How the eye focuses: Organism level systems: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Pupil
Centre of the iris, it varies in size to regulate the amount of light that reaches the retina
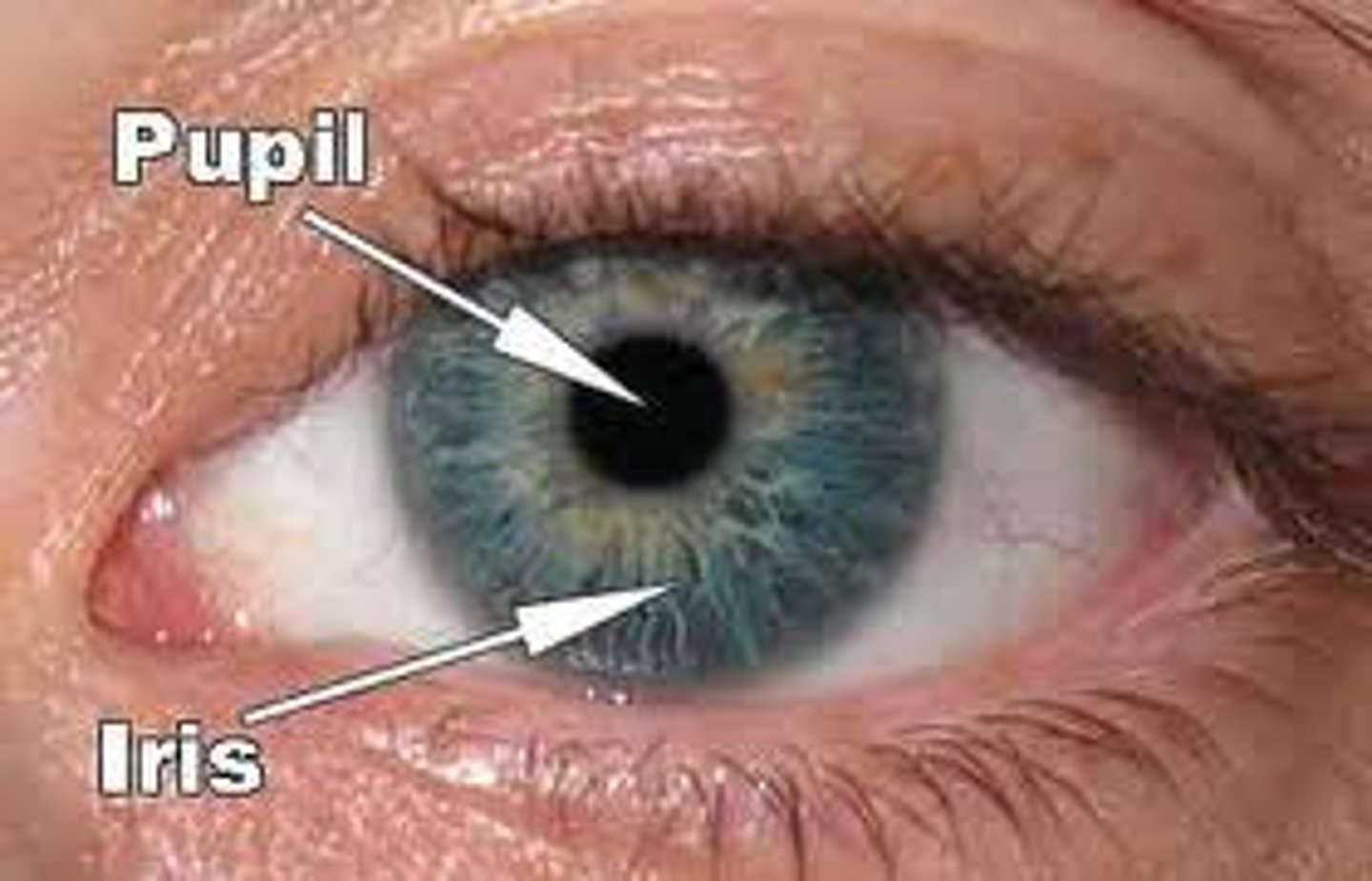
Iris
Made up of muscles called circular and radial muscles that work antagonistically to regulate the size of the pupil
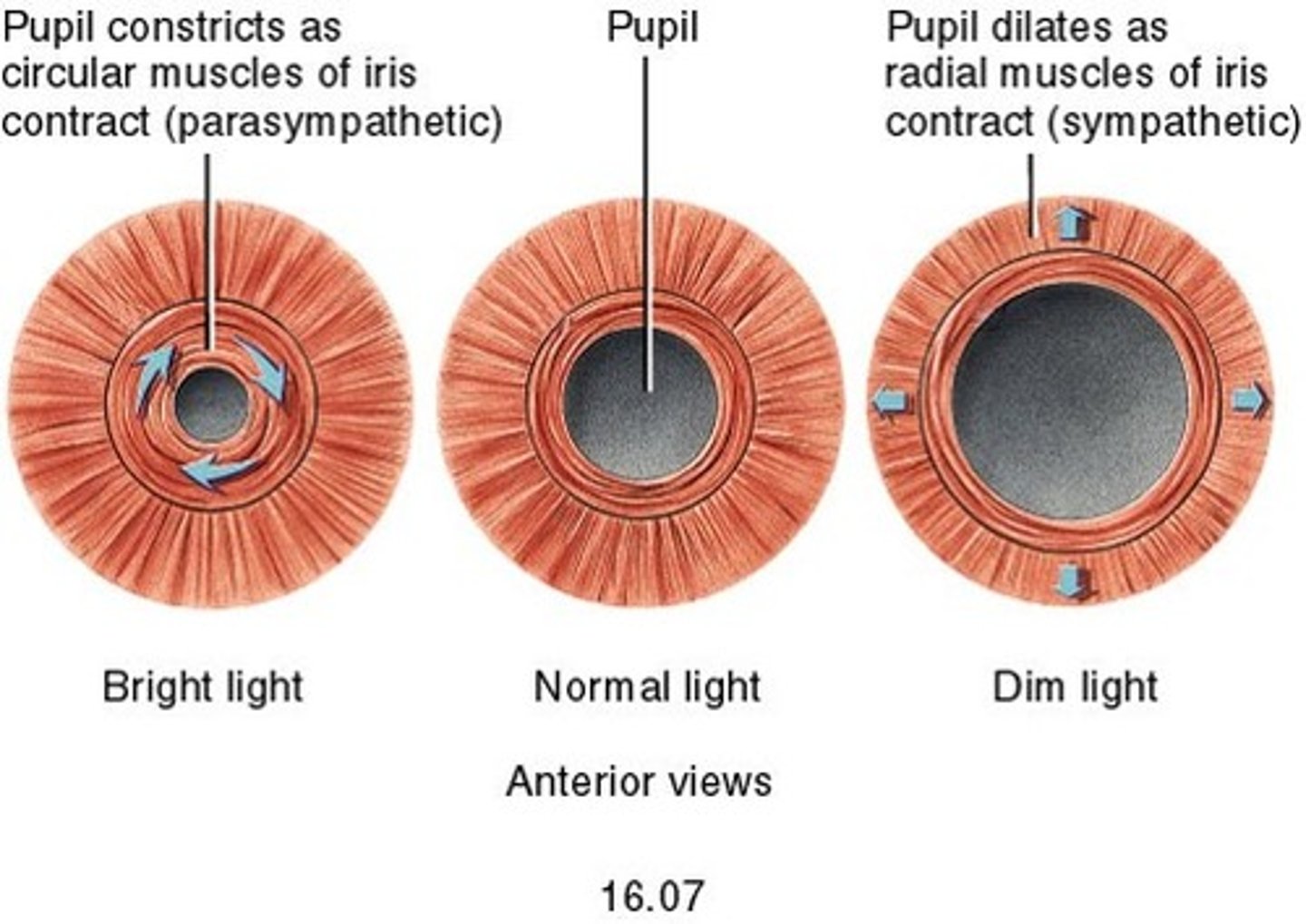
