physics revisoin
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what are scalar quantities
a quantity that only has size
what are vector quantities
a quantity with size and direction
what is displacement
how far an object has moved from its original position
or
the distance between two points
what is speed
the distance covered per unit time
equation for speed
speed = distance / time
what is the equation for velocity
velocity = displacement / time
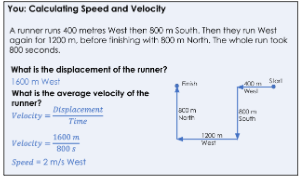
a runner runs 400 metres west then 800m south. then they run west again for 1200m before finishing with 800m north . the whole run took 800 seconds.
what is the displacement of the runner?
what is the average speed of the runner?
what is a resultant vector
is the combination of 2 or more single vectors
what is newtons 3rd law
every action has an equal and opposite reaction
if the tyres exert a force on the road what does the road do
exert an equal and opposite reaction on the tyres
what is newtons 1st law
an objects motion will not change unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
what is acceleration
the rate of change in velocity
what does a negative acceleration mean
the object is decelerating
if an object is moving in a circle is it accelerating or deceleration
it’s accelerating as the object is constantly moving
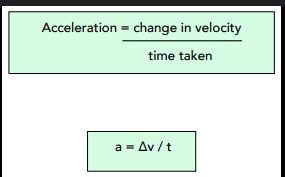
what is the equation of acceleration
calculate the acceleration of a car that goes from rest to 10 m/s forward in 5 seconds
acceleration = change in velocity / time
a = 10 m/s - 0 m/s /5 s
a = 2m/s²
what is internal energy
it is the total kinetic and potential energy of all the particles in a system
what are thermal transfers
the movement of heat energy from one place or object to another
what is specific heat capacity
the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1ºC.
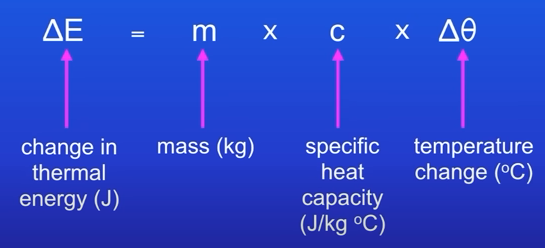
how do you calculate the amount of energy stored in or released from a system as its temperature changes (specific heat capacity)
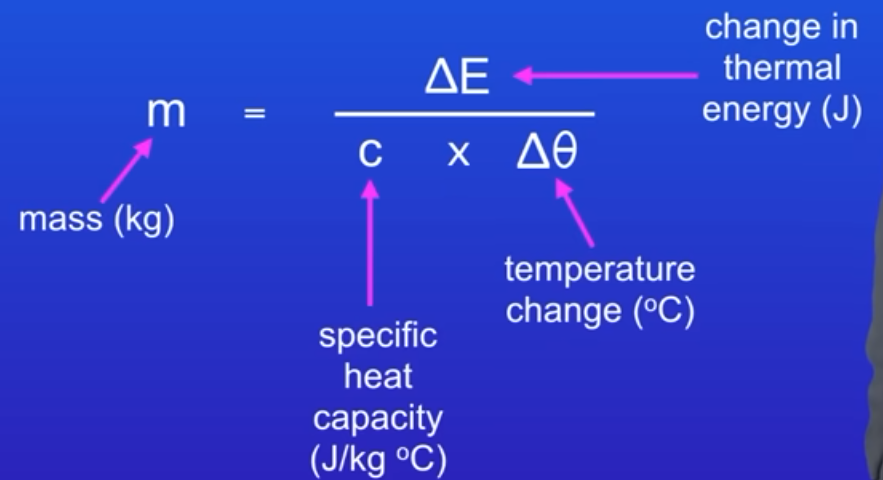
rearrange the equation so we can find mass
A copper kettle has a mass of 0.8 kg. Calculate the thermal energy stored in the kettle when its temperature rises from 25∘C to 100∘C. The specific heat capacity of copper is 385 J/(kg∘C).
Formula Used: ΔE = m × c × Δθ
How to Solve:
Identify the knowns:
Mass (m) = 0.8 kg
Specific Heat Capacity (c) = 385 J/(kg∘C)
Initial Temperature = 25∘C
Final Temperature = 100∘C
Calculate the change in temperature (Δθ):
Δθ=Final Temperature−Initial Temperature
Δθ = 100∘C − 25∘C = 75∘C
Substitute the values into the formula:
ΔE = 0.8 kg × 385 J/(kg∘C) × 75∘C
Calculate the result:
ΔE = 23100 J
Answer: The thermal energy stored in the kettle is 23100 J.
A 3 kg block of lead cools down, releasing 27600 J of thermal energy. If the temperature of the lead changed by 20∘C, what is the specific heat capacity of lead?
Formula Used: Rearranged from ΔE = m × c × Δθ to c = ΔE / (m × Δθ)
How to Solve:
Identify the knowns:
Change in Thermal Energy (ΔE) = 27600 J
Mass (m) = 3 kg
Change in Temperature (Δθ) = 20∘C
Substitute the values into the rearranged formula:
c = 27600 J / (3 kg × 20∘C)
Calculate the denominator first:
3 kg × 20∘C = 60 kg∘C
Perform the division:
c = 27600 J / 60 kg∘C
c = 460 J/(kg∘C)
Answer: The specific heat capacity of lead is 460 J/(kg∘C).
what is specific latent heat
the amount of energy required to change the stat of 1 kg of a substance by no change in temp.
how do you calculate the energy change taking place when an object changes state (specific latent heat)

