HMI104 - Hip, gluteal region and thigh
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms











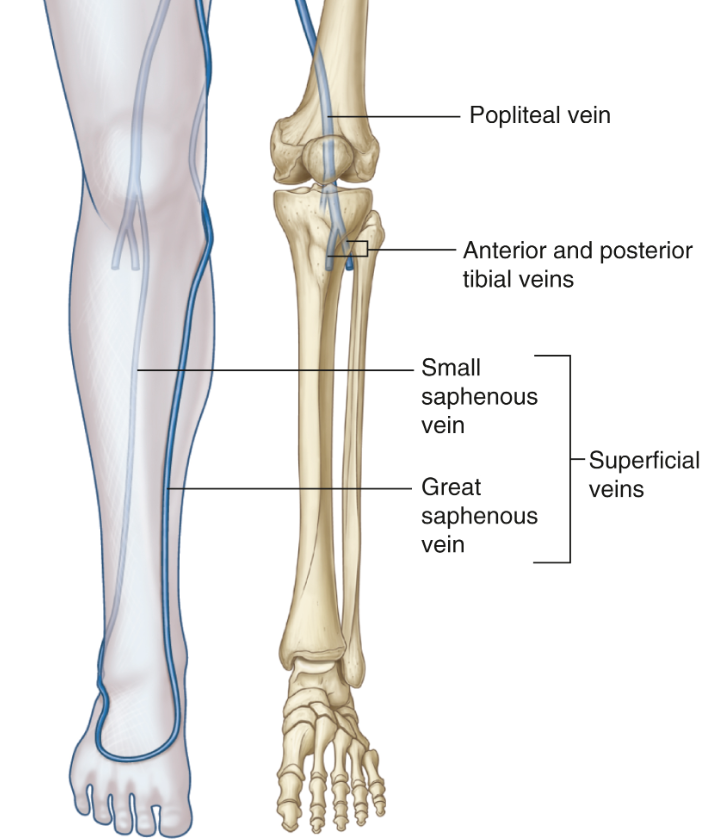

What are the three thigh compartments?
Anterior, medial and posterior
What are the functions of the three thigh compartments
Anterior: Acts primarily on knees (quadriceps)
Medial: acts mainly on hips (adductors)
Posterior: acts on hip and knee (hamstrings)
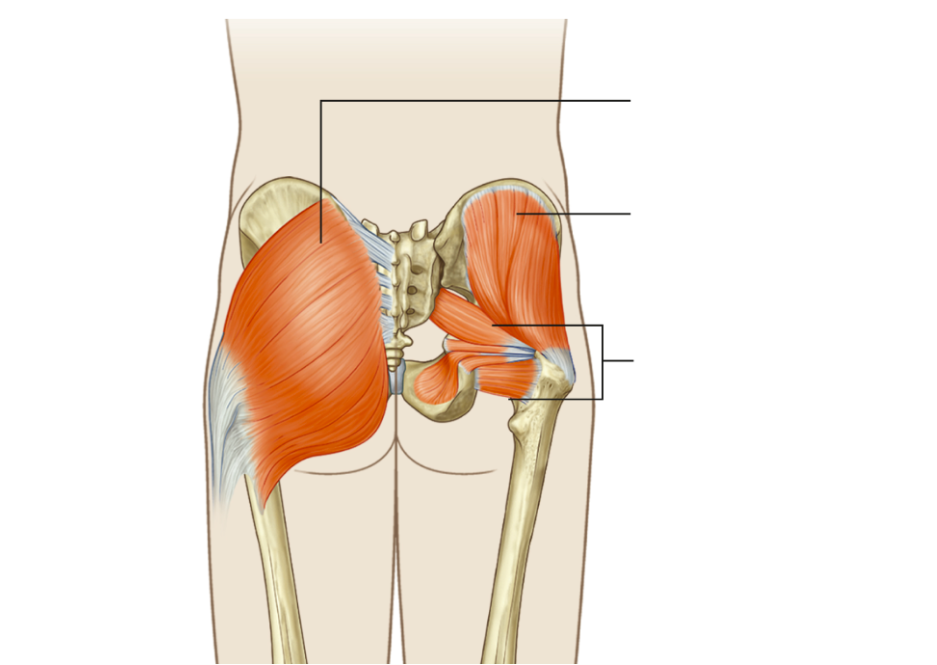
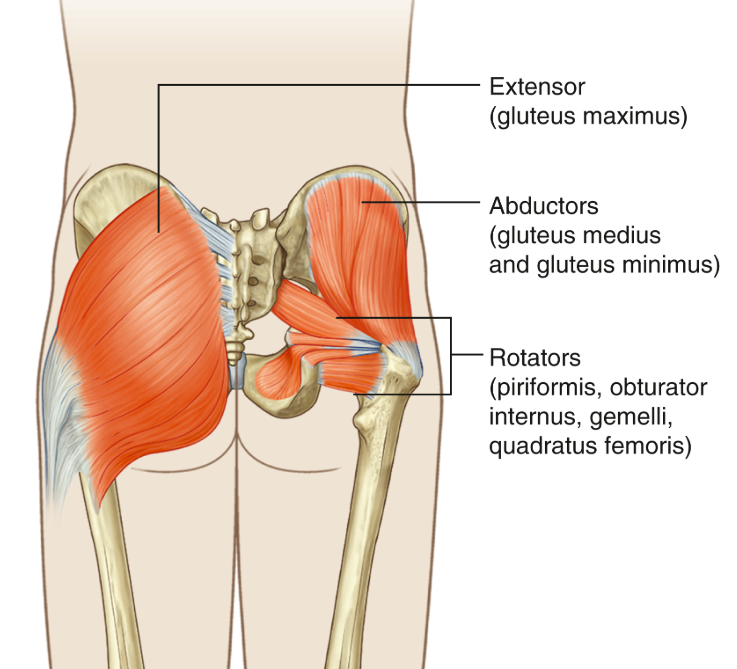
What is the function of the first group (superficial) gluteal region?
Extend and abduct hips
What is the function of the second group (deep) gluteal region?
