Cell theory & molecular mechanism of DNA processes
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What key features comprise a cell
Genetic systems allowing hereditary, replication & metabolism, compartmentatlisation
What is cell theory
All organisms are composed of one or more cells
Cells are the basic unit of life
All cells arrive from pre-existing cells —> leading back to LUCA
Theory of how life evolved in the molecular soup
Hostile volcanic environment, frequent storms including UV light and lightning that would have been catalysing reactions of atmospheric gases
Key biological precursor molecules like amino acids, sugars, nucleobases form and fall into oceans
Condensation by chance into polymers
Possibility of a polymer catalysing own replication
Self-replicating polymer would dominance molecular soup and begin evolving
Problem with DNA as the first self-replicating molecule
DNA cannot replicate itself as it requires protein catalysts
Could RNA be the first self-replicating molecule
Is not strictly self-replicating as it requires another RNA molecule to act as a template, but one RNA can make a copy of another
Catalytic RNA (ribozymes) can catalyse synthesis of a new RNA molecule
2 problems with making RNA in a molecular soup
Dilution very weak, chance of two nucleotides meeting to form a chain eventually forming RNA is very small
RNA is unstable in water. Ocean favours hydrolysis and condensation is needed to convert nucleotides to RNA
Theory of where RNA could have originated
Clay mineral layers
Why would clay mineral layers be the perfect site for prebiotic RNA
All the molecules needed to make RNA (nucleotides, nucleobases, phosphates, sugars) bind to surface of clay-silicate minerals and become concentrated together in the layers - greater chance of molecules meeting
Repeated cycles of wetting and drying, condensation becomes favoured
Problems with RNA world theory
Dependence on the wet-dry cycle, really really slow
Lots of molecules, especially lots of sugars, would be present in primordial soup —> why is RNA made out of ribose specifically
Only ticks the box of hereditary, unclear how RNA would lead to cell membrane, metabolism, and cells
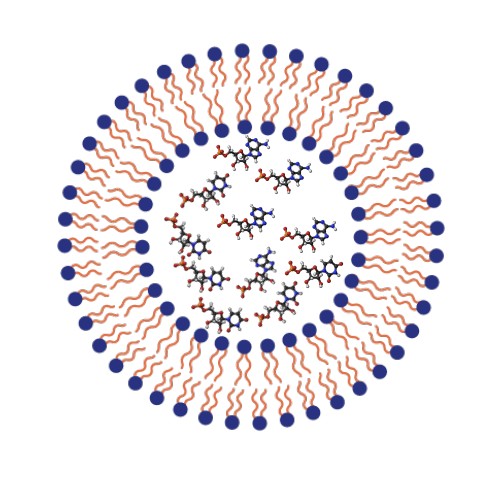
What are membranes made out of and how
Amphiphile molecules - molecule with both polar and non-polar properties
They are self-assembling, spontaneously form in the presence of water (which is polar)
Types of membrane structures
Micelles, vesicles, bilayers
Could phospholipids have formed prebiotically
No too complex, but simpler amphiphiles may have been present and self-assembled into vesicles and micelles
Evidence of membranes forming
Experiment where nucleotides and lipids heated and concentrated until total dehydration micelles formed and then fused with one another to create multilamellar films with nucleotides inside
Then after dehydration and rehydration cycles RNA molecules were formed, ending up with RNA inside vesicles
What conditions are needed for spontaneous metabolism
High temperature
High pressure
Redox active metals to act as catalysts (e.g. iron or nickel)
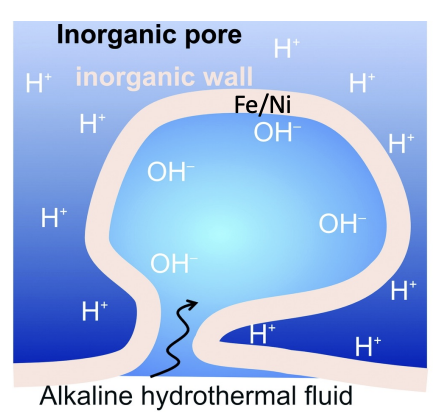
Why are alkaline smokers thought to be potential sources of life
They form due to exposure of the mantle to seawater, reaction called serpentinisation occurs forming new minerals - with minerals like iron, nickel
The reactions generates heat, hydrogen gas, hydroxide ions
There is high pressure at the bottom of the ocean
Sets up all the conditions for spontaneous metabolism - between hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide dissolved in the water
How are hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide made to react
CO2 reduced to organic hydrocarbons by the proton gradient, capturing electrons from H2. FeNiS and FeS act as catalysts
Proton gradient needs to be established so enzymes can capture electrons, done using an inorganic Fe/Ni wall with acidic seawater on the outside and alkaline hydrothermal fluid coming up
Problems with the alkaline smokers origin theory
Self-assembling molecules eventually form, wouldn’t they stop molecules interacting with the metals?
How did this basic chemistry evolve into non-enzymatic metabolism and complex molecules?
