ORGS 2100 - Class 9: Leadership Styles and Behaviour
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
What is the leadership myth?
challenge assuming leadership exerts significant influence
What is leadership?
power & influence → other’s goal activity
What did Drew Dudley comprehensively claim in TED-Ed’s “Everyday leadership” video?
leader
thing one’s going to deserve
lollipop moment
moment: one said / did thing fundamentally making life better without knowing
What did early leadership approaches identify?
trait
What is Leader-Member Exchange theory?
// LMX theory
leader → follower need
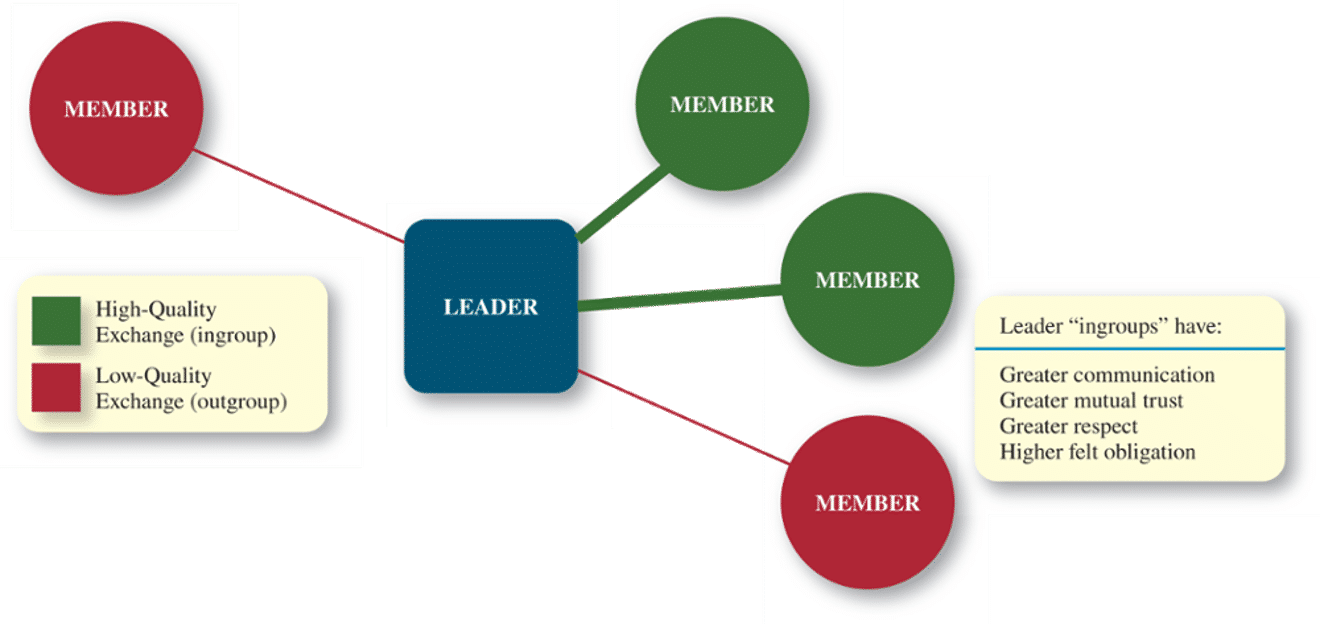
What is a Leader-Member Exchange theory ingroup?
high-quality exchange
What is a Leader-Member Exchange theory outgroup?
low-quality exchange
What do leader ingroups have?
communication
trust
respect
obligation
What are some examples of ways to build stronger LMX relationships?
open & honest communication
individual support
trust & reliability
shared goal & vision
What explains how leaders play a psychological safety role?
create environment where employee feels comfortable expressing idea without fear
openly communicate
actively listen
value diverse perspective
What is an example of a way one might not feel comfortable sharing new ideas?
not feel psychologically safe
What does Dr. Amy C. Edmondson comprehensively claim in Harvard Business School’s “Leading in Tough Times” article?
