AP Bio Ch.3 Nucleic Acids (49-56)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Nucleic acids store and _______ what kind of info?
transmit, heredity
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a _____
gene
Genes are made of ______ which is made of ____________
DNA, nucleotides
what is smaller unit is DNA made of?
nucleic acids
What is a gene
A segment of a DNA strand in a chromosome
A DNA sequence in a chromosome contains many ______.
Each ______ contains the code for making a specific __________.
The __________ sequence of the gene is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA).
The mRNA is translated into a sequence of _____________ to form a ___________.
A DNA sequence in a chromosome contains many genes.
Each gene contains the code for making a specific polypeptide.
The nucleotide sequence of the gene is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA).
The mRNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids to form a polypeptide.
Draw a nucleic acid
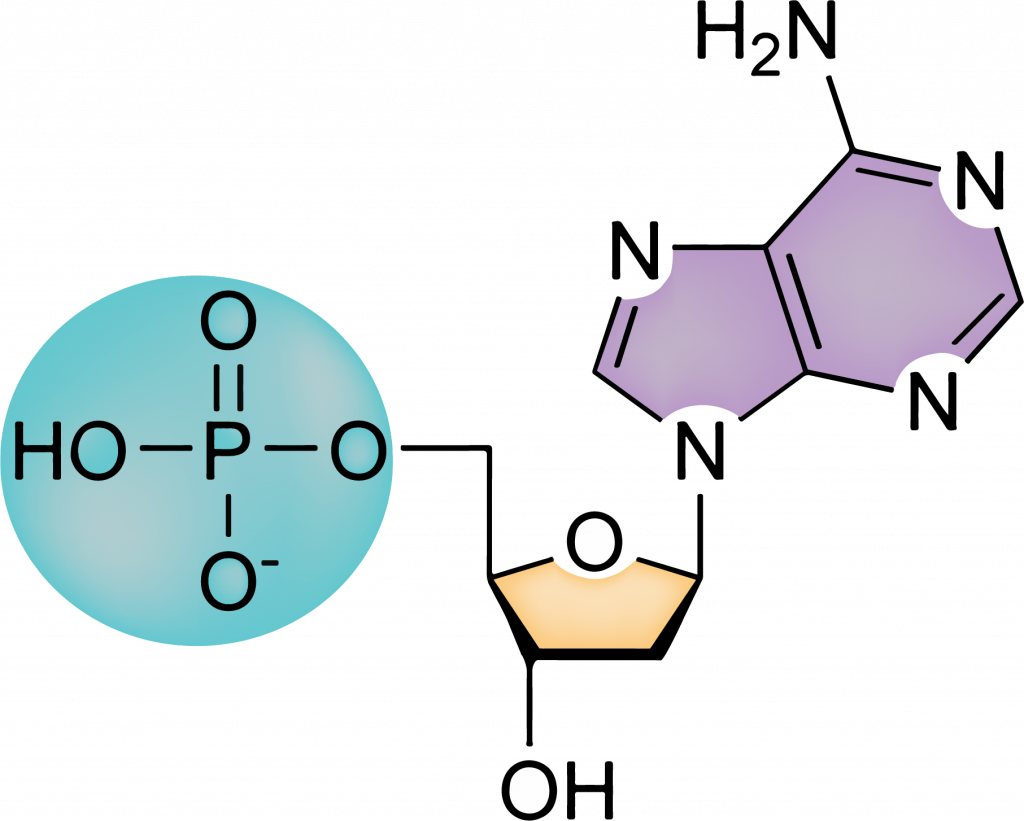
Each DNA has 3 parts. Explain each one.
A phosphate group
A deoxyribose sugar (a 5-carbon sugar)
A nitrogenous base — one of the following:
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
Each RNA has 3 parts. Explain each one.
✅ A phosphate group
✅ A ribose sugar (a 5-carbon sugar — not deoxyribose like in DNA)
✅ A nitrogenous base — one of the following:
Adenine (A)
Uracil (U) ❗ (instead of Thymine in DNA)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
What are the differences between DNA and RNA
Sugar: RNA uses ribose, DNA uses deoxyribose
Base: RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T)
Strands: RNA is usually single-stranded, DNA is double-stranded
What sugar does DNA use? What sugar does RNA use? What is the difference between them?
