UWORLD Endocrine, DM, Metabolism Step 2 CK
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Primary tx for all prolactinomas.
Dopaminergic agents (Bromocriptine and Carbergoline)
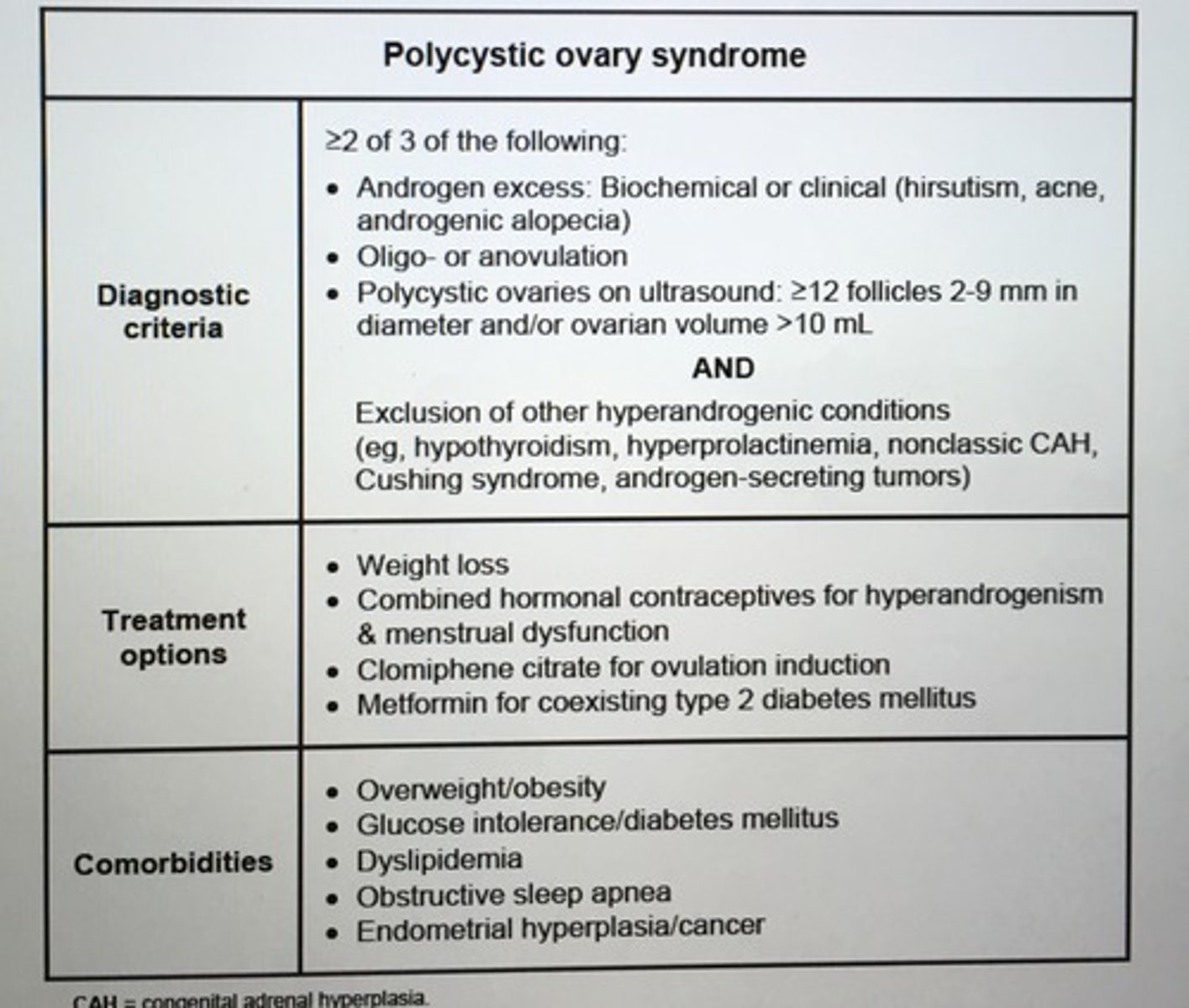
Polycystic ovary syndrome diagnostic criteria.
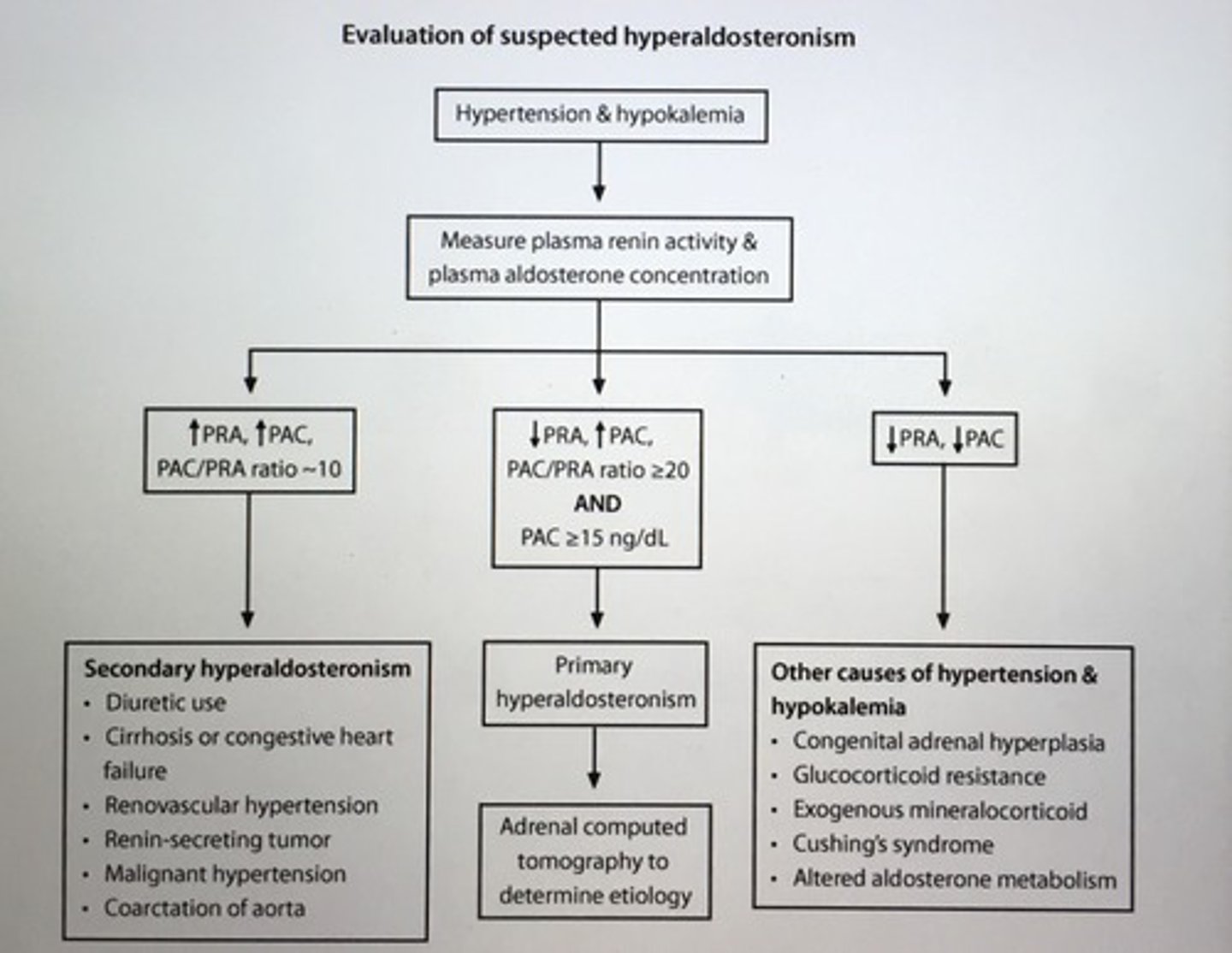
Pts with mild primary hyperaldosteronism may not have spontaneous hypokalemia but they are prone to developing ___ induced hypokalemia.
Diuretic
- early morning plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) to plasma renin (PRA) ratio > 20 with plasma aldosterone > 15 = primary hyperaldosteronism
Evaluation of suspected hyperaldosteronism
Most common side effect of radio iodine therapy.
Hypothyroidism (Common in tx Graves)
- tx with levothyroxine therapy
- pt eye dz may worsen at the beginning of radioiodine therapy give high dose steroids before and after tx to prevent this
Characteristics features of hypopituitarism?
1. Glucocorticoid deficiency (low ACTH, low cortisol) - fatigue, loss of appetite, hypoglycemia, hyponatremia, eosinophilia
2. Testosterone deficiency (low/normal FSH and LH, low T) - low libido, ED
3. Hypothyroidism (low or normal TSH, low free T4) - cold intolerance, constipation, bradycardia
What is required to differentiate follicular cancers from follicular adenomas?
Demonstrate invasion of the capsule and blood vessels
- follicular thyroid cancers invade blood vessels and metastasize to distal organs
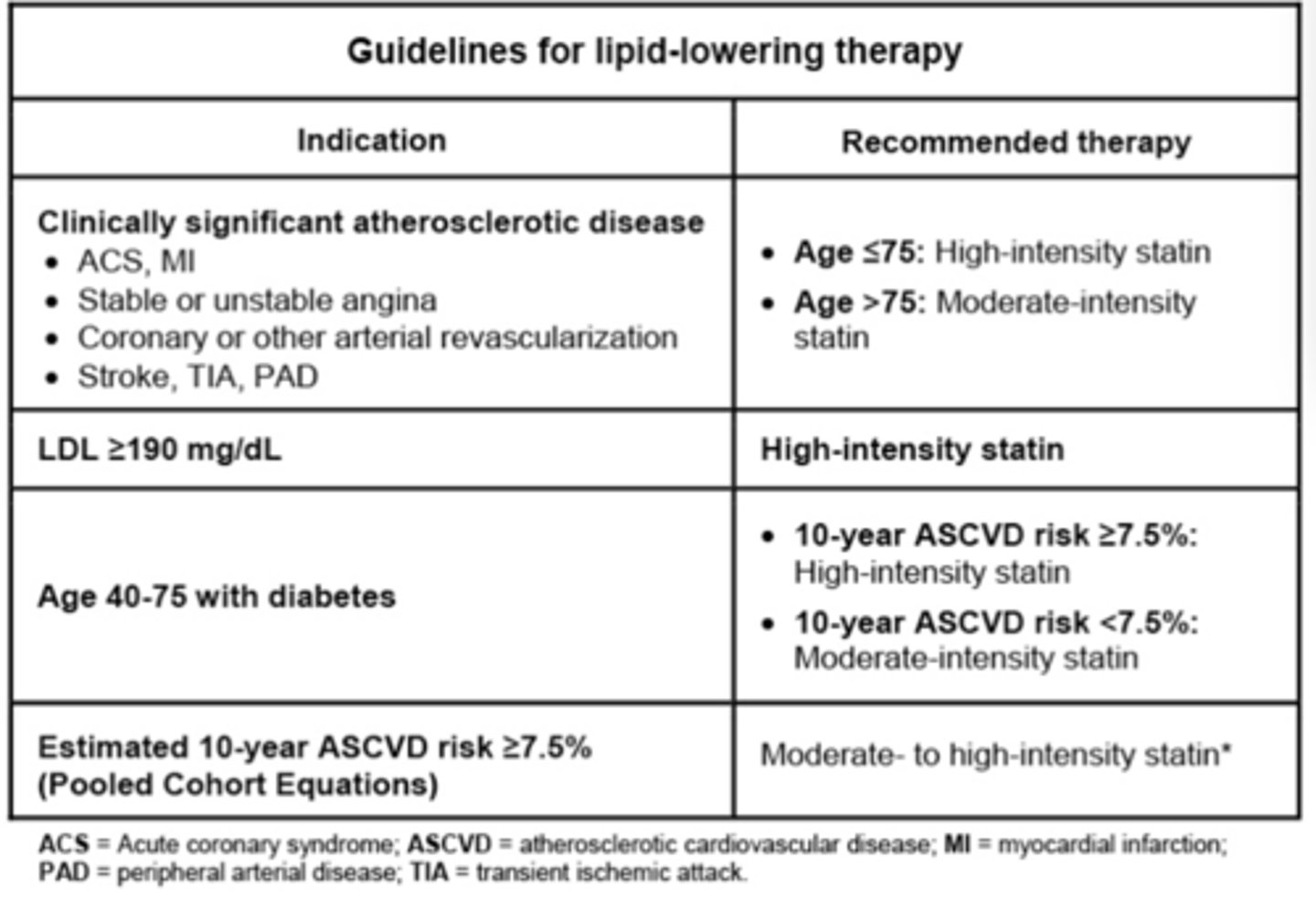
Guidelines for lipid-lowering therapy
When to start tx HTN?