psychological safety founder
low interpersonal fear
hard because avoid:
incompetence → don’t admit
ignorance → don’t ask
intrusion → don’t offer
negativity → don’t criticize
organization need to address new challenge
candor
speed
creativity
candidly speak → multiple people work
examples of things leaders do to create psychological safety
frame work → learning problem
make clear that group needs voices
→ honest input & idea flow
BY ask question
psychological safety v.s. accountability
tradeoff2 dimensionstake foot off brake & step on gas
comfort & anxiety
learning // high-performance … zone
psychological safety v.s. inclusion
improve psychological safety → improve inclusion
What does the “Why good leaders make you feel safe | Simon Sinek | TED” video comprehensively claim?
military v.s. business
military: medal to one sacrificing self so other gains
business: bonus to one sacrificing other so self gains
→ because safe environment ‘they would’ve done for me’ » trust & cooperation = feeling instruction
leadership = rank choice
What is 1 decision-making leadership approach example?
time-driven leadership model
What is 1 behavioural leadership approach example?
life cycle leadership model
What do leaders promote when they attend to relations & cultivate psychological safety?
innovation
well-being
What is transformational leadership?
inspire follower to commit to shared vision providing meaning while serving as role model developing potential & viewing problem from own perspective
What are the leadership dimensions motivating transformation & change?
idealized influence
inspirational motivation
intellectual stimulation
individualized consideration
Dr. King communicated a clear vision for the future, equality for all persons through nonviolent change. (Module)
Idealized influence
Inspirational motivation
Intellectual stimulation
Idealized consideration
Dr. King clearly articulated an inspirational vision for a better future.
Dr. King used a number of techniques to create a sense of familiarity that allowed his message to resonate with his listeners, such as references from The Bible. (Module)
Idealized influence
Inspirational motivation
Intellectual stimulation
Idealized consideration
Dr. King's use of terms that the audience would understand and feel passionate about helped them identify with him and his message, a form of idealized influence.
Dr. King called upon the audience to question their taken-for-granted assumptions about how society works, suggesting that society is not fair for Black Americans and that they need to think about the problem differently. (Module)
Idealized influence
Inspirational motivation
Intellectual stimulation
Idealized consideration
Dr. King used intellectual stimulation to challenge the audience to re-examine some of their assumptions about the fairness of society and rethink how it can be changed through non-violent means.
What does Psychology Today’s Emeric Kubiak comprehensively claim in the “Leadership for Today: Let's Ask the Right Questions” article?
identify whatleadersshould look likequestion way one makes decisions & focus on means to objectively identify
The Future of Leadership?
AI → behavioural skill refocus
leadership =
power over peoplepower with peopleopenness & emotional stability & agreeableness /
task-orientedbehaviour-oriented → success / team effectivenessinfluence employee satisfaction & psychological safety
what leaders should be v.s. what leaders are =
collective misunderstanding of good leaderpoor intuition-based decision practice consequence
Emergence…Is Not Performance
intuition = myth
select leader to match
true potential‘implicit leadership theory’emerge criteria ≠ perform criteria
select leaders for confidence
→ narcissism » value employee like them
v.s.
select leader on objective data
psychometric test
What are some examples of why social identity groups continue to be underrepresented in leadership positions?
leader emergence
leader effectiveness
What does the “The Likability Dilemma for Women Leaders | Robin Hauser | TED” video comprehensive claim?
women face double bind in leadership
align with masculine norms but be penalized for violating gender stereotype
decisive
competent
assertive
strong
do not align with masculine norms but risk not being seen as effective leader
kind
nurturing
helpful
supportive
deferential
competence / likability dilemma
rarely perceived competent & likable
« unconscious bias
women > men when negotiating for self other
selfish v.s. helpful ≠ leader
→ speak up
→ forget likability
What does Stephen Friedman’s Leadership Lessons on “How To Deal with Difficult People.” Changing Our Frames” article comprehensively claim?
dispositional attribution
easily categorizing / blaming / conceptualizing frame
→ difficult people people not yet learned to get with
Frame
difficult people = antagonism // argumentativeness // hostility
Reframe
difficulty ≠ broken thing
judgemental & lacking equanimity frame
exclusive focus on other ≠ help
Move Forward
→ 1: one is difficult v.s. one needs to be less difficult
→ 2: not able to manage interaction with other v.s. learn to somehow manage
→ 3: evaluative sympathetic
What does LMX refer to? (Quiz)
Leaders More eXtraverted
Leader Management eXchange
Loyalty Member eXchange
Leader Member eXchange
LMX = leader member exchange
In describing the double bind that women leaders face, Robin Hauser references the __________________ dilemma. (Quiz)
Competence
Assertiveness
Likability
Warmth
According to Robin Hauser, the likability dilemma describes a dilemma that women can face when they are penalized by others for not being likeable, but if they are likeable then they are not seen as suited for leadership.
