Comprehensive Earth Science: Storm Systems, Climate, and Plate Tectonics
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
What are the three scales of storm systems?
Microscale (< 1km), Mesoscale (up to 300/400 km), Synoptic-scale (> 1000 km)

What is a tropical cyclone?
A low pressure system in the tropics with sustained winds of 119 km/h (74 mph) or more.

What is the fastest wind gust ever recorded?
408 km/h (253 mph) on April 10, 1996, at Barrow Island, Australia.
What direction do tropical cyclones rotate in the Northern Hemisphere?
Counterclockwise.
What are the essential ingredients for a tropical cyclone to form?
Warm ocean water (26° C/80° F), depth of at least 60 m (200 ft), no wind shear, significant Coriolis deflection, and a trigger.
What is the eye of a tropical cyclone?
The central area of low pressure where cold air sinks, usually calm and clear.
What is the eyewall in a tropical cyclone?
A severe ring of towering thunderstorms with the highest winds and heaviest rain.
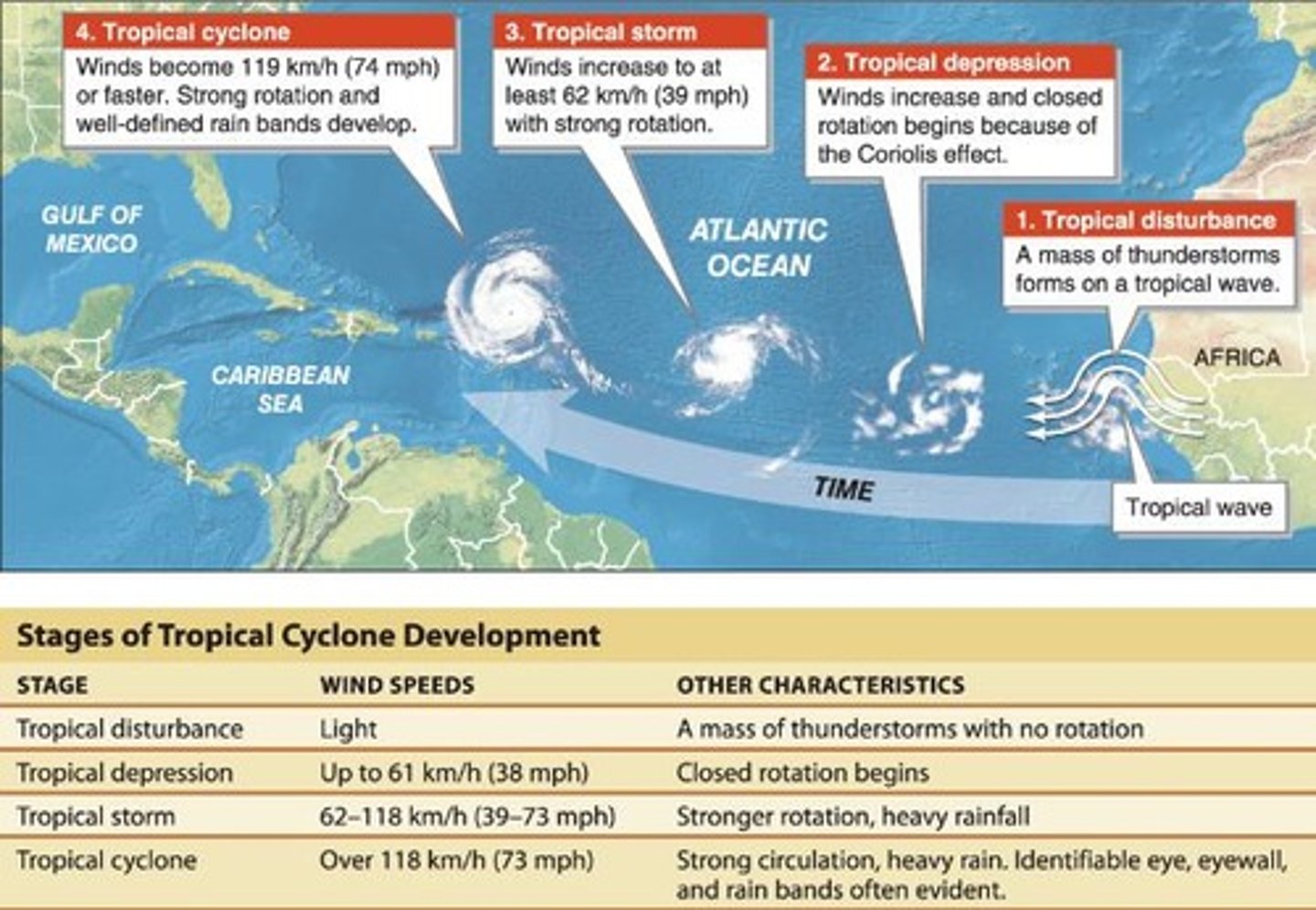
What are spiral rain bands?
Arms of heavy precipitation extending out from the eye of a tropical cyclone.
What was the world record for rainfall from a single storm?
3.93 m (12.89 ft) in 3 days during Cyclone Gamede on Reunion Island.
What was the rainfall amount during Hurricane Harvey in 2017?
164 cm (64.6 in) in Houston.
What are the hazards associated with tropical cyclones?
Wind and water hazards, including flooding and storm surge.
What was the impact of Hurricane Mitch in 1998?
11,000 died and 1.5 million were left homeless in Honduras/Nicaragua.