Reflex response to dim light
Circular muscles relax, radial muscles contract, pupil dilates so that more light can enter the eye
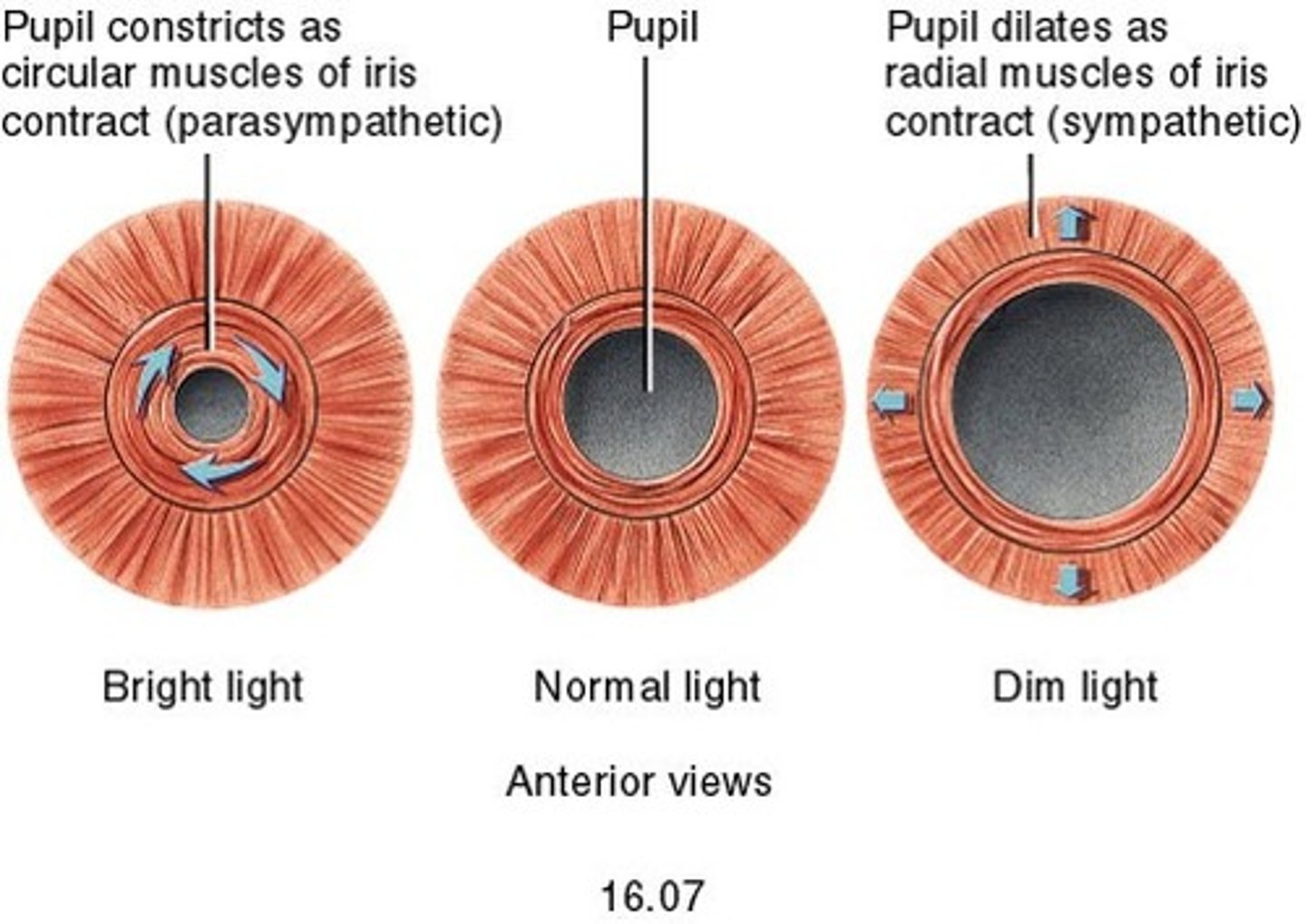
Reflex response to bright light
Circular muscles contract, radial muscles relax, pupil constricts so that less light can enter the eye
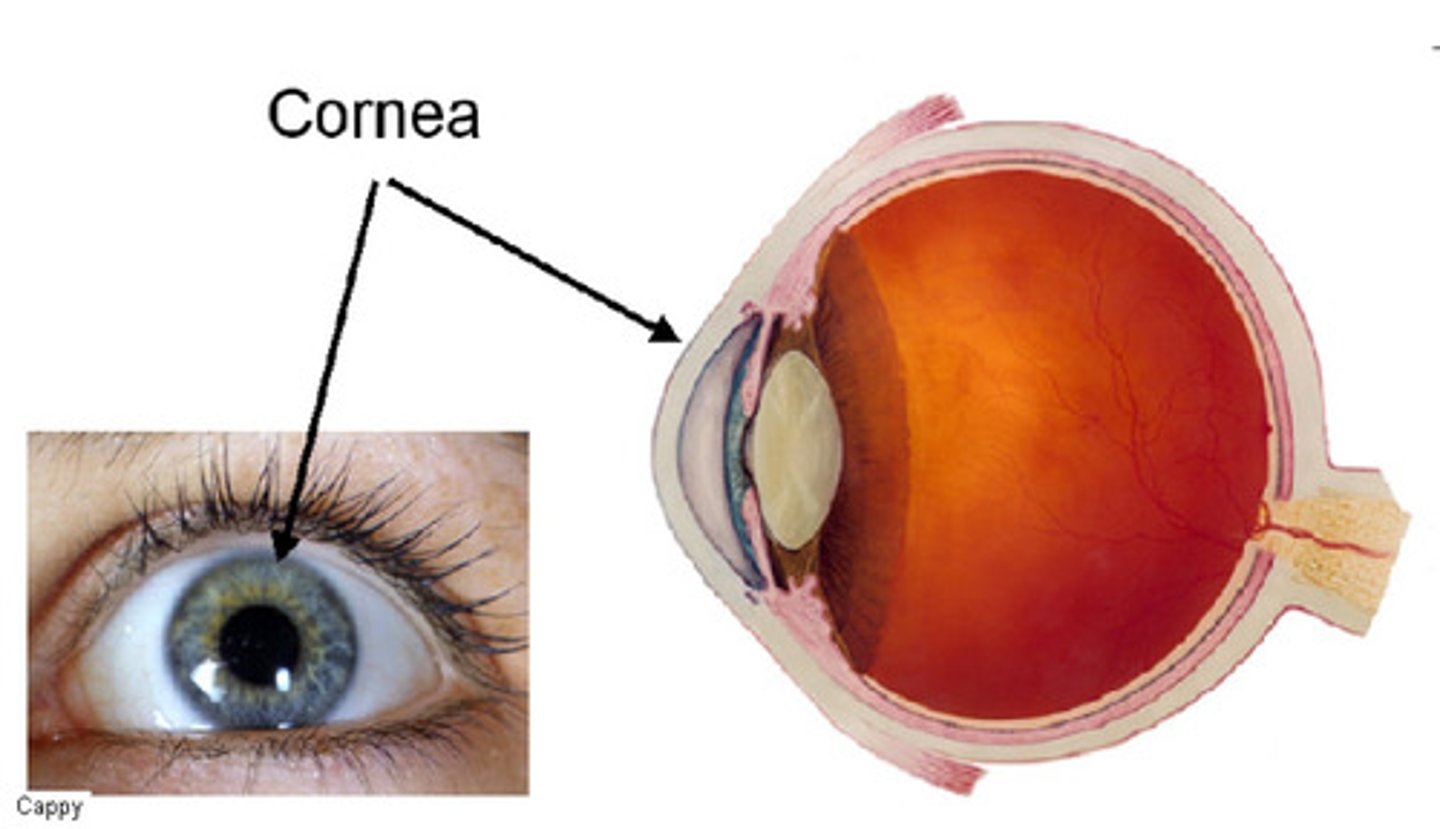
Cornea
Focuses the entry of light into the eye but is fixed and unable to adjust its focus
