Radiology Midterm 1 Review
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is the criteria needed for a periapical radiograph?
-Entire crown if possible
-Entire Root
-2-3mm past apical region
What percent of contact overlap constitutes a retake?
50%
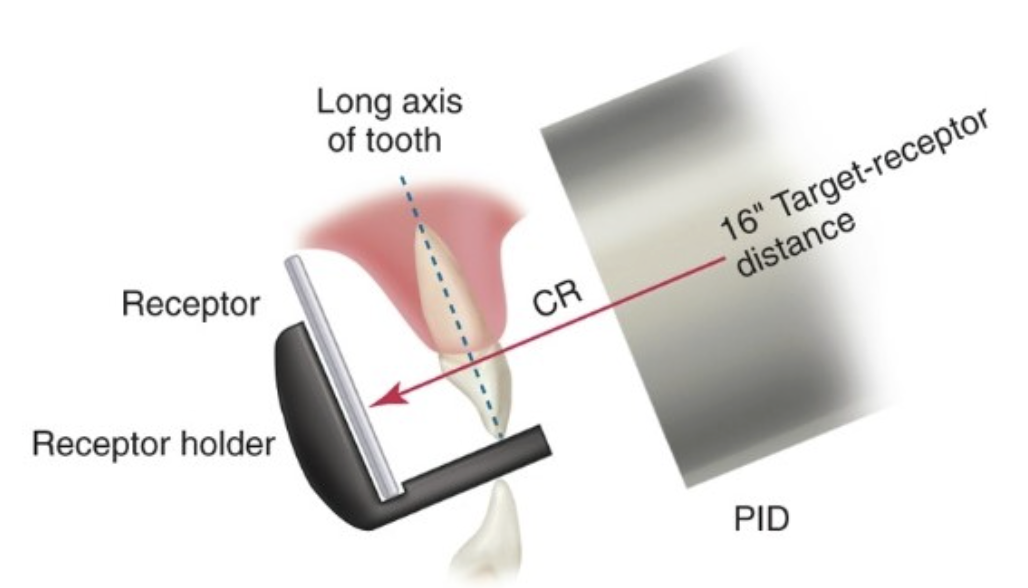
What are the advantages of paralleling technique?
Accuracy- Image is free of distortion
Simplicity- Technique is simple
Duplication- Easy to standardize
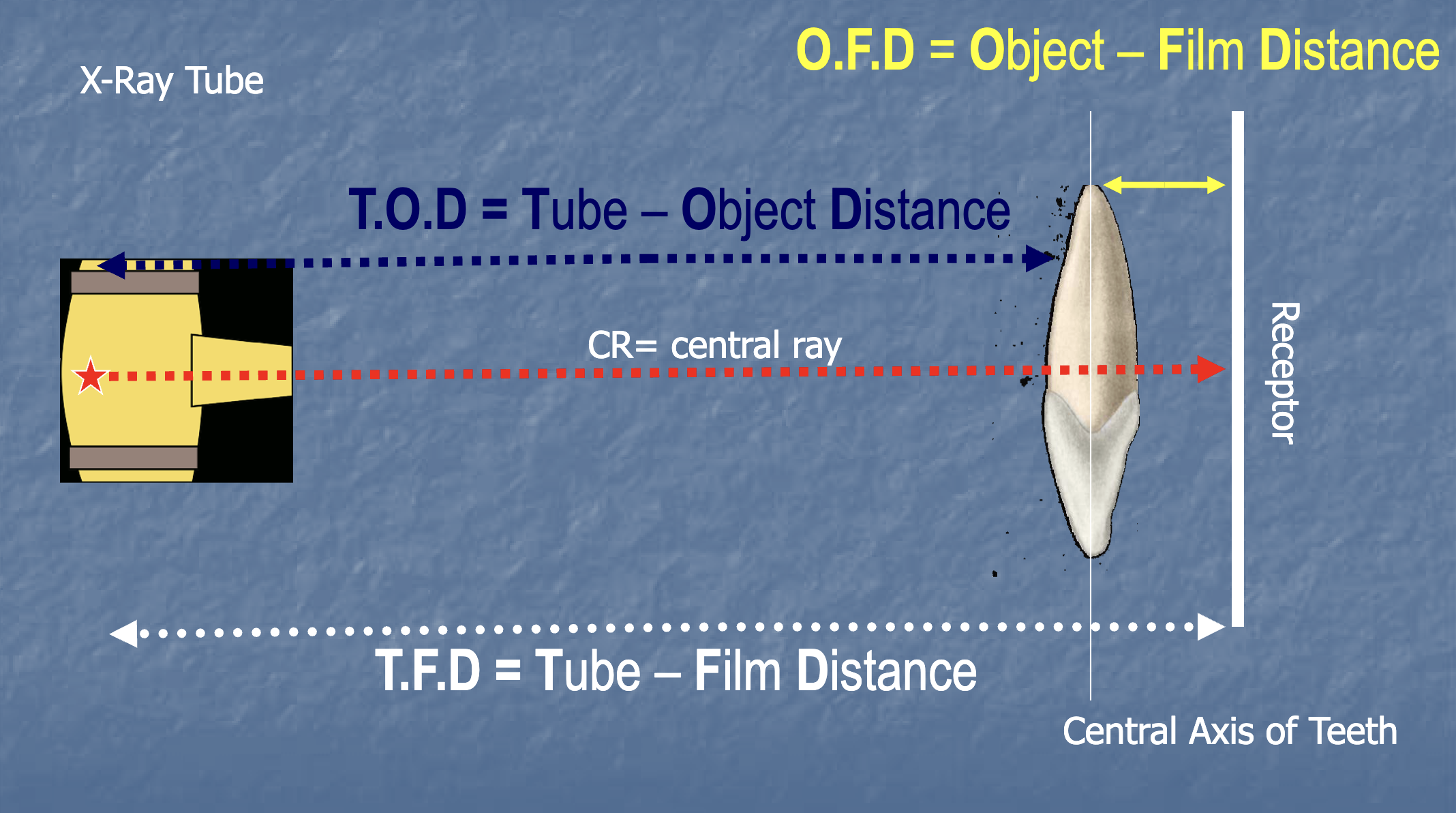
For a Long cone beam radiograph, what should the tube to film distance be?
16 inches
What are the 4 factors that are needed to get a good parallel technique image?
-Film (receptor) is parallel to the tooth long axis
-Central ray is perpendicular to tooth
-Increase object to film distance
-Use a 16 inch long cone
What is the sequence of taking FMX radiographs?
-Maxillary incisors
-Mandibular Incisors
-Maxillary premolars-Maxillary molars
-Mandibular premolars-mandibular molars
-Bitewings
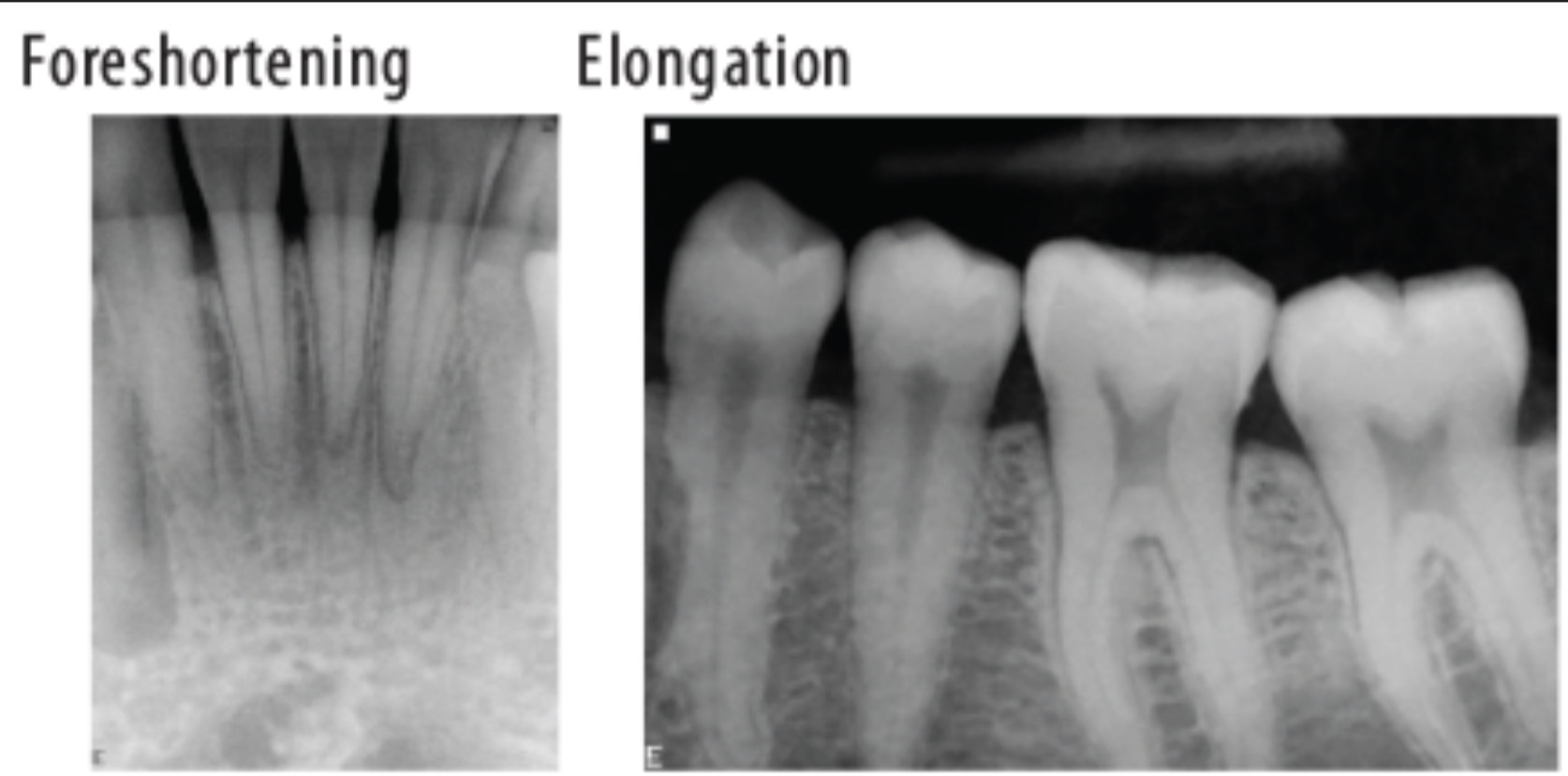
What is foreshortening the roots?
