C1 - Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Element
substance with only one type of atom
Compound
2 or more different elements combined in fixed proportions
Molecule
2 or more atoms bound together
Mixtures
2 or more elements not chemically combined together
e.g., oil and water
Methods to separate mixtures
filtration
crystallisation
simple distillation
fractional distillation
chromatography
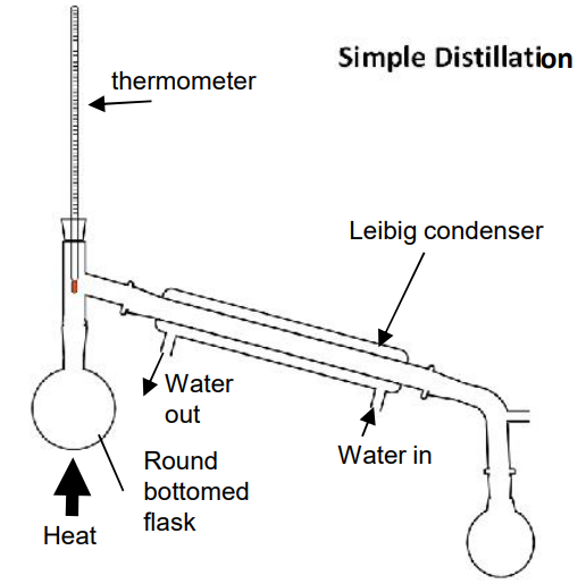
Simple Distillation
separates liquid from a solution
liquid boiled to gas
vapour rises from flask into condenser
cooled by cold water back into liquid
collected into second flask
dissolved solids left in first flask
Fractional Distillation
separates liquids with different boiling points and are miscible
mixture heated and boiled
vapour enters fractioning columns
rise, condense, drip back into flask, re-evaporate
lower boiling point liquid rises first to condenser and into flask
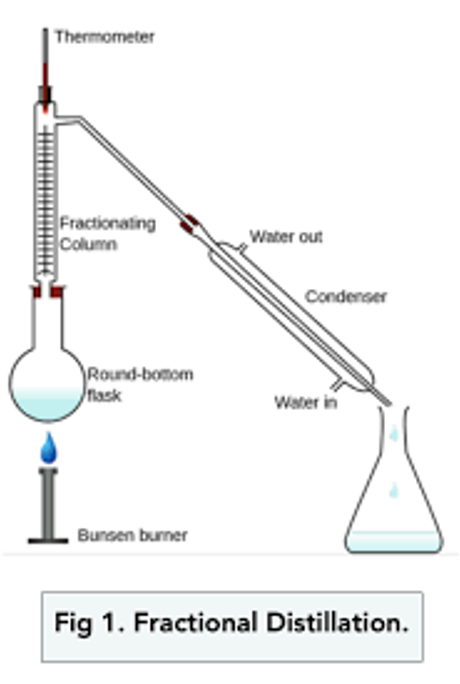
Fractional distillation:
Why are glass beads used?
