3. Water Balance, feedback, soil water budget, flood hydrographs
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Give 2 examples of the water cycle negative feedback?
River Flooding → Overbank Flow Deposits Sediment → Builds Up Natural Levees
Increased Evaporation → More Cloud Formation → More Reflection of Solar Radiation
Give 2 examples of the water cycle positive feedback?
Melting Ice → Lower Albedo → More Melting
Atmospheric Warming → More Evaporation → More Water Vapour → Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Give 2 examples of the water cycle dynamic equilibrium?
Seasonal River Flow - high discharge in winter seasons and low in summer balancing out. Droughts may be countered by floods
Drainage basin water budget - surpluses and deficits usually balance out from inputs and outputs.
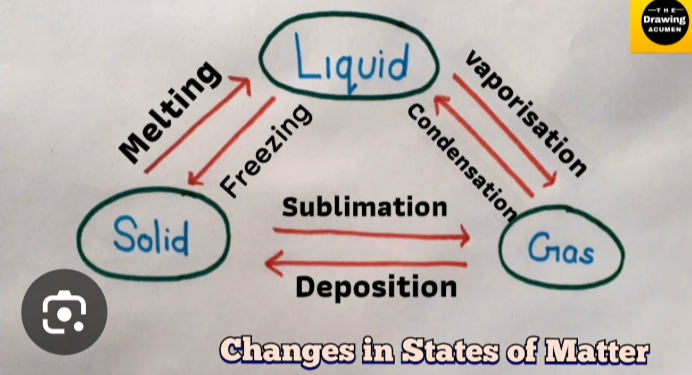
Explain the changes in matter diagram and transfers in energy?
- when freezing, deposition or condensation happens energy is RELEASED it's absorbed for all other transfers
- solid -> gas = latent heat of sublimation
liquid -> solid = latent heat of fusion
liquid -> gas = latent heat of vaporisation
What would encourage high evaporation rates?
- large amount of solar energy
- warm dry air - can hold more water vapour, dry air creates a steep humidity gradient
- plenty of available water eg: high soil moisture
What is the equation for the water balance? And what can affect the water balance?
Precipitation = total runoff + evapotranspiration +/- change in storage
Changes in seasons eg: summer to winter can lead to more run off
Explain the soil water budget graph?
Balance between inputs and outputs in the water cycle and their impact on soil water storage/availability
The maximum amount of water to be stored in the soil is the field capacity, once this is reached any further rainfall will become runoff and flood the area.
The water budget is dependent on type, depth and permeability of the soil.
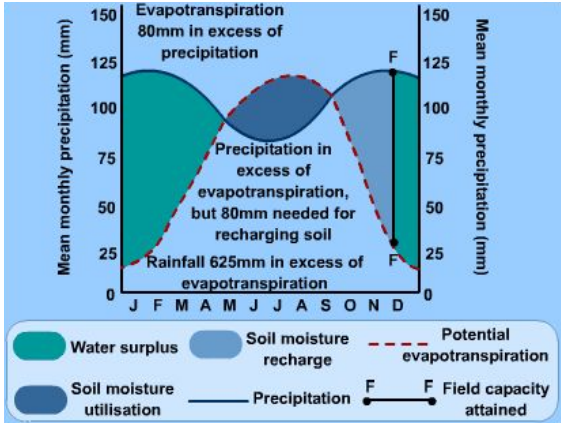
What is a water surplus and deficit?
- water surplus is when precipitation exceeds evapotranspiration, and the soil is saturated, leading to excess water that cannot be stored in the soil and becomes runoff
- water deficit is when the amount of water needed by plants (potential evapotranspiration) is greater than the amount of water available in the soil
What is the seasonal variation in the soil water budget in autumn?
greater input from precipitation than there is output from evapotranspiration
because deciduous trees lose their leaves + cooler temperatures so plants photosynthesise less
soil moisture levels increase + water surplus
What is the seasonal variation in the soil water budget in winter?
- potential evapotranspiration reaches a minimum due to cold temperatures
- precipitation refills soil water stores as well as infiltration and percolation
- more chance of flood
What is the seasonal variation in the soil water budget in spring?