It means we have an excessive angulation which shortens the roots and elongates the crown.
Foreshortening= excessive vertical angulation
Elongation= insufficient vertical angulation
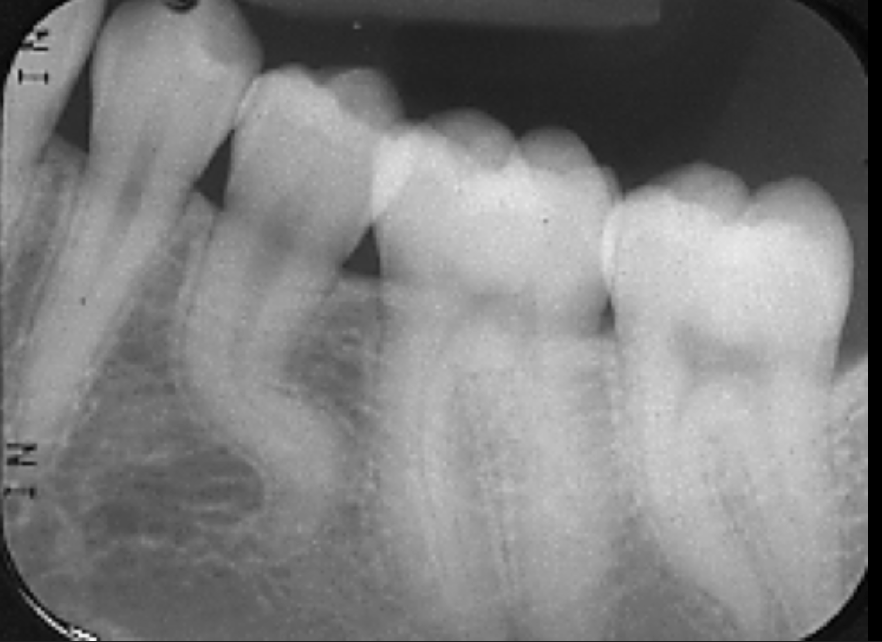
If the contacts get worse as we move back in the mouth, what radiograph error is happening?
It means we are rotated mesial-distally.
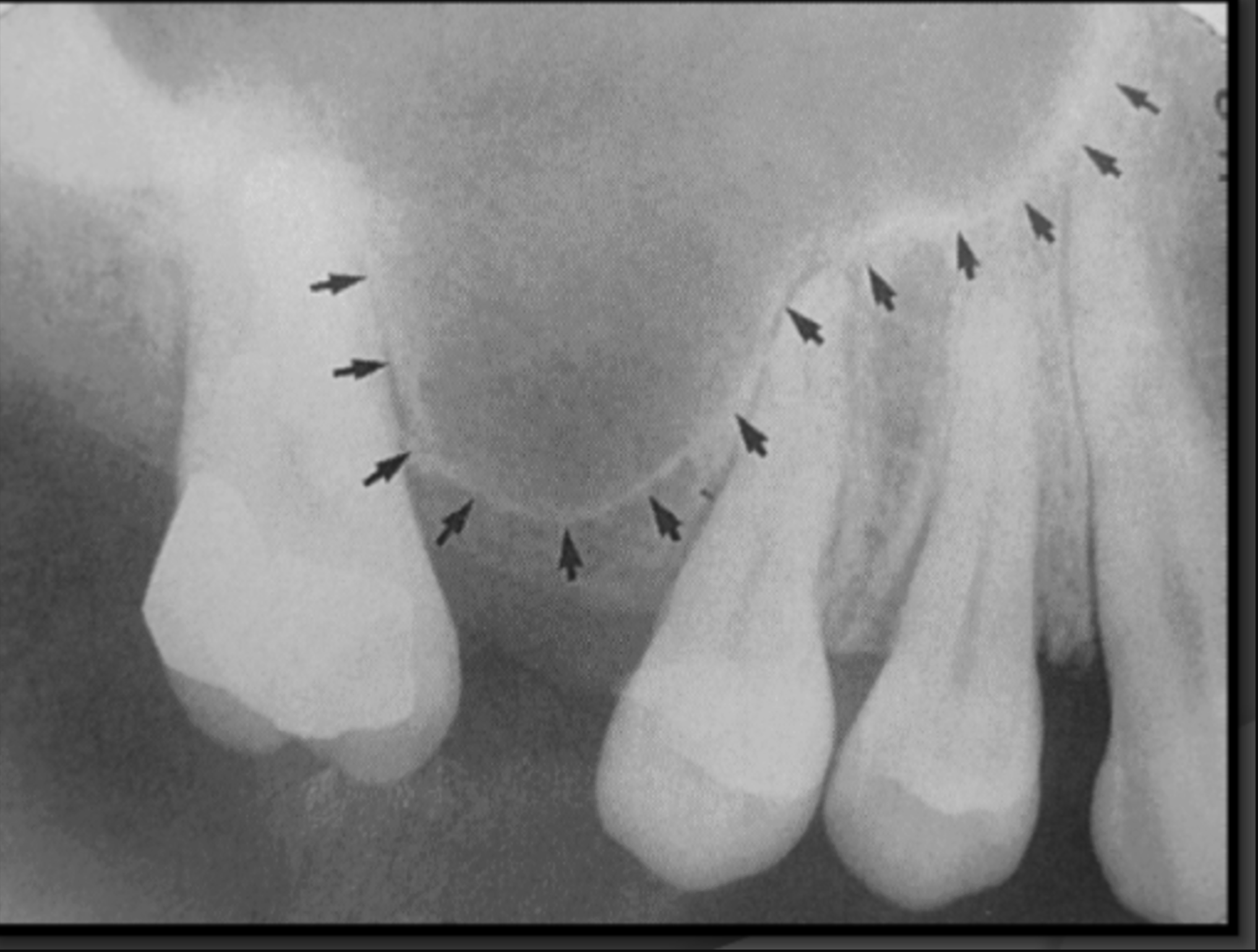
On a molar bitewing, what contacts should be open?
All contacts surrounding the 2nd molar
On a premolar bitewing, what contacts should be open?
All contacts surrounding the 2nd premolar
Why do we set a vertical angle when taking radiographs?
To account for the curve of Wilson, where the contacts are tipped 8-10 degrees.
What leads to elongation in a radiograph?
When there is insufficient angulation when taking a maxillary or mandibular photo.
What do we want to see in the front of the molar bitewing radiographs?
-Between the first furcation (where the roots divide) of the 3rd molar and half the 2nd premolar

What do we want to see in the front of the premolar bitewing radiographs?
-Between half the canine and the pulp chamber of the 1st premolar

Do we need to see an open contact in a maxillary canine-premolar PA?
No
What is the central landmark of a Premolar-canine PA?
The contact between the two should be in the middle 1/3 of the frame.

In a lateral PA what should be the central landmark that is found in the middle 1/3 of the frame?
The lateral incisor

Which contact should be open in a lateral PA radiograph?
The contact between the lateral and central.

Do we need an open contact in a mandibular premolar-canine PA?
Yes
What are the 3 critical errors in radiology lab?
-No start check
-No lead apron
-Retakes without approval
What is spatial resolution?
The ability to distinguish separate objects that are close together.
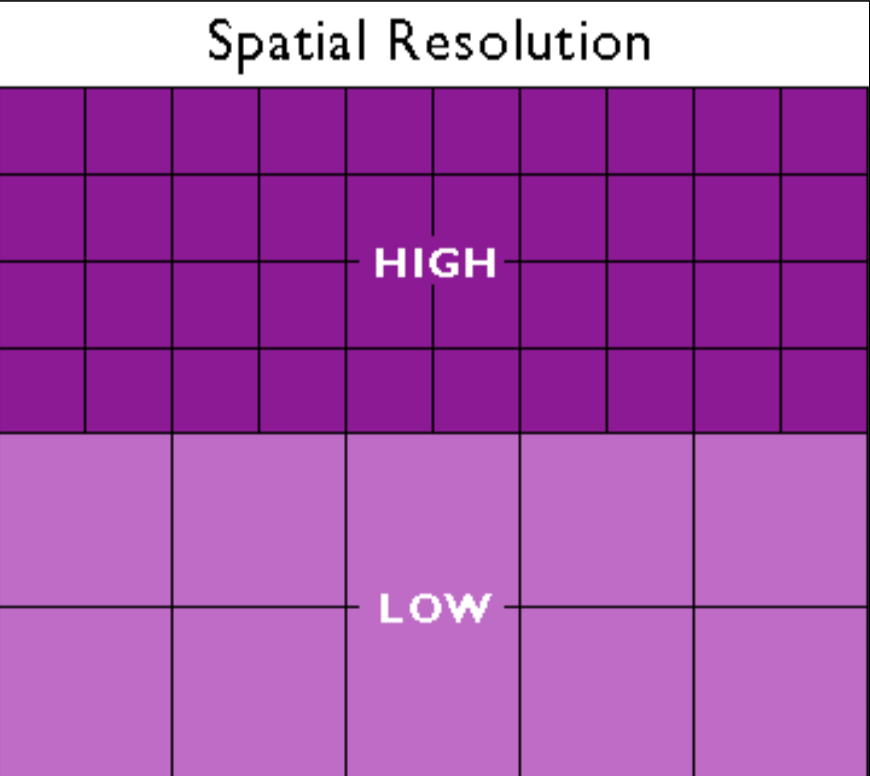
What is contrast/intensity resolution?
The ability to distinguish between different shades of gray.

Which type of radiograph has the best spatial resolution?
Film
Which type of radiograph has the worst spatial resolution?
PSP
What is latitude?
How much dose variation a radiograph can have while still providing a good diagnostic image.
Which type of radiograph has the worst latitude?
Film
Which type of radiograph has the best latitude?
PSP
What are the radiograph image processing tools that are safe to use?
-Density/Brightness
-Contrast
What are the radiograph image processing tools that need to be used with extreme caution or not at all?