Lens
Focuses light rays to the back of the eye and can change shape to adjust focus for distant and near objects
Retina
The light-sensitive surface at the back of the eye containing receptor cells that detect light
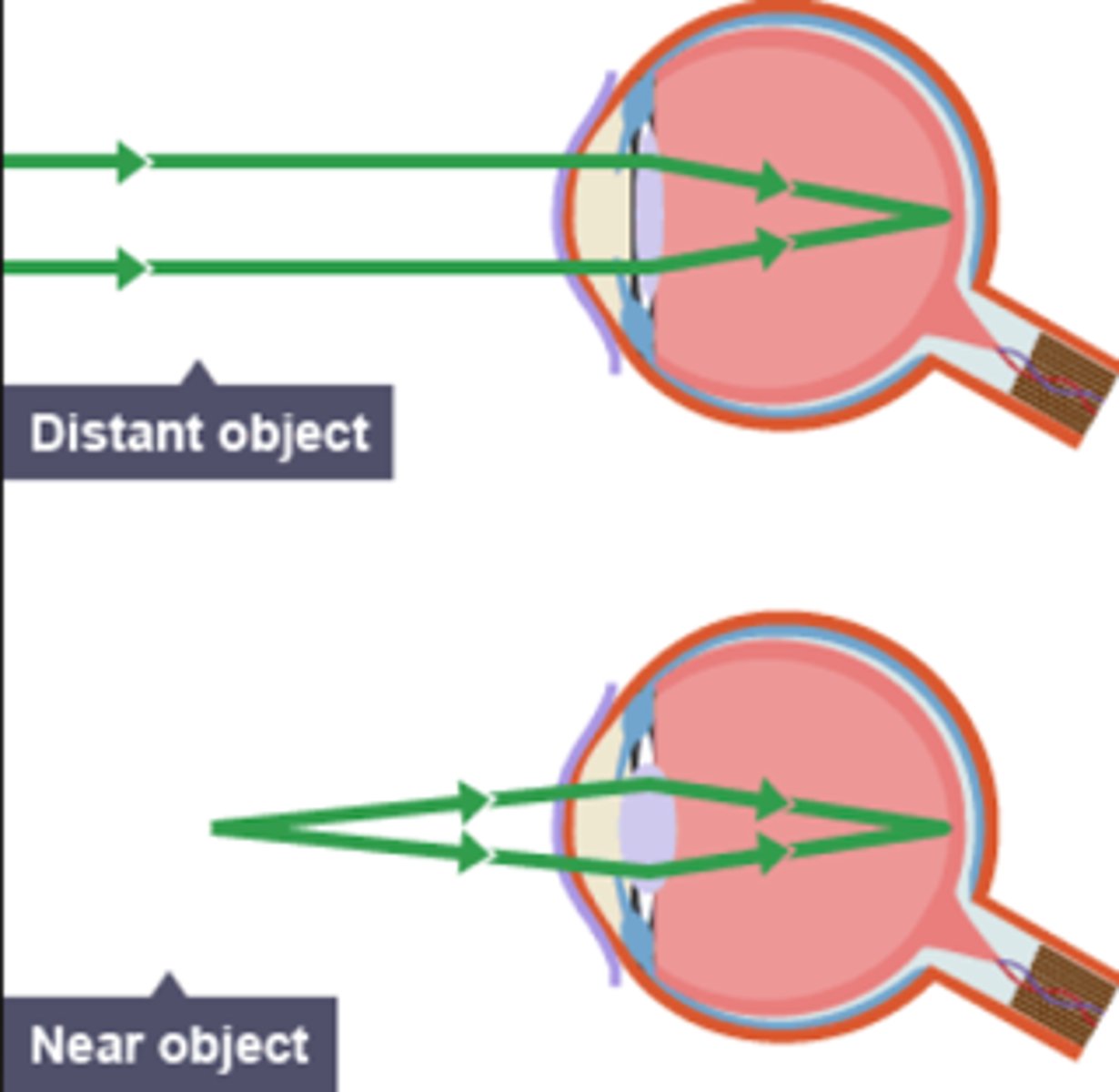
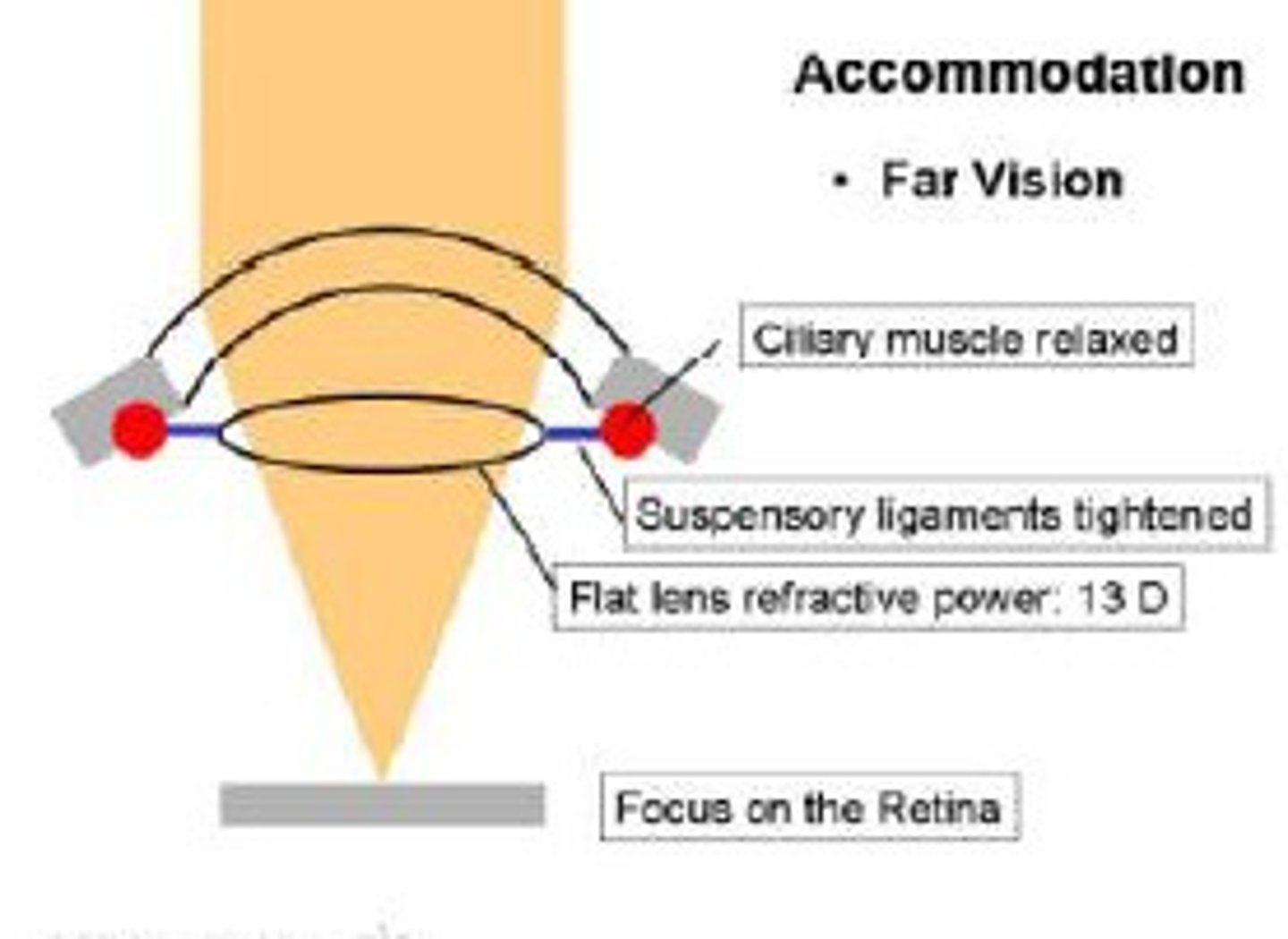
Accommodation
The process by which the eye lens changes shape to focus on near or distant objects
