Fall Semester Final Study Guide 2022 Biology
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Last updated 7:51 PM on 12/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
LIst the 8 charcteristics of a living thing.
***DNA, Reproduction, Growth, Cells, Homeostasis, Energy, Evolution, Respond to Environment***
2
New cards
List the 3 parts of Cell Theory
* All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
* A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms.
* All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
* A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms.
* All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
3
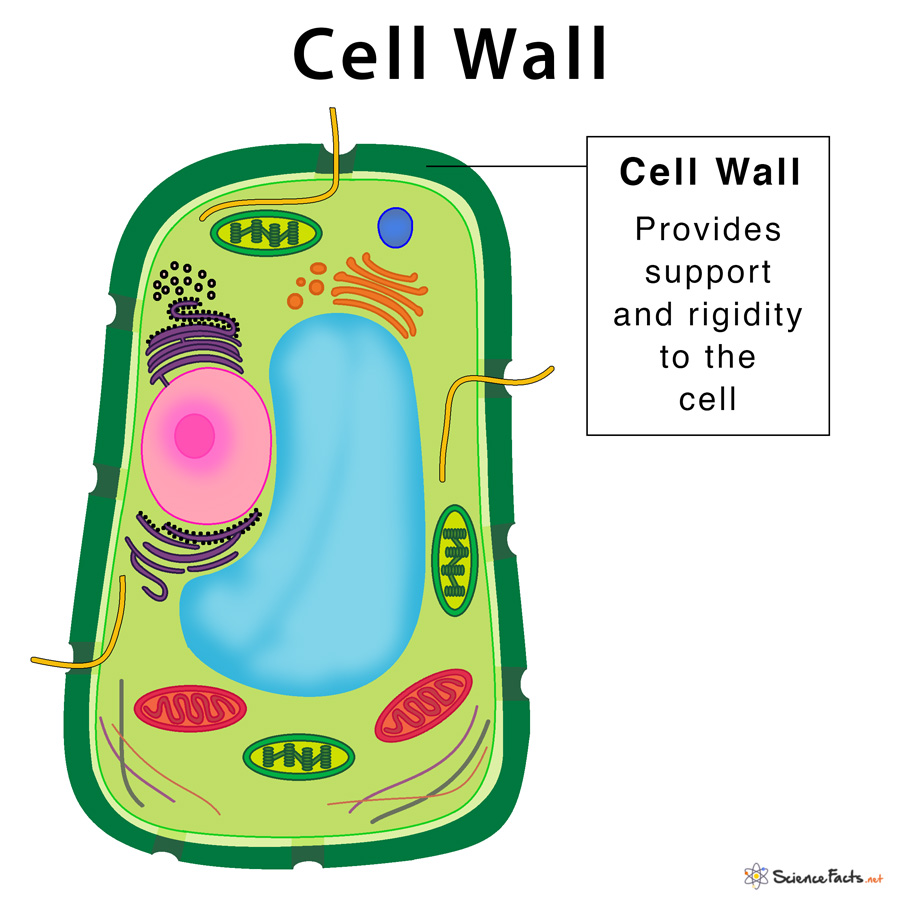
New cards
Cell Wall
Gives the cell a definite shape and structure. Provides structural support. Protection against infection and mechanical stress.
