Unit 4: Soil
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
weathering
mechanical and chemical processes that cause exposed rock to decompose or break down into smaller parts, creating soil

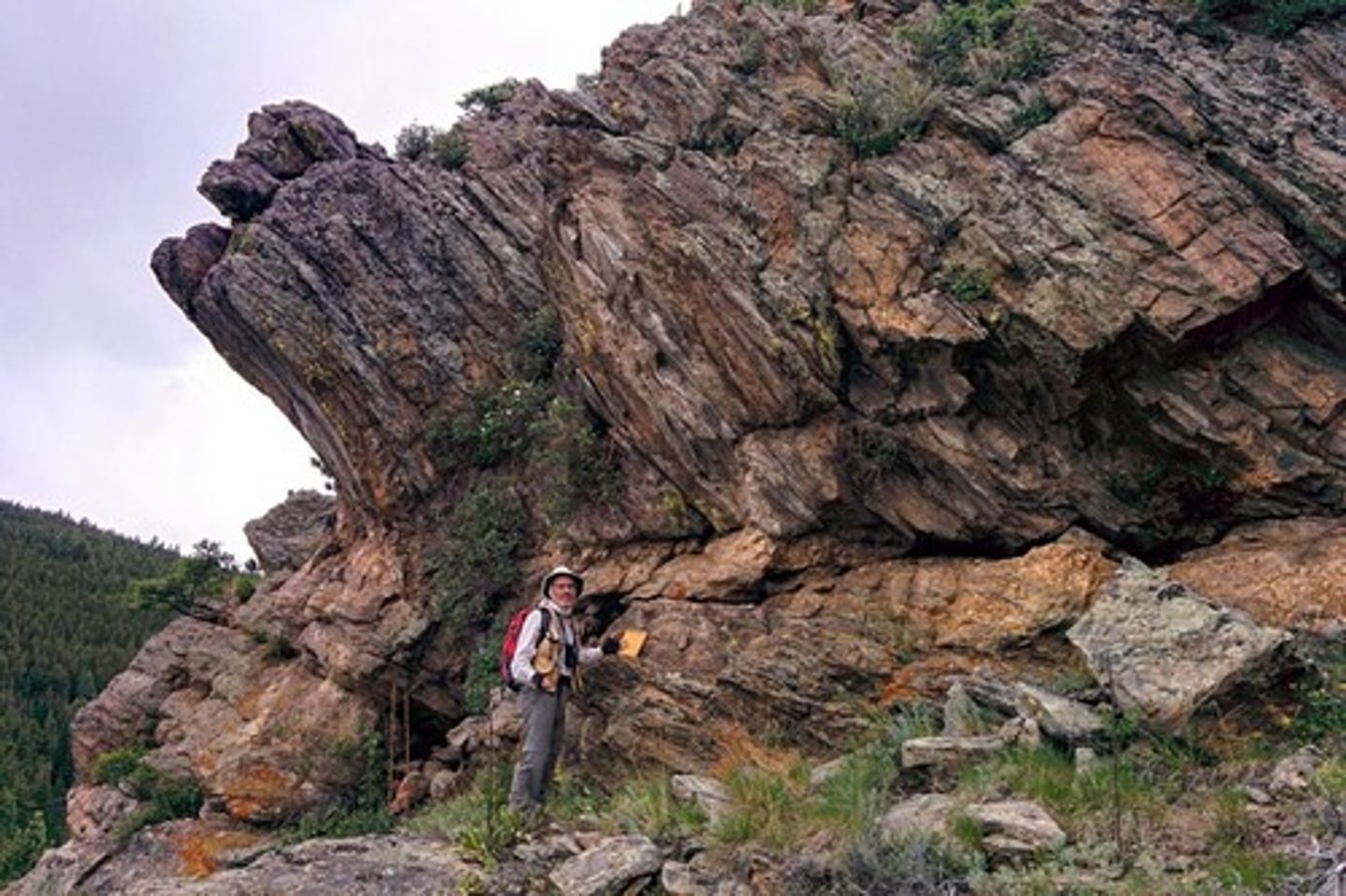
erosion
process by which the surface of the earth is worn away by the action of water, glaciers, winds,waves, etc.

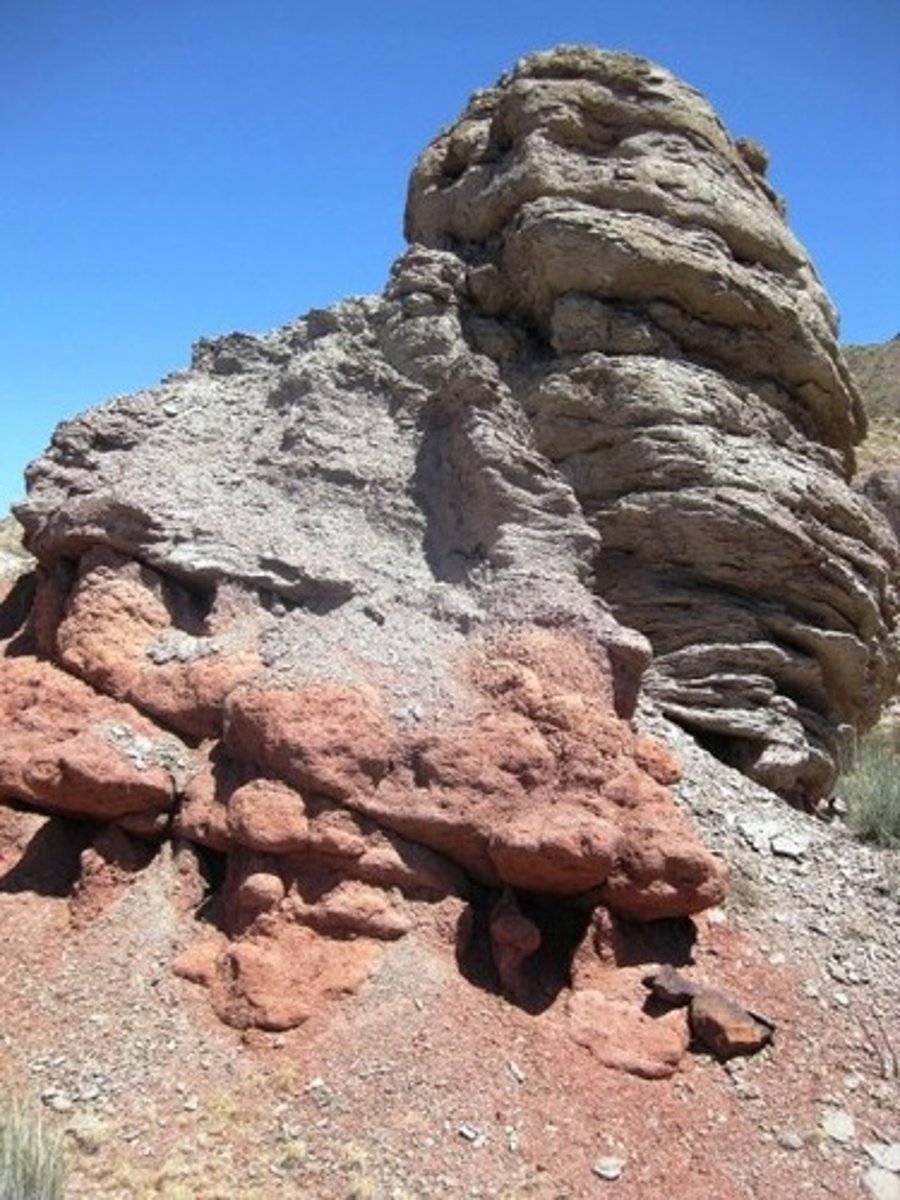
texture
how something feels to the touch

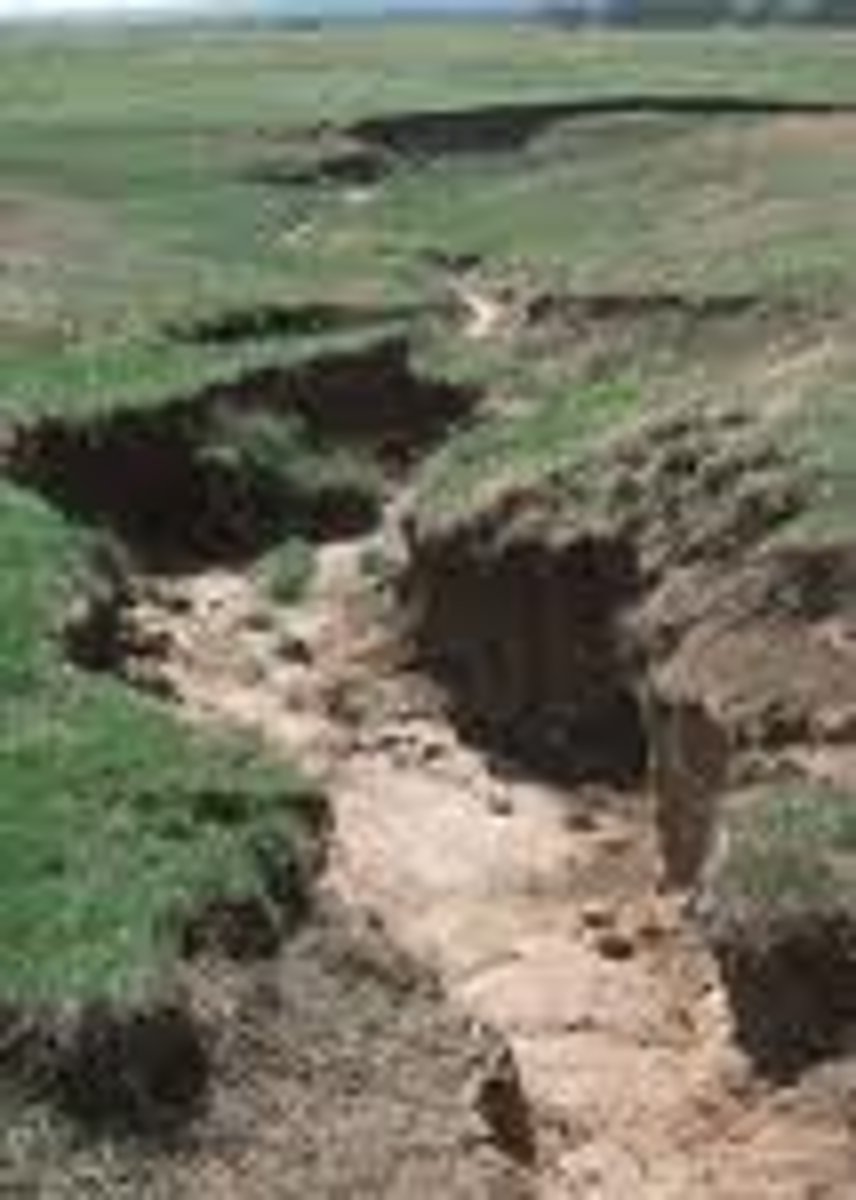
soil