-Edge enhancement/sharpening
-Noise reduction/softening
-Optimization
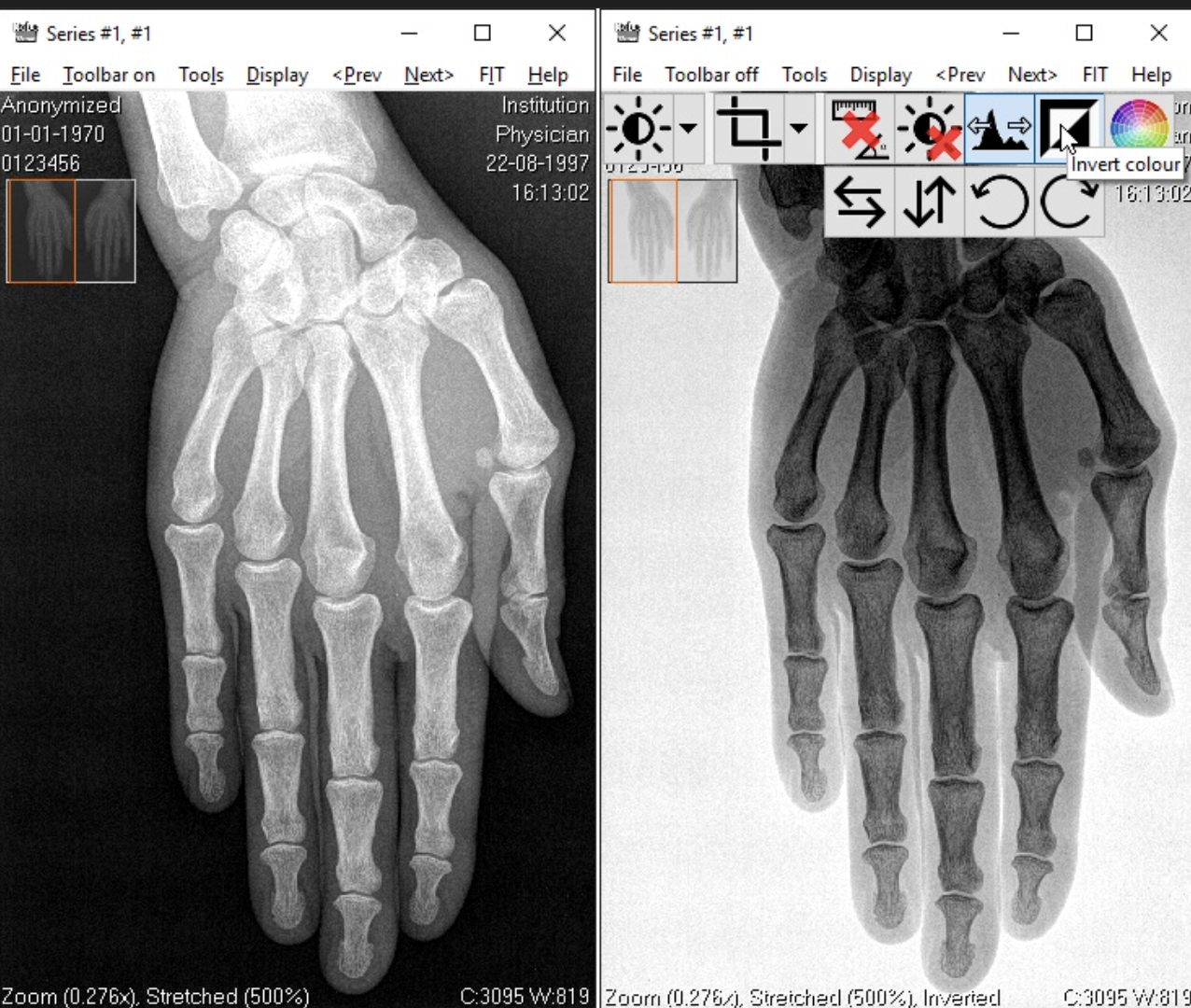
When is the inversion of gray scale tool used in radiograph processing?
Can be useful for endo and visualizing the pulp chamber.
For a patient without any caries or high risk for caries, how often should we order bitewing radiographs?
Every 24-36 months
For a patient with clinical caries or of high risk for caries, how often should we order bitewing radiographs?
Every 6-18 months
What is the LLUSD policy for radiographs on pregnant patients?
Only ordered when there is an urgent care situation.
Does a routine X-ray ever exist?
No. It should always be personalized to a patients needs.
What type of beam is used in a panoramic radiograph?
A vertical beam
What is the focal trough in a panoramic image?
This is the area that we want to see in focus without distortion.
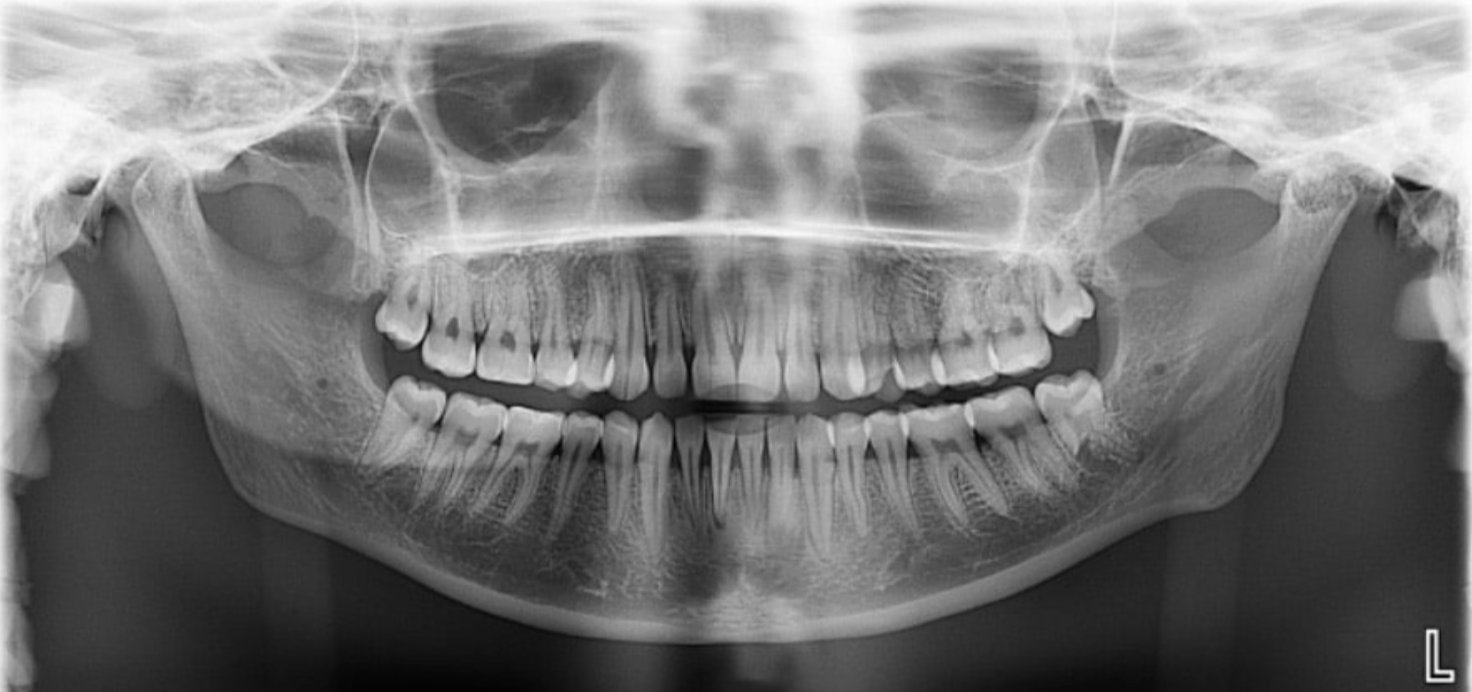
Where is the film located in a panoramic radiograph?
In front of the patient.
Also note the tube is behind the patient
If teeth are seen as narrow in a panoramic image, what is happening?
It means the teeth are too far buccal/forward, and closer to the film
If teeth are seen as wider in a panoramic image, what is happening?
It means the teeth are too far lingual in the focal trough and are closer to the x-ray source.
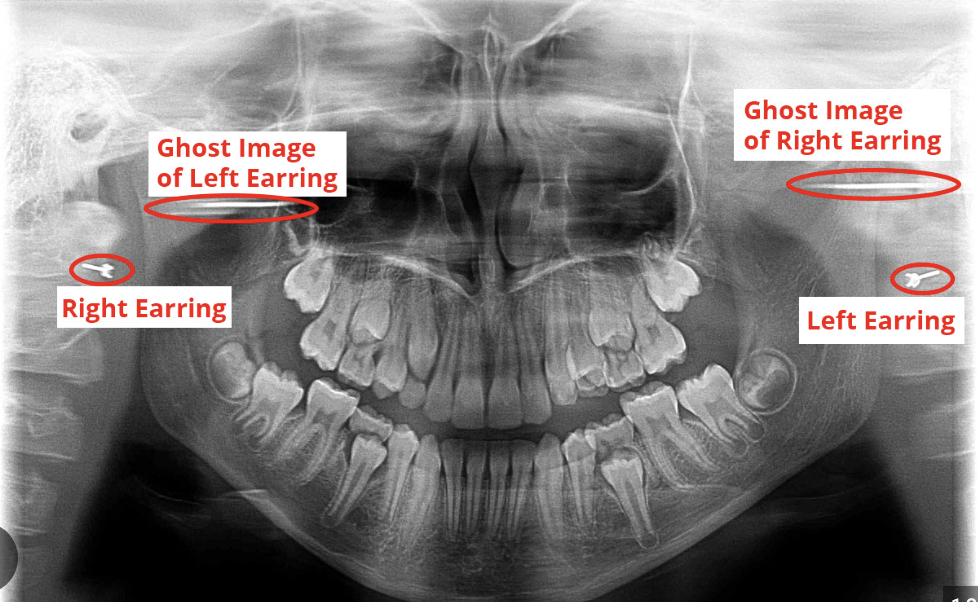
What is a double real image?
When a body structure in a radiograph is projected on both sides as mirror images. They will have similar proportions and be in the same location. It will only be seen on midline objects.
