APHG Unit 1 CED Vocabulary - Thinking Geographically
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Human Geography
study of people AND places: how we make places, how we organize space and society, how we interact with each other in places and across spaces, how we make sense of others and ourselves in our localities, regions, & the world
reference maps
maps used to show locations of landforms and/or places
physical map
reference map that shows identifiable natural landmarks such as mountains, rivers, oceans, elevation
political map
reference map that shows political boundaries
e.g. countries, cities, capitals, etc.
thematic maps
maps used to display specific types of information (theme) pertaining to an area
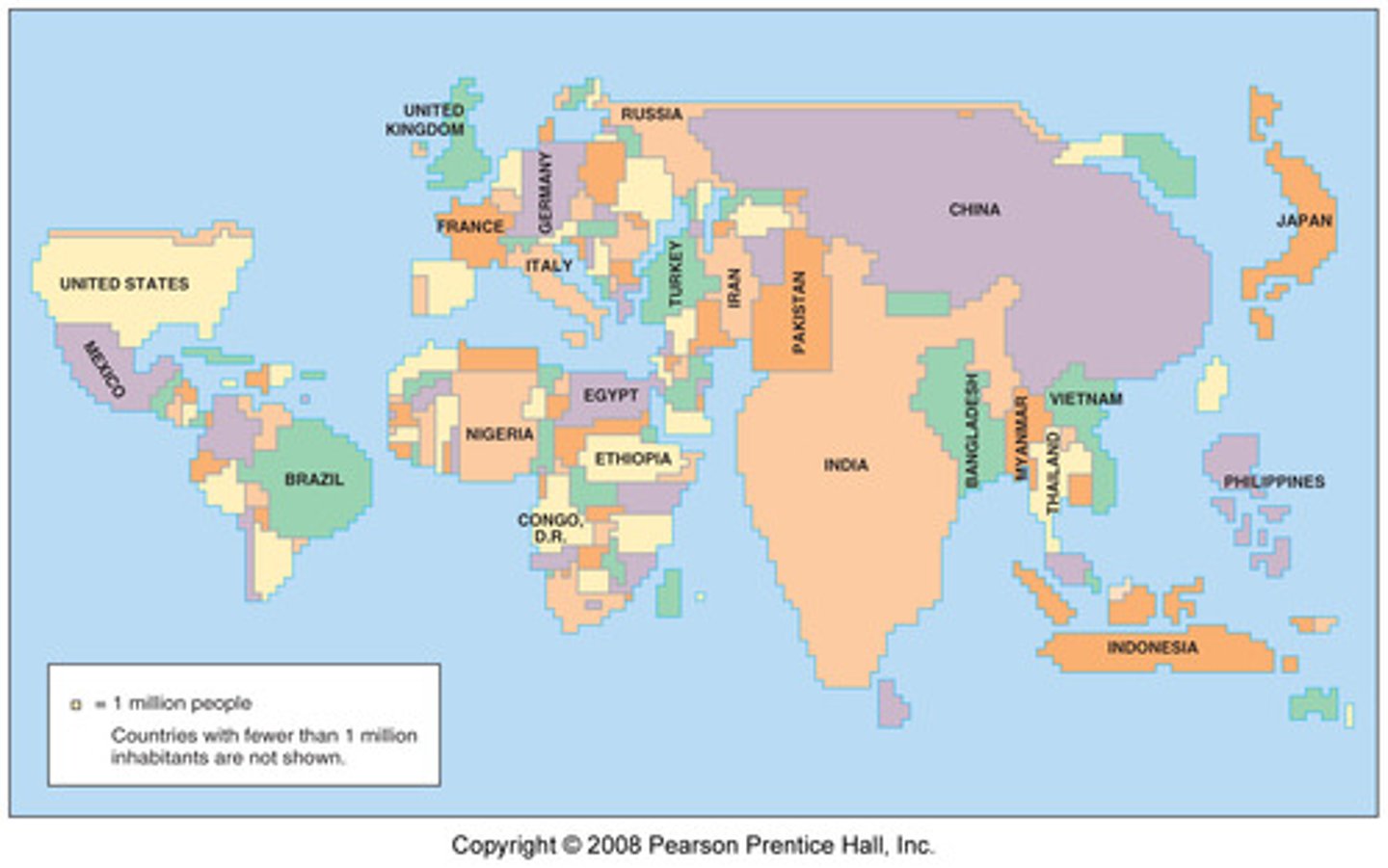
cartogram
thematic map that shows statistical data by transforming space
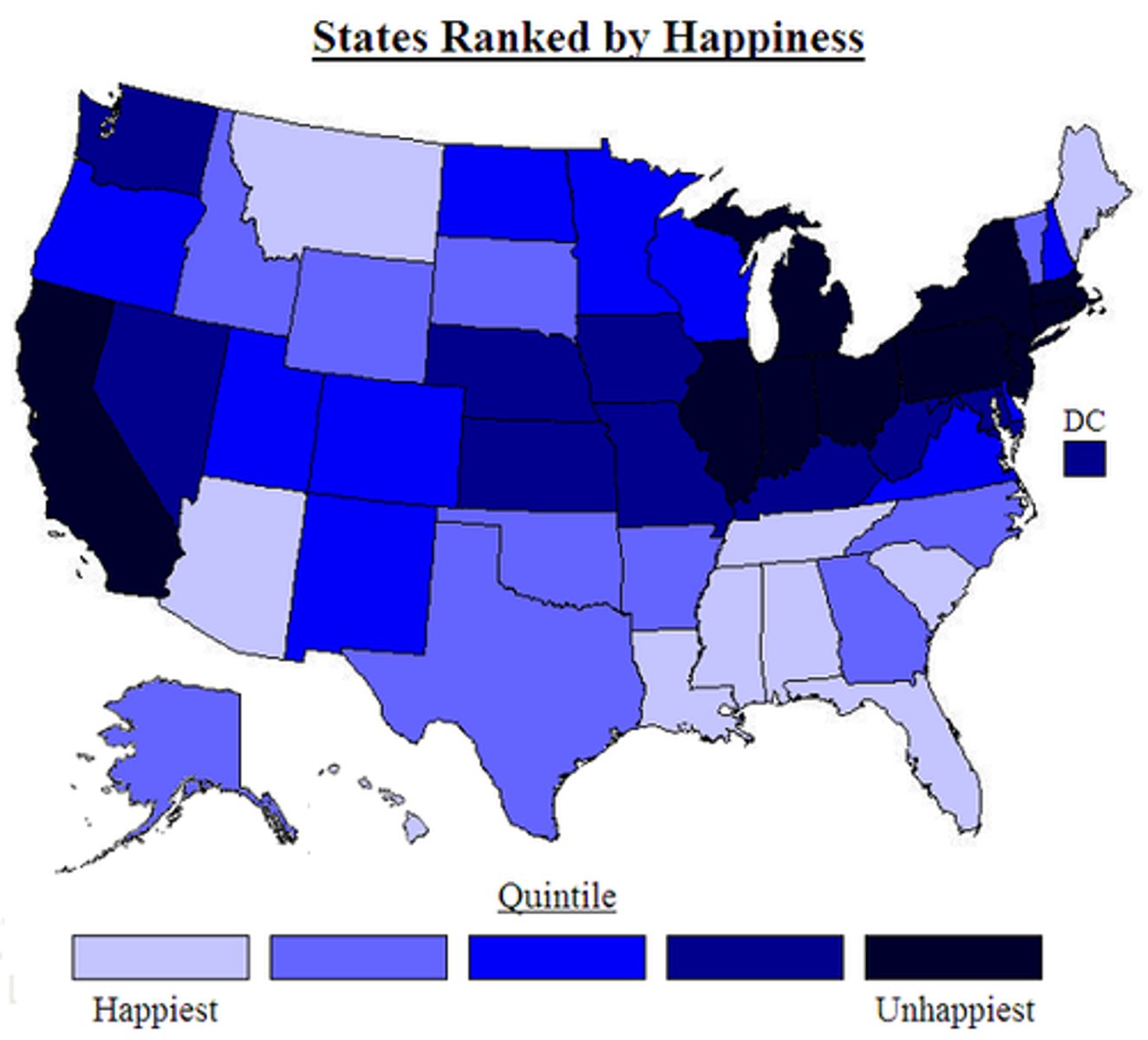
choropleth map
thematic map that uses shading or coloring to show statistical data
dot density map
thematic map that uses dots to indicate a feature or occurrence
graduated symbols map (proportional symbols map)
thematic map that indicates relative magnitude of some value for a geographic region in which the symbol varies in proportion to data
absolute distance
measurement of distance using a standard unit of length
relative distance
measurement of the social, cultural, and/or economic connectivity between places (how connected or disconnected)
absolute direction
finding a location using compass/cardinal direction
relative direction
finding a location without using compass direction
spatial pattern
the way things are laid out and organized on the surface of the Earth
clustering
objects that form a group
dispersal
objects that are scattered
elevation
height above sea level
spatial (geographic) scale
hierarchy of spaces (global, regional, national, local)
map distortion
all maps are distorted as a result of projecting a 3-dimensional surface onto a 2-dimensional surface in area, distance, shape, and/or direction
map projection
