CHAPTER 8: GDP and National Income - Measuring Economic Performance
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The inflation-adjusted value of all newly produced goods and services calculated and published by a government.
Nominal GDP
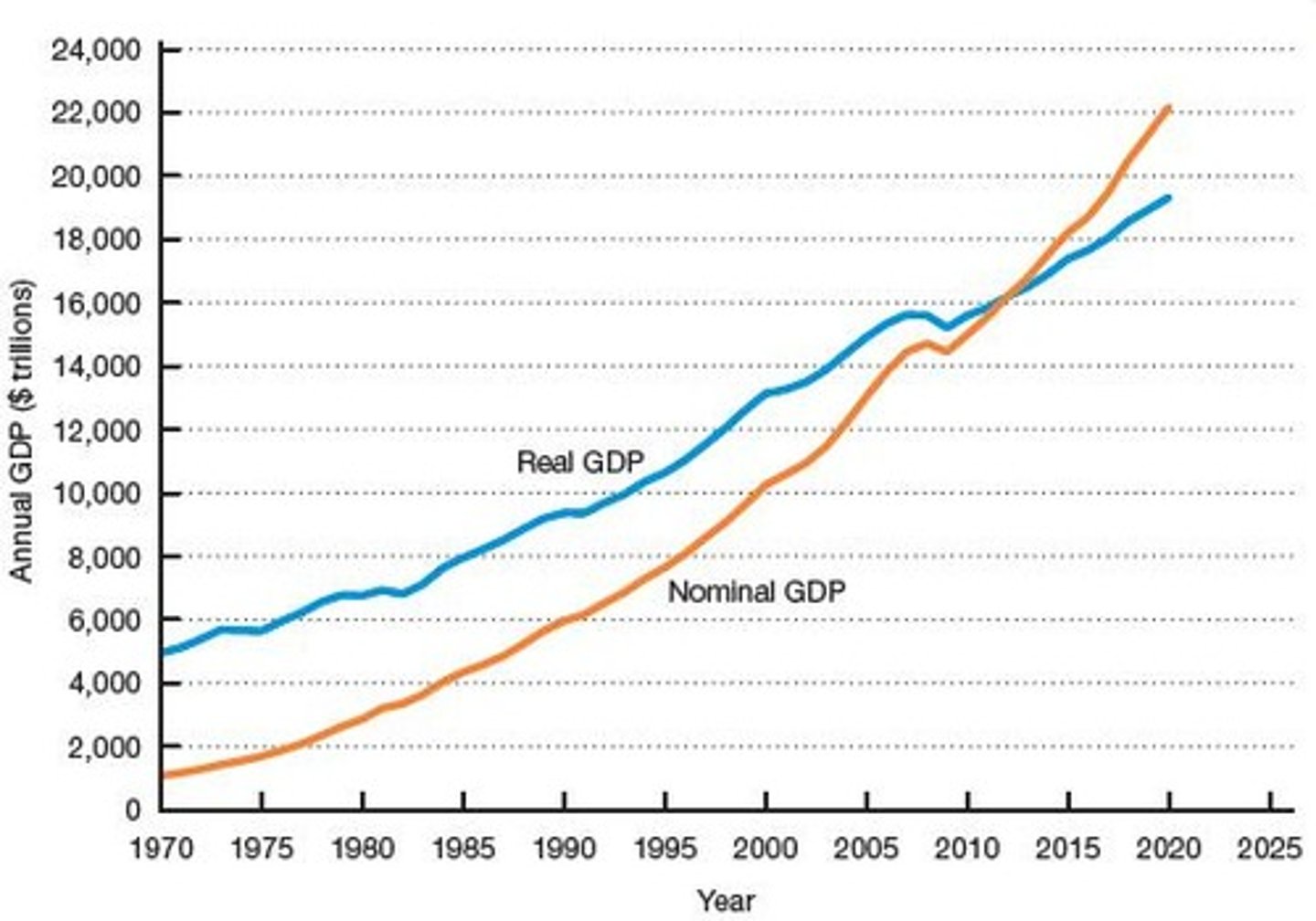
The total value of all goods and services produced in a country at current market prices, without adjusting for inflation.
