Biology II Lesson 1: Immune System Part II
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the difference between MHC I and MHC II?
MHC I are presented in any regular cell in your body that has a nucleus. The MHC I can add foreign components (often after infection/ cancer) to signal to Tc Cells to destroy them.
MHC II are presented on Professional Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) such as Macrophages, B Cells, etc. They signal to Th Cells to raise the alarm bells and release Cytokines.
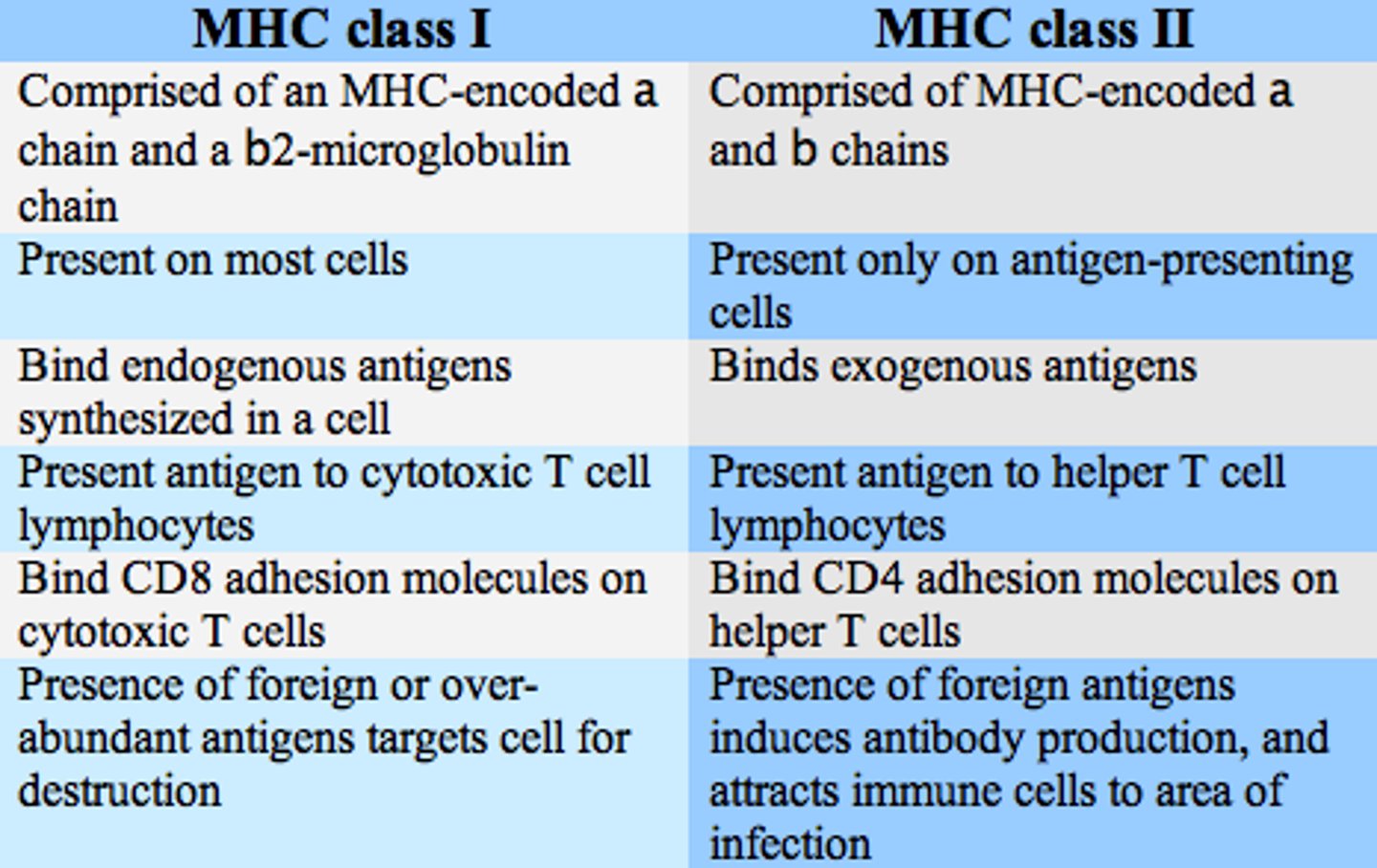
When Tc Cells bind to MHC I, they divide into both Memory Tc Cells and Effector Tc Cells. What are the different roles of these Tc cell types?
Memory Tc Cells are copies of the original Tc Cell.
Effector Tc Cells will bind to other cells presenting the same MHC I and release chemicals such as Perforins or Granzymes, which will destroy the infected or cancerous cell.
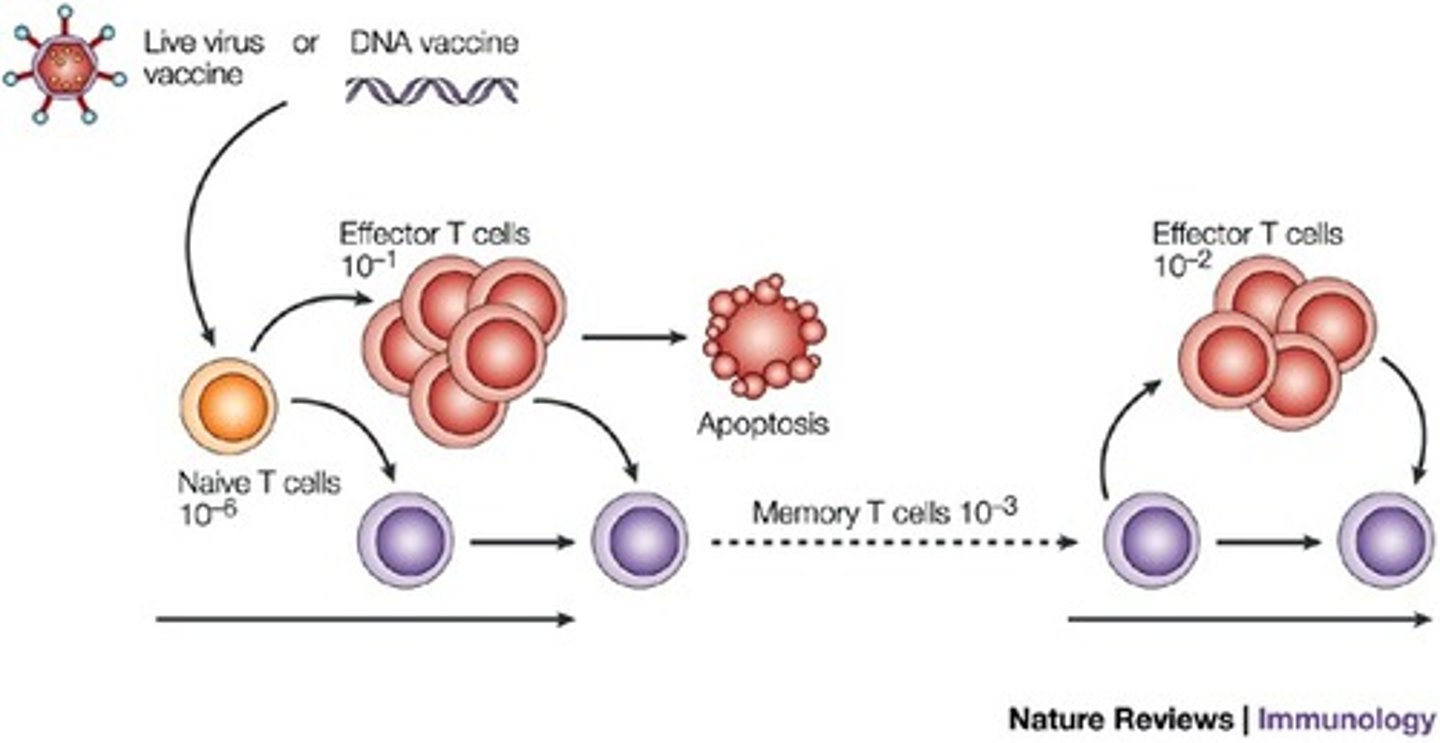
Describe the mechanism of action of Perforins vs. Granzymes.