portion of the earth's surface consisting of disintegrated rock and organic matter
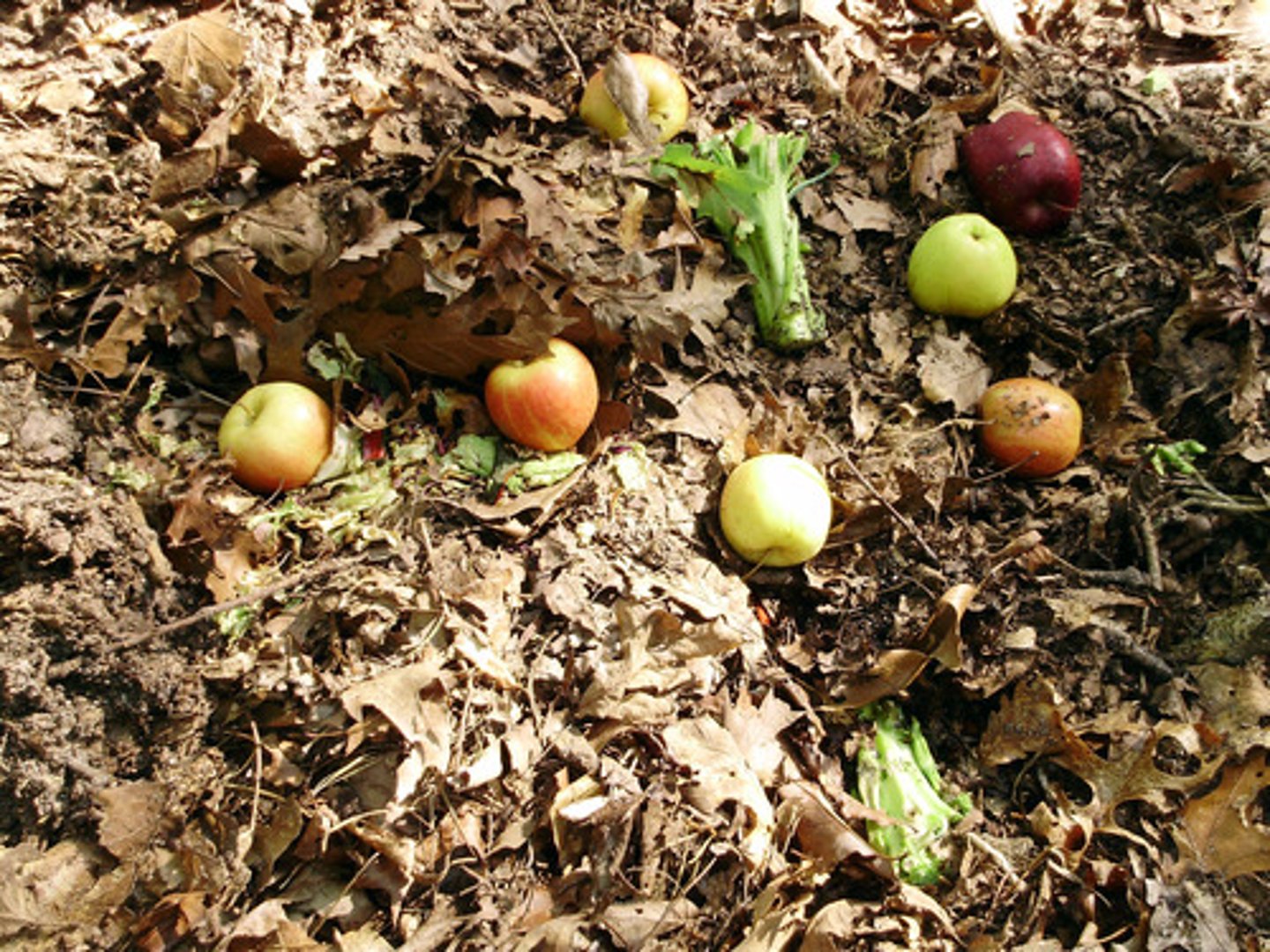
organic matter
made up of living, or once living organisms

sand
Largest of the soil texture classified particles. Consists of small pieces of rocks, made up of small, loose grains, often of quartz.

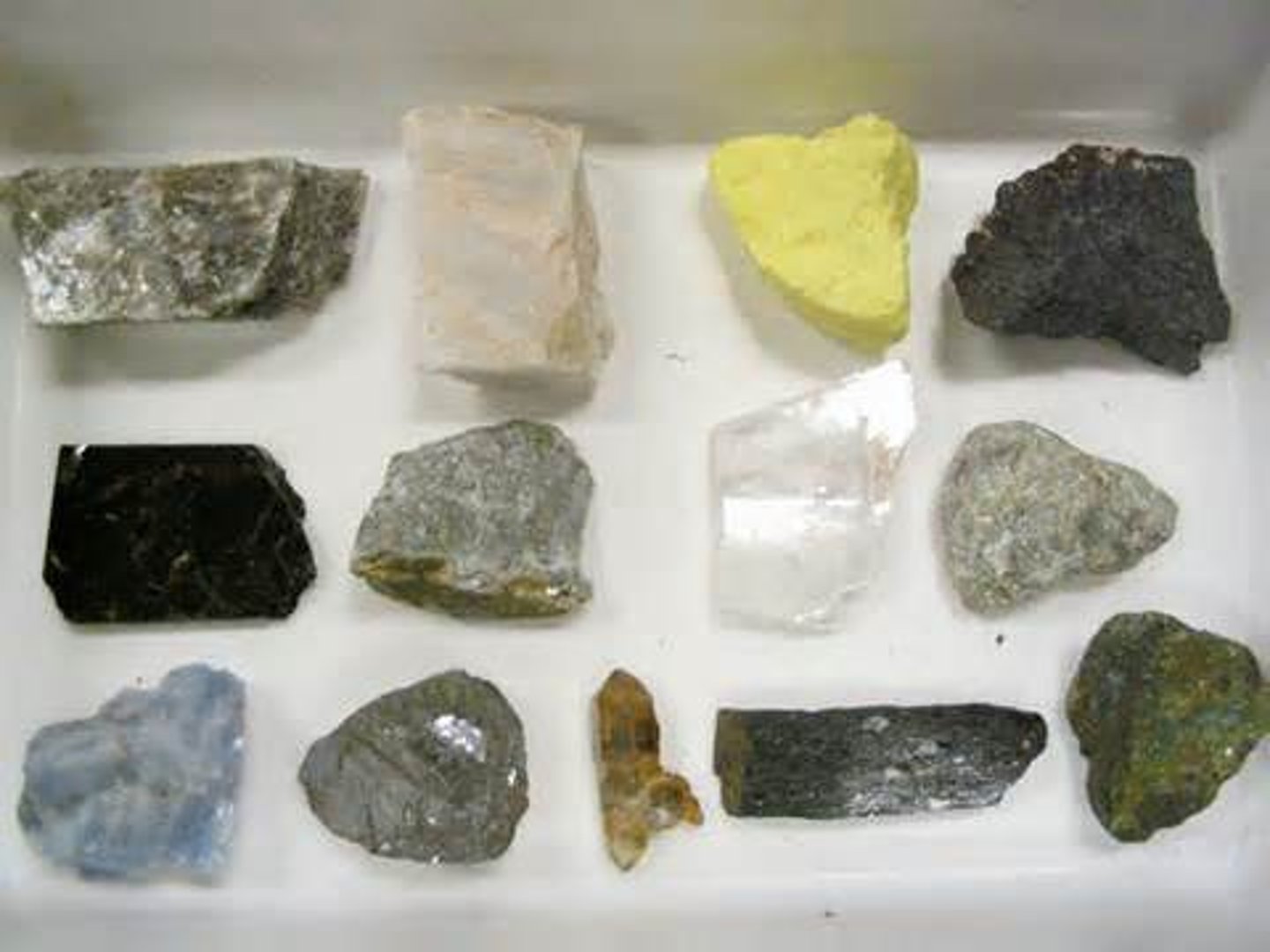
minerals
inorganic substances (not living), such as quartz or feldspar, usually formed as crystals in the rock cycle.

