CVS 106 Exam 3: M-Mode Ultrasound Terms & Definitions
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
M-mode (motion mode)
Produces one-dimensional information on a time-motion graph,
Displayed along a line representing the ultrasound beam direction ( provides a single line of information at a higher frame rate)
Temporal and spatial resolutions are higher because the focus is on only one of the lines from the 2D trace
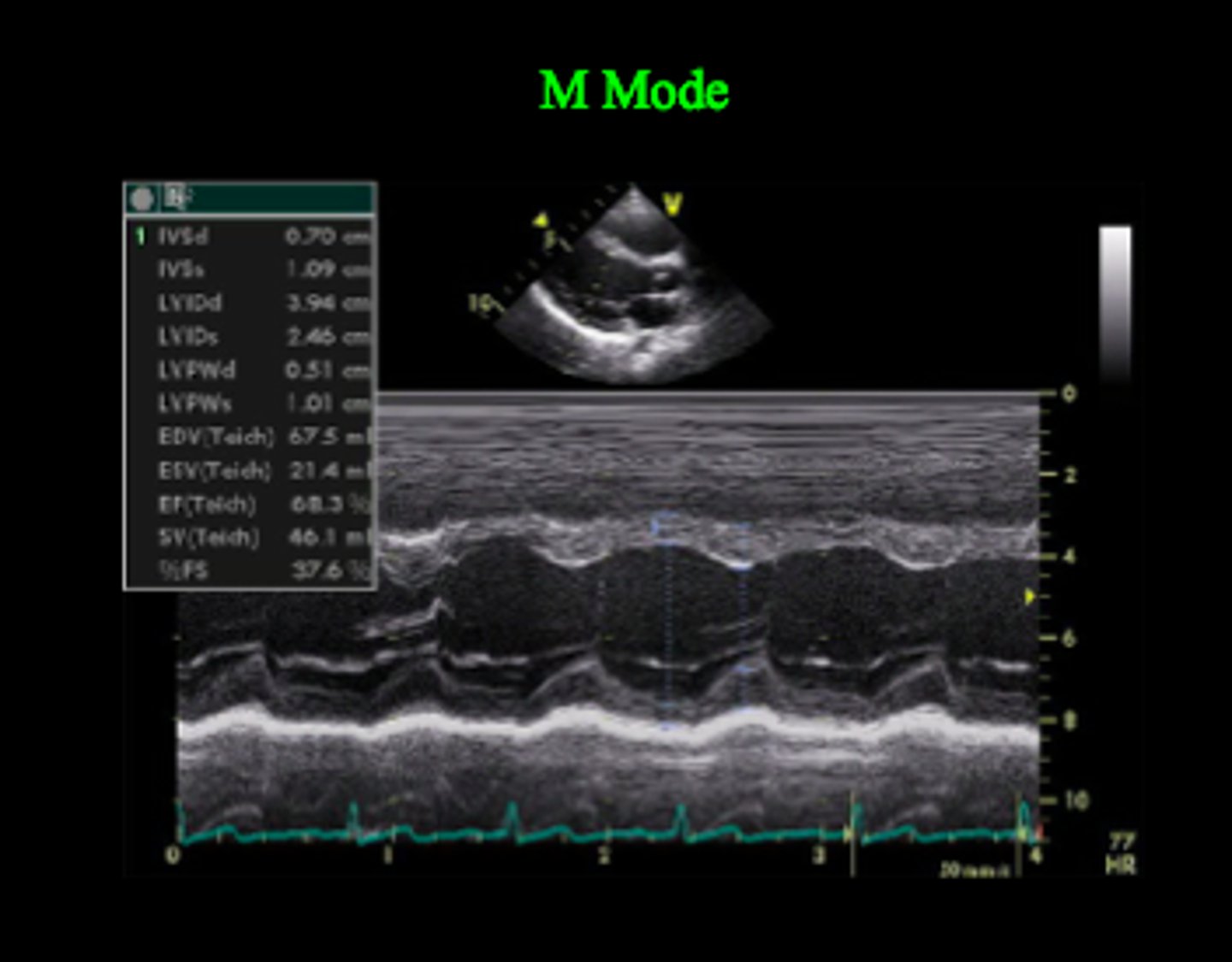
The M-mode trace records
the depth and motion of echoes arising from intracardiac structures relative to time
Provides a 1D view and is used for fine measurements.