Age > 60: BP > 150/90
Age < 60, CKD, DM BP > 140/90
Diabetic autonomic neuropathy effect on the bladder.
Neurogenic bladder with DEC ability to sense a full bladder, incomplete emptying, urinary retention, and distended bladder
Distended bladder PVR > 50 mL
Develop overflow incontinence (dribbling, poor urinary stream)
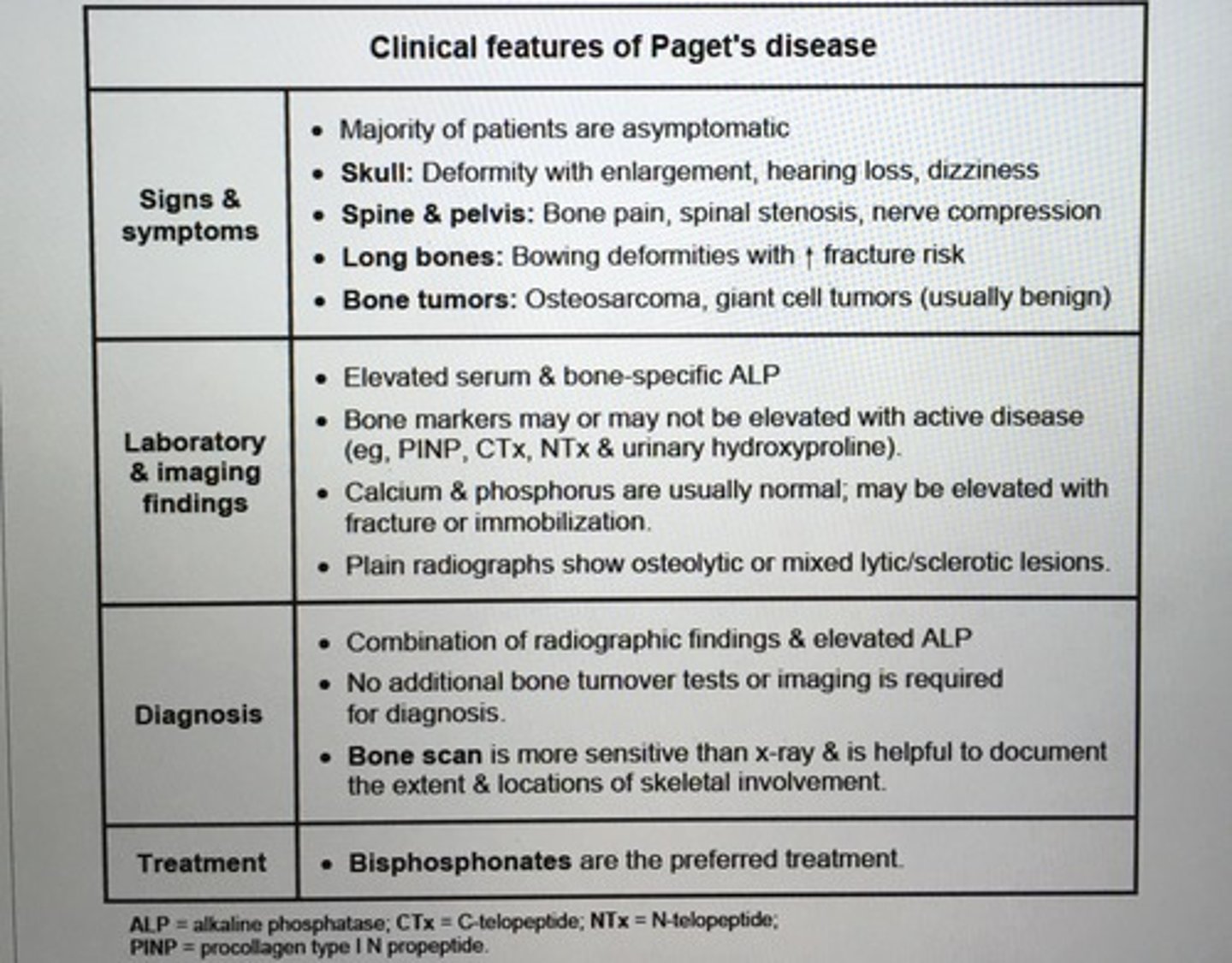
Clinical features of Paget's disease
MEN 2 A disorders.
Medullary thyroid cancer
Pheochromocytoma
Parathyroid tumors
RET
MEN 2B disorders.
Medullary thyroid cancer
Pheochromocytoma
Marfanoid habitus
Mucosal neuromas (tongue, GI trac)
-> kyphoscioliosis, lordosis
RET
MEN1 disorders.
Pancreatic islet cell tumor
Parathyroid tumors
Pituitary adenomas
MEN1 tumor suppressor gene
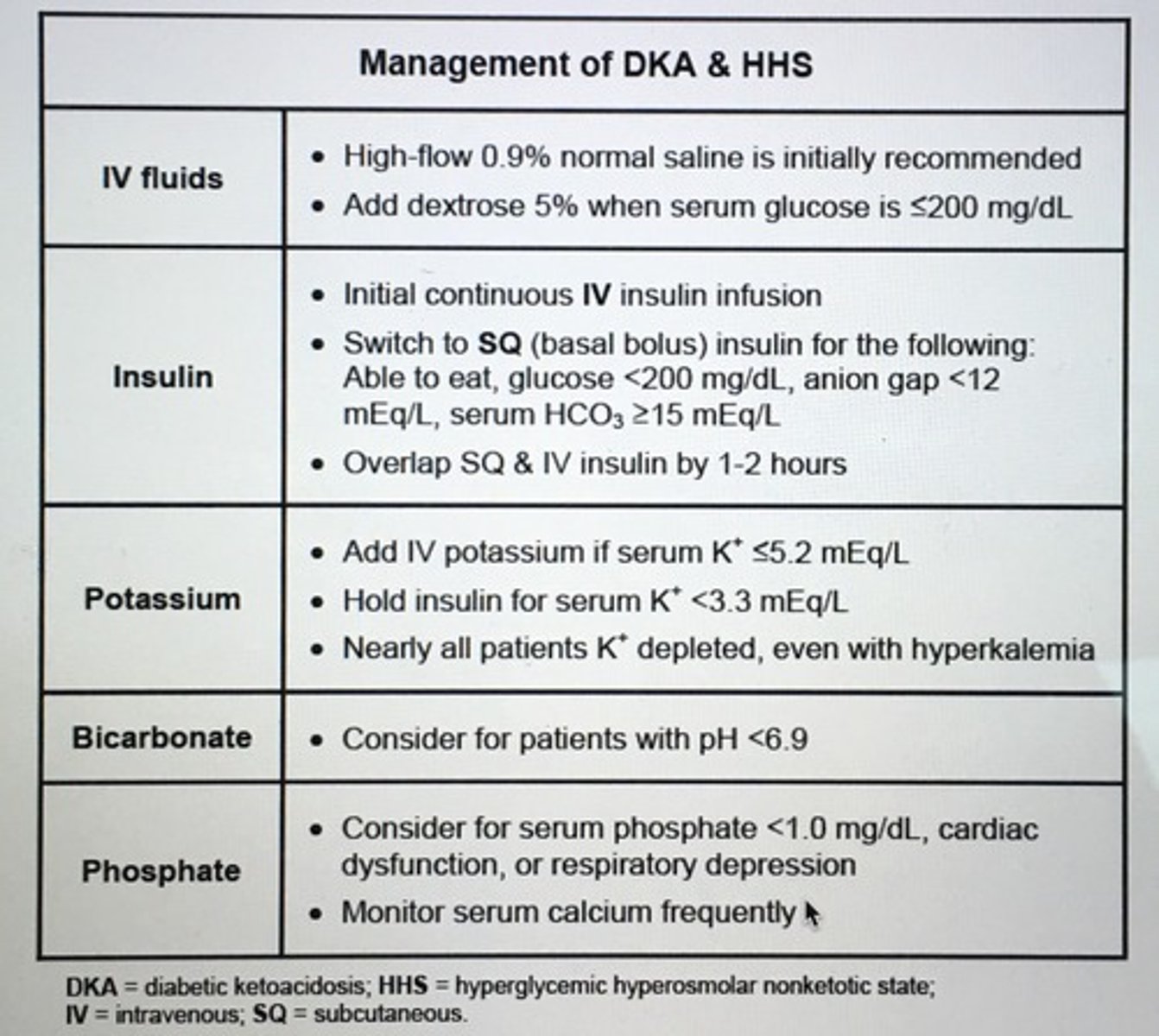
Dx DKA 3 things are necessary.
Blood glucose > 250
pH < 7.3 or serum bicarb < 15-20
Detection plasma ketones
Tx DKA
1. Restore volume : 0.9% saline (NS)
2. Correct hyperglycemia: IV regular insulin
3. Correct electrolytes: K+ correction
4. Tx ppt factors such as infection: Abx
Metabolic syndrome diagnosed when at least 3 of the following 5 criteria are met:
1. Abd obesity (M waist > 40 in, W waist > 35)
2. Fasting glucose > 100-110
3. BP > 130/80
4. Triglycerides > 150
5. HDL (M<40, W < 50)
ADA recommends screening all pts age > ___ as well as those with additional risk factors (BMI > 25, high risk ethnicity, first degree relative diabetes, hx gestational diabetes, dyslipidemia, HTN, etc.)
> 45 years
- screening fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test, hemoglobin A1c
Hypothyroidism can cause additional metabolic abnormalities such as?
Hyperlipidemia
Hyponatremia
Asx elevations of CK and serum transaminases
Causes of primary adrenal insufficiency.
TB
Fungal infections
CMV infections
Autoimmune adrenalitis
Adrenal ___ typical feature of adrenal TB.
Calcification
In Asx patients, single elevated serum calcium must be confirmed by a second serum calcium level. What is the next lab to order?
After hypercalcemia has been confirmed, get a serum PTH level to distinguish between PTH mediated and non-PTH mediated hypercalcemia
The best screening test for virilizing neoplasm is the measurement of?
Serum testosterone and DHEAS levels
INC testosterone, normal DHEAS = ovarian source
Normal testosterone, INC DHEAS = adrenal
Tx diabetic gastroparesis.
prokinetic agent
- Metoclopramide
- Erythromycin
- Cisapride
Central DI typically has > __ INC in urine osmolality with desmopressin.