Lateral rotation of hips
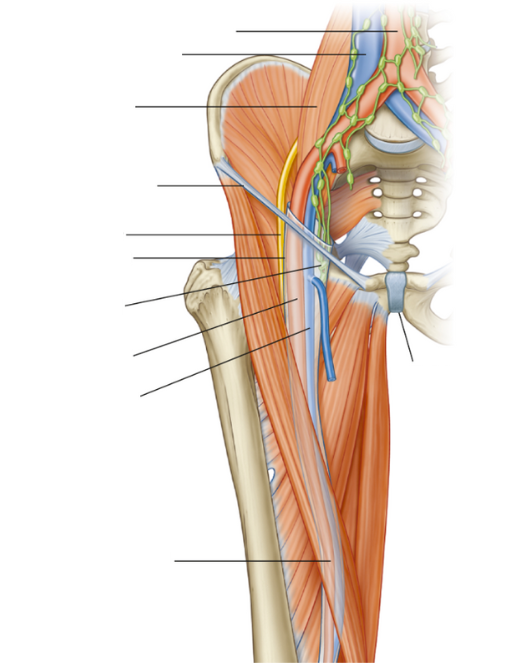
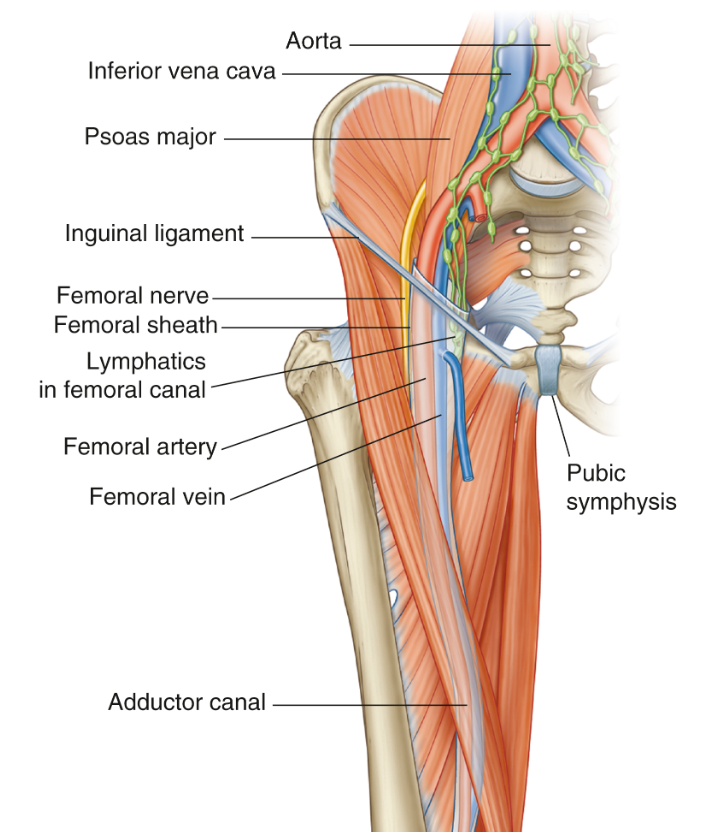




Why do we have lower limbs?
To support our body weight for minimal expenditure of energy, support body weight and move efficiently
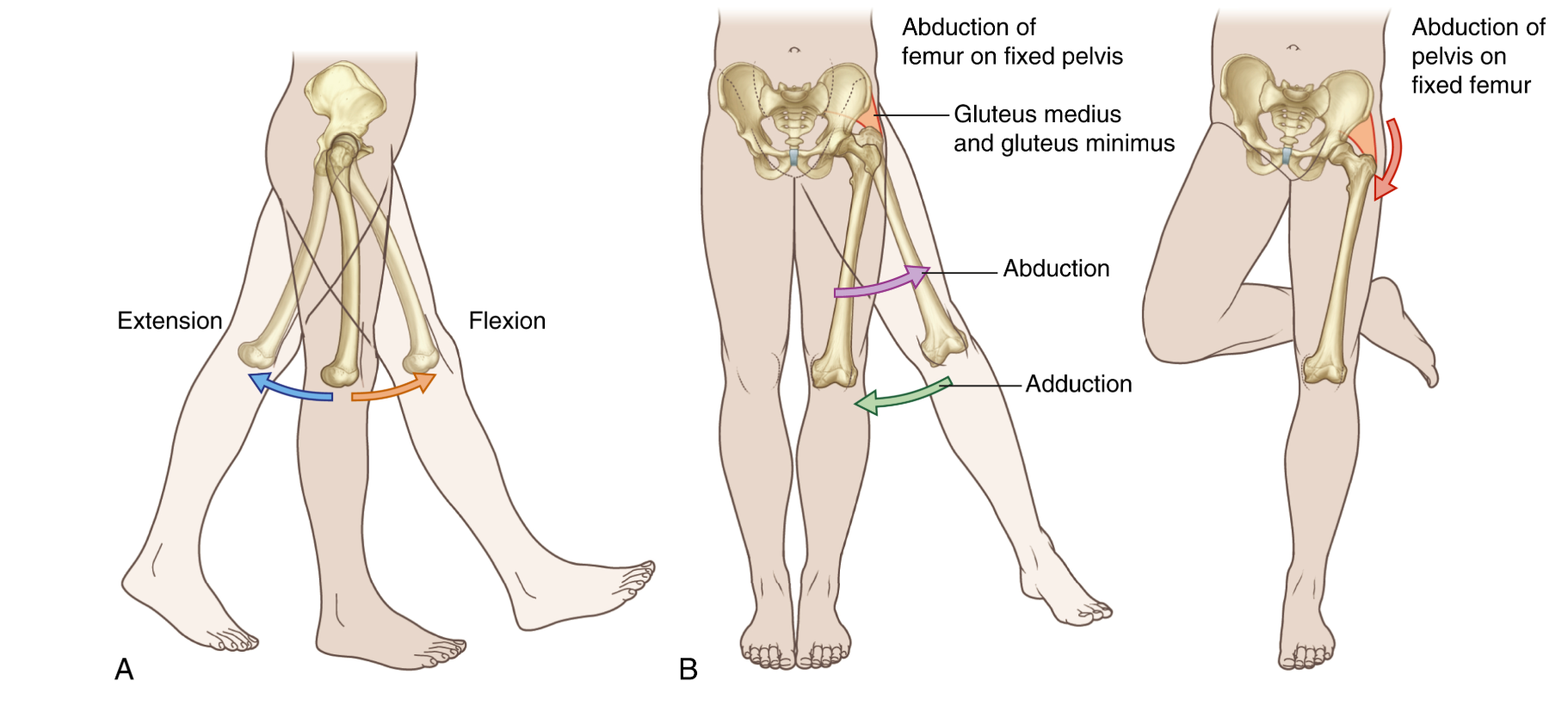
What is the function of having the hip joint be a ball and socket joint?