Real GDP
The total value of all goods and services produced in a country, adjusted for inflation.
National Income Accounting
A measurement system used to estimate national income and its components.
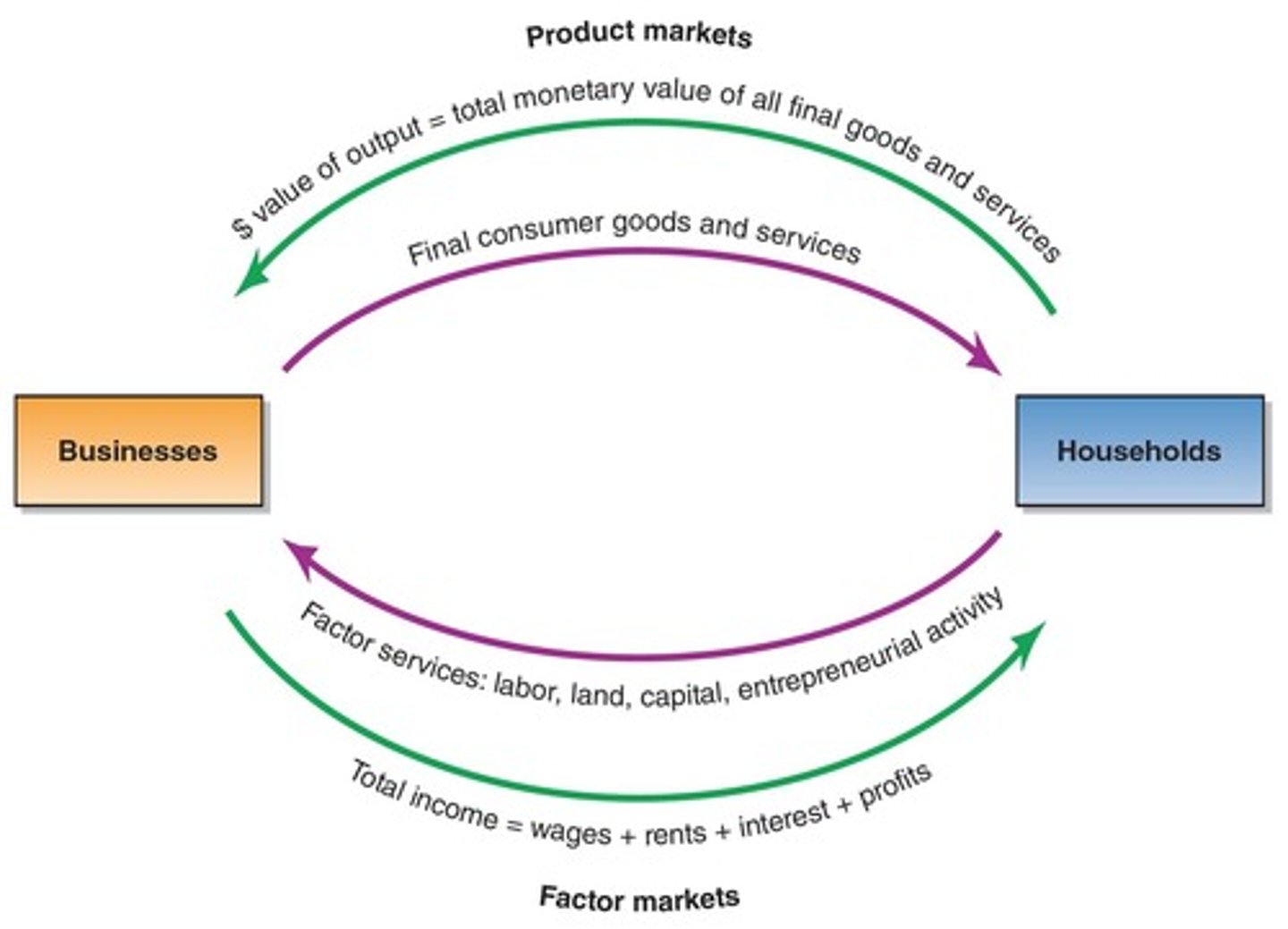
Product Markets
Transactions in which households buy goods.