- plants start to grow again so potential evapotranspiration increases as temperatures get higher and plants photosynthesise more
- water surplus still
What is the seasonal variation in the soil water budget in summer?
- hot weather leads to utilisation of soil water as evapotranspiration peaks and rainfall is at a minimum
- output from evapotranspiration is greater than input from precipitation so soil water stores are depleting -> water deficit may potentially occur
What does a flood hydrograph represent?
Rainfall for the drainage basin of a river and the discharge of the river on the same graph.
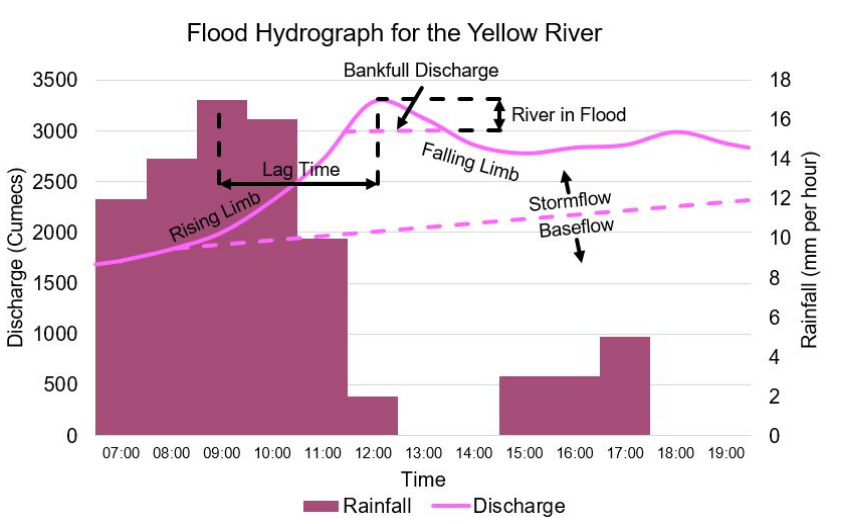
Describe the differences between a flashy and non-flashy hydrograph?
Flashy
Short lag time
Steep rising and falling limb
Higher flood risk
High peak discharge
Subdued
Long lag time
Gradually rising and falling limb
Lower flood risk
Low peak discharge
What’s the purpose of a flood hydrograph?
By analyzing the shape and peak of the hydrograph, authorities can assess flood risk and identify vulnerable areas -> this helps in designing flood defences
Reveals how characteristics like soil type, land use, and slope affect runoff and river flow.
shows how quickly a river responds to a flood
How does high rainfall intensity make flashy hydrographs?
Higher discharge potential from rivers so more likely for soil to reach its field capacity increasing surface runoff
How does antecedent rainfall make flashy hydrographs?
This rainfall occurs the day before the studied event meaning the ground may already be saturated and reached its field capacity so increased surface runoff
How does impermeable underlying geology make flashy hydrographs?
Decreased percolation so greater levels of throughflow
How does high drainage density make flashy hydrographs?
Many tributaries to the main river means a faster speed of drainage and decreased lag time
How does small basin make flashy hydrographs?
Rainfall reaches the central river quicker decreasing lag time
How does circular basin make flashy hydrographs?
Rainfall reaches the central river faster decreasing lag time because distances from the basin edge to the river channel are more equal.
How does lower temperatures make flashy hydrographs?
Less evapotranspiration so greater peak discharge
How does precipitation type make flashy hydrographs?
Snow/hail takes time to melt before moving towards the river so rainfall increases the flood risk
How does vegetation cover make flashy hydrographs?
Forested areas intercept more rainfall decreasing flood risk whereas exposed areas will transfer water to the river more rapidly decreasing lag time
How does urbanisation make flashy hydrographs?
More impermeable surfaces so runoff increases and infiltration is reduced
How does pastoral farming make flashy hydrographs?
Ground may be trampled and compacted so less interception and more surface runoff
How does deforestation make flashy hydrographs?
Less interception by trees so water reaches ground and river faster.