silt
Second smallest particle of soil. A sedimentary material consisting of grains or particles of disintegrated rock.
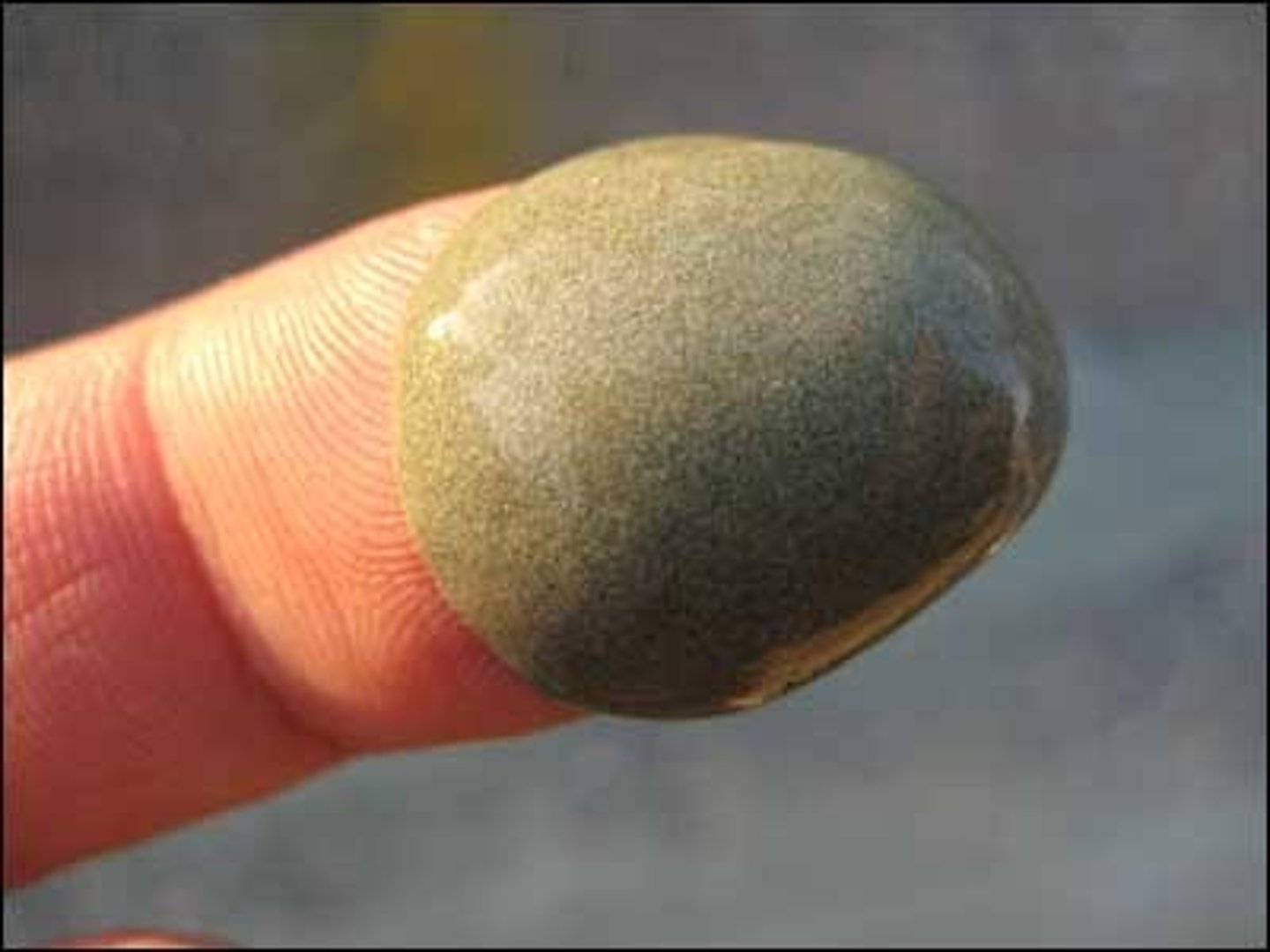

clay
Smallest classfied particles of soil. Material that is plastic (moldable) when wet, consisting mostly of hydrated silicates of aluminum
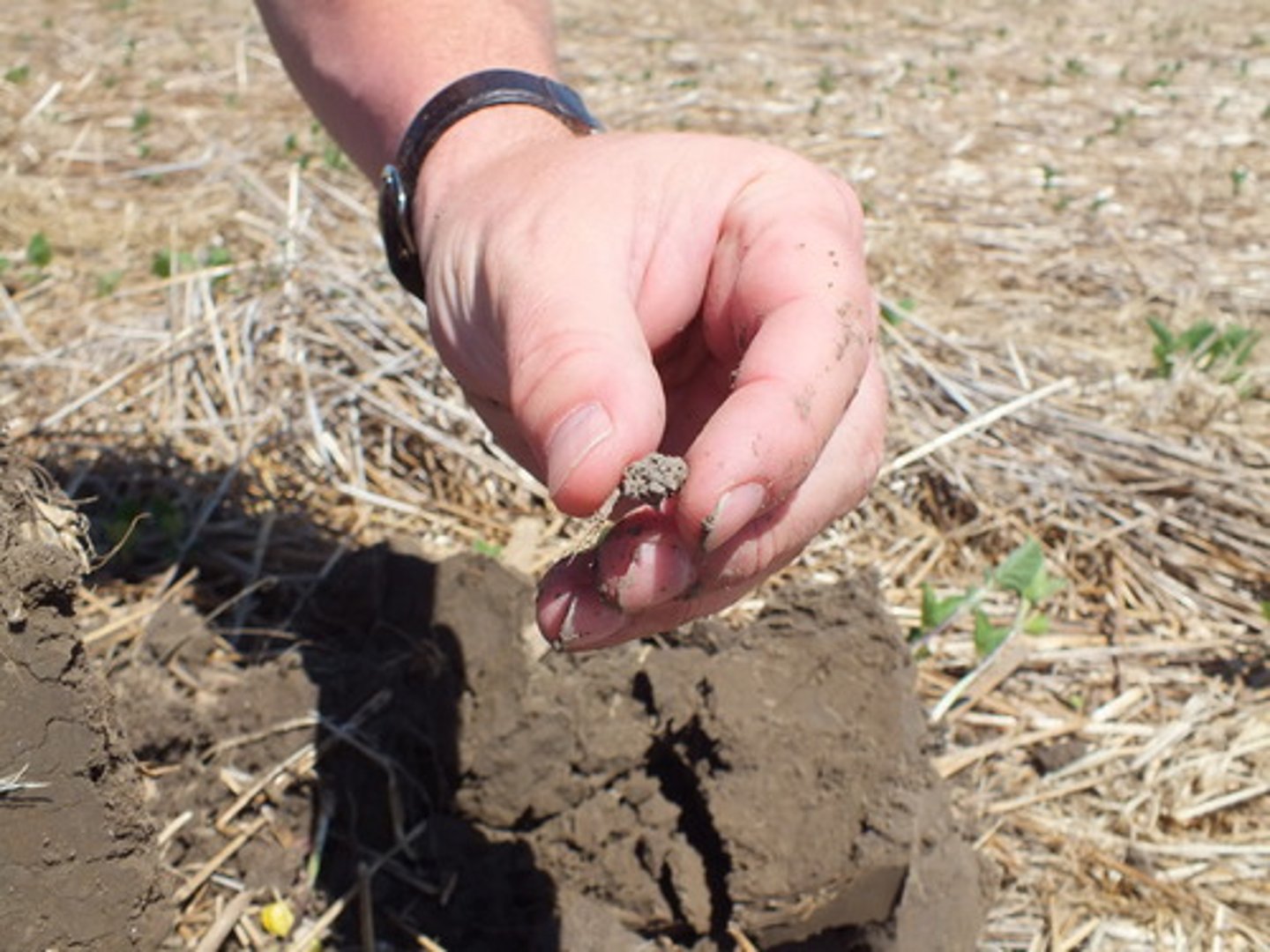

