physiology of the mouth, pharynx and oesophagus
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 1 ctb
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
saliva function
lubricates and wets food: helps create bolus for swallowing
helps with taste
begins digestion of starch (via α-amylase) and lipids (via lingual lipase)
protects oral environment
washes away bacteria and food particles
keeps mucosa moist
cools hot foods
contents destroy bacteria
maintains alkaline environment
key features of saliva
hypotonic solution
800-1500ml produced each day
pH 6.2-8
composition of saliva
water
high conc of some electrolytes
K+ : compared to plasma/initial saliva
HCO3- : maintains alkaline environment
relatively low conc of some electrolytes (compared to plasma/initial saliva)
Na+
Cl-
calcium phosphates: prevent demineralisation of teeth
mucus: lubrication
digestive enzymes: salivary alpha amylase, lingual lipase
antibacterial agents: proteolytic enzymes (lysozyme), ABs (IgA)
salivary glands
exocrine glands
parotid gland: serous saliva, watery and rich in alpha amylase
sublingual gland: mostly mucous saliva
submandibular gland: mixed serous and mucous saliva
many tiny buccal glands
von Ebner’s glands of tongue: lingual lipase
histological structure of major salivary glands
compound (branched) tubuloacinar glands
secretory portion: acinar cells
serous cells: alpha amylase and immune components
mucous cells: mucin
myoepithelial cells: contract to compress acinus → saliva forced into ducts
highly vascularised
branching duct system
small intercalated ducts: lined by simple cuboidal epithelium and myoepithelial cells
straited ducts lined by simple cuboidal to complue columnar epithelium
terminal (principle) duct → oral cavity
saliva production: primary secretion
acinar cells secrete initial saliva
initial saliva is isotonic and has a similar electrolyte concentration to plasma
saliva production: ductal modification
transporters on luminal and basolateral membranes of ductal cells enable modification of initial saliva
absorption of NaCl is greater than secretion of potassium and bicarb → net absorption of solute
ductal cells are relatively impermeable to water → hypotonic solution
effect of flow rate
degree of modification is dependent on flow rate
bicarb (HCO3-) secretion is selectively stimulated so its conc increases with increasing flow rate
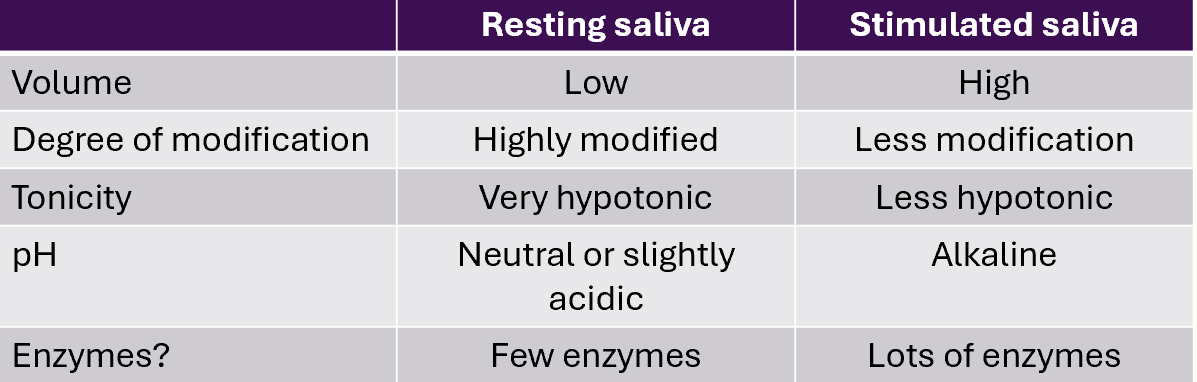
resting saliva vs stimulated saliva
control of saliva secretion
the dominant neural input to the salibary glands is the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS): rest and digest
stimulation results in:
increased saliva production
increased bicarb and enzyme secretions
contraction of myoepithelial cells
increased blood flow (PNS)
xerostomia
dry mouth from reduced/absent salivary secretion or change in the compositionof saliva
many potential causes including:
dehydration
anxiety
damage to salivary glands or their innervation
medication side effect
Sjogren’s syndrome
signs and symptoms of reduced saliva secretion
dry and painful throat
dry and rough tongue
dry and cracked lips
problems with swallowing and speaking
difficulty keeping dentures in place
altered taste
halitosis (bad breath)
dental caries and periodontal disease
signs of oral infections
taste (gustation)
5 classifications: sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami
taste buds are found on the tongue, palate, larynx and pharynx
taste buds in tongue are located in taste papillae
taste buds:
taste receptor cells