> 50% sometimes 200-400%
Tx SIADH
Demeclocyline
Fluid restriction
Tolvaptan
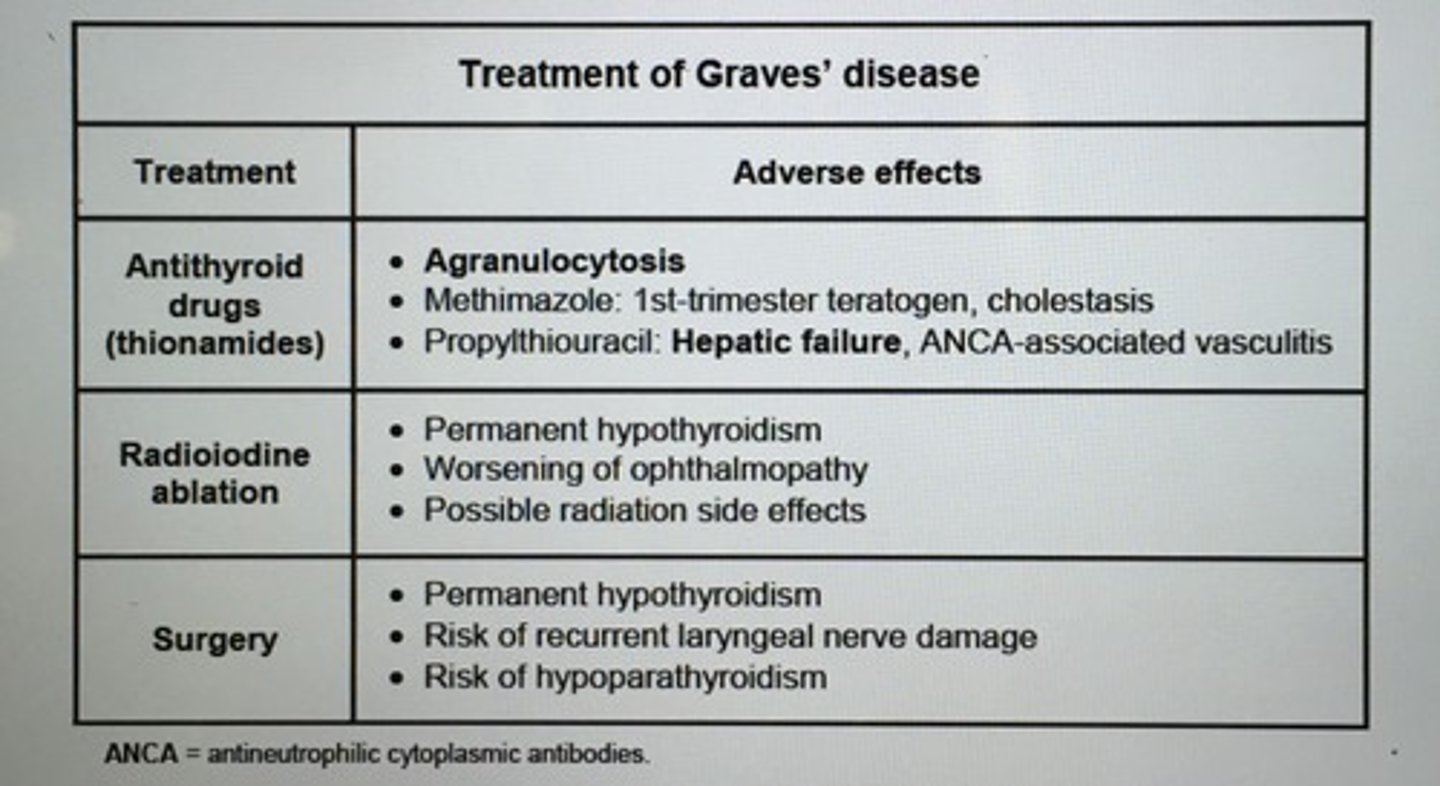
SE Methimazole
Agranulocytosis - pt develop sore throat and fever should stop drug check CBC
1st trimester teratogen
Cholestasis
PTU SE
Agranulocytosis
Hepatic failure (severe liver inj)
ANCA-associated vasculitis
- preferred over Methimazole in first trimester
PTH levels suppressed < 20, calcium > 13 mg/dL what is the cause of elevated calcium.
Hypercalcemia of malignancy
- osteolytic metastasis, INC PTHrP
The ___ helps differentiate psychogenic from organic cause of male ED.
Nocturnal penile tumescence
Pt presents with hypothyroidism despite having elevated circulating thyroid hormone levels. Dx.
Generalized resistance to thyroid hormones
- high serum T4 and T3
- normal mildly elevated TSH
- receptor defect on peripheral tissues
- usually presents younger age with growth and mental retardation, milder defects can present later in life
Mildly elevated TSH levels and normal circulating thyroid hormone levels.
Subclinical hypothyroidism
Pt presents with fever and sore throat after using antithyroid drugs (PTU/methimazole) next step?
STOP drug
- WBC count check
- WBC count < 1,000/cubic mm permanent D/C of the drug
- total WBC > 1500 antithyroid drug less likely cause sore throat
*drugs can cause life threatening agranulocytosis (do not routinely check granulocyte count since not cost effective)
RF for diabetic foot ulcers?
Diabetic neuropathy
Previous foot ulcerations
Vascular disease
Foot deformity
*monofilament testing predicts the risk of future ulcers
Dx: Fever (104-106), tachy, HTN, CHF, arrhythmia (a.fib), agitation, delirium, lid lag, tremor, N/V, seizure, coma that is ppt by trauma, infection, childbirth.
Thyroid storm
- thyroid/non-thyroid sx
- acute iodine load (iodine contrast)
Tx Thyroid storm
1. BB (propranolol) to DEC adrenergic manifestations
2. PTU followed by iodine solution (SSKI) to DEC hormone synthesis and release
3. Glucocorticoids (hydrocostisone) to DEC peripheral T4 to T3 conversion and improve vasomotor stability
4. ID trigger and treat, supportive case
Type 2 DM patient presents with altered mental status, volume depletion, polyuria is consistent with dx of?
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)
- nonketotic hyperosmolar syndrome and hyperglycemic, hyperosmolar coma
*thiazide diuretics can ppt HHS by reducing intravascular volume, DEC GFR and activates counter-reg hormones, DEC renal glucose excretion
Dx: glucose > 600, plasma osmolality > 320, absent ketonemia
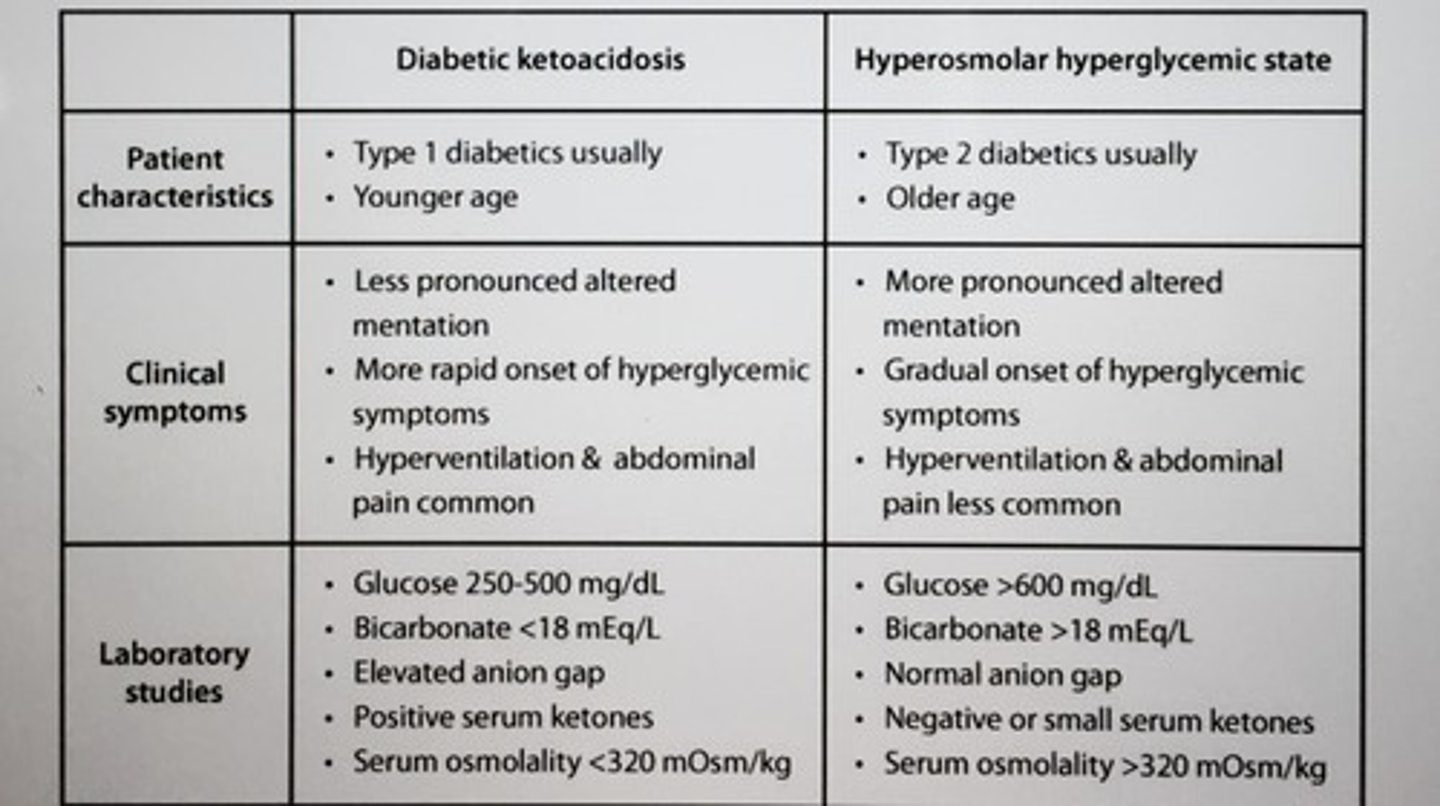
INC extracellular pH (respiratory alkalosis) has what binding effect on calcium?
Dissociation of hydrogen ions from albumin, INC binding Ca2+ and drop in unbound (ionized) calcium
Ionized calcium is the active form, DEC levels leads to clinical signs of hypocalcemia
___ of the pituitary is indicated in pts with elevated serum prolactin, serum testosterone < 150, visual field defects, or features of other pituitary hormone dysfunction.
MRI
Which tx for Graves disease can worsen Graves ophthalmopathy?
Radioactive iodine (RAI)