4
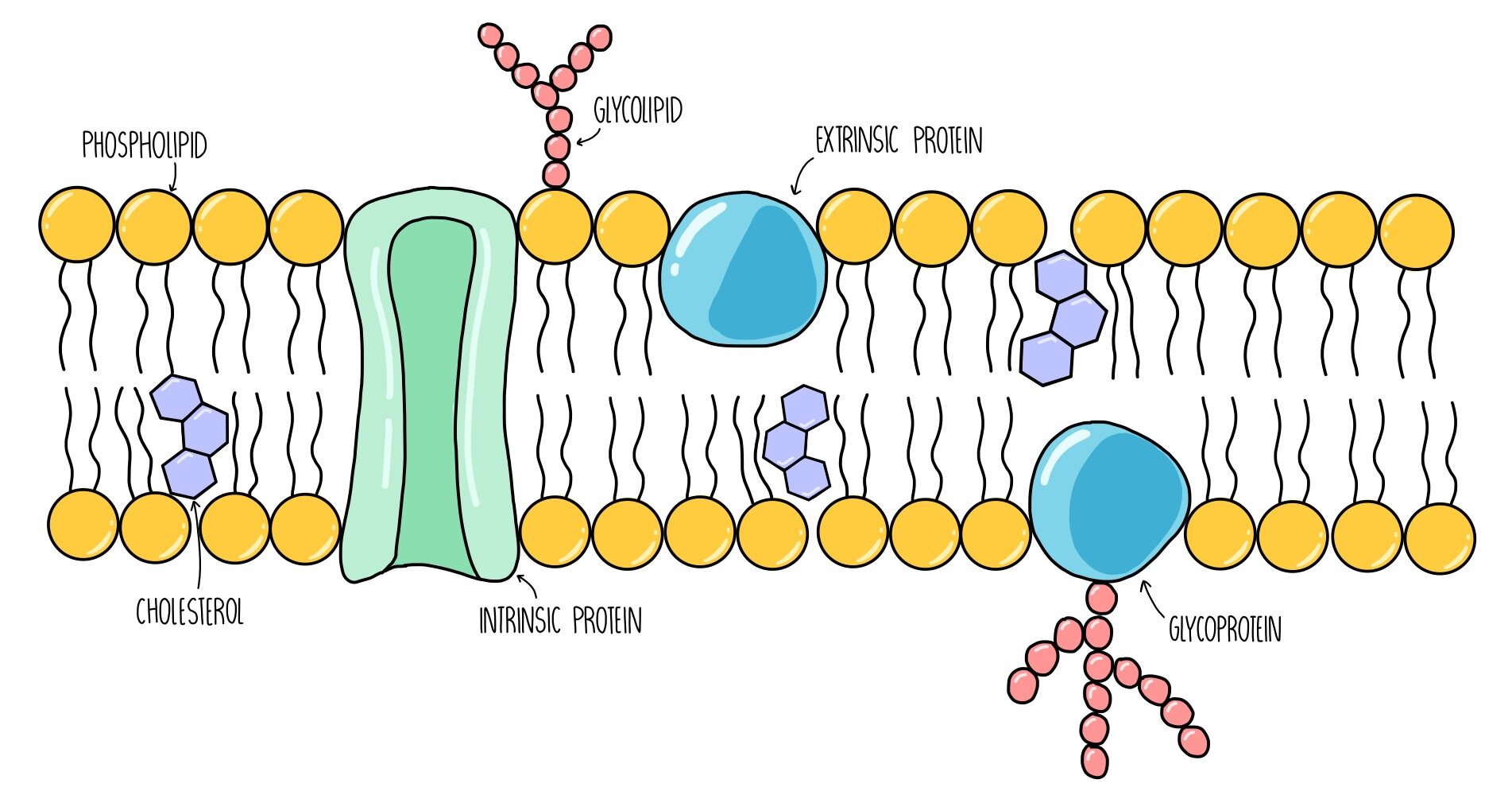
New cards
Cell Membrane
Provides protection for a cell. Has many functions, one is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
5
New cards
Cytoplasm
medium for chemical reaction
6
New cards
Mitochondria
generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions

7
New cards
Chloroplast
produce energy through photosynthesis and oxygen-release processes
8
New cards
Golgi apparatus
Processes proteins and lipids
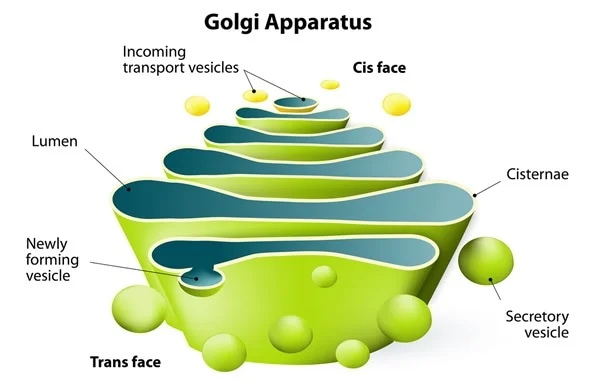
9
New cards
Ribosome
The site of protein synthesis in the cell. The ribosome reads the messenger RNA
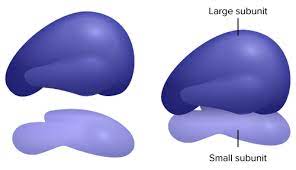
10
New cards
Lysosome
Rid cells of waste products and scavenge metabolic building blocks that sustain essential biosynthetic reactions during starvation.