What are the wind speed ranges for a Category 1 hurricane?
Winds of 74-95 mph.
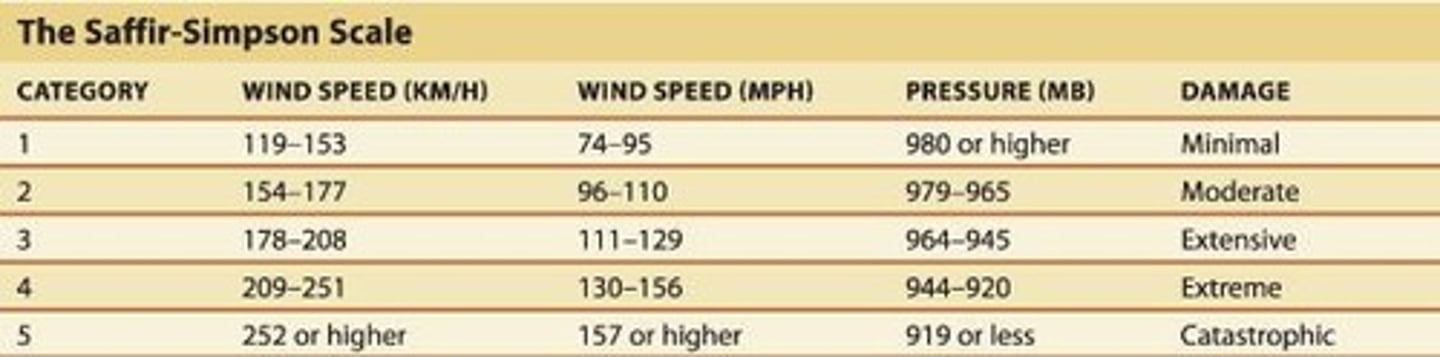
What type of damage can a Category 2 hurricane cause?
Considerable damage to shrubbery and mobile homes, with storm surge of 6-8 feet.
What are the characteristics of a Category 3 hurricane?
Winds of 111-130 mph, significant damage to trees and structures, and storm surge of 9-12 feet.
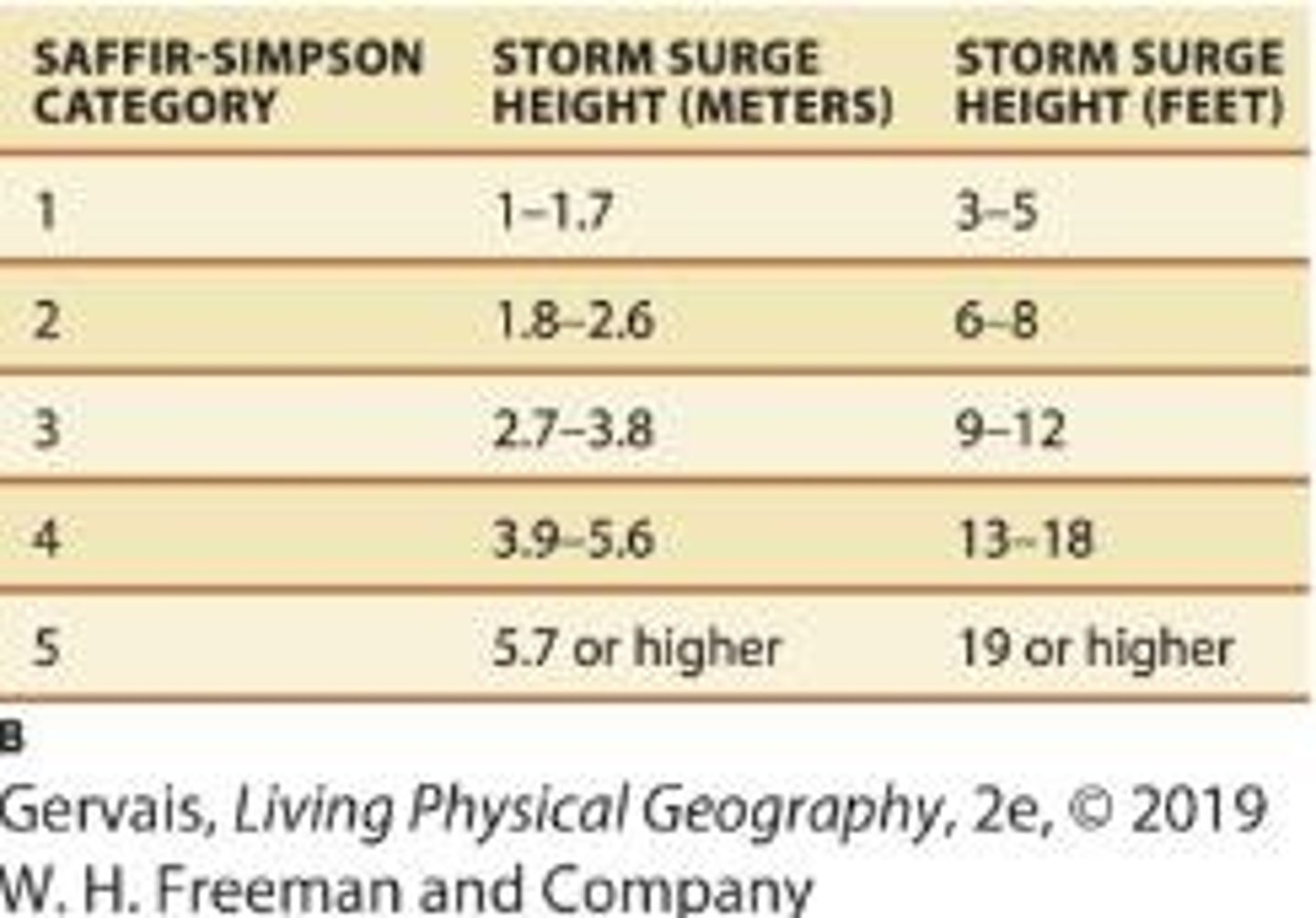
What is the damage potential of a Category 4 hurricane?