_________________________ is an approach to leadership that inspires followers to commit to a shard vision that provides meaning to their work while also serving as a role model who helps followers develop their own potential and view problems from their own perspective. (Quiz)
Transactional leadership
Transformational leadership
LMX
Laissez-faire
Transformational leadership is an approach to leadership that inspires followers to commit to a shard vision that provides meaning to their work while also serving as a role model who helps followers develop their own potential and view problems from their own perspective.
Which if the following is the definition of psychological safety? (Quiz)
Employees feel comfortable expressing their thoughts, ideas, and concerns without fear of retribution
Employees feel worried about expressing their thoughts, ideas, and concerns for fear of retribution
Employees feel like they have access to necessary safety equipment in case of injury at work
Employees feel like the workplace is not stressful
Psychological safety is defined as employees feeling comfortable expressing their thoughts, ideas, and concerns without fear of retribution
All of the following are ways leaders can develop high quality relationships with followers, EXCEPT: (Quiz)
Treat all followers the same
Open and honest communication
Trust and reliability
Individualized support
For high quality LMX relationships, leaders much consider followers' specific needs and thus treating each follower the same may not achieve that aim.
In calling upon the audience to question their taken-for-granted assumptions about how society works, Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. leveraged which one of the four dimensions of transformational leadership? (Quiz)
Idealized influence
Inspirational motivation
Intellectual stimulation
Idealized consideration
Intellectual stimulation involves challenging followers to be innovative and creative by questioning assumptions and reframing old situations in new ways.
What type of leadership approach is Indra Nooyi, former CEO of PepsiCo, known for? (Quiz)
TransformationalTransactional
LMX
Laissez-faire
Indra Nooyi is known for her LMX approach to leadership.
2023 research shows that, because of harmful and incorrect stereotypes, people continue to associate white people with leadership qualities more so than Black people. This is likely to be a source of bias in _____________________. (Quiz)
Leadership emergence
LMX
transformational leadership
Transactional leadership
If people are less likely to associate leadership qualities with certain social groups, then members of those social groups are less likely to be "seen" as leaders and are less likely to have opportunities to emerge as leaders, affecting leadership emergence.
Which of the following best characterizes the relationship between psychological safety and employees' innovation (Quiz)
Psychological safety is not related to employees' innovation
Psychological safety decreases employees' innovation
Psychological safety improves employees' innovation
Psychological safety is not related to employees' innovation, but rather to employees' well-being
Psychological safety improves employees' innovation by helping employees feel more comfortable taking risks.
All of the following are dimensions of transformational leadership, EXCEPT: (Quiz)
Idealized influence
Inspirational motivation
Individualized consideration
Interdisciplinary collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration is not a dimensions of transformational leadership.
What does leadership affect in follower direction?
event interpretation
activity organization
goal commitment
other relation & support
cooperation access
What are some employee-centred leader effectiveness measure examples?
unit
dyad
… -focused approach
What is a unit-focused approach?
employee-centred leader effectiveness measure
survey & average
What is a dyad-focused approach?
employee-centred leader effectiveness measure
survey relation & differentiate in- / out- … group
What is leader-member exchange theory?
//LMX theory
develop dyadic leader-member relation over time
What is role taking?
LMX phase
leader provides expectation & follower meets expectation
What is role making?
LMX phase
follower voices expectation → opportunity / resource v.s. activity / effort flow
What are the leader-member dyads?
high-quality exchange dyad
v.s.
low-quality exchange dyad
What is a high-quality exchange dyad?
LMX ingroup
high…
communication
trust
respect
obligation
What is a low-quality exchange dyad?