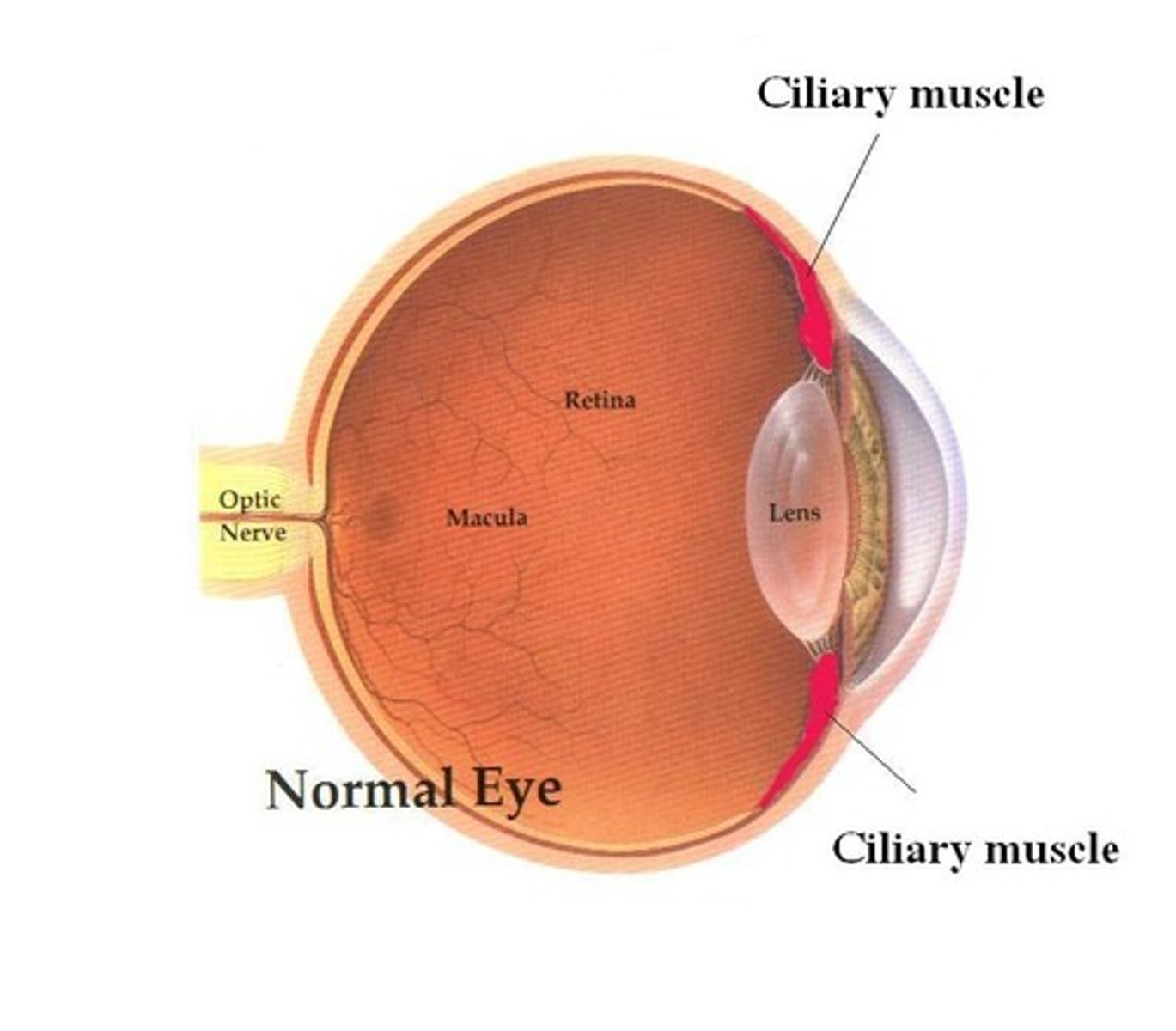
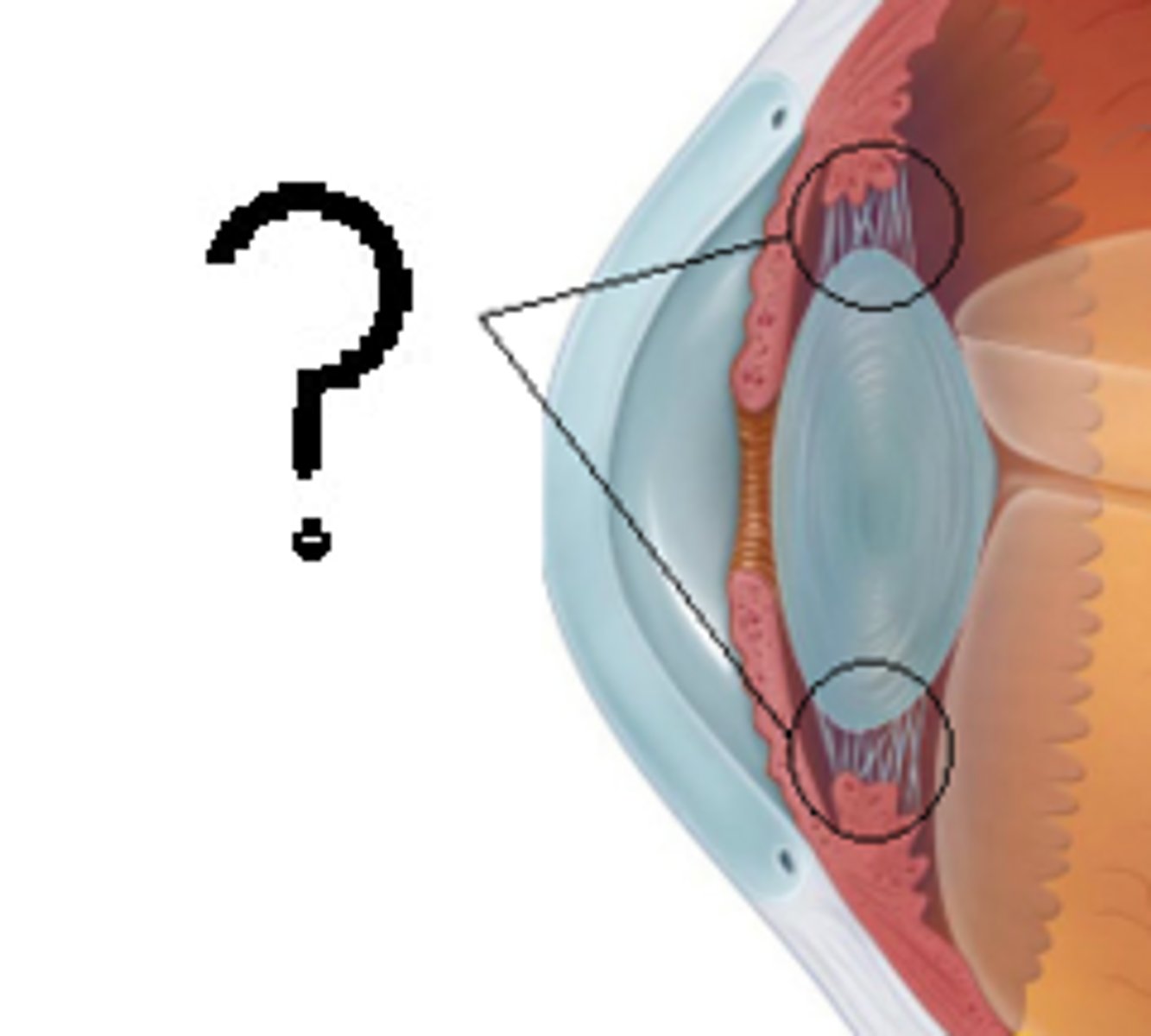
Ciliary muscles
Works with the suspensory ligaments and can contract or relax to adjust the shape of the lens
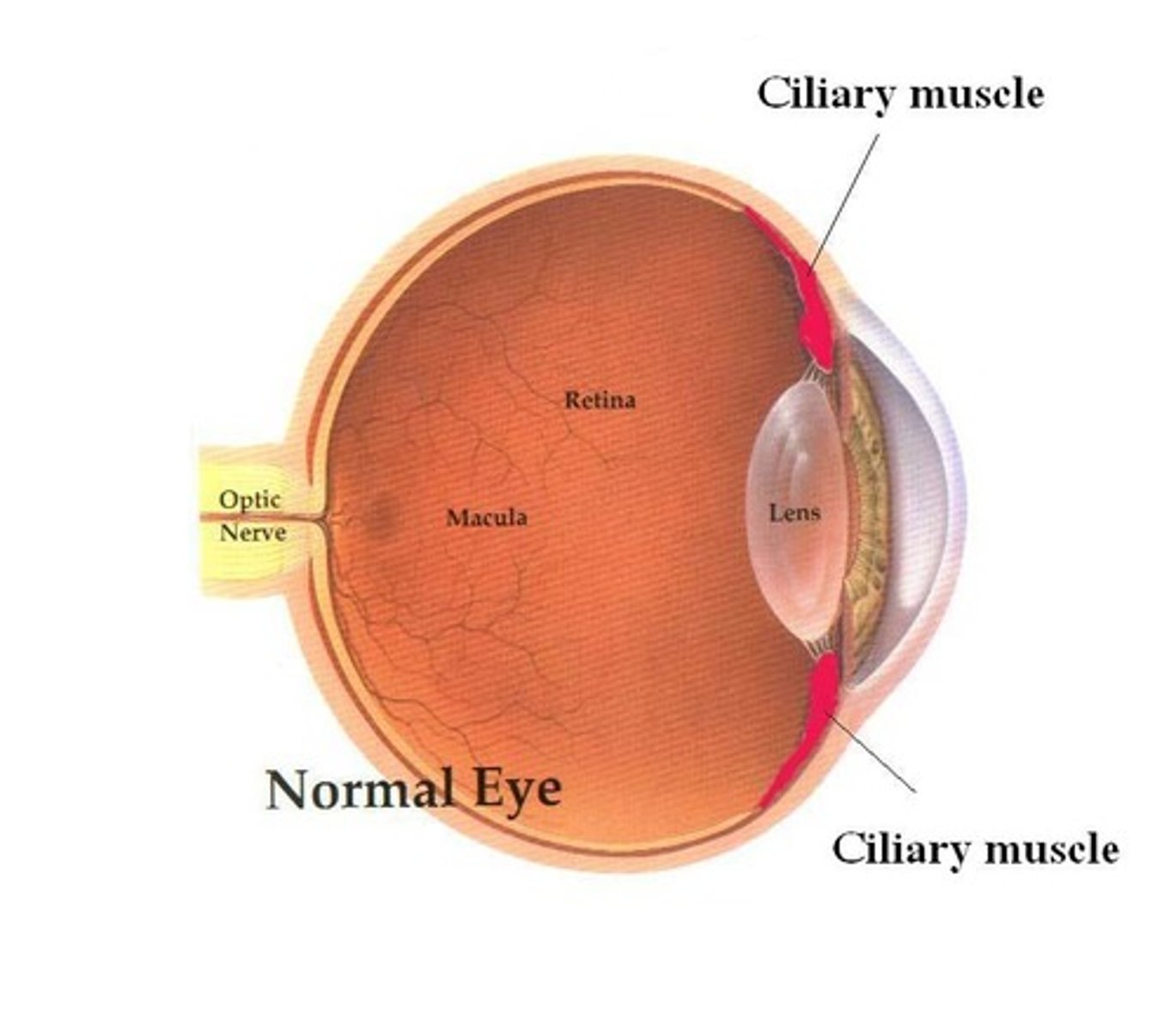
Suspensory ligaments
Works with the ciliary muscles and can loosen or be pulled tight to adjust the shape of the lens
Focusing on a near object
