biochemistry 1st year
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
biochemistry
study of chemistry of living organisms
atoms and atomic structure (4)
number of protons— atomic number— number of electrons
number of electrons lead to different number of orbitals
s orbitals: spherical
p orbitals: dumbbell shaped
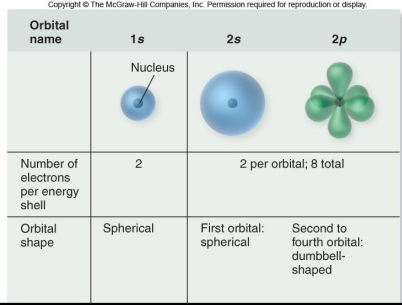
valence electrons
electrons in outer shell that are available to combine with the electrons of other atoms to form bonds
chemical bonds and molecules
incomplete valence shells can share or transfer valence electrons with certain other atoms, resulting in atoms staying close together called chemical bonds
molecule
2 or more atoms bonded together
compound
molecule composed of 2 or more elements
molecular formula
contains chemical symbols of elements found in a molecule, subscript indicates how many of each atom are present
octet rule
atoms are stable when outer shell is full
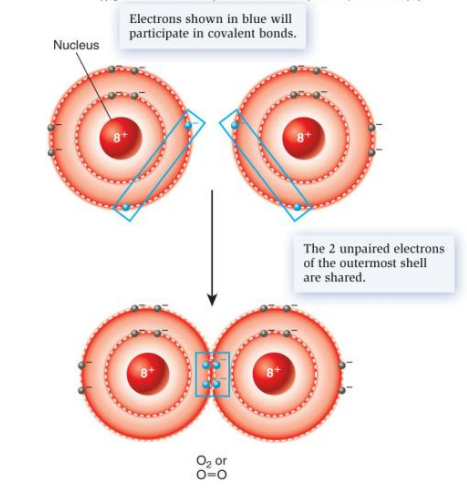
covalent bonds
atoms share pair of electrons
strong chemical bonds, behave as if they belong to each atom
occurs between atoms whose outer electron shells are not full
polar covalent bonds (3)
electronegativity: atoms attraction for the electrons in a covalent bond, more electronegativity the stronger it pulls shared electrons toward itself
polar covalent bonds occur because the distribution of electrons around the atoms creates a polarity across the molecule
water soluble
non polar covalent bonds (3)
atoms share electron equally
bonds between atoms with similar electronegativities
water soluble poor
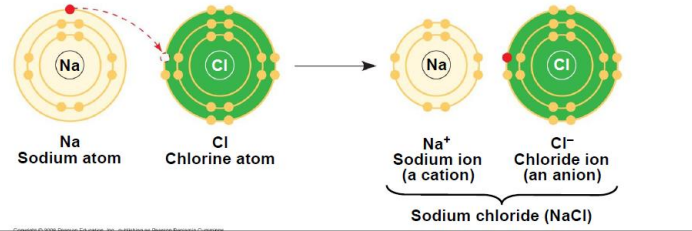
ionic bonds (4)
an ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, now has net electric charge
cations: net positive charge
anions: net negative charge
ionic bond occurs when cation bonds to anion
hydrogen bonds
hydrogen atom from one polar molecule attracted to an electronegative atom
organic molecules
carbon containing molecules
functional groups (5)
carbohydrates, lipids, protein and nucleic acids contain small reactive groups of atoms called functional groups
confer specific properties to biological molecules