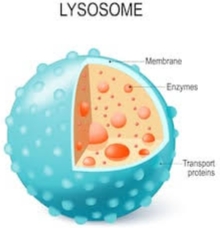
11
New cards
Centriole
Organizing microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system
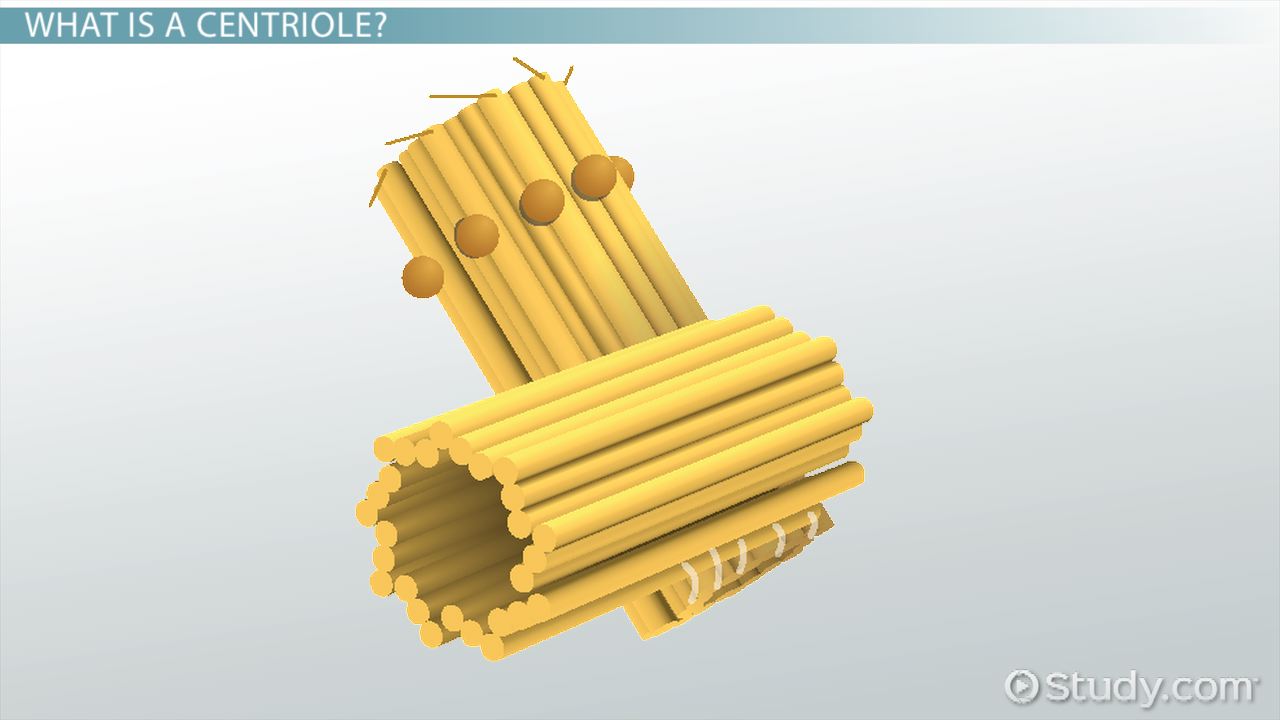
12
New cards
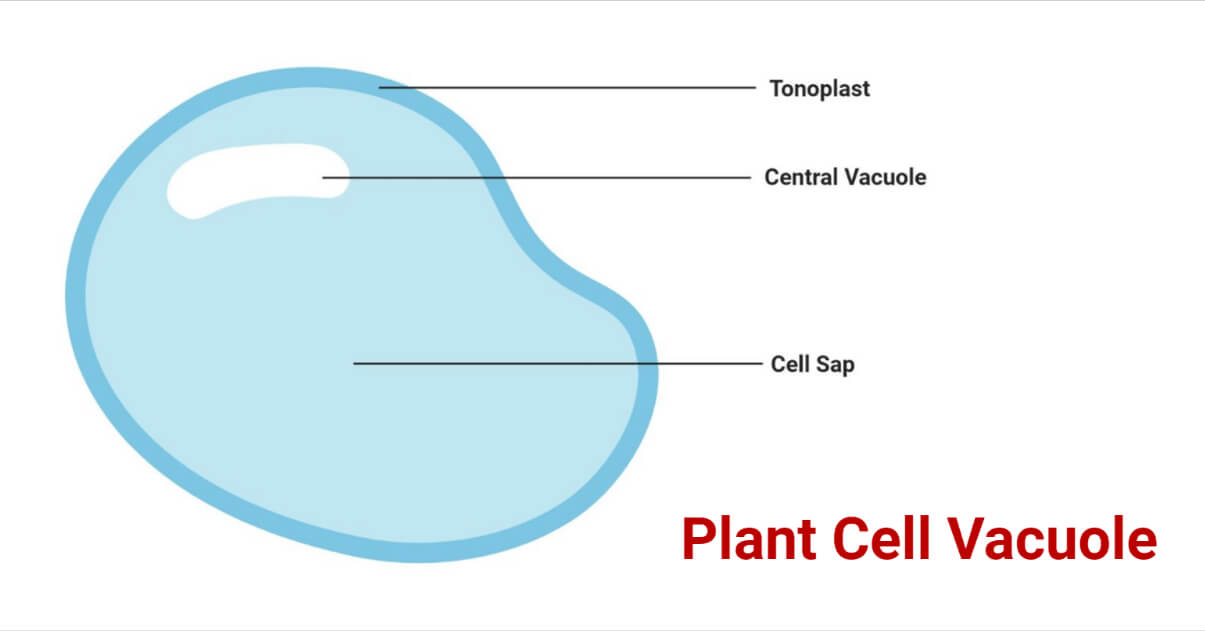
Vacuole
help sequester waste products
13
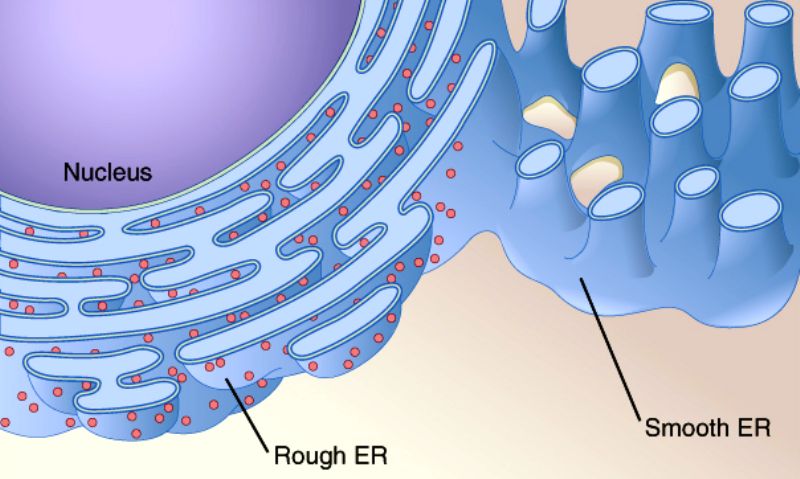
