SHS 300 - Intro to Basic Concepts
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
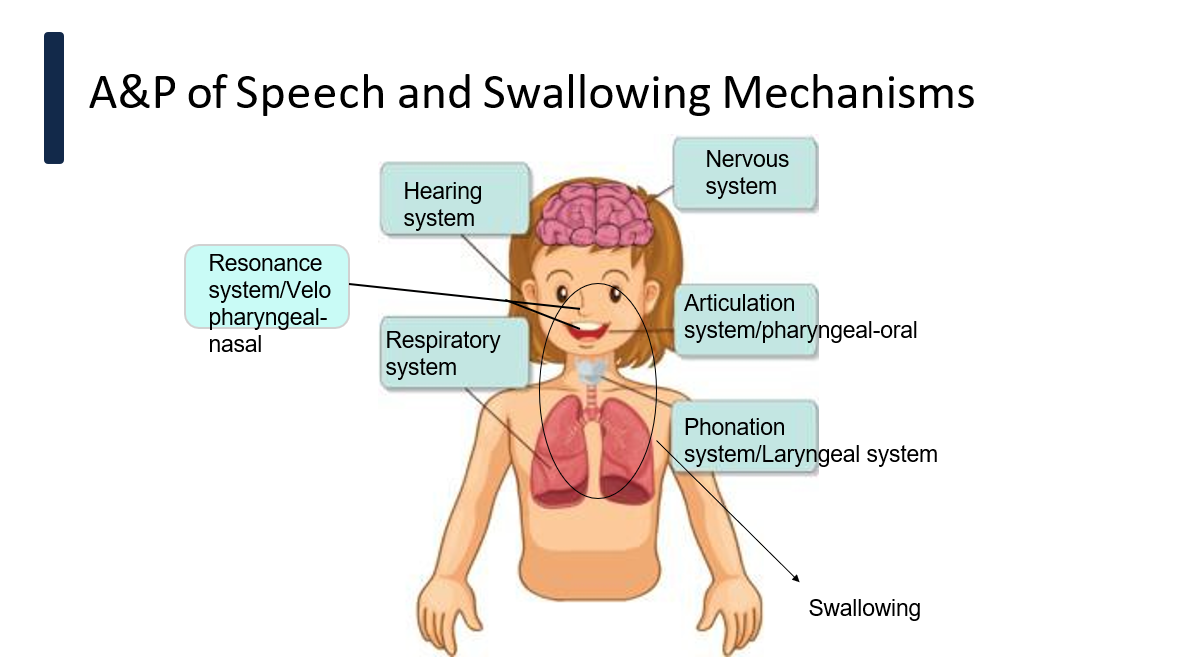
systems involved in speech and swallowing
nervous system
respiratory system
phonation/laryngeal system
resonance/velopharyngeal-nasal system
articulation/pharyngeal-oral system
hearing system
basic anatomical position (describe)
POV: body of observation; NOT the perspective of the observer
requirements:
standing erect and at rest
feet are hip-distance apart
arms are rotated outwards (palms face FORWARD); thumbs are pointed AWAY from the body
arms are slightly out from the body (hands do NOT touch the sides)
importance: establishes a universal standard which ensures that communication among professionals is clear and consistent