LMX outgroup
low…
communication
trust
respect
obligation
What does LMX theory suggest?
competent / likable / similar personality to leader = ingroup
effectiveness should gauge critical leader-member dyad
What culture is high-LMX relationship effective for?
individualistic > collectivistic = Western > Asian
What is leader effectiveness?
degree
action → achievement
commitment
dyad
What do traits predict?
leader emergence
What explains traits’ leader emergence prediction?
increase motivation to lead
What limitations cause leadership research to move in a different direction?
weak trait correlation
> leader effectiveness
practical relevance: trait < action
What can leaders do to make them more effective?
decision making style
day-to-day behaviour
behaviour out of duty
What traits are related to leader emergence?
high conscientiousness
low agreeableness
What traits are related to leader effectiveness?
none
What traits are related to leader … emergence & effectiveness?
high…
openness
extraversion
cognitive ability
energy levels
stress tolerance
self-confidence
What is the most important leader decision-making style element?
decide for self / involve other
What are the leader decision-making styles?
high follower control
delegative
facilitative
consultative
autocratic
high leader control
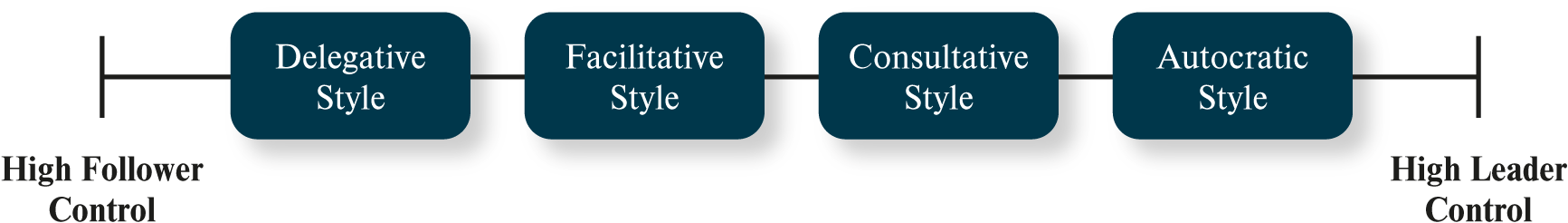
What is facilitative style?
leader style
present problem to group & seek consensus
What is delegative style?
leader style
give employee decision making responsibility
What are some examples of factors to consider when leaders choose a style?
