Darwinian Evolution: Descent, Natural Selection, and Evidence
1/264
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
265 Terms
What is the main idea of Darwin's theory of evolution?
Descent with modification, proposing that Earth's species are descendants of ancestral species that were different from present-day species.
What are the three key observations about life illustrated by the headstander beetle?
1. Organisms are suited for their environments. 2. There are shared characteristics (unity) of life. 3. There is a rich diversity of life.
What significant publication did Charles Darwin release in 1859?
On the Origin of Species.

What does the term 'evolution' refer to in a narrow sense?
A change in the genetic composition of a population from generation to generation.
How can evolution be viewed in two related ways?
As a pattern (revealed by scientific data) and as a process (mechanisms producing the observed pattern).
What role did paleontology play in Darwin's understanding of evolution?
It provided evidence from fossils that indicated changes in species over time and the occurrence of extinctions.
Who was Georges Cuvier and what was his contribution to evolutionary thought?
A French scientist who studied fossils and noted that older strata contained dissimilar fossils compared to current life forms, inferring that extinctions were common.
What is the scala naturae?
A concept proposed by Aristotle that arranged life forms on a ladder of increasing complexity, viewing species as fixed and unchanging.
What classification system did Carolus Linnaeus develop?
A nested classification system grouping similar species into increasingly general categories, using a binomial format for naming species.
What did Darwin argue about classification of species?
That classification should be based on evolutionary relationships rather than the pattern of creation.
What was the significance of the observations made by Darwin during his travels on the HMS Beagle?
They influenced his understanding of species variation and adaptation, contributing to his formulation of the theory of evolution.
What is meant by 'natural selection' in the context of evolution?
The process by which individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to adaptations in populations over time.
What does the term 'unity of life' refer to?
The shared characteristics among diverse organisms that indicate common ancestry.
What is the significance of the term 'descent with modification'?
It encapsulates the idea that species evolve over time, with changes passed down from ancestors.
How did the work of Thomas Malthus influence Darwin?
Malthus's ideas on population growth and resource limitation helped Darwin understand the struggle for existence among species.

What evidence supports the theory of evolution?