Ball and socket because it can move in 3 different planes
All three planes of motion are effective for walking and running with miniimal energy expenditure
This mean it helps to extend and flex better, and also cover more distance when walking
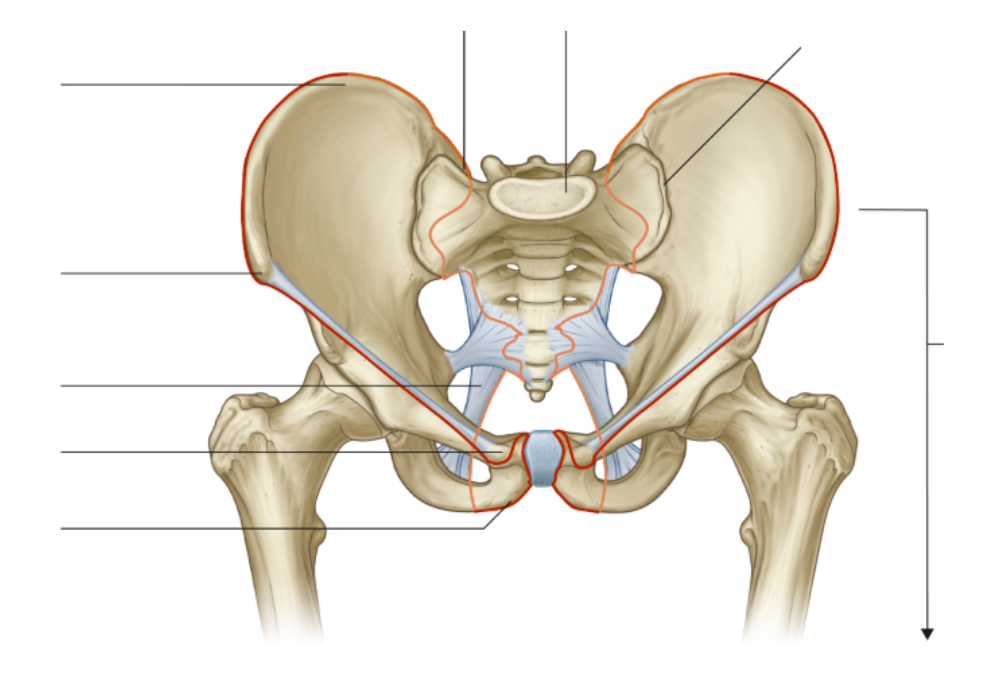
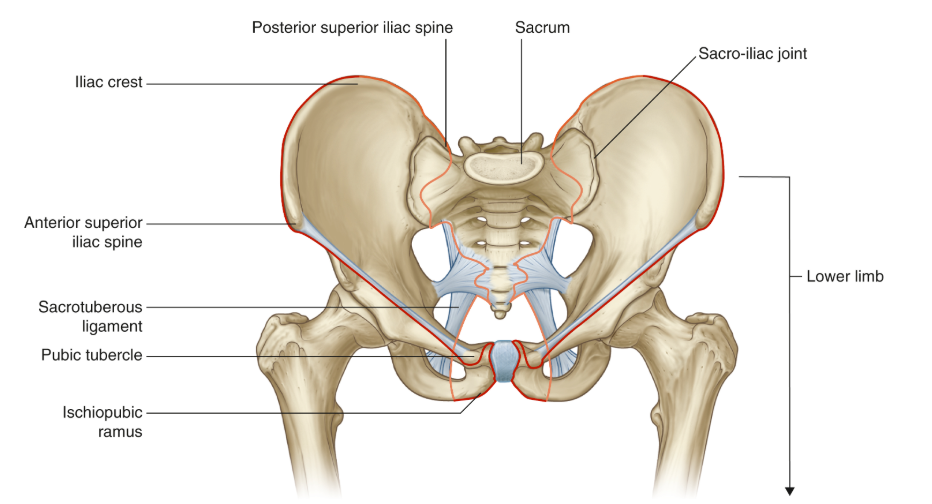
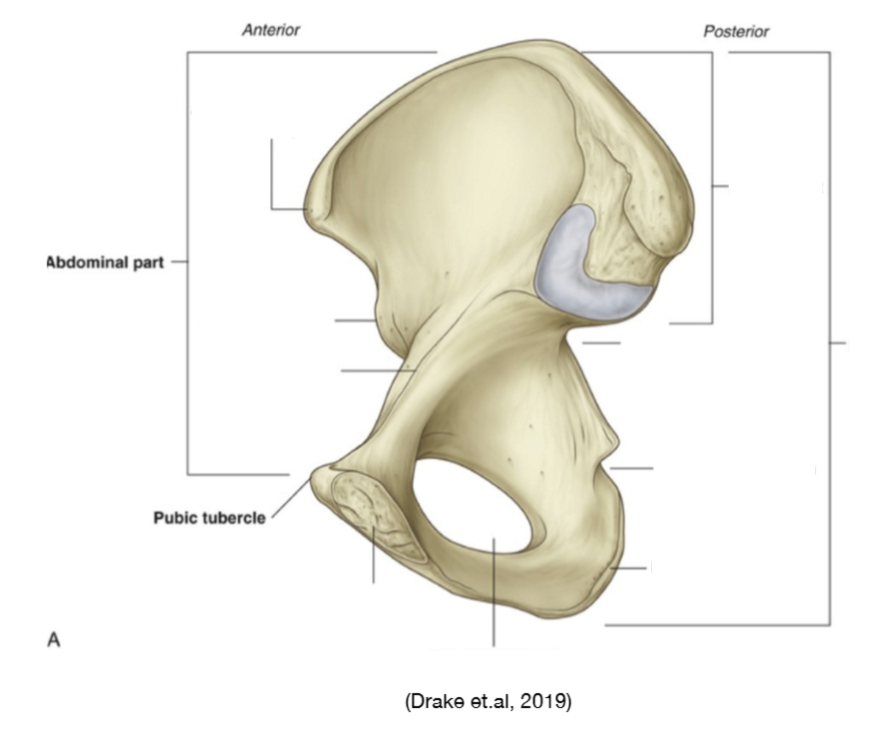
Purpose of linea terminalis?
