Bio104 unit 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
woooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
Law of Tolerance
populations have optimal survival conditions within critical minimal and maximal thresholds.
2
New cards
\
autotroph
autotroph
Organisms that can produce their own food using energy from the sun or chemicals are called autotrophs. They are also known as producers and form the base of the food chain. Examples include plants, algae, and some bacteria.
3
New cards
Biome
an area classified according to the species that live in that location
4
New cards
Carrying Capacity
The size of a population allowed by all of the limiting factors
5
New cards
Commensalism
Relationship between two organisms where one benefits and the other does not benefit but is not harmed
6
New cards
Limiting Factors
Anything that constrains a population and slows or stops it from growing.
7
New cards
Deciduous
Trees that annually lose their leaves
8
New cards
Density
Concentration of individuals within a species in a specific locale.
9
New cards
Dispersion
the scattering of organisms over periods within a given area or over the Earth.
10
New cards
Distribution
How a population is spread out throughout their habitat.
11
New cards
Fecundity
An individuals ability to reproduce
12
New cards
Heterotroph
an organism that cannot produce its own food and relies on consuming other organisms or organic matter to obtain nutrients and energy
13
New cards
R strategist
Lives in an unstable and unpredictable environment, many offspring, low survival rate
14
New cards
K strategist
Lives in stable environment, few offspring, high survival rate
15
New cards
Type 1 Survivorship curve
\
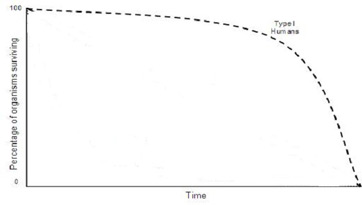
16
New cards
Type 2 Survivorship curve
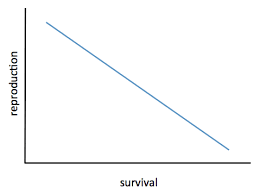
17
New cards
Type 3 Survivorship curve
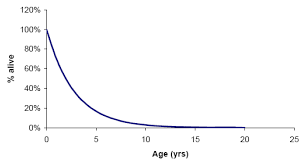
18
New cards
Mutualism
An interaction between two or more organisms where both have a net benefit.
19
New cards
mychorrizae
fungi that have a symbiotic relationship with the roots of many plants, fungal root
20
New cards
Parasitism
A relationship between organisms when one lives on or inside of the other and harms it while gaining for itself