Theories of Motivation: KK2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what are the three theories?
maslow - hierarchy of needs
locke and latham - goal setting theory
lawrence and nohria - four drive theory
Locke and Latham - Goal Setting Theory
locke and latham’s goal setting theory is motivational strategy that is based on the concept that employees are motivated to achieve goals. businesses can focus on setting goals for employees with the aim of improving motivation and performance.
factors that influence motivation when setting goals:
clarity
task complexity
feedback
commitment
challenge
L&L clarity
Goals should be clear and specific
this ensures the employee understands exactly what needs to be accomplished and how they will be assessed which will reduce errors and misinterpretation
to achieve this business’ may:
Define measurable metrics for success
L&L challenge
Challenging goals increase effort and motivation as employees are likely to work harder and put in more effort to achieve something that will extend them
Goals should push employees while remaining achievable
L&L commitment
Employees must be committed to the achievement of their goals to generate the drive towards its achievement
the more committed an employee is, the more motivated they will be to work hard towards the goal
commitment can be gained by:
manager setting the goals and convincing the employee why it is important
manager setting the goal collaboratively with employees
L&L feedback
regular feedback is important as it helps the employee monitor their progress towards the goal
the feedback can allow the employee to make adjustments if required
helps maintain momentum towards the goal
L&L complexity
goals should be challenging but not so complex that the employee does not have the ability to complete
if goals are too complex it can harm motivation and employees can become overwhelmed
managers need to consider the skills and ability of the employee when setting goals
training and support may be provided
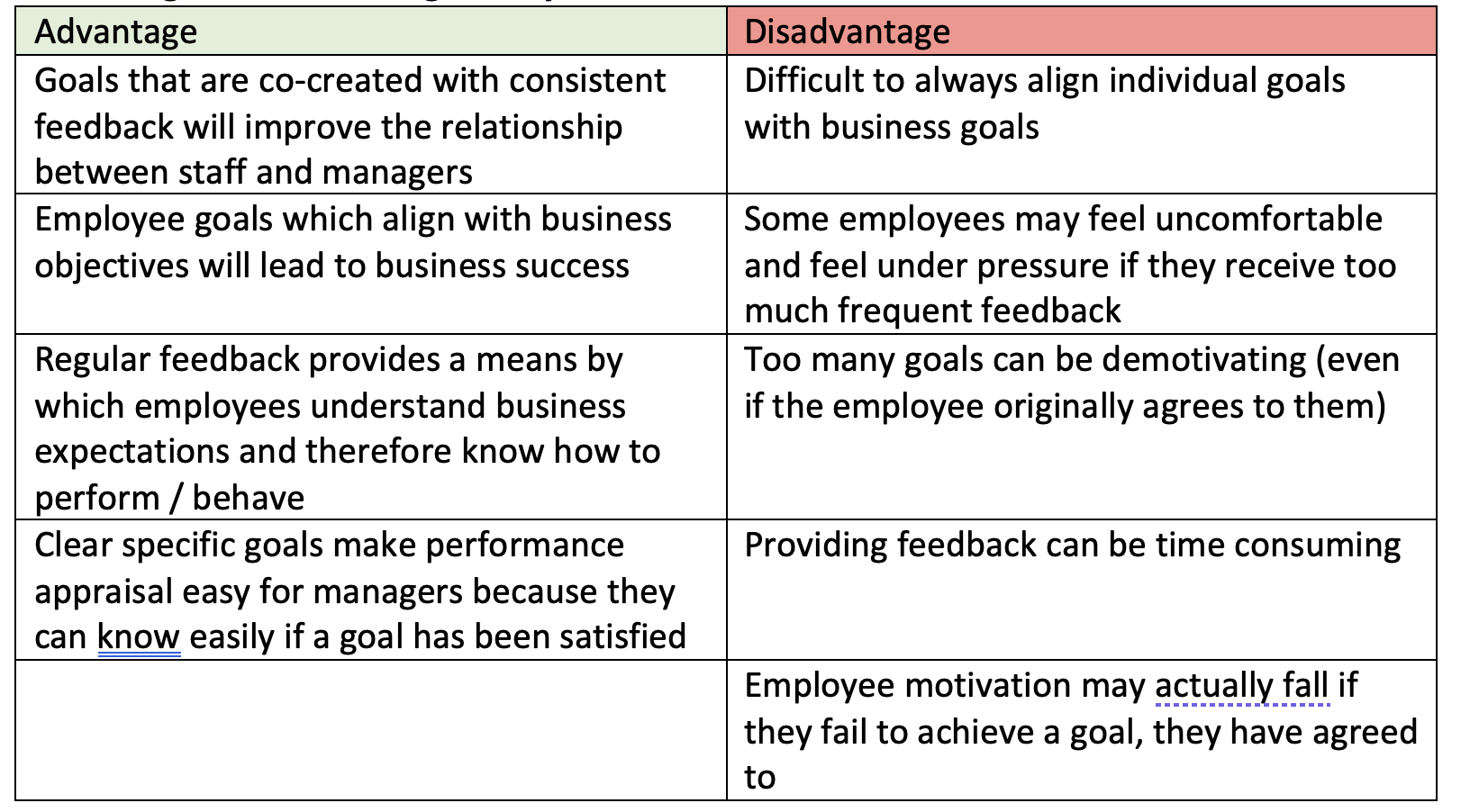
advantages and disadvantages of L&L
Lawrence and Nohria's Four Drive Theory
motivation theory that is based on the concept that humans are motivated by four basic drives. businesses need to implement strategies to provide employees the opportunity to satisfy these drives, as a result it creates a productive work environment
the four drives
drive to acquire
the drive to bond
the drive to learn
the drive to defend
the drive to acquire