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Produce proteins for the rest of the cell to function
14
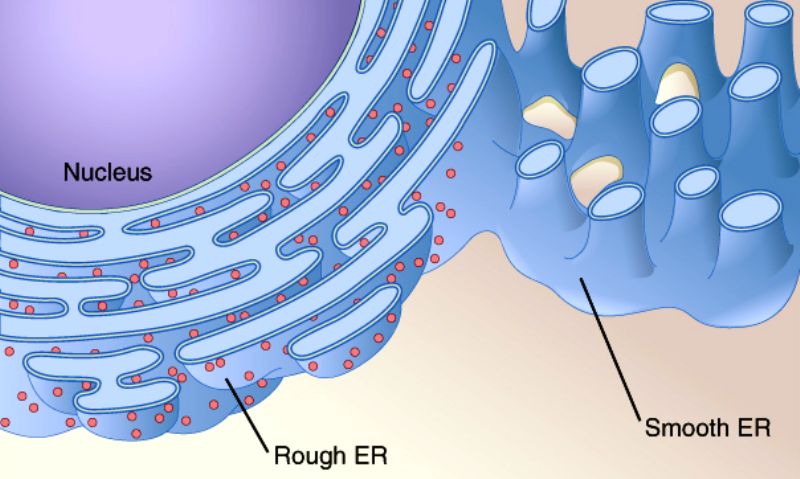
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
synthesizes lipids, phospholipids as in plasma membranes, and steroids.