increase separation efficiency by increasing surface area for evaporation and condensation
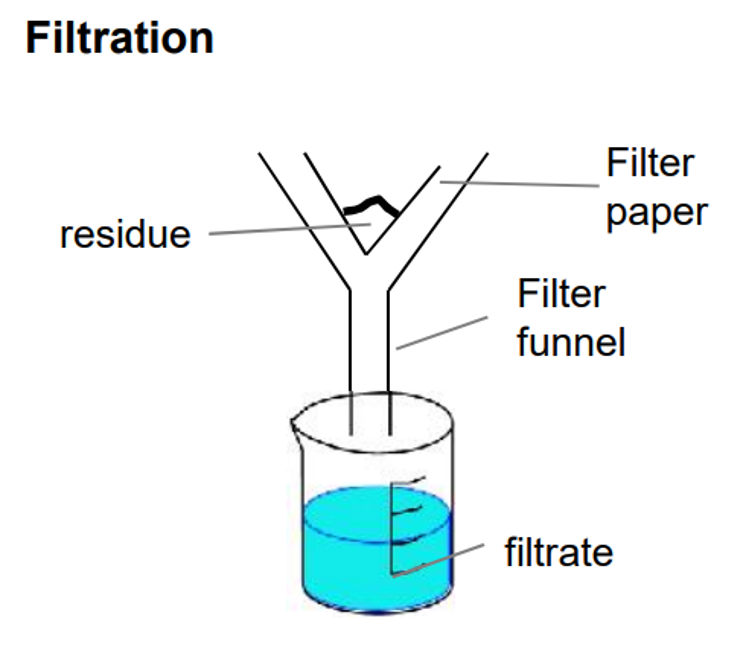
Filtration
separates insoluble solid from liquid
e.g., sand and water
solid gets stuck on filter paper
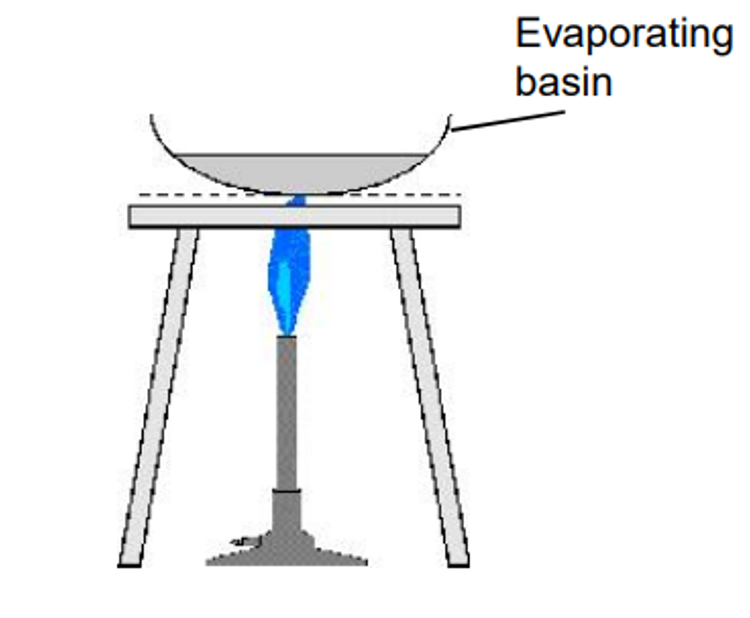
Crystallisation
separates soluble solid in liquid
e.g., seawater
bunsen burner lit
liquid evaporates
solid crystals left behind
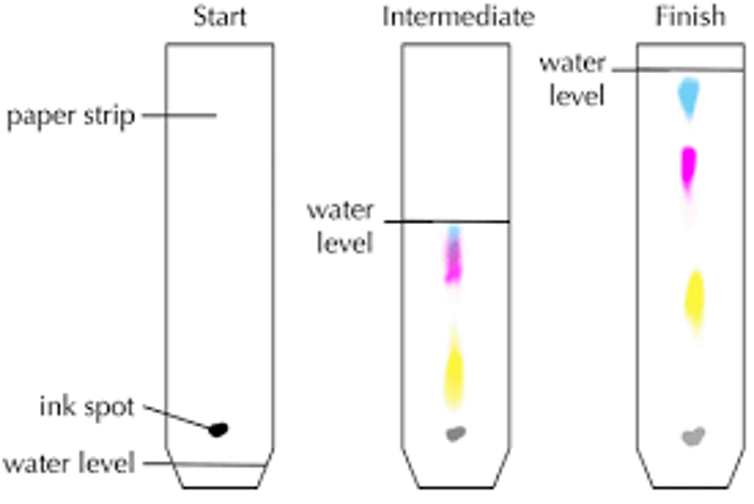
Chromatography
separates mixtures of soluble substances
stationary phase - absorbent paper
mobile phase - solvent, moves through paper and carries substances
different substances within mixture attracted to each phase in different proportions - so will move to different extents up the paper
Ideas of modelling the atom - Past to Present
Plum-pudding
Nuclear
Bohr
Chadwick
Plum-Pudding Model of an Atom
ball of + charge
electrons embedded within
Nuclear model of an atom
alpha particles directed at gold foil
under vacuum conditions
most went straight through - most of an atom is empty space
small number delfected at large angles - concentration of + charge
Bohr model of the atom
electrons orbit nucleus at specific distances away (shells)
explains patterns of different elements burning differently
What is in an atom?