Winds of 131-155 mph, extensive damage to roofs and structures, and storm surge of 13-18 feet.
What defines a Category 5 hurricane?
Winds greater than 155 mph, severe damage to structures, and storm surge higher than 18 feet.
What factors contribute to the deadliness of tropical cyclones?
Population density, development/infrastructure, and landscape.
What was the cost and death toll of Hurricane Sandy in 2012?
$65 billion in damages and 186 deaths.
What advancements have been made in hurricane forecasting since 1992?
3-day forecast error improved from +/- 270 miles in 1992 to +/- 90 miles in 2016.
What is a hurricane watch?
Issued 48 hours in advance of tropical storm-force winds.
What is a hurricane warning?
Issued 36 hours in advance of a storm's landfall for coastal locations.
What is the role of weather data in forecasting?
Fundamental for science, collected from surface stations, marine buoys, and weather balloons.
What are numerical forecasting models?
Computer models that integrate weather data for predictions, requiring supercomputers for calculations.
How often are radiosondes launched?
Twice daily at 750 locations worldwide.
What is the significance of ensemble forecasting?
It examines multiple model runs to improve accuracy in weather predictions.
What does climate refer to?
An aggregate of weather conditions over a long period, usually requiring a 30-year record.
What challenges exist in climate classification?
Climate is continuously variable, making it difficult to define and classify.
What factors did early Greeks note about climate variation?
They classified the known world into Frigid, Temperate, and Torrid zones based on temperature and latitude.
What type of damage can hurricanes cause to buildings?