drive to acquire: is where individuals desire material possessions, status and power
employees are motivated by the prospect of gaining more resources, whether it be money, promotions, or power
can satisfy the drive by:
offer financial incentives such as competitive remuneration and bonuses
provide opportunities for career progression through promotion
recognising good work through recognition/reward programs
drive to bond
drive to bond: is where individuals desire social interaction and connection with others
employees want to feel as though they belong to the business they work in
This drive can be met by providing:
Create a positive and supportive work environment
Opportunities for positive, two-way communication.
Fostering and supporting trusting friendships
increase opportunities for social interactions. e.g. social gatherings, or eating lunch together
drive to learn
drive to learn: is where individuals desire personal and professional growth and development
employees are driven to seek out new challenges and learn new skills
this drive can be met by providing:
Stimulating, interesting tasks with plenty of variety.
Opportunities for training and development (e.g. TAFE)
provide constructive feedback to provide a learning experience
drive to defend
drive to defend: is where individuals desire to protect themselves and others from harm
employees are driven by a sense of security (job security)
This drive is different from the other drives as it is a dormant drive which becomes active only in the face of a threat.
to satisfy this drive, businesses can:
provide a welcoming, supportive and safe workplace.
ensure systems and processes are fair (eg. reward and recognition).
address any job security issues (e.g. ongoing contracts)
other factors
all drives occur at the same time
needs to be a balance between the four drives as they compliment each other
advantages of four drive theory
based on both short term and long term motivation for employees, therefore the business can continue to implement the strategies
business performance can improve with the improved motivation
can implement multiple strategies at once
simple, can implement quality and effectively - increasing likelihood of it being successful
disadvantages of four drive theory
Some of the workplace applications involve competition between employees, which can have detrimental effects; for example, a workplace may suffer from a lack of cooperation or a lack of information sharing.