An overwhelming amount of scientific evidence from various disciplines, including biology, geology, and genetics.
What is the role of ongoing discoveries in the study of evolution?
They help refine and test our understanding of evolutionary patterns and processes.
What is the relationship between evolution and the environment?
Evolution is influenced by environmental factors, which include both physical surroundings and interactions with other organisms.
What does the term 'adaptation' mean in evolutionary biology?
A trait that enhances an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
What was one of the major influences on Darwin's development of his theory?
The work of earlier scientists, including Aristotle, Linnaeus, and Cuvier, as well as his observations during his voyage on the HMS Beagle.
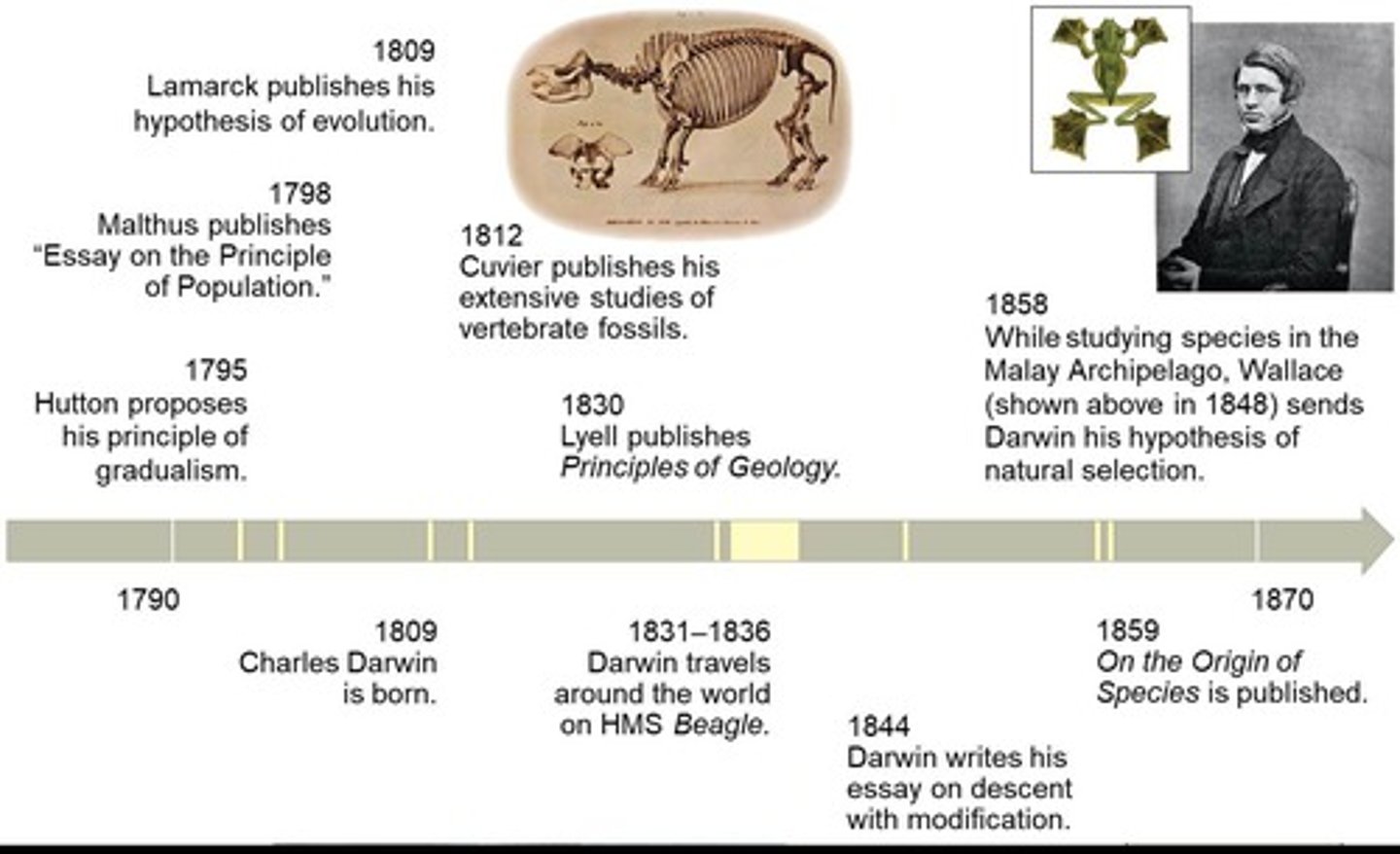
What can be inferred from the fossil record regarding species?
That species have changed over time, with some appearing and others going extinct.
What did Darwin propose about the relationship between species?
That species are related through common ancestry and that their similarities and differences arise from evolutionary processes.
What principle did Cuvier advocate regarding geological events?
Catastrophism, which suggests that past events occurred suddenly and were caused by mechanisms different from those operating in the present.
What did Cuvier speculate about the boundaries between strata?
He speculated that each boundary represented a catastrophe that destroyed many species, which were later repopulated by different species immigrating from other areas.
Who proposed the idea of gradual mechanisms explaining Earth's geologic features?
Lyell proposed that Earth's features could be explained by gradual mechanisms still operating today.
What is the principle of uniformitarianism, and who formulated it?
The principle of uniformitarianism, formulated by Thomas Hutton, states that the same geologic processes are operating today as in the past and at the same rate.
How did Hutton and Lyell influence Darwin's thinking?
Their ideas suggested that if geologic change results from slow processes, then Earth must be much older, leading Darwin to consider gradual biological changes.
What was Lamarck's contribution to evolutionary theory?
Lamarck proposed that life evolves as environments change and introduced the concepts of use and disuse and inheritance of acquired characteristics.

What is the concept of 'use and disuse' as proposed by Lamarck?
The idea that parts of the body that are used become larger and stronger, while those not used deteriorate.
What does 'inheritance of acquired characteristics' mean in Lamarck's theory?
It means that organisms could pass modifications acquired during their lifetime to their offspring.
What was the primary mission of the HMS Beagle voyage?