electrons
protons
neutrons
What is in the nucleus of an atom?
protons
neutrons
How are electrons arranged in?
shells/energy levels
Atomic number
number of electrons which = number of protons
Why does the number of electrons = number of protons in an atom?
atoms have neutral charge
Mass number =
number of protons + protons
Number of Neutrons in an atom =
mass number - atomic number
Isotopes
atoms of the same element
same number of protons and electrons
different number of neutrons
What is the Relative Atomic Mass of an atom?
average mass number of an atom of an element
Formula for Relative Atomic Mass =
sum of (isotope mass x abundance) / 100
Maximum number of electrons in 1st shell
2
Maximum number of electrons in 2nd shell
8
Maximum number of electrons in 3rd shell
8
Elements in the same group (column) in the periodic table have the same number of….
outer shell electrons
Elements in the same period (row) of the periodic table have the same number of….
shells
Why are noble gases (group 8/0) unreactive?
full outer shells of electrons
energetically stable
Early Ideas of the period table: How did scientists classify elements? (Before the discovery of sub-atomic particles)
In order of atomic weight (relative atomic mass)
incomplete - many elements unknown
How did Dmitri Mendeleev change the periodic table?
Accounted for properties of elements
gaps in the table for unknown elements - predicted properties of these!
How are metals different from non-metals?
metals loose electrons = positive ions
How do non-metals differ from metals?
gain electrons = negative ions
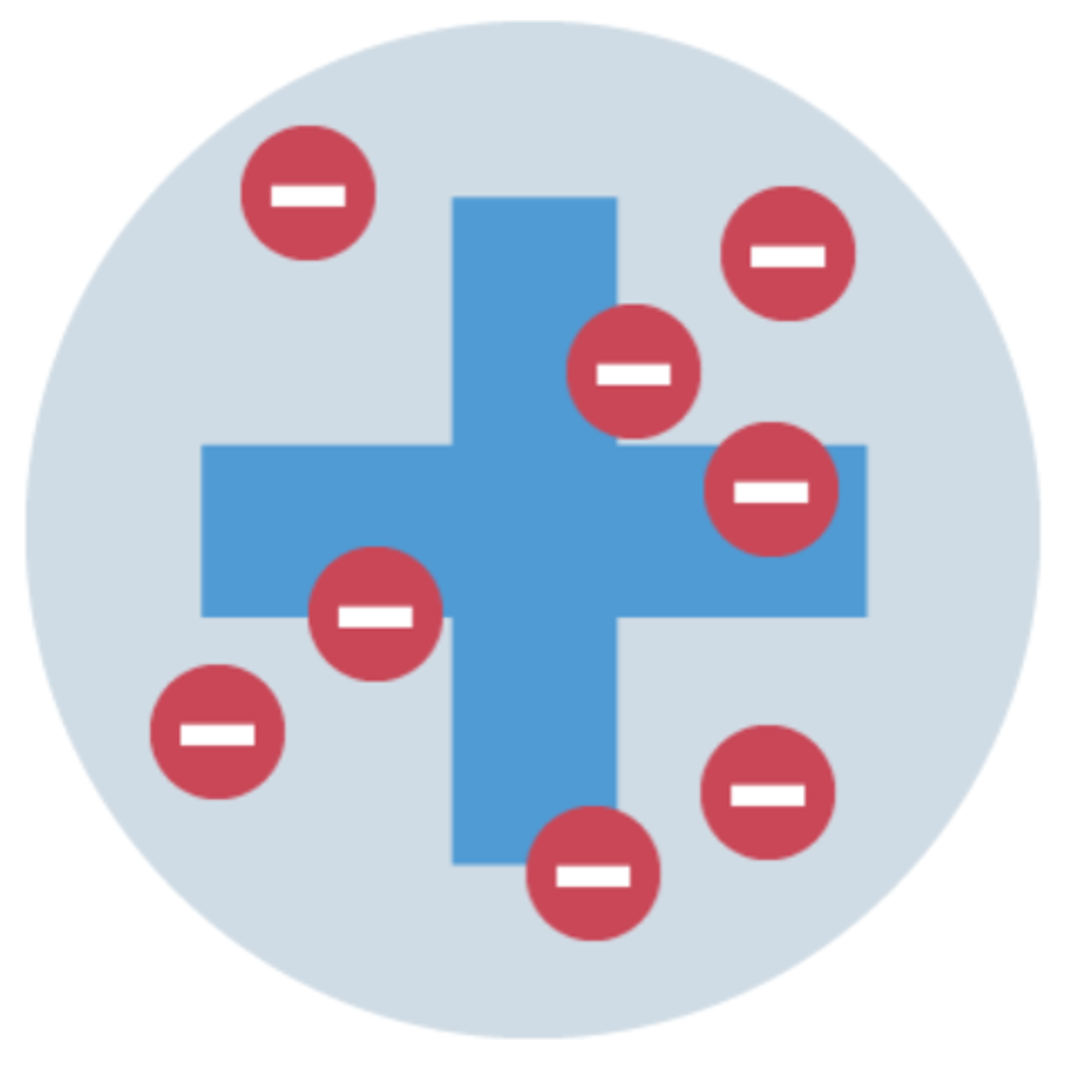
Group 1 metals
form +1 ions
low density
stored under oil - prevents reacting with O and water
reactivity increases down group
Why does the reactivity in group 1 metals increase down the group?
atoms get larger
outer electron further away from the nucleus
less attraction between the 2
more easily lost
Group 1 reactions with non metals form…
ionic compounds
Group 1 reactions with water
metal hydroxides
fizzing
reactivity increases down group
Group 7 non-metals (Halogens)
7 outer electrons
coloured vapours
diatomic molecules
less reactive down group
Why does reactivity of group 7 non-metals decrease down the group?
higher molecular mass
stronger intermolecular forces
higher boiling/melting points
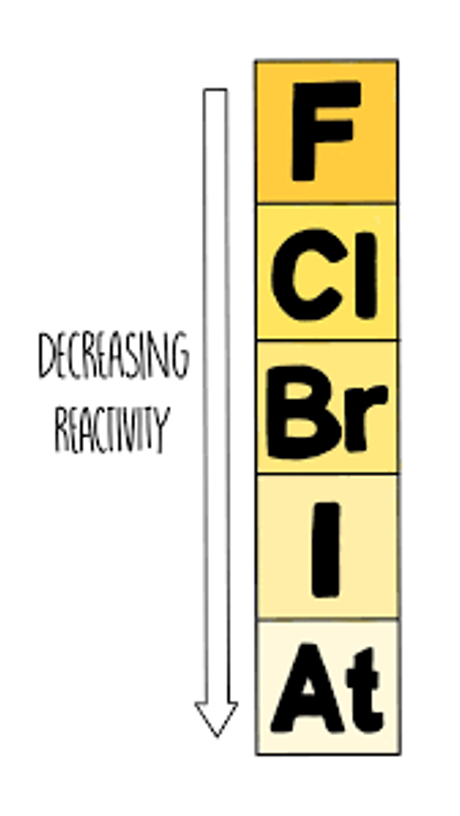
Group 7 Displacement Reactions
more reactive halogens displace less reactive halogens in reactions
Transition Metals
ions with different charges
form coloured compounds
useful catalysts
hard
strong
high densities and melting points