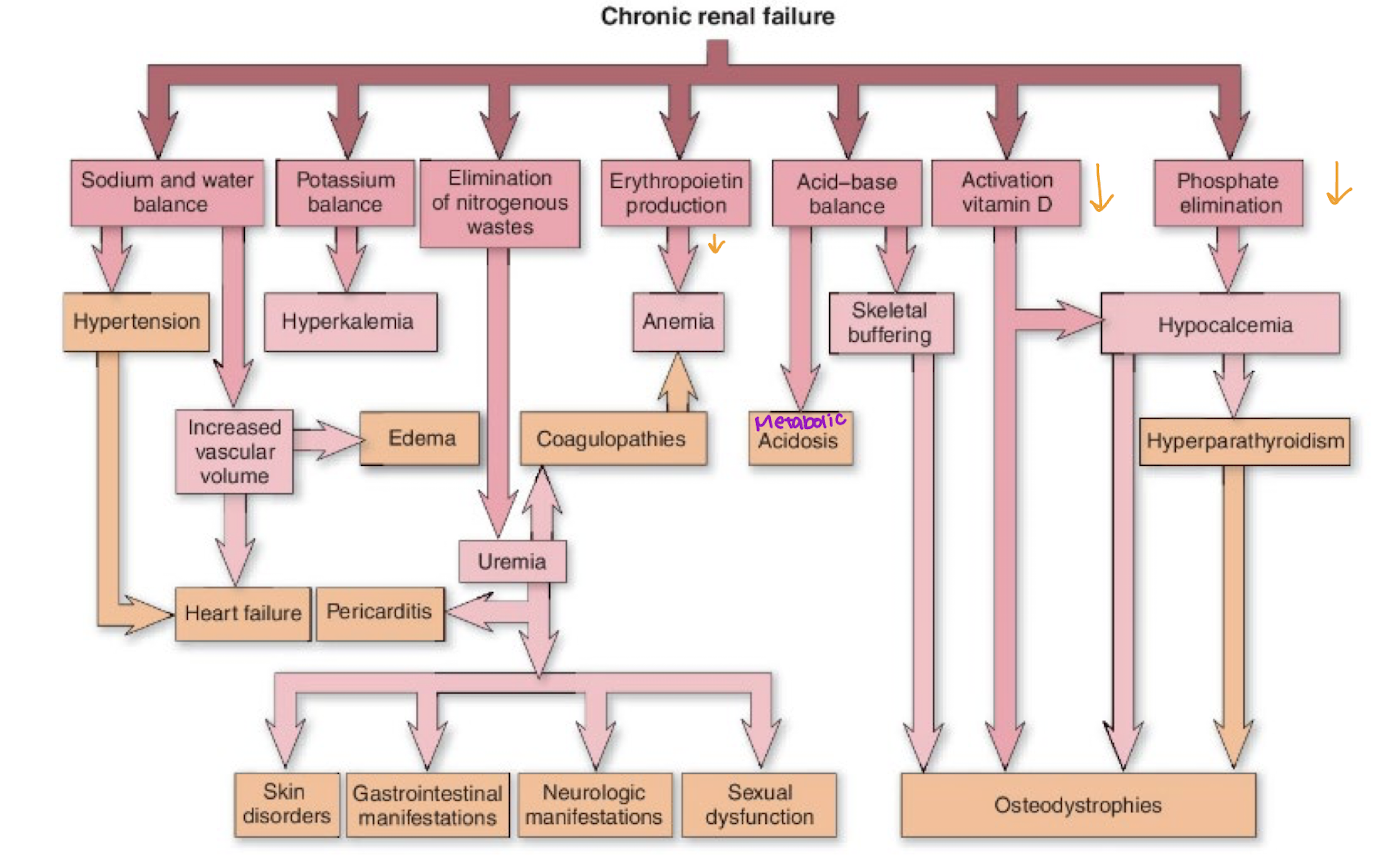
What is chronic kidney disease? What does it specifically damage? How does it try to cope? What does coping result in?