groups of atoms with special chemical features that are functionally important
each have special chemical properties
most common are hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate and sulfhydryl
condensation/ dehydration reaction
links monomers to form polymers
hydrolysis
polymers broken down into monomers
carbohydrates (3)
composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
most of the carbons linked to a hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group
most have 5 or 6 carbons
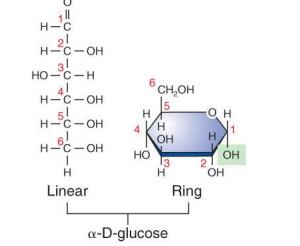
monosaccharides (8)
linear form, each carbon has -H and -OH attached except one
the remaining is part of carbonyl group
if has more than 5 carbons can fold back on themselves to ring form
has 4 different structures
location of carbonyl group
number of carbon atoms present
spatial arrangement of groups
linear and alternative ring forms
disaccharides (4)
composed of two monosaccharide monomers
joined by dehydration/ condensation reaction
broken apart by hydrolysis
glycosidic bond
polysaccharides (3)
any monosaccharides linked together to form long polymers
may be linear, unbranched molecules or may contain one or more branches in this side chains of sugar units attach to a main chain
2 functions: energy storage and structural role
lipids (2)
do not form polymers
hydrophobic
phospholipids (4)
two fatty acids attached to glycerol
amphipathic molecules
hydrophilic head hydrophobic tail
major component of all cell membranes- bilayer
steroids (4)
four interconnected rings of carbon atoms
usually insoluble in water
tiny differences in structure can lead to different specific biological properties
eg. oestrogen vs testosterone
fats
made of glycerols and fatty acids
glycerol: 3 carbon alcohol with hydroxyl group to each carbon
fatty acid: carboxyl group to long carbon skeleton
saturated fats: all carbons linked by single covalent bonds, solid at room temp
unsaturated fats: contain one or more double bonds, liquid at room temp
diet rich in saturated fats may contribute to cardiovascular disease
fat used as insulation
glycerol enters glycolysis
2 carbon molecules help makes AcetylCoA