Expensive because they have implement multiple strategies - target all the drives
difficult to satisfy the drives for all employees (e.g. drive to acquire can be expensive or challenging to promote all employees)
hmr using the four drive theory
allows managers to more quickly provide the solutions or resources that could allow the workers to become satisfied and motivated
Maslow Hierarchy of Needs
maslow’s theory is based on the concept that people have 5 basic needs that need to be met and that each need will act as a source of motivation while it remains unsatisfied
an employee must satisfy a specific stage before they can move up a stage
once a particular need is satisfied it is not longer a motivator
order of needs
highest
self-actualisation
esteem
social
safety
physiological
lowest
physiological needs
basic requirements for human survival
business: basic pay and working conditions
safety needs
security, stability, and protection from harm
business: safe workplace (abiding by oh&s laws) and job security
social needs
strong relationships, affection, and a sense of community
business: team-based work, social events (birthdays ect.), and supportive management
esteem needs
self- esteem, respect, and recognition
business: recognising high performers with rewards, expanding job responsibilities, promotions
self actualisation needs
personal growth, reaching full potential
business: providing employees with challenging work, and opportunities for skill and knowledge development
evaluate maslows
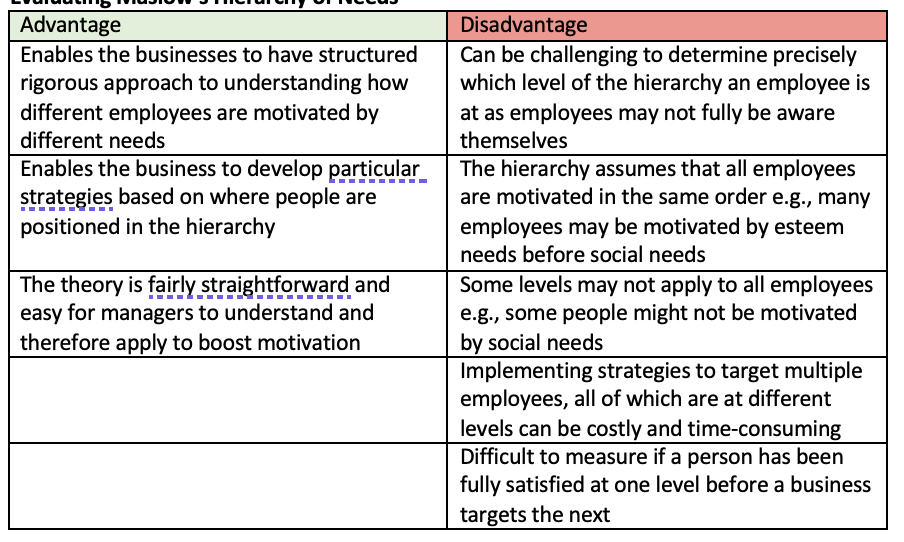
weakness of maslow
doesn’t consider individual differences, not all stages in the hierarchy apply to all employees
can be difficult to identify the stage at which each individual employee is — this may make it difficult to determine an appropriate strategy to motivate each employee.
the hierarchy of needs is very simplistic and one motivation strategy may not be able to satisfy several needs at the same time
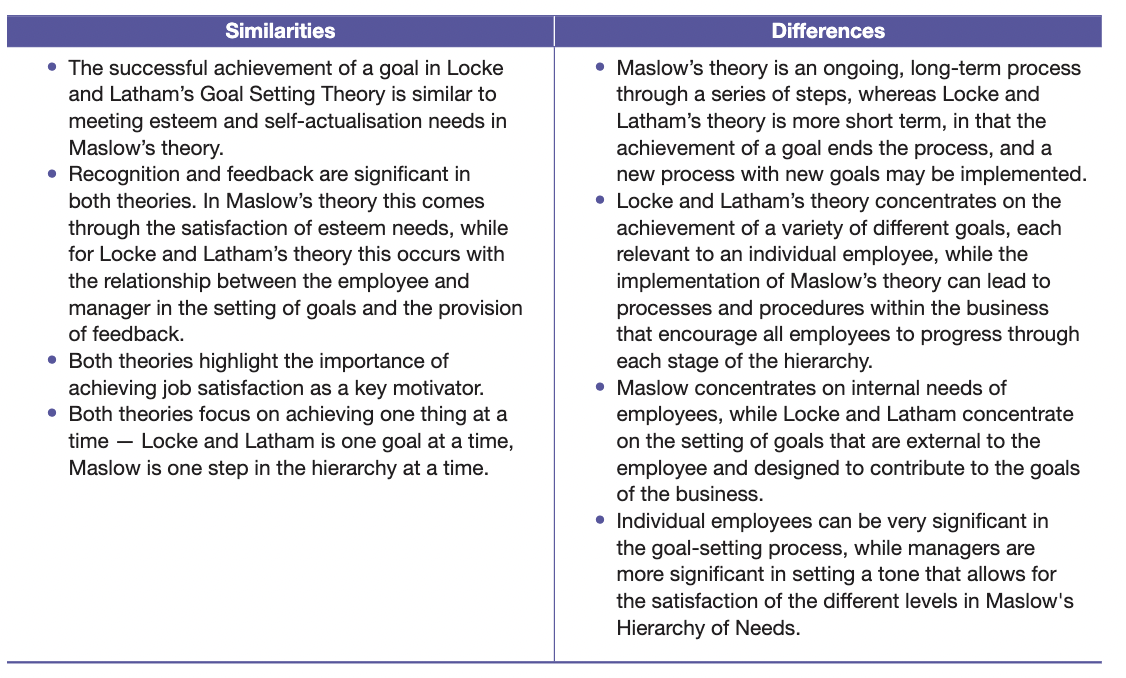
Maslow compared with Locke and Latham
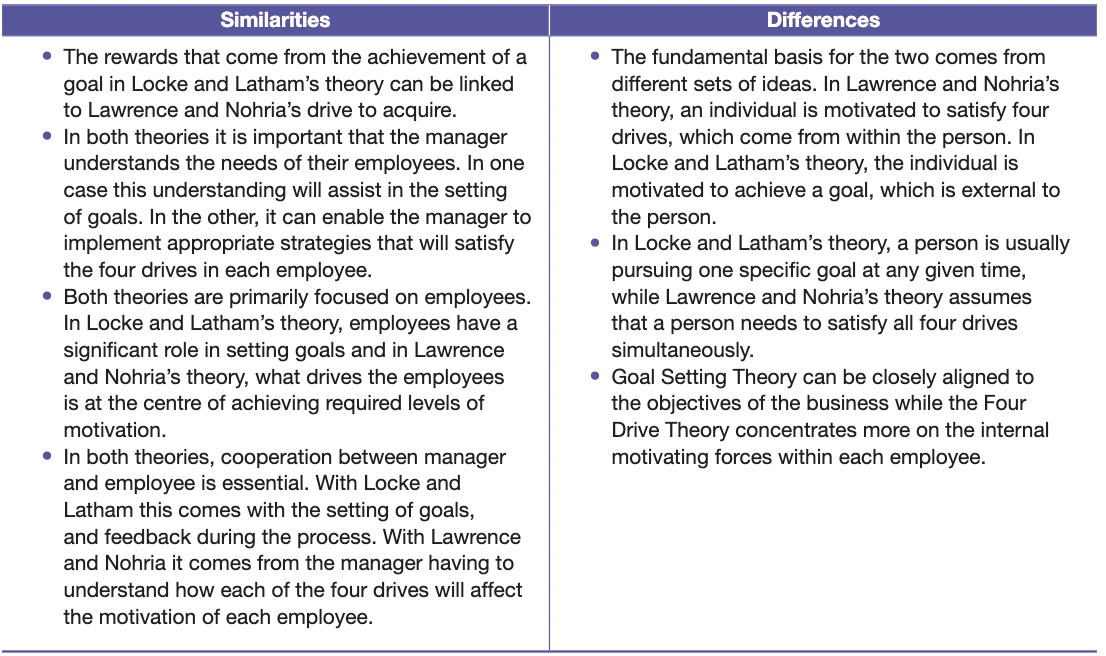
Locke and Latham compared with Lawrence and Nohria
Maslow compared with Lawrence and Nohria