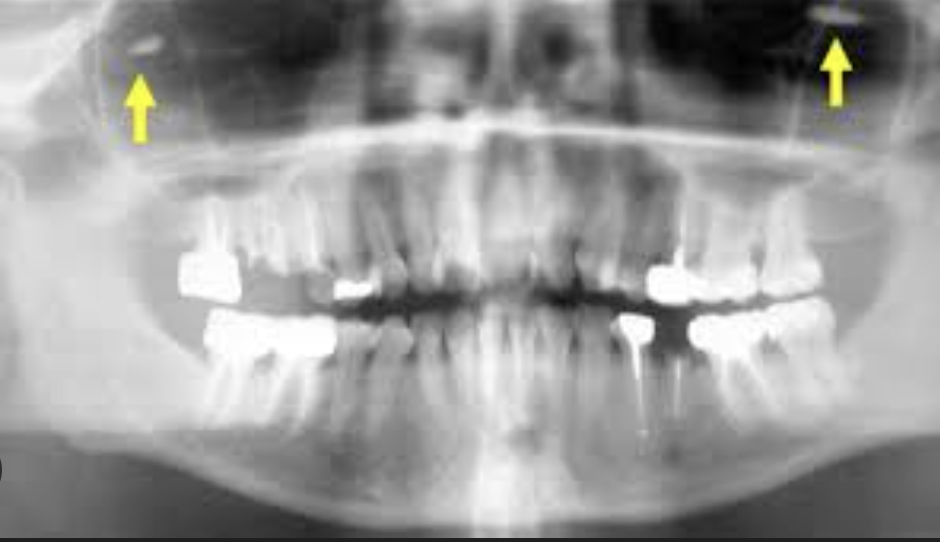
What is a ghost image?
This is when a real object on one side of the body is projected on the opposite side as more magnified, blurry, and higher up. It will have the same general shape as the object and will not be a mirror image.
Which way is a patient rotated in a panoramic radiograph if the ramus is larger on the right?
The ramus is larger based on which way they are rotated. This patient would be rotated to the right.
What leads to a superimposed ghost image of the spine at the midiline of a panoramic radiograph?
The patient is in a slumped posture.
If the condyles are projecting off the side of a panoramic image, what is the error?
The chin is too far up
If the condyles are projecting off the top of a panoramic image, what is the error?
The chin of the patient is down
If there is an exaggerated smile line in a panoramic image, what is the error?
The chin of the patient is down.
If there is an exaggerated frown line in a panoramic image, what is the error?
The chin of the patient is up.
How does cortical bone look on a radiograph as compared to cancellous bone?
More uniform and radio opaque
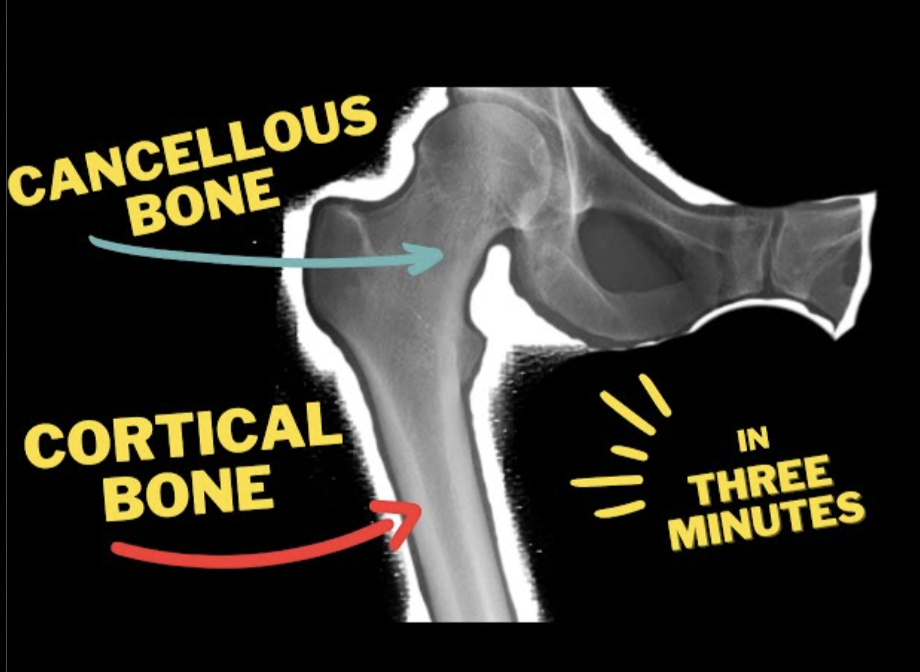
What is the radiolucency of the inferior border of the mandible in a radiograph?
It appears radio opaque due to the cortical bone.
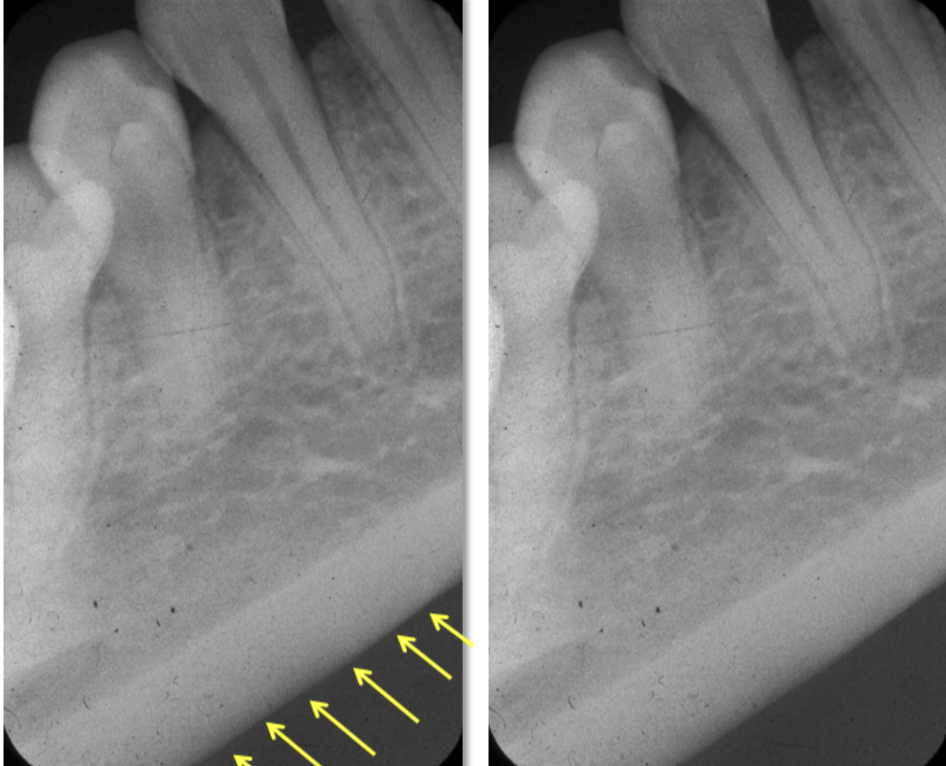
What does the internal oblique ridge of the mandible look like in a radiograph?
A radio opaque streak that follows the line of the jaw.
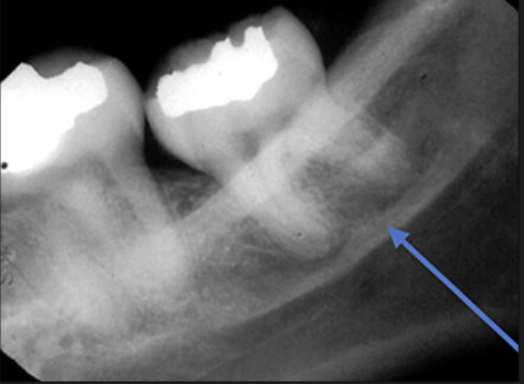
What is the gingival shadow?
This is a very light radio opacity that is present behind the molars.
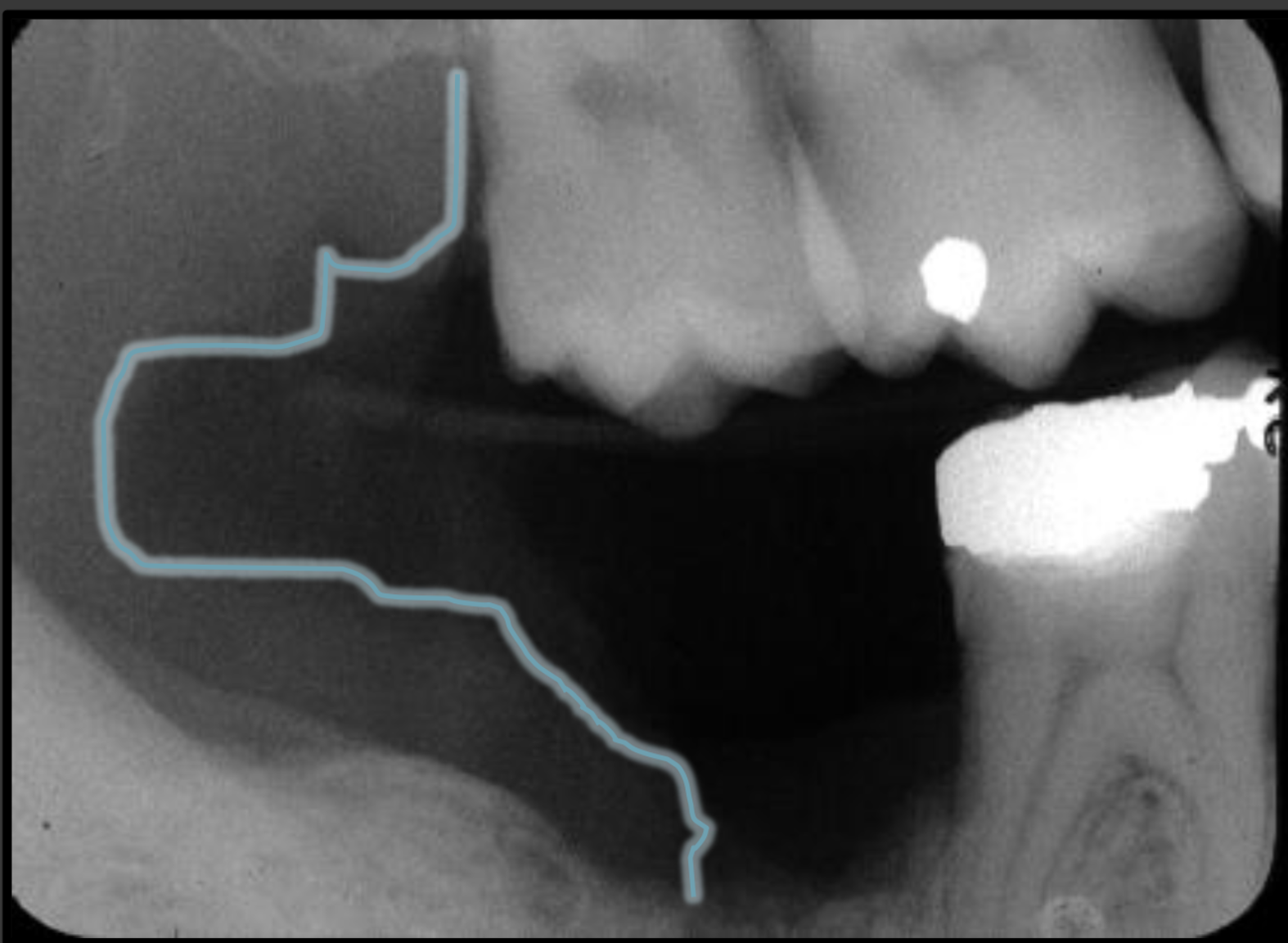
How does the coronoid process present in a radiograph?