decision quality
>
acceptance & commitment
What is the time-driven leadership model?
model
autocratic / consultative / facilitative / delegative
leadersituationcombine factors to make decision-making styles more effective
What are the time-driven leadership model factors?
decision significance
commitment importance & likelihood
leader & employee expertise
shared objective
teamwork skill
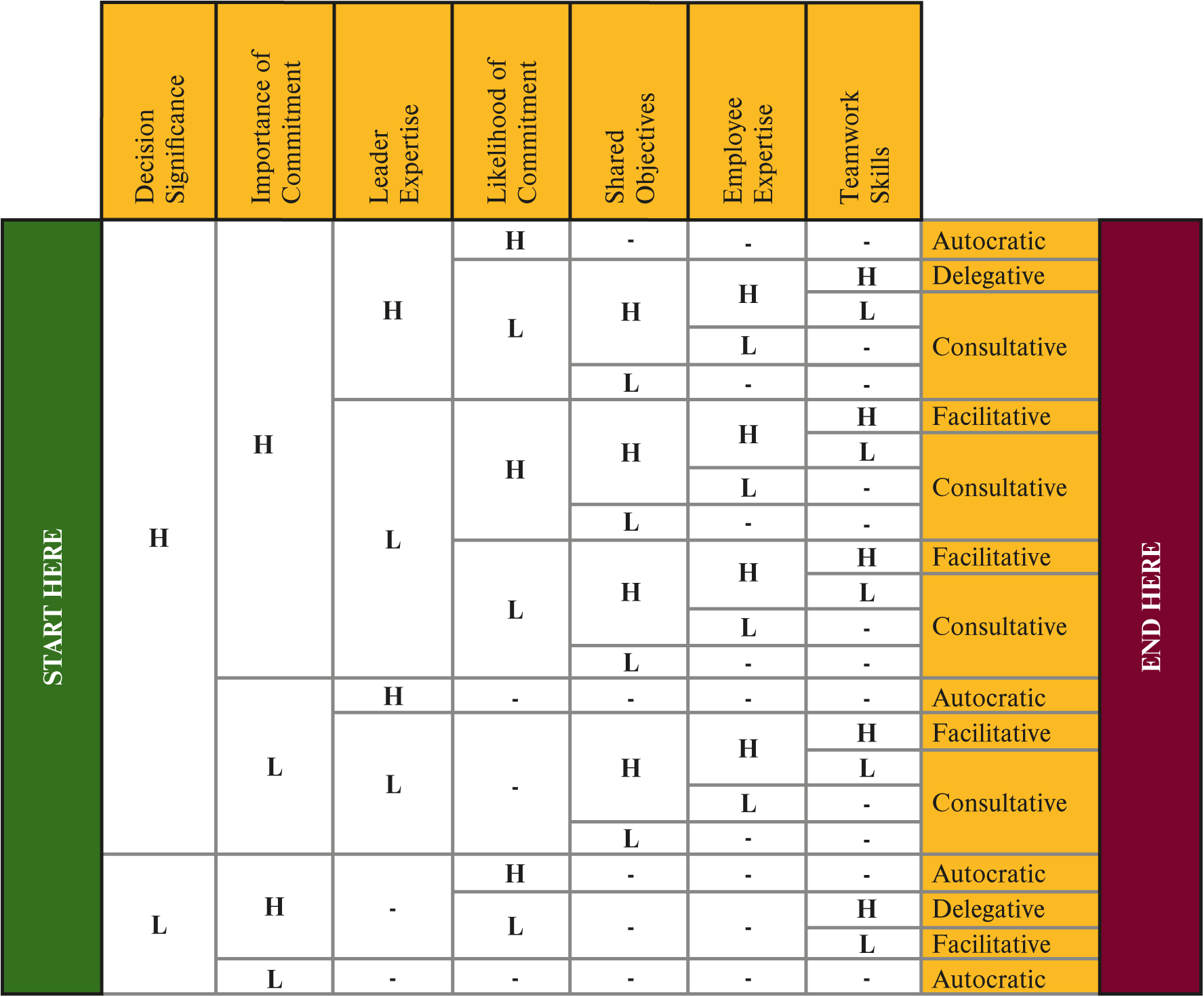
What are the autocratic style principles?
low decision significance
low commitment importance
or
high leader expertise
>
high commitment likelihood
What are the delegative style principles?
high teamwork skill
low commitment likelihood
What is the overused leader style?
consultative
What are the underused leader styles?
autocratic
facilitative
What are the day-to-day leader behaviour dimensions?
initiating structure
consideration
What are the initiating structure behaviours?
initiation
organization
production
What are the consideration behaviours?
membership
integration
communication
recognition
representation
What is initiating structure?
day-to-day leader behaviour pattern
define role → goal
What is consideration?
day-to-day leader behaviour pattern
create relation by mutual trust / idea respect / feeling consideration
What is the life cycle leader model?
// situational leader model
model
optimal initiating structure & consideration combo depends on employee readiness
What is readiness?
degree
ability
willingness
.. to accomplish task
What are the life cycle leader model snapshots?