Perforins make holes in the cell's membrane, resulting in fluid flowing into the cell. This causes Cytolysis by bursting the cell.
Granzymes will induce Apoptosis (a type of programmed cell death) in the infected or cancerous cell.
True or False? All B cells can produce antibodies.
False. Effector B cells are the only subtype of B cells that can create antibodies. Memory B cells cannot!
Effector B cells that make antibodies are often called Plasma Cells once they start making the antibodies.
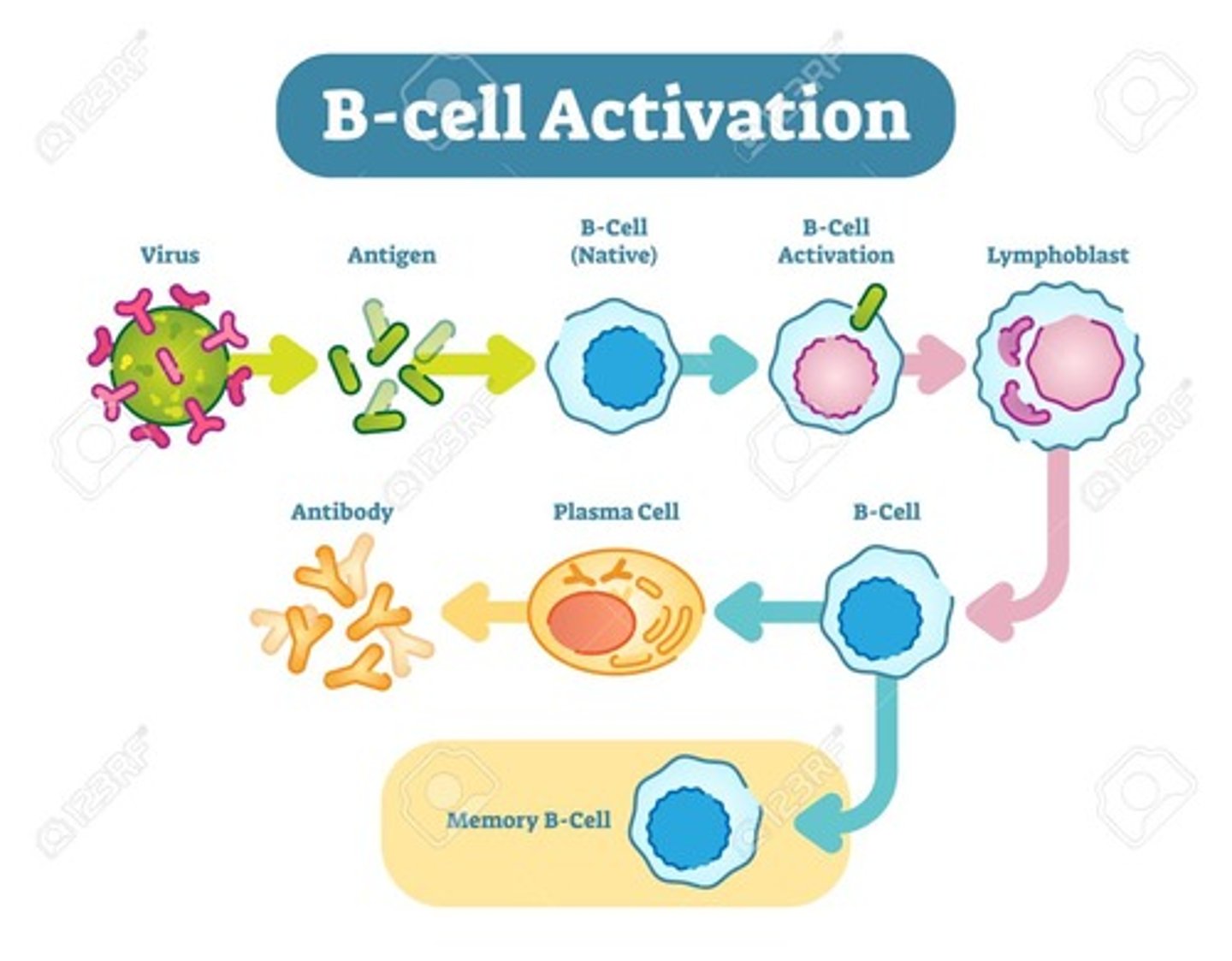
CRB Which of the following terms best describe the B cells that have not been activated or exposed to antigens yet, and can proliferate into Plasma and Memory B Cells?
(A) Progenitor B Cells
(B) Naive B-Cells
(C) Early Stage B-Cells
(D) Hematopoetic B-Cells
(B) Naive B-Cells
Naive B-Cells are the B cells that have not been activated or exposed to antigens yet, and can proliferate into Plasma and Memory B Cells.
CRB In which of the following places would you expect Naive B-cells to be found, where they are waiting to be activated by antigens?
