EDEXEL GCSE BUSINESS paper 1
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
why do business carry out market research
assess risk
find gap in market
identify/understand competition
to make informed decisions
primary research
collecting information that didn't exist before but found through field research - valuble first hand contact
secondary research
research that gathers information that already exists
primary research pros and cons
pros
more relevant/specific to needs
up to date
direct customer contact
cons
need a well-designed questionnaire
time-consuming
expensive
secondary research pros and cons
pros
easier to find/collect quantitative data
can be free
less time consuming
cons
many not be reliable
more general
can be out-of-date
types of research methods
internet research
government reports
observation
questionnaire
focus group
customer feedback
what is a marketing mix
the 4 variables that are important when marketing a product
-product
-price
-promotion
-place
Product range
- all products made or sold by a business
-can mean a higher cost per unit due to less economies of sales
product differentiation
making your product stand out from competitors
- to position products/target market segments
- to gain advantage over rivals when faced with competition
demand
quanitity that consumers are willing to be able to buy at a current price level
e-commerce pros
pros
can be cheaper than renting/buying a store
wide market
direct form of selling with no middlemen so they don't need to give discounts to wholesalers
Wholesaler
buys in bulk hold stocks and sells to mainly retailers not customers. They get a discount from producers
factors affecting location
cost of site
labour costs
transport costs
sales potential
manager preferences
name six sources of finance available to a business (there are nine)
bank loan
overdraft
crowdfunding
family and friends
venture capital
share capital
trade credit
selling assets
retained profit

cash flow-forecast
predicts the businesses future cash inflows and outflows
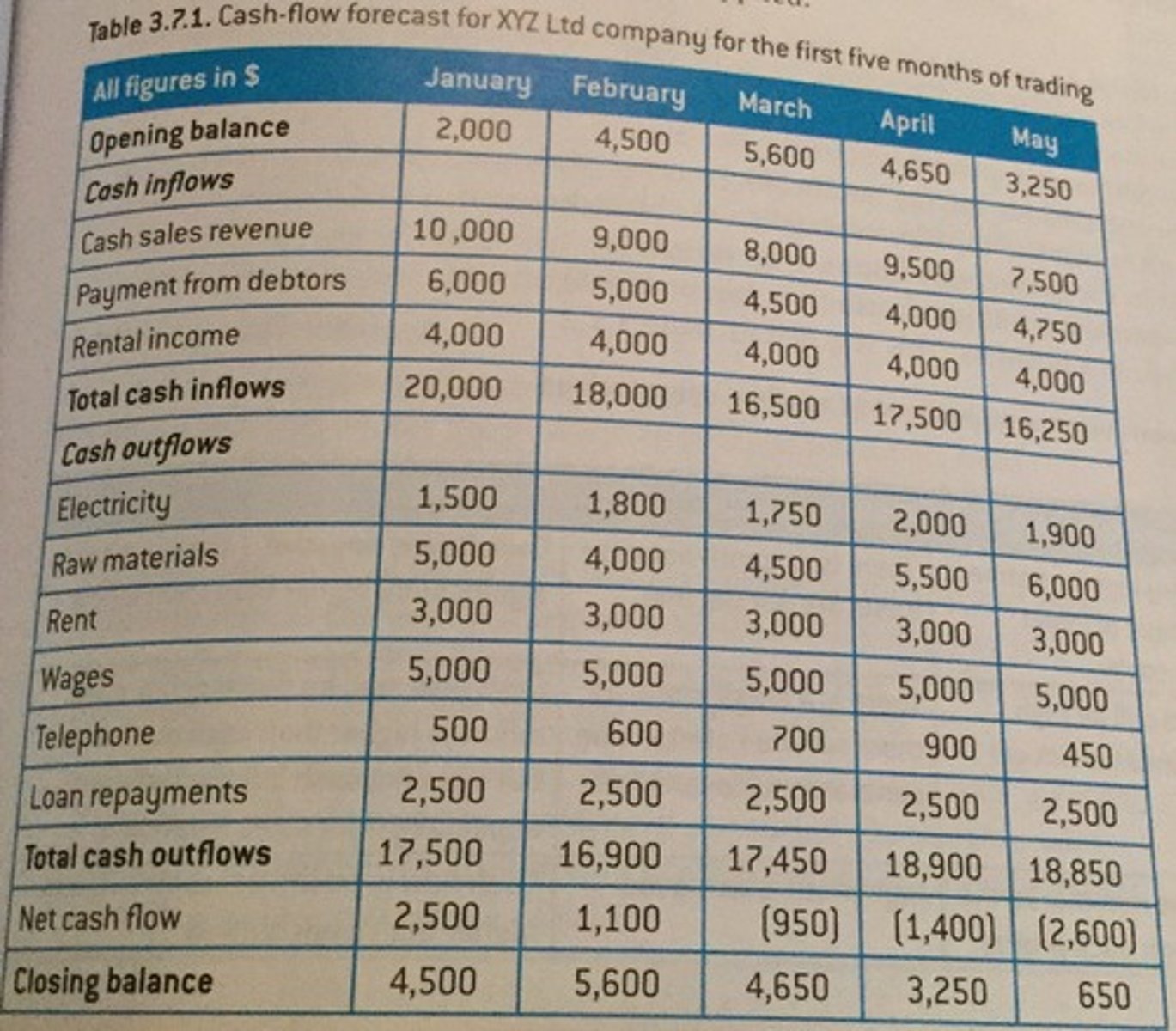
solutions to cash flow problems
pay debts later, when u havs cash
ask for bills eariler
get a source of finance
gross profit margin
the percentage of sales revenue that is gross profit = gross profit/sales revenue *100

net profit margin
the percentage of sales revenue that is net profit = net profit/sales revenue *100
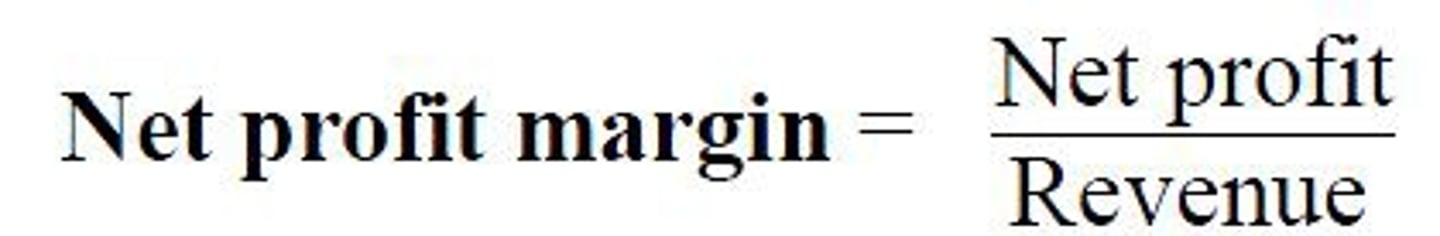
name laws that exist to protect employees
equal pay act
minimum wage act
discrimination legislation
health and safety acts
break-even
the point at which the costs of producing a product equal the revenue made from selling the product
Entrepeneur
A person who organizes, manages, and takes on the risks of a business