R1
R2
R3
R4
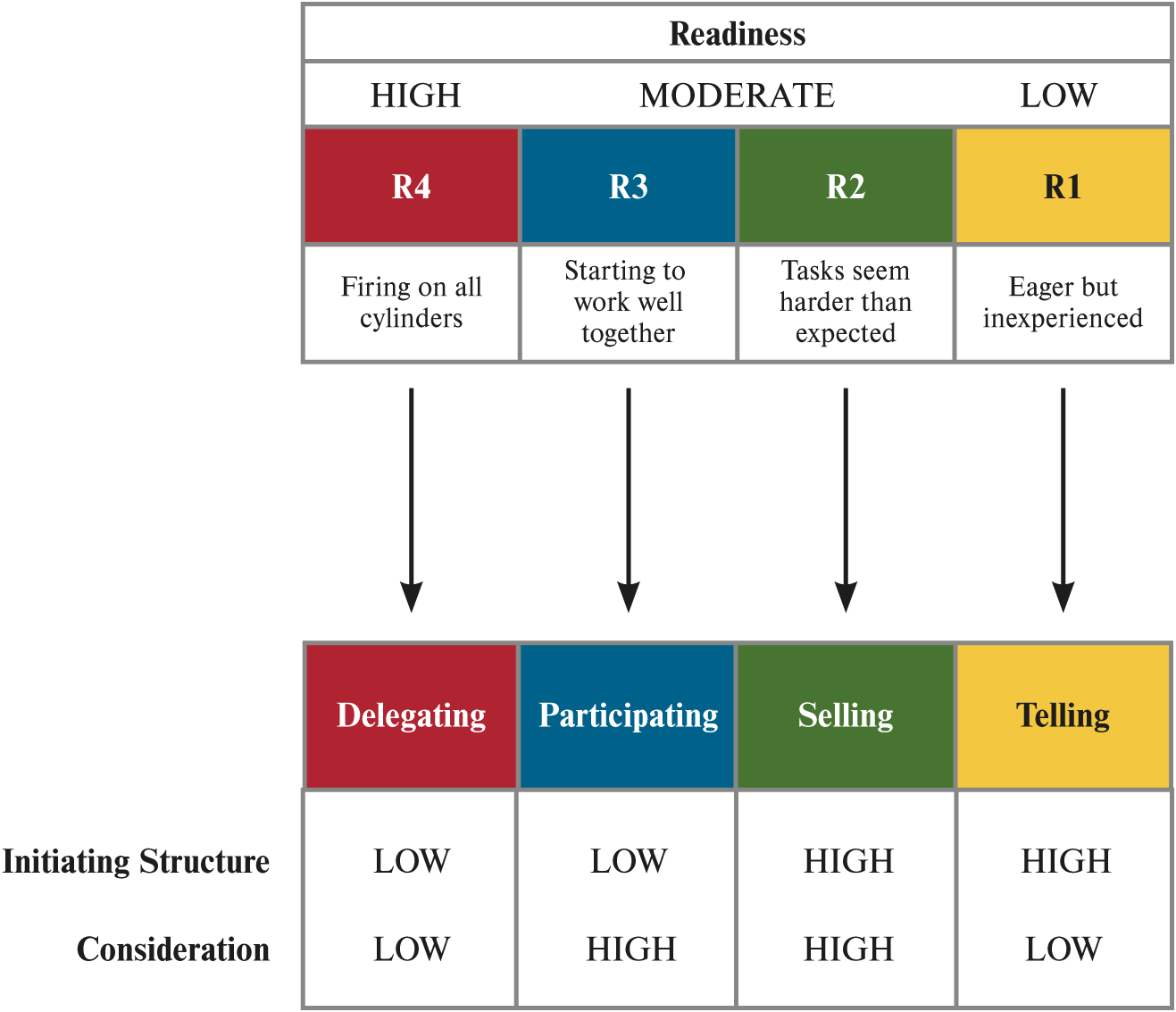
What is R4?
readiness snapshot
firing on all cylinders
What is R3?
readiness
starting to work well together
What is R2?
readiness
seeming harder than expected task
What is R1?
readiness
inexperienced but eager
What is the R4 leader behaviour combo?
delegating
What is the R3 leader behaviour combo?
participating
What is the R2 leader behaviour combo?
selling
What is the R1 leader behaviour combo?
telling
What is telling?
low initiating structure
low consideration
What is selling?
low initiating structure
high consideration
What is participating?
high initiating structure
high consideration
What is delegating?
high initiating structure
low consideration
What does life cycle leader model research suggest?
telling / selling > if lacking ability / confidence / motivation
high readiness = leader behaviour <
What gets transformed in transformational leadership?
follower work view
collective good > short-term self-interest
What is laissez-faire leadership?
type
avoid duty
What are the leader approaches?