superior/rostral
towards the head
inferior/caudal
towards the feet
proximal
closer to the trunk of the body
distal
farther from the trunk of the body
medial
towards the midline
lateral/peripheral
away from the midline
anterior/ventral
towards the front (of the body)
posterior/dorsal
towards the back (of the body)
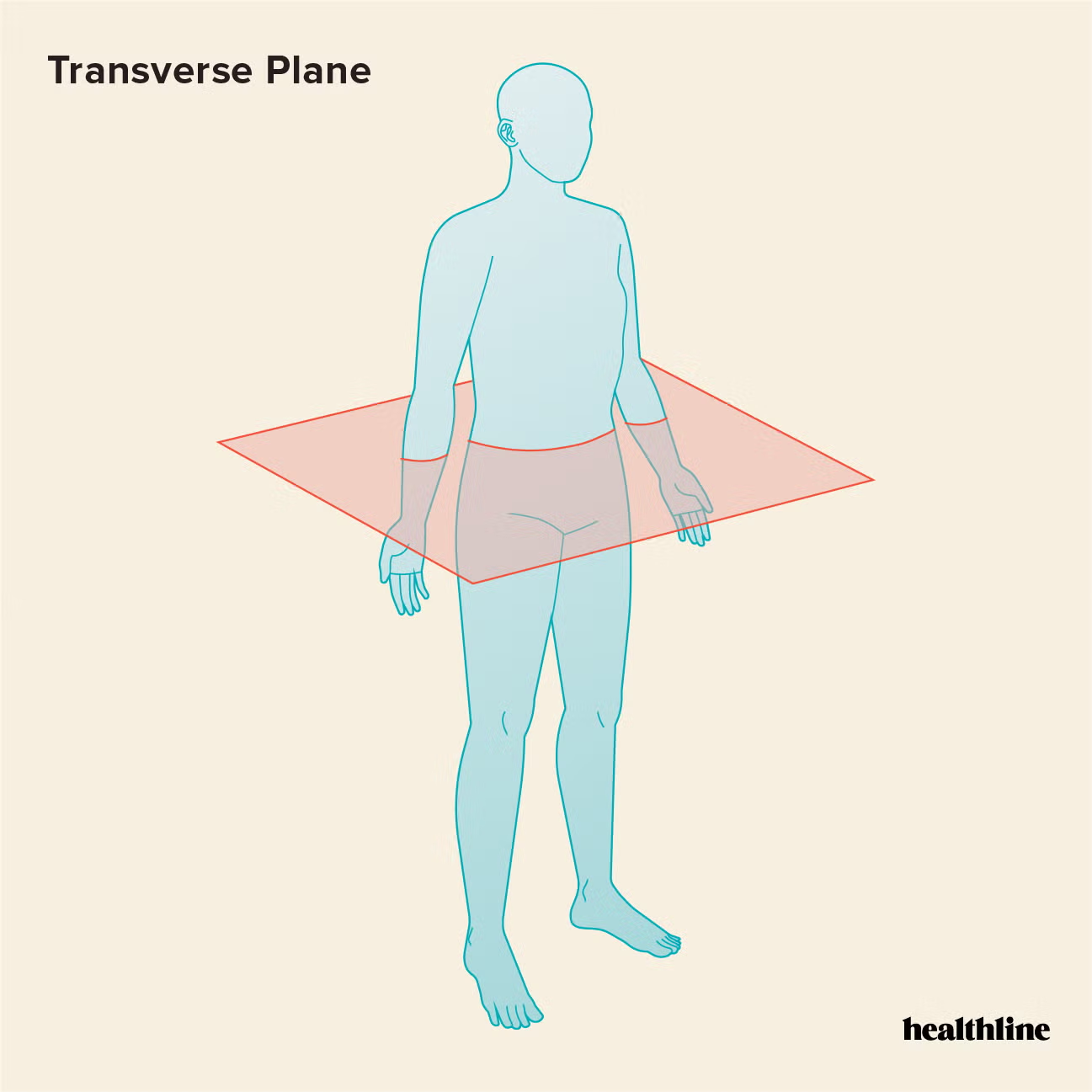
transverse/horizontal/axial plane
horizontal plane that divides the body into upper and lower parts
can occur at any level throughout the body
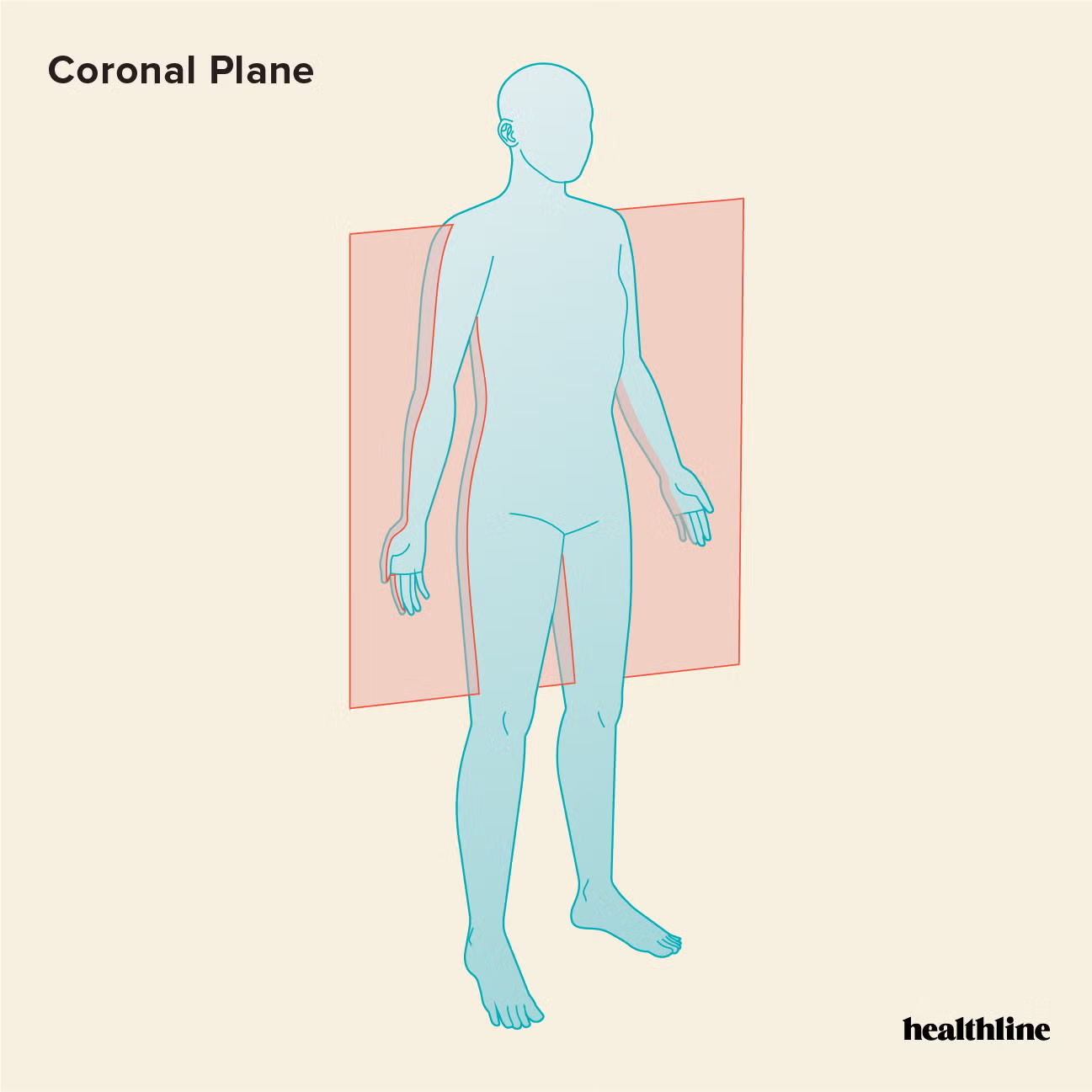
frontal/coronal plane
vertical plane parallel to the forehead (“ear to ear cut”)
divides the body into a front and back
all planes parallel to it are also called frontal/coronal