Severe and extensive damage to windows and doors, complete roof collapse, and destruction of glass.
What is the storm surge height that can occur during hurricanes?
Storm surge can be higher than 18 feet above normal.
What areas are at risk for major damage during a hurricane?
Lower floors of all structures less than 15 feet above sea level within 500 yards of shore.
What evacuation measures may be necessary before a hurricane?
Massive evacuation of residential areas on low ground within five to 10 miles of shore may be required.
What advancements have been made in hurricane forecasting from 1992 to 2016?
In 1992, the average error for a 3-day forecast was +/- 270 miles; by 2016, it improved to +/- 90 miles.
What is the role of Doppler Radar in weather forecasting?
Doppler Radar provides real-time data from 159 fixed sites in the US and a mobile fleet.
What are the primary sources of weather data for forecasting?
Surface stations, marine buoys, radiosondes (weather balloons), satellites, and Doppler Radar.
What is the purpose of numerical forecasting models?
To integrate weather data into computer models for predicting weather patterns.
How long does it take to advance a weather model forward by one day?
It takes one hour to advance the model forward by one day.
What is ensemble forecasting?
Ensemble forecasting examines multiple model runs to interpret various outcomes.
What are the classifications of climate based on the Köppen system?
A - humid tropical, B - arid, C - humid mesothermal, D - humid microthermal, E - polar, H - highlands.
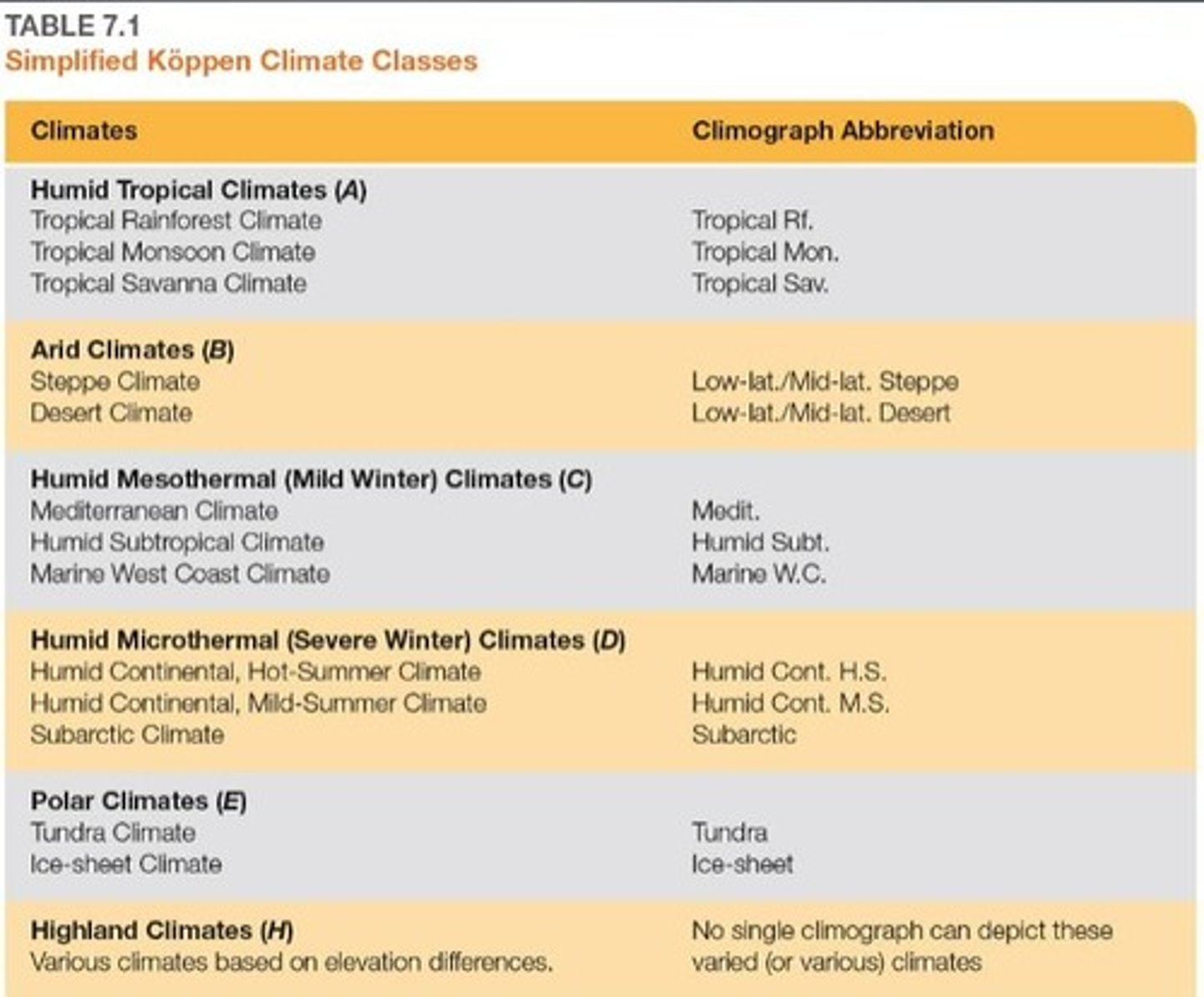
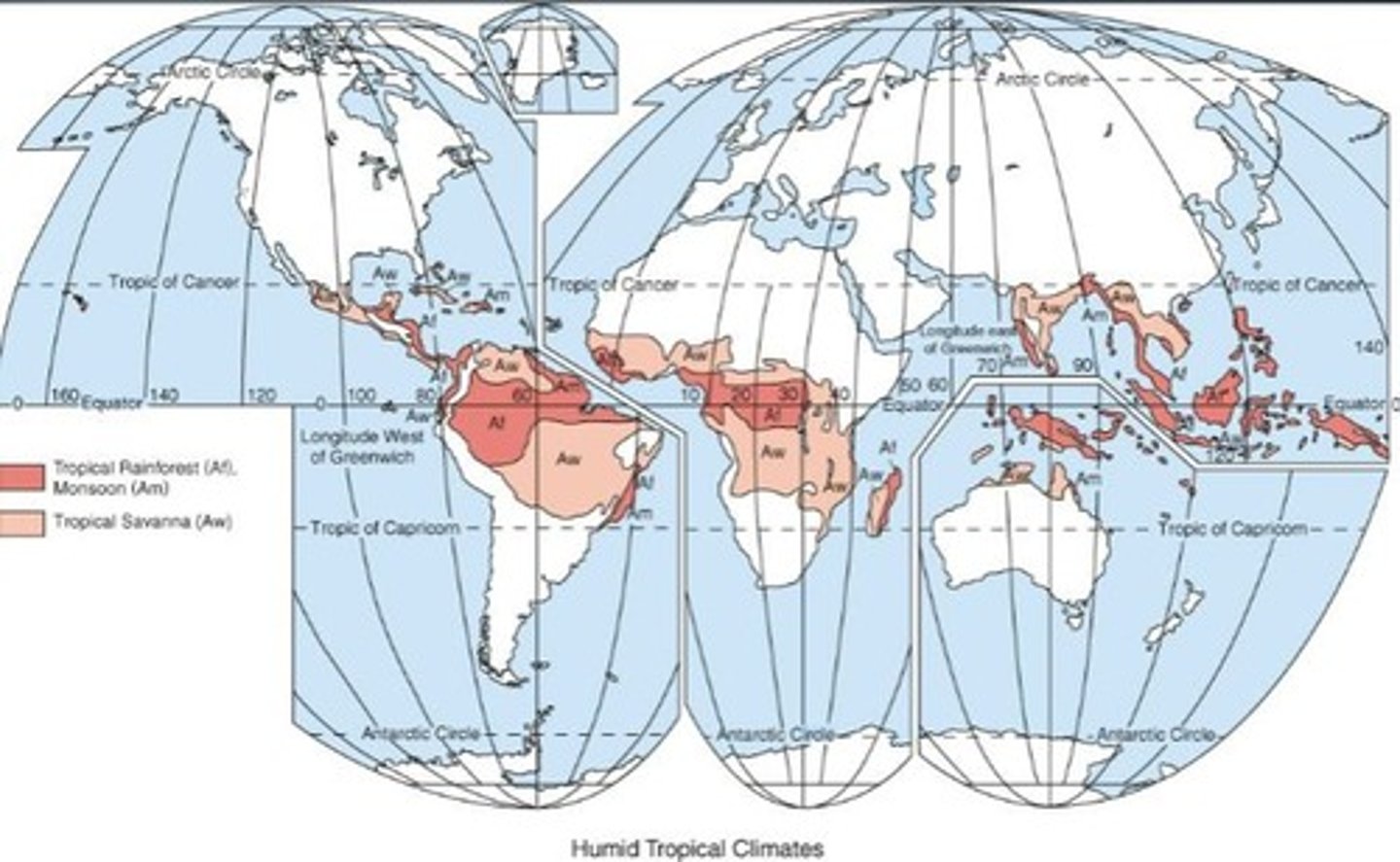
What defines a humid tropical climate (A climates)?