(A) Bone Marrow
(B) Lymph Nodes
(C) Thymus
(D) Circulating in the blood
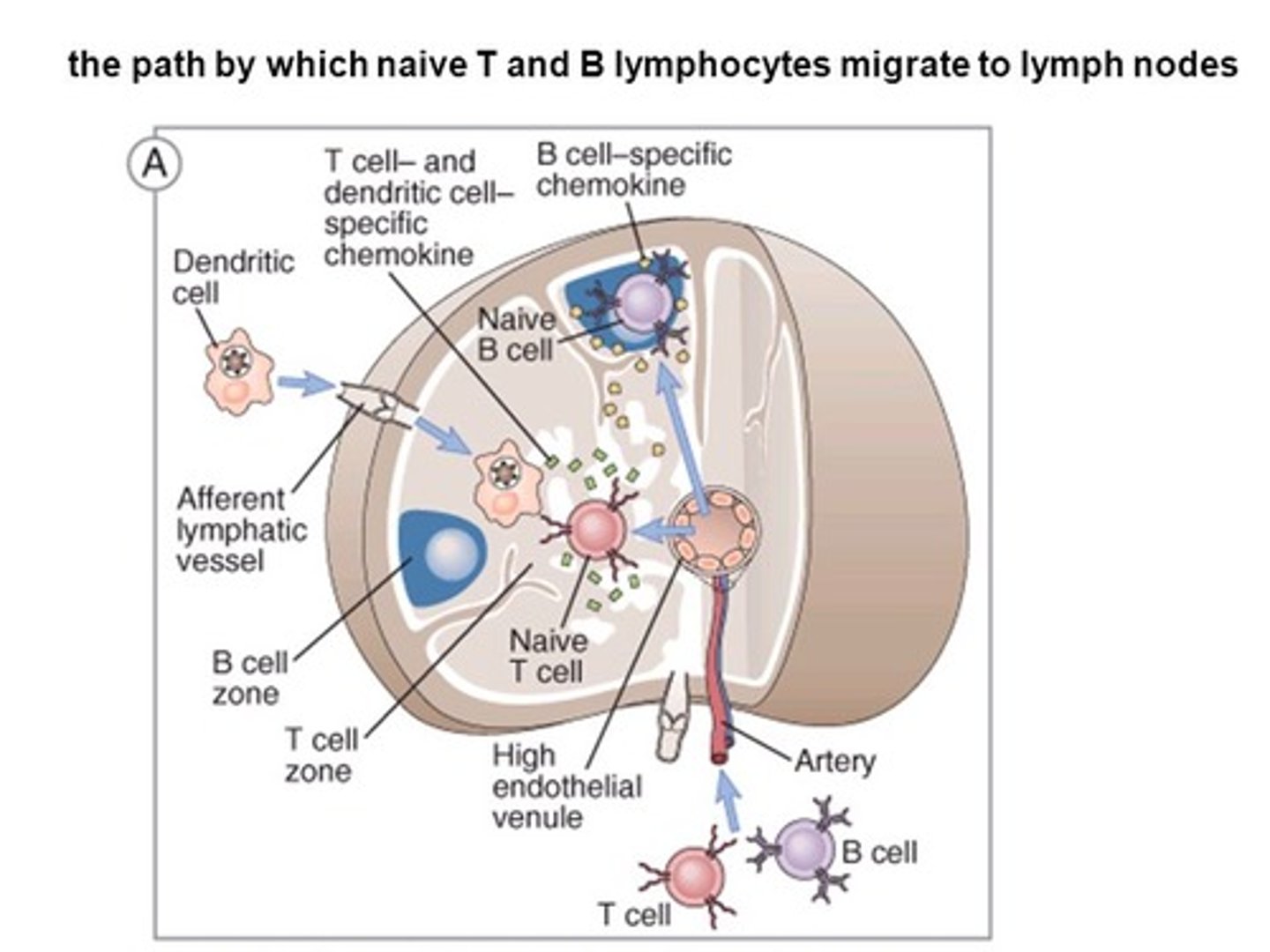
(B) Lymph Nodes
Naive B Cells will be found in the Lymph Nodes, waiting to be activated by antigens.
CRB How long could it take for Humoral Immunity (which is based off antibody production) to become fully effective after the initial infection?
(A) 1 day
(B) 1 week
(C) 1 hour
(D) 1 month
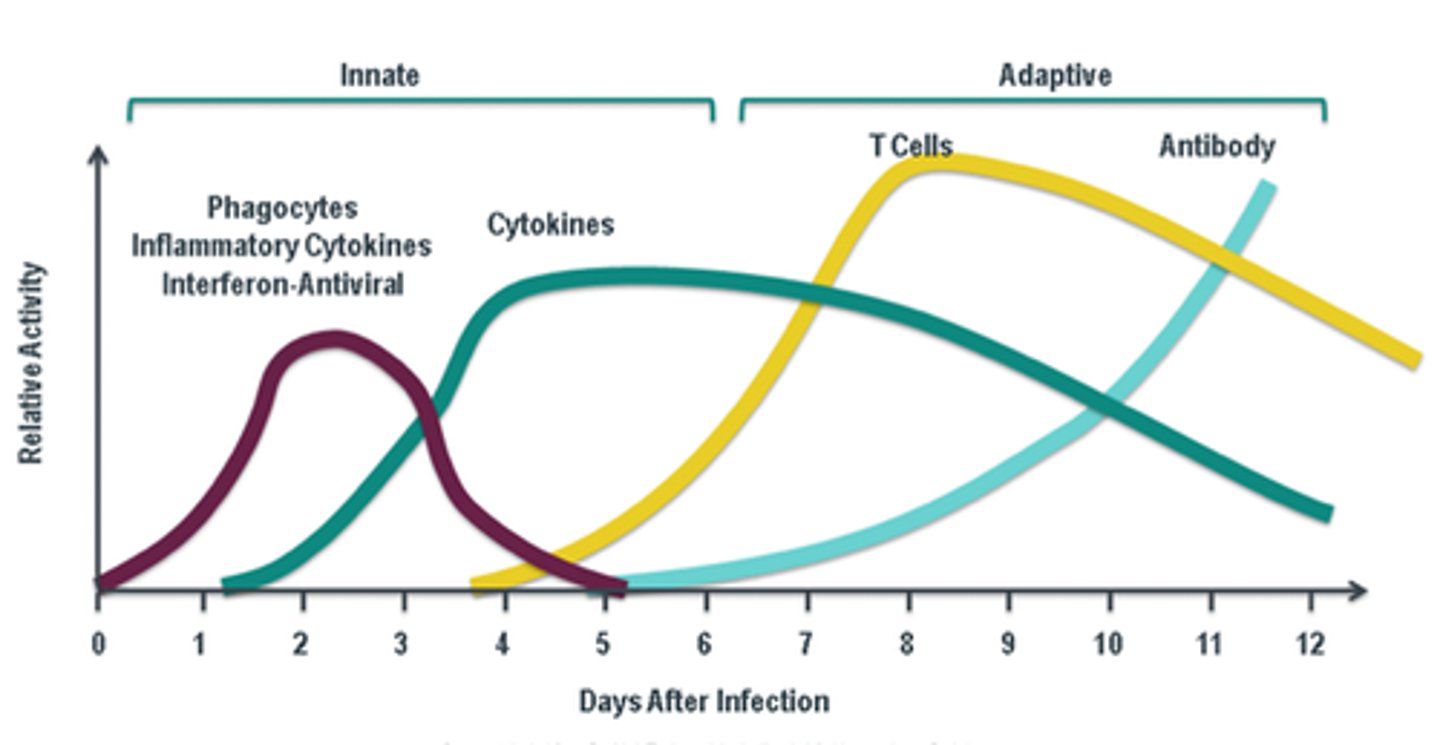
(B) 1 week
It can take up to 1 week for Humoral Immunity to become fully effective after the initial infection.
CRB Fill in the blanks: That one week long phase where the B-cells are initially activated is called the ____________ response, whereas any subsequent infection triggers the _____________ response, and is much quicker.