Why are Temporal and spatial resolutions higher
because the focus is on only one of the lines from the 2D trace
Three types of information can be obtained from the M-mode exam
Motion or time which is displayed on the horizontal axis/ X axis
Distance or depth, which is displayed on the vertical axis/ Y axis
Echo strength, which is represented as the brightness of structures appearing on the image display
( this echo brightness is directly proportional to the strength of the reflected echoes.)
The displayed image shows the structures as they change over time
The principle application of M-mode in an echo exam is?
in the assessment and measurement of cardiac chamber dimensions, valvular motion, and left ventricular systolic function.
What technique enhances M-mode?
accurate determination of linear dimensions
improves the quantification of chamber size
wall thickness
What is the optimum window selected for M-mode interrogation?
is the view in which the ultrasound beam passes perpendicular to the structures of interest
What is the principle advantage of M-mode over other modalities such as 2D imaging and Doppler?
is its superior temporal resolution
(the ability to precisely position moving structures from instant to instant. And is determined by the frame rate.)
What is the sampling rate (frame rate)for M-mode?
approx 1000-2000 frames per second,
far greater than 2D echo frame rate of between 30 -100 frames per second
Therefore M-mode provides valuable information regarding fast moving structures such as cardiac valves
It provides excellent interface definition, enhancing the accuracy of measurements
What is sampling rate (frame rate)?
The measurement of how quickly a number of frames appears within a second, which is why it's also called FPS (frames per second).
Multiple frames produced in rapid succession form the moving or real-time image we see on the ultrasound monitor.
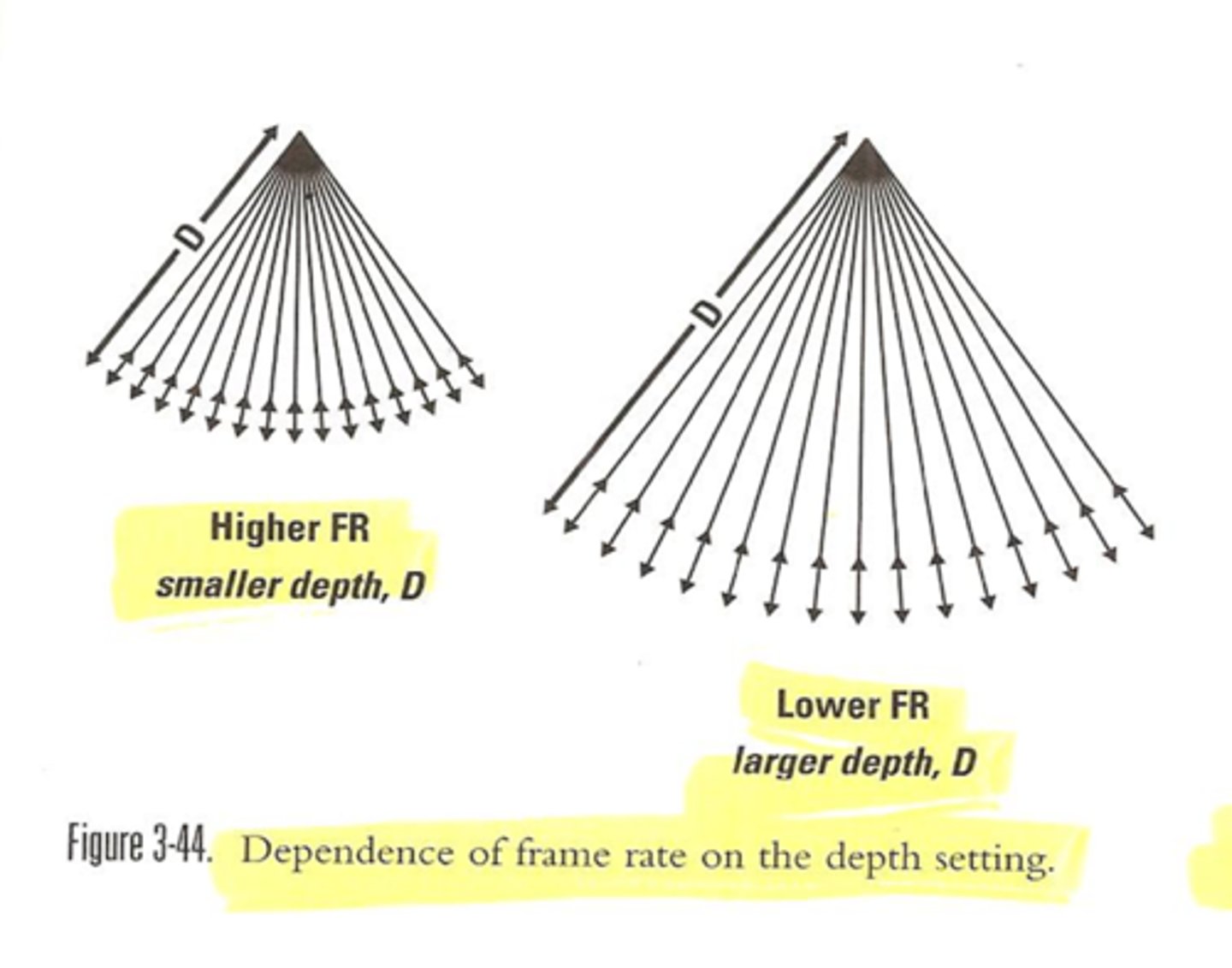
Improving temporal resolution
Temporal resolution refers to the ability to precisely position moving structures from instant to instant.
Minimize depth of view
Use single focus
Narrow sector
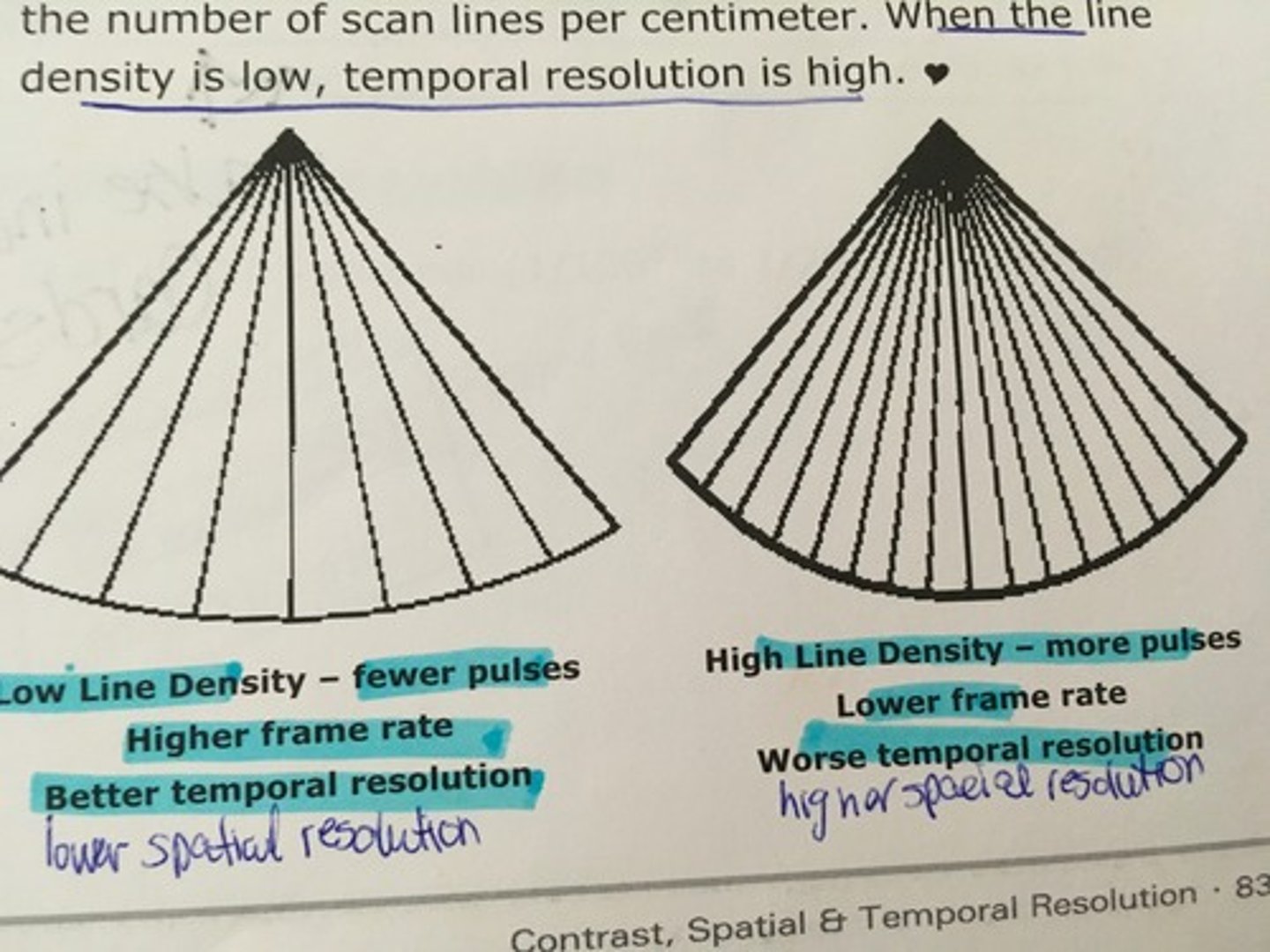
Minimize line density
As temporal resolution improves, so does the image quality
What is the main determinant of temporal resolution ?