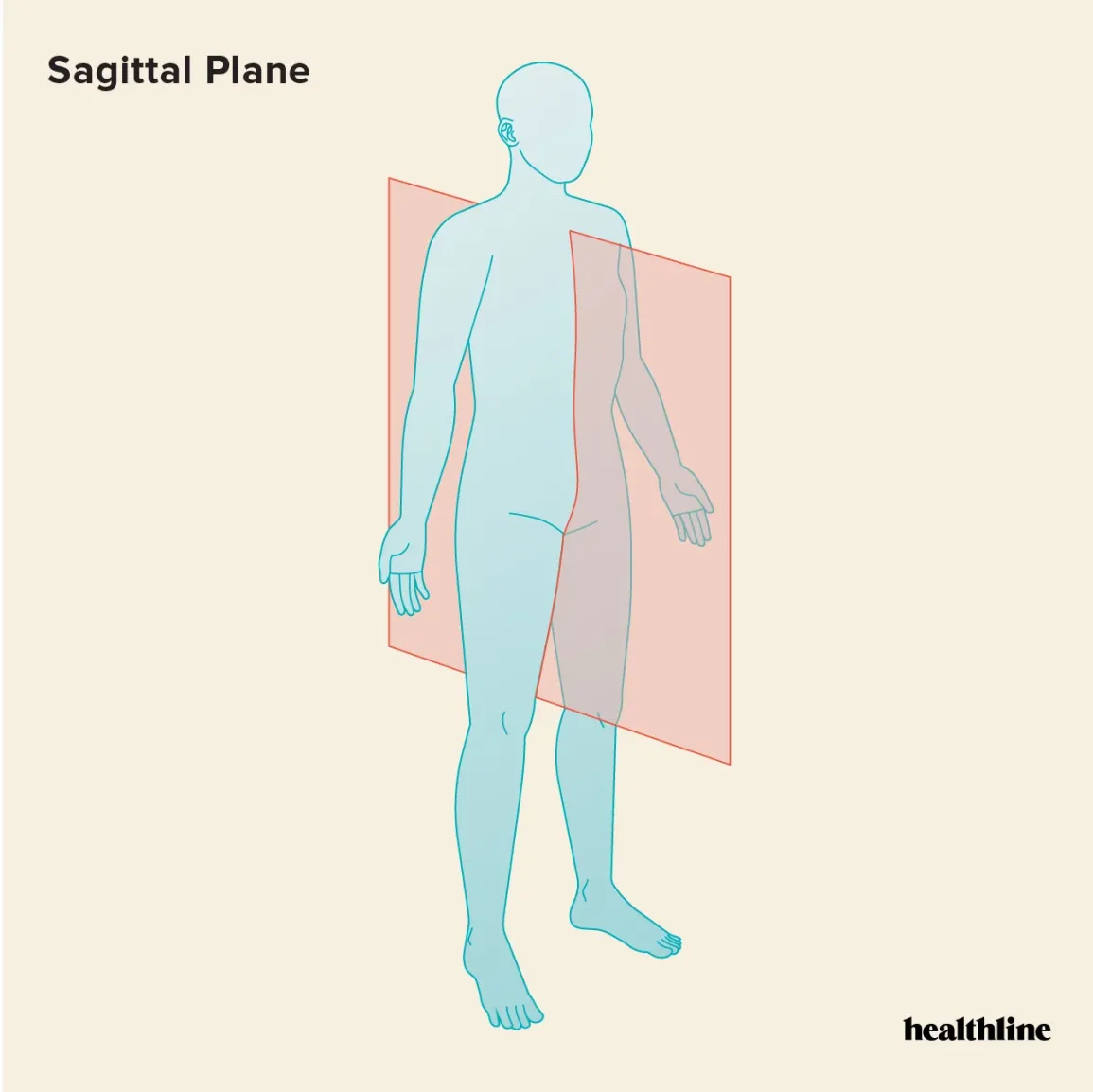
sagittal/median plane
vertical plane/cut that divides the body into right and left halves
two types:
midsagittal - cut down the center
parasagittal - not down the center
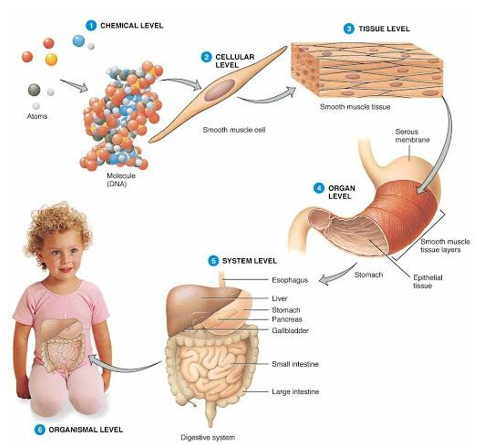
hierarchical organization of the human body (smallest to biggest)
cell - smallest contained living unit (made up of chemicals)
tissues - a group of cells that perform a particular function
organs - two or more tissues that perform a particular function
system - two or more organs that perform a particular function
organism - composed of organ systems
epithelial tissue (definition)
definition: superficial layer of cells; closely approximated
covers external surface of body (ex: skin)