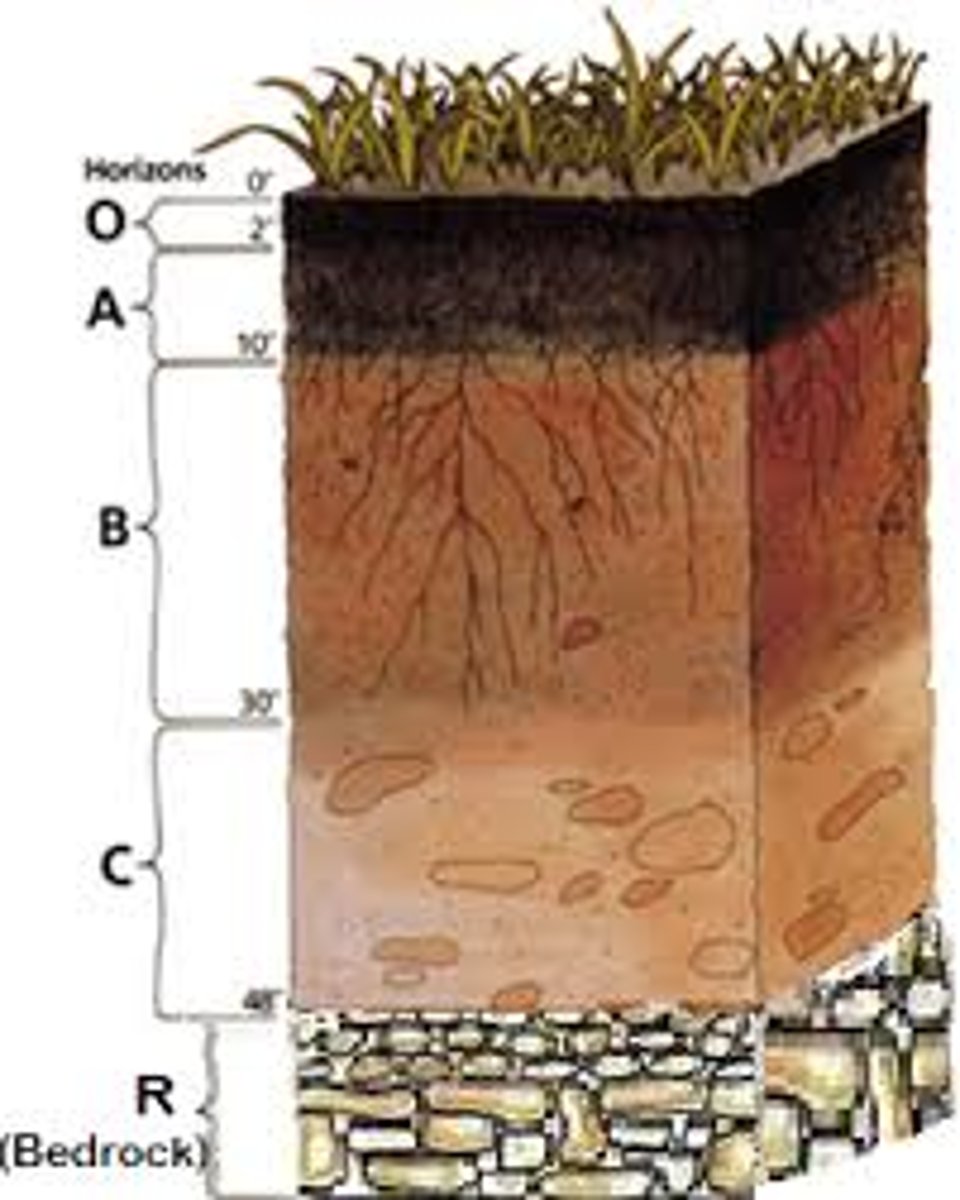
horizons
A horizontal layer in a soil defined by distinictive physical features such as texture and color.
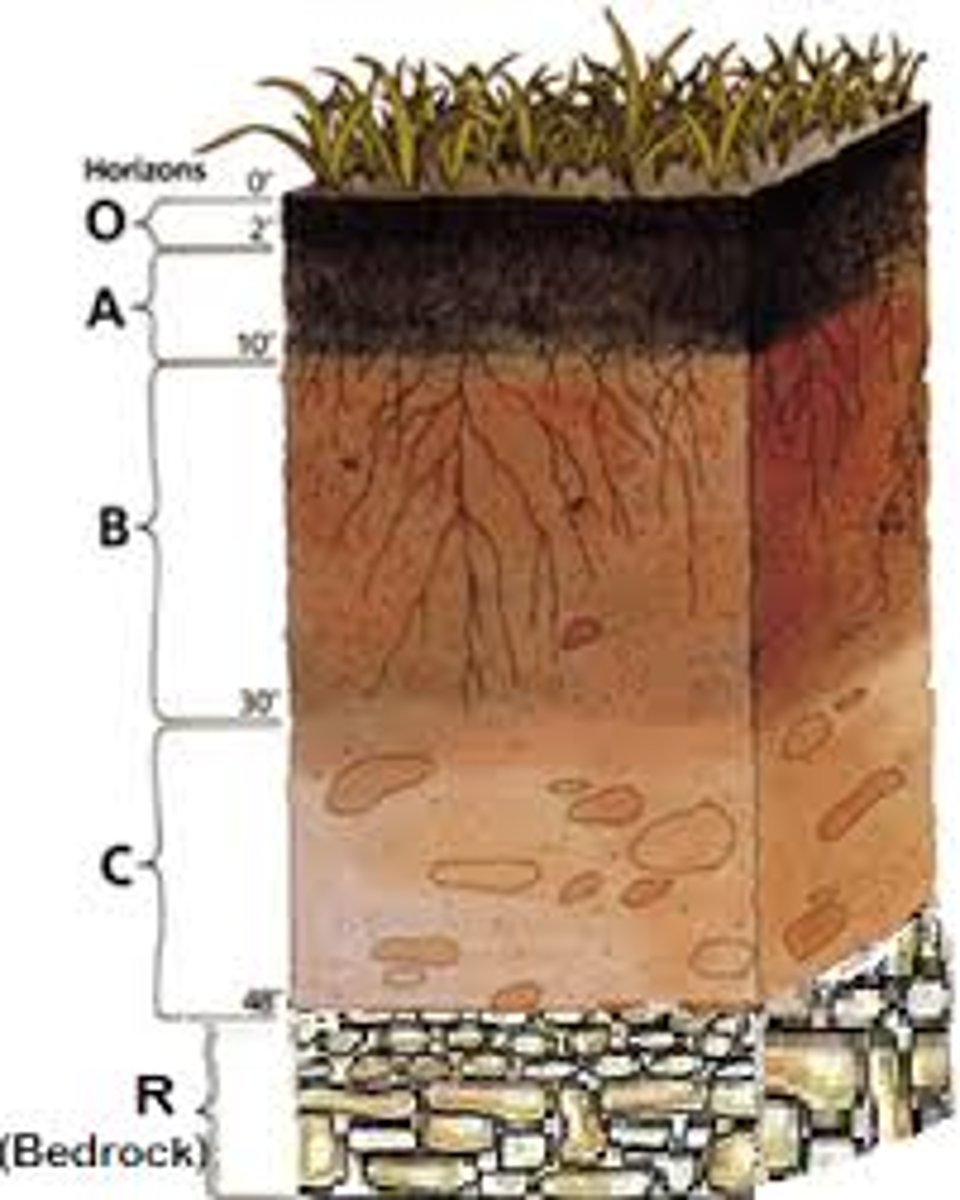
O Horizon
The organic horizon at the surface of many soils, composed of organic detritus in various stages of decomposition.