-Radio-opaque
-Triangular/shark tooth shape pointing to the maxilla
-Point sits behind the maxillary molars
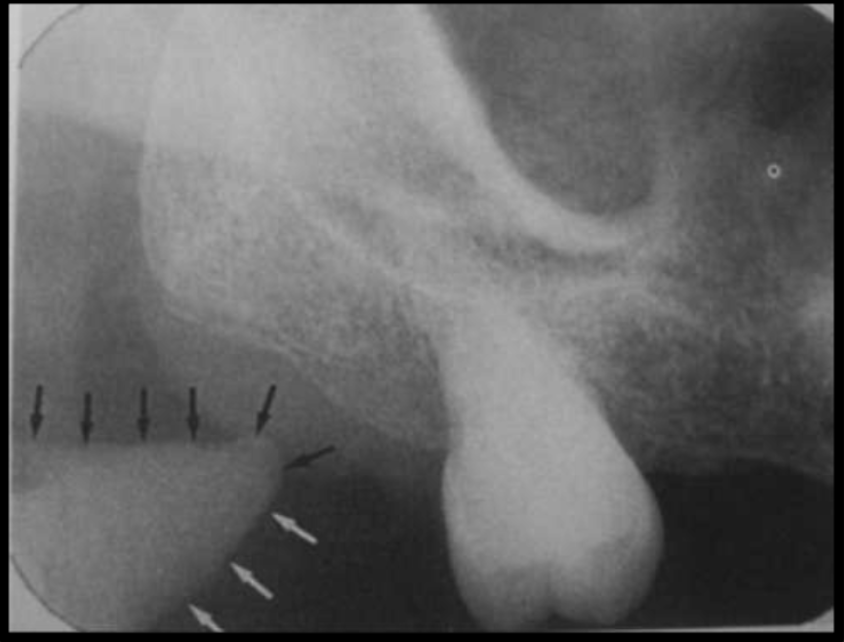
Alveolar ridge/crest
This is the line of bone that houses the teeth
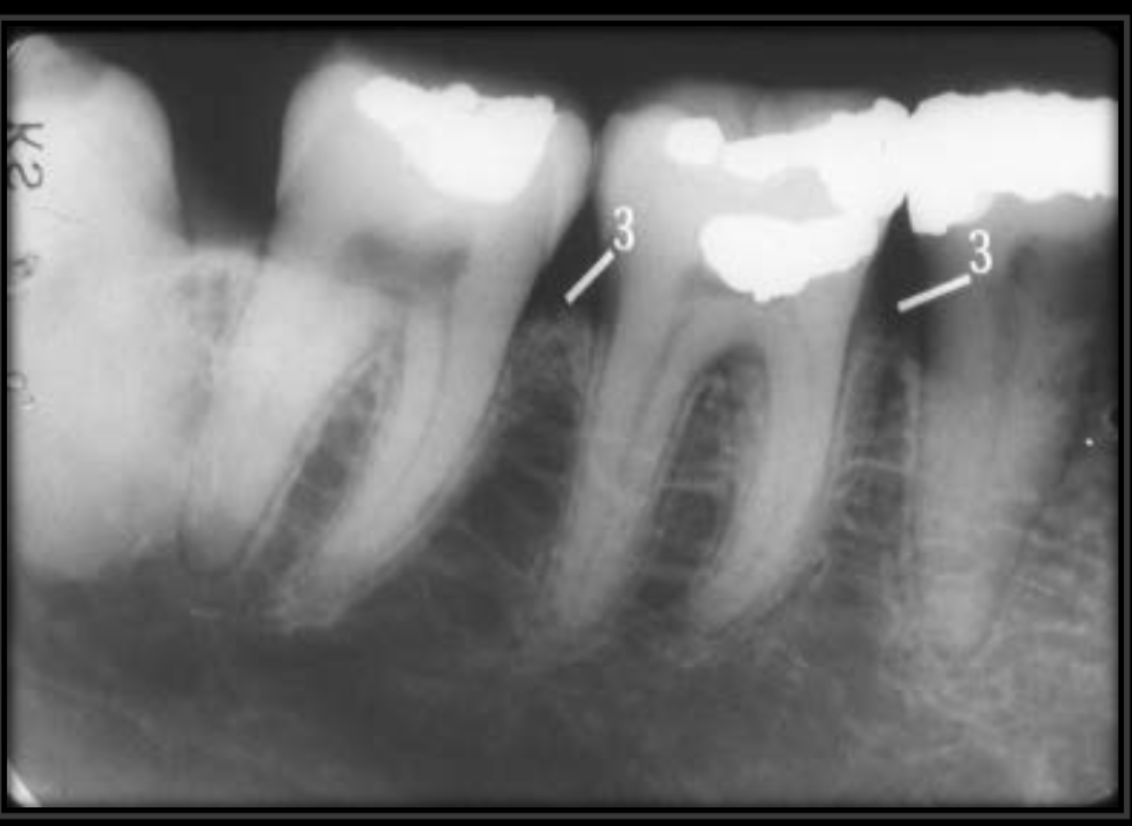
What is the hamulus/hamular process?
A projection off of the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
How does the hamulus present in a radiograph?
-Radio opaque
-A hook like shape
-Appears like it is extending off of the maxilla.
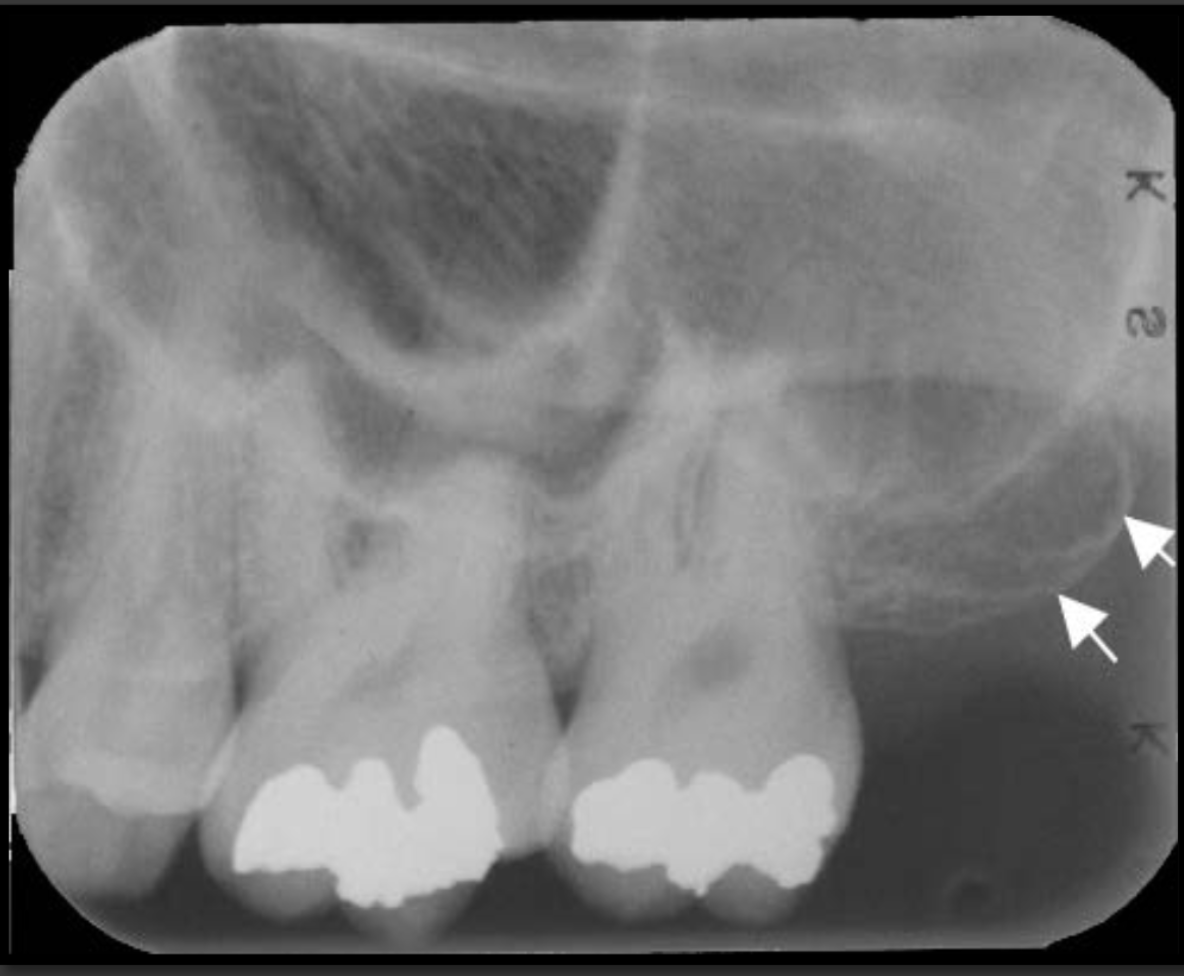
How does the maxillary tuberosity present in a radiograph?