frame rate
What is temporal resolution?
the time to take the multiple measurements of the cross-section and then reconstruct the image
Which two factors determine temporal resolution?
propagation speed and depth of view have the greatest effect upon frame rate and temporal resolution.
What is the principle disadvantage of M-mode?
M-mode has limitations due to its one-dimensional nature and lack of spatial information.
It's also limited in deriving information about 3D structures.
The ejection fraction derived from M-mode is misleading when CAD alters the long (major) axis to short(minor) axis ratio.
optimize M-mode traces
Many instrument controls used to optimize 2D images can also be manipulated
Gains and TGCs
B –color maps
Sweep speed
Gains and TGCs
should be adjusted to ensure blood appears echo free and structures of similar acoustic properties are displayed at similar echo amplitudes.
B –color maps
can be applied in an attempt to enhance soft tissue differences
Sweep speed
which refers to the horizontal display rate is adjusted according to information required.
Example is if the heart rate is increased or decreased
The sweep speed defaults at 50mm/s
Higher sweep speeds such as 100mm/s -
fewer waveforms
Lower sweep speed such as 35mm/s -
more waveforms
The sweep speed defaults
at 50mm/s
Higher sweep speed
100mm/s will display fewer waveforms
Lower sweep speed
35mm/s will display more waveforms
sweep speed
Changes a number of cardiac cycles that can be is shown on the horizontal axis of the M-mode display.
incorrect M-mode plane
if the LV apex is tipped too far up on the parasternal long axis view
the LV M-mode will be oblique and the chamber dimensions will be inaccurate
correct M-Mode plane
the M-mode cursor must be perpendicular(right angle,two lines meet) to the septum and posterior wall of the left ventricle
What can be examined from Aortic- PSLA or PSSA view?
aorta
aortic valve
left atrium
From the Aortic -PSLA view the cursor is
directed perpendicular to the long axis of the aorta and through the aortic root at the tips of the aortic cusps
From the Aortic- PSSA view (aortic level) the cursor is directed
perpendicular through the short axis view of the aorta and left atrium
During systole, the aortic root move
anteriorly as left atrial volume increases with pulmonary venous return
The anterior and posterior walls of the aortic root move
parallel throughout the cardiac cycle
During diastole, the aortic root moves
posteriorly as the left atrial volume decreases as blood flows from the left atrium to the left ventricle
What does the motion of the aortic root throughout the cardiac cycle reflect?
left atrial dimensions
What happens on the onset of ventricular ejection, the aortic valve cusps?
snap open
RCC move anteriorly
NCC moves posteriorly
They remain open during left ventricular ejection
They lie parallel to the anterior and posterior walls of the aorta
What happens on the onset of diastole , the aortic valve cusps?
close and coapt( fasten or to close) in the center of the aortic root producing a singular linear echo
From the Q wave to the onset of ventricular ejection is a period known as pre ejection or isovolumic contraction time
Where does the left atrium lies directly?
behind the aorta
The anterior left atrial wall and posterior wall of the aortic root are anatomically separate structures BUT seen as ?