To chart poorly known stretches of the South American coastline.
What observations did Darwin make during his voyage on the Beagle?
He observed and collected diverse South American plants and animals, noting their adaptations to various environments.
How did Darwin's observations challenge the idea of species permanence?
Darwin noted that species in South America resembled each other more than those in Europe, suggesting that species are not fixed and can change over time.
What did Darwin conclude about the age of the Earth based on Hutton and Lyell's ideas?
He concluded that Earth must be much older than the previously accepted age of a few thousand years.
What did Darwin find significant about the fossils he discovered?
He found that the fossils were distinctly South American and different from living species, indicating a historical connection to current organisms.
What misconception about evolution is Lamarck primarily remembered for?
He is remembered for proposing the incorrect mechanism of evolution through inheritance of acquired characteristics.
What did Darwin think about the gradual change in biological evolution?
He reasoned that slow and subtle processes could produce substantial biological change, similar to geological changes.
What was the significance of the sedimentary rock layers in Darwin's observations?
They contained fossils that provided evidence of the chronological series of life forms and their evolution over time.
What role did John Henslow play in Darwin's career?
Henslow was Darwin's botany professor and recommended him to Captain FitzRoy for the HMS Beagle voyage.
What did Darwin observe about the relationship between South American species and European species?
He observed that South American species were more similar to each other than to European species, suggesting a unique evolutionary path.
What did Darwin collect during his time on the Beagle?
He collected thousands of plants and animals, which he studied to understand their adaptations to different environments.
What did Lamarck correctly believe about the evolution of the giraffe?
He believed that giraffes evolved long necks because they stretched to reach higher leaves, and this trait was inherited by their offspring.
What did Darwin's findings on the Beagle lead him to question?
They led him to question the permanence of species and consider the mechanisms of evolution.
What was a key difference between Cuvier's and Darwin's views on species?
Cuvier denied that species evolve, while Darwin proposed that species change over time through natural selection.
What was the name of the ship Darwin traveled on during his voyage?
HMS Beagle
What geological concept did Darwin study during his voyage?
Geology, particularly the principles outlined in Lyell's 'Principles of Geology'
What significant geological event did Darwin experience in Chile?
A violent earthquake that raised coastal rocks several feet
What did Darwin infer from finding ocean fossils high in the Andes?
That the rocks containing the fossils had been raised by earthquakes
What was the geographic location of the Galápagos Islands?
About 900 km west of South America, near the equator
What unique observation did Darwin make about the finches on the Galápagos Islands?
They seemed to be different species, some unique to individual islands
What hypothesis did Darwin propose regarding the Galápagos species?
That they were colonized by organisms from South America that then diversified
What is adaptation in the context of Darwin's theory?
Inherited characteristics that enhance survival and reproduction in specific environments
What process did Darwin identify as a mechanism for evolution?
Natural selection
What did Darwin conclude about the relationship between adaptation and the origin of new species?
They are closely related processes, with new species arising from ancestral forms through adaptations
What did Darwin publish in 1844?
A long essay on descent with modification and its underlying mechanism, natural selection
Who urged Darwin to publish his ideas on evolution?
Alfred Wallace
What was the name of the manuscript Darwin received from Alfred Russel Wallace?
A manuscript outlining a hypothesis of natural selection nearly identical to Darwin's
What was the title of Darwin's book published in 1859?
On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection
What did Darwin's book aim to explain?
The unity of life, diversity of life, and the match between organisms and their environments
How did Darwin view the history of life?
As a tree with multiple branchings from a common trunk, representing evolution
What did Darwin believe about the common ancestor of all organisms?
That all organisms share many characteristics due to descent from a common ancestor
What are the three broad observations about nature that Darwin's theory addresses?
The unity of life, the diversity of life, and the match between organisms and their environments
What did Darwin realize was essential to understanding evolution?
Explaining how adaptations arise
What did Darwin's observations of Galápagos finches reveal?
Their beaks and behaviors are adapted to the specific foods available on their home islands
What did Darwin's theory ultimately convince most scientists of?
That life's diversity is the product of evolution
What was the significance of Darwin's logical presentation of his ideas?