Factor Markets
Transactions in which businesses buy resources.
Total Income
The yearly amount earned by the nation's resources, including wages, rent, interest payments, and profits.
Final Goods and Services
Goods and services that are at their final stage of production and will not be transformed into yet other goods or services.
Profits
The return entrepreneurs receive for the risk they incur when organizing productive activities. Gross corporate profits and proprietors' income.
Economic Exchange
A transaction where goods and services flow in one direction and money payments flow in the other.
Aggregate Production
The total output of goods and services produced in an economy.
Inflation
The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising.
Labor Force Participation
The percentage of the working-age population that engages in the labor market.
Economic Performance
A measure of how well an economy is performing, often assessed through GDP and national income.
Smooth Growth
A term used to describe growth that appears too consistent or regular, raising skepticism about its accuracy.
Households
The economic agents that buy goods in product markets.
Businesses
The economic agents that buy resources in factor markets.
Components of National Income
The various elements that make up the total national income, including wages, rents, interests, and profits.
Economic Indicators
Statistics that provide information about the economic performance of a country, such as GDP, unemployment rates, and inflation.
Aggregate Income
The total income earned by all factors of production in an economy.
Rent
Payments made for the use of land or property.
Interest Payments
Payments made to capital owners for the use of their funds.
Entrepreneurs
Individuals who organize and manage the factors of production, taking on the associated risks.
Total output
The dollar value of total output must equal total income.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The total market value of all final goods and services produced by factors of production located within a nation's borders during a year. Gross domestic income plus indirect business taxes and depreciation.
Final output
The dollar value of final goods and services produced per year by factors of production located within a nation's borders.
Final good
A good that is sold to the end consumer, such as bread or an automobile.
Intermediate goods
Goods used up entirely in the production of final goods.
Value added
The dollar value of an industry's sales minus the value of intermediate goods used in production.
Income payments
The total value added is equal to the sum of all income payments.
Gross Output (GO)
The total market value of all goods and services produced during a year by factors of production located within a nation's borders.
Double Counting
The inclusion of all forms of business-to-business expenditures in GDP, which counts business spending across all stages of production.
Financial Transactions
Transactions that do not involve the production of final goods and services, including securities and government transfer payments.
Securities
Financial instruments such as stocks and bonds.
Government Transfer Payments
Payments made by the government to individuals, such as Social Security and unemployment compensation.
Private Transfer Payments
Payments made between individuals or corporations, such as individual gifts and corporate gifts.
Transfer of Secondhand Goods
The sale of used items, which is not counted as part of GDP.
Excluded Transactions
Transactions that are not included in GDP, such as household production and underground transactions.
Household Production
Nonmarket production activities performed within the household that are not included in GDP.
Underground Transactions
Legal and illegal economic activities that are not reported and thus excluded from GDP.
GDP Limitations
GDP excludes nonmarket production and is not necessarily a good measure of the well-being of a nation.
Behavioral Economists
Economists who study psychological factors in economic decision-making and may use surveys to measure well-being.
Market Values
Dollar values assigned to activities that occur in the market, which can increase measured GDP.
Economic Activity
The production of goods and services measured in terms of market prices.
Welfare Measurement
GDP is not a measure of a nation's overall welfare.
Data Science Campus
A facility established by the United Kingdom's Office for National Statistics to analyze data from digital devices.
Machine Learning in GDP Computation
The application of machine learning techniques to improve existing GDP computations and develop alternative measures of economic activity.
Expenditure approach
Computing GDP by adding up the dollar value at current market prices of all final goods and services.
Income approach
Measuring GDP by adding up all components of national income, including wages, interest, rent, and profits.
Consumption expenditures (C)
Expenditures on durable consumer goods, nondurable consumer goods, and services.
Durable consumer goods
Items that last more than three years (e.g., automobiles, furniture).