To divide the true pelvis from the false pelvis
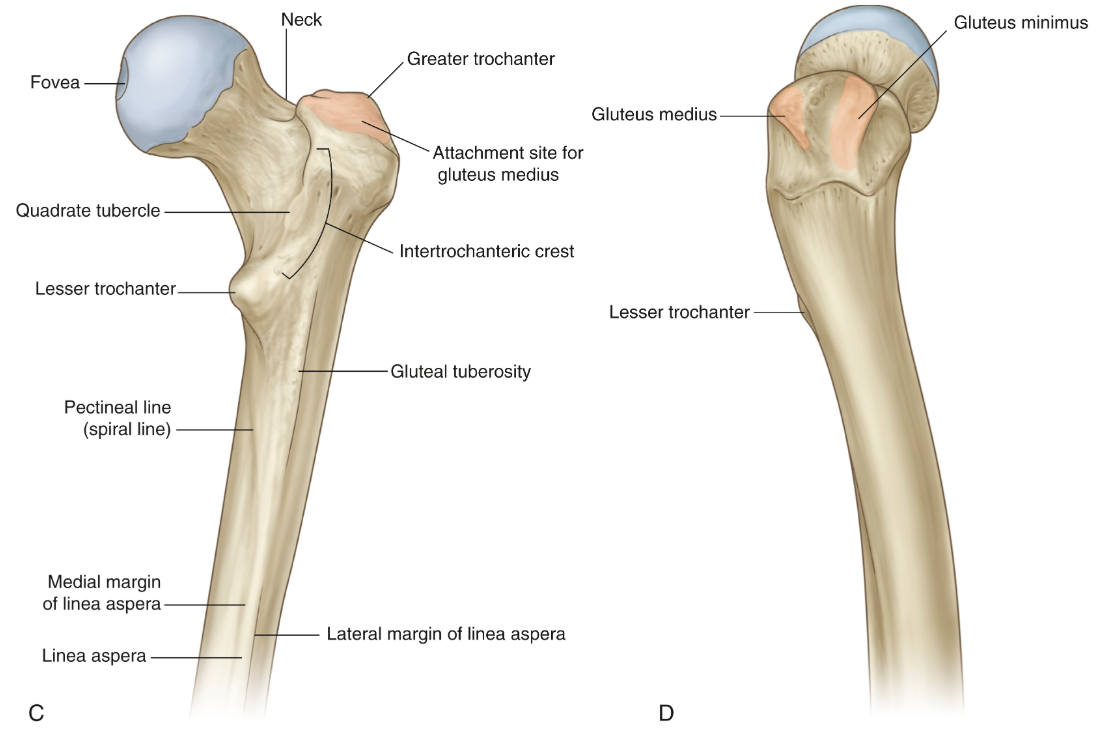
Purpose of greater trochanter?
Attachment of hip abductor muscles
Purpose of lesser trochanter?
Attachment site for hip flexor muscles, specifically the iliopsoas.
Function of a long femoral neck?
To provide better range of motion
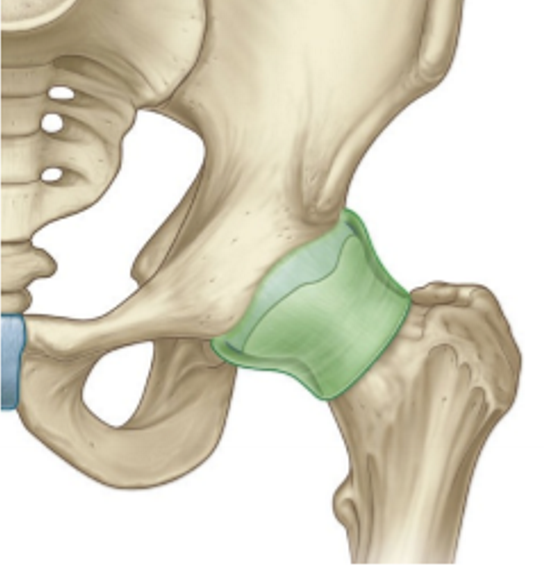
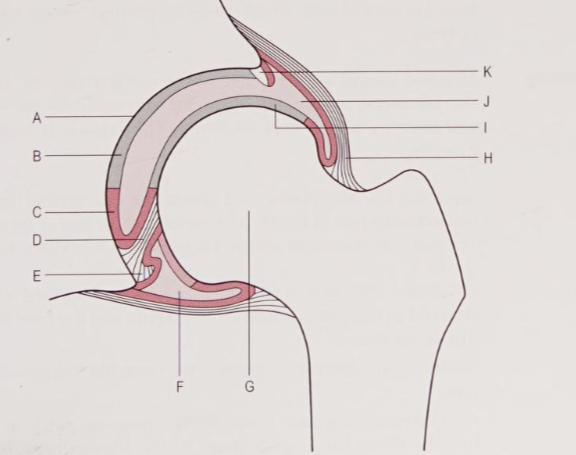
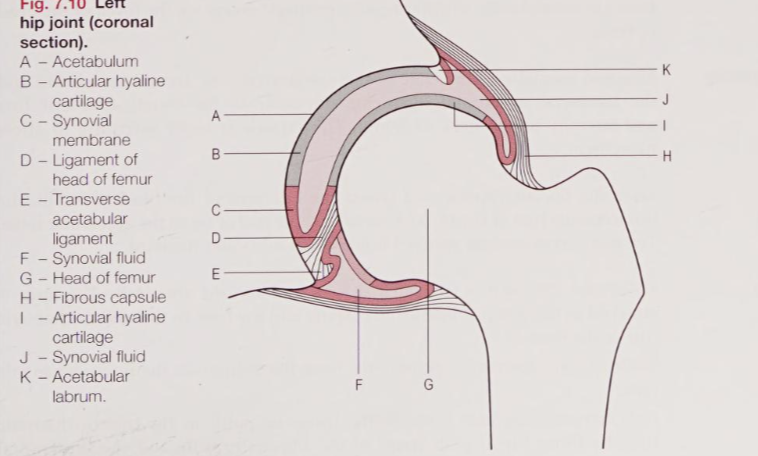
Function of the synovial membrane
