Cytology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What does the plasma membrane include
Lipid bilayer, proteins, glycocalyx
What types of proteins
Peripherial and transmembrane proteins
transmembrane proteins
passes completely through lipid bilayer
peripheral protein
are just attached on the inner or outer layer of the phospholipid bilayer, but dont go through the phospholipid bilayer.
glycolipid
sugar attached to lipid

glycoprotein
carbohydrate thats attached to a protein

glycocalyx
on the extracellular face(outer) and is the sugar coating to the cell which identifies other cells as friend or foe
hydrophobic
scared of water
the little tails
hydrophilc
likes water
the actual head
Cytoskeleton
made up of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
like network of ropes and beams that give cell its shape, support, and helps move substances from one end to another end of a cell.
mitochondria
Synthesizes ATP, which creates energy for the cell to live/function.
proteasome
breaks down or recycles damage or unneeded proteins
peroxisome
breaks down fatty acids and detoxifies harmful substances in cell
lysosome
breaks down and recycles unwanted or harmful materials in cell
Golgi Apparatus
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for delivery inside or outside of the cell.
receives proteins from rough ER
nucleolous
produces ribosomes
ribosomes
protein synthesis and assembles amino acids
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
has ribosomes on it and wil make and process proteins
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
has NO ribosomes, makes lipids, detoxify drugs, and stores calcium
cytosol
gel like fluid within the cell
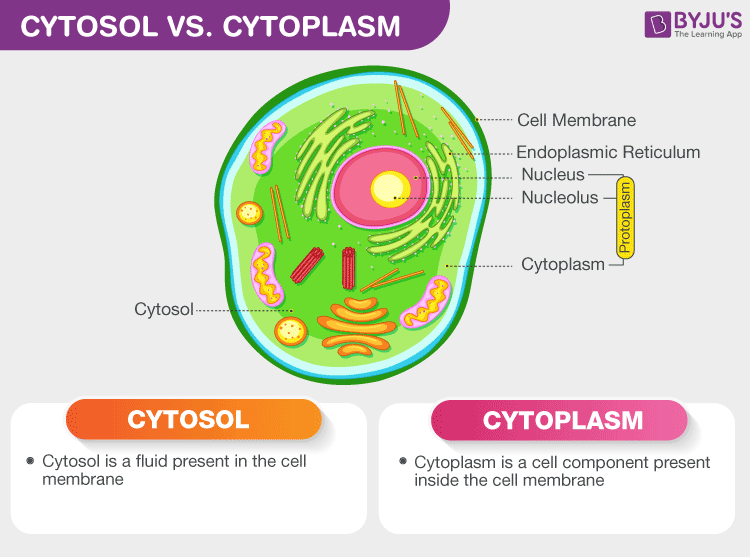
the cytoplasm
surrounds the cytosol, organelles, inclusions, and the cytoskeletom
cell junction
Allows cells to grow, divide normally, resist stress, communicate, and control movement of substances between them
tight junction
zipper like junction between epithelial cells that tightly restricts passage between the 2 cells.
Gap junction
allows for open communication between cells.
like
desmosomes
they are like spot welds that hold two cells together like a connection.
Doesnt allow stuff to pass
hemidesmosome
attach cell to basement membrane of the Extra celluar matrix(ECM)
Extracellular matrix
the outside of a cell that doesn’t hold any of the organelles within a cell
intracellular matrix
the inside of a cell that does hold the cytoplasm and organelles. related to tissue environment
Nucleus structures
Nuclear pores, nuclear envelope, and chromatin
Nuclear pores
lets materials in and out of the nucleus
Nuclear envelope
has two layers the encapsulate the nucleus with the inner and outer membranes. The outer touches the Endoplasmic reticulum.
Chromatin
coiled DNA+protein mixed together
holds genetic instructions
Passive transport
require no energy to move substances inside or outside cell.
includes simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and filtration
Active transport
Drives the movement of molecules across the plasma membrane from low to high concentration requiring ATP.
simple diffusion
movement of molecules directly through the lipid bilayer from high to low concentration.
Facilitated diffusion
Moves across the membrane from high to low but through some type of protein channel or carrier.
filtration
fluid is physically forced through membrane that allows water and some solutes to pass
Cell cycle
consists of G1, S phase, G2 phase, Mitotic phase
interphase
consists of G1, S, and G2 phase.
Mitotic phase
includes prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis
G1
cell synthesizes protein and grows in size. It prepares for DNA replication.
S phase
DNA is replicated so each new cell will receive a full set of chromosomes
G2 Phase
Checks the DNA for errors and makes final preparations for mitosis.
Mitotic phase
Cell divides into two new cells
where cell division occurs
Metaphase
DNA condenses into chromosomes, nuclear envelope starts to break down
chromosomes line up in middle of cell
anaphase
chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite sides of cell
telophase
new nuclear envelopes form around each set of chromosomes
cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm into two cell
what occurs after cytokinesis?
enters the G1 phase
Transcription
In the nucleus the cell copies the instructions from the DNA into a message called mRNA.
Translation
Happens in cytoplasm in a ribosome where the ribosome reads the mRNA and puts the amino acids together to make a protein.
organelles responsible for protein production
Nucleus, ribosomes, RER, Golgi apparatus,
different plasma membrane proteins
receptor, channel, gated channel, cell identity marker, enzyme
Gated channel
opens and closes at certain time to allow ions through
channel
channel protein that constantly allows solutes like ions to pass in and out of the cell
cell identity marker
glycoprotein that distinguishes between good and bad cells
Receptor
receives chemical signal from outside cell then binds to a certain molecule to force a response
cellular permeability
how easily substances can pass through the cell membrane
gene
set of instructions in your DNA that tells the cell how to make a protein that performs a specific job in the body.