lines internal body cavities (ex: endothelial - blood vessels; mesothelial - internal organs)
often contains cilia (but not all)
4 main functions: protection, secretion, absorption, and sensation
main characteristics of epithelial tissue (i.e., how we classify it)
shape: squamous, columnar, cuboidal, ciliated
arrangement: simple, stratified, pseudostratified
function
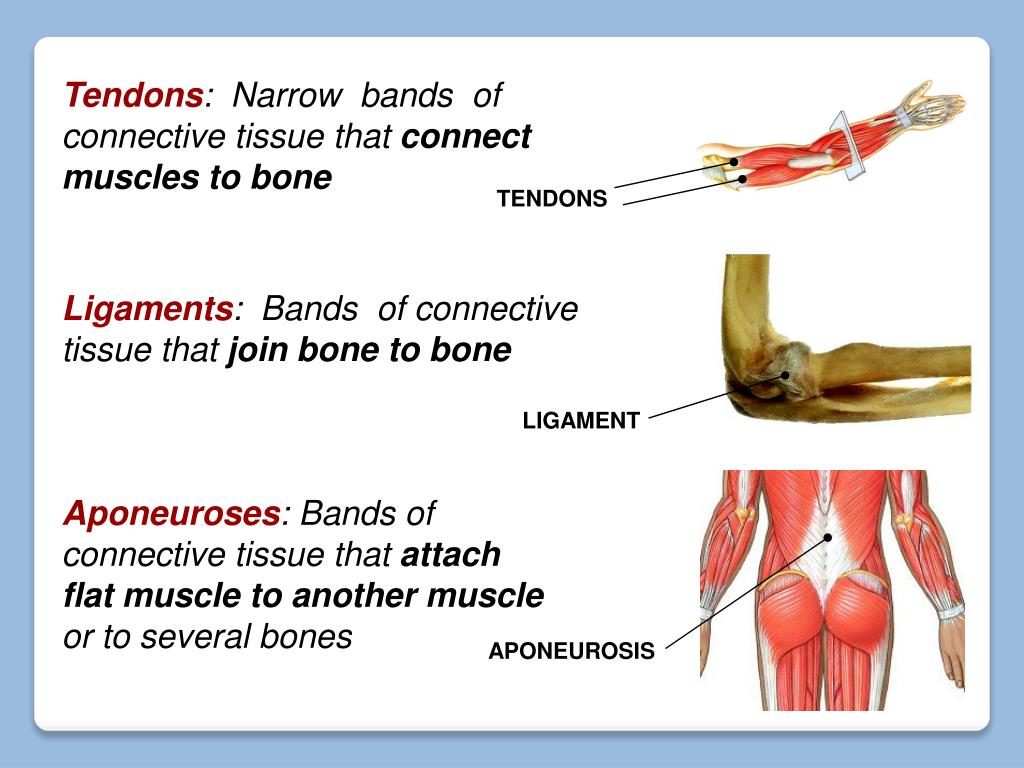
connective tissue (definition)
definition: tissues that connect or bind structures together and support the body
proper connective tissue (3 types)
ligaments: connect bone to bone, bone to cartilage, and cartilage to cartilage (elastic)
tendons: attach muscle to bone (non-elastic)
aponeurosis: large, broad tendinous sheets