Function for secreting synovial fluid which lubricates the joint, which then greatly improves movement, as well as provides nutrition to the cartilage
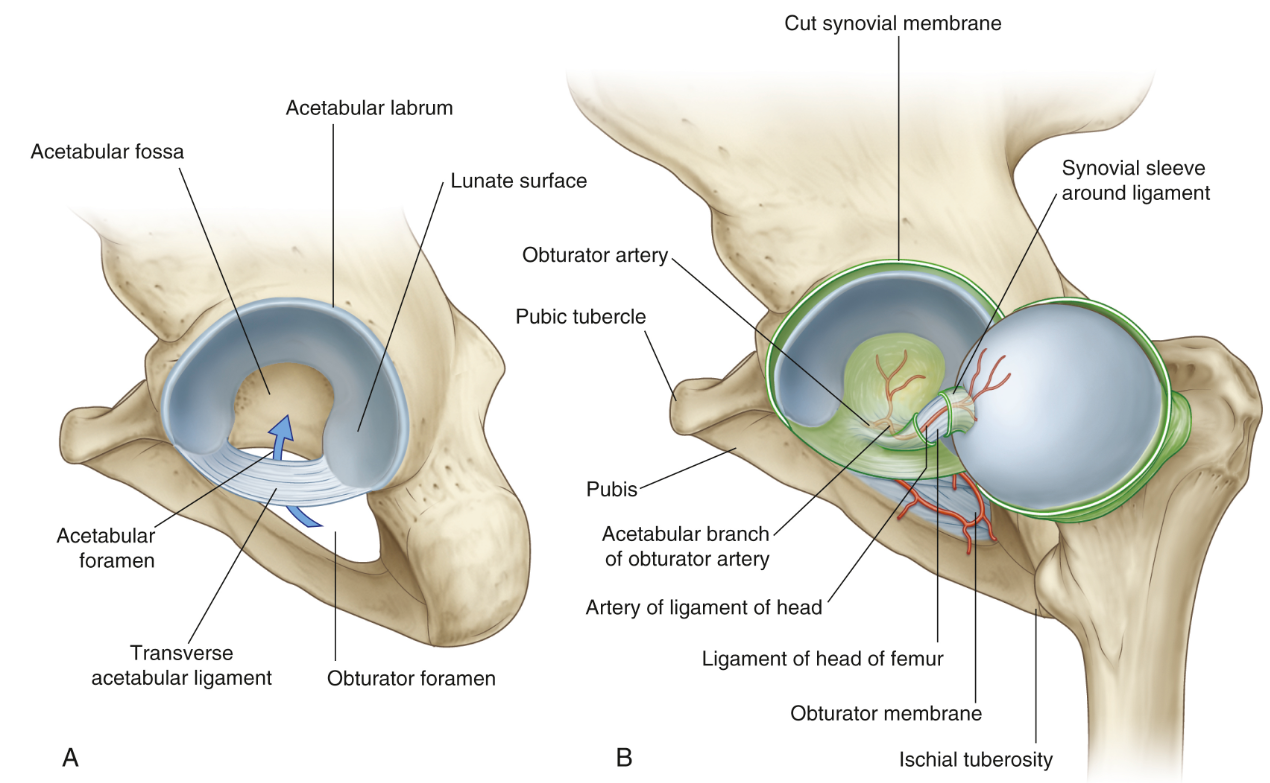
Function of the acetabular labrum?
Functions for more coverage of the femoral head and more stability
Function of the ligament to the head of the femur
It's function is to support the passage of some very small vessels which are branches from the obturator artery, which is the artery to the head of the femur
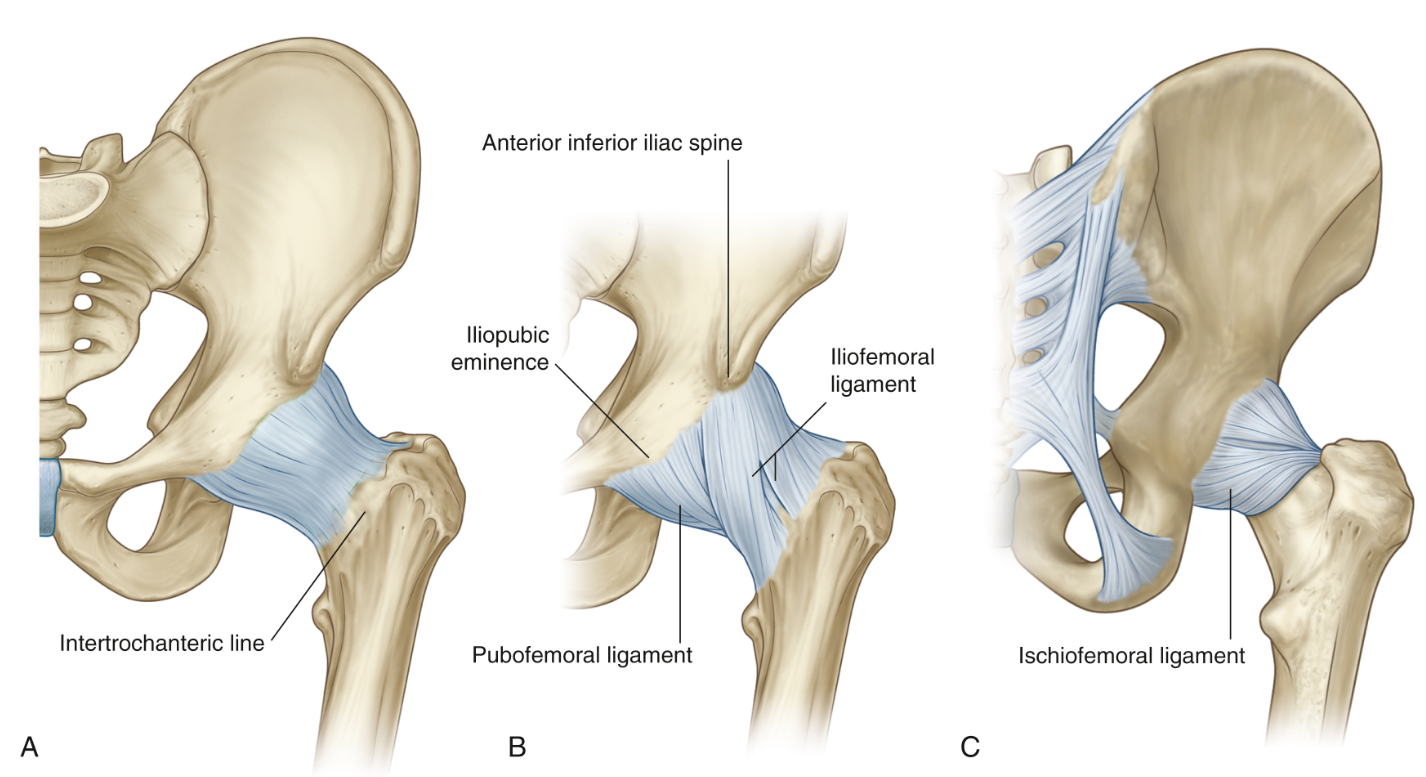
What ligaments restrict hip extension?