___ acne is characterized by monomorphous pink papules and absence of comedones.
Steroid acne (systemic or topical)
- face, trunk, extremities
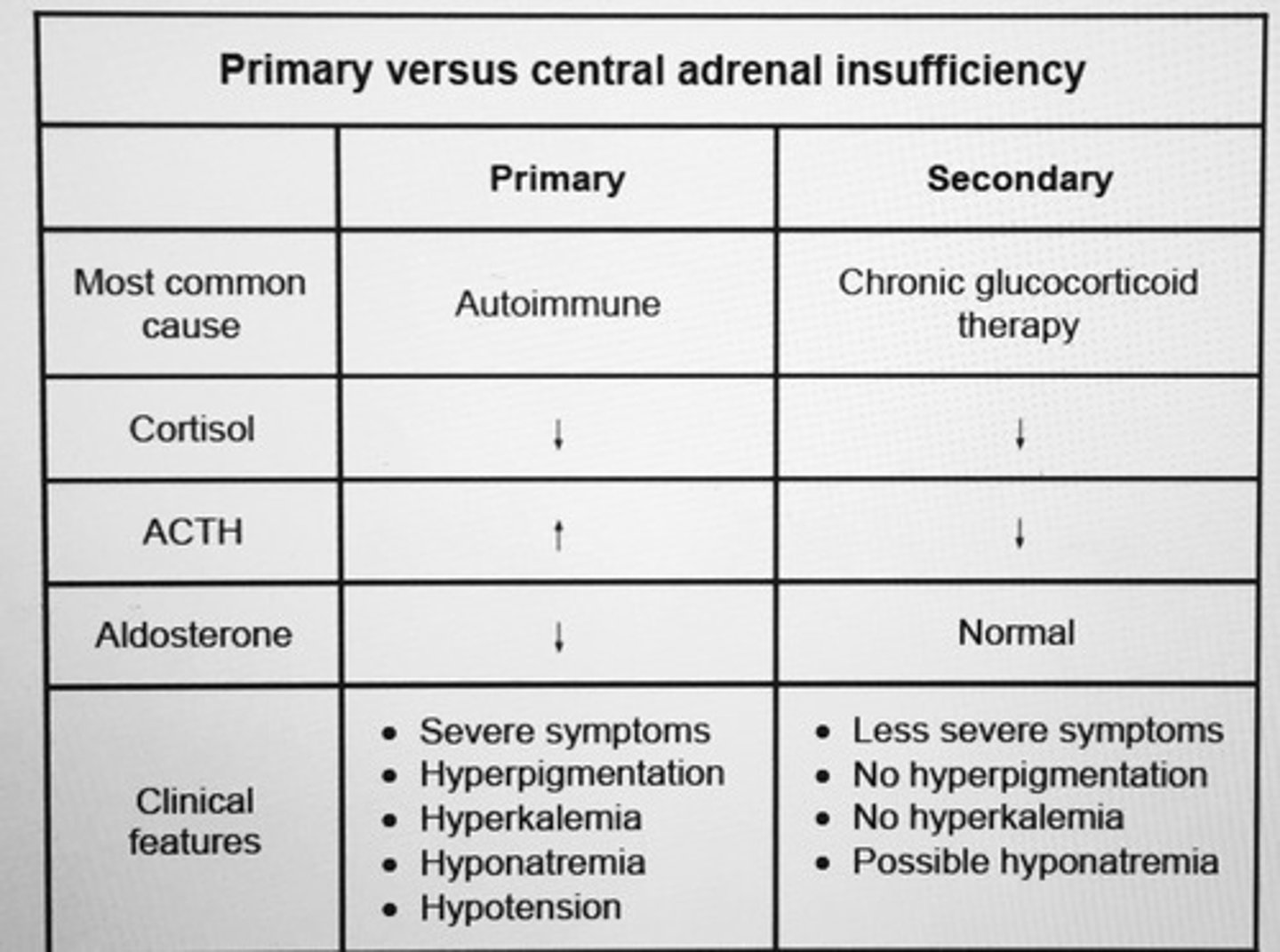
Primary versus secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Hyperpigmentation and signs of mineralocorticoid deficiency suggest primary rather than secondary AI
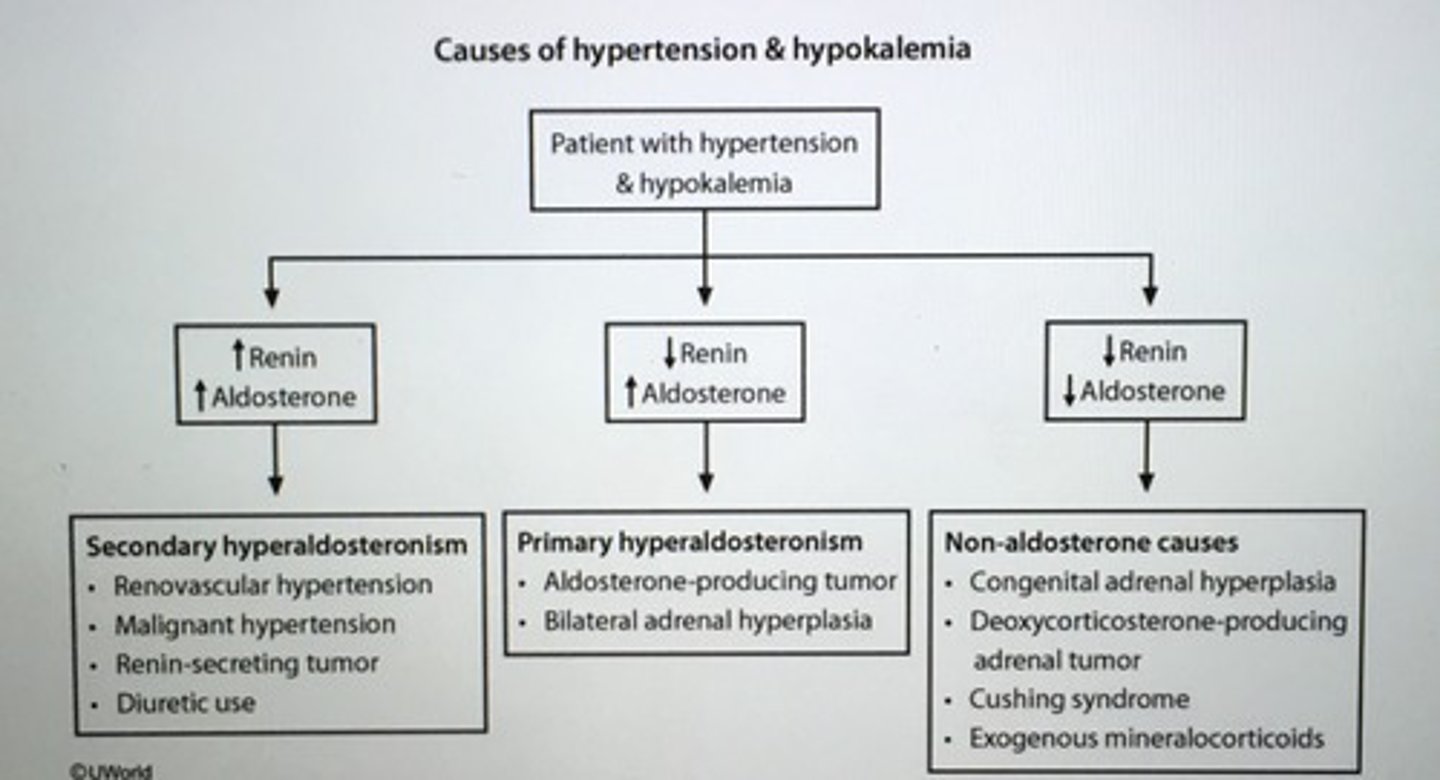
Suspect the following conditions whenever a patient presents with hypokalemia, alkalosis, and normotension.
1. Surreptitious vomiting
2. Diuretic abuse
3. Bartter syndrome
4. Gittelman's syndrome
___ causes HTN, mild hypernatremia, hypokalemia, and metabolic alkalosis.
Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn's syndrome)
- low renin and INC aldosterone
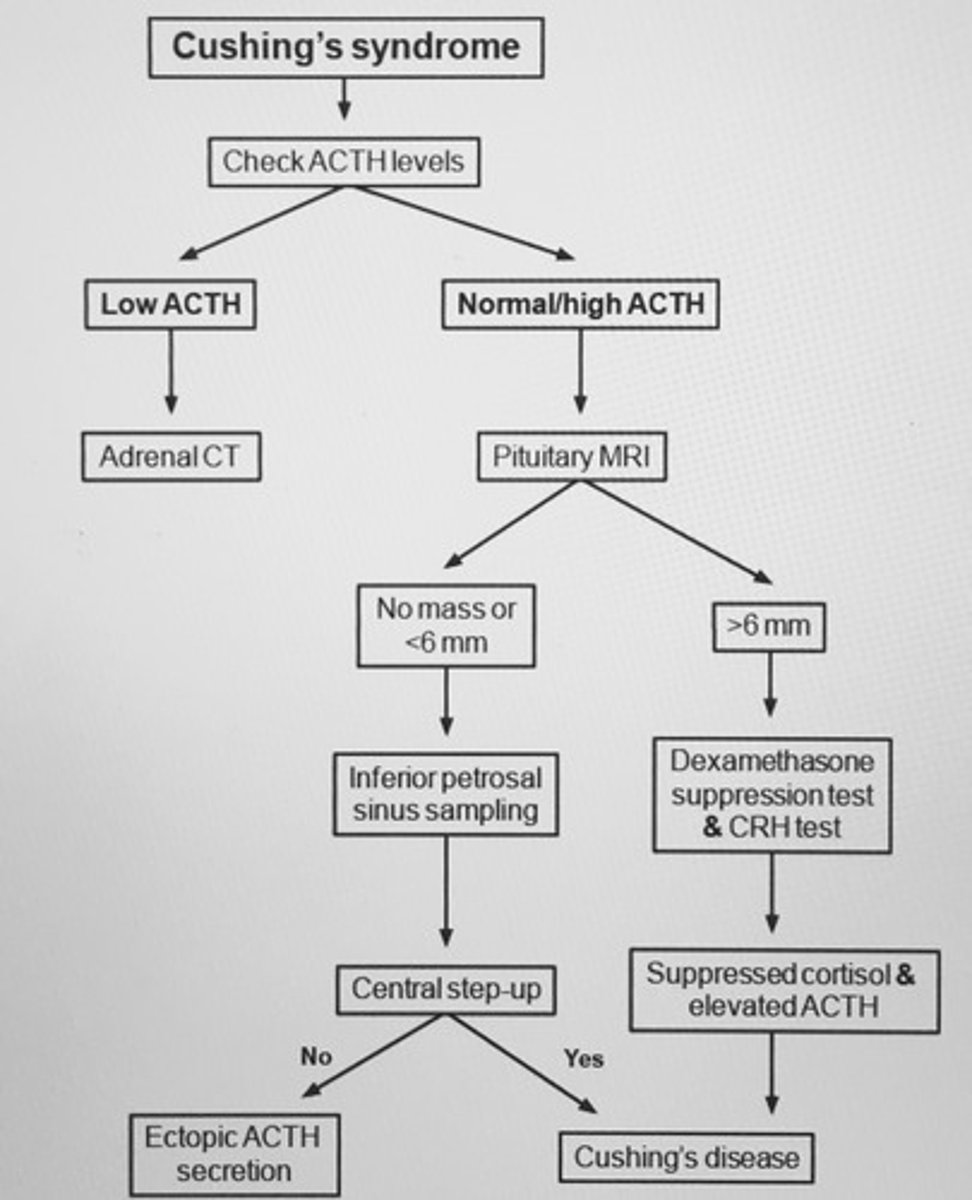
Cushing's syndrome flowchart
Cushing's syndrome: HTN, metabolic alkalosis, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, proximal muscle weakness
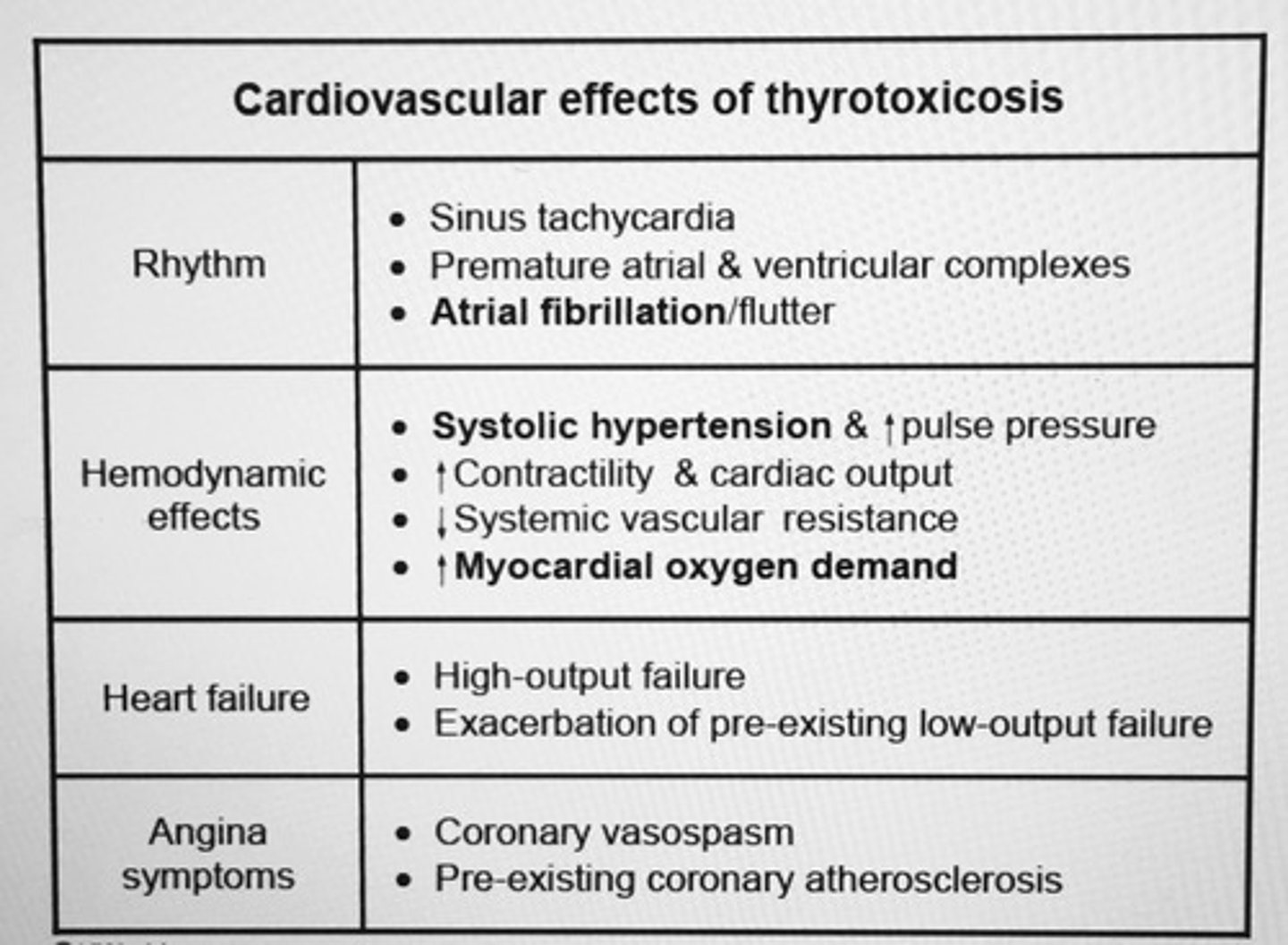
What causes systolic HTN in thyrotoxicosis?
