Fluid mosaic model
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
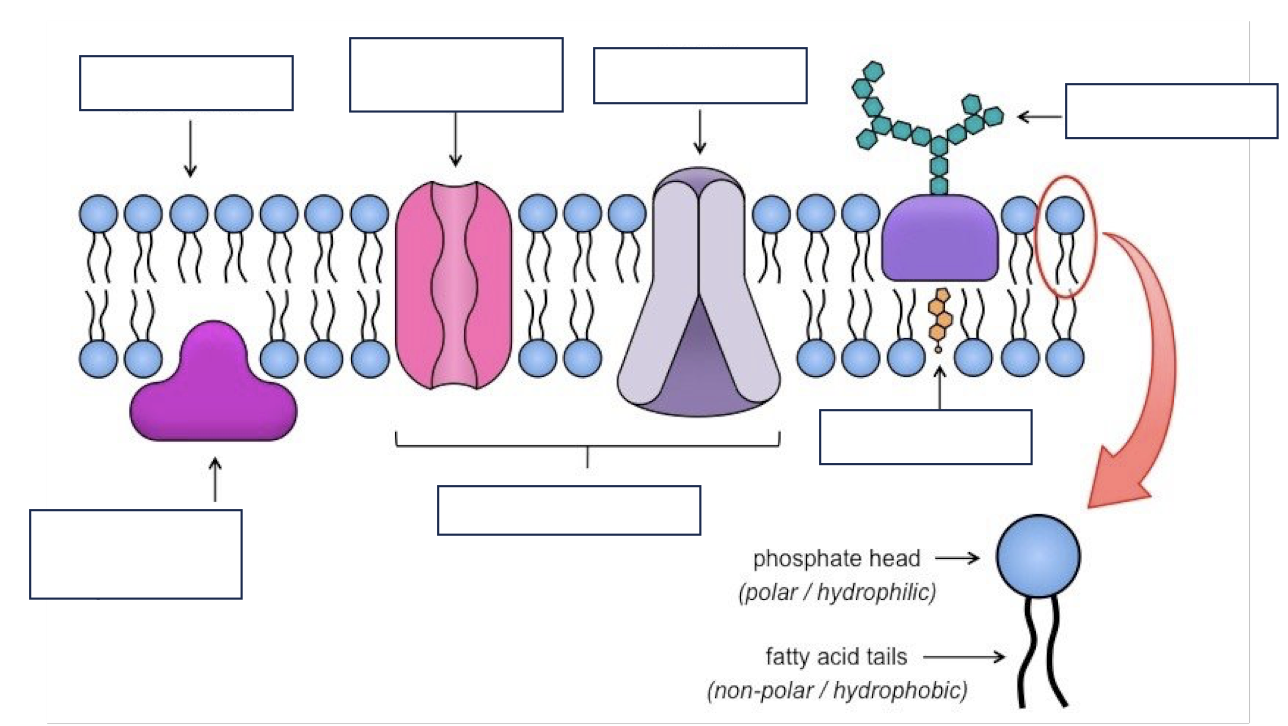
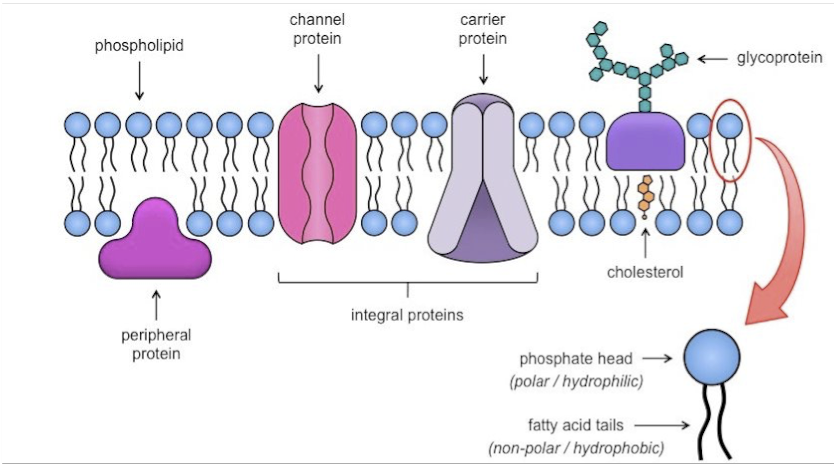
Label the diagram of a plasma membrane
Fluid
The phospholipid bilayer is viscous and individual phospholipids can move position
Mosaic
the phospholipid bilayer is embedded with protiens, resulting in a mosaic of components
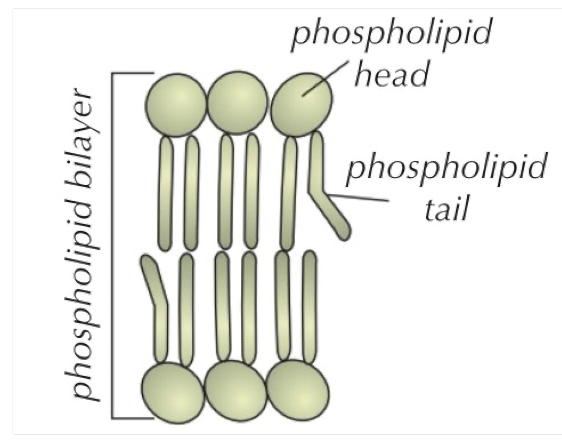
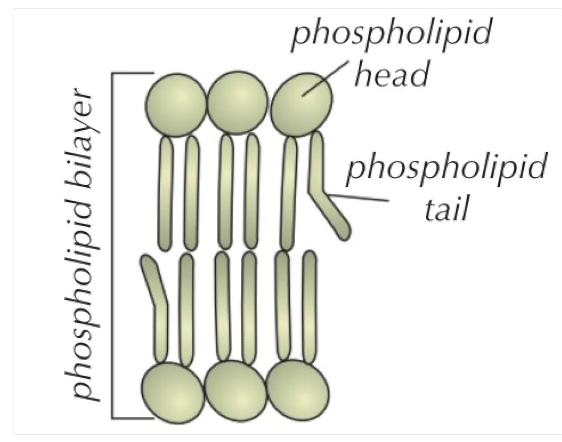
Phospholipid bilayer
The centre of the bilayer is hydrophobic so the membrane doesn’t allow water soluble substances (like ions and polar molecules) to diffuse through it
Small, non-polar and lipid soluble substances such as CO2 can diffuse through the membrane
Name the 2 types of membrane proteins:
Extrinsic - they are found on one surface of the membrane only
Intrinsic - they span the entire membrane
Protein Channels (pores)
Some proteins span the whole membrane and act as hydrophilic (allowing water soluble substances through) pores
They’re very selective and allow ions (Ca, K, etc) that travel in water into and out of the cell