(A) Primary, Secondary
(B) Initial, Secondary
(C) Primary, Primed
(D) Initial, Primed
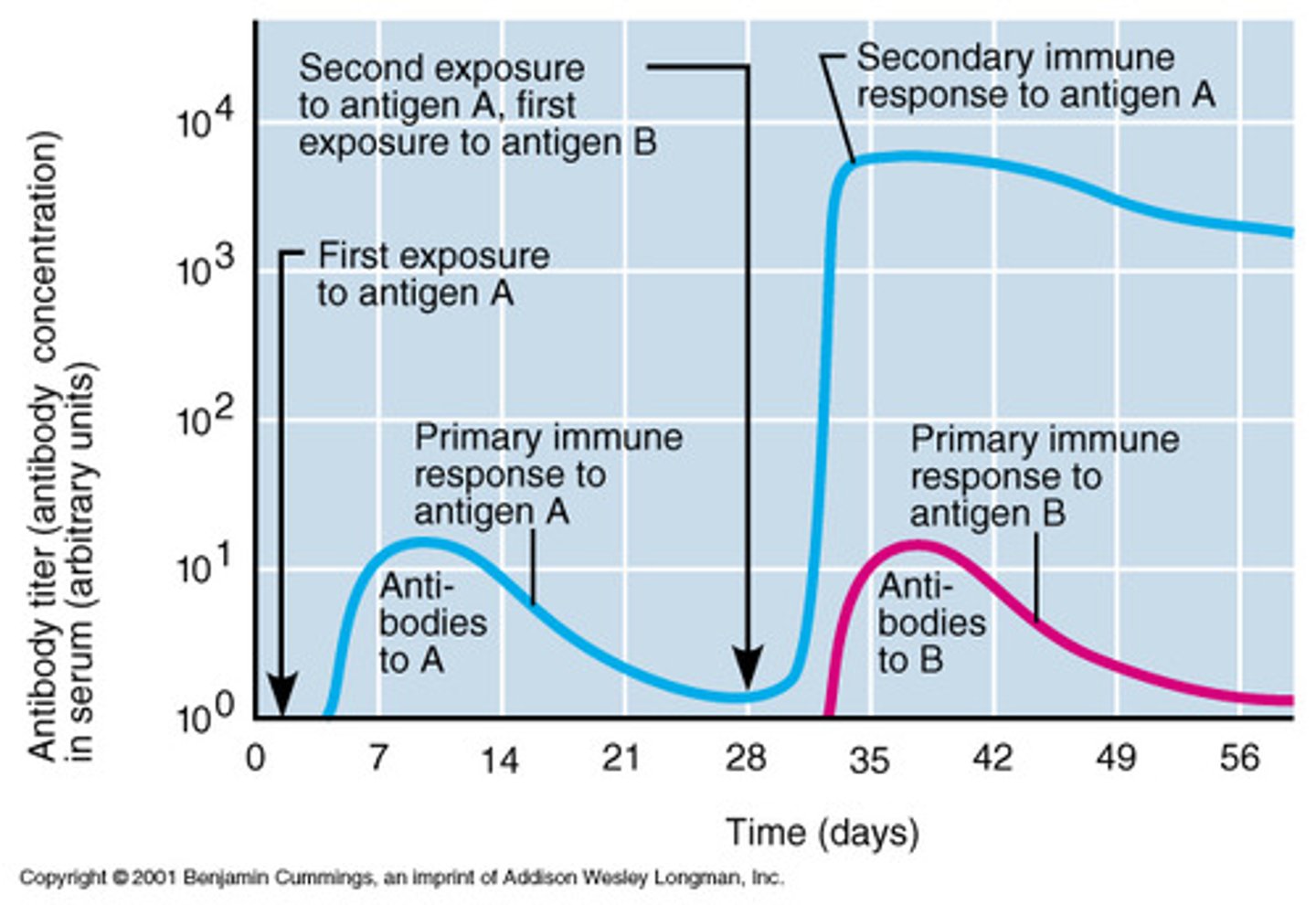
(A) Primary, Secondary
That one week long phase where the B-cells are initially activated is called the Primary response, whereas any subsequent infection triggers the Secondary response, and is much quicker.
CRB Which of the following is not an effect that Antibodies can have on pathogens?
(A) Binding to a specific antigen on the pathogen and attract other leukocytes.
(B) Bind and cause Degranulation, where the granules in the cell undergo exocytosis.
(C) Bind and cause pathogens to Agglutinate, or clump together, so they can be phagocytosed.
(D) Block the ability of pathogens to invade tissues.
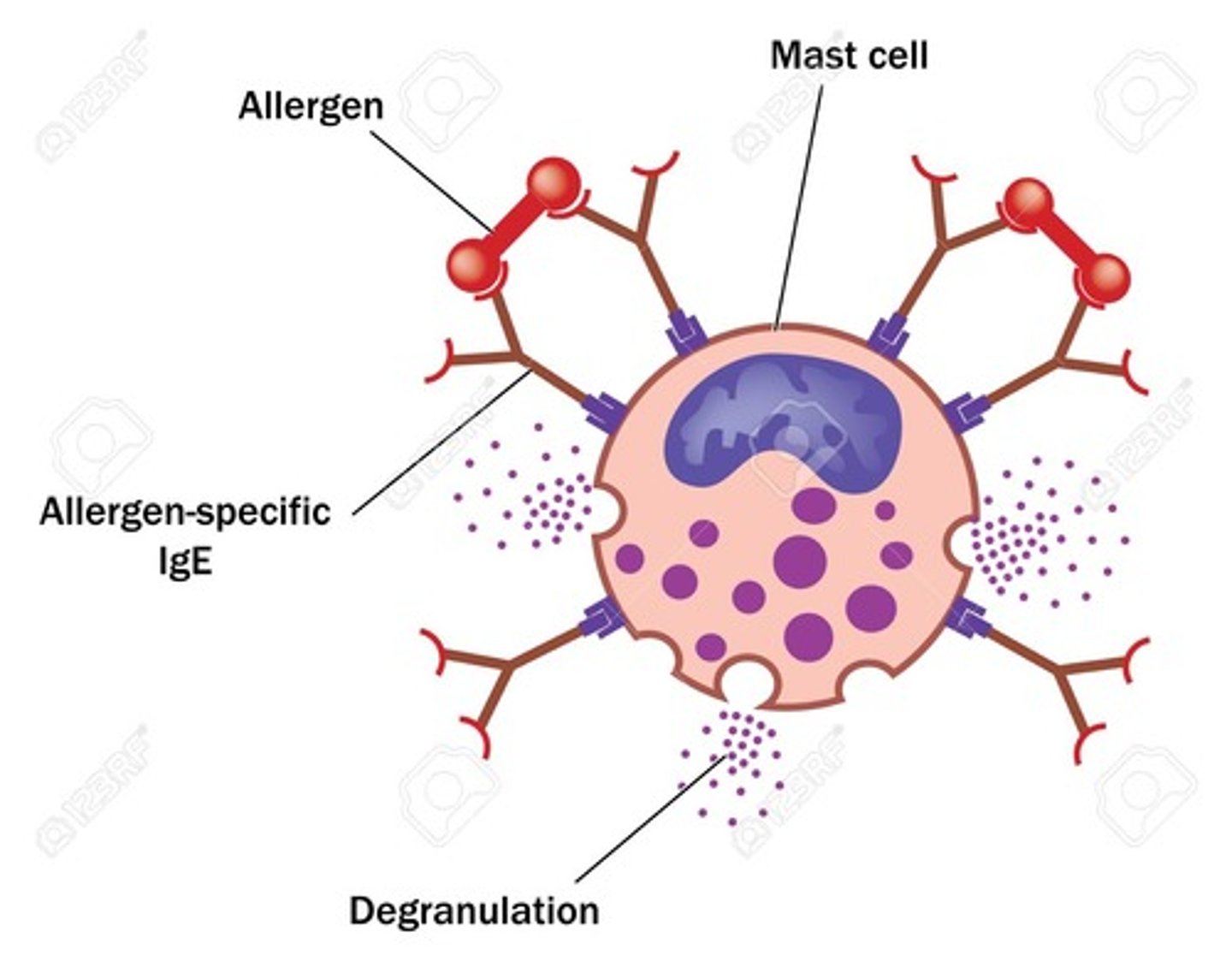
(B) Bind and cause Degranulation, where the granules in the cell undergo exocytosis.
Antibodies actually cause Degranulation in Mast Cells, which leads to the mass release of Histamine and inflammation.
CRB Draw out the general structure of an antibody, including the Light and Heavy Chains, the Constant Region/Domain and the Disulfide Bonds.