one structure on echo
Therefore, the anterior atrial wall follows the same motion of the posterior aortic root wall throughout the cardiac cycle
What does the posterior left atrial wall displays?
minimal motion and remains relatively "flat" during the cardiac cycle
From the PSLA MV M-MODE view the cursor is directed where?
perpendicular to the long axis of the left ventricle and through the tips of the mitral valve leaflets
From the PSSA view at the level of the mitral valve the cursor is positioned where?
perpendicular to the short axis view through the tips of the mitral valve leaflets ( in the PSSA view angling is imperative to make sure your at the tips of the leaflets)
During diastole, the mitral leaflets separate
widely with the AML approaching the IVS and the PML moving toward the LVPW
Comparing MV anterior and posterior leaflets
The larger anterior leaflet has a greater diastolic excursion than the smaller posterior leaflet, the anterior leaflet features a more prominent M configuration
When both MV leaflets close during ventricular systole, the leaflets should form a line called
the C-D line
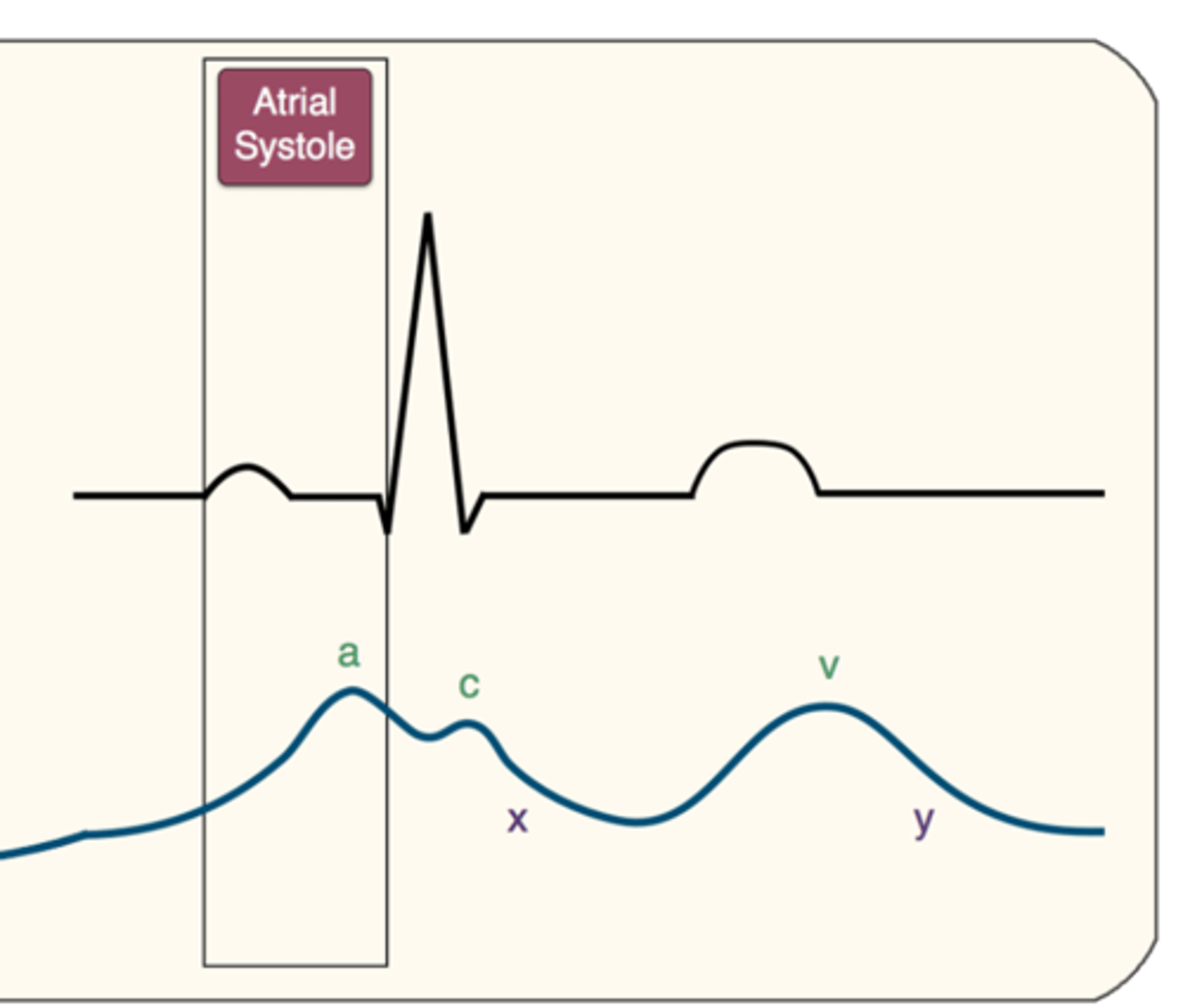
Each characteristic point which forms the pattern of the AML throughout the cardiac cycle has been designated a letter
D-point
E-point
F-point
A-point
C-point
EPSS
D-point-
marks the position of the MV leaflets at the onset of diastole
D-END OF SYSTOLE
E-point-
reflects the maximal opening point of the MV leaflet due to early rapid filling phase (early diastole)
F-point-
is the most posterior position of the MV leaflet following the
E point (diastasis) valve drifts shut
MID DIASTOLIC CLOSURE
A-point-
reflects the point of reopening that occurs following
atrial systole/contraction 20% filling
C-point-
denotes the final position of the leaflet closure immediately prior to ventricular systole
closet of MV
EPSS-
E point septal separation, the distance between the IVS and E point
Where can the M-mode of the left ventricle can be assessed from?
the PSLA and the PSSA at the level of the papillary muscles and from the short axis subcoastal
The cursor is positioned perpendicular to the long or short axis of the left ventricle just past the tips of the open mitral valve leaflets
Wall movement during M-mode of the left ventricle
As the RV contracts during systole the ARHW moves posteriorly,
As the RV fills during diastole, the
ARHW moves anteriorly
The LV walls reflects changes in ventricular dimensions (expansion and contraction)
Following the onset of systole (isovolumic concentration),