It helped convince scientists of the validity of evolution where previous theories had failed
What did Darwin mean by 'descent with modification'?
The idea that organisms accumulate diverse modifications over time as they adapt to various environments
What role did Alfred Russel Wallace play in the history of evolutionary theory?
He independently developed a hypothesis of natural selection and prompted Darwin to publish his work
What did Darwin's sketches illustrate about evolution?
The branching pattern of evolution, representing common ancestry and diversification
What term did Darwin never use in the first edition of The Origin of Species?
Evolution
How did Linnaeus contribute to the understanding of biological classification?
He organized the diversity of organisms into 'groups subordinate to groups', which aligned with Darwin's hypothesis of descent from common ancestors.
What does the term 'descent with modification' refer to?
The process by which species evolve over time, branching from common ancestors.
What is the significance of fossils in understanding evolution?
Fossils of extinct species can document the divergence of present-day groups by filling in gaps between them.
What does Darwin's tree diagram illustrate?
The branching history of life, showing relationships among species and highlighting extinct lineages.
What is artificial selection?
The process by which humans breed plants and animals for desired traits, leading to significant changes over generations.
What are the two key observations Darwin made regarding natural selection?
1) Members of a population often vary in their inherited traits. 2) All species can produce more offspring than their environment can support.
What is inference #1 from Darwin's observations?
Individuals with inherited traits that enhance survival and reproduction tend to leave more offspring.
What is inference #2 from Darwin's observations?
The unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce leads to the accumulation of favorable traits in the population over generations.
What connection did Darwin make between natural selection and overpopulation?
He realized that the potential for overpopulation drives competition for resources, influencing survival and reproduction.
How does natural selection lead to adaptation?
Natural selection favors traits that enhance survival in a given environment, leading to adaptations over generations.
What is the estimated percentage of species that have ever lived and are now extinct?
Over 99% of all species that have ever lived are now extinct.
What role do heritable traits play in natural selection?
Heritable traits influence an organism's performance and its offspring's ability to cope with environmental challenges.
What is the outcome of natural selection over time?
An increase in the frequency of individuals with favorable adaptations in a population.
What did Darwin conclude about the speed of evolutionary changes?
If artificial selection can cause rapid changes, then natural selection can also lead to significant modifications over many generations.
What is the relationship between natural selection and environmental changes?
Natural selection can result in adaptation to new conditions, potentially leading to the emergence of new species.
What is the main idea of natural selection?
It is a process where individuals with certain heritable traits survive and reproduce at higher rates than others.
How does natural selection affect the match between organisms and their environment?
Over time, it increases the match between organisms and their environment, enhancing survival and reproduction.
What is the significance of Thomas Malthus's essay to Darwin's theory?
Malthus's ideas on population growth and resource limitations influenced Darwin's understanding of competition and natural selection.
What is an example of artificial selection in agriculture?
Breeding different varieties of vegetables from a single species of wild mustard.
What does the concept of descent with modification explain about the unity of life?
It illustrates how diverse species share common ancestors, reflecting both unity and diversity in life.
What is the primary mechanism through which evolution occurs?
Natural selection
Do individuals evolve or do populations evolve?
Populations evolve over time, not individuals.
What type of traits can natural selection amplify or diminish?
Heritable traits that differ among individuals in a population.
What happens if all individuals in a population are genetically identical for a trait?
Evolution by natural selection cannot occur.
What are the four types of data that document the pattern of evolution?
Direct observations of evolution, homology, the fossil record, and biogeography.
What is an example of direct observation of evolutionary change?
The adaptation of soapberry bugs to different food sources.
How do soapberry bugs demonstrate natural selection?
Their beak lengths evolved to match the depth of seeds in different fruit types.
What was the prediction about soapberry bugs feeding on goldenrain trees?
Natural selection would result in shorter beak lengths compared to those feeding on balloon vines.
What was the conclusion of the soapberry bug study regarding beak length?
Beak lengths were shorter in populations feeding on the introduced goldenrain tree.
What is an example of ongoing natural selection affecting humans?
The evolution of drug-resistant bacteria.