Hyperdynamic circulation resulting from INC myocardial contractility and HR
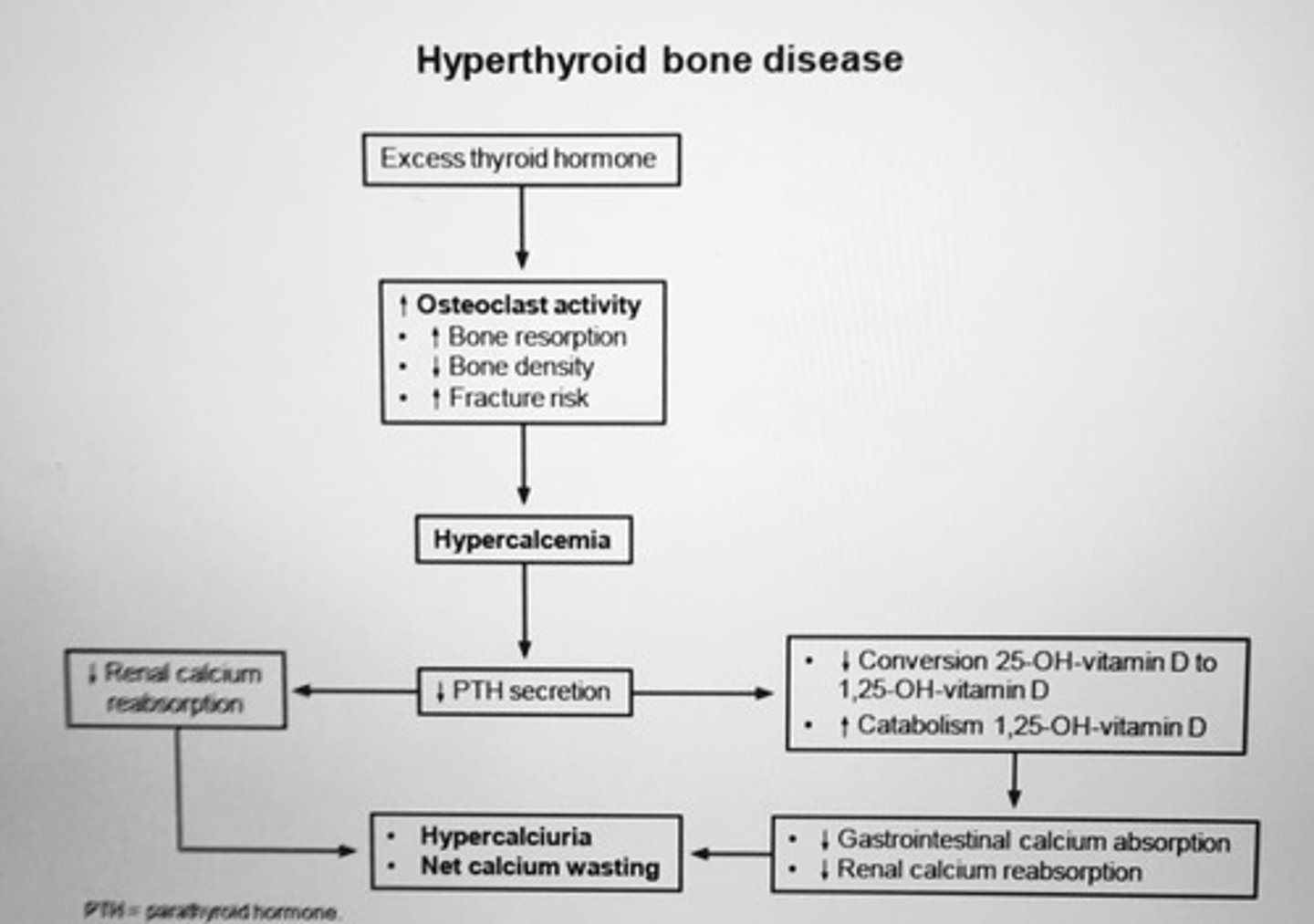
Untreated hyperthyroid patients are at the highest risk for?
Rapid bone loss from INC osteoclastic activity in the bone cells
- also INC risk arrhythmias such as a. fib
Most important causes of thyrotoxicosis with low radioactive iodine uptake include?
1. Subacute painless thyroiditis
2. Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis
3. Iodine-induced thyroid toxicosis
4. Levothyroxine overdose
5. Struma ovarii
Chronic GI disease (steatorrhea, celiac disease) can lead to what changes in Ca+, Phosphorus, and PTH?
vitamin D deficiency -> malabsorption
HYPOcalcemia
Low phosphorus
Elevated PTH
Pt can be asx or have bone pain/tenderness, muscle weakness or cramps, and gait abnormalities due to ostemalacia
Main substates for gluconeogenesis are?
1. Gluconeogenic amino acids (alanine, breakdown of muscle protein)
2. Lactate (anaerobic glycolysis)
3. Glycerol-3-phosphate (triacylglycerol in adipose)
Elevated serum ___ are specifically seen in patient with androgen producing adrenal tumors.
DHEA-S (dehydroepiandrosteron-sulfate)
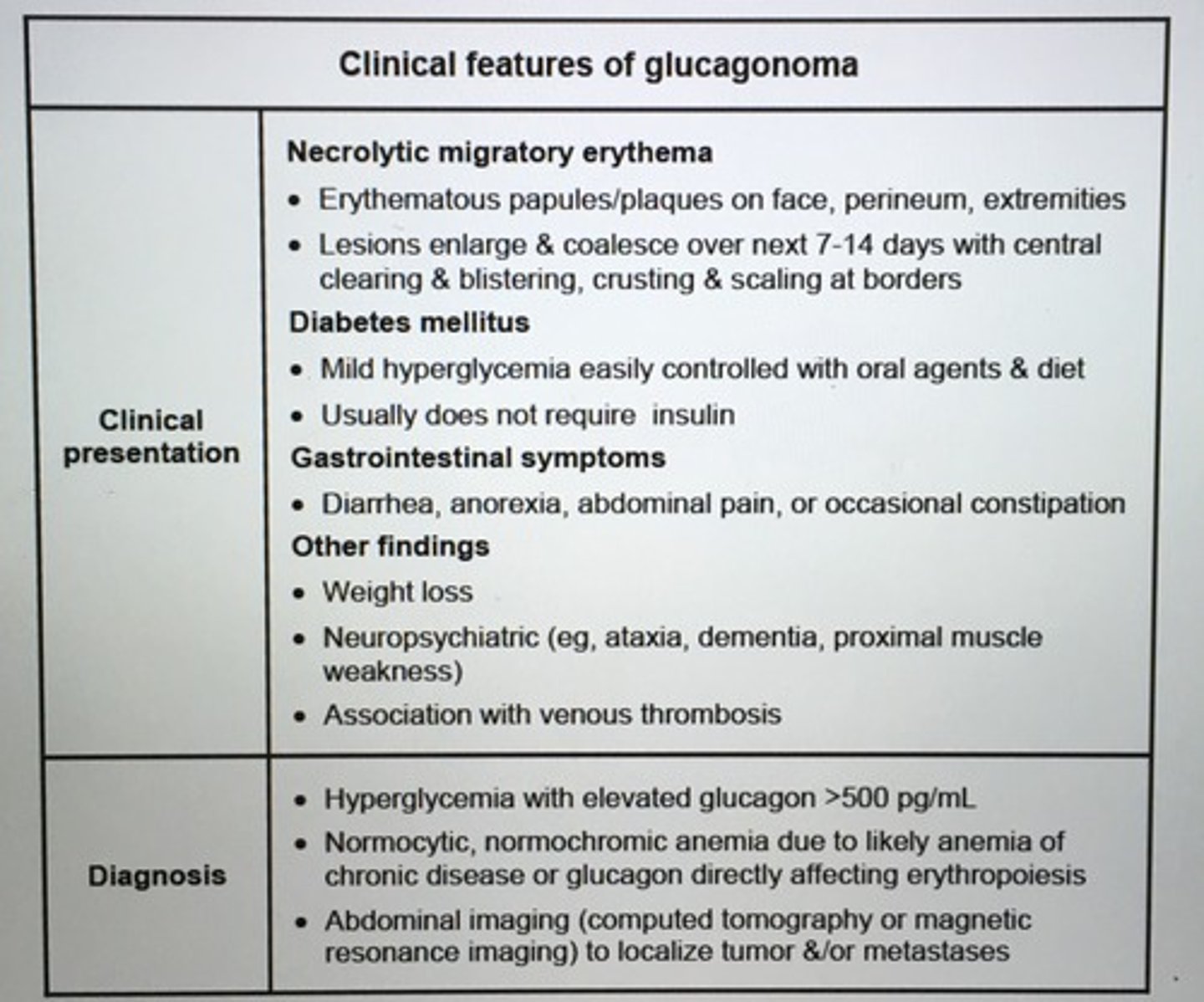
Clinical features of glucagonoma
Corrected calcium calculation?
= (Measured total calcium) + 0.8 (4.0 g/dL - serum albumin in g/dL)
The serum calcium concentration DEC by 0.8 for every 1 g/dL decrease in serum albumin
Patients with hypoalbuminemia can have DEC total serum ___. However, ionized ___ (physiologically active form) is hormonally regulated and remains stable.
Calcium
Clinical dx primary hyperaldosteronism.
Plasma aldosterone: renin ration > 20
Adrenal suppression testing after oral saline load confirms dx
Abd imaging (CT) & adrenal venous sampling to distinguish btw Uni adrenal adenoma and B/L adrenal hyperplasia
Tx primary hyperaldosteronism.
1. Unilateral adrenal adenoma
- Sx (preferred)
- Aldosterone antagonists (spironolactone, eplerenone) for poor sx candidates or for pts refusing sx
2. B/L adrenal hyperplasia
- aldosterone antagonists
The most common cause of death in patients with acromegaly is ___.
CV
Non-cardiac causes of death in pts with acromegaly.