the IVS moves rapidly posteriorly (down)while the LVPW moves anteriorly (up)
As early filling phase continues, the IVS continues to move steadily anteriorly while the LVPW move steadily posteriorly. This gradual anterior and posterior motion of the IVS and LVPW continues into diastasis
Following atria contraction, the IVS and the LVPW (to a lesser extent) move abruptly anteriorly and posteriorly
What can be mistaken as the posterior wall of the left ventricle?
The chordae tendineae
careful evaluation must be taken to visualize a minimal echo free space.
electrical events and mechanical events do not occur
at the same time.
For example atrial contraction on the M-mode trace will actually follow the P wave of the EKG and does not occur at the P wave
Why is the M-mode examination is the most difficult part of the echo examination to master when learning?
This is because of the need to align the ultrasound beam perpendicular to the structures transected by it
If a bump or notch is noted between the A and C point, this may be called
"B" bump.
The C - D line is where you would look for mitral valve prolapse.
Why is Correct cursor placement is crucial in the M-mode
examination of the left ventricle ?
because many quantitative
values are measured from this trace
M-mode of the left ventricle can be assessed from where?
PSLA and the PSSA at the level of the papillary muscles and from the short axis subcoastal
Where is the cursor is positioned on the M-mode of LV?
perpendicular to the long or short axis of the left ventricle just past the tips of the open mitral
valve leaflets
As the RV contracts during systole, where does the ARHW moves?
posteriorly,
As
the RV fills during diastole, where does the ARHW moves ?
anteriorly
The LV walls reflects changes in ventricular dimensions do to?
expansion
and contraction
Following the onset of systole, where does the IVS moves ?
rapidly posteriorly while the LVPW moves anteriorly
Normally, the LVPW peaks slightly after the peak of the IVS
As early filling phase continues, the IVS continues to move steadily
_______________ while the LVPW move steadily______________
anteriorly
posteriorly
This gradual anterior and posterior motion of the IVS and LVPW continues into diastasis
diastasis
middle phase of diastole
rapid filling phase and the active filling phase.
Following atria contraction, the IVS and the LVPW move abruptly where?
anteriorly and posteriorly
What can be mistaken as the posterior wall of the left ventricle?
chordae tendineae
but careful evaluation must be taken to
visualize a minimal echo free space.