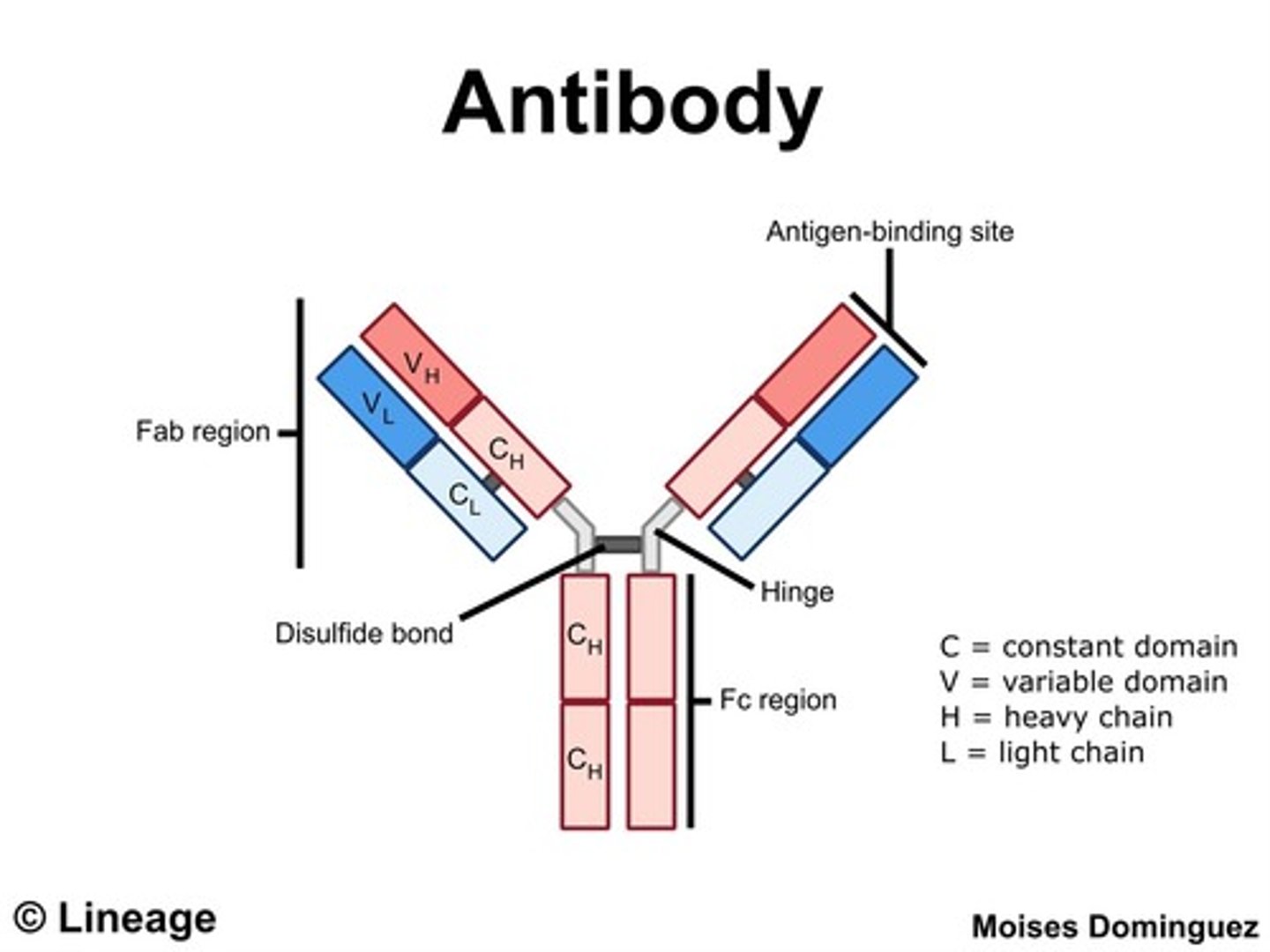
CRB Which of the following statements about Antibody Structure is FALSE?
(A) The heavy chains and light chains on one side of the antibody and the other side in a single antibody are identical.
(B) The heavy and light chains are both needed to form the Antigen-Binding Site.
(C) Only the tips of the heavy chains exhibit Hypermutation, so that there are many possible Antigen Binding Sites circulating at any time.
(D) The varieties of Antigen Binding Sites that most successfully bind the pathogen will proliferate quickly via Clonal Selection.
(C) Only the tips of the heavy chains exhibit Hypermutation, so that there are many possible Antigen Binding Sites circulating at any time.
Hypermutation affects the whole Antigen Binding Site, so it includes both the Heavy and Light chains!
CD4+ T Cells vs. CD8+ T Cells are also known as?
CD4+ T Cells are also known as Helper T Cells (Th Cells). Think "What can I do 4 you"? Also, 4 * 2 = 8, so these guys bind to MHC II.
CD8+ T Cells are also known as Cytotoxic T Cells (Tc Cells). Think that 008 is almost 007 and these guys are killers like James Bond. Also, 8 * 1 = 8, so these guys bind to MHC I.
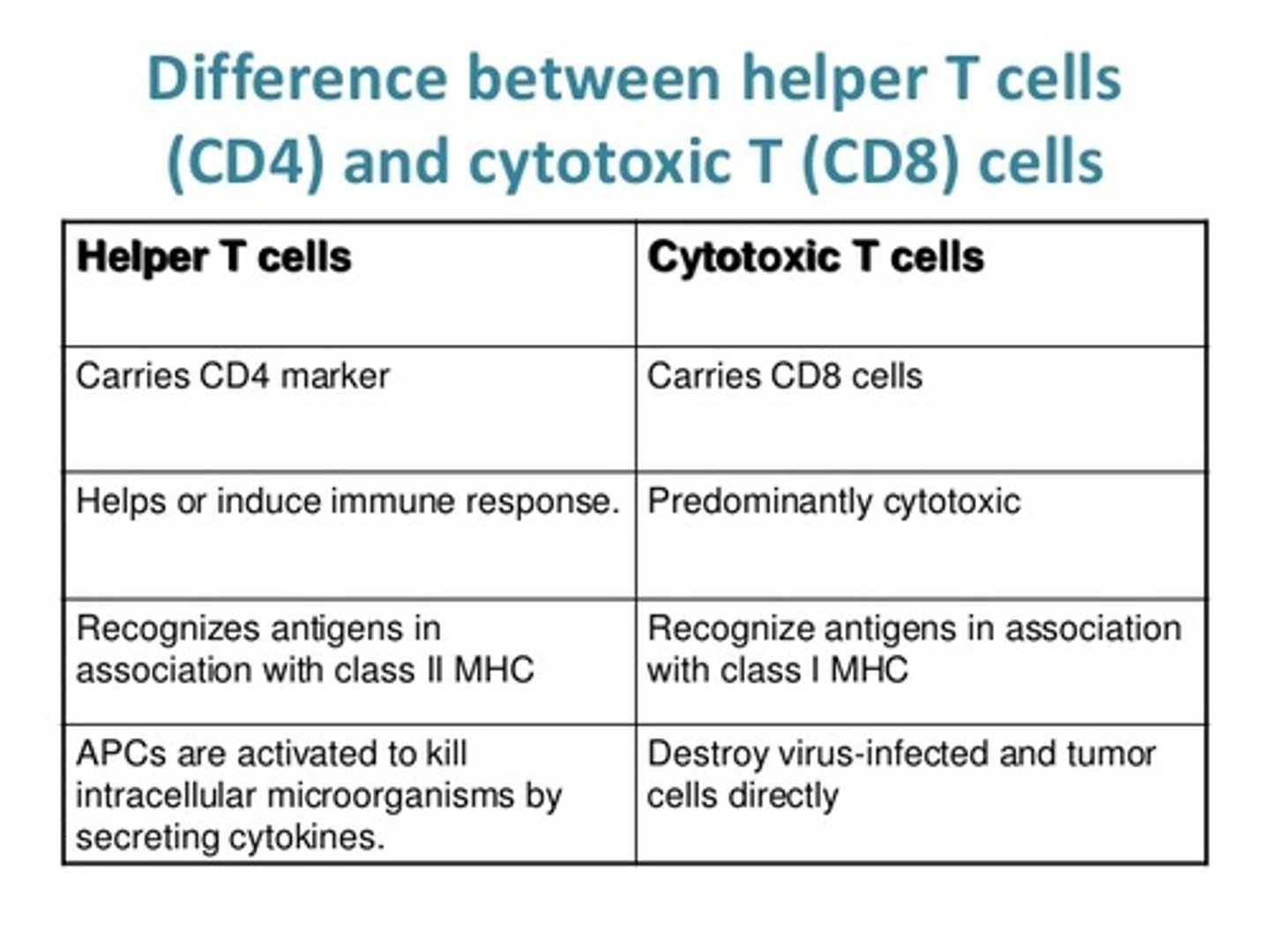
CRB True or false? There are also CD4+ Regulatory T-Cells, which express Foxp3 and can limit the immune response once infections have been contained, and are often affected in auto-immune diseases.