a way to transfer the 3-dimensional earth onto a 2-dimensional map to reduce distortion in area, distance, shape, and/or direction
geographic data
information that identifies the geographic location of features and boundaries on earth (natural and constructed)
geospatial technologies
technology that provides geographic data that is used for personal (navigation), business (marketing), and governmental (environmental planning) purposes
GIS (Geographic Information System)
- map created by a computer that can combine layers of spatial data
- data is displayed and analyzed to gain insights into geographical patterns/relationships
e.g. vulnerability of the Florida Aquifer, school boundaries, crime rates
satellite navigation systems
system of satellites that provide geo-spatial positioning (GPS)
remote sensing
collecting data with instruments that are distant from the area of study
online mapping and visualization
compilation and publication of web sites that provide graphical and text information in the form of maps/visuals
census data
systematically acquiring and recording information about the members of a given population
satellite imagery
images of earth collected by satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world
absolute location
describes the precise location of a place using the Earth's Graticule (latitude & longitude)
relative location
describes the location of a place relative to other human and physical features
space (geography)
relational concept that acquires meaning and sense when related to other concepts
place
describes an area on the surface of the Earth with distinguishing human & physical characteristics
pattern
an arrangement of objects on earth, including the space in between those objects
human-environment interaction
describes the ways humans modify or adapt to
the natural world
distance decay
the idea that the likelihood of interaction/influence diminishes with increasing distance
time-space compression
term that refers to the increasing sense of connectivity that seems to be bringing people closer together even though their distances are the same