Possible process of cells forming from primitive membranes with amino acids and FeS crystals
Amino acids bind to FeS crystals
Some amino acids would be hydrophobic, could embed in cell membrane
Then act as catalyst to produce the proton gradient across the cell membrane, driving the reduction of CO2 into hydrocarbons and more amino acids and fatty acids produced
Fatty acids produced would increase the cell membrane, at one point would divide into two due to the size —> cell replication
Cells with the best catalysts (fastest growth) ‘selected’ for
It has a 2’OH group that can both accept and donate hydrogens for hydrogen bonds, allows RNA to fold into lots of different combinations.
And the 2’OH group can bind to proteins in the various RNA functions
Store information
adapt/mutate,
sense the environment,
catalyse reactions,
replicate itself
It can sense ions, temperature, pH, salt concentrations etc.
Metabolites bind to riboswitches in RNA sequence and regulate gene expressio
Ribozymes are enzymes based on RNA
Also have RNA-based ligases and polymerases
Cofactors essential for reactions and metabolism like FAD, CoA, NAD, ATP have adenosine as a base — suggesting it was a conserved element. RNA used to make proteins, is part of ribosome
Formation of proteins - levels of their structure
primary - chain of amino acids/residues
seconary - folding into a-helixes and b-sheets
tertiary - more folding due to proteins seeking lowest energy state
quaternary - multiple protein subunits arranged together
Bonding between amino acids
Peptide bond between carboxyl and amino group, formed in condensation reaction.
leads to partial double bond at both C=O and C=N giving it resonance structure, and peptide bond cannot rotate.
What is the secondary structure determined by
Steric hindrance (interactions of atoms in the molecule)
Four main interactions in the tertiary structure, and how do they fold
Hydrophobic effect, disulphide bridges, hydrogen bonds (between polar amino acids), ionic bonds (between charged amino acids)
Fold themselves or use chaperones
What is conformational change
Change of the tertiary structure and active site due to initiation, e.g. substrate binding in induced fit model
What is allosteric regulation
Binding of molecule at an allosteric site to assist uptake of substrate
What are often used as cofactors
metals
What can occur to proteins after translation
PTMs - over 200 types, reversible or not.
e.g. phosphorylation, nitrosylation, acetylation
Why are proteins better catalysts than RNA
Smaller molecular machines w/ more chemistry and detail - 20 amino acids compared to 4 bases of RNA, so better for catalysis
Downfall of proteins (compared to RNA and DNA) and why
Cannot replicate - no method to recognise different residues
Proteins can only make peptides - using non-ribosomal peptide synthases
Structure of mRNA into reading frames etc.
RNA has open reading frames (translates into functional protein) and untranslatable regions.
Three reading frames in mRNA - correct one identified using start and stop codons
Initiation sites for transcription in euks vs proks
Eukaryotes - frame begins with first AUG from the 5’ end in Kozak sequence
Prokaryotes - frame begins with AUG after Shine-Dalgarno sequence
Special property/bonding of the third base in the codon - why
Can change but still code for the same amino acid
Exhibits ‘wobble pairing’ with the corresponding base on the tRNA anticodon which can act as a ‘wobble' base’ - can move to pair with multiple bases and mRNA codons
Important as it reduces number of tRNA molecules needed
Difference between euks and proks - how many proteins genes code for
Eukaryotes - mRNA is monocistronic, each gene codes for one protein. Allos for greater regulation and diversity.
Prokaryotes - mRNA is polycistronic, genes can code for multiple proteins under same promotor and operator
Different types of mutations
Silent - doesn’t change aa sequence, change third base in codon
Missense - changes aa sequence, either first or second codon
Nonsense - cause premature termination by creating stop codon
Frameshift mutation - either insertion or deletion
Steps for tRNA biogenesis
tRNA precursors are often tandem arrays of different tRNAs, transcribed and then cleaved by RNAse P at 5’ end, and RNAse D at 3’ end
tRNA is then modified, including addition of CCA at the 3’ end - by tRNA nucleotidyl transferase, and base modifications by small nucleolar RNAs
Sometimes spliced
Structure of tRNA
Clover shaped secondary structure. Anticodon on the middle loop (one base being the wobble base).
The CCA at the 3’ end carries the activated aa
Variable loop that can change shape/twist to give some variety
Charging of tRNA / becoming carrier
Done by aminoacyl-tRNA synthase (aaRS)
Amino acid is adenylated by addition of ATP (pyrophosphate leaves, with H2O, making it condensation)
Amino acid transferred to the 3’OH of tRNA, releasing AMP
aaRS can detect if wrong aa is added, will hydrolyse bonds and start over
Structure of ribosome
Large subunit - containing peptidyl transferase, that forms peptide bonds
Small subunit - containing mRNA guide
Mixture of protein and RNA
Eukaryotes size is 80S, prokaryotes size is 70S
How many tRNAs and mRNAs are in the ribosome at one time
3 tRNAs at different sites.