It is the rounded segment of maxillary bone that sits immediately behind the molars. Radio opaque bulge
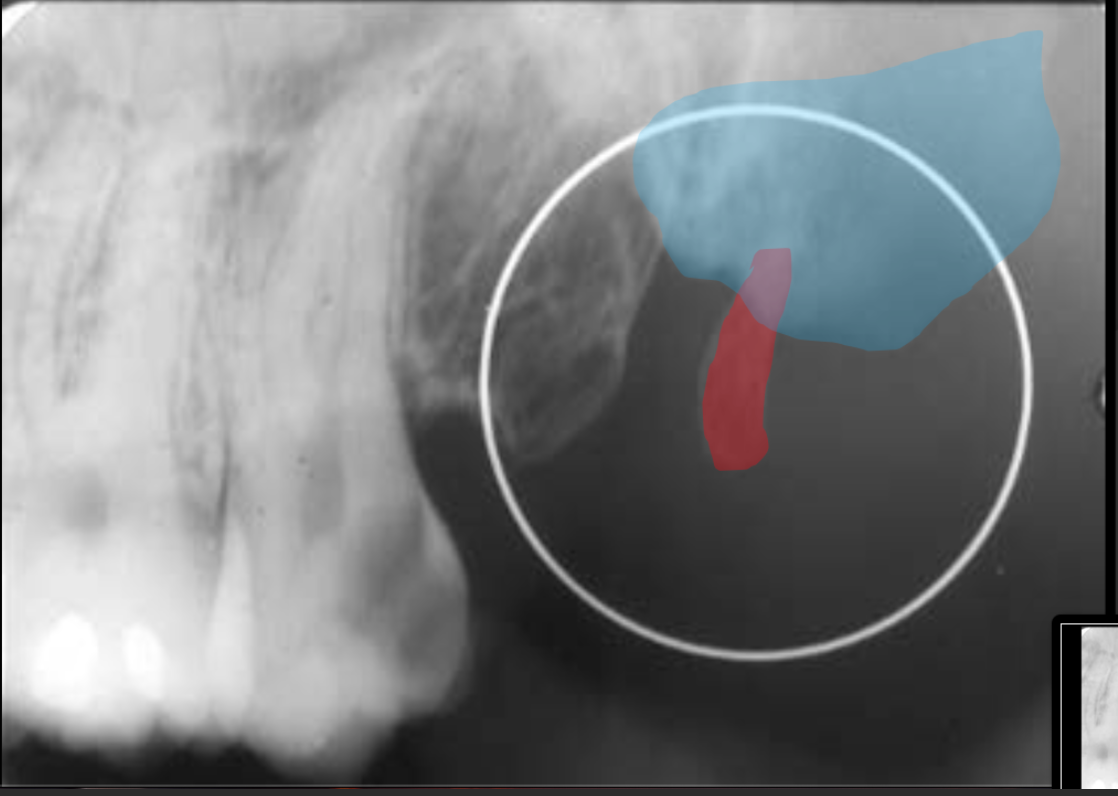
How does the zygomatic process of the maxilla present in a radiograph?
-Radio-opaque
-A U shaped line that sits above the molars
How does the zygomatic arch of the maxilla present in a radiograph?
It is a radio opacity that extends off of the U shaped structure of the zygomatic process of the maxilla.
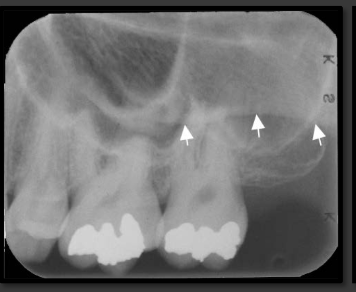
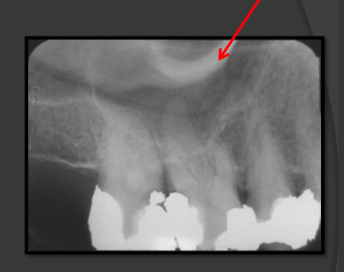
How does the floor of the maxillary sinus present in a radiograph?
It is a thin radio opaque line that travels low near the roots of the teeth.
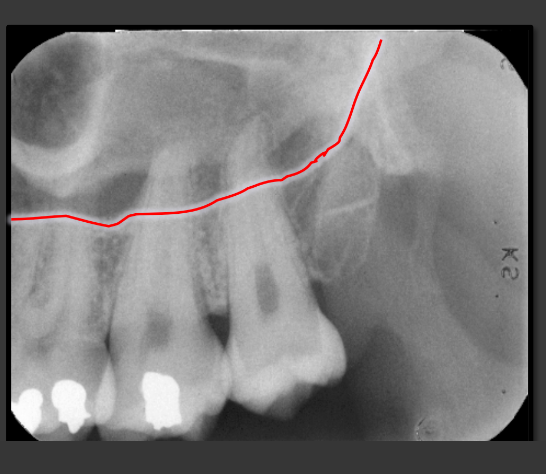
How does the maxillary sinus present in a radiograph?
It is a radiolucent space that sits above the maxillary teeth.
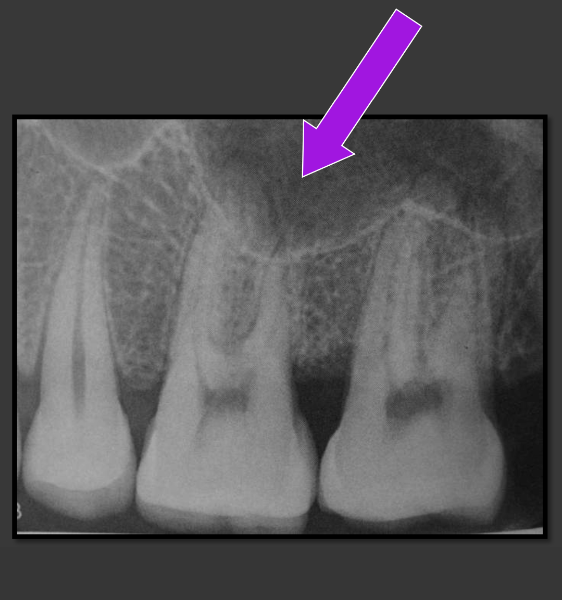
Pneumatization
A name for when the sinus recedes into the bone where a tooth is missing.
How does the floor of the nasolabial fold present in a radiograph?
This is the cheek. It is an oblique line that runs down the sides of the radiograph
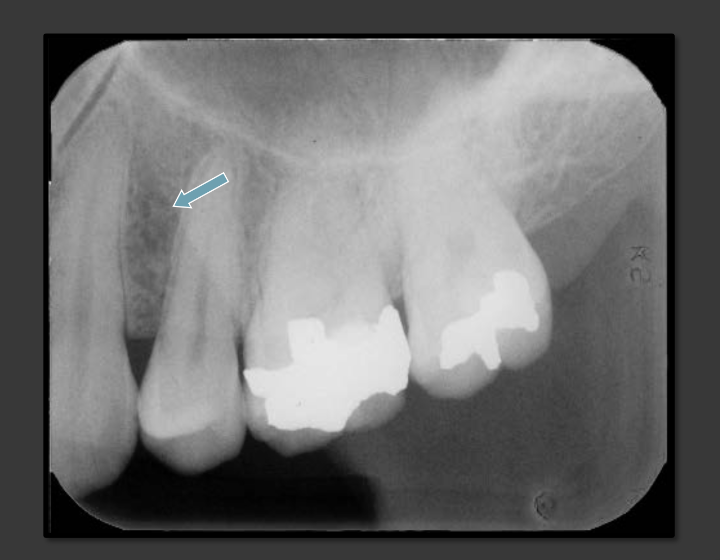
How does the floor of the nasal cavity present in a radiograph?
It is a dense radio opacity line above the maxillary centrals. Not quite as low as the floor of the maxillary sinus.
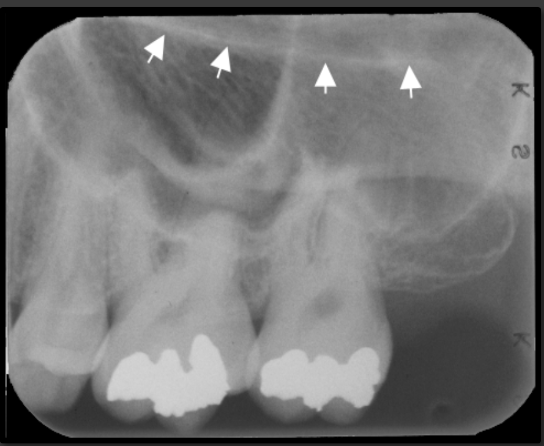
What does the lip line look like in a radiographic image?
-Radiolucent
-Horizontal line that runs across the central incisors usually
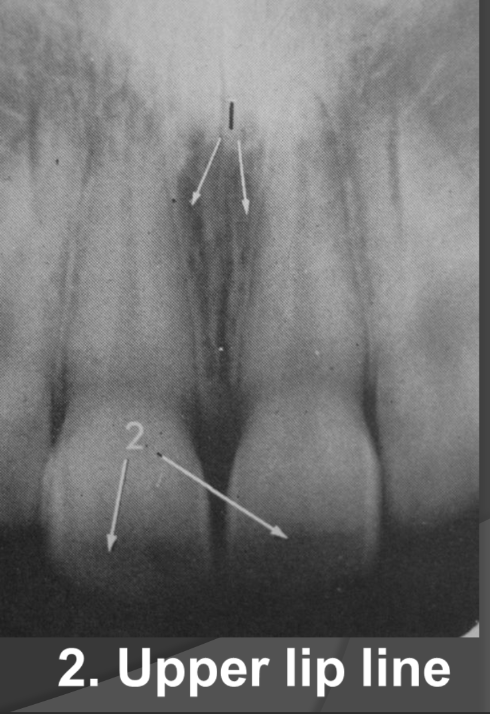
How does the conchae present in a radiograph?
It is seen in the nasal cavity. It looks like two round circles with light radio opacity.