1. Strokes
2. Colon cancer
3. Renal failure: HTN and hyperglycemia via IGF-I
4. Adrenal failure
___ is the most common thyroid malignancy.
Papillary carcinoma
- RF: exposure to radiation during childhood and family history
- best prognosis of the thyroid cancers
- met to local lymph nodes
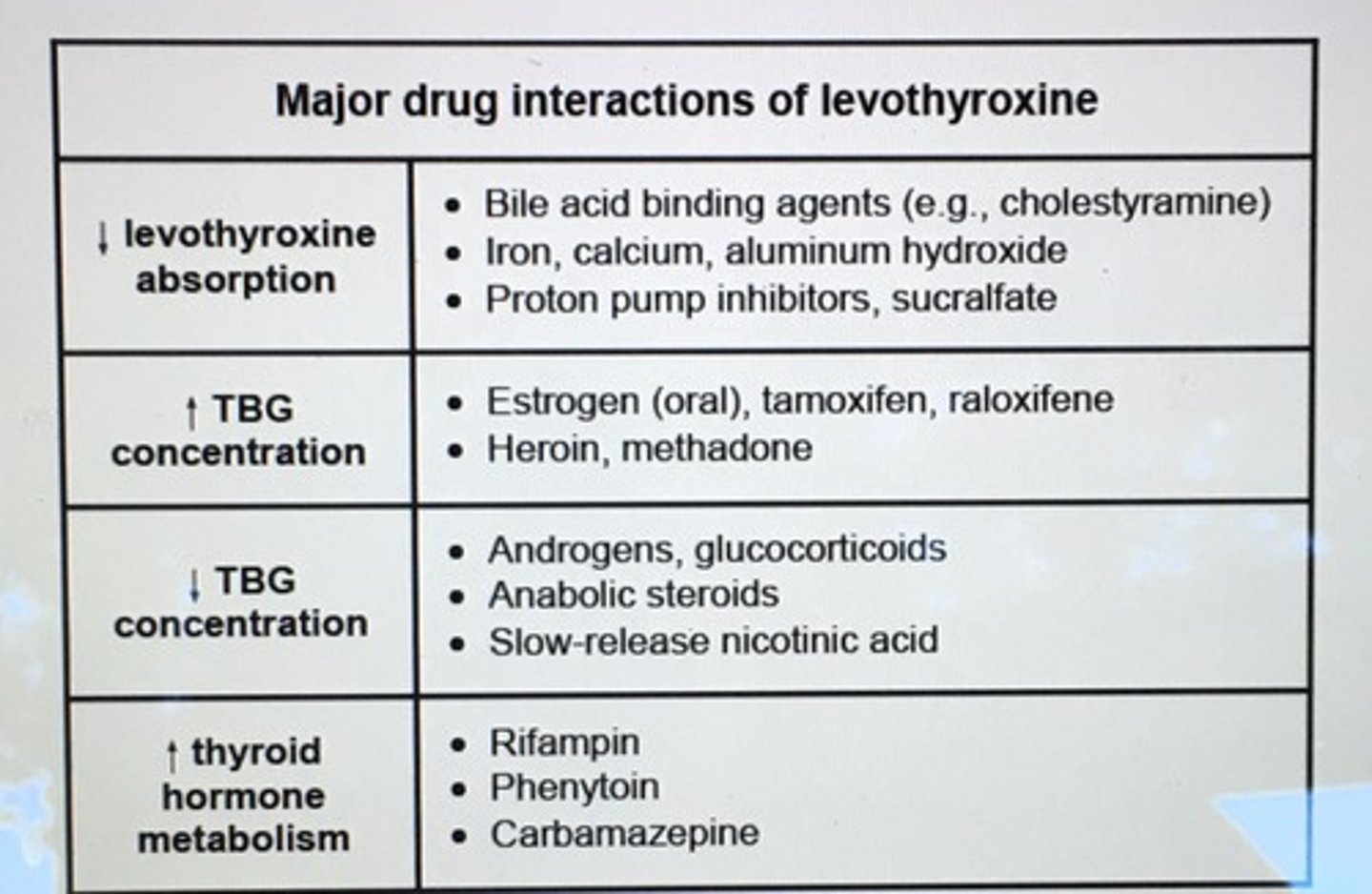
Oral estrogen preps INC levels of ____ which requires an INC in higher dose of thyroid hormone to saturate the INC number of __ binding sites.
thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)
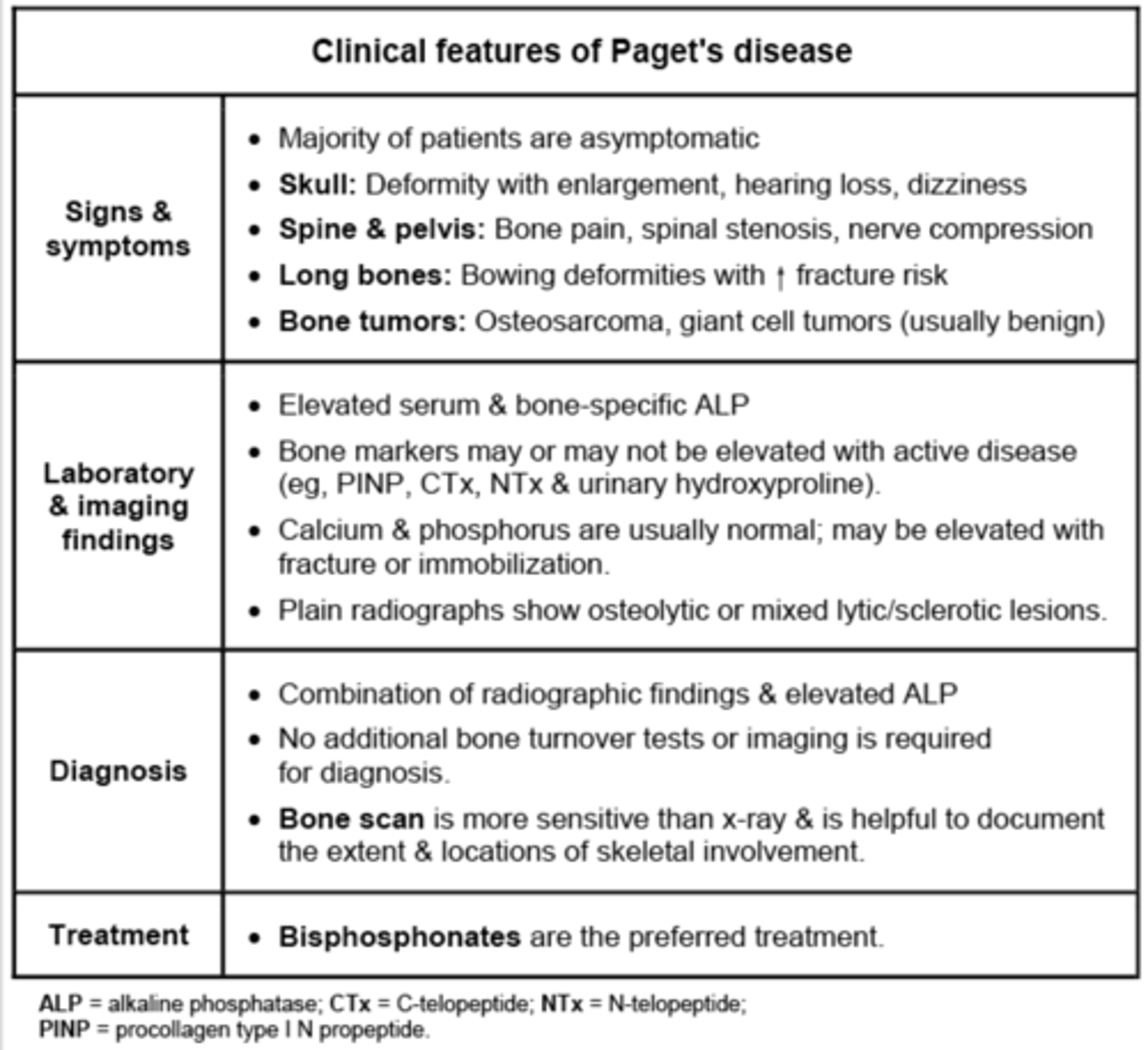
Pt has elevated alkaline phosphatase with normal calcium, phosphorus, and other liver enzymes. Has headaches, deafness, neuropathy, or bone/back pain. Dx.
Paget disease of bone
- INC bone remodeling and abnormal osteoid formation
Contraindications of radioactive iodine tx for Grave's?
Pregnancy
Very severe ophthalmopathy
* Radioactive iodine therapy is the preferred tx for Grave's disease
The most beneficial therapy to reduce the progression of diabetic nephropathy is?
Strict BP control
- pts with diabetic nephropathy should be tx toward a target BP of 130/80
Giving a BB before giving an alpha-blocker can result in a rapid INC in ___ in a patient with pheochromocytoma.
INC BP
- BB leads to an unopposed stimulation of vascular alpha-receptors by circulating catecholamines, rapid INC in BP (labetolol is safe has both alpha and beta blocking activity)
Proximal muscle weakness with or w/o muscle atrophy can occur in 60-80% of patient with untreated ___.
Hyperthyroidism
- correlates with duration of hyperthyroid state
- hip flexors and quads are affected
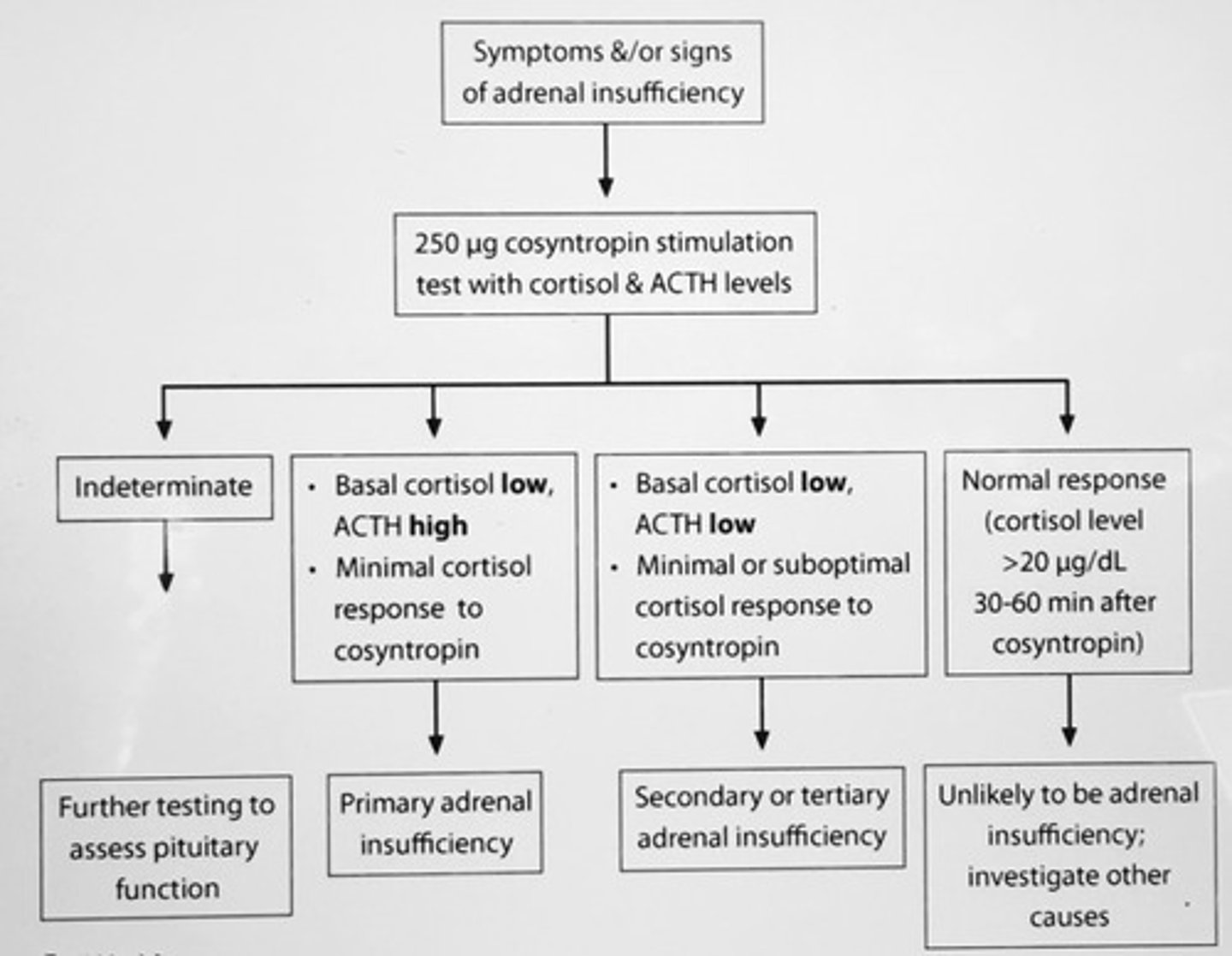
The best initial tests for patients with suspected adrenal insufficiency are?
Early-morning cortisol, ACTH, and cosyntropin (ACTH) stimulation
INC serum cortisol level > 20 (30-60 min) after administration of 150 cosyntropin r/o primary adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison's disease)
Six-interventions that have been shown to be useful in the management of diabetic foot ulcer.