15
New cards
Nucleus
Stores the cells DNA
16
New cards
Nucleolus
facilitating ribosome biogenesis, through the processing and assembly of RNA into preribosomal particles.
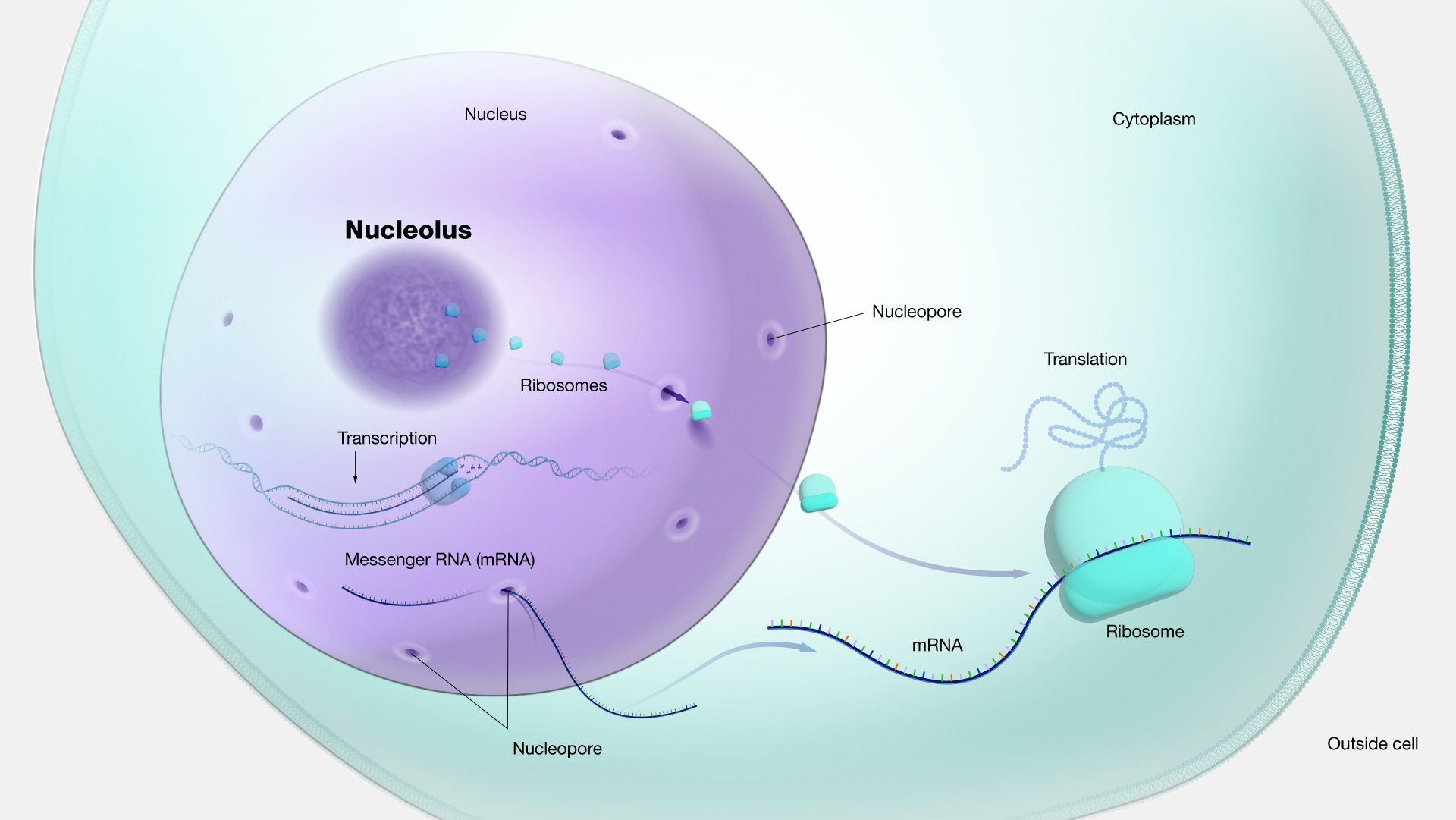
17
New cards
What cell parts do plants have that animal cells don’t?
**Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, plasmodesmata, and plastids used for storage, and a large central vacuole, whereas animal cells do not.**
18
New cards
What’s the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote?
\
\
**✳️** In a prokaryotic cell,size of cell is generally small, nucleus is absent and DNA lies directly in the cytoplasm, one single chromosome is present, Membrane bounded cell organelles are absent, smaller and randomly scattered ribosome are present in the cytoplasm.
\
**✴️** Size of cell is generally large, A distinct nucleus is present which is surrounded by a nuclear membrane, Many chromosome are present, Membrane bounded cell organelles are present. Ribosomes are bigger and can be free or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
\
\
**✳️** In a prokaryotic cell,size of cell is generally small, nucleus is absent and DNA lies directly in the cytoplasm, one single chromosome is present, Membrane bounded cell organelles are absent, smaller and randomly scattered ribosome are present in the cytoplasm.
\
**✴️** Size of cell is generally large, A distinct nucleus is present which is surrounded by a nuclear membrane, Many chromosome are present, Membrane bounded cell organelles are present. Ribosomes are bigger and can be free or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
\
19
New cards
A student is doing an experiment to see which additives help water boil faster. The student measures the speed that plain water boils. Then measures a 5% solution of each of the following, vinegar, salt water, and sugar water. She then times how long it takes for all to boil. Identify the IV, DV, control, and 2 constants she would have to use.
IV: Type of solution
DV: How fast it takes to boil
Control: Plain water
Constants: Amount of water to solution ratio, temperature of stove (or whatever used to boil the solutions) is.
DV: How fast it takes to boil
Control: Plain water
Constants: Amount of water to solution ratio, temperature of stove (or whatever used to boil the solutions) is.
20
New cards
Least to most complex
1. Atom
2. Molecules
3. Cells
4. Tissue
5. Organ
6. Organ Systems
7. Organism
21
New cards
Describe the difference between a hypothesis and theory.
A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data.
22
New cards
Define homeostasis
the tendency toward a relatively stable __equilibrium__, especially as maintained by physiological processes.
23
New cards
Convert 235 ml to L. 25 cLto mL. 80000g to kg.
1. 0.235 L
2. 250 mL
3. 80 kg
24
New cards
LIst the steps of the scientific method.
* State problem in question form
* Research Question
* Hypothesis
* Conduct experiment
* Record/Analyze data
* Conclusion
* Report findings
* Research Question
* Hypothesis
* Conduct experiment
* Record/Analyze data
* Conclusion
* Report findings
25
New cards
What does it mean when I say a solution is hypertonic to a cell?
Its solute concentration is higher than that inside the cell, and the solutes cannot cross the membrane.
26
New cards
If a cell were in a hypertonic solution, what would happen to it?
The solution will cause the cell to shrink.
27
New cards
If a cell were in an isotonic solution, what would happen to it?