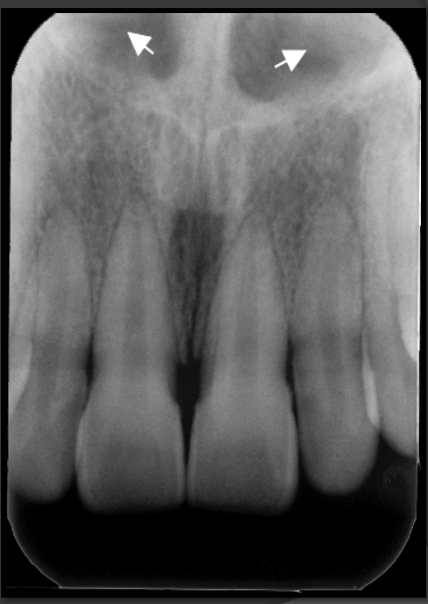
How does the nasal septum present in a radiograph?
It is the radio opaque vertical line that seperates the two nasal cavities.
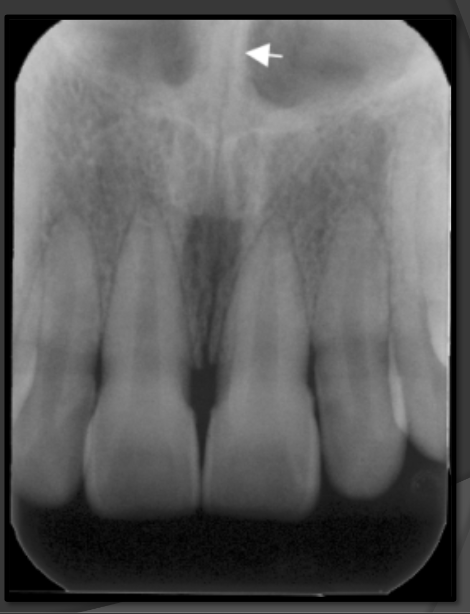
How does the anterior nasal spine present in a radiograph?
It is the sharp triangular point of the nose that has the tip pointing to the central incisors. It is radio opaque and triangular in shape.
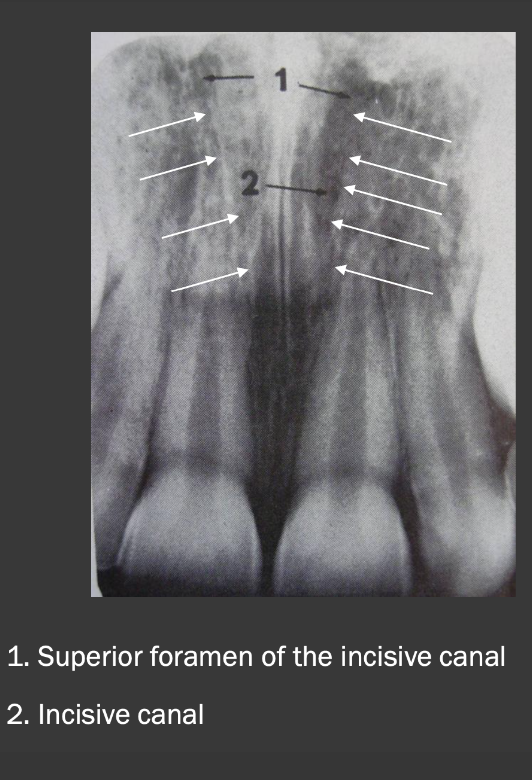
How does the incisive foramen present in a radiograph?
It is a radiolucency that presents between the roots of the maxillary centrals. It is variable in shape, size, and border.
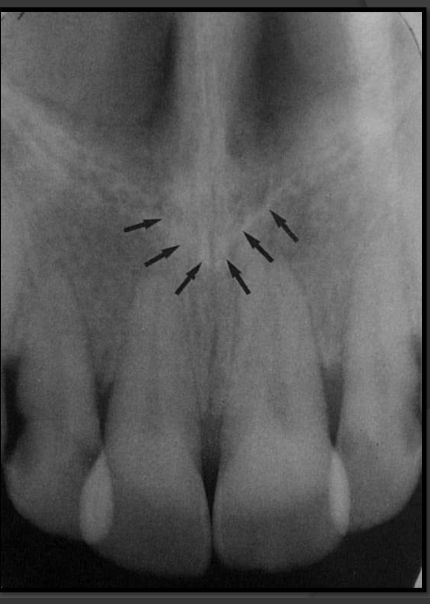
How does the superior foramen of the incisive canal present in a radiograph?
These are radiolucencies that present near the floor of the nasal cavity. They are tiny/circular in shape. Join to form the incisive canal and then the incisive foramen below.
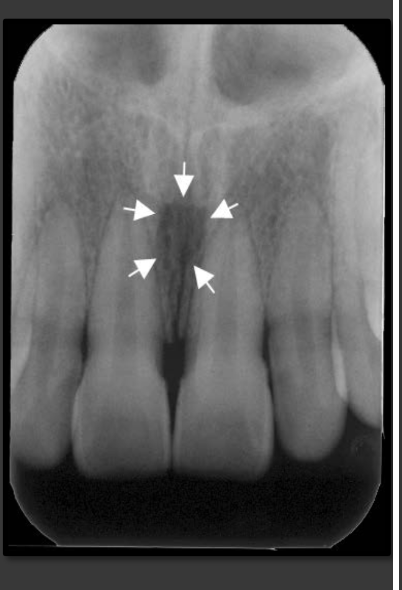
How does the median palatine suture present in a radiograph?
A thin radiolucent line that runs directly between the maxillary incisors.
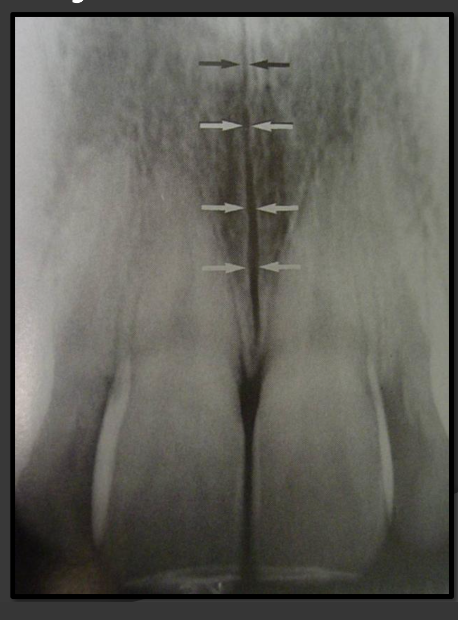
How does the lateral fossa present in a radiograph?
It is a radiolucency that appears in the bone that can surround the canine, lateral, and central.
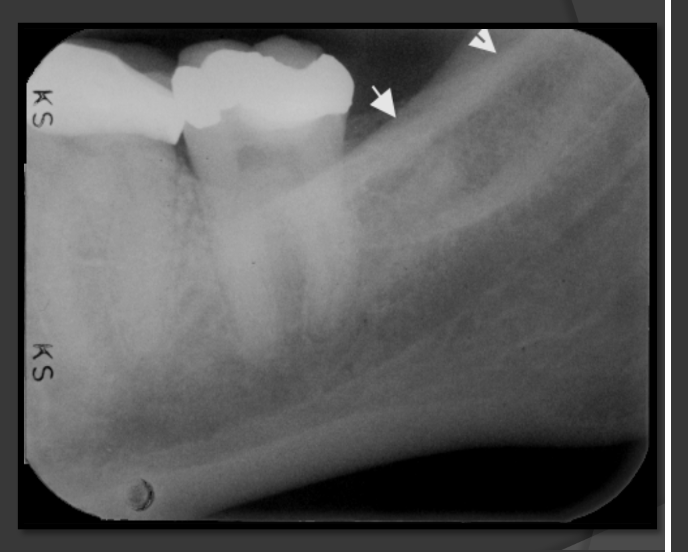
How does the external oblique ridge present in a radiograph?
Always the highest opaque line of the mandible that follows the contour of the jaw.
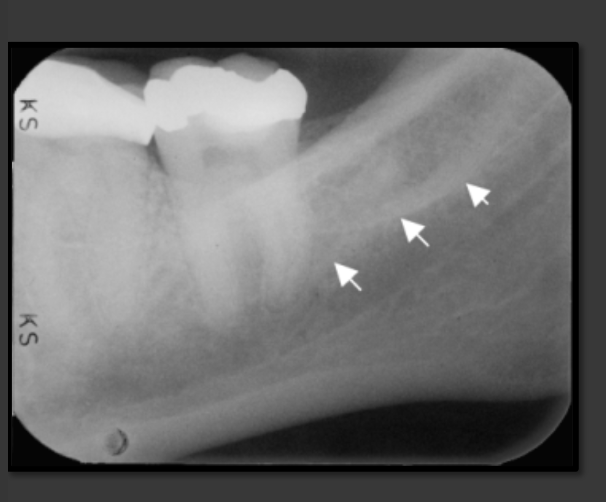
How does the internal oblique ridge present in a radiograph?
The second highest opaque line on the mandible that follows the contour of the jaw. Will always be below the external oblique ridge
How does the mandibular canal present in a radiograph?
It is a radiolucencent band that follows the contour of the mandible that runs under the teeth.
What is the diameter of the beam of an x-ray?
2.75 inches
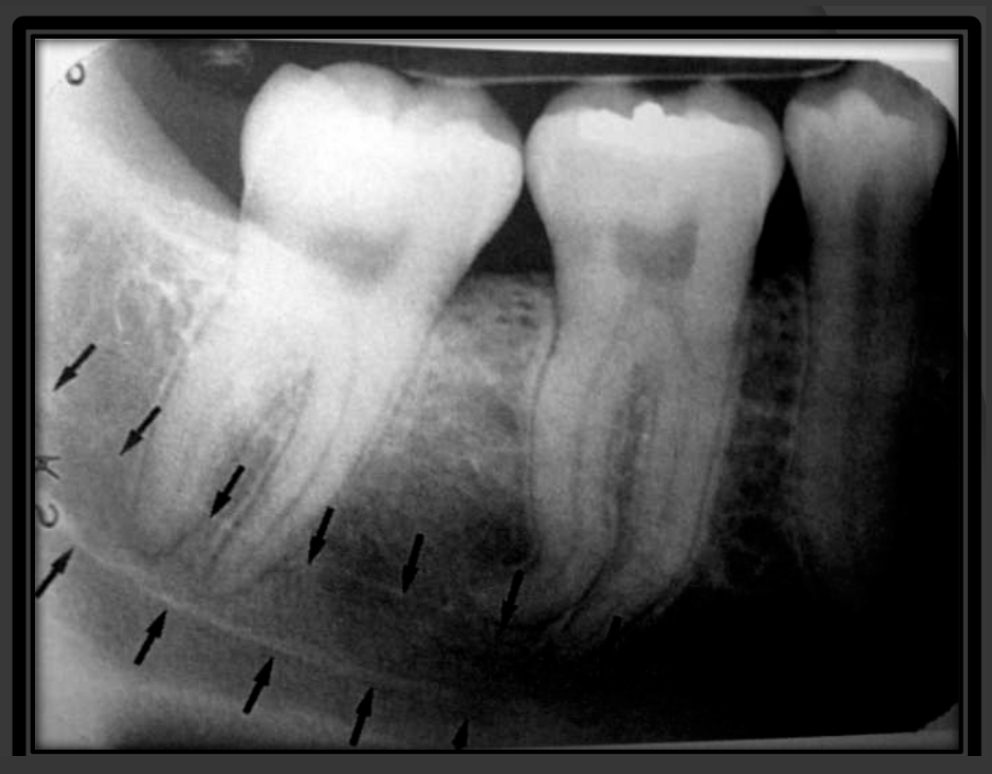
How does the submandibular fossa present in a radiograph?