Ciliary muscles contract, suspensory ligaments loosen, lens is thicker and refracts light rays strongly
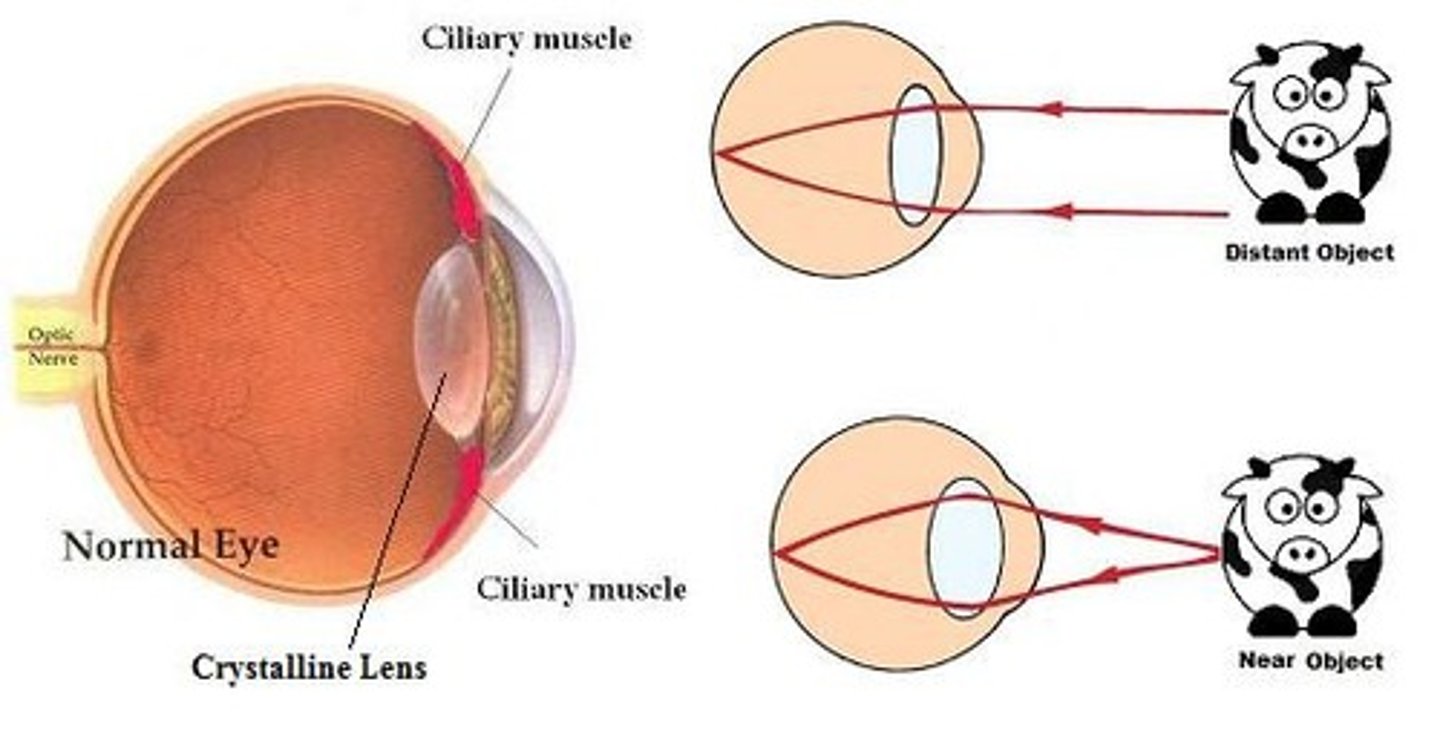
Focusing on a distant object
Ciliary muscles relax, suspensory ligaments pull tight, lens is pulled thin and only slightly refracts light rays
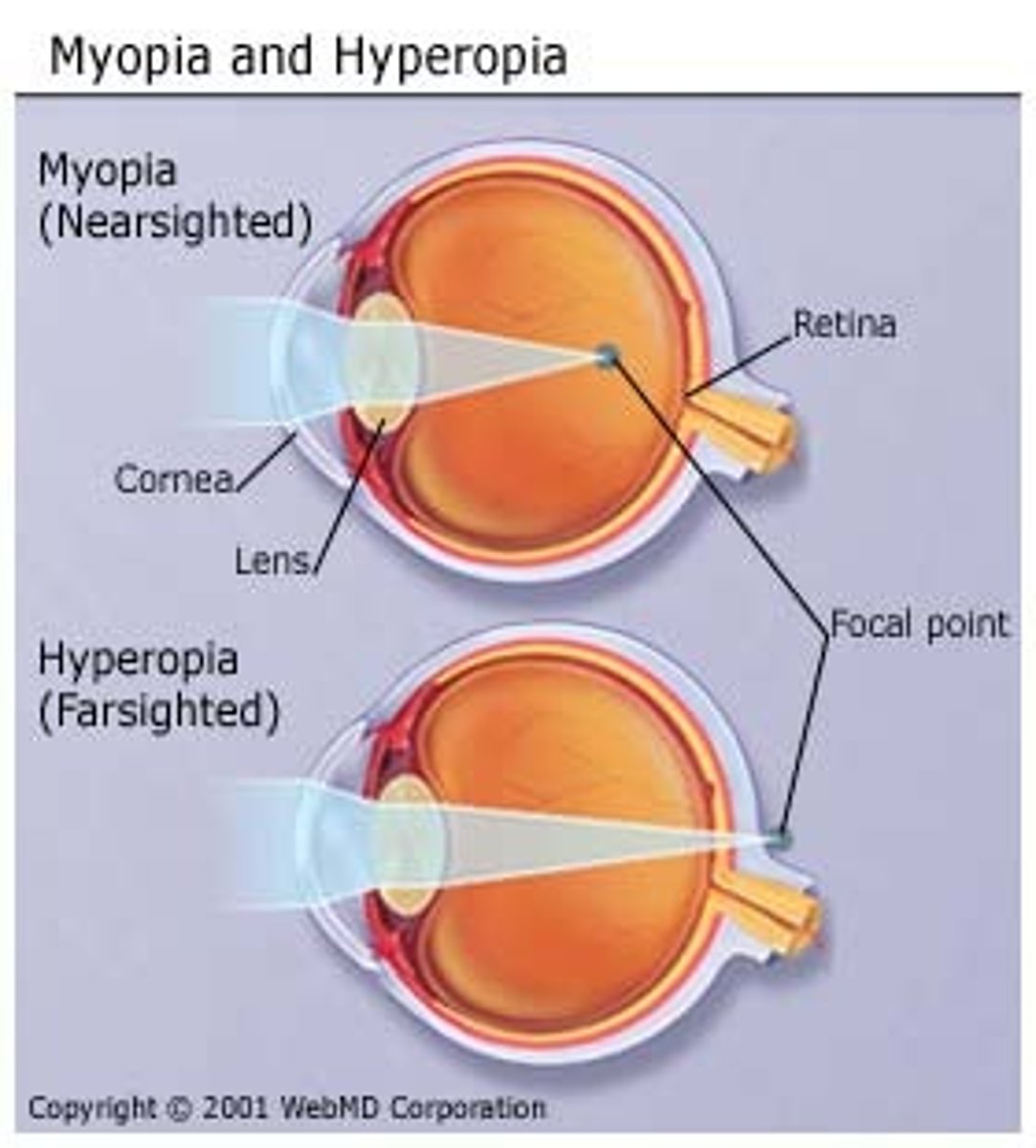
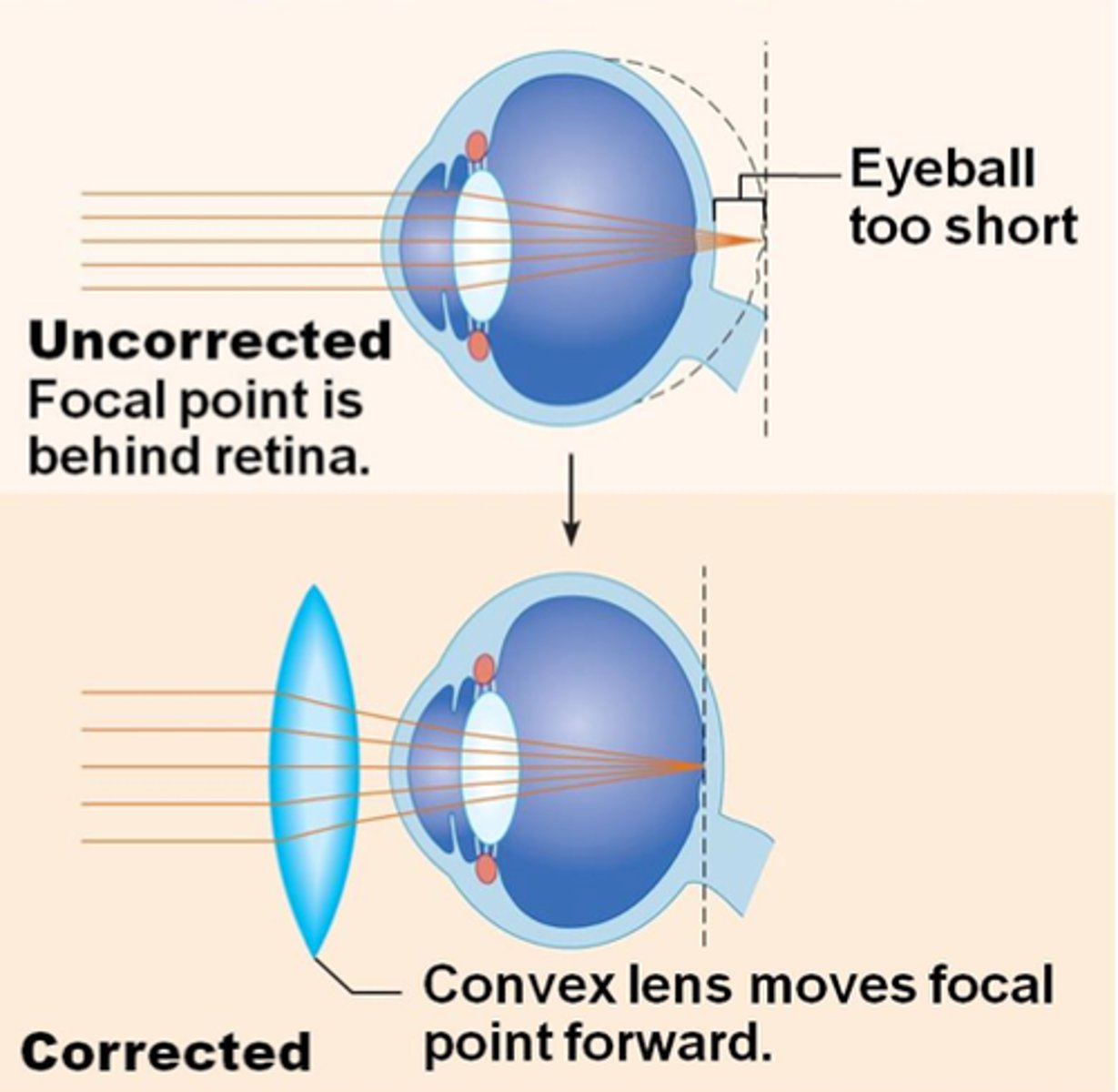
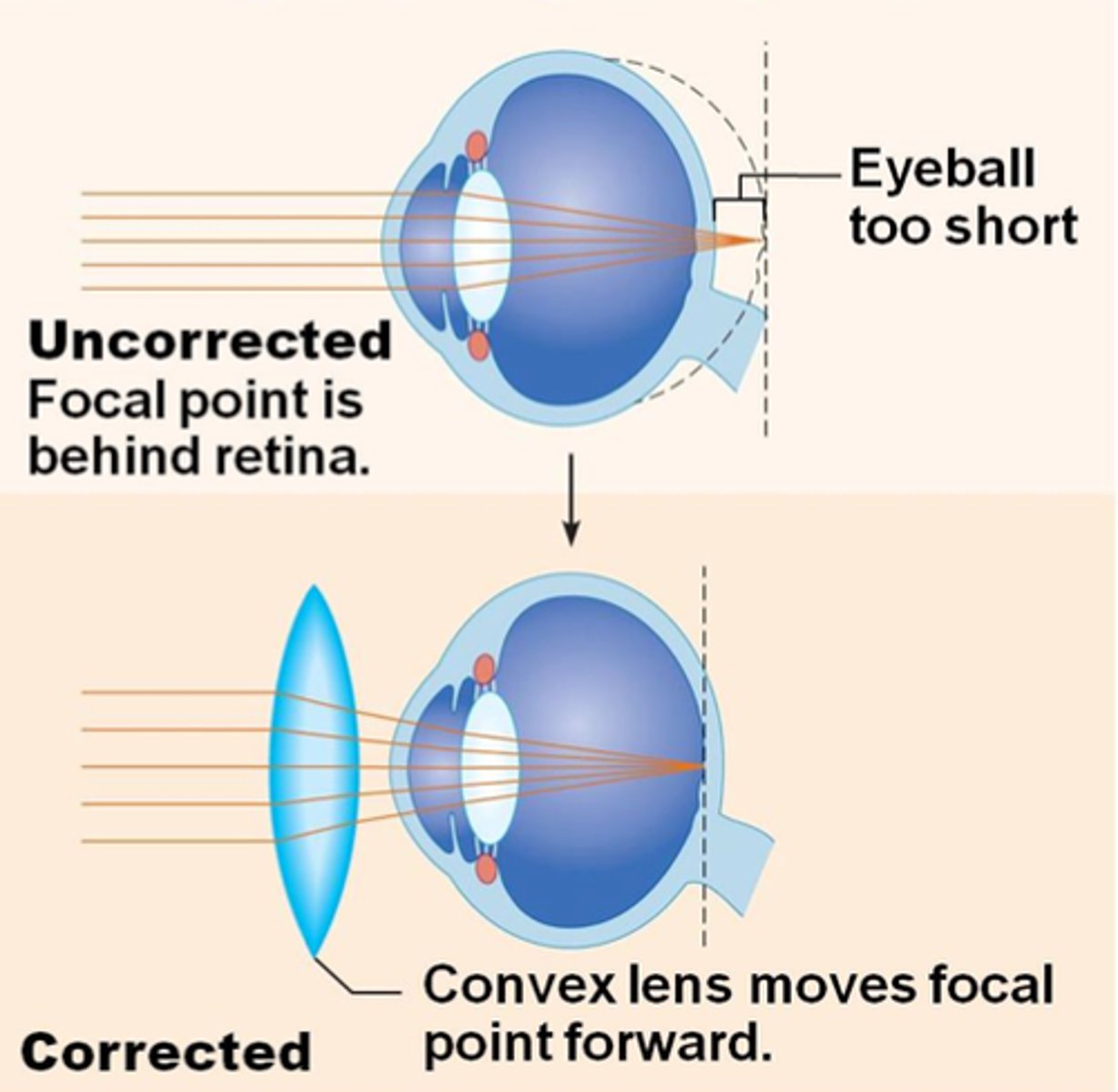