Warm temperatures with the coolest month above 18º C and varying precipitation.
What is a climograph?
A graphical summary of the pattern of temperature and precipitation.
What are biomes?
Major terrestrial ecosystems characterized by dominant vegetation and climate conditions.
What is the significance of the Köppen-Trewartha climate classification?
It modifies the Köppen system by adding a class based on elevation.
What challenges do tropical rainforest climates (Af) present to humans?
Hot, humid conditions with many disease-carrying insects like mosquitoes.
What is the typical temperature range for tropical rainforest climates?
Highs of 30 to 35 C (86 F to 95 F) and lows of 20 to 24 C (68 F to 75 F).
What is the main agricultural practice in tropical rainforest regions?
Slash-and-burn agriculture and plantation agriculture for crops like rubber and sugarcane.
What defines a tropical savanna climate (Aw)?
Located in the tropics, it has a seasonal climate with distinct wet and dry periods.
What are the major factors impacting climate classification?
Sun angles, prevailing winds, elevation, and proximity to large water bodies.
What is the significance of climate variability?
Climate is always changing, making it difficult to define and classify accurately.
What is the role of climatologists?
To examine means, totals, and extremes to understand long-term climate conditions.
What is the temperature range in warm climates?
Very warm all year, with an annual range of 3 to 6 °C (5 to 11 °F).
What defines the wet and dry seasons?
The wet season is marked by the arrival of the ITCZ, while the dry season is influenced by subtropical high pressure.
What is the average precipitation in warm climates?
Summer rains of 100 to 180 cm (40 to 70 in) and very dry winters.
What biome is characterized by a mixture of grasses and trees?
Savanna.
What are B climates?
Arid regions with desert cores transitioning to semiarid steppe climates.
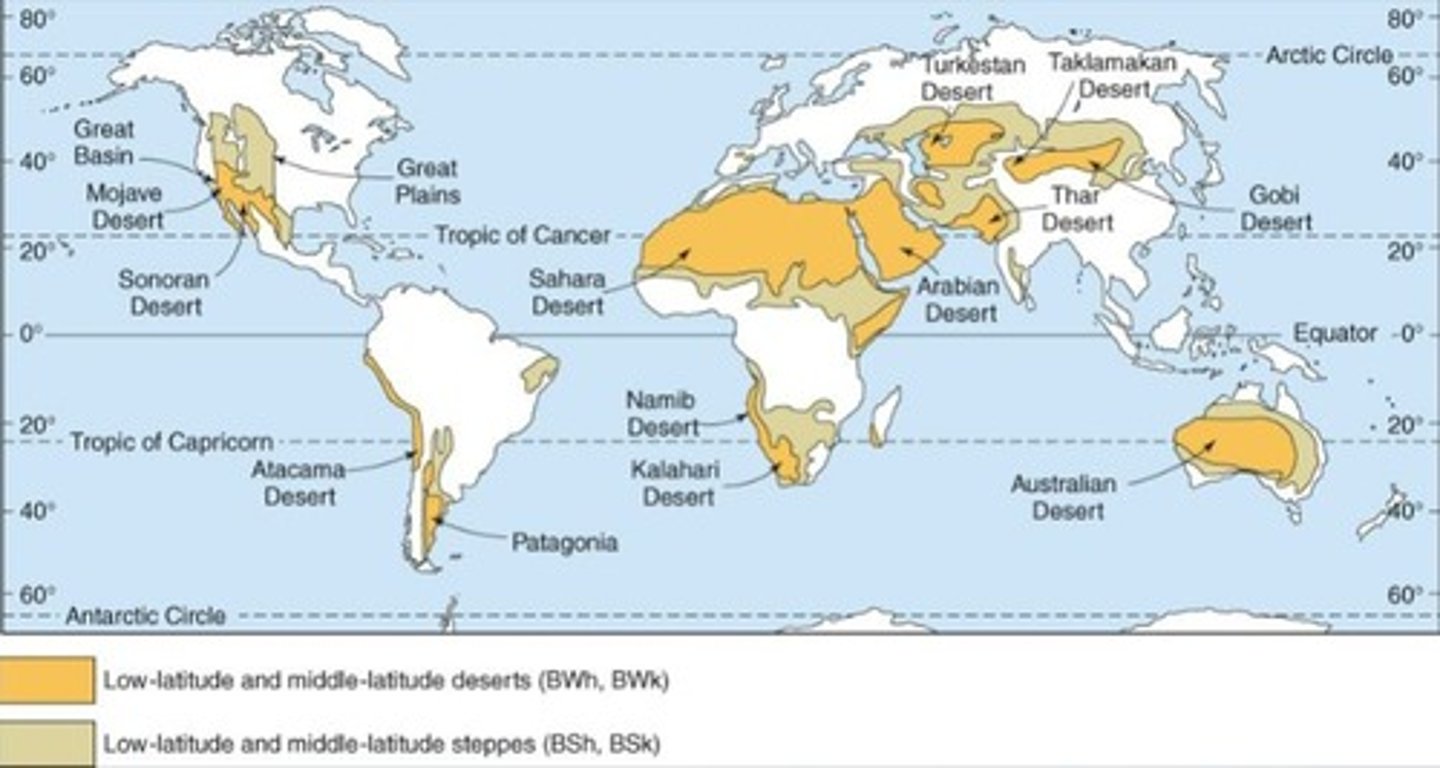
Name some of the most extensive deserts in the world.