unlimited liability benefits
- owner 100% control
- owner keeps profits
- accounts not public
- quick easy to set up
unlimited liability drawbacks
- more risks (owner legally responsible for any debts)
- potential loss of belongings to pay off debt
Partnership Benefits
- Easier to raise financial capital
- Partners may combine ideas and expertise
- shared risk
Partnership Disadvantages
- decisions made by one partner affect all
- one partner leaves and business no longer exists
- profit shared
- desagreements
Private limited company benefits
- limited liability; can only lose money up to what invested
- customers may trust 'ltd'
- continues trade even when shareholders change
Private limited company drawbacks
- shareholders reduce control of main owner (depending on proportion of business sold as shares)
- shareholders may disagree
- financial information published
- more info reported to government
- more complex set up
Franchise Advantages
- brand image/reputation already established
- expensive marketing costs covered
- training provided
- established customer base
- increased chance of survival
Franchise Disadvantages
- high initial investment
- owner has little decision freedom
- have to pay royalty to franchisor (%revenue)
- restrictions on where
Impact of technology on marketing mix
- customers can easily compare price online
- new tech demands continuously innovated products
- many businesses switching to social media for promotion
- e-commerce provides customisablility
Interest rate calculation
total repayment-borrowed amount / borrowed amount *100
Stakeholder objective examples
- manager wants bonus
- employees want good pay/working conditions
- customers want value for money
- local community want investmet and >pollution
- government wants low unemployment and competitive markets
- shareholders want dividends + growth
- suppliers want regular orders
stakeholder conflict
This can occur in business when stakeholder objectives are different
e.g. shareholders want more profit, managers want o reinvest and grow
- workers want higher pay, customers want lower prices
consumer law
- right to return
- goods delivered safely
- business should disclose full information about product
- to a good standard
Employment Law
- health and safety requirements met in workplace
- fair recruitment/redundancies
- minimum wage
advantages of legislation
- compliant businesses less likely to be fined
- compliant businesses veiwed as proffessional / caring
- compliant businesses have improved relationship with stakeholders
disadvantages of legislation
- laws can be restricting
- uncompliant businesses get bad publicity
- uncompliant businesses may be fined
- business must know law and keep up to date
increased unemployment?