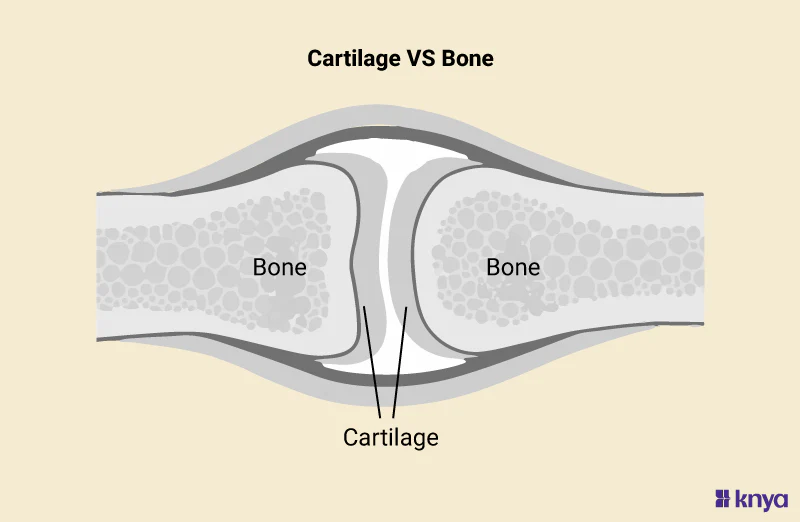
supportive connective tissue (2 types)
cartilage: stronger than some proper connective tissue, but it is flexible and capable of growth (includes hyaline, elastic, and fibrous)
bone: rigid and very strong; the hardest type of connective tissue
muscle tissue (definition)
definition: specialized tissue that can contract, which produces movement and force
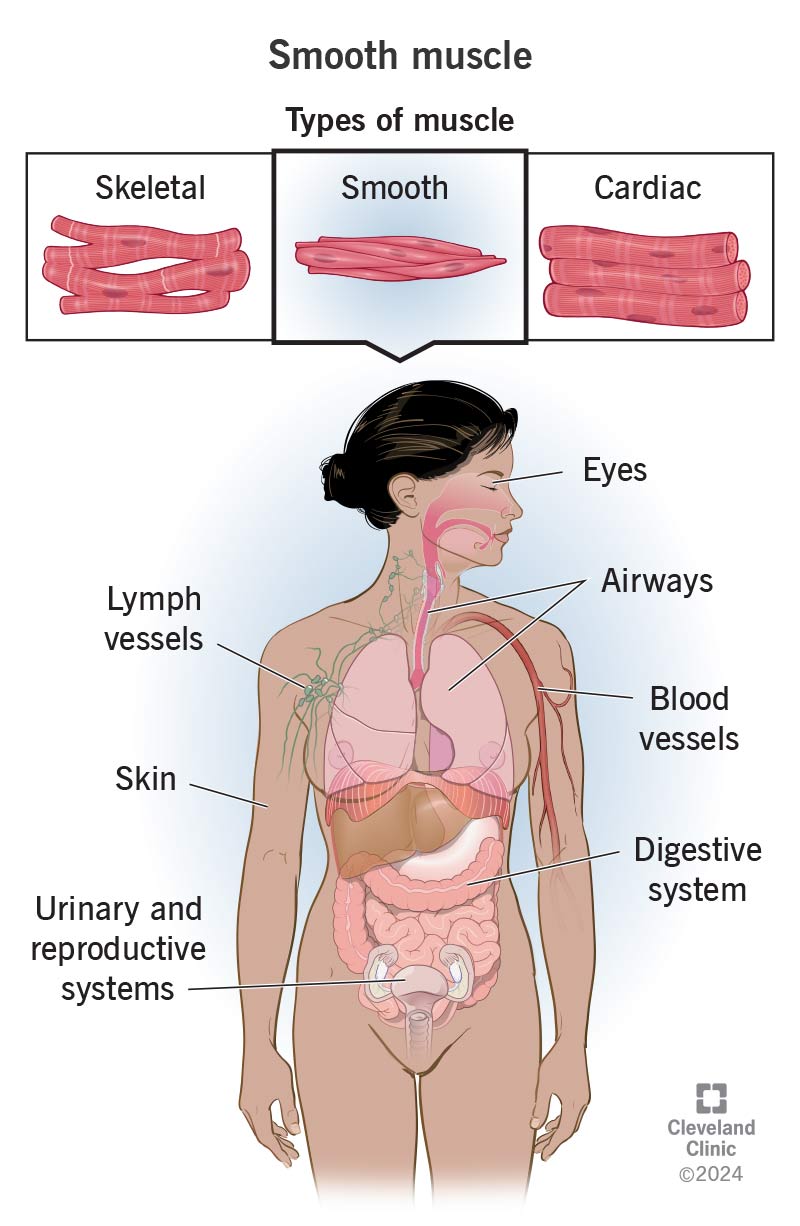
smooth muscle tissue (definition and examples)
nonstriated
involuntary contraction
innervated by the autonomic nervous system
examples:
muscles of GI tract
blood vessels
urinary bladder
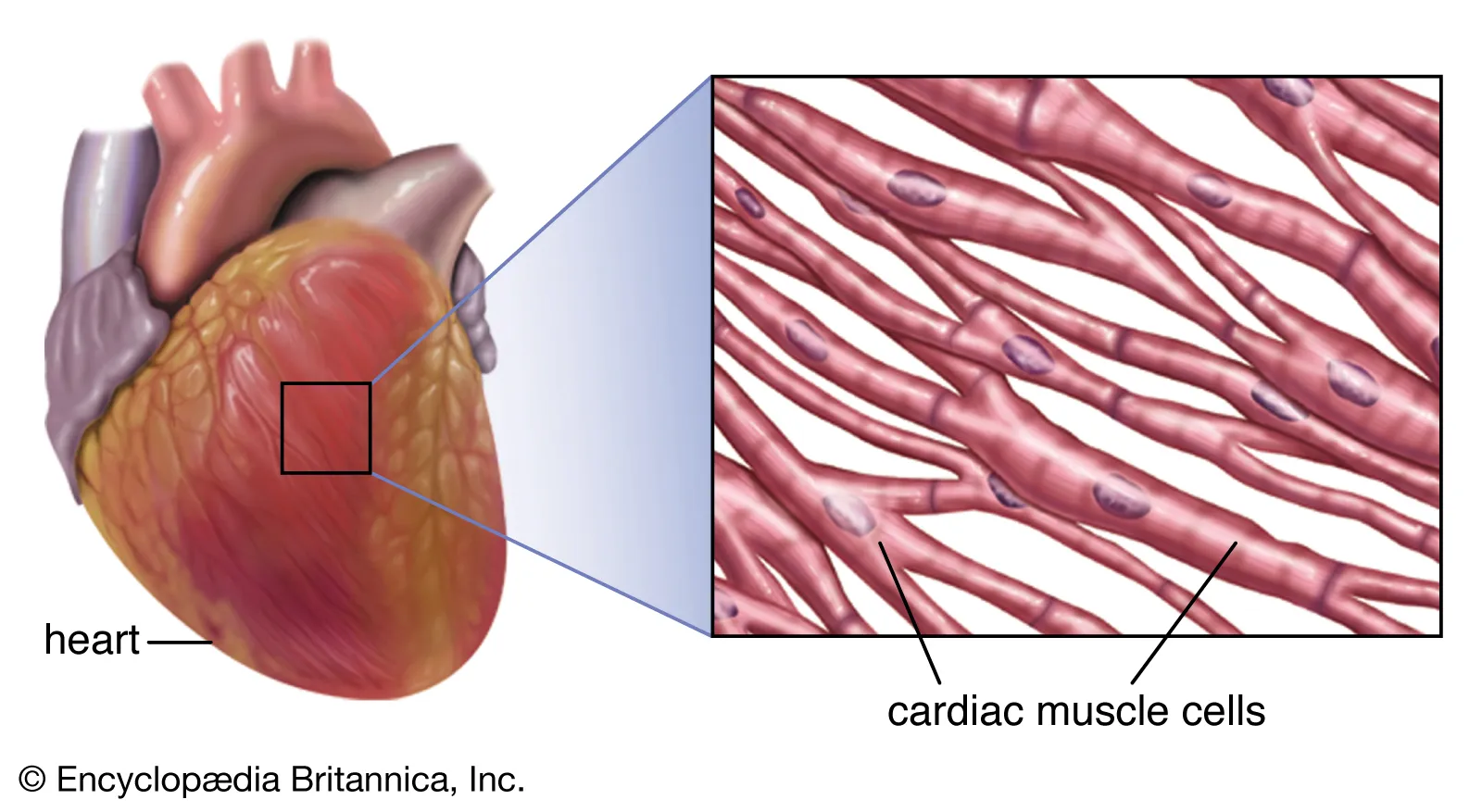
cardiac muscle tissue (definition and examples)
striated
involuntary constriction