Sahara, Arabian, Thar, and Australian Deserts.
What is the difference between desert and steppe climates?
Desert climates have less than half potential evapotranspiration, while steppe climates have more than half but less than total potential evapotranspiration.
What adaptations do xerophytic plants have?
Thick bark, thorns, little foliage, compact shape, waxy leaves, and moisture storage in stems.
What defines C climates?
Mesothermal climates with no winter month temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F).
What are the two types of Mediterranean climates?
Csa (hot-summer) and Csb (warm-summer).
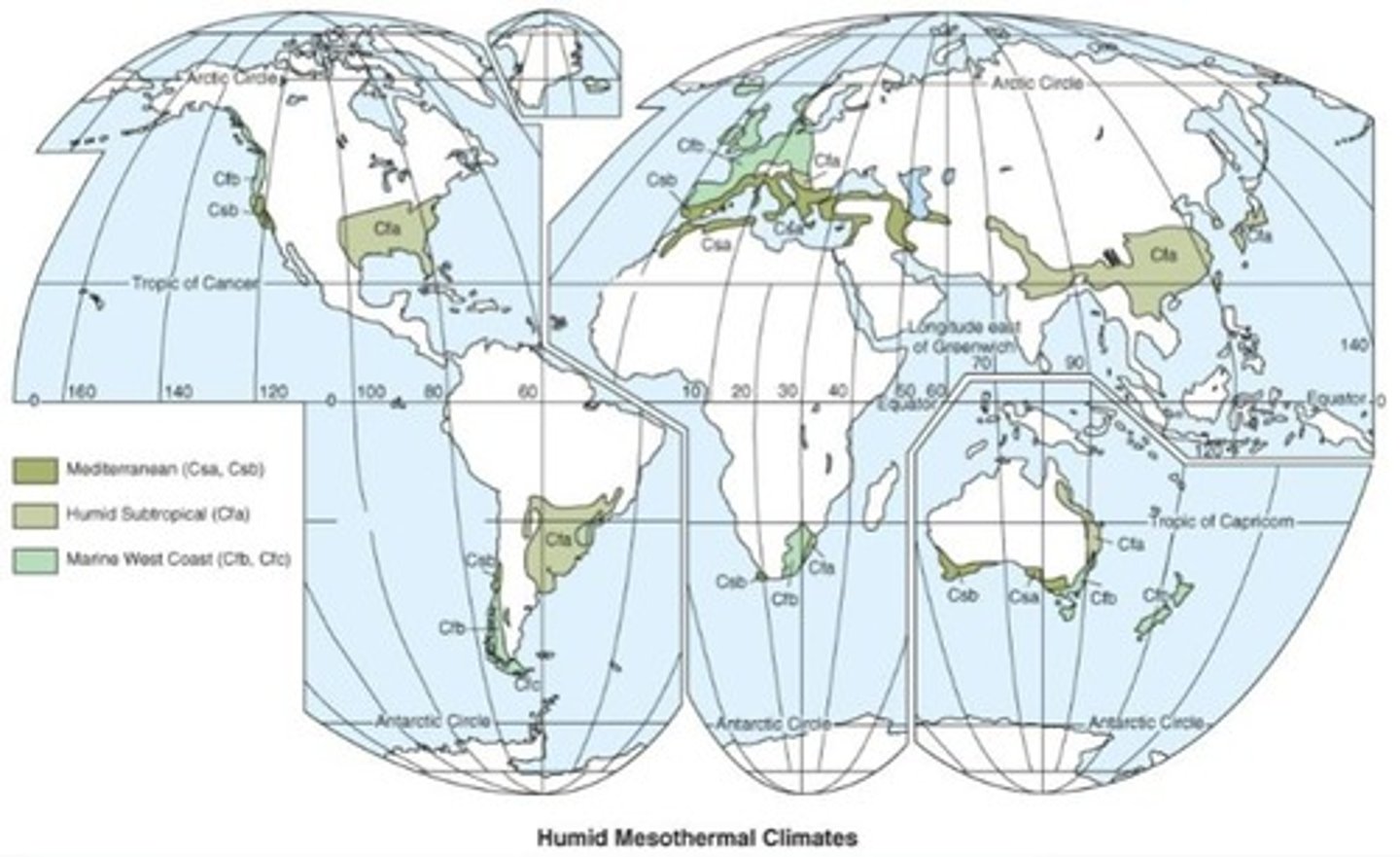
What is the average precipitation in Mediterranean climates?
35 to 75 cm (15 to 30 in) annually.
What type of vegetation is found in Mediterranean climates?
Chaparral, which includes low, tangled scrubby bushes and some trees.
What characterizes Cfa climates?
Humid subtropical climates with hot, humid summers and cool to cold winters.