supporting cells
basal cells
taste receptor cells
taste receptor cells = chemoreceptors
they detect chemical signals and transfuce into electrical signals
microvilli provide a large surface area
tastant molecules bind to receptors or enter taste receptor cells → depolarisation → AP generation in afferent nerves
appreciation of flavour involves olfaction
mastication
physical digestion
breaks down food into small pieces
increases surface area for enzyme action
mix food with saliva
create bolus for swallowing
structures involved:
teeth
tongue
mandible
temperomandibular joint
muscles of mastication
pharynx
muscular tube that connects nasal cavity, oral cavity, larynx, oesophagus
3 parts:
nasopharynx: posterior to nasal cavity
oropharynx: posterior to the oral cavity
laryngopharynx: posterior to the larynx
muscle of the pharynx
inner longitudinal layer
shortens, elevates and widens the pharynx during swallowing
external circular layer (pharyngeal constrictors)
contract sequentially to force bolus through pharynx and into oesophagus
cricopharyngeus: upper oesophageal sphincter
lower oesophageal sphincter (LOS)
physiology sphincter at gastro-oesophageal junction
prevents reflux of gastric contents into oesophagus
components of LOS
intrinsic components
smooth muscle
extrinsic component
right crus of the diaphragm
other components:
acute angle at which the oesophagus enters stomach
muscosal folds present at the gastro-oesophageal junction
gastro-oesophageal refulx disease (GORD)
refulx of stomach contents through the LOS into the oesophagus
occurs due to the impairment of normal anti-reflux mechanisms
increased frequency of transient lower oesophageal sphincter relaxations
increased intra-abdominal pressure (pregnancy, obesity)
low LOS pressure
hiatus hernia
can cause inflammation of the oesophageal mucosa
symptoms:
heartburn
acid brash
regurgitation
GORD complications
oesophageal strincture
scarring and narrowing of the oesophagus
Barrett’s oesophagus
metaplasia of squamous epithelium of oesophagus to gastric mucosa (columnar epithelium)
associated with an increased risk of oesophageal cancer
swallowing
oral phase
voluntary
pharyngeal phase
involuntary
oesophageal phase
involuntary
oral phase
tongue moves bolus back towards oropharynx
somatosensory receptors, including mechanoreceptors, send afferent information to the swallowing centre in medulla (in brainsteam)
via vagus (CN X) and glossopharyngeal (CN IX) nerves
involuntary swallowing reflex initiated
motor information sent to muscles of pharynx and upper oesophagus
pharyngeal phase
respiratory tract protected
soft palate elevates
glottis closes abnd larynx elevates
respiration inhibited
epiglottis tilts to cover larynx
upper oesophageal sphincter relaxes
peristaltic wave of contraction
oesophageal phase
upper oesophageal sphincter closes
larynx falls, glottis opens and respiration recommences
primary peristatic wave
mediated by swallowing reflux
lower oesophageal sphincter relaxes
secondary peristatic wave
stimulated by mechanoreceptors in wall of oesophagus
mediated by ENS
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
causes:
neurological: dementia, stroke, head injury
stomach: gastric cancer
mouth: cleft lip/palate, mouth cancer
pharynx: tonsilitis, pharyngeal pouch, pharyngeal cancer
oesophagus: mediastinal tumour, achalasia, GORD
assessment of swallowing
history and examination
SALT
clinical assessment
bedside swallow test
instrumental assessment
investigations:
endoscopy
barium swallow
manometry