True. There are also CD4+ Regulatory T-Cells, which express Foxp3 and can limit the immune response once infections have been contained, and are often affected in auto-immune diseases.
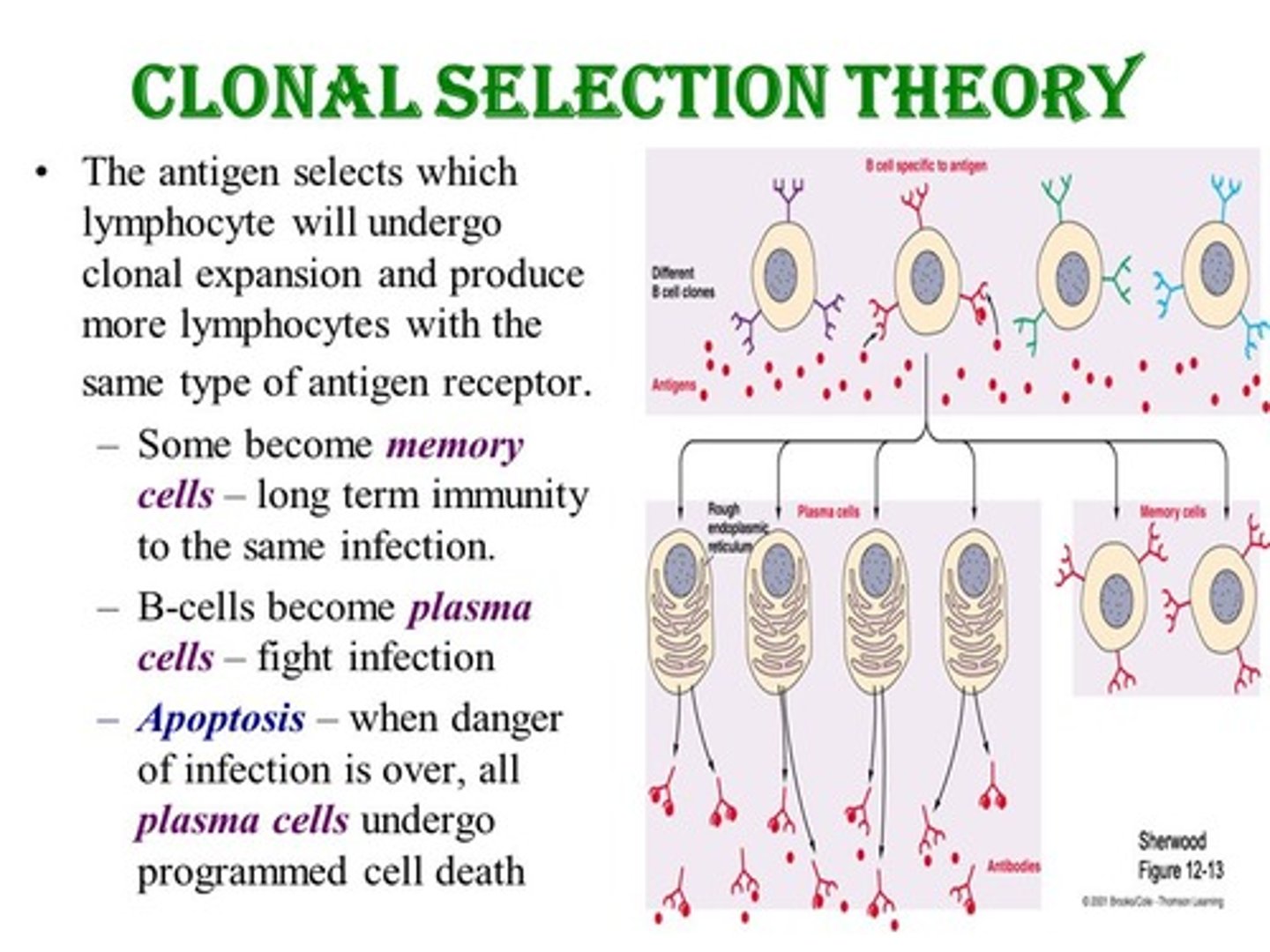
True or False? Just like other cells in the body, every daughter cell of a B Cell or T Cell will be completely unique.
False. B Cells and T Cells are different from other cells in the body in that each of their daughter cells are unique, having a different receptor that is specific to a certain antigen or MHC.
True or false: In clonal selection, the receptors on B or T cells do not change.
True. In clonal selection, the receptors on B or T cells do not change.
Cloning occurs because its receptor bound to an antigen, so cloning to give a different receptor would lose that specificity!
CRB Which of the following terms best describes how B cells can change the type of antibody they produce (between IgM, IgG, etc.)?
(A) Clonal Selection
(B) Natural Selection
(C) Isotope Switching
(D) Isotype Switching
(D) Isotype Switching
Isotype Switching is when B cells can change the type of Antibody they produce.
B cells are produced in the ___________. T Cells are produced in the ____________.
(A) thymus, thymus
(B) thymus, bone marrow
(C) bone marrow, bone marrow
(D) bone marrow, thymus
(C) bone marrow, bone marrow
B cells are produced in the bone marrow. T Cells are produced in the bone marrow.
B cells are mature in the ___________. T Cells are mature in the ____________.
(A) thymus, thymus
(B) thymus, bone marrow
(C) bone marrow, bone marrow
(D) bone marrow, thymus
(D) bone marrow, thymus
B cells are mature in the bone marrow. T Cells are mature in the thymus.
Note: Think B and B vs T and T.