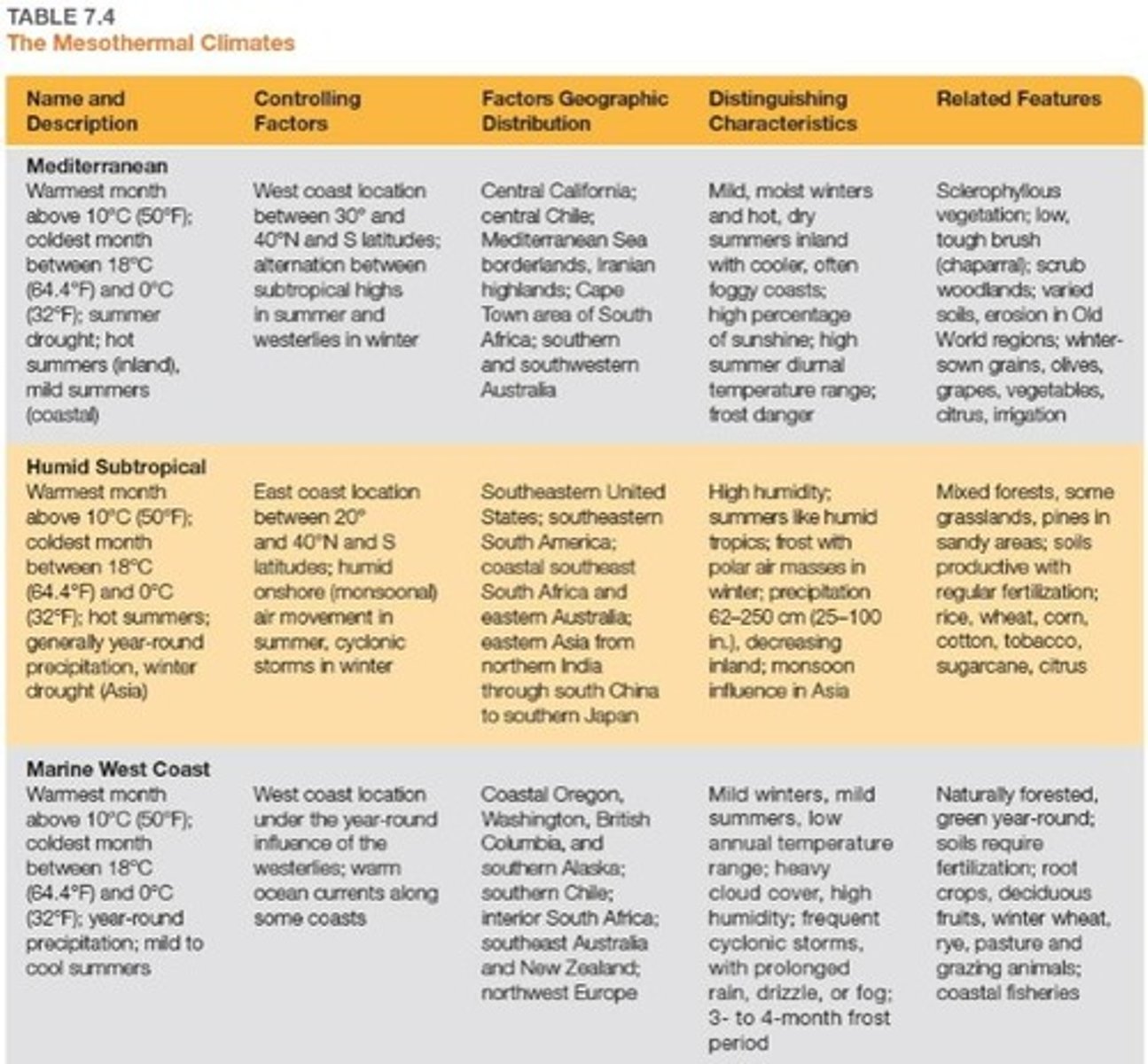
What is the average precipitation range in Cfa climates?
60 to 250 cm (25 to 100 in) annually.
What defines Cfb and Cfc climates?
Marine West Coast climates with consistent onshore westerly winds and abundant moisture.
What is a key feature of D climates?
Microthermal climates with one month above 10 °C (50 °F) and one month below 0 °C (32 °F).
What are the three subtypes of D climates?
Humid continental, subarctic, and polar.
