SHS 300 Quiz 3
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What makes up the respiratory system?
chest wall
airways
lungs
What makes up the chest wall?
thorax
diaphragm
abdomen
What makes up airways?
upper airways
lower airways
larynx
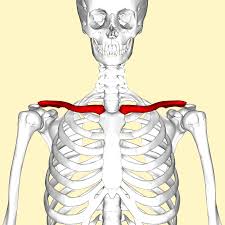
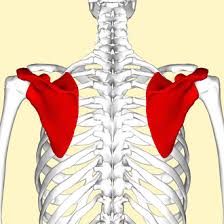
What structures make up the Pectoral Girdle?
clavicle
scapula
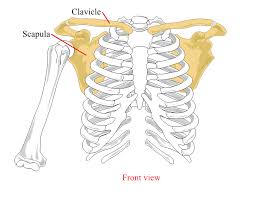
clavicle
Scapula
What makes up the sternum
manubrium
body
xihiod process
Manubrium
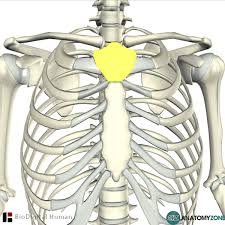
Body of Sternum
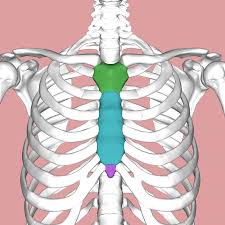
Xihoid Process
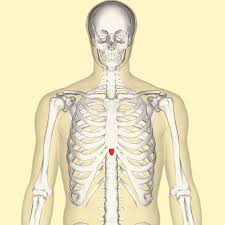
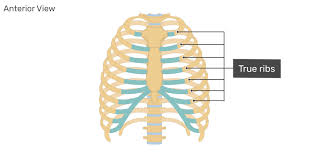
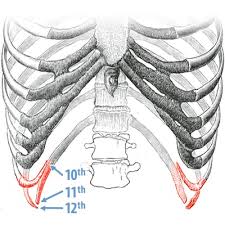
How many ribs are there?
12 pairs
Ribs 1-7
true ribs
Ribs 8-10
false ribs
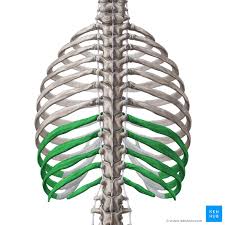
Ribs 11-12
Floating ribs
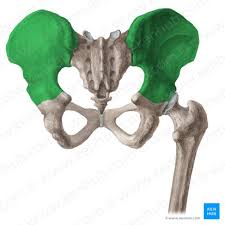
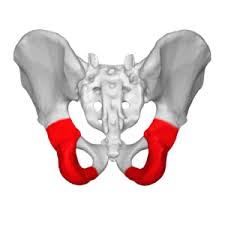
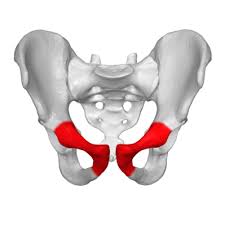
What structures make up the pelvic girdle?
illium
ishium
pubis
sacrum
coccyx
Illium
Ishium
Pubis
Sacrum
Coccyx
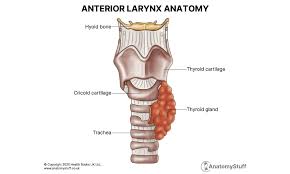
What separates the respiratory airways?
Larynx
What makes up the upper airways?
oral cavity
nasal cavity
pharynx
What makes up lower airways?
trachea
bronchial tree
lungs
What is the airways function?
articulation and resonance
filter, moisten, and warm incoming sound
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
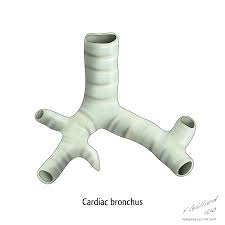
Bronchial Tree
Inner membrane of trachea
Consists of pseudostratified
columnar epithelium
• Contains cilia
• Cilia in constant motion
• Beating/upward sweeping motion
helps rid trachea of small particles
• Goblet cells: release mucus
Vertebral column function
protects spinal cord
What are the 5 divisions of the vertebral column?
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
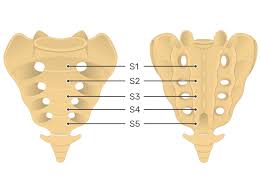
sacral
coccygeal
Cervical
1-7
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Coccygeal
What are the functions of the respiratory system?
gas exchange for life
movement of air - inspiration and expiration
provides air to power the voice for speech
Pulmonary Alveoli
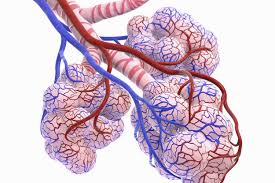
Terminal bronchioles
communicate with alveolar ducts which open alveolar sacs of lungs
Left lunf
2 lobes, 1 fissure
Right lung
3 lobes, 2 fissures
What is function of alveoli?
exchange of CO2 and O2
What is the function of pleurae?
translates movements of rib cage and abdomen to lungs
Parietal pleura
covers inner rib cage and top of diaphragm
Visceral pleura
covers outer surface of lungs
What are the main muscles of inhalation?
diaphragm
external intercostal
What is the main function of diaphragm?
pulls central tendon downward and forward and increases thoracic volume and decreases pressure (inspiration)
Diaphragm
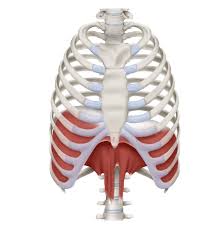
What is innervation of diaphragm?