Progressive, irreversible loss of renal function
Specifically damage to nephrons
Initially nephrons hypertrophy to keep up with demand
Urine will have elevated protein, RBC, WBC, but other values normal until reach end stages
Ultimately see decreased GFR and tubular function
Impaired electrolyte balance and fluid conversion
Can maintain normal function until 75% of nephrons destroyed
What does chronic renal injury look like?
Renal → Dry mouth, Decreased urine, Irregular pulses, Fatigue
Cardio → Arrhythmias
Respiratory → Infection, crackles, pleuritic pain
GI → Sore + Bleeding gums, Hiccups, Metallic taste, Ammonia smell to breathe
Skin → Pallid, Yellowish bronze color, Dry, Brittle nails/hair, Flaky urea deposits
Neuro → Altered consciousness, muscle cramps/twitching, Itchy legs + feet
Hematologic → Eady bruise / bleed
Musculoskeletal → Fractures, Abnormal gait
How is chronic kidney injury diagnosed?
Blood studies
Decreased → pH, Bicarb, HCT, Hgb
Increased → BUN, Creatinine, Sodium, Potassium
Urine specific gravity
Fixed at 1.010
Urinalysis
Xray
Renal biopsy
EEG
Stages of chronic kidney injury?
1
Usually no symptoms
GFR >90
HTN common
2 “Mild CKD”
Subtle symptoms
GFR 60-89
HTN more visible
Increasing creatinine + urea levels
3 “Moderate CKD)
GFR a 45-59
GFR b 30-40
Same as 2
4 “Severe CKD”
GFR 15-29
Erythropoietin deficiency anemia
Hyperphosphatemia
Increased triglycerides
Metabolic acidosis
Hyperkalemia
Salt/water retention
5 “End stage KD”
GFR <15
As above
Waste elimination severely impaired
Urea + Creatinine levels build up in blood
CKD prevention / treatment?
Conservative
Low protein diet
Reduce sodium / potassium intake
Manage fluid balance
Dialysis
Transplant
A 35 year old who was severely burned is now demonstrating symptomology associated with acute tubular necrosis (ATN). Which form of renal failure is this patient experiencing?
A) Extrarenal
B) Intrarenal
C) Prerenal
D) Postrenal
B) Intrarenal
A patient is diagnosed with renal calculus that is causing a urinary obstruction. Which symptoms would be most likely experienced?
A) Flank pain
B) Pyuria
C) hematuria
D) Anuria
A) Flank pain
A 42-year-old male is involved in a motor vehicle accident that has resulted in prerenal failure. What is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
A) Kidney Stones
B) Obstruction of the proximal tube
C) Inadequate renal blood flow
D) Obstruction of the ureters
C) Inadequate renal blood flow
Which type of acute kidney disease are associated with each cause (prerenal, intrarenal, postrenal)
1) Nephrotoxic antibiotics
2) Massive hemorrhage
3) Renal ischemia during surgery
4) Bilateral renal calculi
5) Untreated enlarged prostate
Intra
Pre
Intra
Post
Post
What mechanism most directly contributes to neurological symptoms such as confusion and peripheral neuropathy in patients with chronic kidney disease?
a. Accumulation of uremic toxins due to decreased renal clearance
b. Excessive deposition of calcium in neural tissues
c. Increased production of neurotransmitters due to metabolic imbalance
d. Elevated circulating catecholamines from sympathetic overactivity
a. Accumulation of uremic toxins due to decreased renal clearance
In chronic kidney disease, which mechanism is primarily responsible for the development of peripheral edema?
a. Increased capillary permeability from systemic inflammation
b. Reduced renal excretion of sodium and water due to decreased glomerular filtration
c. Excessive protein loss from the kidney causing hypoalbuminemia
d. Elevated hydrostatic pressure from uncontrolled hypertension
b. Reduced renal excretion of sodium and water due to decreased glomerular filtration