1. Off-loading
2. Debridement - grade 1 or 2
3. Wound dressings - grade 1 or 2
4. Antibiotics - grade 3 ulcer (deep with cellulitis)
5. Revascularization
6. Amputation - gangrene stage 4/5 ulcer
Dx Phenochromocytoma
24 hour urine metanephrines and free catecholamines or plasma free metanephrines
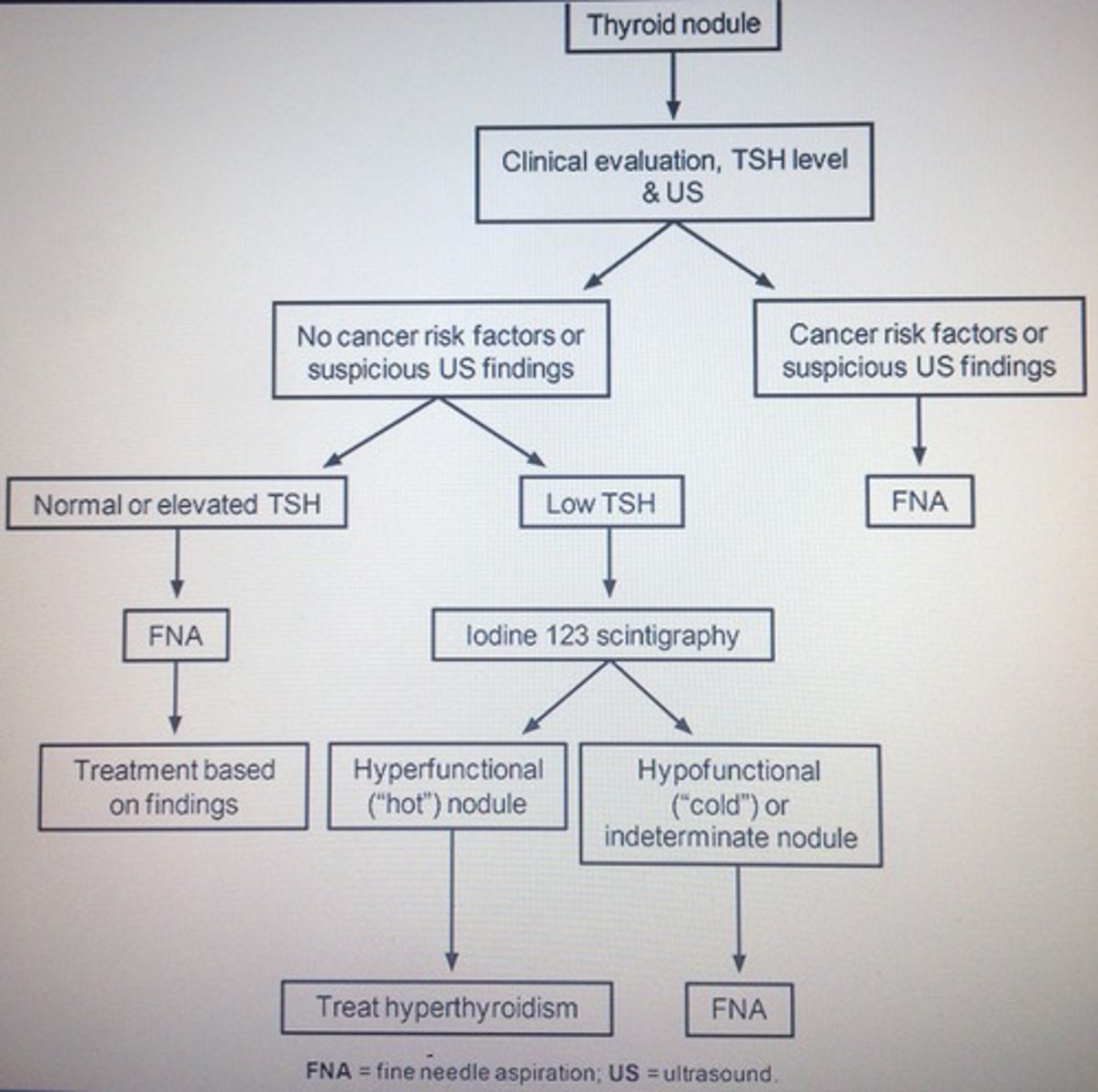
Thyroid nodule algorithm
Preferred Initial screening test primary hyperaldosteronism (HTN, hypokalemia)
ratio of plasma:renin >20
Evaluation of hyperthyroidism
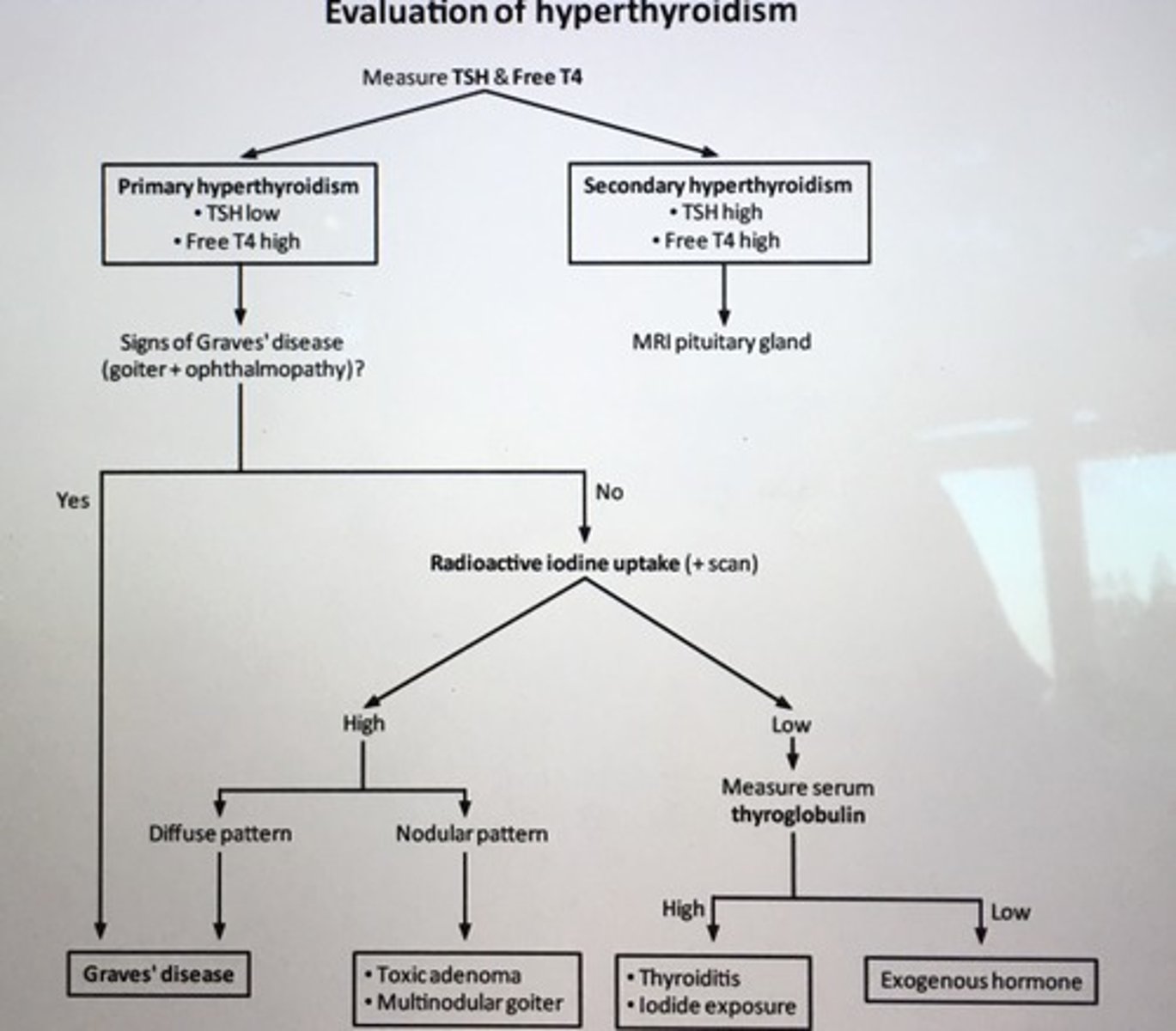
Thyrotoxicosis due to exogenous thyroid hormone is characterized by low ___.
Low serum thyroglobulin levels
Immobilization of an individual with high bone turn over results in increased osteoclastic activation that can lead to ___.
Hypercalcemia
- bisphosphonate therapy in immobilized pts is helpful in reducing hypercalcemia and preventing osteopenia and hydration
The best markers indicating resolution of DKA are the ___ and ___ levels.
Serum anion gap and beta-hydroxybutyrate (measured by nitropursside test)
Radioactive iodine uptake in a nodule, TSH undetectable, T3 and T4 elevated. Thyroid has 2x2 cm left-sided thyroid nodule. Dx.
Toxic adenoma
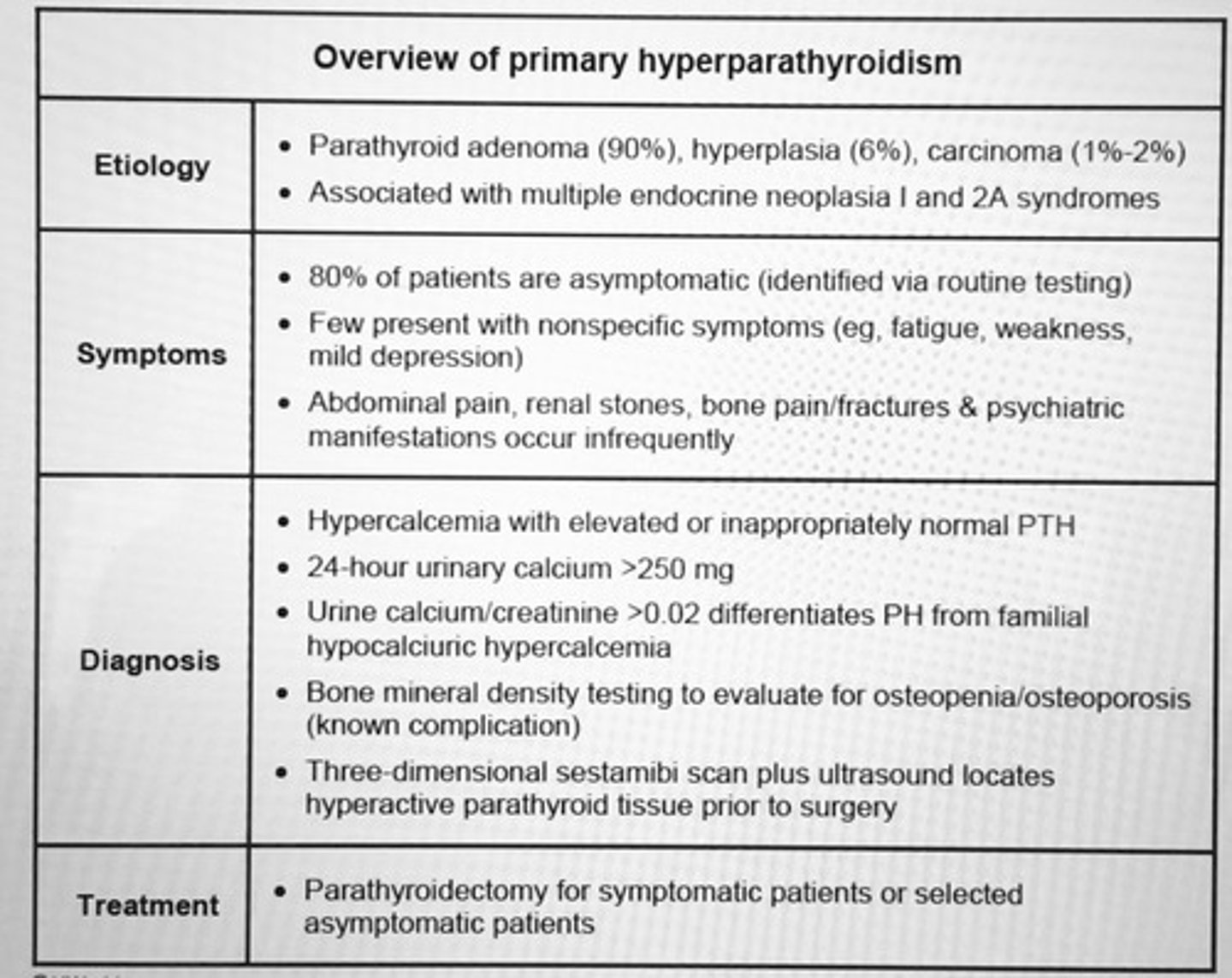
Parathyroidectomy for primary hyperparathyroidism is recommended for patients who have any of the following clinical features?