Appears as a radiolucent area below the mandibular molars
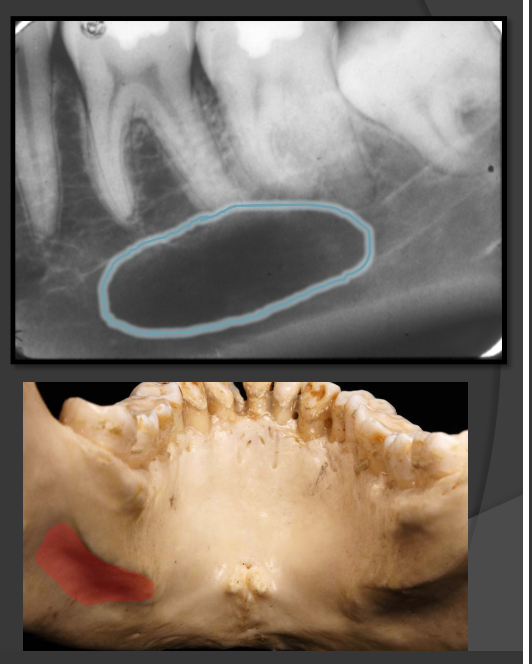
How does the mental foramen present in a radiograph?
Presents as small ovoid radiolucent areas near the apical region of the premolars in the mandible.
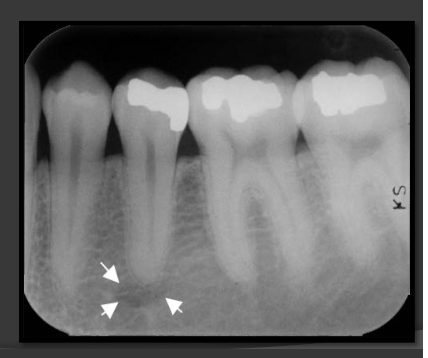
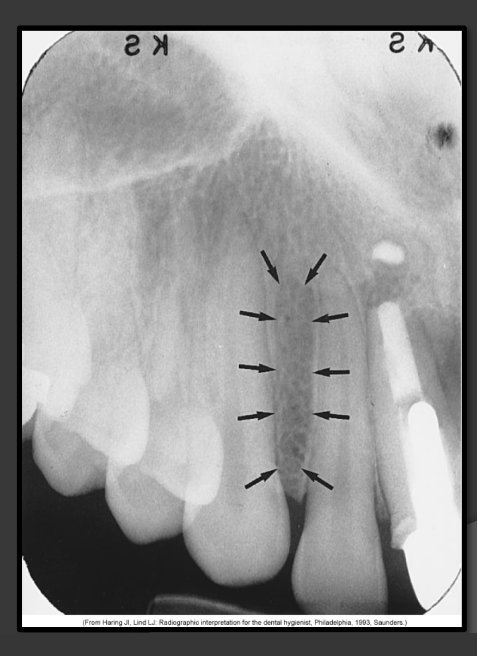
How does the genial tubercles/mental spines present in a radiograph?
Presents as a ring shaped radio opacity (white donut). Sits below the centrals on the mandible. It is the white portion. The radiolucent dot is a different structure
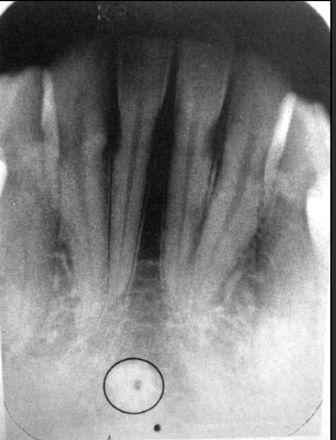
How does the lingual foramen present in a radiograph?
Presents as a tiny radiolucent dot below the mandibular centrals. Looks like a white donut because it is overlapping with the genial tubercle.
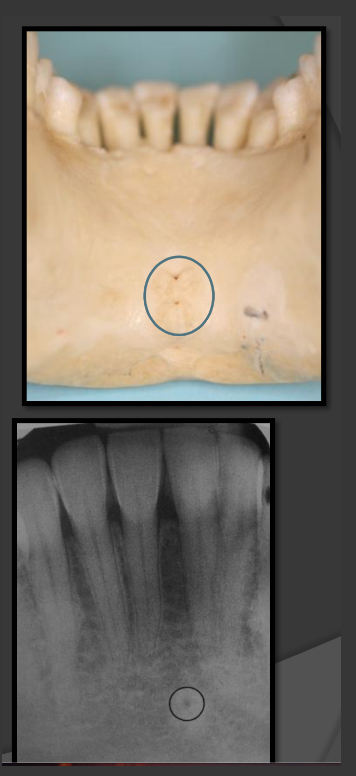
Where are nutrient canals most often seen?
Below the mandibular anterior teeth.
How do nutrient canals present in a radiograph?
They are thin radiolucent bands that can be seen in the sinus or in bone.
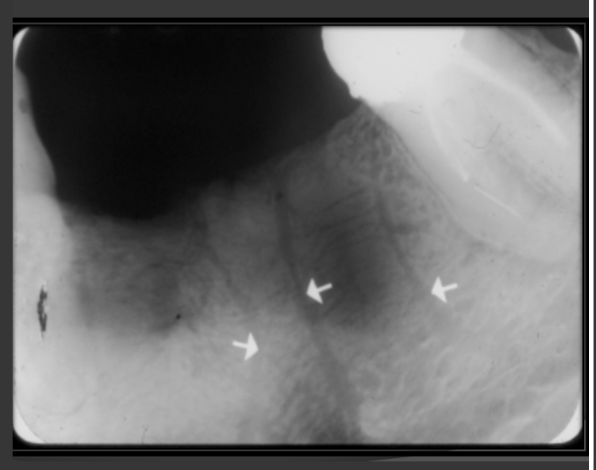
How does mandibular tori present in a radiograph?
It usually an area in the mandible where there is dense patches of radio opaque bone. Usually near the roots of teeth.
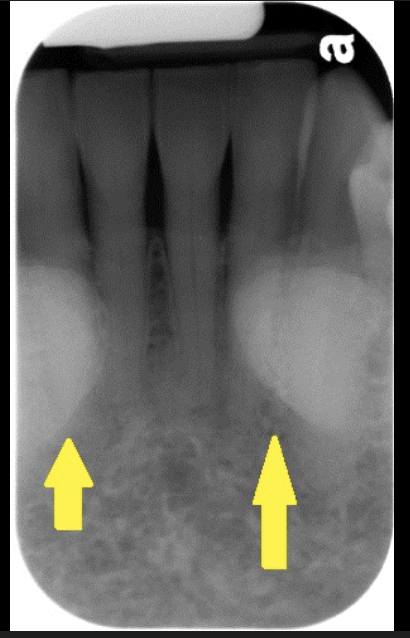
How does the mental ridge present in a radiograph?
-Radio opaque band
-It looks like an upside down V.
-Runs from the premolar region to the incisal region of the mandible
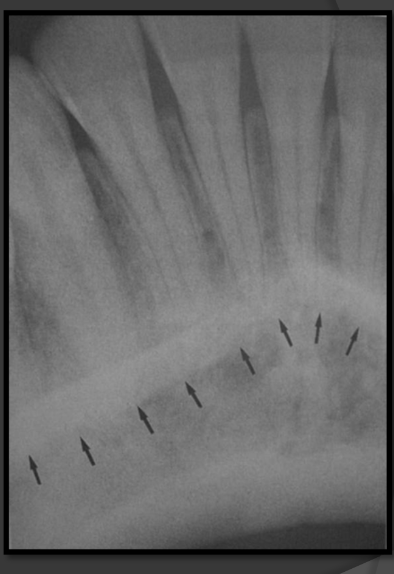
How does the mental fossa present in a radiograph?
A radiolucent area that site between the alveolar crest and mental ridge of the mandible. Usually surrounds the roots of the laterals and centrals.
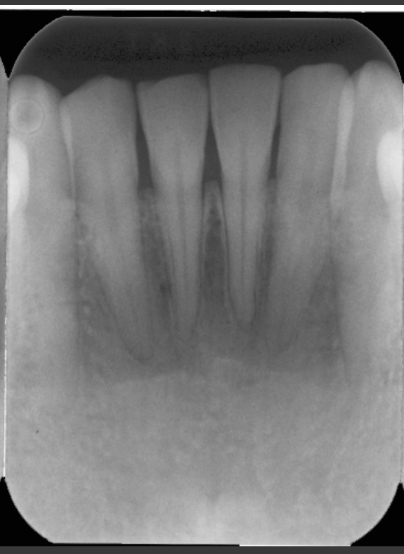
How does the soft tissue of the nose present in a radiograph?
It looks like a light radio opaque V shape that extends down below the anterior nasal spine and overlaps with the roots of the maxillary centrals.
What should be implemented in every dental office when trying to ensure quality in radiograph and infection control outcomes?
-Create a radiograph retake log
-Daily we should be writing down a log
-Weekly equipment should be checked
-Monthly there should be staff meetings to assess