what are the 2 types of waves
longitudinal and transverse
do waves transfer energy using matter
no they are transferred by oscillations
do the objects producing the wave in longitudinal waves vibrate parallel or perpendicular to the direction of the waves energy transfer
parallel
do the objects producing the wave in transverse waves vibrate parallel or perpendicular to the direction of the waves energy transfer
perpendicular at 90∘
what is an example of transverse waves
light and water waves
what is an example of a longitudinal wave
sound waves
what do both waves transfer
energy
what is the peak in a wave
the maximum point of a wave
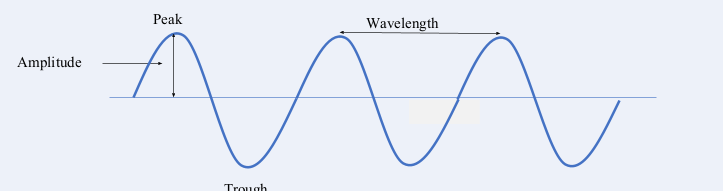
what is the trough in a wave
the minimum point of a wave
what is the wavelength
the distance from one point of a wave to the same spot on the next wave
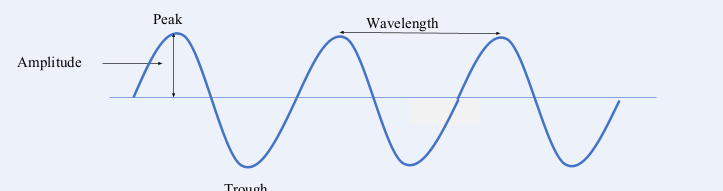
what is the amplitude
the maximum distance of a point on the wave from its rest position
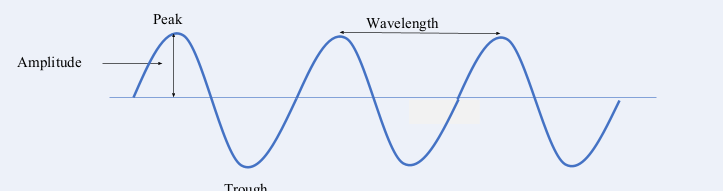
what is frequency
the number of waves that pass by each second. Unit = Hz, hertz
what is a period
the amount of time it takes a wave to pass a given point. Unit = s, seconds
what is the equation for frequency

what is the equation for period?
period = 1 / frequency
how do you work out the velocity of a wave

what does luminous mean and non luminous mean
luminous - gives out light
non luminous - does not give out light
what does opaque and translucent mean
opaque - light cannot be transmitted
translucent - some light can be transmitted but it is not very clear
what is refraction
refraction is when light (or other waves) changes direction as it passes from one transparent medium into another, due to a change in its speed.