Media Theories
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Aice media studies
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Theory of Media Language
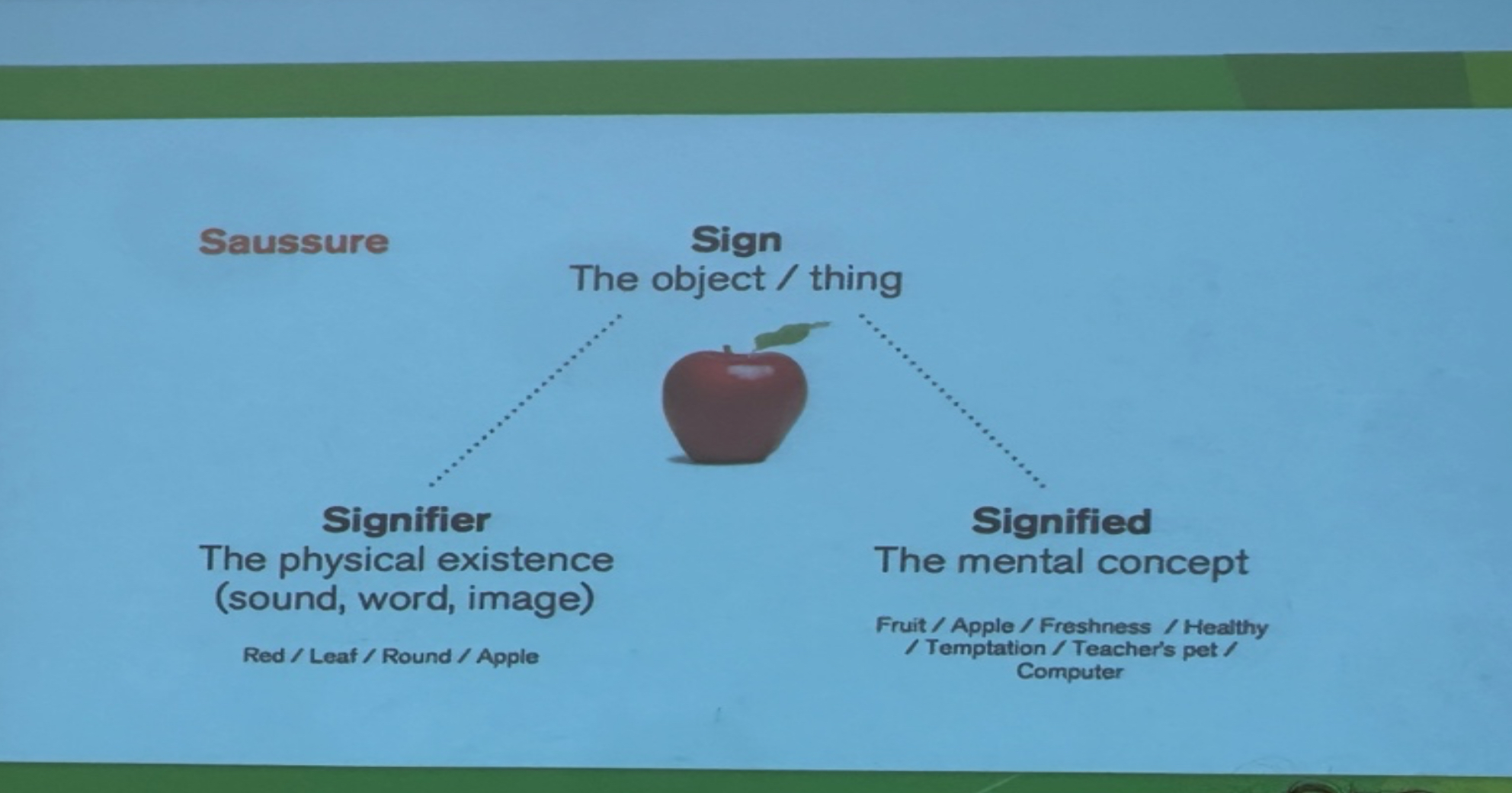
Semiotics
Roland Barthers
The study of signs and meaning texts communicate their ideas through signification
Signs that function at a literal level (signifier, denotation) as well as a figurative level (signified, connotation)
Exposure to certain symbolic constructions can become self-evident, as the sign becomes myth through naturalization.
Narratology
Tzvetan Todorov
All narratives share a basic structure, moving from one equilibrium to another
These 2 states of equilibrium are separated by disruption or imbalance. The way that narratives resolve can have ideological significance

Genre Theory
Steve Neale
Genre are dominated by repetition of codes and conventions but also incorporate differences variation and change.
Genres change as they borrow from overlap with each other (hybridity and subgenres)
Genres exist within specific economic, institutional and industrials contexts
Structuralism
Claude LeviStrauss
Texts can be understood through an analysis of their underlying structure
Meaning is often produced through oppositional pairs (e.g. good vs. evil) The resolution of these binary opposites can have ideological significance.