decreased consumer demand
good economy?
people earn more, more disposable income
increased inflation?
business costs sharply rise
lower interest rates
make it cheap to borrow money, so businesses borrow and therefore spend more money on labor and machinery
- demand increases
increased taxes
reduced disposable income
weaker pound?
foreign demand rises
SPICED?
Strong Pound Imports Cheap Exports Dear
technology investment
expensive, but improves efficiency and long term costs
Why does cash matter?
- to pay suppliers/debts
- to promote business/buy raw materials
How to improve cash flow
- reducing cash outflow (costs)
- increasing price inflow (increasing selling prices)
- finding new sources of finance to make payments
- insist customers pay on time
- take longer to pay debt
Benefits of market segmentation
- differenciate
- meets customer needs
- build close customer relationships
reliable date
- come from representative sample
- questions should enable relavant answers
Purpose of market research
To identify and understand customer needs
To identify gaps in the market
To reduce risk
To inform business decisions
financial aims/objectives
survival
profit
sales
market share
financial security
Non-financial aims and objectives
Social goals
personal satisfaction
challenge
independence and control
location depends on
labour
raw materials
market
transport
to add value
speed of service
convinience
USP
branding
better quality/design
bank overdraft
covers short term expenses that can be repaid quickly
flexibility
variable interest rates
trade credit
the practice of buying goods and services now and paying for them later
but there's a trade credit limit
Why new business ideas come about
- changes in technology
- changes in what consumers want
- products and services becoming obsolete
personal savings
Personal savings is money that has been saved up by an entrepreneur. This source of finance does not cost the business, as there are no interest charges applied
venture capital
Venture capital is money invested by an individual or group that is willing to take the risk of funding a new business in exchange for an agreed share of the profits. The venture capitalist will want a return on their investment as well as input into how the business is run.
share capital
Share capital is money raised by shareholders through the sale of ordinary shares. Buying shares gives the buyer part ownership of the business and therefore certain rights, such as the right to vote on changes to the business. This can slow down decision-making processes.
share capital benefits
- Share capital is a source of permanent capital - Shareholders cannot have a refund on their shares. Instead, if they want to sell their shares, they must find someone else to sell them to
- There are no dividends to be paid if the business has a poor year - Shareholders are not promised dividends every year, as dividends are only paid if the business has made sufficient money to pay all of its costs
Disadvantages of share capital
- Loss of control as new shareholders must have a say in the business.
- Dividends may need to be paid
- vunerable to takeover
- Only available to LTD's and PLC's
bank loan
A fixed amount loan from a bank which is generally used to finance long-term assets
long time to approve
crowdfunding
Crowdfunding involves a large number of people investing small amounts of money in a business, usually online
benefit crowdfunding
It acts as a form of market research. If people don't invest, it means the business idea is not attractive or distinctive enough, indicating that the business is likely to fail.
It provides opportunities for individuals to start up a business even if they don't have access to other sources of funding
Disadvantages of crowdfunding
A share of the business may have to be given to investors
May not be able to raise the money needed / difficult
business must be interesting