Iliofemoral ligament, pubofemoral ligament, ischiofemoral ligament.
Why do they restrict hip extension?
Minimizes energy expenditure on the muscular system
What nerve supplies the anterior (quadricep) compartment?
Femoral nerve
What nerve supplies the posterior (hamstring) compartment?
Sciatic nerve
What nerve supplies the medial compartment?
Obturator nerve
What is the purpose of the sartorius attaching to the ASIS?
It will try to protect vascular structures, mainly the superficial femoral artery
usually for avulsion fractures
Why does the abductor magnus have a little canal?
The canal is important because it is the transition point between the superficial femoral artery, which is is anterior and goes through the canal and exits posteriorly into the popliteal fossa to then become the popliteal artery
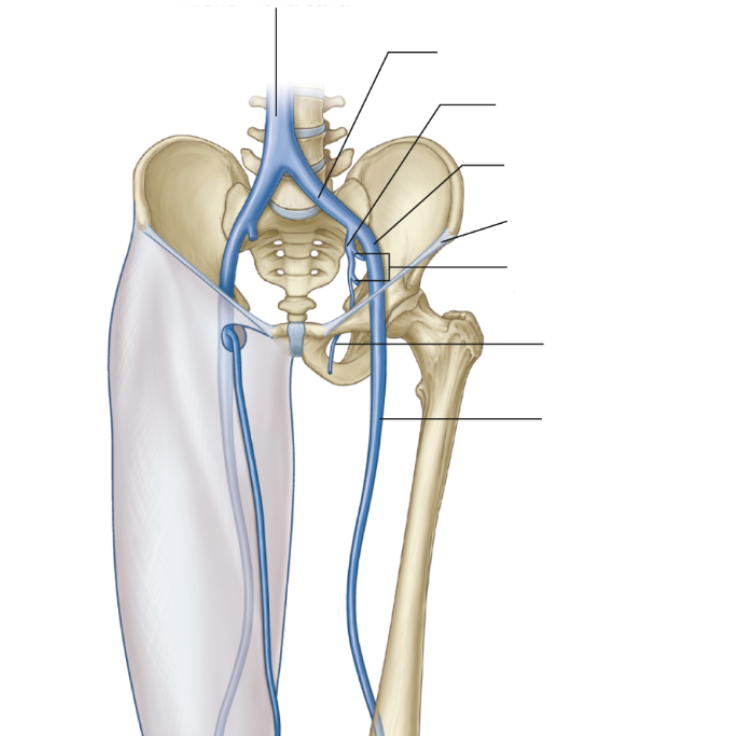
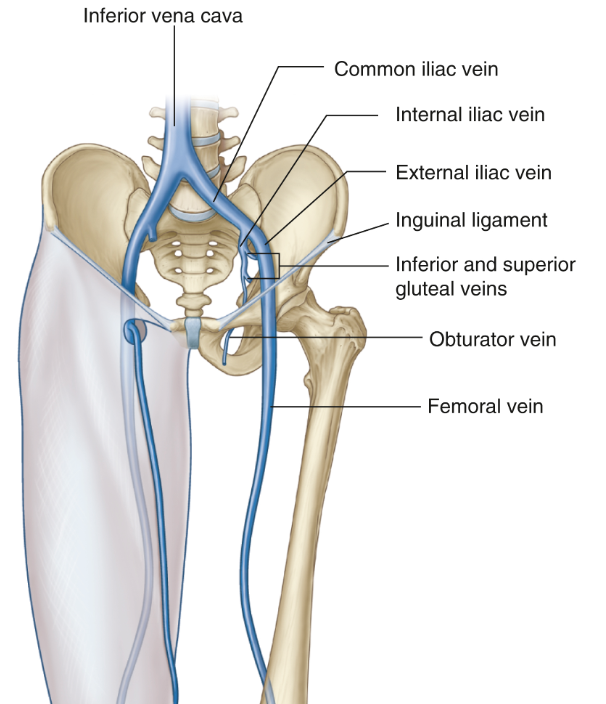
Purpose of common iliac artery?
Supplies lower limb and pelvis
Purpose of internal iliac
Supplies the pelvis and gluteal region
Purpose of external iliac
Supplies the thigh, lower limb and branches to the foot
What are the pros of the arteries being pinned down by fibrous capsules
Protection
What are the cons of the arteries being pinned down by fibrous capsules
If there was a fracture through the neck, they are going to be damaged, leading to the risk of avascular necrosis to the head of the femur.
The portion of the acetabulum responsible for weightbearing is best described as the:
Lunate surface
During ultrasound-guided central access, the clinician notes that the femoral vein lies directly medial to which structure at the femoral triangle?