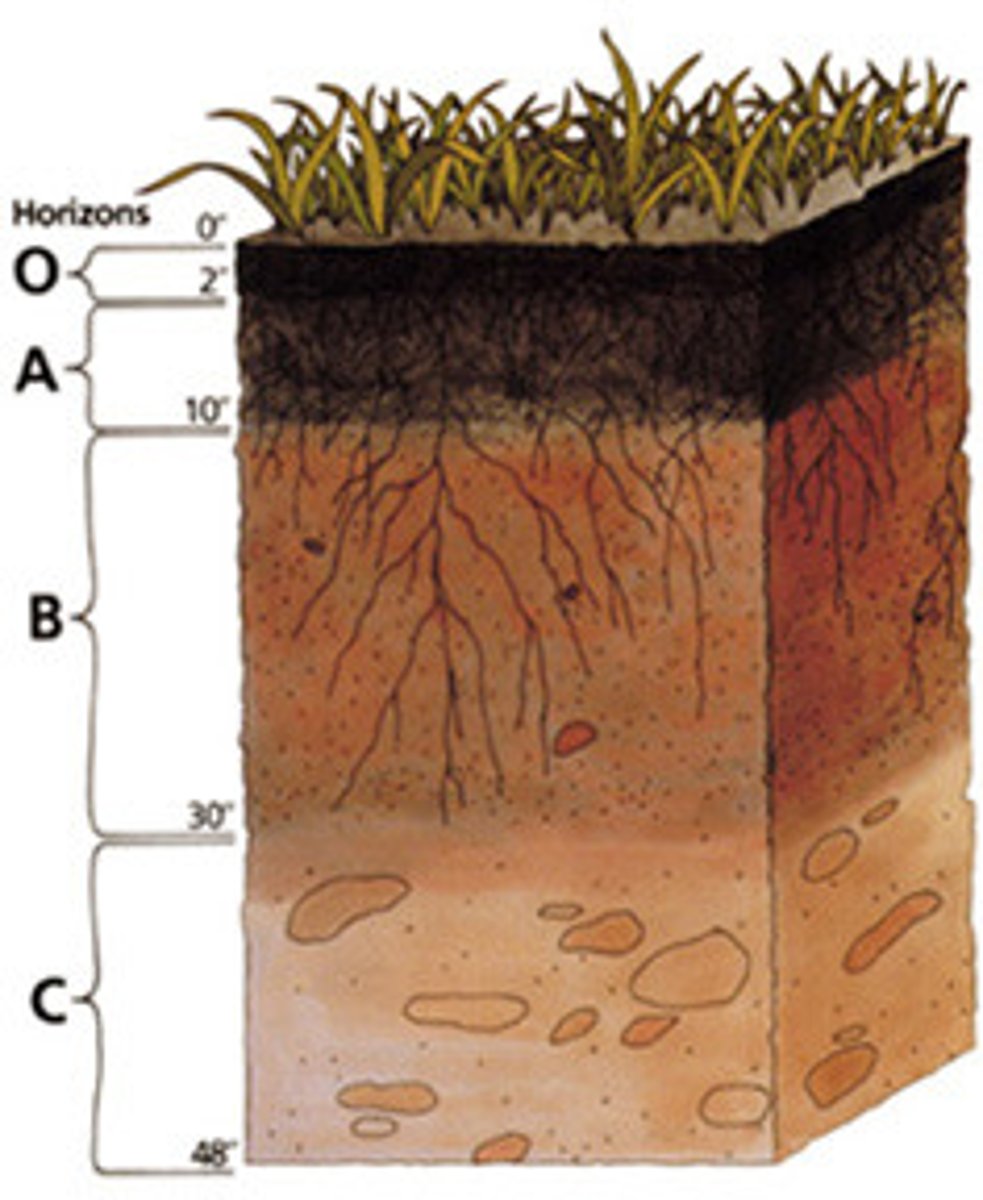
A horizon
Frequently the top layer of soil, a zone of organic material and minerals that have been mixed together. Also known as topsoil.
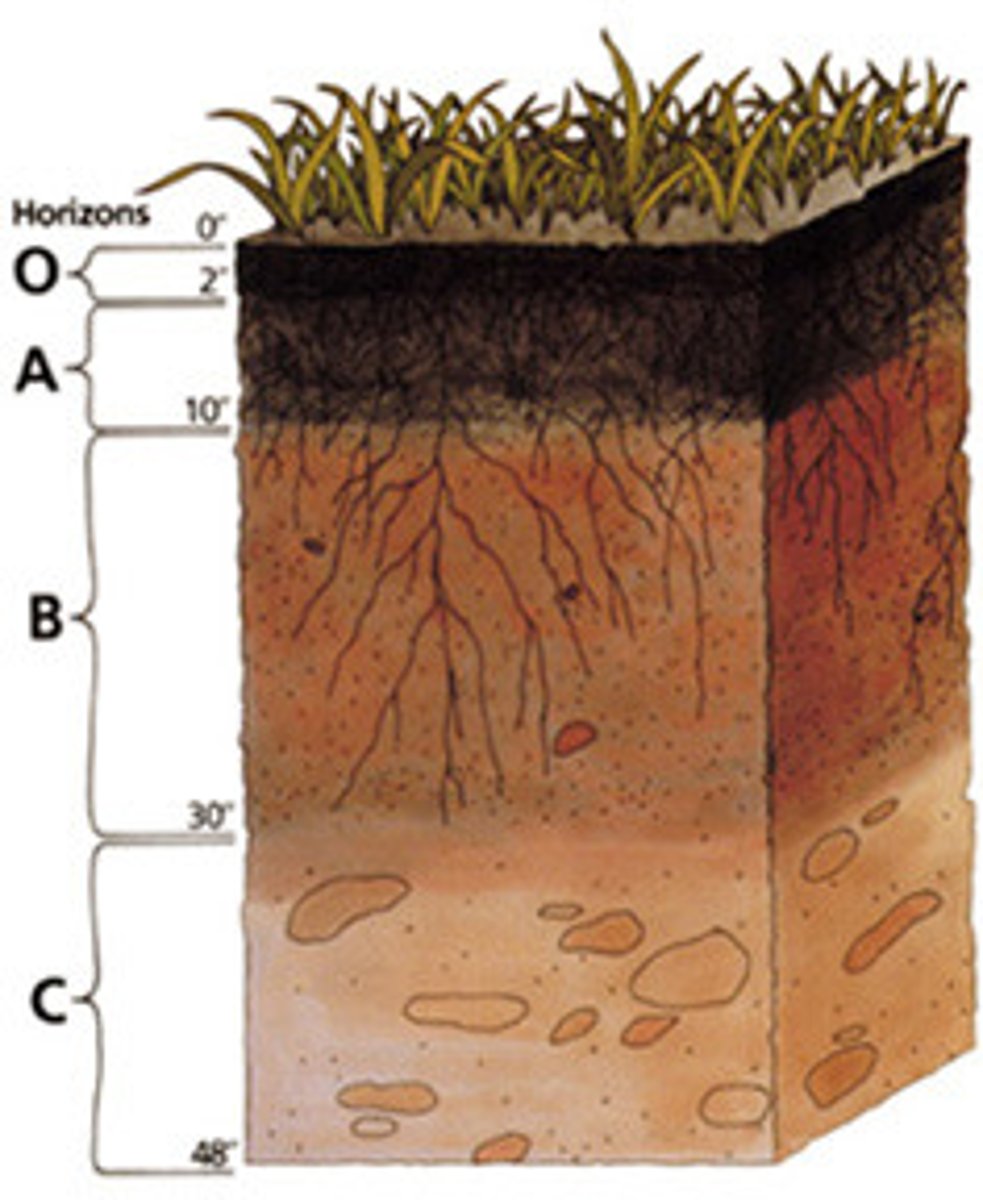
B Horizon
A soil horizon composed primarily of mineral material with very little organic matter.