C3, C4, C5 - phrenic nerve
External Intercostal function
Lifts ribcage up and outward by fixing upper rib and lowering others
External intercostal innervation
T1-T11
External Intercostal
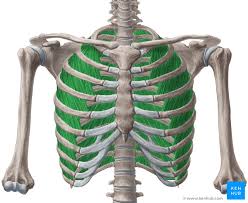
What make up the accessory muscles for Inhalation?
pectoralis minor
pectoralis major
sternocliedomastoid
scalene muscles
levatores costarum
serratus posterior superior
subclavius
serratus anterior
Pectoralis Minor
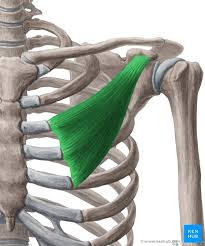
Pectoralis Minor Innervation
C5-C8
Pectoralis Minor function
lift ribs 2-5
shoulder extension
Pectoralis Major
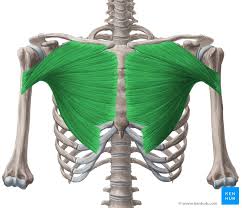
Pectoralis Major innervation
C5-C8
Pectoralis Major Function
Draw sternum and ribs up
rotates arm
Sternocleidomastiod
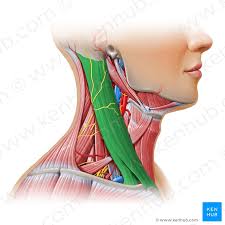
Sternocleidomastiod Innervation
CN XI
Sternocleidomastoid Function
elevate sternum and clavical
unilateral contraction - turn head to side
bilateral contraction - flex neck down
Scalene Muscles
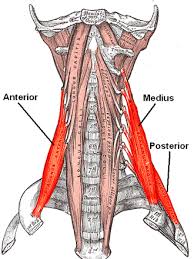
Scalene Muscle innervation
C2-C8
Scalene Muscle Function
elevates ribs 1 and 2
What are the main muscles for exhalation?
rectus abdominis
external obliques
internal obliques
transverse abdominis
Rectus Abdominis
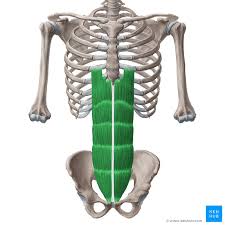
Rectus Abdominis Innervation
T7-T12
Rectus Abdominis Function
Compress AB and depress ribs and sternum
External Obliques
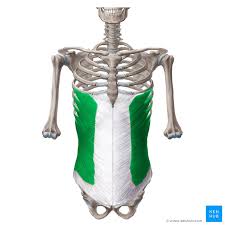
External Oblique Innervation
T8-L1
External Oblique Function
Compress AB and Depress lower ribs (5-8)
Internal Obliques
Internal Obliques Innervation
T8-L1
Internal Oblique Function
Compress AB and depress lower ribs (9-12)
trunk support and posture
Transverse Abdominis
Transverse Abdominis Innervation
T7-T12
Transverse Abdominis Function
Compress AB
Internal Intercostals
Internal Intercostal Innervation
T1-T11
Internal Intercostal Function
pulls ribs downwards
What is alveolar pressure?
pressure within the alveoli
inspiration - reduction of pressure
exhalation - increase in pressure
Passive force
Elastic recoils
Active force
muscles
inspiratory checking
a mechanism that occurs when the lungs are inflated to very large volumes—close to or near total lung capacity (TLC)—and the speaker begins to exhale to produce an extended steady utterance.
What muscles are responsible for inspiratory checking?
Main and accessory muscles of inhalation
What muscle groups are active during running speech?
expiratory main and accessory muscles
AB wall
What are the most active muscles during running speech?
AB wall
How does breathing change as we develop?
change in respiratory rate
airway path changes
lung capacity
breathing patterns
How does breathing change as we get older?
decrease in vital capacity
stiffer
weaker muscles
Inspiratory Reserve Level
maximum amount of air that can be inhaled from the tidal end-inspiratory level
Tidal Volume
amount of air inhaled or exhaled
during resting breathing
Expiratory Reserve Level
maximum amount of air that can be exhaled from the tidal end expiratory level
Residual Volume
amount of air remaining in lungs after maximum exhalation
Inspiratory Capacity
maximum amount of air that can be inhaled from the resting end expiratory level
TV + IRV
Functional residual capacity
amount of air in the lungs at tidal end expiratory level
EVR + RV
Vital Capacity
maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after maximum inhalation
Total Lung Capacity
volume of air in lungs and airways after maximum inhalation
(IRV + TV + ERV + RV)
the motor supply for diaphragm
phrenic nerve