laissez-faire
<
transactional
passive management-by-exception
<
active management-by-exception
<
contingent reward
<
transformational
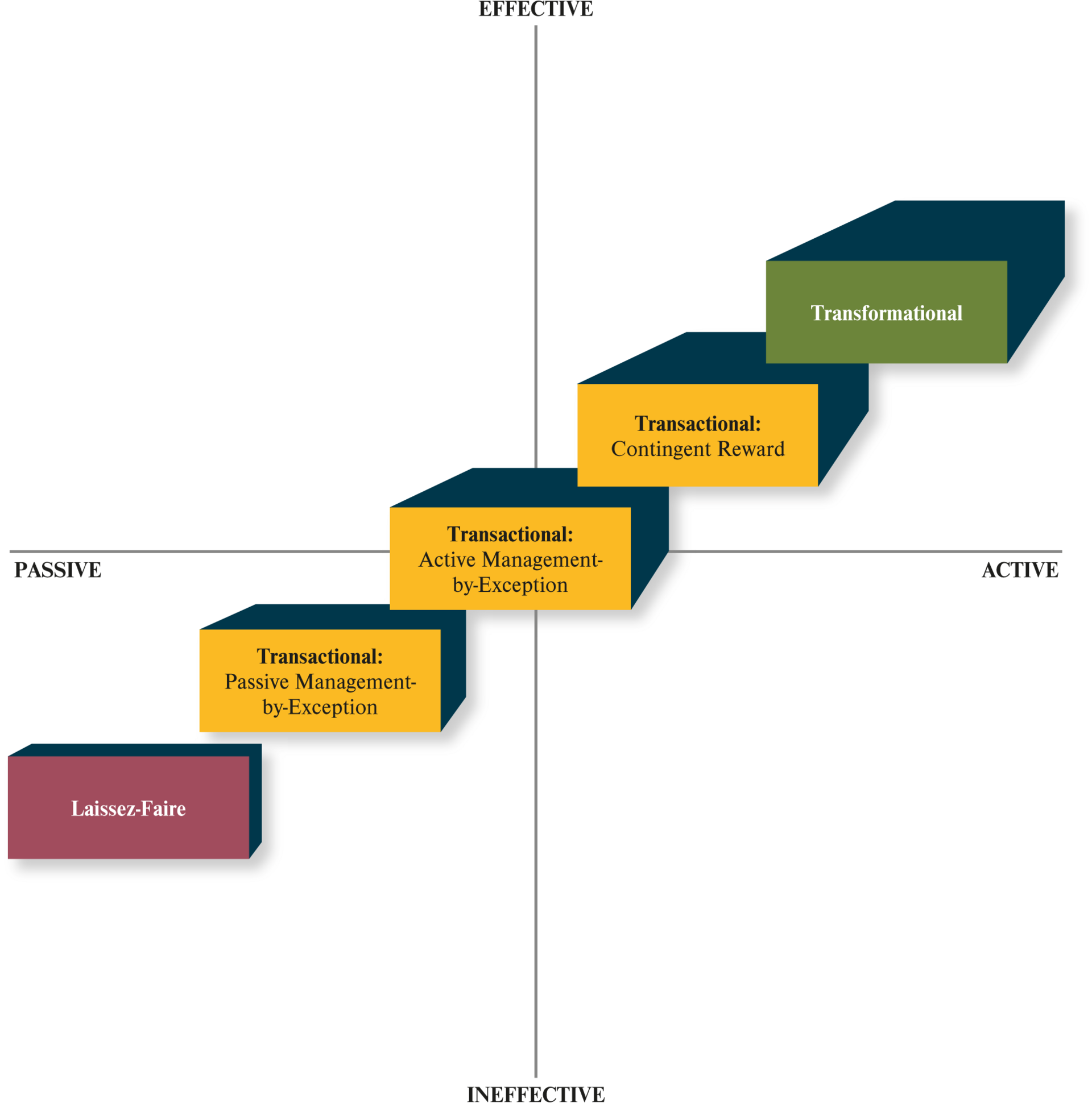
What is transactional leadership?
approach
performance reward / discipline
What is passive management-by-exception?
transactional leadership
wait & correct error
What is active management-by-exception?
transactional leadership
monitor & correct error
What is contingent reward?
transactional leadership
agree on what needs to be done using reward / performance exchange
What is the carrot-&-stick leader approach?
management-by-exception → stick + contingent reward → carrot = transformational → carrot-&-stick
What are The Four I’s?
idealized influence
inspirational motivation
intellectual stimulation
individualized consideration
What is culturally endorsed implicit leader theory?
leader = in beholder eye
What explains international transformational leader appeal?
idealism
virtue
What is idealized influence?
// charisma
behave in way earning admiration / trust / respect
→ follower wants to identify / emulate
What is inspirational motivation?
behave in way fostering enthusiasm / commitment to shared future vision by meaning-making