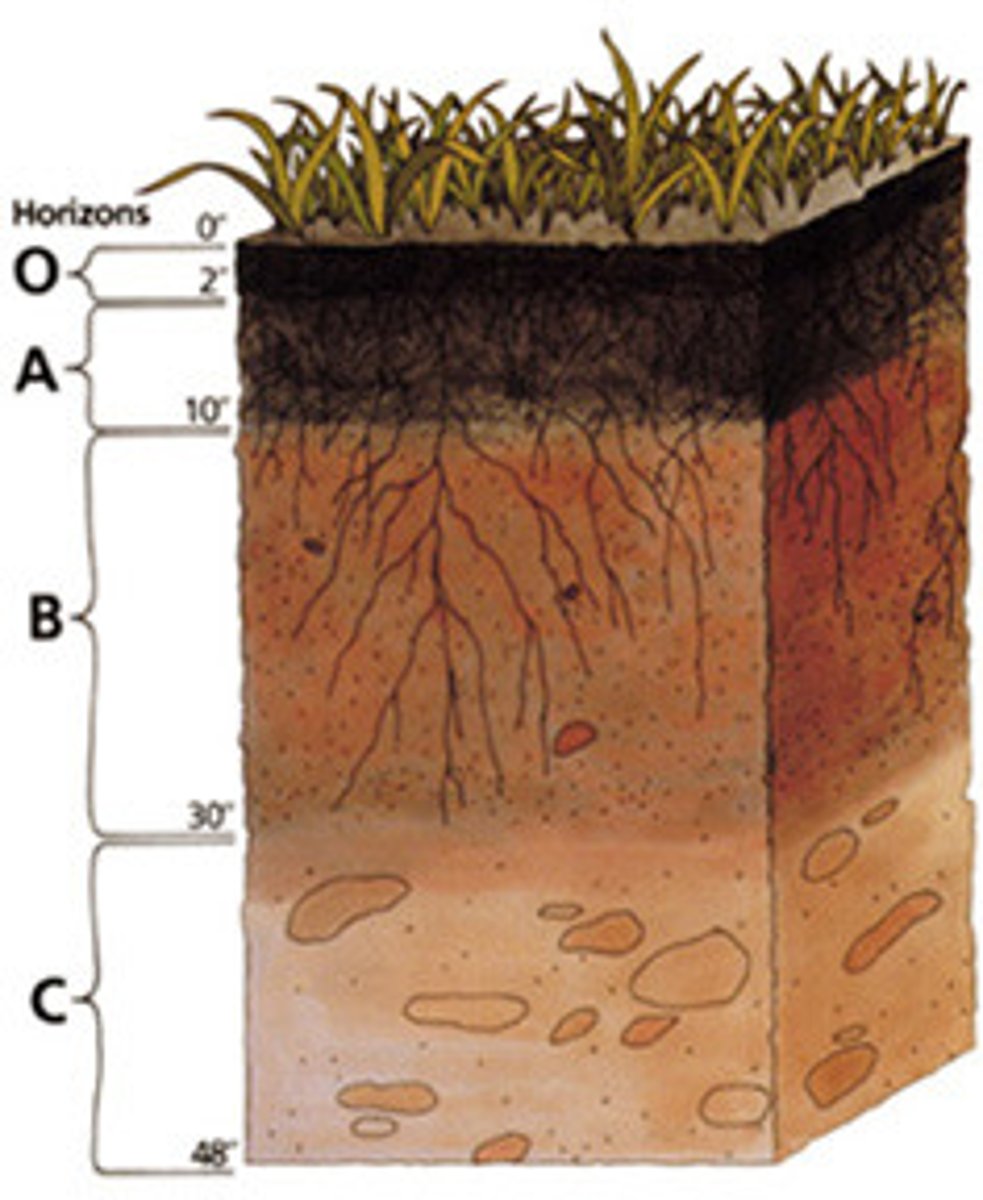
C Horizon
The least-weathered soil horizon, which always occurs beneath the B horizon and is similar to the parent material.
E Horizon
A zone of leaching, or eluviation, found in some acidic soils under the O horizon or, less often the A horizon.
soil degredation
The loss of some or all of a soil's ability to support plant growth.

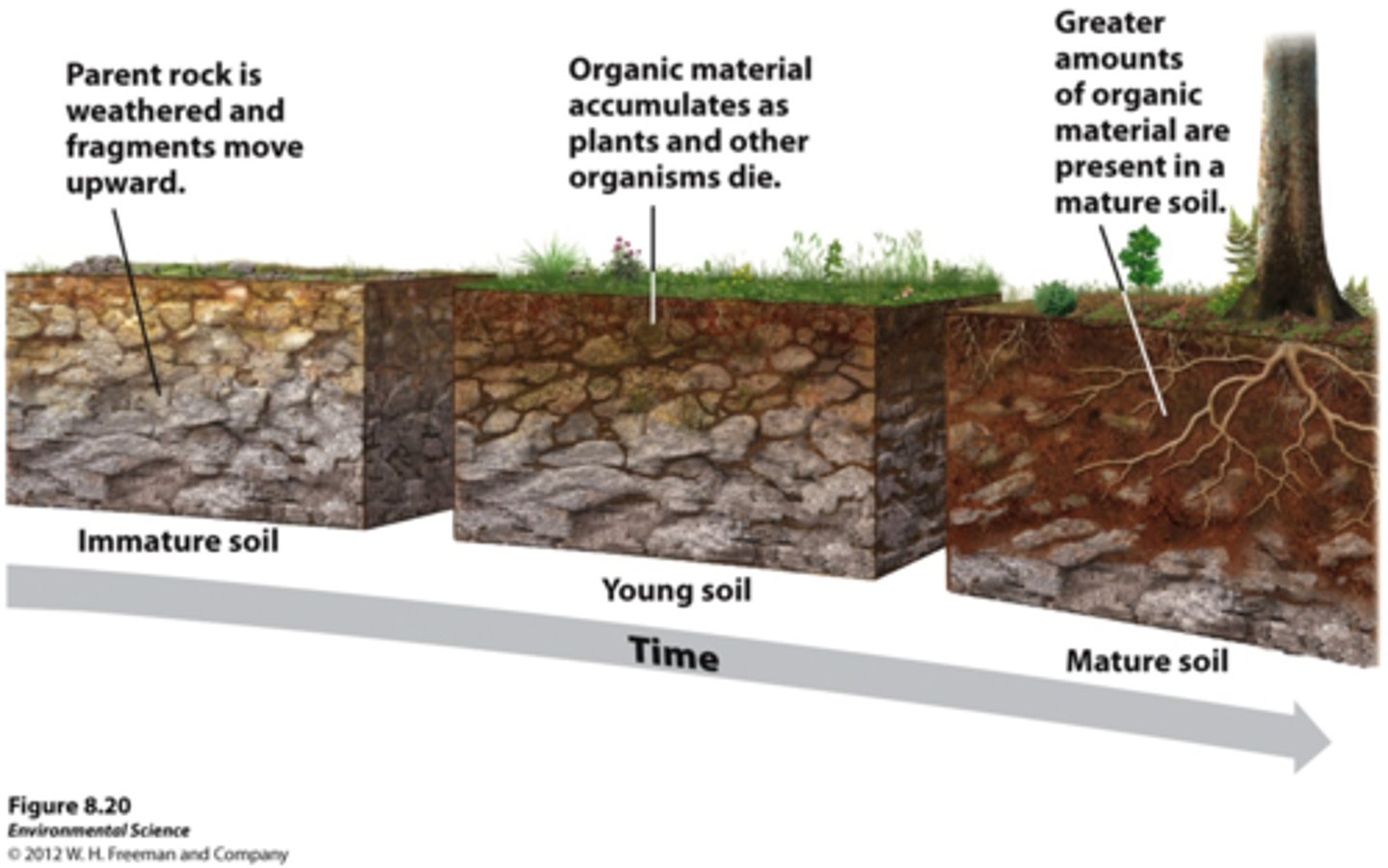
parent material
The rock material from which the inorganic components of a soil are derived.
leaching
The transportation of dissolved molecules through the soil via groundwater.