RNA uses ribose
DNA uses deoxyribose
Ribose has one more oxygen
Base: RNA uses ___ instead of _______
RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T)
DNA Bases
ATGC
RNA Bases
AUGC
DNA base pair rules
G-C
A-T
RNA base pair rules
A-U
G-C
T-A
How many strands are in DNA?
2
How many strands are in RNA?
1
DNA function
Stores genetic code for proteins
RNA function
builds proteins
In DNA, how do the two strands act?
They form a double helix and go antiparallel
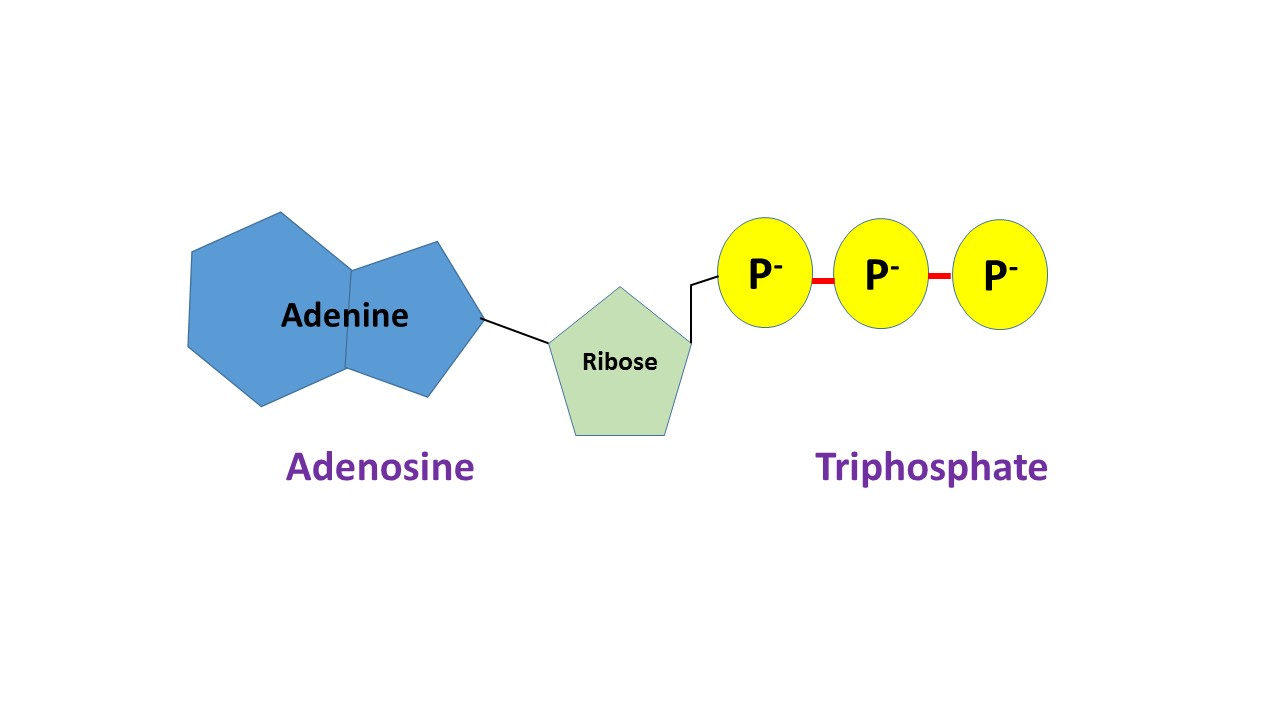
Is ATP a nucleotide?
Yes
What is ATP used for
cell’s energy currency. (energy released when loses phosphate)
In DNA, adjacent nucleotides are covalently bonded. This creates the ______________.
Nucleotides form a covalent bond between
____ group on the 3′ carbon of one nucleotide
The __________ on the 5′ carbon on the next.
OH group on the 3′ carbon of one nucleotide and the phosphate on the 5′ carbon on the next.
These links create a backbone of sugar-phosphate units with nitrogenous bases as appendages.
The nitrogenous bases act as ______________ kinda like a _________. The bases connect with _________ bonds.
Backbone, ladder, hydrogen
In the DNA double helix, the two strands called backbones run in opposite ___′ → __’ directions from each other
5 to 3