nucleic acids (2)
polymer of nucleotide monomers
responsible for storage, expression and transmission of genetic information
nucleotide
phosphate group, five carbon sugar and either single or double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms called nitrogenous base
DNA structure (5)
purine: adenine and guanine
pyrimidine: cytosine and thymine
pairs held together by hydrogen bonds
2 H bonds between A and T
3 H bonds between C and G
DNA vs RNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid ribonucleic acid
deoxyribose ribose
thymine uracil
2 strand double helix single strand
1 form several forms
diversity of protein function (6)
motor proteins- initiate movement
defence proteins- protect against infection/ disease
cell signalling- cell to cell communication
structural proteins- provide support
transport proteins- movement of solutes across plasma membrane
enzymatic proteins- many proteins are specialised to catalyse or speed up reactions
metabolism
biochemical modification and use of organic molecules and energy to support the activities of life
metabolic pathways
series of chemical reactions that occur in a cell
protein (2)
biologically functional molecule that consists of one or more polypeptides
composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and other trace elements
protein structure (4)
primary structure: unique sequence of amino acids
secondary structure: found in most proteins, consists of coils and folds in the polypeptide chain
tertiary structure: determined by interactions among various side chains (R groups)
quaternary structure: protein consists of multiple polypeptide chains
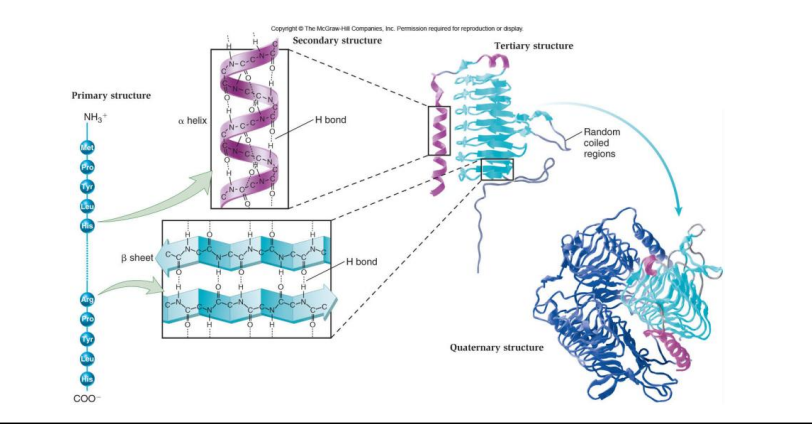
Catabolism
breakdown of products to components, releases usable energy in the process
eg carbohydrates into water
anabolism
synthesis of complex products from simpler components
eg amino acids to proteins
metabolism (C&A)
sum total of all the anabolic and catabolic reactions in a cell
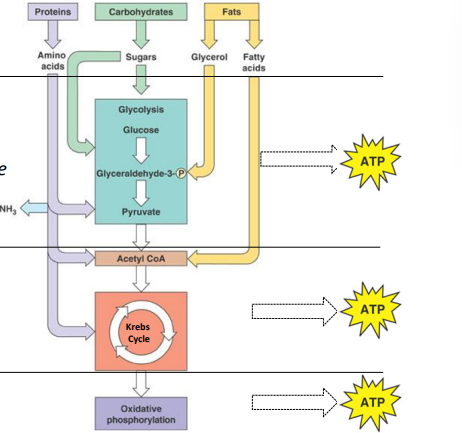
cellular respiration definition
breakdown of energy rich molecules to produce cellular energy, O2 and water necessary
cellular respiration(4)