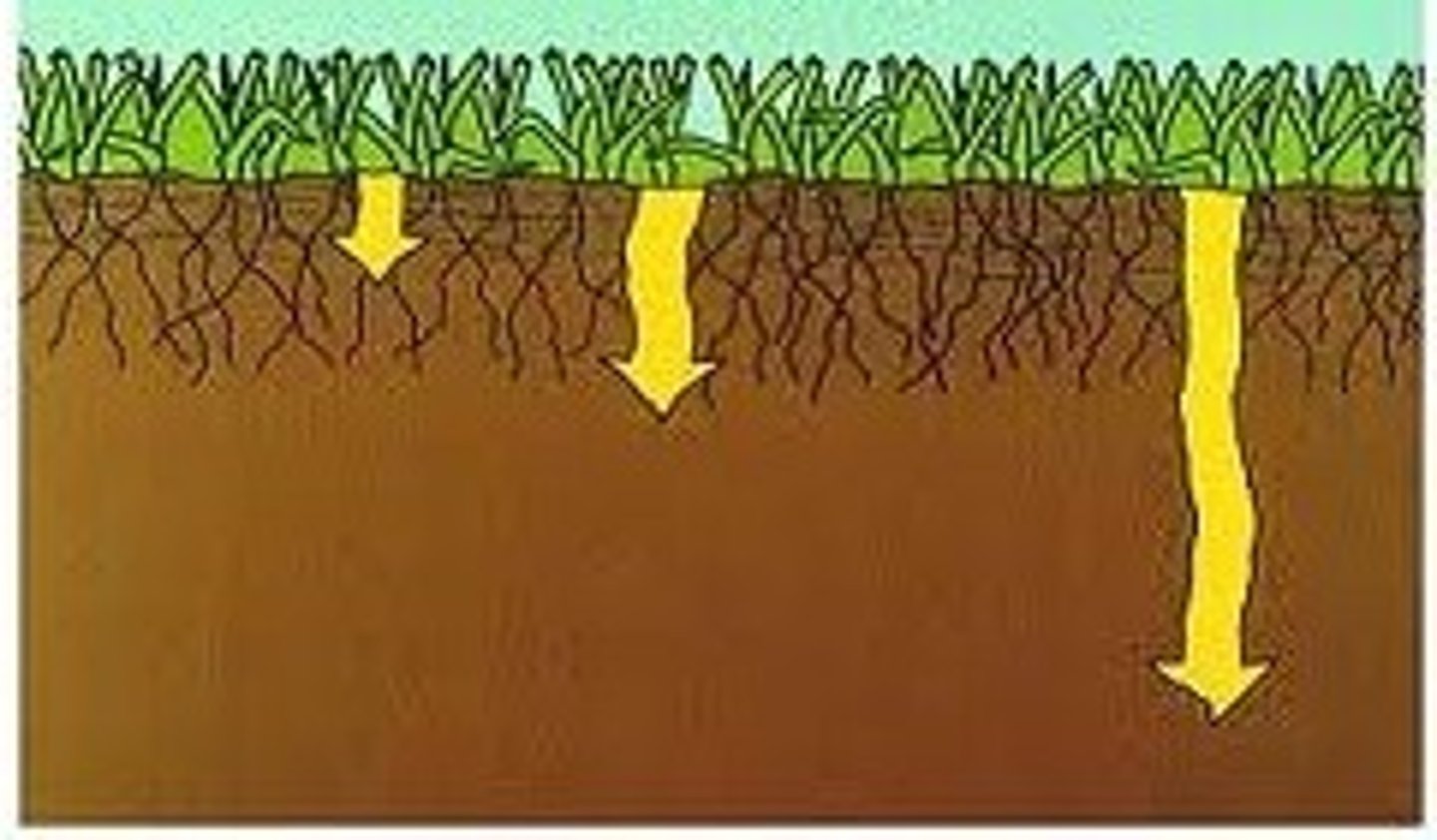
permiability
The state or quality of a material or membrane that causes it to allow liquids or gases to pass through it.
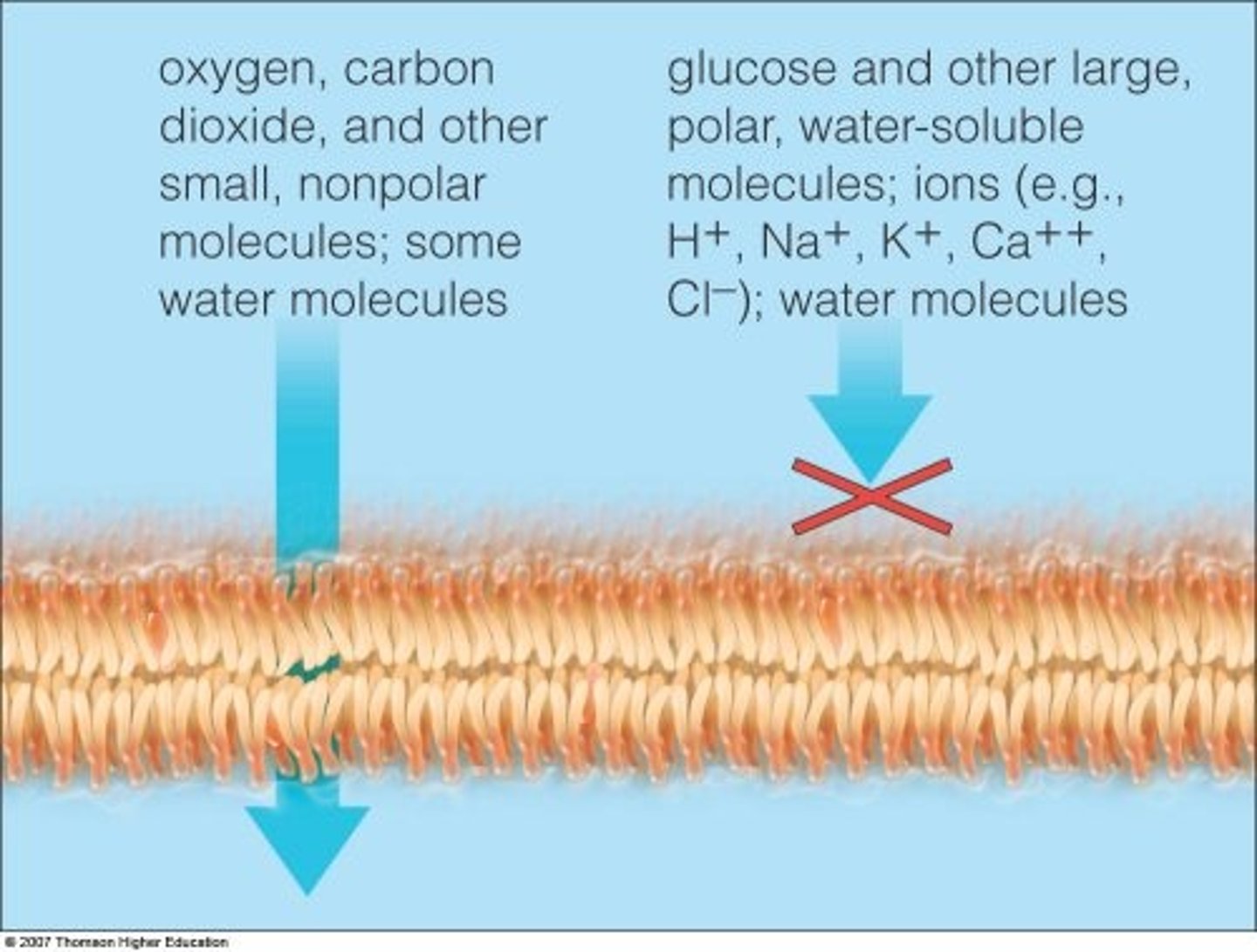
porosity
The quality of being porous, or full of tiny holes. Liquids go right through things that have porosity
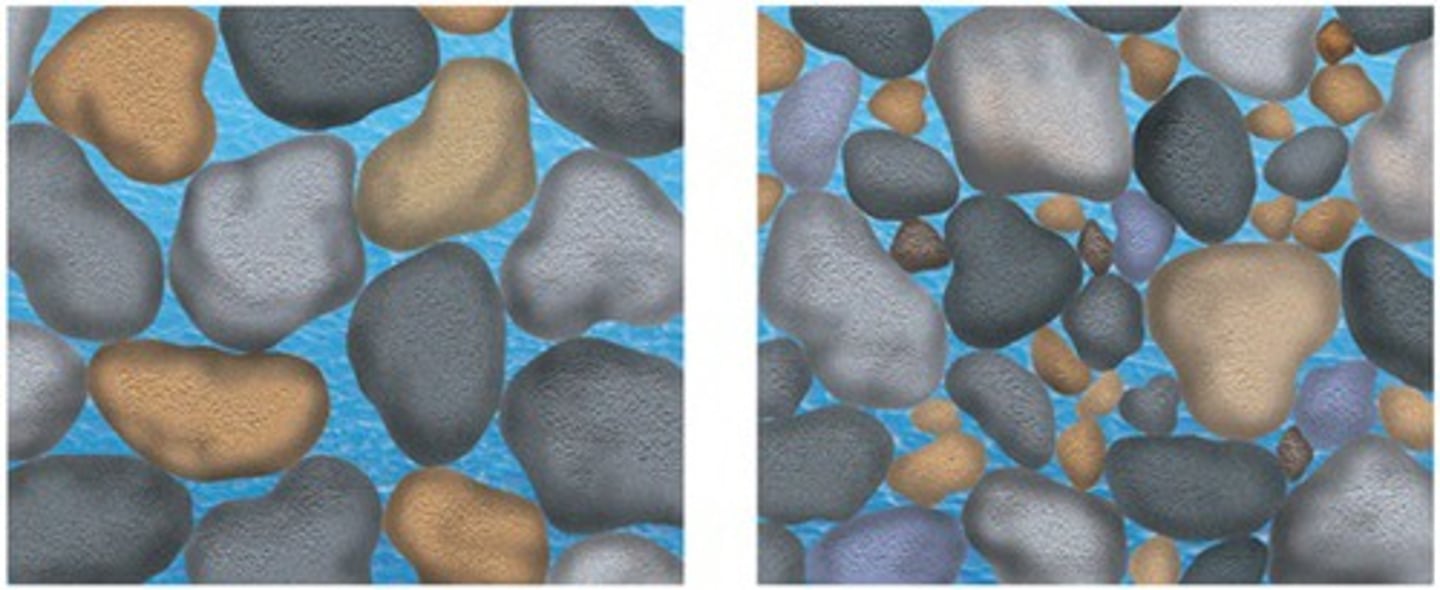
aeration
The process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or substance.