Carrier Proteins
Allow substances to pass through them in facilitated diffusion e.g glucose
Act as carriers for active transport, moving substances in and out of the cell against a concentration gradient
Cholesterol
They add strength to the membranes
Very hydrophobic so prevent loss of water and ions from cells
They pull together the fatty acid tails of the phospholipids, making the membrane more rigid and ensure the membrane is less fluid at high temperatures
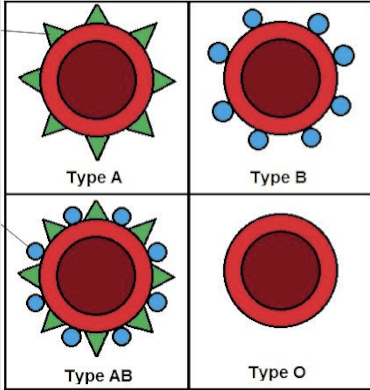
Glycolipids
Carbohydrate covalently bonded to the lipid
Extends from the bilayer into the extrinsic environment outside the cell
One type of glycolipid found in human Red Blood Cells is involved in the ABO blood type antigens
They act as recognition sites (ABO blood grouping)
Help cells attach to one another and so form tissues
Help maintain the stability of the membrane
Glycoproteins
Carbohydrate chains are attached to many extrinsic proteins
These act as cell - surface receptors more specifically for hormones
They also help cells attach to one another and allow cells to recognise one another