Femoral artery
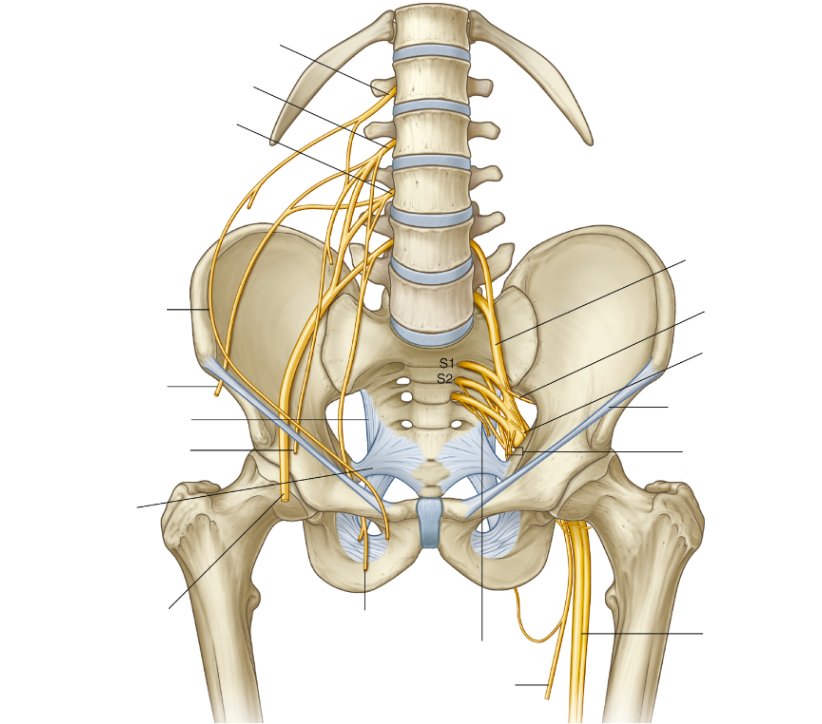
The sciatic nerve enters the gluteal region by passing through the _____________ foramen, inferiorly to _______________ muscle.
Greater sciatic foramen, Piriformis
True or false: The capsular ligaments of the hip joint form a ringlike collar that encircles the femoral neck. When the hip is extended, these ligaments become twisted upon themselves pushing the femoral head more firmly into the acetabulum.
True
A 16-year-old footballer presents with a slipped capital femoral epiphysis, damaging arteries that supply the femoral head. Damage to which vessels are most likely to lead to avascular necrosis of the femoral head?
Retinacular arteries
Which of the following statements is most correct regarding the developmental ossification centres of the hip?
The acetabulum develops from a single ossification centre and forms fully by 6 months of age, corresponding with when infants begin to bear weight. | |
The triradiate cartilage separates the ilium, ischium, and pubis until fusion during adolescence | |
The secondary ossification centre of the greater trochanter appears before the femoral head | |
The primary ossification centre for the femoral head appears in utero at around 12 weeks and should be visible on X-ray at birth. |
The triradiate cartilage separates the ilium, ischium, and pubis until fusion during adolescence
Which of these statements is most correct regarding the fiberous capsule of the hip joint?
The fiberous capsule extends from the acetabular rim to encircle the femoral head, meaning all fractures of the femoral neck and trochanters are extracapsular. | |
Extends from the acetabular rim to the intertrochanteric line, and femur fractures proximal to the intertrochanteric line are described as intracapsular. | |
Extends from the acetabular rim to the greater trochanter, making all greater trochanteric fractures intracapsular. | |
Extends from the acetabular rim to the greater and lesser trochanter, making all trochanteric fractures intracapsular. |
Extends from the acetabular rim to the intertrochanteric line, and femur fractures proximal to the intertrochanteric line are described as intracapsular.
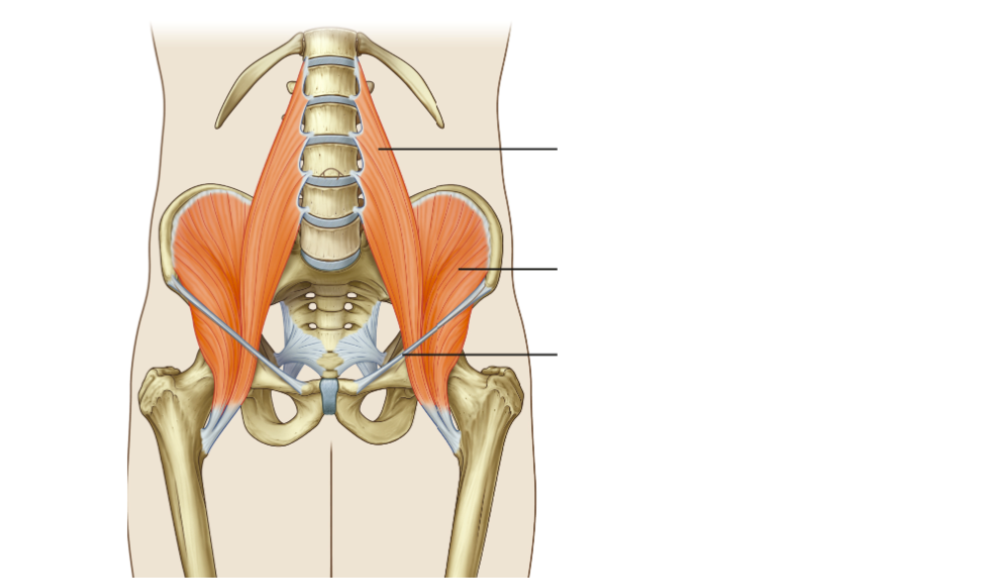
What muscle fits this description: This group includes iliopsoas, originates from the lumbar spine and iliac fossa, inserts on the lesser trochanter, and contributes significantly to hip flexion. Avulsion of the lesser trochanter may occur due to sudden eccentric loading in young athletes.
Hip flexors
What muscle fits this description: Muscles in this compartment adduct the thigh, are primarily innervated by the obturator nerve, and can be involved in avulsion injuries at the pubic body during forceful kicking or pivoting movements.
Medial compartment of the thigh
What muscle fits this description: This group includes the gluteus medius and minimus, is innervated by the superior gluteal nerve, and contributes to pelvic stability during gait.
Gluteal muscles (superficial group)
What muscle fits this description: Muscles in this group are responsible for hip extension and knee flexion, are innervated by the sciatic nerve, and may avulse from the ischial tuberosity, particularly in adolescent athletes performing sprinting or hurdling activities.
Posterior compartment of thigh
What muscle fits this description: This group is responsible for knee extension and hip flexion, receives its innervation from the femoral nerve, and is associated with avulsion fractures of the anterior inferior iliac spine (AIIS) due to forceful contraction of the rectus femoris
Anterior compartment of thigh
What muscle fits this description: These muscles include piriformis, obturator internus, gimelli and quadratus femoris and play a key role in external rotation of the hip.
Gluteal muscles (deep group)
When does greater trochanter usually occur?