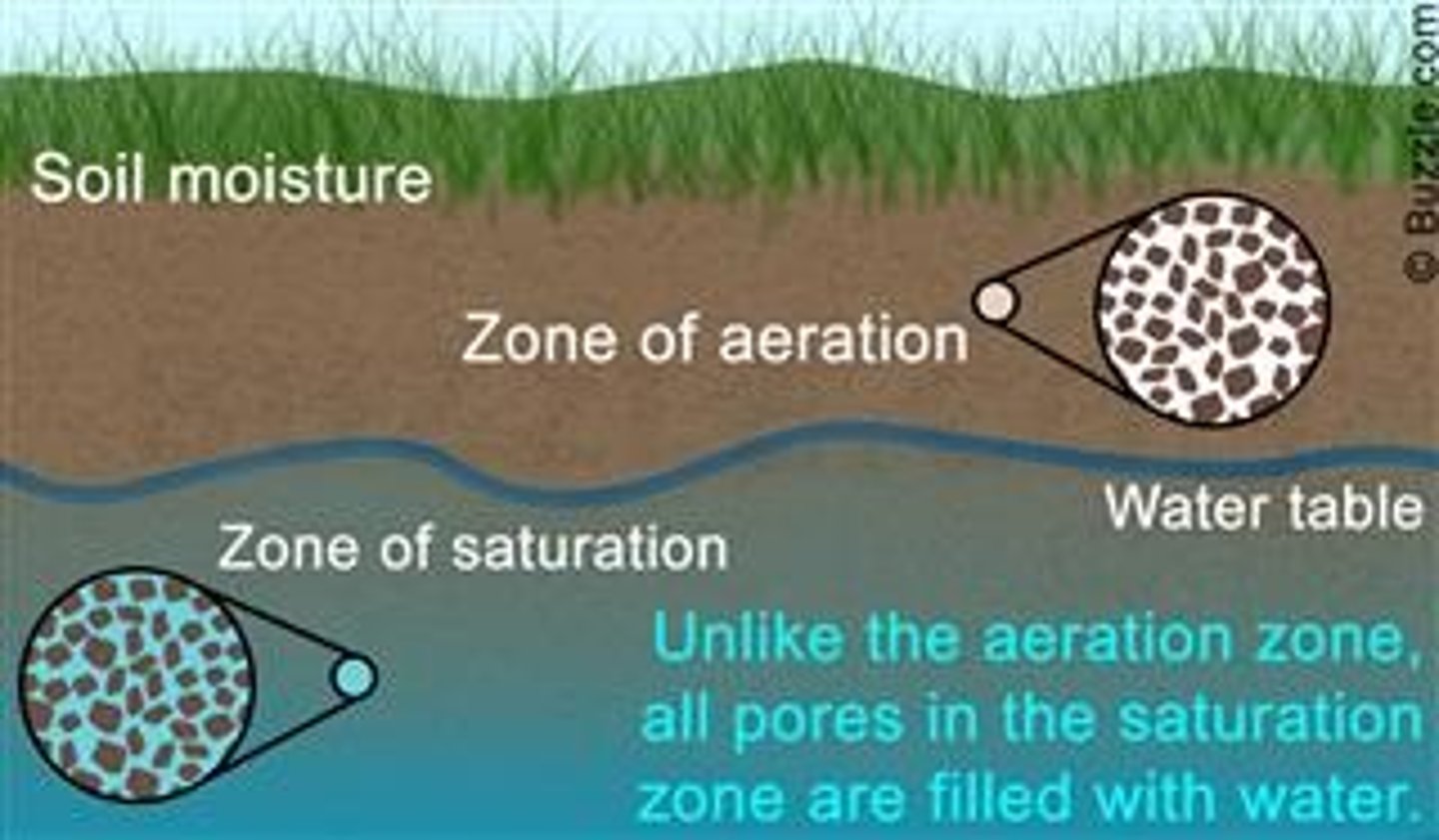
infiltration
The process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil.
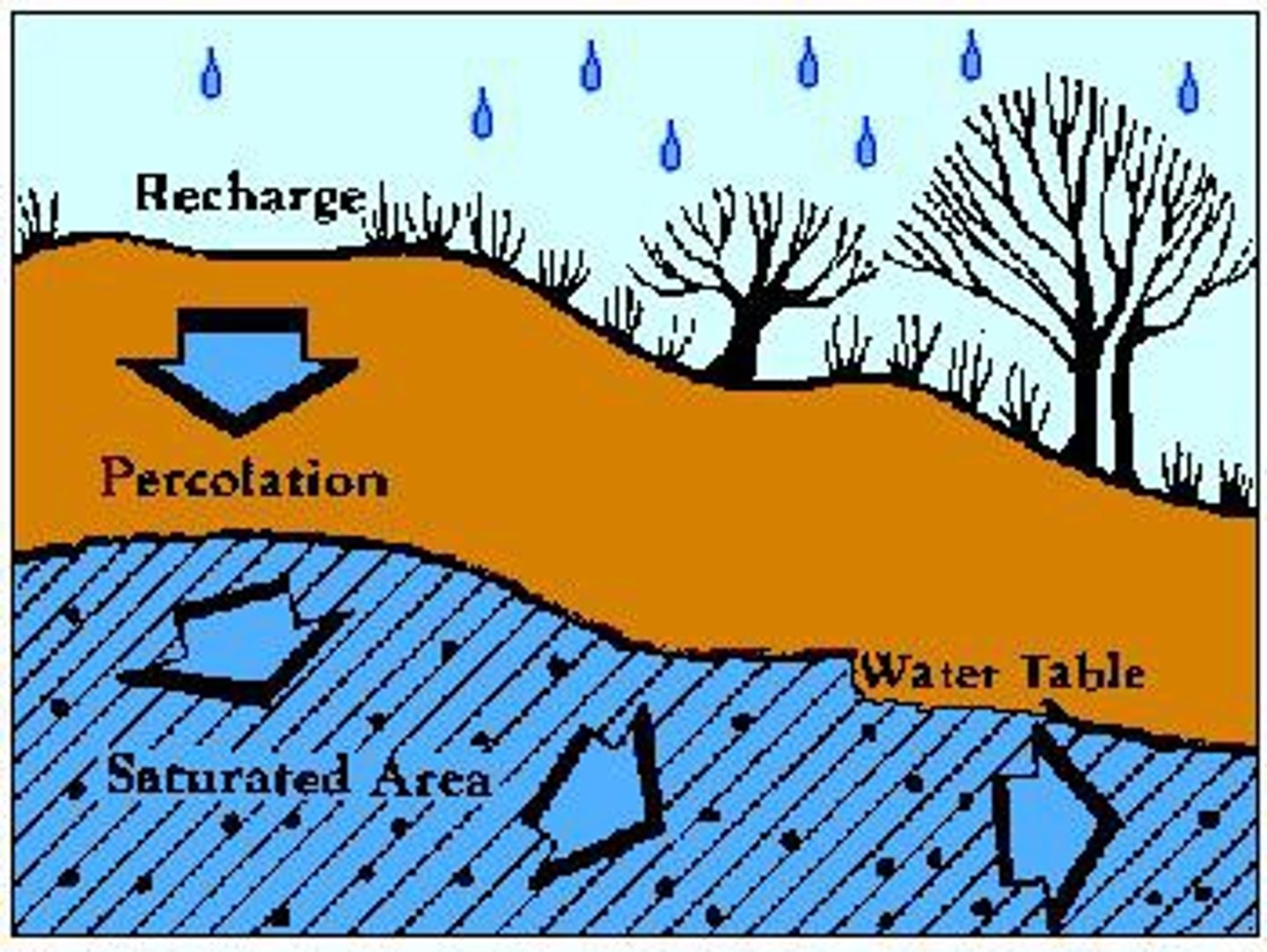
deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations.

bedrock
The solid layer of rock beneath the soil.
