Geodatabase Rasterization
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
How is Raster Supported in ArcGIS
For Raster deployment/storage/management:
raster provisioning
within a geodatabase(when you want to manage rasters)
raster datasets
mosaic dataset
Advantages of Raster Provisioning
simplicity flexibility, transparency, performance, portability, cost effectiveness
Advantages of geodatabase raster datasets
centralized management, advanced querying, scalability, metadata management, compression and storage optimization, supports complex workflow acros the platform
What is Mosaic Dataset?
Collection of raster datasets(i.e., images or dems) stored i as a catalog and viewed/access as a single mosaicked image or individual images (rasters)
what do mosaic datasets consist of?
A catalog providing the source of pixels, footprints of rasters
feature class that defines the boundary
a set of mosaic rules used to dynamically mosaic the rasters
properties used to control mosaicking and nay image extraction
colour correction table defining colour mapping for each raster
Pros of Mosaic Datasets
efficient data management, on the fly processing, improve performance , supports multiple projections and formats, centralized data source, customization and sharing
Themaitc Rasters are…
data sets that are derives data that can be used for modeling and analysis(raster datasets that group cell values into classes to represent features like land use, soils, or elevation)
Can be created from:
interpolation from sample point
remote sensing based approaches
conversion of vector data
Rasterization
the process of converting a vector to a raster dataset
drape a fishnet containing square cells over the entire study area each cell given a code or values corresponding to an attribute type
Rasterization: Centroid based
assignment based on data vales at the cells geometric center
goo when there is little localized variability in attribute
generally only for raster encoding or polygons
problems: when a minority type is assigned location of object relative to centroid
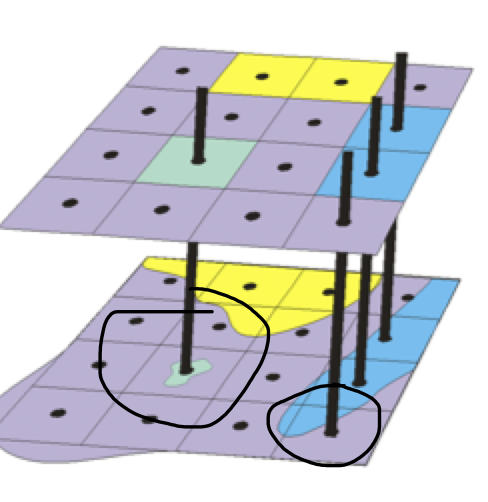
Rasterization: Most Important Type
output cell value dependent on whether the most important feature occupies this cell
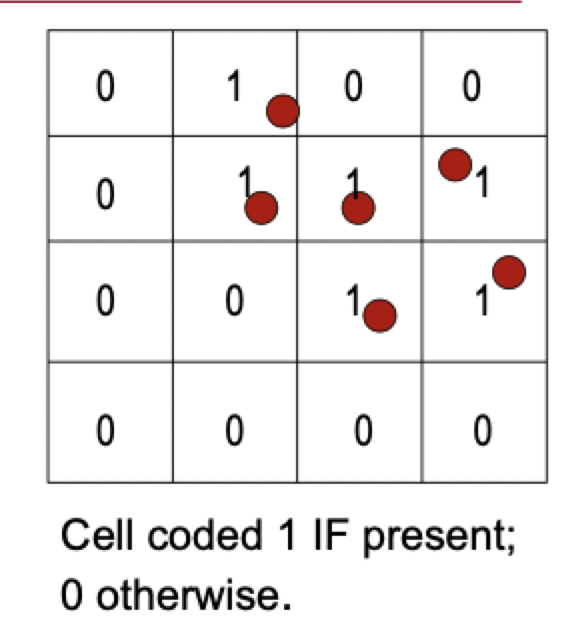
best for coding points and lines
Rasterization: Predominat Type Encoding
proportion of feature within a cell is considered
good for categorical data
coarse resolution and high variability