Hyperopia (long-sightedness)
Where a person has difficulty focusing on nearby objects because the light rays focus behind the retina
Causes of hyperopia
When the lens is too weak or the eyeball is too short
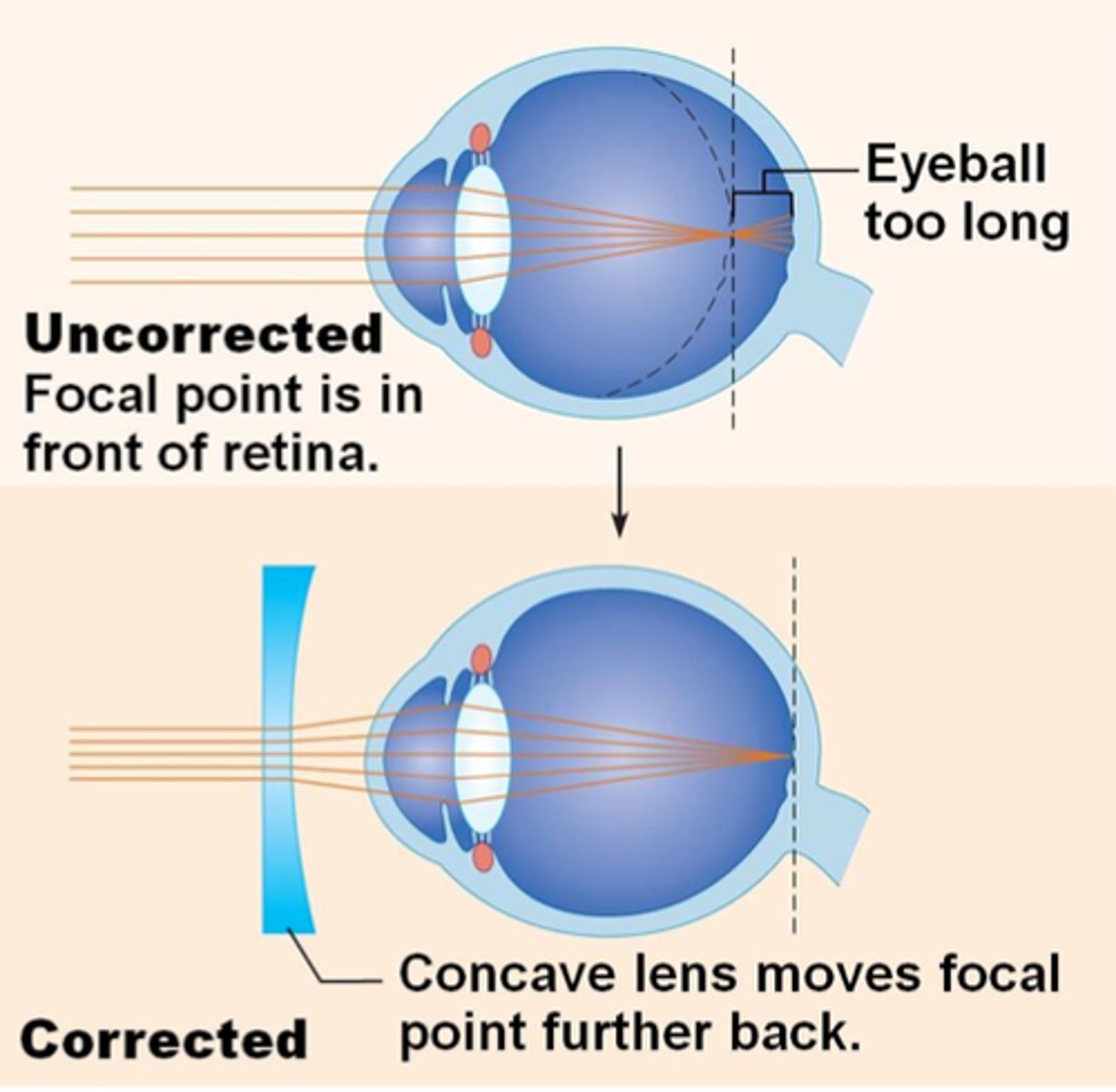
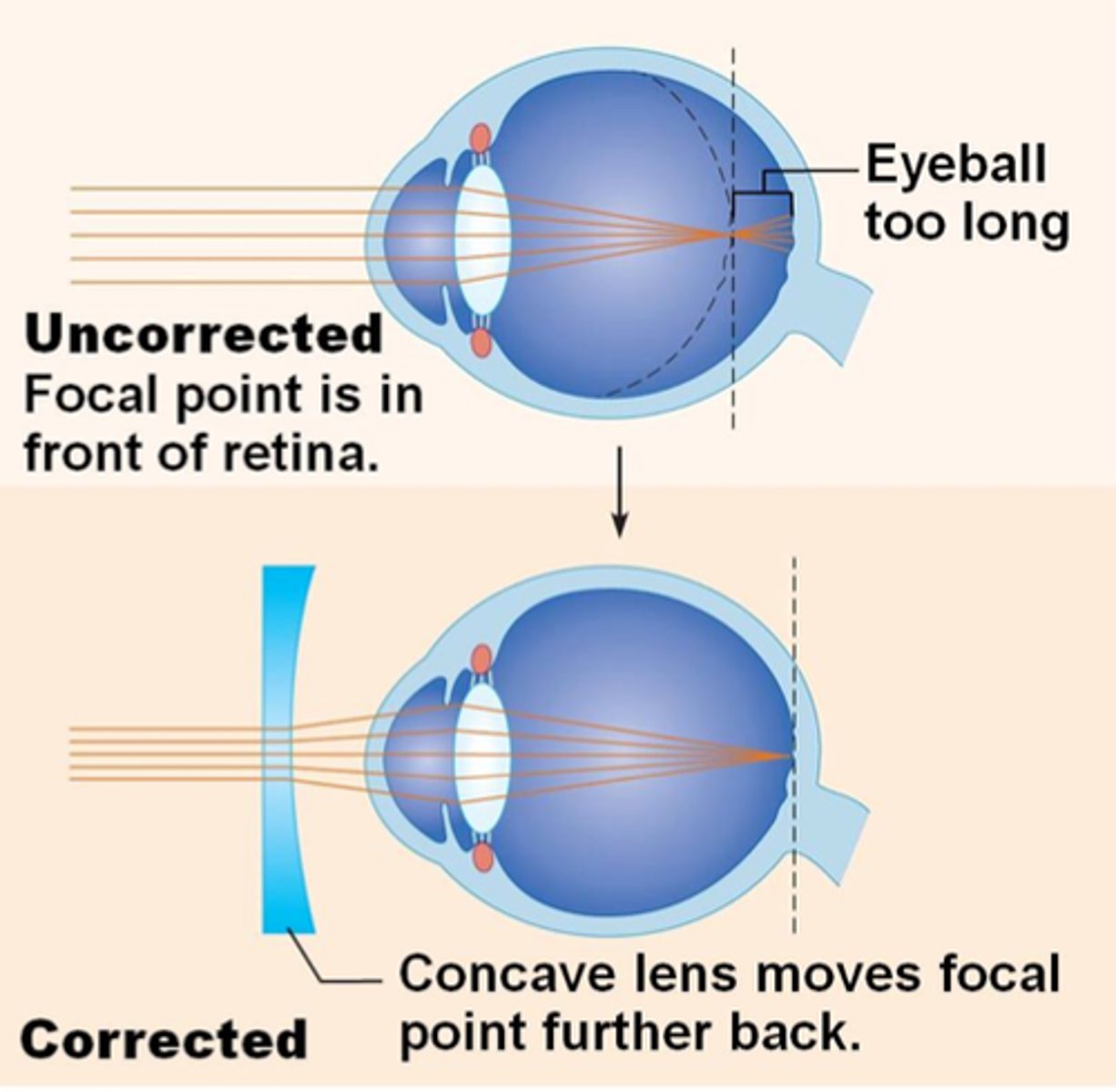
Myopia (short-sightedness)
Where a person has difficulty focusing on distant objects because the light rays focus in front of the retina