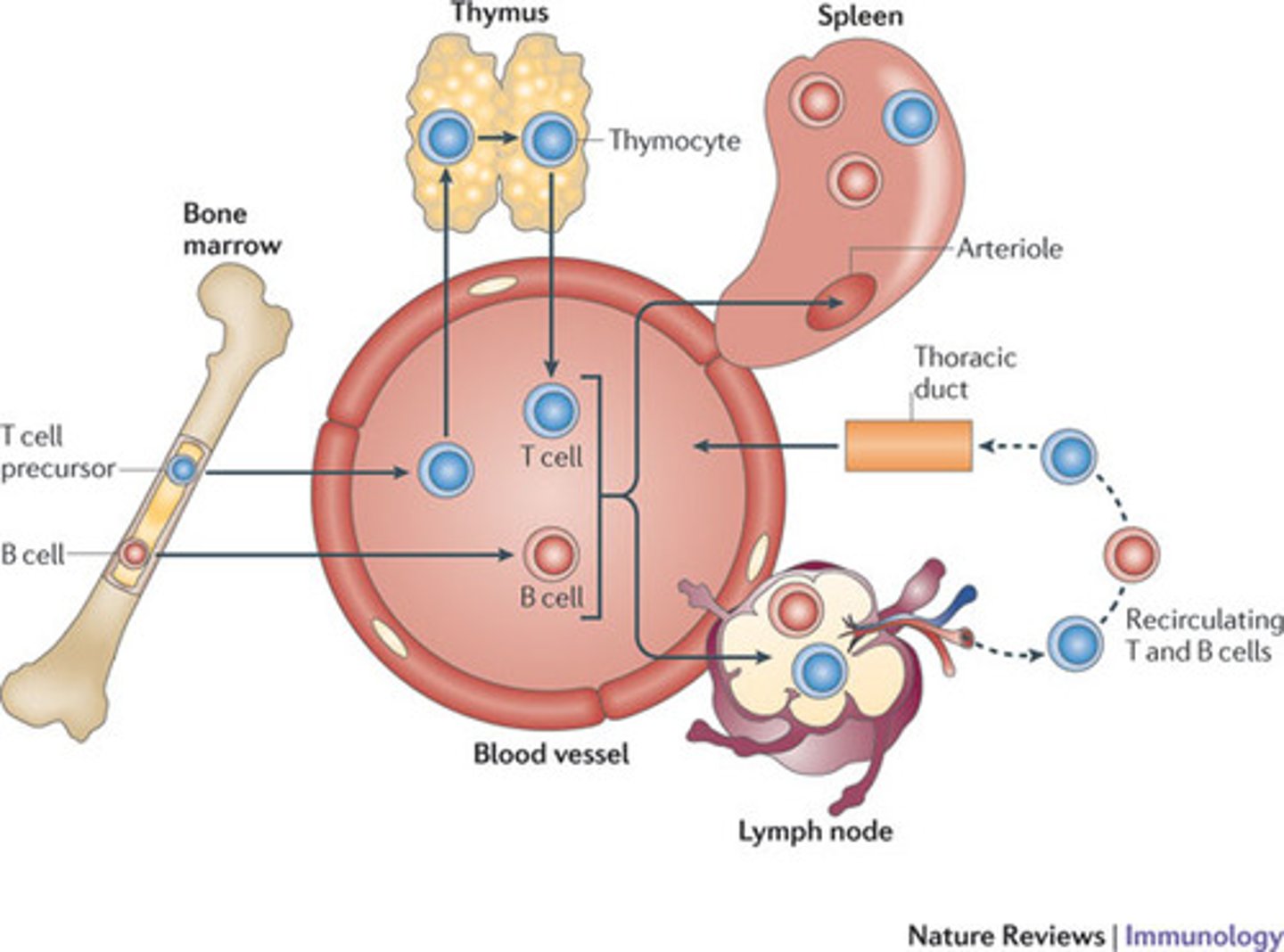
True or False. B Cell receptors can bind both directly to invaders or to MHC complexes that are presenting part of that invader.
False. B Cell receptors do not bind to MHCs.
True or False? Although production of self-recognizing B and T Cells is rare, thankfully our body has ways of destroying such cells.
False. Production of self-recognizing B and T Cells is impossible to prevent, making them common, which makes it essential that our body has ways of destroying such cells.
CRB Compare Positive and Negative Selection of T Cells during maturation.
Positive Selection of T Cells means only the T cells that can respond to antigens being presented on the MHC will mature (to pass the test, must have a Positive reaction).
Negative Selection of T Cells means cells that are self-reactive will not be allowed to mature (to pass the test, must have a Negative Reaction).
What type of B Cells will be destroyed/not activated in the bone marrow? In the lymph nodes?
In the bone marrow, any B Cell that binds to an antigen is destroyed and will not continue its development.
In the lymph nodes, any B Cell that doesn't bind to a Th Cell with its MHC II will never be activated.
What happens if a bacteria gets into your bone marrow and binds to a B Cell?
The B Cells that recognize that antigen will be destroyed, leaving you susceptible to infection!
How do Autoimmune diseases relate to these ideas?
When you have B or T Cells that recognize self-antigens, that is known as an Autoimmune Disease.
CRB There are five types of infectious pathogens, and all but one of them will normally trigger an immune response. Which of the following is that pathogen type?
(A) Prions
(B) Fungi
(C) Plaques
(D) Parasites
(A) Prions
Prions, Fungi, Parasites, Bacteria and Viruses all are infectious pathogen types, but there are no immune defenses against prions.
Plaques are not a type of infectious pathogen.
Neutrophils are the most common type of white blood cell. Describe how they are able to get from the blood stream into tissues and how they know when and where to do it.
Macrophages are located in your tissues. Upon activation, macrophages will release chemicals that will signal to the endothelial cells lining your blood vessels to present certain chemicals on the inner wall of the blood vessel. Neutrophils will be attracted to and bind to these chemicals, allowing them to then squeeze between the endothelial cells and enter the tissues.