M-mode for Plumonary Valve-
how many leaflets can be visualized from the
RVOT or PSSA AOV views
2 of the 3
but only one leaflet can be transected by the M-mode cursor at any one time
From the PSSA AOV view the cursor is usually directed
through the right cusp rather than through the left,
as the right is less likely to be overshadowed by lung tissue
What is the only structure of interest that is transected by the
ultrasound beam
cusp
During systole, the pulmonary valve opens and is seen to move
posteriorly
During diastole the cusps move
Anteriorly to their closed position
PV M-mode
A wave-
reflects the small posterior motion following atrial
contraction ( with atrial contraction an extra bolus of blood is ejected into the RV which slightly increases RV pressure which causes the PV to move posteriorly)
PV M-mode
B point-
denotes the small anterior motion occurring at the onset
of ventricular systole
PV M-mode
C point -
is the largest posterior motion immediately
following ventricular ejection ( the pulmonary valve abruptly opens)
PV M-mode
D point -
reflects the gradual anterior motion of the cusps
during ventricular ejection period ( as the RV pressure decreases, the pulmonary valve moves into the center of the root)
PV M-mode
E point-
refers to the closed position of the cusps upon
completion ( pulmonary valve snaps closed at the end of ejection)
PV M-mode
F point-
represents the slight posterior movement of the cusps during diastole and is the point immediately prior to atrial contraction and the next a point
pulmonary valve- M mode
the M-mode pattern produces one half of the box as
seen on the
aortic M-mode trace
When pulmonic stenosis is present, what wave is
increased ?
A wave
greater than 7mm.
When pulmonary hypertension is present, what wave
is decreased?
A wave
less than 2mm.
What may be seen when pulmonary hypertension is present?
Mid systolic notching or "flying W"
The best way to describe the evolution of the IVC diameter through the respiratory cycle is ?
to use M-mode
You will place the ultrasound beam on the cross-section of the IVC, activate M-mode.
You will see the structures on this beam line moving depending on the time.
It is then easy to measure the smallest and largest diameter of the IVC.
You will see the structures on this beam line moving depending on the time. It is then easy to measure the smallest and largest diameter of the IVC.
What is The assessment of the IVC ?
is the cornerstone of the patients'
volume status evaluation.
The interpretation of these
parameters will be different depending on the patient's respiratory mode
(spontaneously breathing or mechanical ventilation).
Spontaneously breathing patients
Patients with mechanical ventilation
Spontaneously breathing patients
In these patients, the IVC diameter and respiratory variation reflects the pressure in the right atrium (RA).
Patients with mechanical ventilation
In these patients, the presence of respiratory variations of the IVC will help you to predict responders to volume challenge and should be recorded for 3 to 4 cycles.
TAPSE
Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion
Is a echocardiographic measurement that allows us to assess Right Ventricular function
Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE), also
known
as tricuspid annular motion (TAM)
Normally during ventricular contraction the tricuspid
annulus descends toward
the cardiac apex as the RV
shortens
The degree of systolic descent of the tricuspid annulus is a reflection of RV longitudinal fiber shortening and overall RV systolic function
How is TAPSE measured?
by placing the M-mode cursor at the
lateral tricuspid annulus from the apical 4 chamber view
From the M-mode trace, how is TAPSE measured ?
as the vertical distance of the lateral annulus between end diastole and end systole
What is relatively an easy measurement for assessing
longitudinal RV systolic function?
TAPSE
it remains a one dimensional
measurement of RV function
What happens when the M-mode cursor is not placed
perpendicular to annular motion for TAPSE?
underestimation of TAPSE ,
and RV systolic function will occur
The normal rang for TAPSE?
1.6 cm
Measurements of Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion
(TAPSE) in a normal individual
-24 mm
Measurements of Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion in a patient with Pulmonary Hypertension
-9mm
MAPSE
Mitral Annular Plane Systolic Excursion
MAPSE
Purpose : assessing Left Ventricular function
could be used for critically ill patients
management of hemodynamic instability
assessing the ejection fraction
MAPSE
Limitation:
Inadequate m-mode
Regional wall motion abnormalities
Measures only longitudinal LV function
Where on the Leftside is MAPSE assessed with M-mode?
apical four-chamber view,
placing the m-mode cursor on the lateral mitral annulus.
The annular plane is identified on the m-mode as the first continuous line
immediately below the LV cavity
Where on the Right side of MAPSE does the measurement take place ?
from the end of diastole,
until maximal expansion in systole.