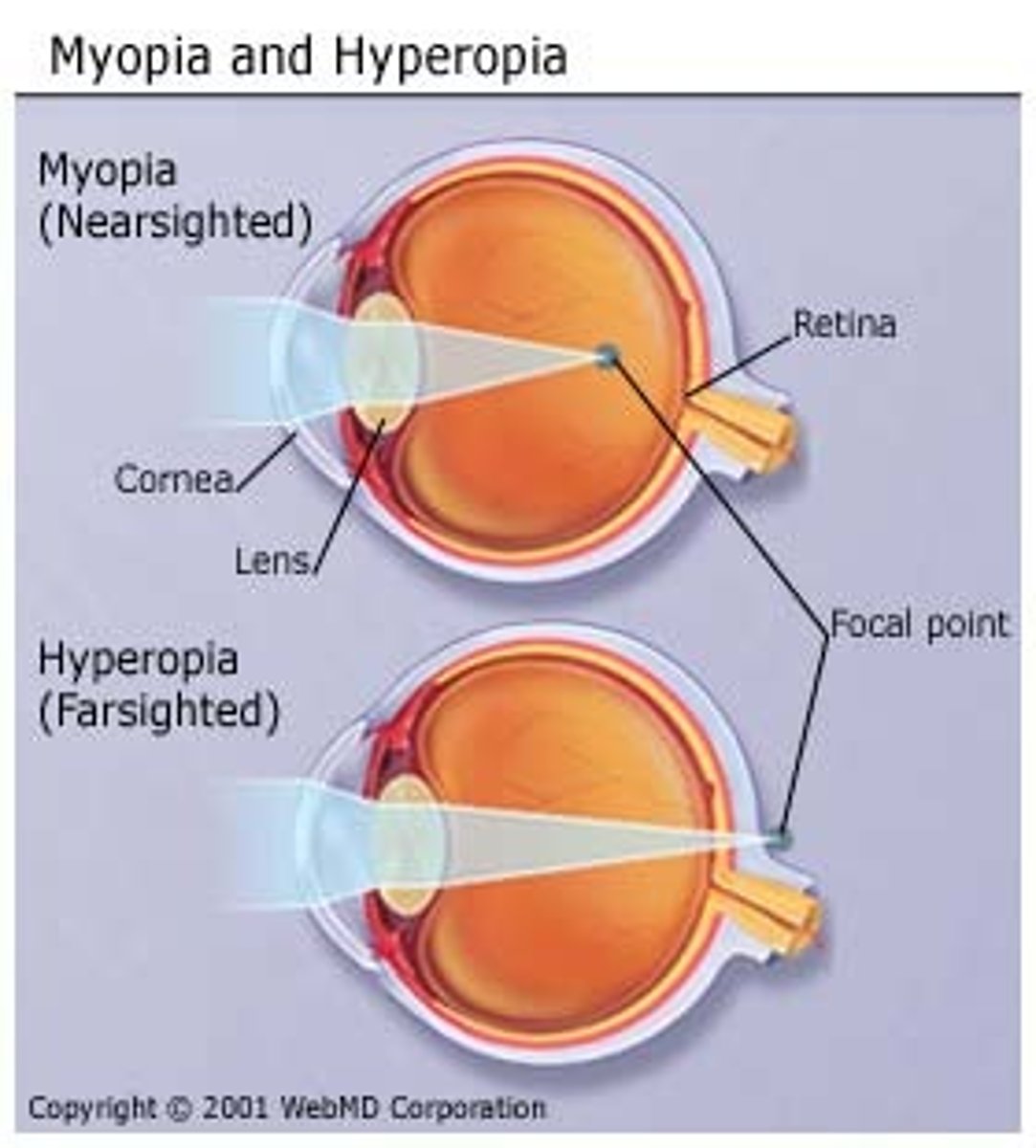
Causes of myopia
When the lens is too strong or eyeball is too long
Convex lenses
Used for correcting hyperopia by moving an image forward and focusing it on the retina
Concave lenses
Used for correcting myopia by moving an image further back and focusing it on the retina
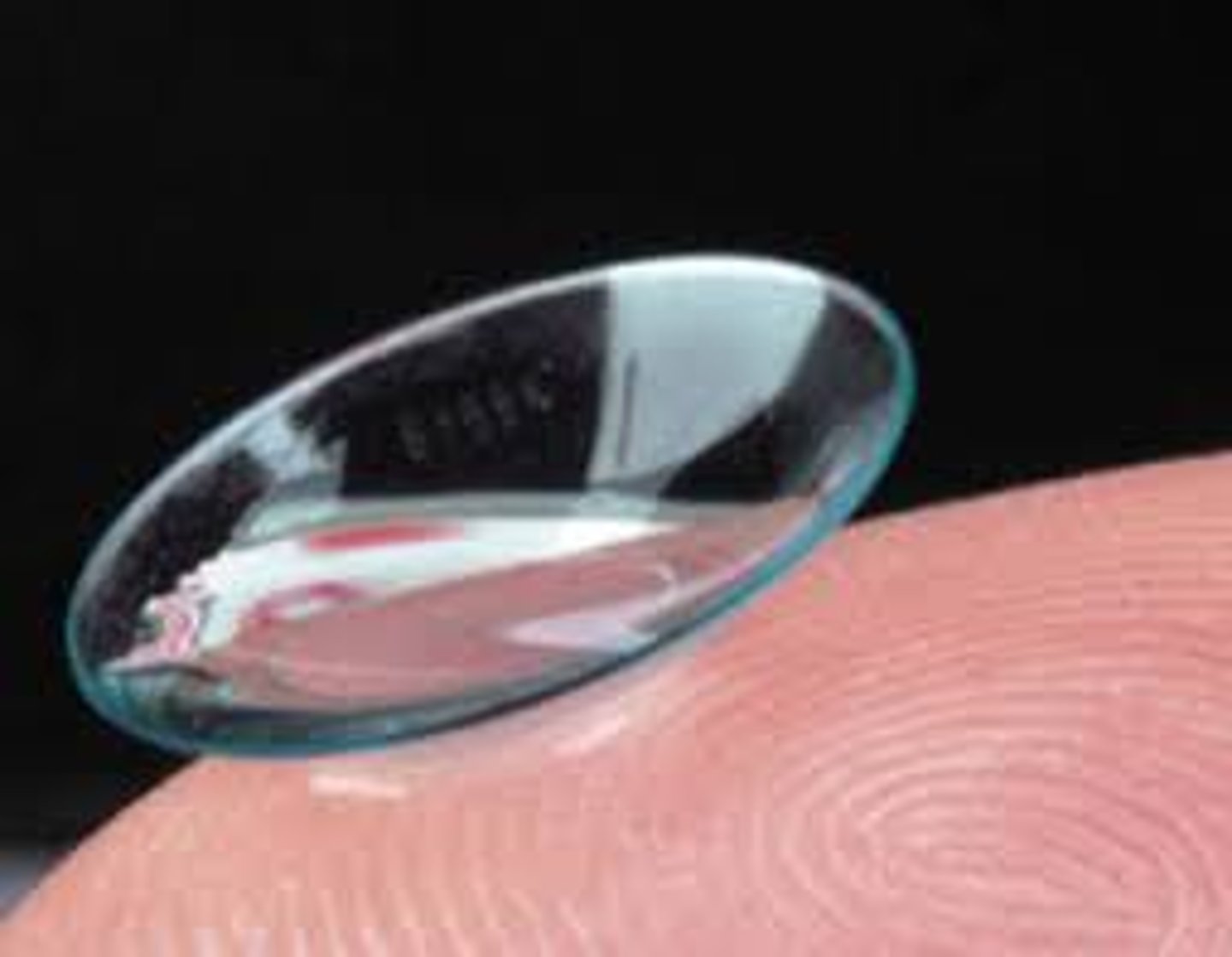