located only in the heart
designed for endurance
innervated by the autonomic nervous system
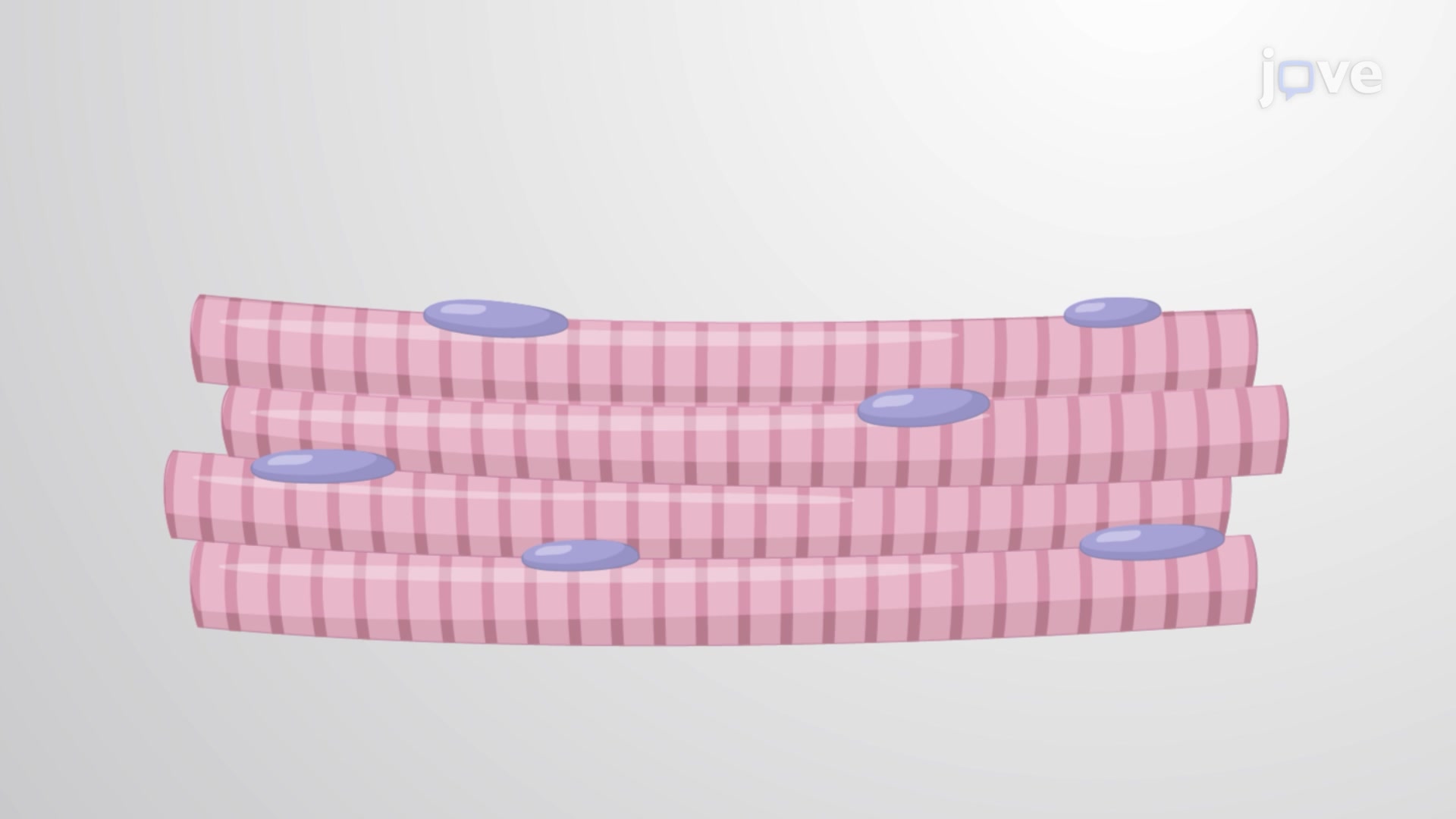
skeletal muscle tissue (definition and examples)
voluntary constriction
striated
paired - one right and one left
predominant type of muscle in speech/swallowing
innervated by the somatic division of the peripheral nervous system
two points of attachment: origin and insertion
structures are linked through muscle fibers (name is a combination of origin and insertion)
cell structure
see image
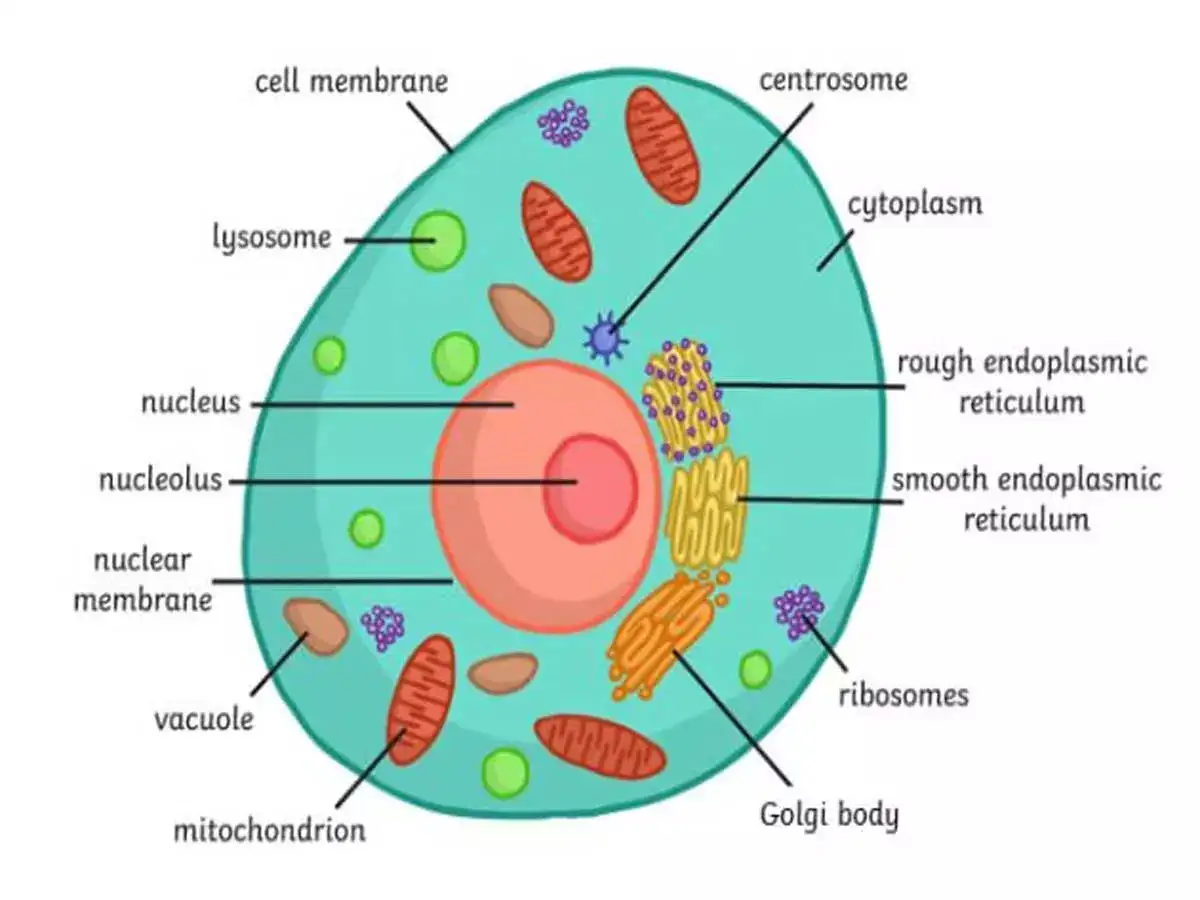
main function of the cell membrane
separates the cell’s internal environment from the external surroundings
regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell
main function of the nucleus
houses the cell’s genetic material (DNA)
regulates gene expression and protein synthesis (produces ribosomes)
main function of the cytoplasm
contains the cell’s organelles
site of multiple metabolic processes and chemical reactions
helps maintain cell shape and structure
main function of the ribosome
synthesize proteins
main function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
located closest to the nucleus; ribosomes are attached to its surface
helps synthesize, fold, and initially modify proteins
transports proteins throughout the cell
main function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
synthesizes lipids (fats) and steroid hormones
stores and releases Ca2+ ions
metabolizes carbohydrates
main function of the Golgi body
stores and packs proteins until they are ready to be released (received from the ER)
main function of the mitochondria
produces the energy we need at the cellular level (ATP)
responsible for cellular respiration
main function of the lysosome
breaks down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign invaders
nervous tissue
definition: receives and processes stimuli; transmits signals to effector organs
located in the brain and spinal cord
function of ciliated epithelial cells
definition of cilia: hair-like structures located in epithelial tissue; the main function is protection
capable of movement so they can remove contaminants
lines the nasal cavity, larynx, and trachea