time space convergence
term that refers to the greatly accelerated movement of goods, information, and ideas during the 20th century made possible by technological innovations e.g. TV, internet, satellite communication
movement (geography)
describes the ways in which people, goods, and ideas move from place to place
flows (geography)
movement in a steady stream
globalization
the process of increased interconnectedness among countries most notably in the areas of economics, politics, and culture
network
a system of interconnected people or things
sustainability
meeting an increased demand for resources (energy, food, fuel) in a way that protects the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
natural resources
something found in nature and is necessary or useful to humans
land use
the function of land
environmental determinism
theory that a society is formed and determined by the physical environment, especially the climate; the physical environment predisposes societies towards particular development; human society development is controlled by the environment
possibilism
theory that the environment sets certain constraints or limitations but people use their creativity to decide how to respond to the conditions of a particular natural environment
spatial scale
analyzing data at a variety of scales-global, regional, national, local
scale of data (scale of analysis)
analyzing data at different scales reveals variations/different interpretations of data
region
describes an area on Earth marked by similarity in some way (a way to organize space)
regionalism
refers to a group's perceived identification with a particular region
formal region
region marked by a shared trait (cultural, physical, etc.)
functional region
region marked by a particular set of activities that occur
perceptual/vernacular region
region that exists as an idea or as part of someone's "mental map"
regional boundaries
transitional and often contested and overlapping
regional analysis
analyzing regions at a variety of scales-global, national, local