Modern sight treatments
Hard and soft contact lenses, laser surgery and lens replacement

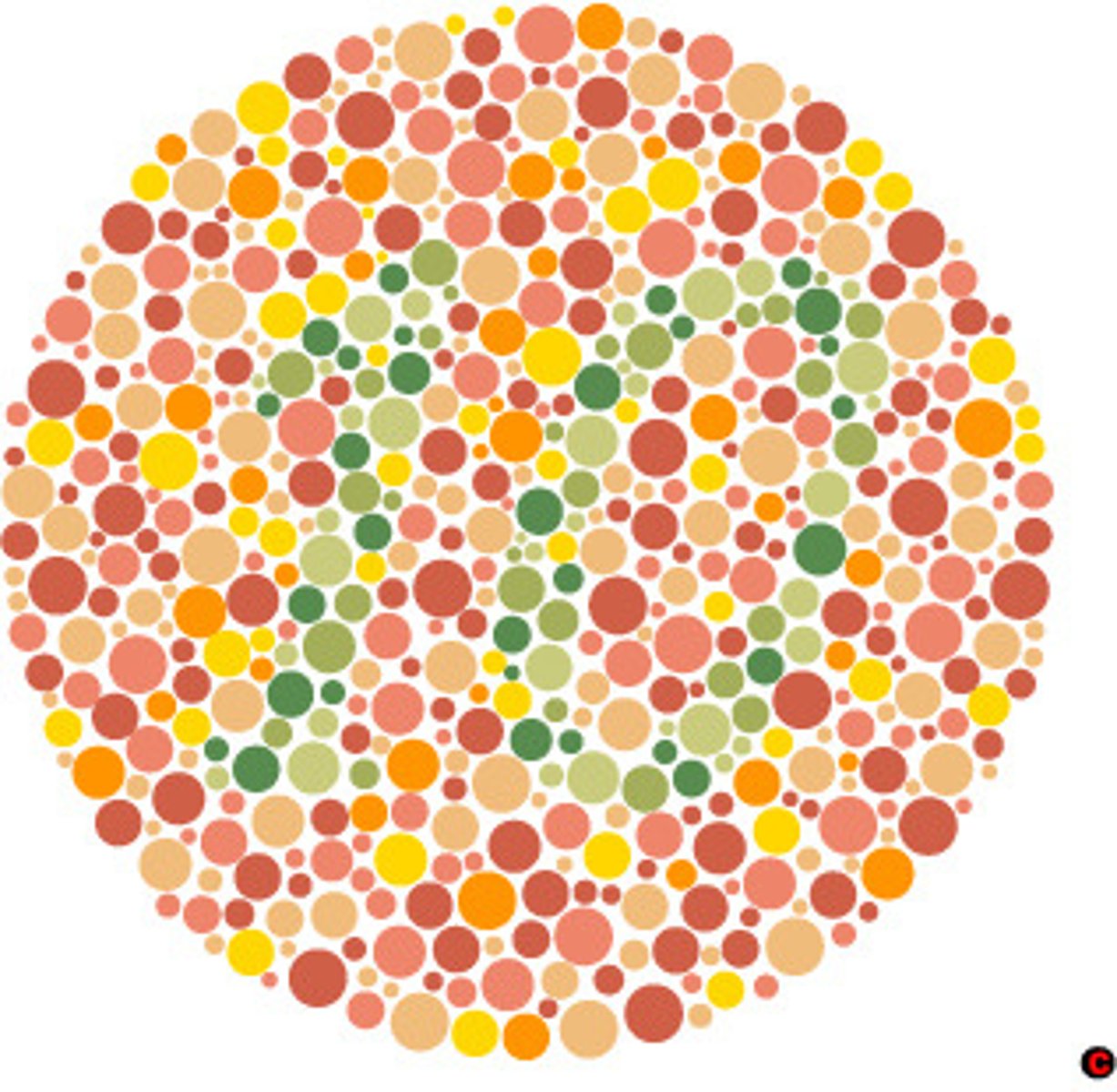
Colour blindness
An abnormal genetic condition that is characterised by the inability to clearly distinguish different colours of the visible light spectrum, as a result of deformed or altered cone cells

Still learning (19)
You've begun learning these terms. Keep up the good work!