2 - 4 years
When does lesser trochanter usually occur?
Around puberty
Ages for ossification of acetabulum
Triadiate - appears at birth
Fuses at 13 - 16
What age does the femur fuse
16 - 18
What muscles does the ischial tuberosity attach to?
Hamstring muscles
What muscles does the ASIS attach?
Sartorius muscles
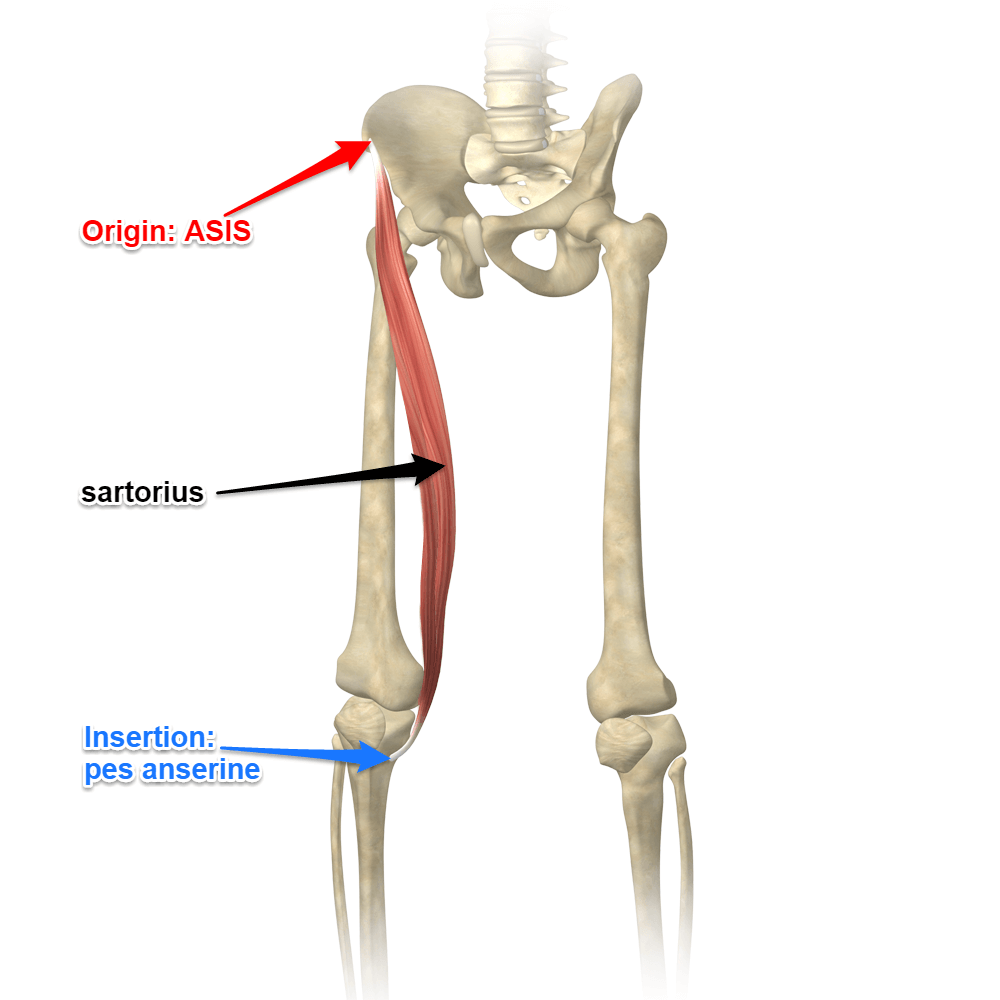
What muscles does the AIIS attach?
Rectus femoris
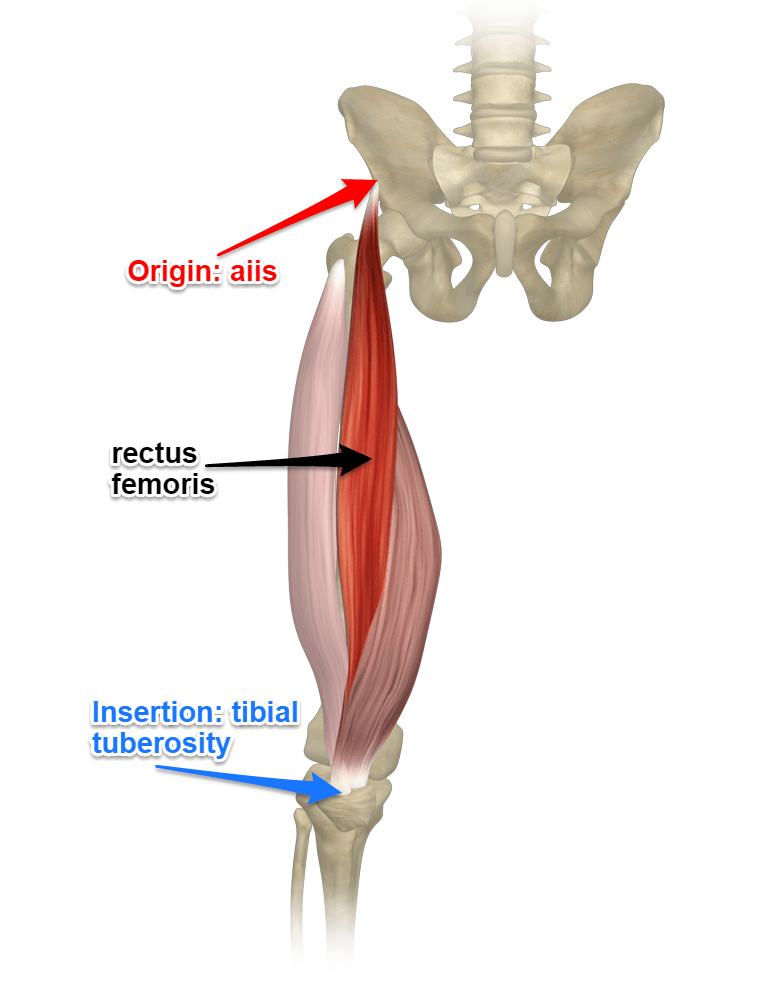
What muscles does lesser trochanter attach?
Iliopsoas muscles
What muscles does greater trochanter attach?
Gluteus minimum, Medius and maximus