Nondurable consumer goods
Goods that are used within three years (e.g., gasoline, food).
Services
Mental or physical help provided to consumers.
Gross private domestic investment (I)
The creation of capital goods, such as factories and machines, that can yield production and hence consumption in the future.
Producer durables
Capital goods with a life span of more than three years.
Fixed investment
Purchases by business of newly produced producer durables or capital goods.
Inventory investment
Changes in stocks of finished goods and goods in process, as well as changes in raw materials.
Government expenditures (G)
Expenditures by state, local, and federal governments, valued at cost.
Net exports (X)
Net exports (X) = total exports - total imports.
GDP formula
GDP = C + I + G + X.
Net domestic product (NDP)
GDP allowing for depreciation (capital consumption allowance).
Depreciation
The amount that businesses would have to save in order to repair and replace deteriorating machines and other equipment.
NDP formula
NDP = GDP - depreciation.
Net investment (net I)
Net investment = I - depreciation.
Change in capital stock
The change in the capital stock over a one-year period.
Gross domestic income (GDI)
The sum of all income (wages, interest, rent, and profits) paid to the four factors of production.
Wages
Salaries and labor income. Payments made to labor for their contribution to production.
Interest
Interest received (savings accounts) minus interest paid (mortgages).
Indirect business taxes
All business taxes except the tax on corporate profits, including sales and business property taxes.
National income (NI)
The total of all factor payments to resource owners.
Personal income (PI)
The amount of income that households actually receive before they pay personal income taxes.
Disposable personal income (DPI)
Personal income after personal income taxes have been paid.
Nominal values
Measurements in terms of the actual market prices at which goods are sold; expressed in current dollars, also called money values
Real values
Measurements after adjustments have been made for changes in the average of prices between years; expressed in constant dollars
Constant dollars
Dollars expressed in terms of real purchasing power
Real GDP formula
Real GDP = nominal GDP / price index × 100
Per capita real GDP
Real GDP divided by total population
Per capita real GDP formula
Per capita real GDP = real GDP / population
Foreign exchange rate
The price of one currency in terms of another
Purchasing power parity
An adjustment in exchange rate conversions that takes into account differences in the true cost of living across countries
GDP deflator
Used to calculate values for real GDP from 2010 to 2020
GDP
The total market value of a nation's final output of goods and services produced in a year using factors of production located within its borders.
Purchasing Power Parity
A method of measuring the relative value of currencies based on the cost of goods and services in different countries.
Per Capita GDP
The GDP divided by the population of a country, indicating the average economic output per person.
GDP Deflator
A measure of the level of prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy.
Expenditure Approach
A method of calculating GDP that sums consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports (GDP = C + I + G + X).
Income Approach
A method of calculating GDP that sums all incomes earned by factors of production, including wages, rent, interest, and profits.
National Income
The total income earned by a nation's residents and businesses, including wages, profits, rents, and taxes.
Personal Income
The total income received by individuals, including wages, dividends, and other forms of income.
Disposable Personal Income
Personal income minus personal taxes, representing the amount available for spending and saving.
GDP Growth Rate
The rate at which a country's GDP increases from one period to another, often expressed as a percentage.
Quality Changes
Adjustments made to GDP calculations to account for improvements or declines in the quality of goods and services.
Gross Output
A measure of economic activity that includes the total value of all goods and services produced in the economy.
Real GDP Targeting
A practice where governments aim for specific growth rates in reported GDP figures, potentially leading to manipulated data.
Economic Transaction
An exchange of goods and services that involves a receipt of payment.
Circular Flow of Income
A model that illustrates how money moves through the economy, showing the relationship between producers and consumers. In every economic exchange, the seller receives exactly the same amount that the buyer spends.
Economic Performance Measures
Various metrics used to assess the economic health of a nation, including GDP, gross output, and other indicators.