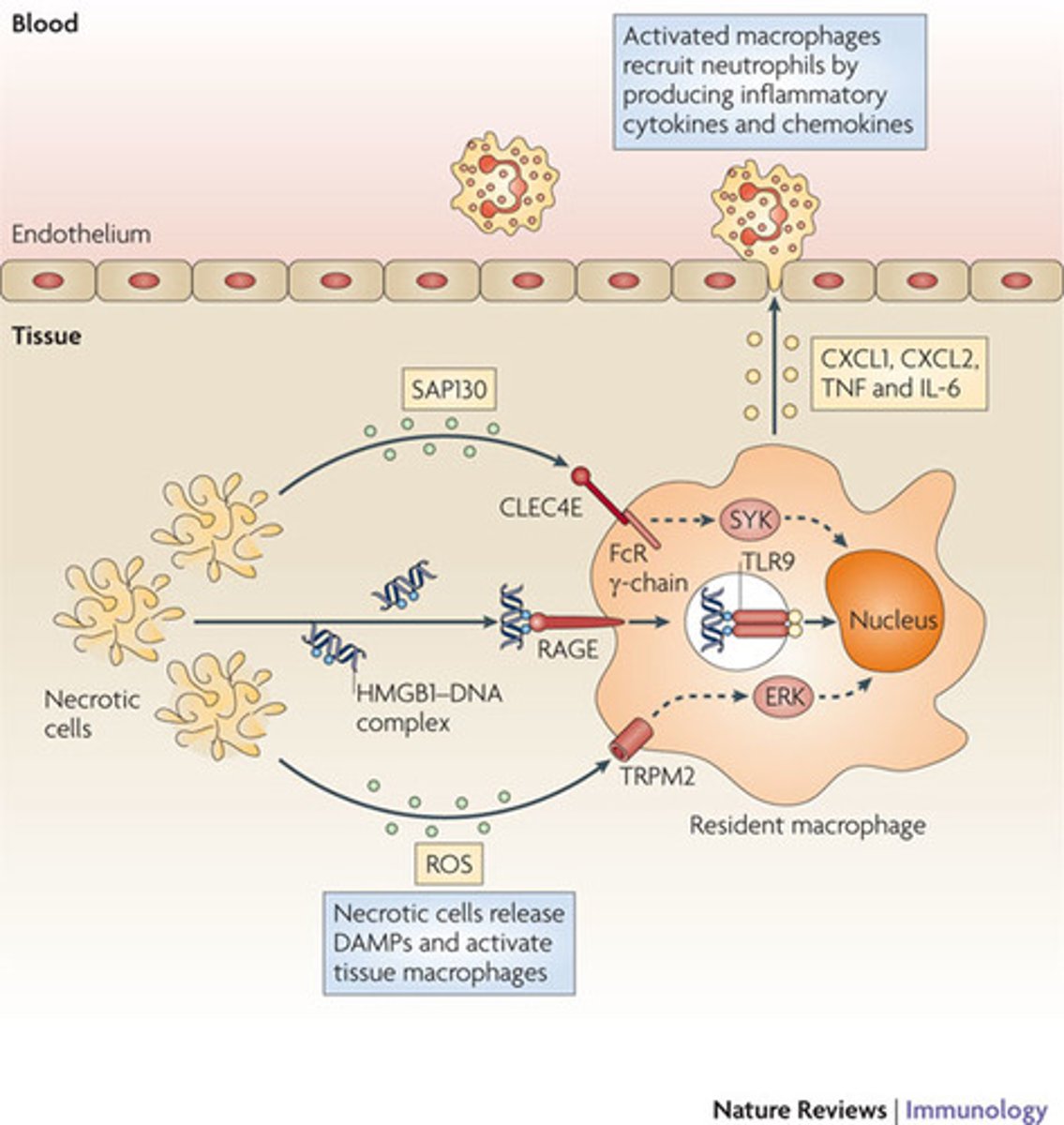
What is the function of a Neutrophil?
Neutrophils function by phagocytosing invaders and then dying. They are like suicide bombers. After they die they make up what we call "pus".
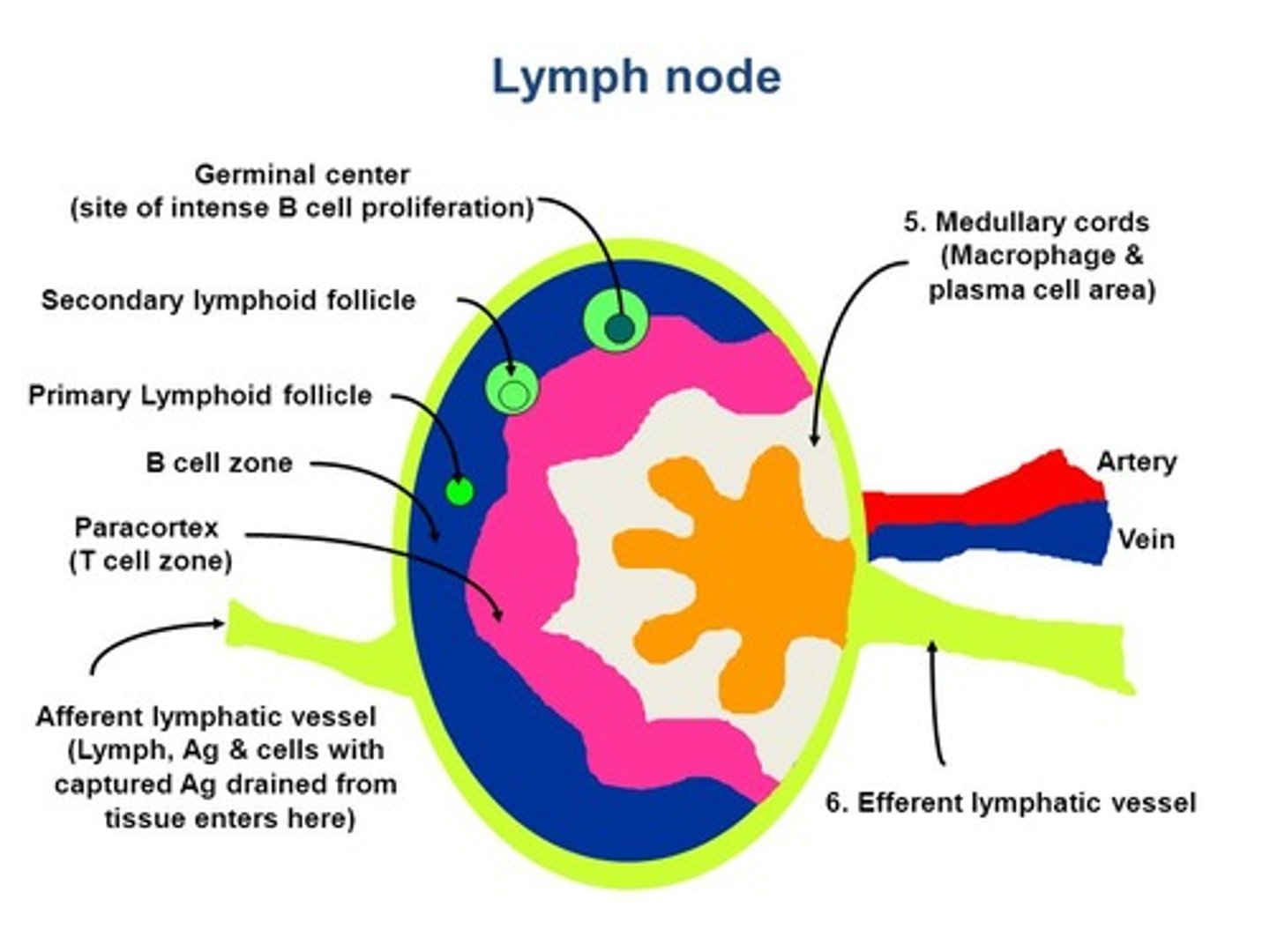
If macrophages are unable to transport through the bloodstream to the B and T Cells, how will it get to them to warn them of invaders?
Macrophages will be transported to the B and T Cells, which are in the lymph nodes, via lymphatic vessels. The Tc Cells and antibodies will then go through the Thoracic Duct, enter the bloodstream and eventually diffuse through the blood vessels into the tissues where they can assist in fighting invaders.
CRB Compare Active and Passive Immunity.
Active Immunity is when the Immune system is activated, and it will create the antibodies it needs to target a specific pathogen.
Passive Immunity is when antibodies are transferred to the individual.
CRB True or false? Passive Immunity can last a lifetime, because these Antibodies can be used to produce Plasma Cells.
False. Passive Immunity is Transient, because only Antibodies are transferred, NOT Plasma Cells.
CRB One of my mentors has recently had a baby, and one way that the baby can receive necessary antibodies is to have them passed to the baby via breastfeeding. Would this be an example of Passive or Active Immunity?
Because these antibodies are being transferred to the baby, this would be an example of Passive Immunity.
CRB Oftentimes, vaccines are given because they can provide Artificial Exposure and trigger the Primary Response. Would these vaccines be part of Active or Passive Immunity?
Vaccines are triggering the creation of antibodies against a specific pathogen (via the Primary Response), making them a part of Active Immunity.