A site - tRNA carrying in amino acid
P site - tRNA linked to growing aa chain, peptidyl-tRNA as peptide bond formed
E site - empty tRNA exits ribosome
One mRNA bound to ribosome
Three steps of translation in prokaryotes:
Initiation
shine-Dalgarno sequence recognised binds to rRNA on small subunit.
fMET-tRNA binds to AUG start codon, bringing in Met
Large subunit binds, placing fMET-tRNA in P site
Elongation
acyl-tRNA (tRNA with amino acid) loaded into A site
Residues from tRNAs in A and P site close causing peptidyl transfer and peptide bond formed
Ribosome shifts one codon in 3’ direction - peptide tRNA enters P site, and empty tRNA exist from E site
Termination
Release factor binds to stop codon
peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysed and product released
Both subunits and tRNAs dissociate from mRNA
RNA world relics in the production of proteins
Core activity done by RNA - mRNA, tRNA, snoRNA, rRNA, RNAse P etc.
Problem with RNA - why DNA needed
RNA generally stable but mutates spontaneously - C to U and cannot be repaired by RNA
Need for stable storage, that can encode all information
Why is DNA more stable than RNA
Has deoxyribose instead of ribose
Has no 2’OH so A=T and C=G always bond, no exceptions unlike RNA
DNA has an extra methyl - base T instead of U. So if C deaminated to U it could be easily detected
How are the building blocks of bases formed
Begin as nucleoside diphosphates
Ribonucleotide reductase removes 2’OH from NDP and kinase adds the 3rd phosphate to form deoxynucleotide triphosphate (dNTP)
Ribonucleotide reductase makes forms for all bases - dADP, dGDP etc
RNA world relic in the formation of bases
dTDP made from dUDP - uracil (and RNA) existed first
DNA replication - importance of DNA polymerase
B-clamp keeps DNA polymerase on strand until whole replication occurs. Polymerase elongates the RNA primer, synthesises 5’ to 3’
What happens with a mismatch / mistake in DNA replication
If mismatch detected, DNA polymerase can reverse - reduces replication errors
If mismatch not detected and is synthesised, the mismatched section is removed and repaired with new nucleotides. Catalysed by various DNA polymerases, lastly ligase.
Lagging strand replication
Primase binds and produces an 11nt RNA primer using the DNA template
A different DNA polymerase synthesises Okazaki fragment (around 1000 bps), RNAse H degrades the RNA primers.
Another DNA polymerase extends the Okazaki fragments, and ligase joins them
Difference in DNA replication between eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Prokaryotes - replication is continuous, single origin of replication
Eukaryotes - only replicate in S cell cycle phase, can have multiple origins
How to deal with end replication problem
Telomerase binds to and extends the parental strand - using RNA template.
Makes a telomere extension using DNA synthesis
Primase produces an RNA primer, DNA polymerase extends the primer and ligase connects the phosphate backbone
RNA polymerase activity in transcription
Synthesises from 5’ to 3’ (like DNA polymerase) but uses dsDNA template
Starts from an initiation site, without a primer
Energy for mRNA synthesis and DNA unwinding comes from pyrophosphate release - condensation reaction forming the mRNA strand
Transcription initiation in prokaryotes
sigma factor of RNAP scans DNA and recognises two upstream motifs - Pribnow at -35 and TATA at -10
RNAP unwinds 17bp, creating a transcription bubble where RNA synthesis starts
Sigma factor dissociates, RNAP produces mRNA
Transcription initiation in eukaryotes
DNA has multiple upstream promoters - but core promoter is the TATA box (others are regulator elements, enhancer sequences).
TATA binding protein (subunit of TFIID) binds to TATA box, recruits TFIIA and TFIIB (transcription factors)
TFIIB recruits RNA polymerase II and TFIIF. TFIIE joins and recruits TFIIH (carries out helicase activity).
When upstream regulatory elements give the signal - transcription bubble forms and RNA polymerase II is phosphorylated
RNA polymerase II dissociates from TFIID and begins transcribing
What is on the 5’ end of transcribed mRNA after transcription - euks & proks
Prokaryotes - triphosphate purine (G or A)
Eukaryotes - 5’ cap - N&-methyl-guanidine-5’-triphosphate (required for splicing, translation, and stability)
Termination of transcription in prokaryotes
Can be rho independent or dependent
Rho-independent - termination signals in the 3’UTR of mRNA cause NusA to produce a hairpin (loop) that interferes with and terminates RNAP
Rho-dependent - rho binds to the rho-utilisation site (rut) and the collision of rho and RNAP terminates transcription
Termination of transcription in eukaryotes
polyA signal leads to cleavage by endonuclease downstream, terminating polymerisation.
Poly-A polymerase then adds a polyA tail to increase RNA stability
What process can happen after transcription - describe it
Splicing to remove intron sequences in the pre-mRNA
Bases in the intron react with each ohter, forming a lasso that removes itself from the RNA - leaving only exons.
Catalysed by the spliceosome (ribozyme) - formed of 5 small nuclear RNAs with proteins
List the extra regulatory steps for eukaryotes - done to mRNA
5’ cap, poly-A addition, splicing, export