The cell’s volume will remain stable
28
New cards
There are 4 macromolecules (biomolecules) that we studied. What are they?
carbohydrates, lipids (or fats), proteins, and nucleic acids.
29
New cards
What is a monomer?
a __molecule__ that can be __bonded__ to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
30
New cards
What is the monomer for a carbohydrate? For a protein?
Monosaccharides, simple sugars like glucose and fructose.
\
Amino acids.
\
Amino acids.
31
New cards
What are the 6 properties of water?
Cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, density, universal solvent, high specific heat, high heat vaporization.
32
New cards
Water will stick to the walls of glass test tubes. Why?
Since water molecules like to stick together, when the molecules touching the glass cling to it, other water molecules cling to the molecules touching the glass, forming the meniscus.
33
New cards
We say that water is because it has two oppositely charged sides.
Polar
34
New cards
What elements are found in carbohydrates? Proteins? LIpids? Nucleic Acids?
* Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
* Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur
* Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
* Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Phosphorus, and Hydrogen
* Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur
* Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
* Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Phosphorus, and Hydrogen
35
New cards
WHat do we call the process of changing one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals?
A chemical reaction
36
New cards
Name the 2 subatomic particles and tell me their charge.
Protons: positive +
Neutrons: neutral =
Electrons: Negative -
Neutrons: neutral =
Electrons: Negative -
37
New cards
What is it about an element that can tell you its atomic number?
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
38
New cards
If an atom has the atomic number of 14, and an atomic mass of 27, how many protons does it have?
\
Neutrons? Electrons?
\
Neutrons? Electrons?
14 protons
\
13 neutrons. 14 electrons.
\
13 neutrons. 14 electrons.
39
New cards
Define solute and solvent.
Solute: dissolved in the solvent
Solvent: ABility to dissolve other substances.
Solvent: ABility to dissolve other substances.
40
New cards
Whis is a compund light microscope called COMPOUND microscope?
Since it uses more than one lens,
41
New cards
A microscope has a magnificent pf 10x in the ocular lens and a magnification of 40x objective lens. What is the total magnification?
400x
42
New cards
Which part of the microscope does the slide sit on?
Stage
43
New cards
What’s the difference between the coarse adjustment knob and the fine adjustment knob?
COARSE ADJUSTMENT KNOB — A rapid control which allows for quick focusing by moving the objective lens or stage up and down. It is used for initial focusing.
\
FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB — A slow but precise control used to fine focus the image when viewing at the higher magnifications.
\
FINE ADJUSTMENT KNOB — A slow but precise control used to fine focus the image when viewing at the higher magnifications.
44
New cards
A cell membrane is called a phospholipid bilayer. Why is that?
The cell membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids, which consist of fatty acids and alcohol. The phospholipids in the cell membrane are arranged in two layers, called a phospholipid bilayer
45
New cards
A cell membrane is a fluid mosaic. What does that mean?
The fluid mosaic model describes the cell membrane as a tapestry of several types of molecules (phospholipids, cholesterols, and proteins) that are constantly moving.
46
New cards
Cell membranes are made of phospholipids that have a (blank) head, and (blank) tails.
Hydrophillic, hydrophobic
47
New cards
What does selectively permeable mean?
ability to differentiate between different types of molecules, only allowing some molecules through while blocking others.
48
New cards
Diffusion
the net movement of anything generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower
49
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
the process of spontaneous passive transport of molecules or ions across a biological membrane via specific transmembrane integral proteins
50
New cards
Osmosis
molecules of a __solvent__ tend to pass through a __semipermeable__ membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one, thus __equalizing__ the concentrations on each side of the membrane.
51
New cards
Active transport
the movement of __ions__ or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by __enzymes__ and requiring energy.
52
New cards
Endocytosis
the taking in of matter by a living cell by __invagination__ of its membrane to form a __vacuole__.
53
New cards
Exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell __vacuole__ are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
54
New cards
What food does most of the carbon in American diet come from?
Beef
55
New cards
What is cohesion?
Like particles sticking together
56
New cards
When I say water has a high specific heat, what does that mean?
it takes more energy to increase the temperature of water compared to other substances.