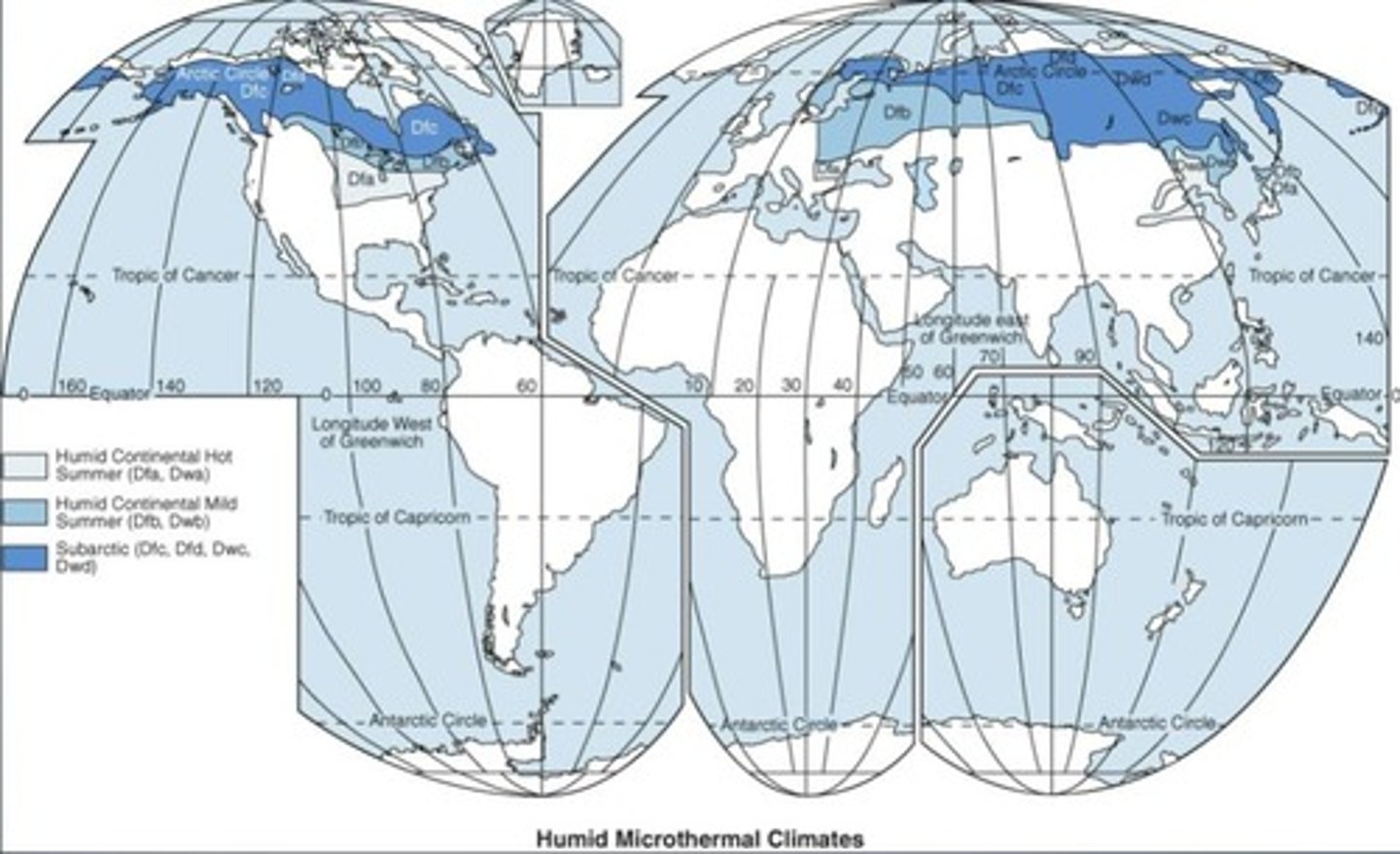
What is the significance of annual average temperature range in D climates?
It varies by latitude, proximity to large water bodies, and continental size.
What type of precipitation pattern is common in D climates?
Year-round precipitation with a surplus over potential evapotranspiration.
What is a common feature of desert climates?
Scare and unreliable precipitation, often less than 25 cm (10 in) annually.
What adaptations do animals in desert climates have?
Nocturnal behavior and physical adaptations like long ears and legs to increase blood circulation and cooling.
What human activities are common in desert climates?
Nomadic, subsistence, hunter-gatherer lifestyles, often clustered near water sources.
What is the impact of human activity on steppe climates?
Grazing and agriculture, often leading to desertification.
What is the Dust Bowl?
A period in the 1930s characterized by severe dust storms and agricultural failure in North America.
What defines the growing season in Marine West Coast climates?
Mild winters and abundant moisture, allowing for successful agriculture.
What types of crops are commonly grown in Marine West Coast climates?
Wheat, barley, root crops, deciduous fruits, and grasses.
What is the climate like in the Great Basin?
It is characterized by a rain shadow effect, contributing to its arid conditions.
What is the significance of the North Atlantic Drift?
It is a warm current that impacts the climate of Europe, particularly in marine west coast regions.
What are the main types of humid continental climates?
Dfa, Dfb, Dwb
Where are humid continental climates predominantly found?
Widespread in North America and Eurasia
What is the typical growing season in humid continental climates?
130 to 200 days
What type of air masses influence humid continental climates in summer?
Maritime tropical air masses
What is a characteristic weather event common in humid continental climates?
Heat waves
What is the average annual precipitation in humid continental climates?
Reliable rainfall
What defines the Dfa climate subtype?
Warm summer with broad-leaf deciduous trees
What types of trees are common in Dfa climates?
Oaks, hickories, and maples
What agricultural products are commonly grown in the hot summer regions of Dfa climates?
Corn, soybeans, wheat, barley, beef cattle, and hogs
What is a key characteristic of the subarctic climate?
Long, brutally cold winters with short, cool summers
What is the temperature range for the subarctic climate?
Average temperatures below freezing for eight months
What is the average annual precipitation in subarctic climates?
25 to 50 cm (10 to 20 in)
What biome is associated with subarctic climates?
Coniferous forest (Taiga, Boreal)
What defines polar climates (E climates)?
Average temperature of the warmest month < 10 °C (50 °F)
What are the two subtypes of polar climates?
ET (tundra climate) and EF (ice-sheet climate)
What is a characteristic feature of tundra climate (ET)?
Average temperatures in warm months are 4 °C to 10 °C (40 °F to 50 °F)
What is the average annual temperature in tundra climates?
-12 °C (10 °F)
What is the defining characteristic of ice-sheet climate (EF)?
All average monthly temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F)
What is a common human activity in polar climates?
Temporary oil exploration and radar facilities
What is a defining characteristic of highland climates?
Complexity due to elevation and exposure
What is the impact of elevation on climate?
Increases in elevation mimic increases in latitude