1. Serum calcium level > 1 mg/dL above the upper limit of normal
2. Young age < 50
3. Bone mineral density T-score <-2.5 at any site
4. Reduced renal function (eGFR<60)
Patient has decreased Calcium and elevated PTH. Dx.
Vitamin D deficiency
CKD
Diagnostic approach to hypocalcemia
1. Low corrected serum calcium level confirm via repeat testing
2. Low magnesium level? Due to a drug (calcium chelators, bisphosphonates, phenytoin) ? Recent blood transfusion (INC citrate, volume)?
3. Measure PTH
Elevated PTH causes with low calcium?
Endocrine
- vitamin D deficiency
- CKD
Inflammatory
- Pancreatitis
- Sepsis
Oncology
- tumor lysis
Normal or low PTH with low calcium causes?
Surgical
- parathyroidectomy
- thyroidectomy
- radical neck surgery
Autoimmune
- polyglandular autoimmune syndrome
Infiltrative disease
- Metastatic cancer
- Wilson's disease
- Hemochromatosis
The main causes of paradoxical hyperkalemia.
1. Extracellular shift of K+ in exchange to hydrogen with resultant intracellular K+ deficit
2. Impaired insulin-dependent cell entry of the K+ ion
* replace K+ if below 4.5
Patient with abdominal pain, constipation, polydipsia has features of hypercalcemia that can be due to excess ___ intake.
vitamin D
- INC GI absorption of calcium when taking >4000 U daily
Despite normal or elevated serum K+ level patient with HHS or DKA have a total body potassium __ due to excessive urinary loss caused by glycosuria-induced osmotic __.
K+ deficit
Osmotic diuresis
*aggressive insulin therapy for HHS can lower serum K+ level further and cause hypokalemia
In the management of pts with hyperthyroidism, ___ generally used for symptomatic relief until the underlying cause is ID and definitively treated.
Propranolol
Labs/imaging prolactinoma.
1. Serum prolactin > 200
2. R/o renal insufficiency (creatinine) and hypothyroidism (TSH, thyroxine)
3. MRI of the brain/pituitary
___ most common type of testicular sex cord stromal tumors principal source of testosterone and are capable of estrogen production, INC aromatase expression.
Leydig cell tumors
- inhibition of LH and FSH
- symptoms of gynecomastia, precocious puberty
Patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis are INC risk of developing thyroid ___.
Lymphoma
Which antibodies are presents in more than 90% of patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
Anti-TPO (anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies) and anti-thyroglobulin antibodies
Any patient with an acute, severe illness many have abnormal thyroid function test. This is called?
Euthyroid sick syndrome ("low T3 syndrome") is characterized by fall in total and free T3 levels with normal T4 and TSH levels
Watery diarrhea, muscle weakness/cramps (due to hypokalemia), hypo-or achlorhydria with a mass on the pancreatic tail. Dx.
VIPoma
- affecting the pancreatic cells that product VIP => met to liver
- pancreatic cholera
- stool studies: secretory diarrhea, VIP levels > 75 confirms VIPoma dx
Tx VIPoma
IV volume repletion
Ocreotide to DEC diarrhea
Hepatic resection in pts with met. to liver
Patients with positive DNA testing shoulder undergo ___ in early childhood as the risk of acquiring MTC is nearly 100% with RET photo-oncogene in MEN2A and 2B.
total thyroidectomy
Current tx options for diabetic neuropathy?
1. TCAs (amitriptyline, desipramine, nortriptyline) - can worsen urinary symptoms (due to cystopathy) and orthostatic hypotension (CV autonomic neuropathy)
2. Gabapentin
3. NSAIDs
Current guidelines recommend initial ___ in type 2 DM w/o contradictions. Patient with suboptimal control with this drug require a second drug such as?
Metformin contraindications (renal insufficiency)
Suboptimal control second drug Sulfonylurea (can cause wt gain, hypoglycemia) or GLP-1 (cause wt loss, lower incidence hypoglycemia, pancreatitis)
GLP-1 (eventide, liraglutide)
___ is the preferred screening test for acromegaly.
Insulin-like growth factor - 1 (IGF-1)
measurement of non-suppressible GH levels following an oral glucose load is more sensitive dynamic test for acromegaly perform after IGF-1
Chronic glucocorticoid therapy effect on ACTH, cortisol, and aldosterone.
Secondary Adrenal insufficiency:
ACTH, cortisol DEC
Aldosterone normal
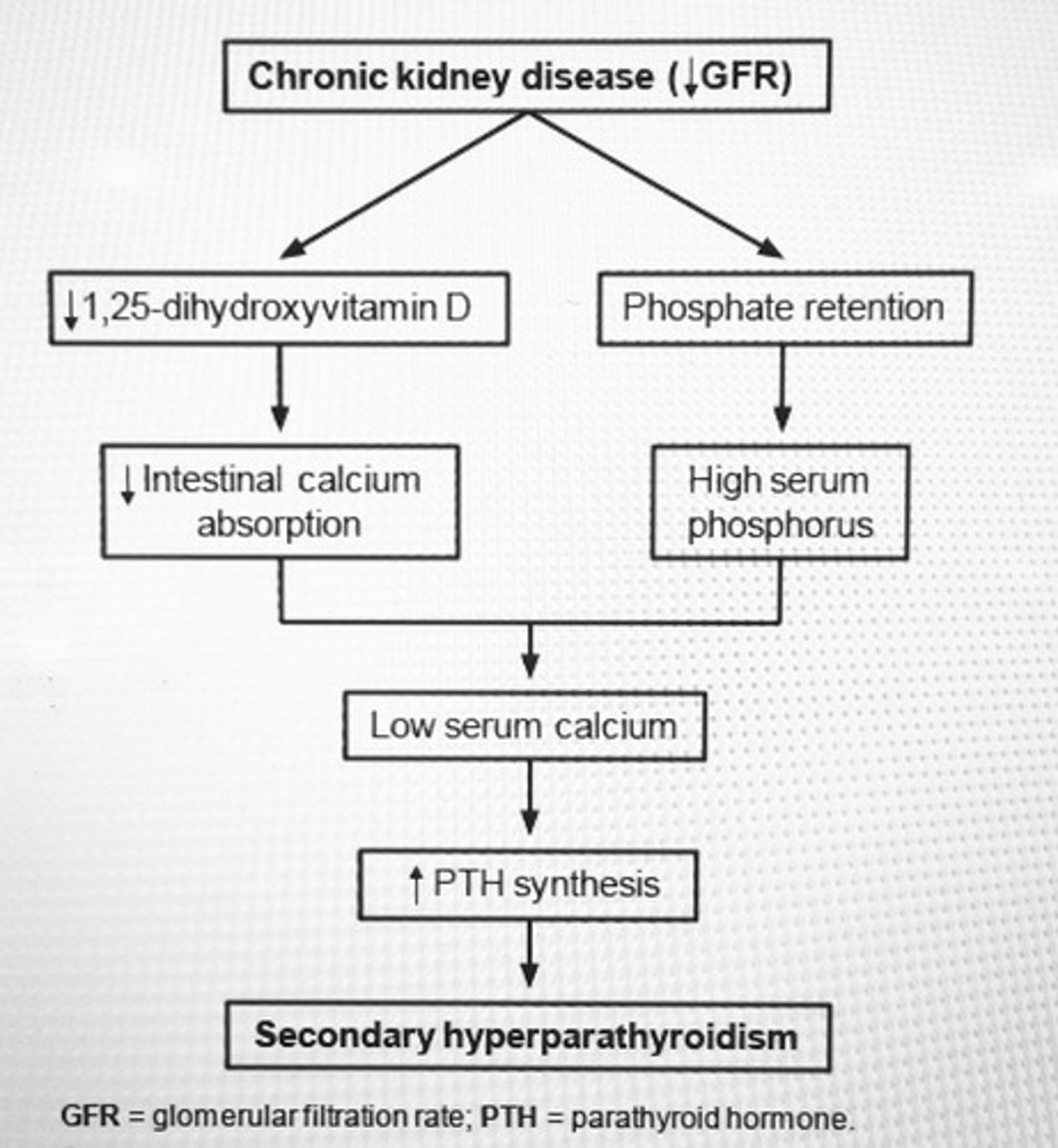
Hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and INC PTH are characteristic biochemical abhormalities of secondary hyperparathyroidism in ___.
Chronic renal failure
Proptosis in Grave's opthalmopathy results from INC ___.
Volume of retro-orbital tissues (connective, muscular, and adipose tissue explosion; lymphocyte infiltration) and is direct result of anti-thyrotropin receptor autoantibodies)
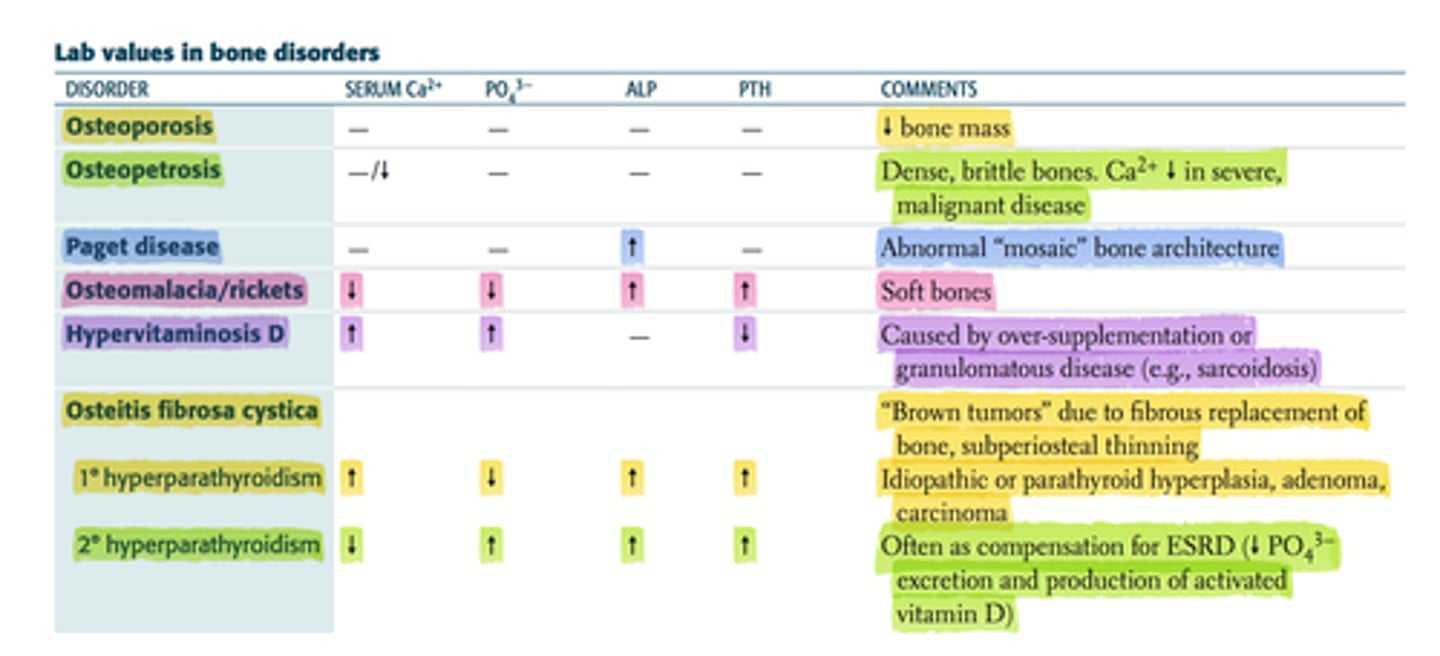
Osteomalacia due to defective mineralization of the organic bone matrix due to vitamin D deficiency leads to which lab findings?
Hypophosphatemia
Hypocalcemia
Elevated alkaline phosphatase
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
Two important causes of hypoglycemia in non-diabetic patients with elevated insulin levels?
1. Insulinoma (beta cell tumor)
2. Surreptitious use of insulin or sulfonylurea