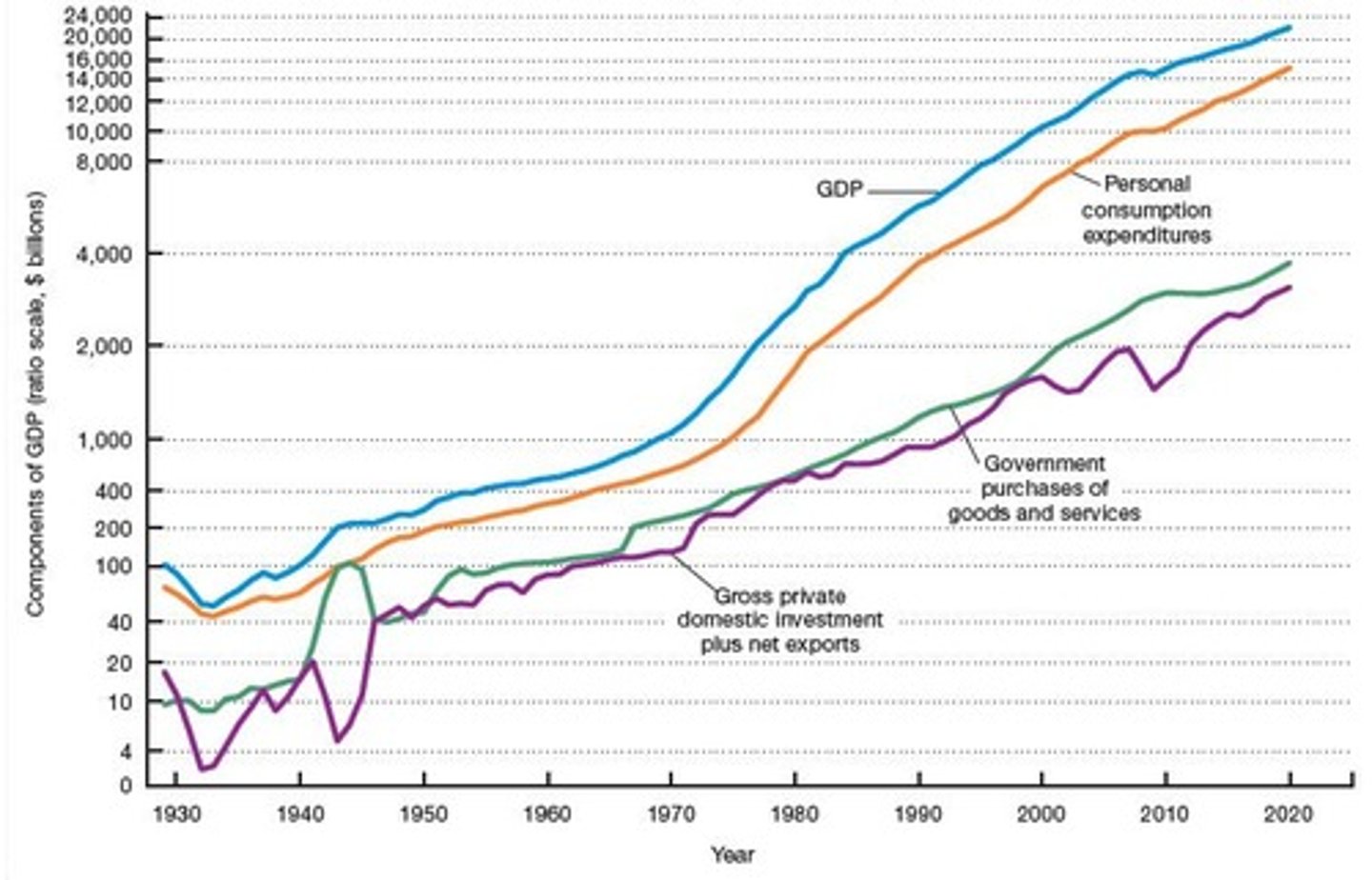
Components of GDP
The major elements that contribute to GDP calculations, including consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
Limitations of GDP
GDP does not account for nonmarket transactions, does not measure national well-being, and reflects production flow rather than wealth.
GDP Exclusions
Nonmarket transactions and informal economic activities that are not included in GDP calculations.