production of organic fuels
glycolysis
citric acid (krebs) cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
oxidation and reduction(3)
transfer of electrons during chemical reaction are referred to as reduction-oxidation reactions (redox)
oxidation: loss of electrons
reduction: gain electrons
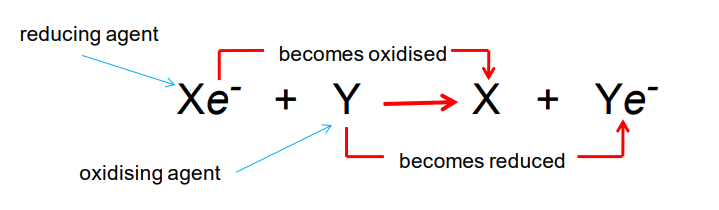
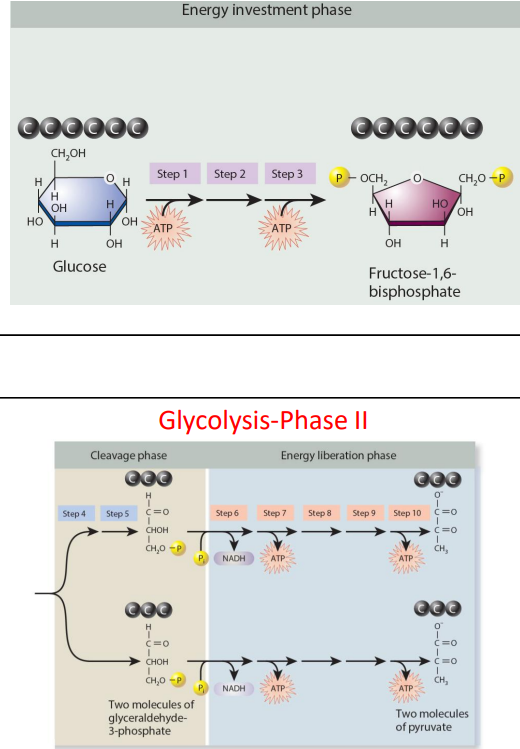
cellular respiration, stage 1 glycolysis (9)
energy investment
steps 1 to 3
2 ATP hydrolysed to create fructose-1, 6 bisphosphate
Cleavage
steps 4 to 5
6 carbon molecules broken down into two 3 carbon molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
energy liberation
steps 6 to 10
two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate molecules broken down into two pyruvate molecules- produces 2 NADH and 4 ATP
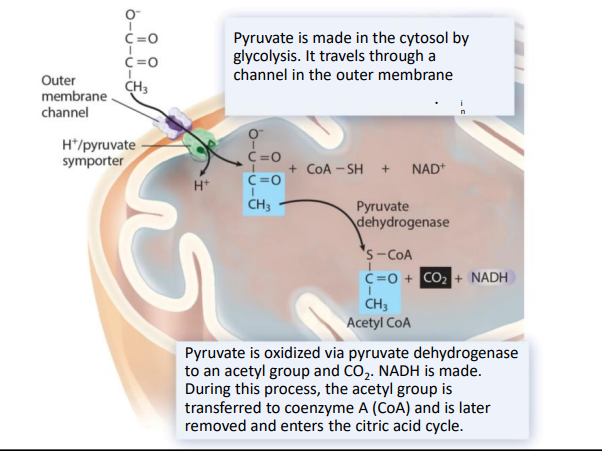
cellular respiration- stage 2 pyruvate breakdown (5)
in eukaryotes, pyruvate transported into the mitochondrial matrix
broken down by pyruvate dehydrogenase
molecule of CO2 removed from each pyruvate
remaining acetyl group attached to CoA to make acetyl CoA
yield= 1 NADH for each pyruvate
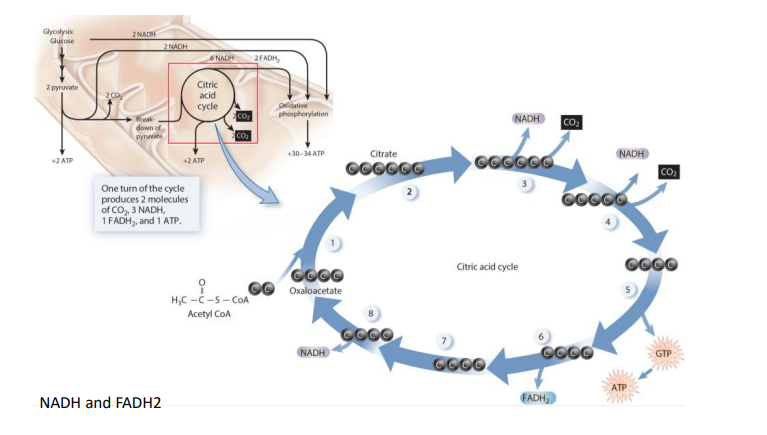
cellular respiration- stage 3 citric acid cycle (4)
metabolic cycle, some enters and some leave, series of organic molecules regenerated in each cycle
acetyl removed from acetyl CoA attached to oxaloacetate to form citrate(citric acid)
series of steps releases 2 CO2, 1 ATP, 3 NADH and 1 FADH2
oxaloacetate regenerated to start cycle again
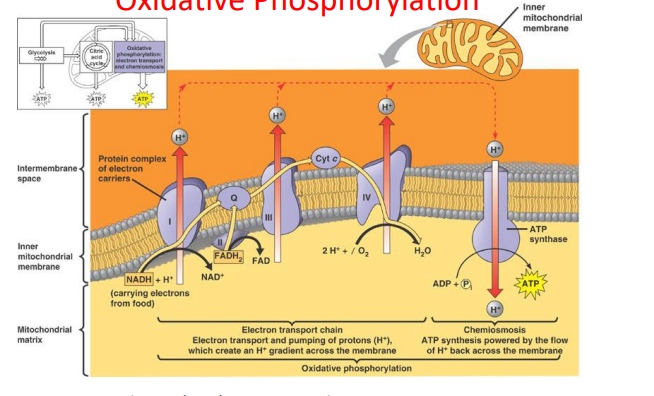
cellular respiration- stage 4 oxidative phosphorylation (10)
high energy electrons removed from NADH and FADH2 to make ATP
requires oxygen
oxidative process involves electron transport chain
phosphorylation occurs by ATP synthase
electron transport chain
NADH donates electrons to complex 1 | H+ pumped across
FADH2 donates electrons to complex 2
when electrons are passed along | H+ pumped across membrane
H+ passed back through ATP synthase where 1 ATP molecule is produced
30-32 ATP produced
fermentation (4)
make ATP my glycolysis only
muscle cells produce lactate
yeast make ethanol
produces less ATP