Postmodernism
Jean Beaudrillard
The boundaries between the “real” and the “mediated” worlds have collapsed
Signs are a process of signification with no signifier underlying them; they no longer refer to anything “real” or “literal”
Mediated images now seem more “real” than the reality they supposedly represent (hyperreality)
Views media as a site of power and ideology, and questions traditional narratives and interpretation. Postmodernist media often emphasizes style over substance, and challenges the idea of objective reality.
Key aspects of postmodernist media
Intertextuality: Blending different media forms
self-referentiality: Acknowledging the artificiality of media
Pastiche: Blending high and low culture
Irony and paradox: Using irony to challenge aspected narrative
Breaking the fourth wall: Drawing attention to filmmaking process
Parody: Using parody to subvert expectations
Theories of Representation
The Theory of Representation
Stuart Hall
Representation is the production of meaning through language ( a system of signs)
Stereotyping reduces people and things to a few simple characteristic or traits
Stereotyping tends to occur where there is a disparity of power, with subordinated/excluded groups being different or “other”
Preferred/ dominant reading: The way media producers want to interpret the text. The type of reading will be culturally dependent
Theories of Identity
David Gauntlett
Media helps us to construct our identities
Media provides us with ‘tools’ and resources that we use to shape our identities.
In the past, these media toolboxes were simple; as the mediated world has become more complicated, we now have a wide range of media models - a pick - and-mix of different ideas that we can choose from
Postcolonial Theory
Paul Gilroy
Exploring the legacy of colonialism and imperialism
Colonial discourses continue to inform contemporary attitudes to race and ethnicity
“Civilisationism” constructs racial hierarchies and sets up binary oppositions based on notions of “other”ness
Like you are at an party (formal) you think of things like tuxedo, gowns (influence from European countries)
Feminist Theory
Liesbet van Zoonen
Gender is constructed through discourse
Gender, as a product of discourse, changes depending on cultural and historical context.
The objectification of women’s bodies is core to Western patriarchal culture. The codes used in mainstream media to construct the male body are different from the mediated/objectified female body.
Ex: Now high heels make us think women. However, in old times in France for instance, it would think men.
Industry Theories
Power and Media Industries Theory
James Curran and Jean Seaton
Media is driven by the logic of power and profit
Media is controlled by a small number of companies primarily concerned with gaining profit and power
Media concentration typically inhibits or limits variety, creativity and quality.
Socially diverse patterns of ownership help to create conditions for more varied and adventurous media products
Regulation Theory
Sonia Livingstone and Peter Lunt
There is an underlying struggle between the end to further the interests of citizens (protection from harmful material) and the interests of consumers (choice, value, competition)
The rise of media conglomerations and the emerging production, distribution and marketing of digital media have placed traditional approaches to media regulation at risk.
Cultural Industries Theory
David Hesmondhalgh
Media companies try to minimize risks and maximize audiences through vertical and horizontal integration and the form of their media/cultural products (through genre, serial format and by including stars)
The largest companies and conglomerates now operate across a number of media industries. The internet, and its radical potential, has been partially contained by its incorporation into large, profit-oriented cultural companies
Media Effects Theory
Albert Bandura
Media is capable of implanting ideas directly into the minds of its audience
Audience respond to the modeling in media, an thereby, acquire new attitude, styles of conduct and emotional responses
Media representation of transgressive or antisocial behavior can lead audience members to imitate those forms of behavior
Cultivation Theory
George Gerbner
Repeated exposure to patterns of representation over long periods of time can shape and influence the way the audience perceives the world around them (i.e. by cultivating particular points of view and opinion
Cultivation reinforces mainstream, or dominant, values, and ideologies
Reception Theory
Stuart Hall
Communication is a process involving encoding by producers and decoding by the audience
There are 3 hypothetical positions from which meanings can be decoded
1. The Dominant-hegemonic position: The encoder’s intended meaning is fully understood and accepted
2. The negotiated position: The legitimacy of the encoder’s message is acknowledged but the message is adapted to better fit the decoder’s individual experiences or context
3. The oppositional position: The encoder’s message is understood, but the decoder disagrees with it, reading it in a contrary or oppositional way.
Fandom Theory
Henry Jenkins
Fans are active participants in the construction and circulation of textual meanings. Fans also appropriate texts and read them in ways that are not fully authorized by the media producers (“textual poaching”)
Fans construct their social and cultural identities by borrowing and inflecting mass culture images and participate in a culture that offers a vital social dimension.
End of Audience Theory
Clay Shirky
The internet and digital technologies have a profound effect on the relations between media and individuals
In the age of the internet, audience members or no longer passive consumers or mass media content: consumers now have the ability to “speak back to media in various ways.
Media Consumers engage in the creating and sharing of content with one another